
Color Image Segmentation upon a New Unsupervised Approach
using Amended Competitive Hebbian Learning
Meriem Timouyas
1
, Souad Eddarouich
2
and Ahmed Hammouch
1
1
ENSET, LRGE, Mohammed 5 University, Rabat, Morocco
2
Regional Educational Center, Rabat, Morocco
Ke
ywords: Probability Density Function, Competitive Neural Networks, Mahalanobis Distance,
Competitive Hebbian Learning, Topology Preserving Feature, K-means, Segmentation,
Competitive Concept, Thresholding.
Abstract: This paper proposes a new unsupervised color image segmentation procedure based on the competitive
concept, divided into three processing stages. It begins by the estimation of the probability density function,
followed by a training competitive neural network with Mahalanobis distance as an activation function. This
stage allows detecting the local maxima of the pdf. After that, we use the Competitive Hebbian Learning to
analyze the connectivity between the detected maxima of the pdf upon Mahalanobis distance. The so
detected groups of Maxima are then used for the segmentation. Compared to the K-means clustering or to
the clustering approaches based on the different competitive learning schemes, the proposed approach has
proven, under a real and synthetic test images, that does not pass by any thresholding and does not require
any prior information on the number of classes nor on the structure of their distributions in the dataset.
1 INTRODUCTION
The aim of automatic classification is to partition a
set of observations into groups or classes such as
observations belonging to the same class are more
similar than those belonging to different classes
(Eddarouich and Sbihi, 2007).
For the multidimensional data classification
methods (Muthanna et al., 2010; Hammouche et al.,
2005; Verikas et al., 1996), cluster analysis
techniques attempt to separate a set of
multidimensional observations into groups or
clusters which share some properties of similarity.
The objects are generally represented by N-
dimensional vectors of observed features. The
statistical approach in cluster analysis postulates that
the input patterns are drawn from an underlying
probability density function (pdf), which describes
the distribution of the data points through the data
space. Regions of high local density, which might
correspond to significant classes in the population,
can be found from the peaks or the modes of the
density function estimated from the available
patterns (Devijver and Kittler, 1982). Then, the key
problem is to partition the data space with a
multimodal pdf into subspaces over which the pdf is
unimodal (Mizoguchi and Shimura, 1976).
Among the most common applications of
automatic classification is image segmentation.
Color image segmentation is one of the most
important pre-processing step towards image
understanding, image compression and coding. It is
a process that consists of partition the image into
disjoint region as sets of connected pixels that are
homogenous with respect one or more color
characteristics (Uchiyama and Arbib, 1994).
Generally, most algorithms of segmentation
treated are based on threshold selection or on
parameters adjustment which may change the its
results.
Considering the analogy between clustering and
segmentation, the color image segmentation is
achieved by pixel classification according to color
features. It is generally assumed that homogeneous
regions in the image correspond to clusters of color
points in the color space. The sample of observations
is composed of image pixels represented as data
points scattered in a color space; it determines a
partition of these points into subgroups in a way that
makes points within a group more similar than
points in different groups. In an unsupervised
context, the number of these subgroups is not a
priori known and has also to be determined.
Timouyas, M., Eddarouich, S. and Hammouch, A.
Color Image Segmentation upon a New Unsupervised Approach using Amended Competitive Hebbian Learning.
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2016) - Volume 2, pages 205-210
ISBN: 978-989-758-187-8
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
205

Amongst the non-classical methods, the
application of artificial neural networks (ANN) is
prominent. In recent years, motivated by the
remarkable characteristics of the human visual
system (HVS), research has applied ANNs to
various problems in classification (Yeo et al., 2005).
ANNs have several advantages over many
conventional computational algorithms, among
which the most important are parallelism,
adaptability to different data sets and optimal
performance.
Many clustering procedures based on modes
detection concepts, have been proposed. In some of
them, modes are considered as local maxima of the
estimated probability density function and are
detected by hill climbing procedures using some
gradient search technique (Fukunagal and Hostler,
1975). As these procedures are based on differential
operators, they face some difficulties where noise is
present in the data set. In practical situations, they
are known to generate a greater number of modes
than the true pdf. Another approach is based on the
analysis of the convexity properties of the
underlying pdf. Modes are then considered as
concave regions of this function and are detected by
means of a test which determines, locally, the
convexity of the multivariate pdf (Vasseur and
Postaire, 1980; Moussa, Sbihi and Postaire, 2008).
Although this approach yields more robust results
than the previous one, it remains sensitive to local
irregularities in the pattern distribution, especially
for small data sets.
In this context, we are going to present a new
unsupervised approach for the segmentation of color
images based on the detection of the modes of
multivariate probability density function (pdf)
without using either differential operators or any
procedures of filtering
The remainder of the paper is organized as
follows. Section 2 presents the different steps of the
proposed approach. Section 3 is consecrated to other
results and discussion. The paper ends with a
conclusion and perspectives.
