
An Application Framework for Personalised and Adaptive
Behavioural Change Support Systems
Ulrich Reimer and Edith Maier
Institute for Information and Process Management, University of Applied Sciences St. Gallen, St. Gallen, Switzerland
Keywords:
Behavioural Change Support System, Systems to Encourage Healthy Behaviour, Nudging, Mobile Health,
Personalisation, User Modelling, User Adaptation, Meta Modelling.
Abstract:
The paper analyzes current weaknesses of behavioural change support systems (BCSS) such as the failure of
adequately taking into account the heterogeneity of target users. Based on this analysis the paper presents
an application framework that comprises various components to accommodate user preferences and to adapt
system interventions to individual users. Among these components is a goal hierarchy which can be set up to
represent the goals a user wants to achieve. The higher-level goals can be broken down into more specific goals
that can be measured and associated with appropriate activities. Furthermore, our BCSS framework includes
components for adapting its interactions according to a user’s observed behavioural preferences as well as
his or her previous reactions to system interventions. User adaptation also takes into account the preferences
of similar users by employing a collaborative filtering approach. Thus, overall user acceptance should be
improved and motivation for behavioural change sustained. The framework is currently being implemented
and will subsequently be evaluated.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the greatest challenges to health systems all
over the world is the growing number of people
with (multiple) chronic conditions such as diabetes,
asthma, cardiovascular disease and obesity. Accord-
ing to the WHO chronic diseases nowadays account
for about 80 % of the burden of disease (World Health
Organization, 2012). Most of these are lifestyle-
related and the risk factors are well-known, including
the lack of physical exercise, smoking, a diet rich in
fat and sugar, and the excessive consumption of al-
cohol. Although people are generally aware of the
long-term negative consequences, they often lack the
motivation as well as the social and emotional sup-
port that is required for changing one’sbehaviour. Be-
sides, we tend to discount long-term gains such as a
higher life expectancy and better quality of life in the
long run in favor of short-term rewards like the one
offered by some delicious cookies. Whilst the ma-
jority of the chronically ill may well agree with their
doctors’ or caregivers’ recommendations and fully in-
tend to adhere to them, e.g. engage in regular exercise
and change their diets, they fail to do so.
Behavioural economics is an approach that
promises to ameliorate the shortcomings of tradi-
tional healthcare management, especially with regard
to chronic disease (see e.g. (Cabinet Office, 2010; Eu-
ropean Commission, 2014)). Behavioural economists
use knowledge from behavioural science as well as
motivational psychology and neuroscience to study
how individuals make decisions which are often non-
rational, and biased by a series of mental shortcuts,
for instance, the so-called “status quo bias” (Kahne-
man, 2011). Apart from the status quo bias, people’s
behaviour is also susceptible to the influence of de-
fault rules, framing effects and starting points. Con-
sequently, persuasion strategies can involve changing
the way options are presented, e.g. by adapting the
rules that drive user interaction.
The philosophy of behavioural economics is also
called “libertarian paternalism”, namely that people
should not be forced to act in certain ways, but rather
encouraged to act in ways that are better for them or
help them stopping bad habits formed over time. This
idea of a “gentle push”, or “nudge” favours invitations
to change behaviours, rather than the introduction of
constraints and sanctions to obtain behaviour change
(Thaler and Sunstein, 2009).
It has been shown that frequent and immediate
feedback is very helpful to nudge people towards
healthy behaviour (Loewenstein et al., 2013; Maier
152
Reimer, U. and Maier, E.
An Application Framework for Personalised and Adaptive Behavioural Change Support Systems.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (ICT4AWE 2016), pages 152-159
ISBN: 978-989-758-180-9
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

and Ziegler, 2015). Mobile devices including smart-
phones and wearables such as smartwatches offer
great opportunities because they can be used for mea-
suring vital parameters such as heart rate, skin con-
ductance or blood pressure but also the number of
steps or sleep patterns. Most mobile health solutions,
i.e. mobile devices connected to medical applications
or sensors, as well as pure lifestyle apps actually in-
clude some kind of support for the users to achieve
their goals. However, these nudges tend to be hard-
wired, i.e. they do not adapt to user preferences and
needs and on the whole they are not grounded in be-
havioural change theory (see e.g. (Lister et al., 2014;
Patel et al., 2015)).
