
Evaluating the Reliability of Ambient-Assisted Living Business
Processes
Ricardo Martinho
1
, Dulce Domingos
2
and Ana Respício
3
1
Polytechnic Institute of Leiria and CINTESIS - Center for Health Technology and Services Research, Leiria, Portugal
2
LaSIGE, Faculdade de Ciências, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal
3
Centro de Matemática, Aplicações Fundamentais e Investigação Operacional, Faculdade de Ciências,
Universidade de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal
Keywords: Ambient-Assisted Living, Reliability, Business Processes, BPMN.
Abstract: Ambient-Assisted Living (AAL) systems provide a wide range of applications in order to improve the
quality of life of patients. These systems commonly gather several components such as sensors, gateways,
Information Systems or even actuators. Reliability of these components is of most importance, mainly due
to the impact that a failure can have on a monitored patient. In spite of the existing reliability evaluations
and countermeasures that can be associated with an AAL system component, we need to take into account
the overall reliability for the several activities and interactions that exist between all the AAL system
components, for each time a certain value is registered or a certain alert is triggered. In this paper, we
propose a new approach to calculate the overall reliability of an AAL system. We take a Business Process
Management (BPM) approach to model the activities and interactions between AAL components, using the
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) standard. By extending the BPMN standard to include
reliability information, we can derive the overall reliability value of a certain AAL BPMN process, and help
healthcare managers to better allocate the appropriate resources (including hardware or health care
professionals) to improve responsiveness of care to patients.
1 INTRODUCTION
The major purpose of Ambient-Assisted Living
(AAL) systems is to improve the quality of life and
care responsiveness for patients at risk while staying
at their homes and performing their normal daily
routines (Islam et al., 2015). AAL provides them
with an overall surveilled environment, allowing the
delivery of care where and when needed, and also
supporting caregivers, families and care
organizations.
Applications of AAL not only provide
continuous health monitoring through, for instance,
vital signs recording for medical history analyses,
but also play a major role in detecting emergency
situations. In turn, caregivers and/or other health
professionals can better organize their care business
processes by receiving alerts and actuating when
needed, and with the appropriate resources. Some
AAL applications can even replace (self) care
activities, such as auto injecting insulin when blood
sugar values increase at a certain rate.
Although many times associated with support in
assisting elderly people (see for instance H2020 calls
of European Commission), AAL systems can also be
used in patients suffering from chronic diseases such
as diabetes, asthma and heart attacks. Therefore, the
impact of a less reliable system can range from a
false alarm transmitted to a certain caregiver and/or
emergency unit service, to serious patient injury due
to wrong, delayed or even non-delivered care.
Current research works and industry products
related with AAL and overall to Internet of Things
(IoT) applied to healthcare already provide
redundancy checks and alerts to prevent greater
impacts to patients using them (see, for instance,
Parente et al., 2011; Siewiorek and Swarz, 2014).
Nevertheless, these efforts to increase reliability are
usually self-contained to some components of an
AAL system, i.e., reliability is commonly evaluated
for each component, regardless of its position in a
certain sequence of activities to trigger some action
(alert, register or even actuate).
In this work, we propose a new and consolidated
approach to calculate the overall reliability of an
AAL system, by using a Business Process
528
Martinho, R., Domingos, D. and Respício, A.
Evaluating the Reliability of Ambient-Assisted Living Business Processes.
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2016) - Volume 2, pages 528-536
ISBN: 978-989-758-187-8
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
Management (BPM) approach and the Business
Process Model and Notation (BPMN) (OMG, 2011)
standard de facto for modelling AAL business
processes. We consider each component of an AAL
system as part of a business process containing
essentially sensors, actuators and gateways, which
interact through a sequence of activities, decision
nodes and messages in order to produce alerts, to
register values in a centralized (healthcare)
Information System, or even to trigger actuators to
provide immediate care. Since these interactions are
usually subjected to several conditions, we model
them as BPMN process models, in order to calculate
their combined reliability. This way, we can derive
the overall AAL system reliability, such as in the
following example: a measure is taken by a heart
rate sensor, transmitted through a network, evaluated
through an Information System, and the appropriate
alerts are triggered to prevent potentially fatal
consequences for the patient.
