
User Request Traffic Condition Providing System for using Location
Information
Sung-Phil Heo
1
, Wansu Lim
2
, Sung-Chul Hur
3
and Dong-Seong Kim
2
1
ICT Convergence Research Center, Kumoh National Institute of Technology, Gumi-si, Korea
2
Department of Electronic Engineering, Kumoh National Institute of Technology, Gumi-si, Korea
3
Appomattox Hull Project, Samsung Heavy Industries Co., Ltd., Geoje-si, Korea
Keywords: Traffic Condition, Location Information, ITS.
Abstract: With respect to traditional method which relates to identifying a traffic state of a particular road from a remote
point, there is a scheme for collecting data sensed by a traffic sensing apparatus of a freeway traffic
management system(FTMS), such as a loop type vehicle detector, which is provided on a road to detect traffic
states, a video type vehicle sensor, Which is configured to identify traffic states on a road through the use of
video photographing, a closed circuit television (CCTV), and an emergency call.. The FTMS is a freeway
intelligent traffic system (ITS) constructed by the Korea Highway Corporation to provide users of a freeway
with exact road information and to manage traffic conditions. However, in order to implement a system for
measuring a speed of a vehicle by using the loop type detection system, installation of a loop coil detector
typically requires earthworks and/or other types of construction, thereby causing delay and/or inconvenience
in transportation during the earthworks and/or construction. Further, in order to collect information, it is
typically necessary to install a separate private cable or to lease a dedicated line. In this paper, we describe a
system for detecting a peripherally located vehicle based on a location of a user or a particular point on a map
which point is selected by a user, so as to be provided with traffic images captured by a smart device installed
in the detected vehicle.
1 INTRODUCTION
Traditional traffic sensing system, it is not possible to
identify an exact speed of a vehicle, i.e., traffic
volume information, at a point where no speed sensor
exists. In order to sense the traffic volume, a large
number of speed sensors should be provided on each
road. As a result, the number of communication lines
increases, and the resultant burden of installation
costs and lease fees for communication increases. The
aforementioned method for using a CCTV camera is
limited, because traffic information can be identified
only at a point where a CCTV camera is provided.
A typical traditional method “System for
Providing Road Traffic Images,” describes detecting
peripherally located vehicles based on location of a
user and purchasing moving images captured in any
one of the detected vehicles. However, this
technology relates to enabling a service server to send
a traffic image purchase request to a multiple number
of vehicles which are located in relatively close
proximity to the user and an intermediate
communication between the user and a vehicle which
first responds to the request.
Accordingly, in the above-described system, it is
not possible to obtain traffic images from a vehicle
which is located at a point selected by the user.
Further, because a certain amount of costs are paid for
provided traffic images, the user may experience
monetary damages resulting from receiving
unnecessary traffic images.
Smartphones are important part of daily life of
people now. Those provide technology which helps
to make human life simpler, easier, and faster. So the
smartphones are used to provide service for saving
the time by use of application of getting better routes
to travel. Smartphones have several advantages for
data collection in intelligent transportation service
(ITS). ITS of smartphone-based method can have
significantly lower cost and larger coverage
compared to traditional transportation service based
on roadside infrastructures or dedicated on-board
units. The increasing smartphone penetration has also
the potential of providing a huge traffic probe base.
194
Heo, S-P., Lim, W., Hur, S-C. and Kim, D-S.
User Request Traffic Condition Providing System for using Location Information.
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2016) - Volume 2, pages 194-198
ISBN: 978-989-758-187-8
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

In order to address the above-described
conventional problems, we propose a method for
detecting a peripherally located vehicle based on a
location of a user or a particular point on a map which
point is selected by a user, so as to be provided with
traffic images captured by a device installed in the
detected vehicle. An exemplary embodiment also
provides an apparatus which enables a user to directly
select a vehicle, from which traffic images are
provided.
2 TRAFFIC INFORMATION
PROVIDING SYSTEM BASED
ON USER REQUEST
In the traditional traffic information providing
systems which are working on the similar concept of
traffic detection and management, different
approaches are used as sensors, GPS, social
networking etc. In the method of using sensor, the
sensor is mounted simply on the signal poles or
placed alongside the roads where they sense the
vehicles passing by the mounted sensors. The data
collected by system using these sensors is then
utilized to provide users information about the traffic
conditions and suggesting routes to manage the traffic.
