
Knowledge Management Framework using Enterprise Architecture
and Business Intelligence
Oswaldo Moscoso-Zea
1
, Sergio Luján-Mora
2
, Cesar Esquetini Cáceres
3
and Norman Schweimanns
4
1
Faculty of Engineering, Equinoctial Technological University, Rumipamba y Burgeois, Quito, Ecuador
2
Department of Software and Computing Systems, University of Alicante, San Vicente del Raspeig, Alicante, Spain
3
Faculty of Systems Engineering, National Polytechnic School, Ladrón de Guevara E11-253, Quito, Ecuador
4
innoCampus, Technische Universität Berlin, Straße des 17. Juni, Berlin, Germany
Keywords: Knowledge Management, Enterprise Architecture, Business Intelligence.
Abstract: Knowledge Management (KM) has emerged as a tool which enables the efficient creation, use, distribution
and transfer of knowledge in organizations. In the core of KM there are three dimensions of analysis:
people, processes and technology. KM Frameworks presented in the past have had a strong theoretical
background, but they have not been well explained in terms of how to implement them in practice to cover
all KM dimensions. In this paper, a novel KM framework is presented. This framework was designed as a
practical guide to implement KM endeavours in organizations. To accomplish our research objective, two
management practices are incorporated in the framework: Enterprise Architecture and Business Intelligence.
Enterprise Architecture allows companies to visualize organizational objects in different areas (business,
applications and technology) through the use of models. Moreover, Business Intelligence technologies as
data warehouses, data mining and visualization can enable the capture, transfer and the creation of new and
purposeful knowledge. This work is intended to be a good resource for companies or individuals that want
to implement a KM initiative.
1 INTRODUCTION
Knowledge Management (KM) has emerged as a
discipline which enables the efficient creation, use,
distribution and transfer of knowledge in
organizations (Campbell, 2006). Innovations in
science and technology have led to the emergence of
intensively information-based organizations. These
organizations need to transform this information into
knowledge to secure competitiveness and improve
decision making.
The core dimensions that need to be examined in
a KM project are: people, processes and technology
(Edwards, 2011). Knowledge derived from these
dimensions should be analyzed and stored using
different information repositories. A Knowledge
Management Framework (KMF) enables
organizations to conduct and implement KM
initiatives. KMFs are the foundation for developing
information infrastructure and information systems
to manage knowledge properly. Karemente, Aduwo,
Mugejjera, and Lubega (2009), describes different
KMFs; however, none of these integrates and
analyzes the three knowledge dimensions as a whole
and are difficult to use in practice.
As a result of a university research project, a
KMF was developed. This framework details how a
KM implementation should be done in order to
capture explicit and implicit knowledge derived
from the three knowledge dimensions previously
mentioned. Moreover, two management practices
are included in the framework to accomplish our
objective: Enterprise Architecture (EA) and
Business Intelligence (BI).
EA is defined as “a coherent set of principles,
methods and models that are used in the design,
realization and maintenance of an enterprise’s
business architecture, organizational structure,
information architecture and technology architecture
with respect to the corporate strategy” (Lankhorst,
2009). The purpose of EA is to optimize the
processes of an organization into a cohesive
environment that is open to change and supportive to
the business strategy (The Open Group, 2011).
On the other hand, BI is “the conversion of
organizations resources to knowledge. It is the data
mining and the integration of information from
corporate data warehouses to produce large amounts
244
Moscoso-Zea, O., Luján-Mora, S., Cáceres, C. and Schweimanns, N.
Knowledge Management Framework using Enterprise Architecture and Business Intelligence.
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2016) - Volume 1, pages 244-249
ISBN: 978-989-758-187-8
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
of information needed for effective decision making
process and for planning strategically to achieve a
competitive advantage in its industry” (Barakat, Al-
Zu’bi, and Al-Zegaier, 2013). In this paper, a KMF
supported by EA and BI is presented. The
framework was designed as a practical guide to
implement KM in organizations.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows:
Section 2 presents the theoretical background; Section
3 explains how the KM framework was developed;
and Section 4 provides conclusions of the work.
2 BACKGROUND
The research objective of this work is to present a KM
framework which can be used in practice to capture,
use and transfer knowledge. In this section, the
literature research made for this work is presented.
2.1 Knowledge Management
Knowledge is one of the key resources that can
strengthen the positioning of an organization
(Curado, 2006). In order to sustain a competitive
advantage, a resource should be valuable, rare and
imperfectly imitable (Wernerfelt, 1984).