This paper is organized as follows: section 2
presents background on AAL and a typical AAL
system scenario modelled with BPMN. In section 3
we refer to related work on reliability applied to
most common components of an AAL system, and
in section 4 we explain how we include reliability
information in an AAL BPMN process model, in
order to calculate its overall reliability and how we
apply the Stochastic Workflow Reduction (SWR)
algorithm to compute the reliability of combined
BPMN process elements. Section 5 presents an
application scenario for the calculus of the overall
reliability for a typical AAL BPMN business
process. Finally, section 6 concludes the paper and
presents future work.
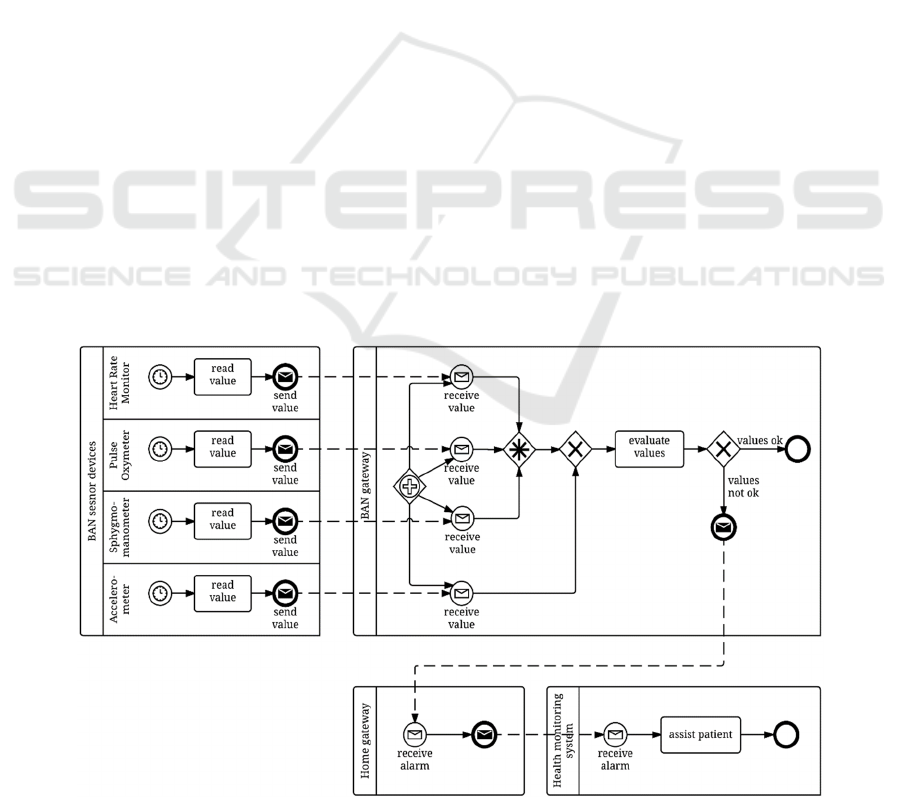
2 BACKGROUND
This section presents a typical AAL process model
(see for instance the proposals of Bui and Zorzi
(2011) and Dar et al. (2014)).
The AAL BPMN process model, as illustrated in
Figure 1, uses a collaboration diagram with four
pools, one for each participant or AAL component
(Rodrigues et al., 2012; Rashidi and Mihailidis,
2013; Memon et al., 2014; and Islam et al., 2015).
The Body Area Network (BAN) sensor devices
are used for monitoring vital signs, i.e., heart and
body activity in this example (based on Parente et
al., 2011). The heart activity is assessed through the
heart rate, the blood oxygen, and the blood pressure,
by using a heart rate monitor, a pulse oxymeter and a
sphygmomanometer, respectively. The system
monitors the body activity by using an
accelerometer. While this process only uses sensors,
BANs can also include actuators. For instance BAN
devices can, on a diabetic patient, auto inject insulin
through a pump, while monitoring the insulin level
(Jara et al., 2011).
As defined in this process, sensors read values
from the patient from time to time by using a timer
and send them to the BAN gateway. The interaction
between sensors and the BAN gateway can also be
implemented through the request-request paradigm,
Figure 1: AAL BPMN process model.
Evaluating the Reliability of Ambient-Assisted Living Business Processes
529

where the BAN gateway starts the interaction asking
for the values. Depending on sensor computational
capabilities, they can also filter the data they
transmit, sending only values that are considered
relevant. However, for this reliability study, these
differences are not significant.