Our recent research therefore focuses on how
to use digital technologies to support behavioural
change in a systematic way and to allow adaptation
to what works best for an individual user.
2 CHALLENGES OF BEHAVIOUR
CHANGE SUPPORT SYSTEMS
Nudging for healthy behaviour using mobile technol-
ogy has to be viewed in the larger context of so-called
behaviour change support systems (BCSS) as intro-
duced and defined by (Oinas-Kukkonen, 2010):
“Behavior change support systems (BCSS)
are information systems designed to form, al-
ter, or reinforce attitudes or behaviours or
both without using coercion or deception.”
The persuasivesystems design (PSD) model, a frame-
work for designing a BCSS introduced in (Oinas-
Kukkonen and Harjumaa, 2009), draws from the sem-
inal work by Fogg on persuasive technology (Fogg,
2002). It distinguishes two major design steps: first,
analyzing the persuasion context, second, designing
the BCSS features. The persuasion context is defined
by the intent, the type of change to be achieved, e.g.
if it is a one-time or a permanent change, the event,
which includes the use context as well as the user’s
goals, and the strategy, which determines what kinds
of message are to be delivered via which route to the
user. The BCSS design features consist of four cate-
gories:
Primary Task Support. distinguishes various prin-
ciples of how to support the user, e.g. by reducing
complex behavioural goals to smaller goals that
can be achieved by simple tasks, or by personaliz-
ing the system to the user’s specific behaviour and
preferences;
Dialog Support. deals with how to set up the dialog
with the user;
System Credibility. addresses the issue how to make
the system credible for the user;
Social Support. deals with how to improve motiva-
tion and adherence by including social influence,
e.g. via the peer group, into the system.
While the model suggested by Oinas-Kukkonen
already mentions personalisation as one of many de-
sign principles, it plays a more important role in
more recent work on persuasive systems. Target user
groups are typically very heterogeneous so that it is
nearly impossible to design a “one-size-fits-all” sys-
tem. (Kaptein et al., 2010) examines individual dif-
ferences in persuadability in the health domain and
concludes that the intervention of a persuasive sys-
tem needs to be tailored to the persuasion profile
of the specific user. For example, some users re-
act best to strongly persuasive messages while other
users respond adversely to too strong an intervention
and would require a more low-key suggestion. (Prost
et al., 2013) build upon these results and describe a
system that employs personalisation based on factors
such as persuadability of the user, social-emotional
attitude and behaviour history. The results of an em-
pirical study on the relationship between personal-
ity and the effectiveness of persuasive technologies is
presented in (Halko and Kientz, 2010).
Laverman and his colleagues (Laverman et al.,
2014) present an approach to personalizing communi-
cation in a BCSS (which they call “self-management
support system”). The authors argue that the system
should provide information in a way that is “relevant
to the user’s situation and match[es] the user’s pref-
erences and abilities to understand and be persuaded
by [it]”. The effect of personalising short text mes-
sages to reduce snacking behaviour was investigated
by Kaptein and his colleagues and the results reported
in (Kaptein et al., 2012). A more general overview of
the possible roles personalisation can play in persua-
sive systems can be found in (Berkovsky et al., 2012).
Behavioural change starts with motivation and in-
tent and requires the setting of clear and measurable
goals which direct attention and effort toward goal-
relevant activities (Locke and Latham, 2002). There-
fore, BCSS include mechanisms for goal setting as
well as measuring goal achievement to give appro-
priate feedback. Many of the smartphone apps that
have come into existence as part of the quantified self
movement for tracking and measuring all kinds of ac-
tivities, support goal setting and typically offer sup-
port for achieving these goals, e.g. by giving feed-
back on current goal achievement, by drawing on peer
group support, or by playful competition. In these
cases, while goal setting is supported, the types of
goals a user can set are very limited due to the spe-
An Application Framework for Personalised and Adaptive Behavioural Change Support Systems
153

cific focus each of these apps has, e.g. on measuring
physical activity, calorie intake, or stress level.