Organizational knowledge meets these
characteristics; therefore, it must be captured and
managed appropriately. Knowledge can be defined
as experience, facts, know-how, processes, beliefs,
that increase an organizational or individual’s
capability (Karemente et al., 2009).
KM is “a process of identifying, capturing and
leveraging the collective knowledge in an
organization to help the organization compete”
(Alavi and Leidner, 2001). Moreover, KM is
“concerned with the exploitation and development
of the knowledge assets of an organization with a
view to furthering the organization’s objectives”
(Rowley, 2000). The reasons for KM include staff
turnover, information overload, increasing need of
expert staff, improved decision making and
digitalization of organizational knowledge.
From the definitions, two important tasks are
necessary to implement KM. Firstly, it is necessary
to develop the technological infrastructure for
facilitating knowledge capturing and sharing; and
secondly, to establish mechanisms and procedures
for retaining knowledge from people and processes.
In order to accomplish these objectives, researchers
have developed KMFs with different approaches.
Nevertheless, a generally accepted framework has
not been established (Heisig, 2009).
2.2 Enterprise Architecture
Enterprise Architecture (EA) supports in describing
the current state (as-is situation) of an organization
and proposes the best alternative solutions for the
desired outcome (to-be situation). EA can be seen as
a map that incorporates methods and techniques to
create architectures in different layers of an
organization. US Federal Enterprise Architecture
Management Office defines EA as “a management
practice to maximize the contribution of an agency’s
resources, IT investments, and system development
activities to achieve its performance goals” (FEA
Program Management Office, 2007).
EA addresses the need to manage increasing
complexity and deal with continuous change by
providing a holistic view of the organization,
including their organizational components and their
relations. EA is often viewed as a management
practice that supports digitalization of knowledge to
improve the performance of organizations (de Vries
and van Rensburg, 2008).
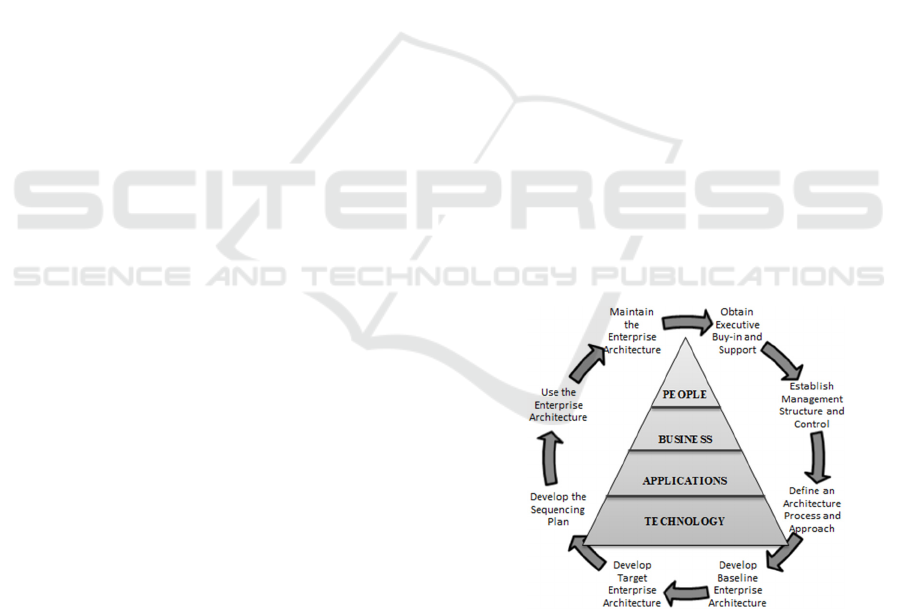
Figure 1 shows a pyramid with the
organizational architecture layers as: people,
business, applications and technology. The circular
arrows sequentially depict the process for
implementing EA in an organization: getting the
stakeholders involved, establishing management and
control, defining the architecture process, the
creation of the as-is and to-be scenario, development
of a sequencing plan, using and maintaining the EA.
Figure 1: Enterprise Architecture Based on: (Tucker and
Debrosse, 2003).
2.3 Business Intelligence
The term Business Intelligence (BI) was coined and
became popular in the 1990s (Chen, Chiang, and
Storey, 2012). According to (Gartner Inc., 2013), BI
builds upon a set of tools and applications that
Knowledge Management Framework using Enterprise Architecture and Business Intelligence
245

enable the analysis of vast amounts of information
(Big Data) to improve decision making and
performance of organizations. To accomplish this
objective, decision makers require having access to
all organization´s data, to analyze the business, its
requirements and its trends.