The BAN gateway, another participant of the
process, is responsible for the communication inside
that BAN and to the home gateway. Besides it
receives the values from sensors, it also validates,
aggregates and analyses these values. The reception
of sensor values is modelled with a BPMN Event-
Based Exclusive Gateway. The information about
heart rate should be provided by at least two out of
three devices, and this behaviour is modelled with a
BPMN Complex Gateway. After evaluating sensor
values, the BAN gateway sends an alarm to the
health monitoring system (HMS) to assist the
patient, in case any emergent situation is detected.
The communication between the BAN gateway and
the HMS is performed through the home gateway.
Smart phones or wireless routers can be used as
home gateways. They communicate with the BAN
gateway through wireless technologies (Bluetooth or
WiFi, for instance) and provide the connectivity to
the internet. From the point of view of the process
model we could omit the Home gateway pool, as it
does not define any business logic. However, this
way, the participants of the process are coherent
with the components of a generic AAL architecture
and it simplifies the reliability study as the process
includes all the components and connections.
Finally, with the health monitoring system,
caregivers and physicians monitor patients remotely.
3 RELATED WORK
Koren and Krishna (2007) define reliability of a
system at time t, denoted by (), as the probability
of the system to be up continuously in time interval
[0,]. This metric is adequate for systems operating
continuously, where a single momentary failure can
have a high or even critical impact.
McNaull et al. (2012) discuss the quality issues
of each component of an AAL system. BAN devices
(sensors and actuators) reliability depends on their
quality and manufacturer. According to the same
authors, the mean-time between failures (MTBF)
metric can be used to assess it. In addition, sensors
data quality (accuracy) also interferes with reliability
as anomalous values can be discarded, for instance,
in BAN gateways. Quality of data depends on sensor
calibration as well as on the correct use and
application of sensors. For instance, other heat
sources can affect temperature sensors.
Parente et al. (2011) present a use case where
they monitor the health of patients considering heart
and body activities. The system uses a heart rate
monitor, a pulse oxymeter, and a sphygmo-
manometer to monitor the heart activity. The body
activity of patients is monitored with an
accelerometer on knees and a motion detector in the
room. Taking into account the required reliability of
the system, the authors determine the minimal
combinations of sensors the system needs. However
they only use the information about the reliability of
each device.
BAN gateways can be used to increase the
reliability of the system. They may evaluate sensor
data and detect anomalous and inconsistent values,
considering the expected ones, which may have been
established during the testing period of the AAL
system (McNaull et al., 2012). In case of anomaly,
erroneous sensor values are discarded and BAN
gateways can request for new sensor values. If the
problem persists, the BAN gateway can alert the
health monitoring system. Another way to increase
system reliability is by defining a fault tolerant
behaviour for the BAN gateway.
Body sensors and actuators communicate with
each other and with the BAN gateway using mostly
wireless technologies, such as IEEE802.15.4
/ZigBee (IEEE, 2011). The latest international
standard for wireless BAN (WBAN) is the
IEEE802.15.6 (IEEE, 2012). Home and BAN
gateways also communicate through wireless
technologies (Bluetooth or WiFi, for instance).
Reliability of wireless networks depends on
interferences of other devices; obstruction of the
signal due to lifts or wall, and attenuation, i.e., the
strength of the signal reduces during transmission.
Baig et al. (2014) compare wireless transmitted data
with manual recorded data and hospital collected
data. They use a total of approximately 2500
transmissions of 30 hospitalized patients and they
conclude that, in wireless transmitted data, losses
vary from 20% (blood glucose) to 80% (blood
pressure and heart rate). They also conclude that
data losses were mainly due to distance and data
transmission delays were due to poor signals, signal
drops, connection loss and/or poor location.
Despite the evaluation of the reliability of each
AAL component is crucial, it is not sufficient to
study the overall system. This way, in the following,
we present related work about computing reliability
for composite tasks and/or even for the overall
process.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
530

Indeed, while reliability has been a major
concern for networking, critical and real-time
applications, as well as middleware (Parente et al.,
2011; Siewiorek and Swarz, 2014); the increasing
use of workflow, specifically, in more critical
systems, justifies the works on workflow reliability.
In the context of workflow modelling, Cardoso
(2002) defines task reliability as the probability that
the components operate on users demand, following
a discrete-time model. In this context, the failure rate
of a task can be described by the ratio number of
unsuccessful executions/ scheduled executions. The
task reliability, denoted by
R(A), is the opposite of
the failure rate, that is:
R(A) = 1 – failureRate(A).