2 THE MODES DETECTION
PROCEDURE
The new algorithm of the modes detection is carried
out in three processing stages. The first one consists
in estimating the underlying pdf using a non-
parametric estimator. In the second stage, we use an
artificial neural network with competitive training
(CNN) to extract the local maxima of the pdf. In the
third stage, we develop a new technique for the
detection of the interneural connection.
2.1 The Estimation of Underlying
Probability Density Function
Let
12
{ , ,..., }
Q
X
XXΓ=
, be the set of Q N-
dimensional observations of a random variable X
with a probability density function P(X).To estimate
this underlying density function when what is
available is only a set
,1 ,2 , ,
{ , ,..., ,..., }
qqq qnqN
Xxx x x=
, q=1,2,...,Q of Q
observations, the analyst may use non-parametric
techniques.
The Parzen (1962) window method proves well
adapted to the proposed procedure in this paper.
However, this estimation procedure needs
prohibitive calculus when the dimension of the space
is very important. So, we have opted for the fast
estimation algorithm which is proposed by Postaire
and Vasseur (1982).
First, the range of variation of each component
of these observations is normalized to the interval [0,
R], where R is an integer such as
2R ≥
, by means
of the transformation defined as:
,
=
,
−min
,
max
,
−min
,
∗
(1)
Each axis of the so normalized data space is then
partitioned into R exclusive intervals of unit width.
This discretization defines a set of
N
ℜ
hypercube of
unit side length. Each hypercube noted
()HX
, is a
site defined by its N coordinates
12
, ,..., ,...,
nN
x
xxx
which are the integer parts of
the coordinates of its center
X
.
To be more specific, let
1, 2, , ,
[ , ,..., ,..., ]
qqqnqNq
Yyy y y=
, q=1, 2, Q be the Q
observations in the normalized space. Each
observation Yq is found inside a non-empty
hypercube with the coordinates
,
int( )
nnq
x
y=
, n=1,
2, N, where
,
int( )
nq
y
designates the integer parts of
,nq
y
. If several observations fall in the same
hypercube, this one appears many times on the list
of non–empty hypercubes. Furthermore, the number
of times the hypercube H(X) appears in that list
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
206

indicates the number of data points q[H(X)] which
falls in this hypercube. Subsequently, the value of
the local density estimated is:
=
(2)
Since the volume of H(X) is equal to unity.
So, this fast procedure allows only the estimation
of the underlying probability density function at the
centers of the non-empty hypercubes whose number
never exceeds the number Q of available
observations. At the centers of the hypercube cells,
which are not on that list, the density estimates are
known to be null. At the end of this fast algorithm,
all the available information for clustering is in the
discrete set
X
of estimated values of the underlying
probability density function
()pX
.
2.2 The Extraction of Local
Maxima by Neural Network
Assimilating the modes to the local maxima of the
pdf, the proposed approach uses the Neural
Networks with Competitive Training (NNCT)
(Eddarouich and Sbihi, 2007).
In the training algorithm, we work only on the
pdf by presenting, sequentially, the centers of the
non-empty hypercubes of the set X to the network,
instead of the Q observations.
The neural network is composed of two layers:
the input layer and the output layer (Cf. Fig.1). The
first one is made of N units I
n
, n=1,2,...,N, such that
unit I
n
is solicited by the attribute X
N
of the non-
empty hypercube H(X) when this one is presented to
the network. However, each output neuron
materializes an hypercube which represents the site
of one local maximum of the pdf in the set X, and
presents its weight by the mean vector µ
k
(X),
k=1,2,…,K. The number of the output neuron is
first initialized arbitrary.
Figure 1: Competitive neural network.
During the training phase, The output neurons
enter into competition with each other by comparing
the distance D[µ
k
(X), H(X)], k=1,2,…,K, between
the input hypercube H(X) and each output neuron
µ
k
(X), the winner is the closest one to the hypercube,
then we compare the values of the pdf associated to
the winner neuron µ
g
(X) and to H(X). The distance
measure used in this learning algorithm is
Mahalanobis distance that gives best results for the
non Gaussian distribution (Timouyas et al., 2012)
instead of Euclidian distance as in the (NNCT).
The following algorithm describes the different
steps of the learning phase:
Training Algorithm:
Initialization Phase:
Initialize the mean vectors
()
k
X
μ
; k=1, 2, K, of
the K output neural, with an arbitrary choice of K
non-empty hypercubes from the set X,
Initialize the coefficients of the training function
0
α
and
τ
. The choice of these parameters is not
a real problem. We should only give a very
important value to
τ
for the algorithm to search
the sites of the local maxima before its
convergence (Eddarouich and Sbihi, 2007).
Processing Phase:
1) Present to the network, with an arbitrary pulling,
a non-empty hypercube H(X),
2) Search for the winner neuron g defined by
calculating the distance that separate µ
k
(X) and
H(X) and seeking for the minimal distance:
D
μ
X
,H
X
=
μ
X−HX
μ
X−HX
.