The LBS (Location Based Services) gives the
geographical location of devices executing
application and provide the services based on the
information of location. LBS gives the real time
location. So it can be used to get the real time traffic
on the routes and avoid the jams.
Use of social networking is the new emerging
field. As the number of people using social
networking sites are increasing day by day, this
method can become a successful way to provide
traffic updates to them. Drivers will post about the
traffic conditions of roads.
A user directly may select one of the detected
vehicles to request traffic images, such that traffic
states relating to the corresponding point can be
identified and/or described in detail. A certain amount
of costs may be paid to the driver of a vehicle
providing traffic images, such that the driver may
obtain additional income. Furthermore, providing and
using traffic images can be promoted, for example,
via advertisement and/or public service
announcement. In case of occurrence of an
emergency circumstance, such as, for example, a
traffic accident or a vehicle violating the traffic rules,
traffic images captured from a peripheral vehicle may
be provided to a related organization such that the
captured traffic images may be used for news
reporting or evidence.
Figure 1 is proposed system configuration for
providing traffic information by using location
information. The system is made up user device,
vehicle device, and a traffic information providing
server.
Figure 1: Overview of proposed system.
The user device may include an application which
provides traffic images to a user of the user device.
An icon or menu form corresponding to the
application is displayed on the screen of the device.
When the user selects the icon or menu, the
application provides traffic images. Hereinafter, the
operation of the user device to provide traffic images
via activation of the application installed in the user
device will be described.
Once the application is activated, the user device
requests a traffic image service from the traffic image
providing server via a network connection. In
particular, the user device may send information
relating to a location of the user device, such as,
global positioning system (GPS) coordinate-based
location information, cell-based location information,
WiFi-based location information, or any other
suitable type of location information, to the traffic
image providing server.
Figure 2 is a flow chart which illustrates a process
for providing traffic images.
The vehicle device displays the traffic image
request of the user device on the screen, and sends a
selection of the driver in response to the traffic image
request, i.e., selection information relating to an
indication of acceptance of the traffic image request
or information relating to an indication of refusal of
the traffic image request to the traffic image
providing server.
User Request Traffic Condition Providing System for using Location Information
195

Figure 2: Flow chart of proposed system.
If the driver accepts the traffic image request, the
device captures the periphery of the vehicle for a
predetermined period of time. For example, if the
driver accepts the traffic image request, the vehicle
device captures the periphery of the vehicle.
Thereafter, the vehicle device sends the captured
traffic images to the traffic image providing server.
3 MECHNISM OF TRAFFIC
CONDITION PROVIDING
SYSTEM
Now days GPS is used mostly in the applications that
work on location based services. GPS technology is
easily available on the mobiles. This technology used
along with mobile network in smart phones gives
better accuracy than other methods. It gives location
in few seconds and has better coverage.
A server for providing a traffic image to a user
device includes a location information receiving unit
which receives information relating to a respective
location of each of a plurality of vehicles. A location
management unit which receives information relating
to a particular area from a user device, and which
detects at least one vehicle located within the
particular area based on the location information.
An information sending unit which sends
information relating to the at least one detected
vehicle to the user device, an image requesting unit
which receives information relating to a vehicle
selected from among the at least one detected vehicle
from the user device, and which requests, from a
device installed in the selected vehicle, transmission
of a traffic image of the selected vehicle, and an
image providing unit which receives the image and
which provides the traffic image to the user device.
The vehicle device displays the traffic image
request of the user device on the screen, and sends a
selection of the driver in response to the traffic image
request, i.e., selection information relating to an
indication of acceptance of the traffic image request
or information relating to an indication of refusal of
the traffic image request to the traffic image
providing server. If the driver accepts the traffic
image request, the device captures the periphery of
the vehicle for a predetermined period of time. For
example, if the driver accepts the traffic image
request, the vehicle device captures the periphery of
the vehicle. Thereafter, the vehicle device sends the
captured traffic images to the traffic image providing
server.