In the same work, Cardoso proposes a predictive
Quality of Service (QoS) model for workflows and
web services that, based on atomic task QoS
attributes, is able to estimate the QoS for workflows,
considering the following dimensions: time, cost,
reliability, and fidelity. To compute QoS for the
overall workflow, the author developed the
Stochastic Workflow Reduction algorithm, which
applies a set of reduction rules to iteratively reduce
construction workflow blocks until only one activity
remains. The QoS metrics of the remaining activity
corresponds to the QoS metrics of the process.
Cardoso defines reduction rules for the following
construction blocks: sequential, parallel, conditional,
loop, fault tolerant, and network systems. He applies
his proposal to the METEOR workflow management
system (Krishnakumar and Sheth, 1995). To
estimate the reliability of web services compositions,
Coppolino et al. (2007) generalize the Cardoso
proposal, covering all the generic workflow patterns
of van Der Aalst et al. (2003).
Within the WS-BPEL context, Mukherjee et al.
(2008) compute the reliability of WS-BPEL
processes taking into account most of the workflow
patterns that WS-BPEL can express, while the
method of Distefano et al. (2014) also incorporates
advanced composition features such as fault,
compensation, termination and event handling.
Using Unified Modeling Language (UML)
models, Rodrigues et al. (2012) annotate system
component interactions with their failure
probabilities. They convert them into a formal
executable specification, based on a probabilistic
process algebra description language, which are
executed on PRISM. This way, they can, for
instance, identify the components that have the
highest impact on the reliability system.
By focusing their work on BPMN, Respício and
Domingos (2015) calculate the reliability of BPMN
business processes by using the Stochastic
Workflow Reduction method of Cardoso (Cardoso,
2002; Cardoso et al., 2004). To meet this goal, they
extend BPMN with reliability information and they
identify the BPMN process blocks for which they
can apply one of the reduction rules.
The work we describe in this paper applies and
extends the proposals of Respício and Domingos
(2015) to evaluate the reliability of AAL processes.
Listing 1: BPMN extension for reliability - XML Schema.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns="http://.../relybpmn"
xmlns:bpmn=http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/20100524/MODEL
targetNamespace="http://.../relybpmn">
<xsd:import namespace="http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/20100524/MODEL"
schemaLocation="BPMN20.xsd"/>
<xsd:group name="relyBPMN">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="ReliabilityInformation" type="tReliabilityInformation"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xsd:element name="Probability" type="tProbability" minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="1"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:group>
<xsd:complexType name="tReliabilityInformation" abstract="false">
<xsd:attribute name="requiredReliability" type="xsd:decimal"/>
<xsd:attribute name="calculatedReliability" type="xsd:decimal"/>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexType name="tProbability" abstract="false">
<xsd:attribute name="value" type="xsd:decimal"/>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:schema>
Evaluating the Reliability of Ambient-Assisted Living Business Processes
531
4 RELIABILITY INFORMATION
IN BPMN PROCESSES
To include reliability information in BPMN business
processes we use the extension, whose XML
Schema we present in Listing 1. The definition of
this extension is based on the work proposed by
Respício and Domingos (2015).
The extension has two elements. The first
element, named
ReliabilityInformation, has
two attributes: the
requiredReliability which
defines the minimum accepted reliability value for
the process or flow node, and the
calculatedReliability which is the reliability
of atomic activities and events (initialised with a
pre-determined value) or the reliability for
decomposable activities (sub-processes) and
processes computed using the SWR method of
Cardoso (2002).
The second element is the
Probability. The
probability value is used with conditional
SequenceFlow elements within conditional process
or loop process blocks and defines the probability of
the process execution path of taking them.