Consequently, while there are many theoretical
models available for guiding the proper design of a
BCSS and for designing mobile systems for support-
ing behavioural change in particular, in the end each
application has to be hand-crafted and tailored to a
specific domain and application scenario. When de-
signing a system, developers make assumptions about
what will work for the target user group, but once
the app has been completed, maybe even evaluated
with a focus group, one cannot but hope that the app
will be effective in supporting the intended behaviour
changes. Should this not be the case, it will be very
difficult to identify the reasons. Thus, despite the the-
oretical guidelines available, the actual task of creat-
ing a BCSS is more an art than a systematic develop-
ment process.
One way to tackle this challenge is to devise a
more generic BCSS which can be easily configured to
meet the needs of a specific user. Ideally, the users can
carry out the necessary configurations themselves. In
this way, fewer assumptions need to be made about
the functions that a user actually wants to have.
To this end, we propose mapping the existing the-
oretical concepts to an application framework for cre-
ating mobile persuasive systems that can be easily
configured to accommodate a wide variety of user re-
quirements without the need to reimplement parts of
the system. Additionally, we propose that the frame-
work includes components for automatic user adap-
tion during system runtime.
In our current research we focus on those aspects
of the framework which we deem most important for
a mobile BCSS. Our framework will
• remedy the limited goal setting capabilities of ex-
isting apps by including a goal network that can
be set up and edited by a user according to his or
her specific needs (maybe together with a person
acting as a coach or therapist for the user);
• distinguish between the ultimate goals a user
wants to achieve and more concrete operational-
ized sub-goals whose achievement can be mea-
sured, e.g. with sensors;
• offer a variety of persuasive interventions (nudge
types) a user can choose from according to his or
her preferences;
• include automatic adaptation mechanisms that
monitor user behaviour, correlate system inter-
ventions with user behaviour and determine which
kinds of system interventions work best for a spe-
cific user and then adapt its intervention strategy;
• permit users to configure a system according to
their needs.
Throughout the paper we use the term “nudge” in the
following meaning:
Definition:
A nudge is a brief persuasive intervention that
encourages a specific behaviour.
In the following section we will describe our frame-
work in more detail.
3 APPLICATION FRAMEWORK
FOR BEHAVIOURAL CHANGE
SUPPORT SYSTEMS
3.1 Goal Hierarchies
At the heart of any BCSS, which also includes mo-
bile health apps, are the goals a user wants to achieve.
An application framework for creating a BCSS there-
fore needs to include some mechanism for specifying
goals or target behaviours. Many of today’s mobile
health apps support the setting of user-specific goals
but fail to consider the larger context within which
these goals are embedded, i.e. what the higher-level
goals are. For example, an app might allow users to
specify the number of steps per day to make. The
higher-level goal behind walking a certain amount
of steps per day could be to keep healthy or to lose
weight. Walking 10000 steps per day is only one pos-
sible way to achieve this; other possibilities could be
to go swimming or cycling. Consequently, in order
to give users more flexibility in how to achieve their
goals, a goal hierarchy is needed which represents
the users’ higher-level goals as well as how to reach
them. This enables a user to achieve a higher-level
goal via (a combination of) alternative sub-goals, e.g.
a combinationof walking, running, cycling and swim-
ming. Goal hierarchies originally go back to cognitive
psychology (e.g. (Schank and Abelson, 1977)) and
play an important role e.g. in interactive systems that
create and maintain models of their users’ goals and
plans.
Our BCSS application framework therefore in-
cludes a construct for specifying one or more goal
hierarchies for the targeted application domain of a
BCSS. A goal hierarchy starts with a top goal which
represents a target user’s primary goal. The top goal
tends to be long-term, it may be measurable, e.g.
“body mass index of below 30”, or be more generic,
e.g. “keep healthy”. It can usually be achieved by a
variety of different ways, e.g. by engaging in physi-
cal activity, lowering the stress level, by eating regular
ICT4AWE 2016 - 2nd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
154

Figure 1: Example of a goal hierarchy (application model level).
meals or a combination thereof. Each option is repre-
sented by a sub-goal, together with an indication if
the sub-goal is sufficient for reaching the higher-level
goal or if several sub-goals need to be reached. Sub-
goals can be broken down into further sub-goals un-
til these can be associated with a measurable activity.