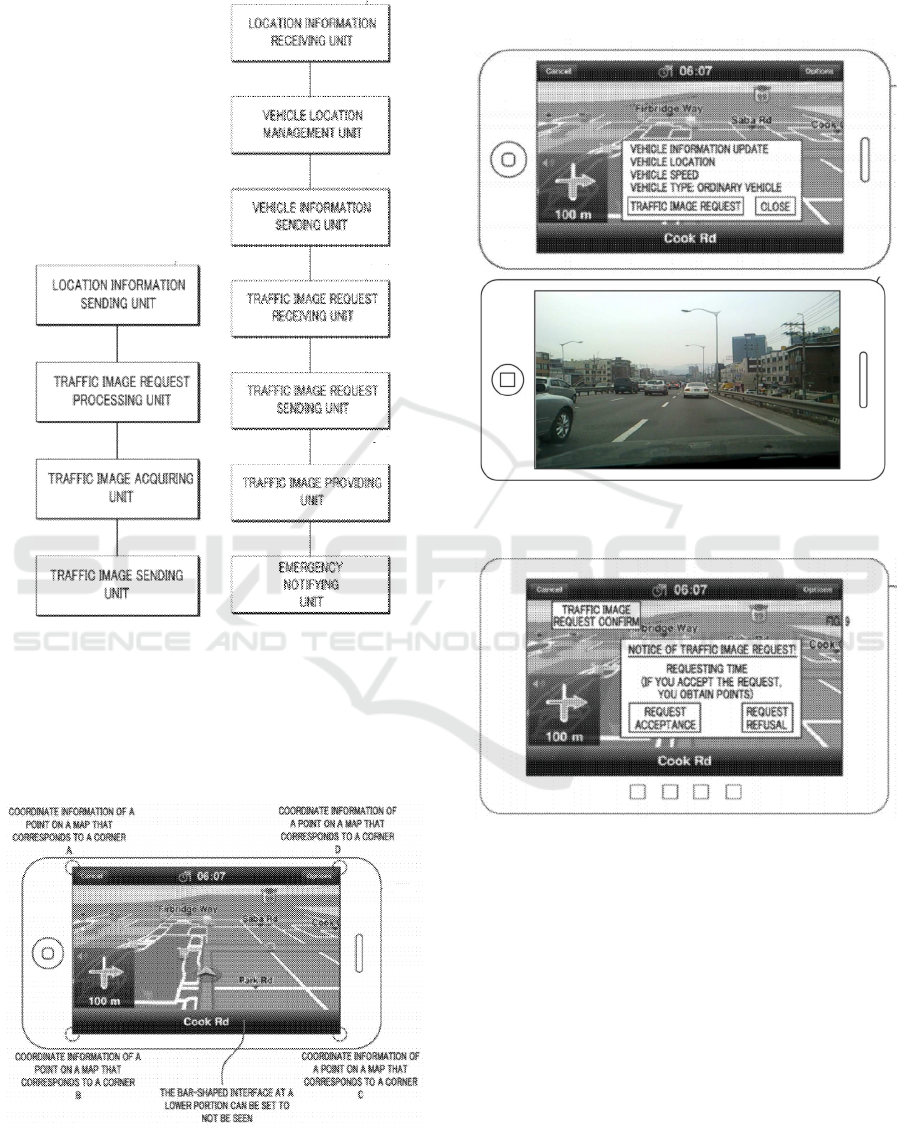
Figure 3 is a block diagram which illustrates a
configuration of a device for providing traffic images,
according to an exemplary embodiment. Figure 4 is a
block diagram which illustrates a configuration of a
traffic image providing server for providing.
According to the above-described aspects of the
exemplary embodiments, it is possible to detect
peripherally located vehicles based on a location of a
user or a particular point on a map which is selected
by a user. A user directly may select one of the
detected vehicles to request traffic images, such that
traffic states relating to the corresponding point can
be identified and/or described in detail.
A certain amount of costs may be paid to the
driver of a vehicle providing traffic images, such that
the driver may obtain additional income. Furthermore,
providing and using traffic images can be promoted,
for example, via advertisement and/ or public service
announcement.