The reliability of processes is calculated with the
SWR method of Cardoso (it is similar for
decomposable activities). This method applies a set
of reduction rules to the process, iteratively, until
only one activity remains. The reliability of the
remaining activity corresponds to the reliability of
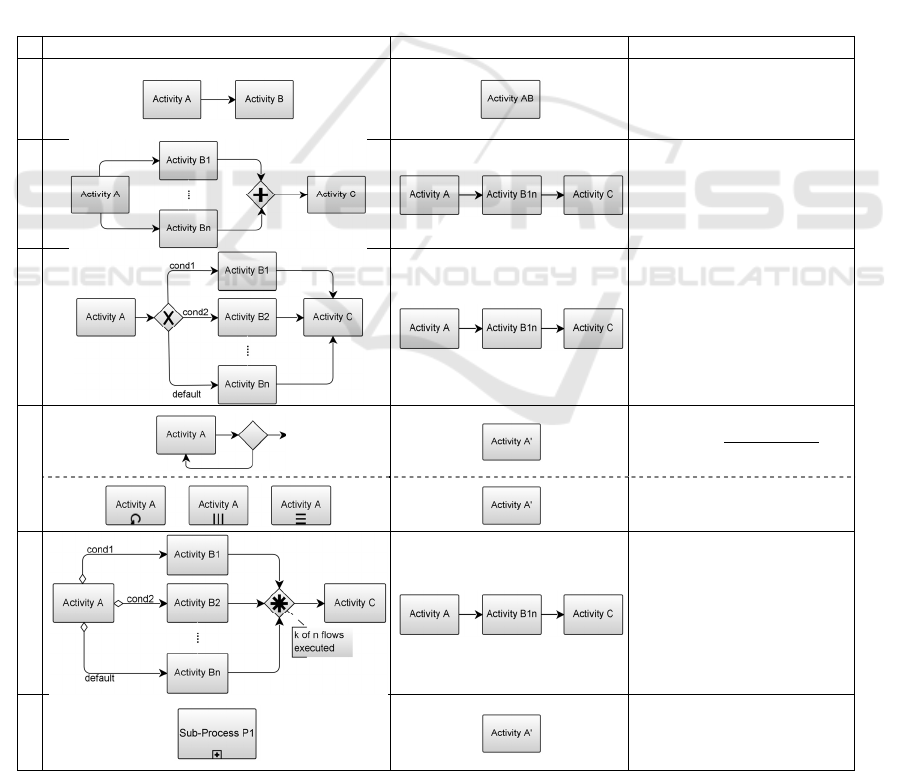
the process. Table 1 presents the application of the
six reduction rules of Cardoso to BPMN, identifying
the BPMN process blocks for which the reduction
rules can be used (Respício and Domingos, 2015).
As the AAL BPMN process subject of our study
Table 1: Reliability of Reduced Block (Respício and Domingos, 2015).
Initial Block Reduced Block Reliability of Reduced Block
Sequential
(
)
=
(
)
∗()
Parallel
(
1
)
=
(
)
1≤≤
Conditional
(
1
)
=
()
1≤≤
Loop
(
′
)
=
(
1 −
)
()
1 − ()
(
′
)
=()
Fault tolerant
(
1
)
=
∑
…
∑(
(∑
−
=1
)
∗
2
=0,1
1
=0,1
∏
1−
+
(
2
−1
)
(
)
=1
)
Network
(′) = (1)
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
532

also has events (see Figure 1), we use the same
reduction rules for process blocks composed by
events or activities, in an undifferentiated way.
In addition, when using reduction rules with
collaboration diagrams, they are applied to the
overall diagram by omitting pools and lanes.
However, to overcome the limitations of the block
structured approach of Cardoso, where one starting
point and one ending point are needed, we transform
the collaboration diagram by adding two new
gateways. To have a unique starting point, we add an
Exclusive Event-Based Gateway without any
incoming sequence flows and with one outgoing
sequence flow to each start event of the
collaboration diagram. Similarly, to have a unique
end point, we add an
Inclusive or Merge
Gateway with an incoming sequence flow from
each end event and without any outgoing sequence
flows (Ouyang et al., 2007).
5 RELIABILITY STUDY
This section presents a case study focusing on the
reliability evaluation of the AAL process presented
in section 2.
Initially, process designers set up the minimum
accepted values for the reliability of activities and
sub-processes (
requiredReliability). The
BPMN process model is then enriched, through the
relyBPMN extension, considering these values as
well as pre-estimated values of the attributes
calculatedReliability
(initialized with pre-
estimated values for atomic activities and events)
and
Probability. Then, the SWR algorithm
iteratively computes the
calculatedReliability
for sub-processes, reaching the reliability value for
the overall process (the collaboration diagram).
In the following, we describe the application of
this method to assess the reliability of the
collaboration diagram displayed in Figure 1,
considering different scenarios.
The experiment started by establishing a base
case scenario and computing the corresponding
reliability. After, a sensitivity analysis on the process
reliability was made. The objective of this analysis
was to evaluate the impact of changes in the
individual reliability of separate elements on the
reliability of the overall process. We made vary the
reliability of the following elements: each sensor,
the transmission from sensors to the BAN gateway,
and the transmission from the BAN gateway to the
HMS through the home gateway.