We call such goals operationalized:
Definition:
An operationalized goal is short-term and is
associated with a measurable activity to reach
the goal.
Figure 1 shows some examples of operationalized
goals. Activities associated with operationalized
goals can e.g. be measured via sensors or diary en-
tries. An activity detection module using a 3D ac-
celerometer and state-of-the-art algorithms can auto-
matically determine if the user is e.g. walking, run-
ning, cycling, or climbing stairs, and thus can help to
keep track of the achievement of alternative goals for
physical activity (see e.g. (Slim et al., 2016)).
Operationalized goals are parameterized so that
they are not yet goals but rather goal types. An ex-
ample of such a goal type is “physical activity > x
steps per day” (cf. Fig.1). The user, possibly together
with a coach or a therapist, selects goal types and sets
values for the goal parameters to obtain specific (op-
erationalized) goals.
We will implement the application framework by
adopting a meta modelling approach (Karagiannis
and K¨uhn, 2002; Atkinson and K¨uhne, 2003). The
meta model defining our application framework (cf.
Fig.2 for its main part) introduces all constructs that
can be used to create a specific BCSS. One example of
such a construct is the goal hierarchy we have already
introduced. A specific BCSS application is then rep-
resented by an application model that is an instance
of the meta model. A specific goal hierarchy with pa-
rameterized goal types would be on this model level
(cf. Fig.1). The parameters of the goal types are set by
a user during runtime to create concrete goals. Thus,
the runtime system is essentially an instance of the ap-
plication model.
Users are not only allowed to set the parameters
in the goal types but they can also delete parts of the
goal hierarchy so that only the goals they wish to pur-
sue are left. For example, a user who does not like
running would delete the associated sub-goal. How-
ever, we do not permit a user to add sub-goals be-
cause this would essentially lead to a new application
model, which then would require additional imple-
mentation effort, e.g. to provide the means to mea-
sure the achievement of the added goal. Therefore the
goal hierarchy in the application model provides the
set of all possible goals for the intended application,
from which users pick the ones they like. Modifying
the goal hierarchy is a task for the developers.
3.2 Adapting Nudges to Users
In the course of our research we have conducted
extensive interviews with potential end-users which
confirm the findings of other researchers (Halko and
Kientz, 2010; Kaptein et al., 2010; Prost et al., 2013)
namely that behaviour is influenced by a variety of
factors, e.g. age, sex, socio-economic status, atti-
tudes, personality, social environment and peer group.
Thus, the fixed set of interventions (or nudges) that
existing BCSS have implemented do not take into ac-
count the heterogeneity of target users. This results
An Application Framework for Personalised and Adaptive Behavioural Change Support Systems
155
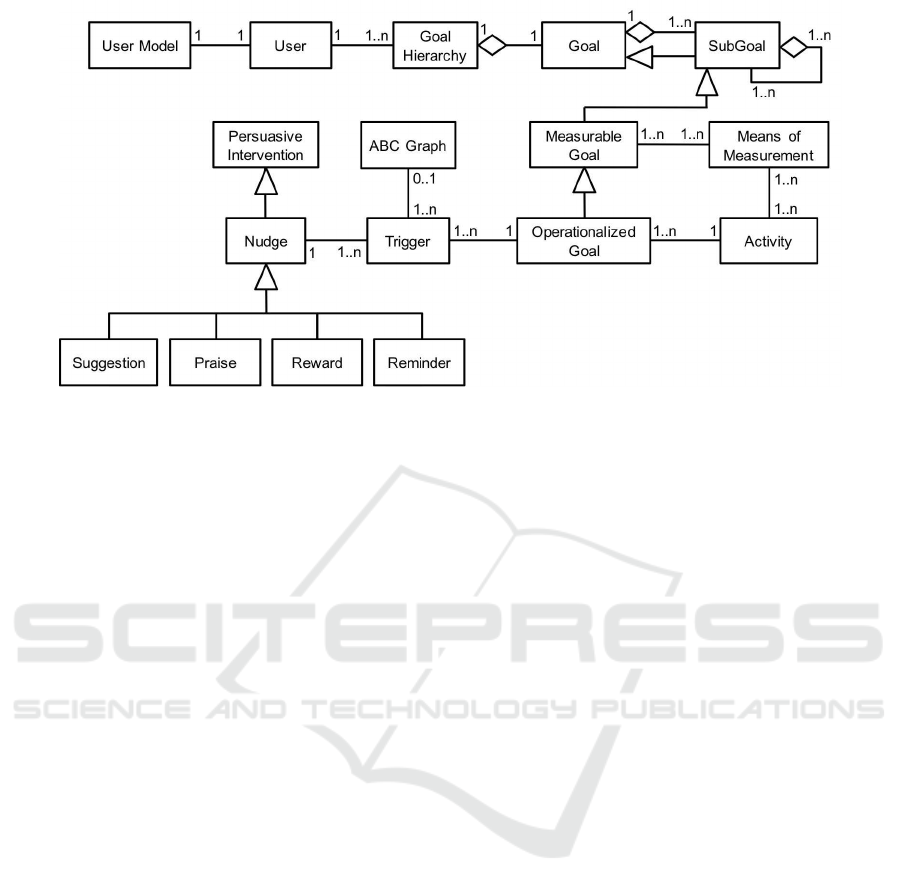
Figure 2: Core fragment of the BCSS meta model.
in low intervention efficacy and low user acceptance.
In our framework we therefore provide for a variety
of nudge types, such as suggestion, praise, reminder,
reward, and we devise different means to control the