The main technology in a BI project is a data
warehouse. The data warehouse is a data repository
which is populated from the integration of different
operational data sources maintained in different
units of the organization. An efficient analysis of
data requires powerful analysis tools. Two main
types of analysis tools exist: Online Analytical
Processing (OLAP) and Data mining tools. OLAP
tools use multidimensional views of aggregate data
to provide access to corporate information for the
purpose of improving decision making. Data mining
uses software techniques for finding hidden patterns
and trends in large databases to support strategic
decisions (Connolly and Begg, 2005).
3 PROPOSAL OF KNOWLEDGE
MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK
As mentioned previously, in the core of KM there
are three dimensions of analysis: technology, people
and processes. Hence, a successful implementation
of a KM initiative in organizations must take into
account mechanisms to effective capture, use and
transfer knowledge acquired from the three stated
dimensions. The design of the framework is
intended to put order in the KM process. Moreover,
a practical framework can support managers in the
creation, capture, digitalization of knowledge and
decision making.
3.1 Technology
The first dimension of analysis in a KM process is
technology. Technology is defined by
(BusinessDictionary, 2015) as “The purposeful
application of information in the design, production,
and utilization of goods and services, and in the
organization of human activities”. In this paper,
technology is referred to as objects used by humans
(tools, software, hardware, machines) for KM.
Information repositories for EA and databases are
the core technologies that support KM.
EA repositories store the objects and processes
modeled from the different architectural layers in an
organization. On the other hand, databases store data
generated from different applications. There are two
main sources in which information can be found
Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) and Online
Analytical Processing (OLAP). The source of data
for OLTP databases is operational data. The main
purpose of OLTP databases is to run and to control
fundamental business data with a highly normalized
design. Data for OLAP databases is integrated and
loaded from different operational sources into a
multidimensional database namely a data
warehouse. The purpose of OLAP databases is to
improve business analysis and decision making. In a
KM implementation, information can be extracted
and processed from these two repositories. Many
methods and techniques can be used to extract useful
knowledge from databases. Some of the most used
techniques in a knowledge discovery process are
data mining and machine learning.
3.2 People
People dimension is one of the pillars for the
exploration and exploitation of knowledge in
organizations. According to Churchman (1975)
“knowledge resides in the user and not in the
collection of data”. Thus, a mechanism should be
designed within the proposed framework in order to
capture and to transfer knowledge from people in
organizations. It is important to note that the staff
turnover rate in the United States in 2014 was 11%
in all industries (Compensation Force, 2014). This is
an indicator that strategies should be implemented to
maintain and transfer knowledge from these and
other groups of employees that are leaving
organizations.
The cost of training of new employees without
the efficient capture of people’s knowledge can
increase exponentially. According to the Association
for Talent Development, the average of spending on
employee training within US is around $1208 per
year and per employee (Association for Talent
Development, 2015). We believe that this value can
be decreased if we plan staff turnover accordingly
and establish mechanisms for the capture of
knowledge with existing technology, for example by
using learning management systems (Sanchez-
Gordon, Calle-Jiménez, and Luján-Mora, 2015).
3.3 Processes
Processes are described by (Edwards, 2011) as “the
way people, organizations and even technology
actually do things”. The importance of processes in
KM initiatives are described in different papers (Bou
and Sauquet, 2004) (Newell, Robertson, Scarbrough,
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
246

and Swan, 2002). Identification and digitalization of
the core processes of an organization is an important
step in a KM initiative. It facilitates the transfer of
knowledge of tasks performed by staff since
processes are divided into activities and procedures
are created for easier interpretation. Processes are
modeled normally in a Business Process
Management (BPM) software or in an EA tool. The
process models and architectures created in this
software become an essential part of the knowledge
base of the organization.
3.4 Proposed Knowledge Management
Framework
A successful implementation of a KM initiative
greatly depends on a well-defined method that
supports the creation, capturing, use, distribution and
transfer of knowledge. Organizational knowledge is
created from different interdependent objects in
different domains: strategy, product, services,
information technology, applications, business
processes and people (Lankhorst, 2009). Explicit
and implicit knowledge can be derived from these
domains. Explicit knowledge is knowledge that can
be formulated, documented and reproduced.