Parente et al. (2011) propose reliability values
for the type of sensors used in our use case, namely
the Heart Rate Monitor (HRM), the Pulse Oxymeter
(POxy), the Shygmomanometer (Shygm), and the
Accelerometer (Acc), which are used to initialise the
atribute
calculatedReliability of the tasks
“read value”.
Based on the measures of Baig et al. (2014), we
establish the reliability value associated to the
transmission from sensors to the BAN gateway,
which is used to initialise the
calculatedRelia-
bility
of the “receive value” tasks. For setting the
reliability value for the transmission from the BAN
gateway to the HMS, through the home gateway, we
consider both connections together to simplify the
study. This reliability value is used to initialise the
calculatedReliability of the task “receive
alarm” of the HMS.
The base case scenario, as illustrated in Table 2,
considers the values proposed for the reliability of
sensors (Parente et al., 2011); the value 0.992 for the
reliability of transmission from sensors to the BAN
gateway; and the value 0.99 for the reliability of
transmission from the BAN gateway to the HMS.
The
calculatedReliability attribute was set
to 1.0 for the remaining activities and events, such as
the process start, the evaluation of the received
values in the BAN gateway, and the “assist patient”
activity. In addition, the
requiredReliability
value for all process activities and events was set to
0.6, as this was assumed to be the minimum
acceptable reliability.
The reduction rule for the fault-tolerant gateway
considers four feasible combinations of receiving
two out of three signal devices: (HRM, POxy,
Shygm), (HRM, POxy), (HRM, Shygm), and (POxy,
Shygm).
Table 2: Reliability values for activities and transmissions
for the base case scenario.
Raw Reliability
BAN
devices
(sensors)
Sensor Sensors to
Gateway
BAN
Gateway
to HMS
HRM 0.8 0.992 0.99
POxy 0.7 0.992 0.99
Shygm 0.6 0.992 0.99
Acc 0.9 0.992 0.99
Overall
reliability
0.6901
For the base case scenario, the reliability of the
process takes the value 0.6901.
Evaluating the Reliability of Ambient-Assisted Living Business Processes
533
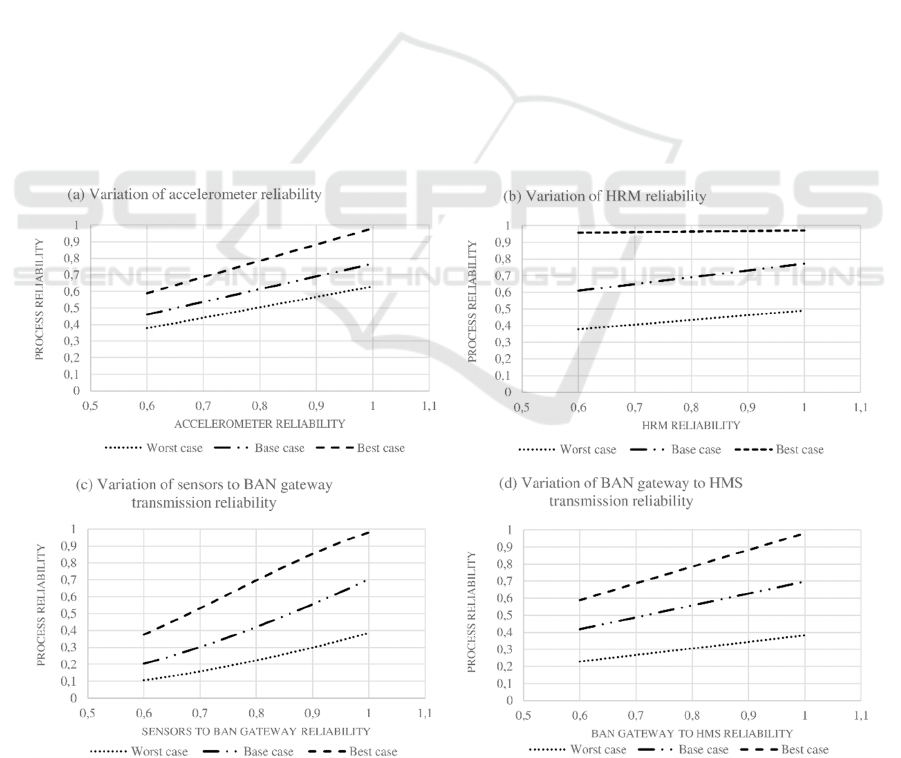
The study continued by making variations on
different reliability values and assessing the
resulting reliability of the global process. Figure 2
displays the results of this study. Chart (a) displays
the results of the variation of the Accelerometer
reliability in three scenarios. The base case scenario
corresponds to fix all the other values of the original
base case (Table 2) and making the reliability of the
accelerometer vary in the interval [0.6; 1], using
steps of 0.01. The worst case scenario differs by
setting the reliability values of the remaining sensors
to 0.6 (the minimum allowed value), while for the
best case the reliability of the other sensors was set
to 0.99 (considering an optimistic value). Chart (b)
shows the effects on the process reliability due to
variation of the HRM reliability considering the
same scenarios. As receiving (or not) information
from the other sensors in the fault tolerant pattern
has the same impact, this chart would be the same
for the sensors POxy and Shygm. Chart (c) displays
the impact of varying the reliability of transmission
from the sensors to the BAN gateway, for similar
scenarios – worst case (all the sensors’ reliability set
to the minimum 0.6), base case (all values set to the
base) and best case (all the sensors’ reliability set to
0.99). Finally, chart (d) discloses the dependence of
process reliability from the reliability of the BAN
gateway to the HMS transmission, using the
previous scenarios.