user-specific selection of nudge types and their tim-
ing. The corresponding constructs of our framework
are defined in the meta model (cf. Fig.2), just like the
construct of goal hierarchies.
The simplest way to adapt nudges to users is to
have them select the preferred nudges. However, as
shown by our interviews the average user will shun
the additional effort and finds it difficult deciding
which choices to make. We therefore aim at enabling
the system to choose the nudge types using a threefold
approach – a) user modelling, b) collaborative filter-
ing, and c) progress-dependent adaptation.
3.2.1 User Modelling
Our framework includes a user modelling compo-
nent (Kobsa, 2001) which allows to monitor user
behaviour and keep track of the user’s preferences
with regard to nudge types, choice between alter-
native goals, and schedule of activities. To de-
duce these preferences, the system starts by selecting
nudge types randomly and monitoring which of them
work best for a user. Once the system has identified
the nudge types that are more successful in terms of
triggering intended behaviour, the system uses those
types more often. However, according to our frame-
work the system does not completely stop using the
other nudge types so that possible future changes in
user behaviour can be detected and the user model
adapted accordingly.
For example, if a user often follows a suggestion
made by the system, this is a good indicator that the
user responds well to suggestion nudges. Also, whilst
some users might respond well to reminders or feed-
backs that they are falling behind their peer group,
other users might simply ignore such messages.
Additionally, the system keeps track of the tim-
ing of different kinds of activities performed by the
user and adjusts the timing of nudges, such as sug-
gestions and reminders accordingly. The user model
also keeps track of the alternatives that a user prefers
to achieve a higher-level goal, e.g. cycling instead of
walking.
Although the user preferences derived by the user
modelling approach can never do justice to the enor-
mous complexity of human behaviour, we neverthe-
less expect our approach to result in superior system
performance with higher user acceptance rates.
3.2.2 Collaborative Filtering
For the purpose of user adaptation our framework will
also make use of collaborative filtering (Adomavicius
and Tuzhilin, 2005). This approach implies that the
system primarily uses those nudges that work best for
similar users. Similarity is determined with respect to
the user profile, i.e. what the user initially said about
himself or herself, and the user model. For exam-
ple, collaborative filtering might indicate that show-
ing the user’s achievements compared to those of the
peer group works poorly for female users in a certain
age range and with a low activity profile.
With collaborative filtering we are able to identify
user preferences much faster than with user modelling
because it can draw on the collected evidence from all
the other users of the system, provided this evidence
has already been collected. Within our BCSS frame-
work initial preferences are determined by collabo-
ICT4AWE 2016 - 2nd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
156

rative filtering and are then continuously fine-tuned
using the user modelling approach described above.