Implicit knowledge also known as tacit knowledge is
knowledge that is difficult to document or formulate,
and is normally associated with human knowledge.
Thus, the proposed framework intends to
comprehensively create mechanisms to guide the
KM process to capture knowledge from all the
organizational dimensions. This framework was
conceived as a part of a research project in a private
university. The main goal of the research project is
the design of a knowledge management framework
(KMF) and the development of a web application
prototype supported by databases, data mining and
business intelligence tools for the planning process
in the university.
One of the main objectives of the university is to
position itself as a research and teaching institution,
through the production, management and transfer of
new knowledge based on institutional research lines.
One of the projects implemented in the past year was
the establishment of an institutional diagnosis in
order to create a new model of corporate
governance.
After analyzing the raised processes and the
outputs of this project a need was identified. The
identified need was to create a KMF for the planning
area of the university to ensure the efficient
management of knowledge and knowledge related
activities. The purpose of the framework is to
support planning, implementation and control of
knowledge related projects and programs required
for the effective management of intellectual capital.
Before the design of the framework started, a
series of interviews was realized with different
stakeholders in order to discover their knowledge
requirements and to structure the framework. The
importance of the three dimensions of knowledge
was confirmed in the interviews. Moreover, certain
activities to include in the framework were
identified. Some of these activities were: discovering
of knowledge in existing databases, digitalization of
existing processes and the definition of mechanisms
to convert tacit knowledge from different people in
the organization into explicit knowledge. The
novelty of the framework resides in the use of EA
and BI to cover all the stated dimensions. Figure 2
depicts the designed framework.
The component in the right presents an analysis
on how explicit knowledge is produced by using BI
and EA tools. This box receives implicit knowledge
as an input. The implicit knowledge is produced by
people and processes in the organization. The
knowledge discovery process inside the box has the
following steps: analysis of existing databases and
files, extraction of useful information,
transformation to the target database format and
loading. This process known as ETL (Extraction,
Transformation, Loading) prepares data into a
customizable format, cleans data with errors and
eliminates duplicates. The purpose of this step is to
load quality data into the target database in order to
improve the analysis processes.
A data warehouse is the best target database for
analysis. A data warehouse conceptual design
consists of a set of dimension tables, fact tables and
their relations. The populated data warehouse can be
analyzed using BI and data mining tools to discover
knowledge. Data mining and machine learning are
popular methodologies for the knowledge discovery
process. There are different methods and techniques
that can be used.
On the other hand, digitalization of knowledge
can be captured in an EA tool. An EA tool supports
the creation of architectures to translate implicit
knowledge into models which describe
organizational structures (people), business
processes, applications and technological
infrastructure.
Most EA tools are based on the Archimate
standard (Schekkerman, 2011). Archimate language
allows the design of architectures in different
domains and the creation of relations between the
different objects of the organization. The
Knowledge Management Framework using Enterprise Architecture and Business Intelligence
247

Figure 2: Proposed Knowledge Management Framework.
digitalization process includes an analysis of the
different units and departments of the organization.
Interviews must be realized with all the staff in order
to document and model the different activities and
processes realized in all architecture layers. The
modeling of EA projects enables the capture and
collection of implicit knowledge from the employees
and the transformation to explicit knowledge in the
forms of views and viewpoints of the architectures.
EA and BI are the main methodologies of creation
of explicit knowledge. It is important to present
explicit knowledge in an easy and understandable
way. The framework suggests the presentation of
knowledge by using a KM system which can be
developed in a web environment. The results of the BI
and EA process can be visualized and analyzed in this
KM system. The output of the component in the right
is explicit knowledge in the form of reports and
dashboards that are presented to be used by people in
all levels of the organization and can support in the
design or redesign of new and existing processes. The
explicit knowledge is the main input of the box in the
left of the framework. Explicit knowledge can support
and enhance decision making activities and can
increase knowledge levels of the people in the
organization. It supports as well the transfer of
knowledge to new employees. As seen in the
framework the KM process is a cycle in which
knowledge is produced in a daily basis.
4 CONCLUSIONS
KM is a practice that organizations are incorporating
to improve the creation, use, distribution and transfer
of knowledge. The implementation of KM must be
guided by a KMF. Many KMFs exist in the
literature. However, these frameworks do not
present practical mechanisms to gather and analyze
all the knowledge dimensions: people, processes and
technology.