The results reveal that the reliability of the
process is mostly sensitive to reliability variations of
the transmission from the sensors to the BAN
gateway (chart (c)), then to variations of the
accelerometer reliability (chart (a)), to variations of
transmission from the BAN gateway to the HMS
(chart (d)), and, finally, to the reliability of a single
sensor (HRM, Pulse Oxy, Shygm) (chart (b)). The
analysis of scenarios for the different charts allows
concluding that the process reliability is more
sensitive to variations of the value under analysis in
the best case scenario and less sensitive in the worst
case scenario. Nevertheless, the process reliability is
insensitive to reliability variations of the sensors
HRM, POxy, and Shygm for the best case scenario.
The charts also allow identifying variation ranges
for reliability values of the different elements that
meet the required reliability for the overall process.
In addition, few conditions allow to reach an overall
reliability greater than 0.9 – if the transmission from
the sensors to the BAN gateway has a reliability of
at least 0.92.
Figure 2: - Impact on the process overall reliability due to varying separate reliabilities: a) variation of accelerometer
reliability (upper left); b) variation of HRM reliability (upper right); c) variation of sensors to BAN gateway transmission
reliability (lower left); variation of BAN gateway to HMS transmission reliability (lower right).
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
534

6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper we presented a new approach to
calculate the overall reliability of a certain AAL
system and the way its components interact with
each other. We use a BPM approach to model these
interactions and to derive the combined reliability.
For this, we extend the BPMN language to include
reliability information for each process element and
use the SWR algorithm to calculate the overall
process reliability.
The study presented in section 5 exemplifies
how to proceed to assess different conditions of an
AAL BPMN process that involves AAL system
components. This assessment can be made at design
time to analyse the feasibility of the process, for
instance, if a minimum level of reliability is assured.
It allows to identify the elements which have the
highest impact on process reliability and, therefore,
to design the system architecture and set the
requirements for system elements.
Additionally, reliability can be computed at run
time to monitor process executions hence providing
an approach to identify low reliability services. In
that case, for instance the sensor timers could be
adjusted as well as the transmission rate increased at
run time. We intend to extend a Business Process
Management System (such as jBPM -
www.jbpm.org/), in order to include reliability
information in BPMN processes, as well as runtime
reliability monitoring features. These features can
then help health care professionals to better allocate
resources to provide the adequate care to certain
AAL-monitored patients, taking into account their
overall reliability.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is partially supported by National
Funding from FCT - Fundação para a Ciência e a
Tecnologia, under the projects
UID/MAT/04561/2013 and UID/CEC/00408/2013.
REFERENCES
Baig, M. M., GholamHosseini, H., Connolly, M. J., &
Kashfi, G. (2014, June). A wireless patient monitoring
system for hospitalized older adults: Acceptability,
reliability and accuracy evaluation. In Biomedical and
Health Informatics (BHI), 2014 IEEE-EMBS
International Conference on (pp. 330-333). IEEE.