3.2.3 Progress-Dependent Adaptation
As already described above, in our BCSS framework
the user modelling component keeps track of a user’s
typical activities as well as their timing and adjusts
the timing of suggestions and reminders accordingly.
Another important mechanism to adapt the time and
type of nudges consists in monitoring the progress
of achieving (operationalized) goals. Plotting goal
achievement along the time axis produces a rectan-
gular area which we divide into the three sub-areas A,
B and C (see Fig.3): Area A signifies good progress,
area B indicates slow progress, while area C indicates
that considerable effort is required to achieve the cor-
responding goal.
For example, a first, still rather simplistic selec-
tion of nudges could work as follows: As long as a
user’s progress lies in area A, no nudges are generated
because the user is performing well. When progress
falls within area B, unobtrusive, low-key nudges are
appropriate, e.g. a suggestion or a discreet reminder.
When goal achievement moves into area C, the user
is at risk to miss the goal and stronger nudges may
be called for than in area B. On the other hand, if the
user catches up and moves back into area B or from
area B to area A, a praise message could be generated.
More elaborate algorithms could fine-tune the system
responses and e.g. consider if the user just crossed
into a new area or is already deep inside it.
In our application frameworkeach operationalized
goal can be associated with nudge types and corre-
sponding trigger conditions (cf. the meta model in
Fig.2):
• A nudge is generated when progress crosses from
one area into the neighbouring one, indepen-
dent from the percentage of achievement and the
elapsed time, e.g. from A to B or from B to C or
back.
• A nudge is generated when a predefined amount
of time has elapsed and the user’s progress is lo-
cated in area A, B or C. For example, when 70%
of the time available for reaching a goal is over
a praise message is generated if progress is in
area A, a reminder if progress is in area B, and
a prompt or a challenge is generated if progress is
in area C.
• Similarly, a nudge is generated when a predefined
percentage of achievement has been reached and
the user’s progress is in a specific area.
The boundaries between the areas in the ABC
graph are initially defined according to the user pro-
file, e.g. taking into account if a user is an early riser
or a night owl. The system monitors a user’s achieve-
ment pattern for each goal and adapts the boundaries
to fit with his or her typical daily routine. For example
for a user who likes to go running early in the morn-
ing, area A would be far to the left and small. On the
other hand, for a user who usually goes running in the
afternoon, area A would stretch far to the right.
Figure 3: An ABC graph for progress-dependent nudges.
4 EVALUATION
We are currently implementing the BCSS framework.
Subsequently we will conduct an evaluation with peo-
ple who wish to reduce their weight or maintain their
previously achieved weight loss. To this end, we
will develop a smartphone app which is based on
our framework and offers a variety of weight-related
goals, including physical activity, self-weighing, eat-
ing behaviour and calorie intake. We will distribute
the app via social media platforms and utilize the Ap-
ple ResearchKit to take care of issues such as seeking
informed consent and giving participants control over
what data they want to share.
The study will randomly divide participants into
two groups. One group will get the version that al-
lows customizing the goal hierarchy and which au-
tomatically adapts to the individual user. The other
group will get a version with predefined goals and
with fixed interventions. Our hypothesis is that the
former version, which makes full use of the capabil-
ities of our framework, is more effective in terms of
achieving one’s goals.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
OUTLOOK
In this paper, we have presented an application frame-
work for behavioural change support systems (BCSS)
An Application Framework for Personalised and Adaptive Behavioural Change Support Systems
157

that comprises various components for tailoring a
BCSS to users’ needs and preferences. One of these
components is a goal hierarchy which can be set up
to represent the goals a user wants to achieve. The
higher-level goals (e.g. reaching a BMI below 30)
can be broken down into more specific goals that are
operationalized, i.e. can be achieved by associated
measurable activities. Furthermore, our BCSS frame-
work includes components for adapting its interac-
tions in line with a user’s previous reactions to system
interventions (nudges) and with observed behavioural
preferences, whilst at the same time taking into ac-
count the preferences of similar users by employing a
collaborative filtering approach. The adaptation com-
ponents do justice to the heterogeneity of target user
groups, which tends to be ignored by most of the cur-
rent systems.