The use of BI and EA tools bridges the gap of
capturing all the knowledge dimensions. On the one
hand, BI allows the transformation of simple
information in valuable knowledge by applying data
mining methods and techniques. On the other hand,
EA supports the digitalization of implicit knowledge
from people and processes by creating architectures in
different domains. These architectures facilitate the
transfer and distribution of knowledge to different
levels of people in the organization. Some benefits of
using this framework are: reduced training costs of
staff turnover, improved decision making processes
and the creation of a knowledge repository.
REFERENCES
Alavi, M., & Leidner, D. E., 2001. Knowledge
Management and Knowledge Management Systems.
MIS Quarterly, 25(1), 107–136.
Association for Talent Development, 2015. 2014 State of
the Industry Report: Spending on Employee Training.
Retrieved November 20, 2015, from
https://goo.gl/MpccrZ.
Barakat, S., Al-Zu’bi, H. A., & Al-Zegaier, H., 2013. The
role of business intelligence in knowledge sharing.
European Journal of Business & Management, 5(2),
237–243.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
248

Bou, E., & Sauquet, A., 2004. Reflecting on quality
practices through KM theory. Knowledge
Management Research & Practice, 35–47.
BusinessDictionary, 2015. Technology Definition.
Retrieved November 20, 2015, from
http://goo.gl/a266MR.
Campbell, H. M., 2006. The role of organizational
knowledge management strategies in the quest for
business intelligence. Engineering Management
Conference, 2006 IEEE International, 231–236.
Chen, H., Chiang, R. H. L., & Storey, V. C., 2012.
Business Intelligence and Analytics: From Big Data
To Big Impact. Mis Quarterly, 36(4), 1165–1188.
Churchman, W., 1975. The design of Inquiring Systems:
Basic Concepts of Systems and Organizations.
American Educational Research Journal, 12-1, 94–96.
Compensation Force, 2014. 2014 Turnover Rates by
Industry. Retrieved November 30, 2015, from
http://goo.gl/hGEuFg.
Connolly, T., & Begg, C., 2005. Database Systems. Essex,
England: Pearson Education Limited.
Curado, C., 2006. The knowledge-based view of the firm.
Instituto Superior de Economia E Gestao, (1959), 18.
de Vries, M., & van Rensburg, A., 2008. Enterprise
Architecture - New business value perspectives.
Southafrican Journal of Industrial Engeneering, 19,
1–16.
Edwards, J., 2011. A Process View of Knowledge
Management : It Ain ’ t What you do , it ’ s the way
That you do it. Journal of Knowledge Management,
9(4), 297–306.
FEA Program Management Office, 2007. FEA Practice
Guidance, (November). Retrieved from
https://goo.gl/QIqI1V.
Gartner Inc., 2013. Gartner Business intelligence.
Retrieved November 9, 2015, from
http://goo.gl/LmJRG3.
Heisig, P., 2009. Harmonization of Knowledge Magagement-
comparing 160 KM frameworks around the globe.
Journal of Knowledge Management, 13(4), 4–31.
Karemente, K., Aduwo, J. R., Mugejjera, E., & Lubega, J.,
2009. Knowledge Management Frameworks.
Strengthening the Role of ICT in Development, 35–57.
Lankhorst, M., 2009. Enterprise Architecture at Work
Modelling Communication and Analysis (2nd ed.).
Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
Newell, S., Robertson, M., Scarbrough, H., & Swan, J.,
2002. Managing Knowledge Work and Innovation
(2nd ed.). Palgrave macmillan.
Rowley, J., 2000. From learning organisation to
knowledge entrepreneur. Journal of Knowledge
Management, 4(1), 7–15.
Sanchez-Gordon, S., Calle-Jiménez, T., & Luján-Mora, S.,
(2015). Relevance of MOOCs for Training of Public
Sector Employees. In 14th International Conference
on IT Based Higher Education and Training (pp. 1–5).
Caparica.
Schekkerman, J., 2011. Enterprise Architecture Tool
Selection Guide. Institute for Enterprise Architecture
Developments.
The Open Group, 2011. TOGAF ® Version 9.1. Retrieved
from http://goo.gl/djuv15.
Tucker, R., & Debrosse, D., 2003. Enterprise Architecture
Roadmap for Modernization. Enterprise
Modernization Issue, 7(2).
Wernerfelt, B., 1984. A Resource-based View of the Firm.
Strategic Management Journal, 5, 171–180.
Knowledge Management Framework using Enterprise Architecture and Business Intelligence
249