Bui, N., & Zorzi, M. (2011, October). Health care
applications: a solution based on the internet of things.
In Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on
Applied Sciences in Biomedical and Communication
Technologies (p. 131). ACM.
Cardoso, A.J.S. (2002) Quality of service and semantic
composition of workflows (Doctoral dissertation).
University of Georgia.
Cardoso, J., Sheth, A., Miller, J., Arnold, J., & Kochut, K.
(2004). Quality of service for workflows and web
service processes. Web Semantics: Science, Services
and Agents on the World Wide Web, 1(3), 281-308.
Coppolino L., Romano L., Mazzocca N., & Salvi S.
(2007). Web Services workflow reliability estimation
through reliability patterns. In: International
Conference on Security and Privacy in
Communications Networks and the Workshops. pp.
107-115, IEEE.
Dar, K., Taherkordi, A., Baraki, H., Eliassen, F., & Geihs,
K. (2014). A resource oriented integration architecture
for the Internet of Things: A business process
perspective. Pervasive and Mobile Computing.
Elsevier.
Distefano, S., Ghezzi, C., Guinea, S., & Mirandola, R.
(2014). Dependability assessment of web service
orchestrations. Reliability, IEEE Transactions
on,63(3), 689-705.
IEEE (2011). IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan
area networks--Part 15.4: Low-Rate Wireless Personal
Area Networks (LR-WPANs).
IEEE (2012). IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan
area networks - Part 15.6: Wireless Body Area
Networks.
Islam, S.M.R., Kwak, D., Kabir, M.H., Hossain, M.,
Kwak, K. (2015). The Internet of Things for Health
Care: A Comprehensive Survey. In Access, IEEE ,
vol.3, no., pp.678-708.
Jara, A. J., Zamora, M. A., & Skarmeta, A. F. (2011). An
internet of things---based personal device for diabetes
therapy management in ambient assisted living
(AAL). Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 15(4),
431-440.
Krishnakumar, N., & Sheth, A. (1995). Managing
heterogeneous multi-system tasks to support
enterprise-wide operations. Distributed and Parallel
Databases, 3(2), 155-186.
Koren I. & Krishna C.M. (2007) Fault tolerant systems.
Morgan Kaufmann.
McNaull, J., Augusto, J. C., Mulvenna, M., & McCullagh,
P. (2012). Data and information quality issues in
ambient assisted living systems. Journal of Data and
Information Quality (JDIQ), 4(1), 4.
Memon, M., Wagner, S. R., Pedersen, C. F., Beevi, F. H.
A., & Hansen, F. O. (2014). Ambient assisted living
healthcare frameworks, platforms, standards, and
quality attributes. Sensors, 14(3), 4312-4341.
Mukherjee, D., Jalote, P., & Nanda, M. G. (2008).
Determining QoS of WS-BPEL compositions.
Evaluating the Reliability of Ambient-Assisted Living Business Processes
535

In Service-Oriented Computing–ICSOC 2008 (pp.
378-393). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Object Management Group (2011). Business Process
Model and Notation (BPMN) Version 2.0.
Ouyang, C., Dumas, M., Ter Hofstede, A. H., & van der
Aalst, W. M. (2007). Pattern-based translation of
BPMN process models to BPEL web services.
International Journal of Web Services Research
(JWSR), 5(1), 42-62.
Parente, G., Nugent, C. D., Hong, X., Donnelly, M. P.,
Chen, L., & Vicario, E. (2011). Formal modeling
techniques for ambient assisted living. Ageing
International, 36(2), 192-216.
Rashidi, P., & Mihailidis, A. (2013). A survey on ambient-
assisted living tools for older adults. Biomedical and
Health Informatics, IEEE Journal of, 17(3), 579-590.
Respício, A., & Domingos, D. (2015). Reliability of
BPMN Business Processes. Procedia Computer
Science, 64, 643-650.
Rodrigues, G. N., Alves, V., Silveira, R., & Laranjeira, L.
A. (2012). Dependability analysis in the ambient
assisted living domain: An exploratory case
study. Journal of Systems and Software, 85(1), 112-
131.
Siewiorek D. & Swarz R. (2014) Reliable Computer
Systems: Design and Evaluation. Digital Press.
van Der Aalst, W. M., Ter Hofstede, A. H., Kiepuszewski,
B., & Barros, A. P. (2003). Workflow
patterns. Distributed and parallel databases, 14(1), 5-
51.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
536