We are planning to embed our framework into a
more general approach where the activities associated
with operationalized sub-goals are chosen from the
predictors of a predictive model. For example, long-
term studies have shown that regular self-weighing
and having breakfast regularly are strong predictors
for weight loss and weight-loss maintenance (see e.g.
(Feller et al., 2015)). Such predictors would therefore
be included as evidence-based goals in the goal hier-
archy. In this scenario, a therapist familiar with such
predictors co-decides with a user which goals to set.
Furthermore, we are planning to develop a deci-
sion support system which utilizes a combination of
predictive models to predict a person’s health out-
comes in the near future based on various input data,
such as genetic, physiological, psychological, and be-
havioural data. The decision support system will
be able to analyse the influence of each predictor in
the predictions. The predictors shown to have the
most impact on the desired health outcomes are good
candidates for evidence-based goals because they are
likely to be most effective in terms of improving the
corresponding person’s future health.
Whilst we consider our approach very promising
and conducive to adopting and maintaining a healthy
lifestyle, we are aware of the ethical issues involved
(see e.g. (McGrady and Nelms, 2010)). Above all, it
is important that users should always stay in control,
participate in all decisions, and can grasp the impli-
cations of a prediction, on what it is based and that it
is only a likely but not a certain outcome. Besides,
it is absolutely essential to guarantee the privacy and
confidentiality of health-related data. We will develop
measures and guidelines that assure users’ autonomy,
privacy and right of control whilst making sure that
the decision support system really supports and moti-
vates them in their every-day lives.
Furthermore, we are considering applying our
BCSS framework to domains other than health, e.g.
to mobility. By encouraging users to use public trans-
port or cycle to work, they will achieve the predefined
goal of causing a smaller ecological footprint (Maier,
2012).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research presented in this paper has been made
possible by a grant from Gebert R¨uf Foundation. Our
thanks go also to the members of the student group
for their contributions to this research: M. Eggen-
schwiler, S. Frigg and R. Zuberb¨uhler. We further
thank the reviewers of an earlier version of this pa-
per whose feedback helped to improve it.
REFERENCES
Adomavicius, G. and Tuzhilin, A. (2005). Toward the
next generation of recommender systems: A survey
of the state-of-the-art and possible extensions. IEEE
Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,
17(6):734–749.
Atkinson, C. and K¨uhne, T. (2003). Model-driven develop-
ment: A metamodeling foundation. IEEE Software,
20(5):36–41.
Berkovsky, S., Freyne, J., and Oinas-Kukkonen, H. (2012).
Influencing individually: Fusing personalization and
persuasion. ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelli-
gent Systems, 2(2):9:1–9:8.
Cabinet Office (2010). Applying behavioural insight to
health. Institute for Government, UK.
European Commission (2014). Green paper on mobile
health.
Feller, S., M¨uller, A., Mayr, A., Engeli, S., Hilbert, A.,
and Zwaan, M. d. (2015). What distinguishes weight
loss maintainers of the german weight control registry
from the general population? Obesity, 23(5):1112–
1118.
Fogg, B. J. (2002). Persuasive Technology: Using Com-
puters to Change What We Think and Do. Morgan
Kaufmann, 1 edition.
Halko, S. and Kientz, J. A. (2010). Personality and per-
suasive technology: An exploratory study on health-
promoting mobile applications. In Proceedings of the
5th International Conference on Persuasive Technol-
ogy, PERSUASIVE’10, pages 150–161, Berlin, Hei-
delberg. Springer-Verlag.
Kahneman, D. (2011). Thinking, fast and slow. Penguin
Books, New York, Toronto, London.
Kaptein, M., De Ruyter, B., Markopoulos, P., and Aarts,
E. (2012). Adaptive persuasive systems: A study of
tailored persuasive text messages to reduce snacking.
ICT4AWE 2016 - 2nd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
158

ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems,
2(2):10:1–10:25.