In case of occurrence of an emergency
circumstance, such as, for example, a traffic accident
or a vehicle violating the traffic rules, traffic images
captured from a peripheral vehicle may be provided
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
196
to a related organization such that the captured traffic
images may be used for news reporting or evidence.
Figure 3, 4: Block diagram of location information sending
and providing unit.
Figure 5 is a view which illustrates coordinate
information relating to points on a map of a user
device that corresponds to comers of a screen,
according to an exemplary embodiment.
Figure 5: Illustrates coordinate information relating to
points on a map of a user device.
Figure 6 is illustrated a traffic information
request-related interface which is displayed on a user
device. Figure 7 is illustrated a screen shot of a
vehicle device.
Figure 6: illustrated a traffic information request-related
interface.
Figure 7: Vehicle device.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Smartphones have several advantages for data
collection in intelligent transportation service (ITS).
ITS of smartphone-based method can have
significantly lower cost and larger coverage
compared to traditional transportation service based
on roadside infrastructures or dedicated on-board
units. The increasing smartphone penetration has also
the potential of providing a huge traffic probe base.
In this paper, we described a system for detecting
a peripherally located vehicle based on a location of
User Request Traffic Condition Providing System for using Location Information
197

a user or a particular point on a map which point was
selected by a user, so as to be provided with traffic
images captured by a smart device installed in the
detected vehicle.
A server for providing a traffic image to a user
device includes a location information receiving unit
which receives information relating to a respective
location of each of a plurality of vehicles, a location
management unit which receives information relating
to a particular area from a user device, and which
detects at least one vehicle located within the
particular area based on the location information. An
information sending unit which sends information
relating to the at least one detected vehicle to the user
device, an image requesting unit which receives
information relating to a vehicle selected from among
the at least one detected vehicle from the user device,
and which requests, from a device installed in the
selected vehicle, transmission of a traffic image of the
selected vehicle, and an image providing unit Which
receives the image and which provides the traffic
image to the user device.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by 'Software
Convergence Cluster Program', through the Ministry of
Science, ICT and Future Planning (2015-GSWC-16).
This research was supported by the MSIP
(Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning),
Korea, under the C-ITRC (Convergence Information
Technology Research Center) (IITP-2015-H8601-15-
1011) supervised by the IITP (Institute for
Information & communications Technology
Promotion)
REFERENCES
Rohit Khobre, Prathamesh Durgude, 2014. System for
Estimation of Traffic Conditions and Providing
Alternative Routes, International Journal of
Engineering Research & Technology.
Peter Handel, Jehns Ohlsson, Martin Ohlsson, Isaac Skog,
Elin Nygren, 2013. Smartphone-Based Measurement
Systems for Road Vehicle Traffic Monitoring and
Usage-Based Insurance. IEEE.
SW Kim, SP Heo et al., 2012. Server for providing traffic
image to user device, and the user device.
Martinez FJ, Chai-Keong T, Cano JC, Calafate CT, Manzoni
P. Emergency Services in Future Intelligent
Transportation Systems Based on Vehicular
Communication Networks, Intelligent Transportation
Systems Magazine, IEEE, 2010, Volume 2, Issue 2:6-20.
Megha Nirbhavane, Shashi Prabha, 2014. Accident
Monitoring System using Wireless Application,
International Journal of Advanced Research in
Computer Engineering & Technology (IJARCET)
Volume 3 Issue 4, April 2014.
Amit Kushwaha, Vineet Kushwaha, 2011. Location Based
Services using Android Mobile Operating System,
International Journal of Advances in Engineering &
Technology, 14 Vol. 1,Issue 1,pp.14-20 , Mar 2011.
V. Manolopoulos, S. Tao, S. Rodriguez, M. Ismail and A.
Rusu, 2010. MobiTraS: A Mobile Application for a
Smart Traffic System, the 8th IEEE NEWCAS
Conference, June 2010, Montreal, pp. 365-368.
Rohit Khobre, Prathamesh Durgude, 2014. System for
Estimation of Traffic Conditions and Providing
Alternative Routes, International Journal of
Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT), Vol. 3
Issue 3, pp. 1896~1897, March 2014.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
198