Kaptein, M., Lacroix, J., and Saini, P. (2010). Individual
differences in persuadability in the health promotion
domain. In Ploug, T., Hasle, P. F. V., and Oinas-
Kukkonen, H., editors, PERSUASIVE, volume 6137
of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 94–105.
Springer.
Karagiannis, D. and K¨uhn, H. (2002). Metamodelling plat-
forms. In Bauknecht, K., Tjoa, A. M., and Quirch-
mayr, G., editors, E-Commerce and Web Technolo-
gies, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, page 182.
Springer.
Kobsa, A. (2001). Generic user modeling systems. User
Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction, 11(1-2):49–
63.
Laverman, M., Neerincx, M. A., Alpay, L. L., R¨ovekamp,
T. A., and Schonk, B. J. (2014). How to Develop Per-
sonalized eHealth for Behavioural Change: Method
& Example. Technical Report TNO 2014 R10758.
Lister, C., West, J. H., Cannon, B., Sax, T., Brodegard, D.,
and Eysenbach, G. (2014). Just a fad? Gamification in
health and fitness apps. JMIR Serious Games, 2(2):e9.
Locke, E. and Latham, G. (2002). Building a practically
useful theory of goal setting and task motivation: A
35-year odyssey. American Psychologist, 57(9):705.
Loewenstein, G., Asch, D. A., and Volpp, K. G. (2013).
Behavioral economics holds potential to deliver better
results for patients, insurers, and employers. Health
Affairs, 32(7):1244–1250.
Maier, E. (2012). Smart mobility - encouraging sustain-
able mobility behaviour by designing and implement-
ing policies. JeDEM-eJournal of eDemocracy and
Open Government, 4(1):115–141.
Maier, E. and Ziegler, E. (2015). Sanfte Stupser f¨ur
gesundheitsf¨orderliches Verhalten – oder Nudging im
Gesundheitswesen. Clinicum, 3-15:76–81.
McGrady, E. and Nelms, L. W. (2010). Ethical issues of
health management predictive modeling. In Pease, W.,
Cooper, M., and Gururajan, R., editors, Biomedical
Knowledge Management: Infrastructures and Pro-
cesses for E-Health Systems. IGI Global.
Oinas-Kukkonen, H. (2010). Behavior change support sys-
tems: The next frontier for web science. In Proceed-
ings of the Web Science Conference 2010.
Oinas-Kukkonen, H. and Harjumaa, M. (2009). Persuasive
systems design: Key issues, process model, and sys-
tem features. Communications of the Association for
Information Systems, 24(1):28.
Patel, M., Asch, D., and Volpp, K. (2015). Wearable devices
as facilitators, not drivers, of health behavior change.
JAMA, 313(5):459–460.
Prost, S., Schrammel, J., R¨oderer, K., and Tscheligi, M.
(2013). Contextualise! personalise! persuade!: A
mobile HCI framework for behaviour change support
systems. In Proceedings of the 15th International
Conference on Human-computer Interaction with Mo-
bile Devices and Services, MobileHCI ’13, pages
510–515, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Schank, R. C. and Abelson, R. P. (1977). Scripts, Plans,
Goals and Understanding: an Inquiry into Human
Knowledge Structures. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale,
NJ.
Slim, S., Atia, A., and Mostafa, M.-S. (2016). An exper-
imental comparison between seven classification al-
gorithms for activity recognition. In Gaber, T., Has-
sanien, A. E., El-Bendary, N., and Dey, N., editors,
The 1st International Conference on Advanced Intel-
ligent System and Informatics (AISI2015), November
28-30, 2015, Beni Suef, Egypt, volume 407 of Ad-
vances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, pages
37–46. Springer International Publishing.
Thaler, R. H. and Sunstein, C. R. (2009). Nudge: improving
decisions about health, wealth, and happiness. Pen-
guin Books, New York, Toronto, London.
World Health Organization (2012). Global Health Esti-
mates: Deaths, disability-adjusted life year (DALYs),
years of life lost (YLL) and years lost due to disability
(YLD) by cause, age and sex, 2000–2012.
An Application Framework for Personalised and Adaptive Behavioural Change Support Systems
159