(3)
∑
.
.
Inverse of covariance matrix.
3) Compare the fdp(µ
g
(X)) and fdp(H(X)):
If fdp(µ
g
(X)) < fdp(H(X)) update the parameters
of the winner neuron as follow:
μ
=
μ
−
−
μ
μ
=
(4)
Where
t is the number of iterations and
()t
α
is a one of
“search then converge” learning functions defined as:
αt=
1
(5)
Then go to step1. Else, go directly to step1,
4) Stopping criteria: after the processing of all
hypercubes, compare
()
t
k
X
μ
to
1
()
t
k
X
μ
−
for k∈K.
If
1
( ( ) ( )) 1, 2,...,
tt
kk
XXk K
μμ
−
≠∀=
, pass to
the next iteration and go to step 1.
Else, end of the processing.
…
X
1
X
2
X
N
µ
1
(X)
µ
2
(X)
µ
K
(X)
Input Layer
Output Layer
Color Image Segmentation upon a New Unsupervised Approach using Amended Competitive Hebbian Learning
207

2.3 Detection of Significant Modes
of Pdf
As the modes that are detected during the learning
phase perfectly mark modal regions and are divided
into a number equal to the number of classes present in
the sample, we thought about connecting each groups
of the closest modes in such a way that we get a map
which preserves the shape and structure of the classes.
One of the perfect methods which forms
topology preserving maps is Competitive Hebbian
Learning (CHL) proved by Martinetz (1993). The
basic principle which governs the change of
interneural connection strength been formulated by
Hebb (1949). According to Hebb’s postulate, a
presynaptic unit i increases the strength of synaptic
link to a postsynaptic unit j if both units are
concurrently active (Martinetz, 1993).
CHL is usually not used on its own but in
conjunction with other method derived as Neural
Gas plus Competitive Hebbian Learning (Martinetz,
1993)
and Growing Neural Gas (Fritzke, 1995).
Let
{}
)X(H),...,X(H),X(HF
K
21
=
, be the set of
K hypercubes which represent the sites in X of the K
detected local maxima; the output of CNN. In this
phase, we are going to seek the interneural
connection of these modes using a new method of
Competitive Hebbian Learning adapting
Mahalanobis distance as measure of resemblance.
The clustering in CHL is based on three
concepts. Firstly, the Vector Quantization (VQ),
which is searching for centroids as density points of
nearby lying samples, it can be also directly used as
prototype-based clustering method: each centroid is
then associated to one prototype. By aiming to
minimize the expected squared quantization error
(Gray, 1984).
The second and third concepts are Voronoi
diagram and the Delaunay triangulation illustrated
below:
(a) 14 point from data set in R
2
(b) The Voronoi diagram
(c) The Delaunay triangulation (d) The induced Dt
Figure 2: The detection of the induced Dt by masking the
Delaunay triangulation with the data set.
The Voronoi diagram V
F
of a set
{}
)X(H),...,X(H),X(HF
K
21
=
of hypercubes H(X
i
)
ϵ R
N
is given by K N-dimensional polyhedra, the
Voronoi polyhedra V
i
, which is defined as follows:
The Voronoi polyhedron V
i
of a hypercube H(X
i
) ϵ F
is given by the set of hypercubes v ϵ R
N
which are
close to H(X
i
) than any other H(X
j
) ϵ F for i≠j
(Martinetz and schulten, 1994) :
=∈
‖
−
‖
−
∀
(6)
The dual graph of Voronoi diagram is Delaunay
triangulation Dt (Delaunay, 1934), it’s the
connection of all pairs H(X
i
), H(X
j
) ϵ F, where the
circumcircles of the triangles consisting of each of 3
hypercubes of the set, such that no hypercube in F is
inside.
The Dt is also the graph where hypercubes with a
common Voronoi edge V
i
and V
j
are connected by an
edge, that is (Martinetz & schulten, 1994):
=,
=1,…,
∩
∅ (7)
To generate the induced Delaunay triangulation
(Fig. 2(a)), competitive Hebbian learning, given the
K modes detected by CNN as prototypes in R
N
,
successively adds connections among them. The
method does not change the weight of prototypes,
but only generates topology according to these
prototypes. For each mode H(X
k
), its two closest
prototypes are connected by an edge using
Mahalanobis distance (3) as measure of resemblance
instead of Euclidian distance, it works as an
activation function for competition between
neurons. This leads to the induced Delaunay
triangulation, which is limited to those regions of the
input space R
N
.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
To illustrate the behavior of the procedure, we
present two examples. The first one is a synthetic
image constituted of 4 regions of colors in different
shapes. The three RGB components, coded on 256
levels, constitute the axes of the coordinates of the
representation space of the image pixels (fig. 3(a)).
The proposed procedure of the pdf modes
detection of the observations sample in figure 3.b
permits to extract the six related regions with the
resolution parameter R=30.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
208
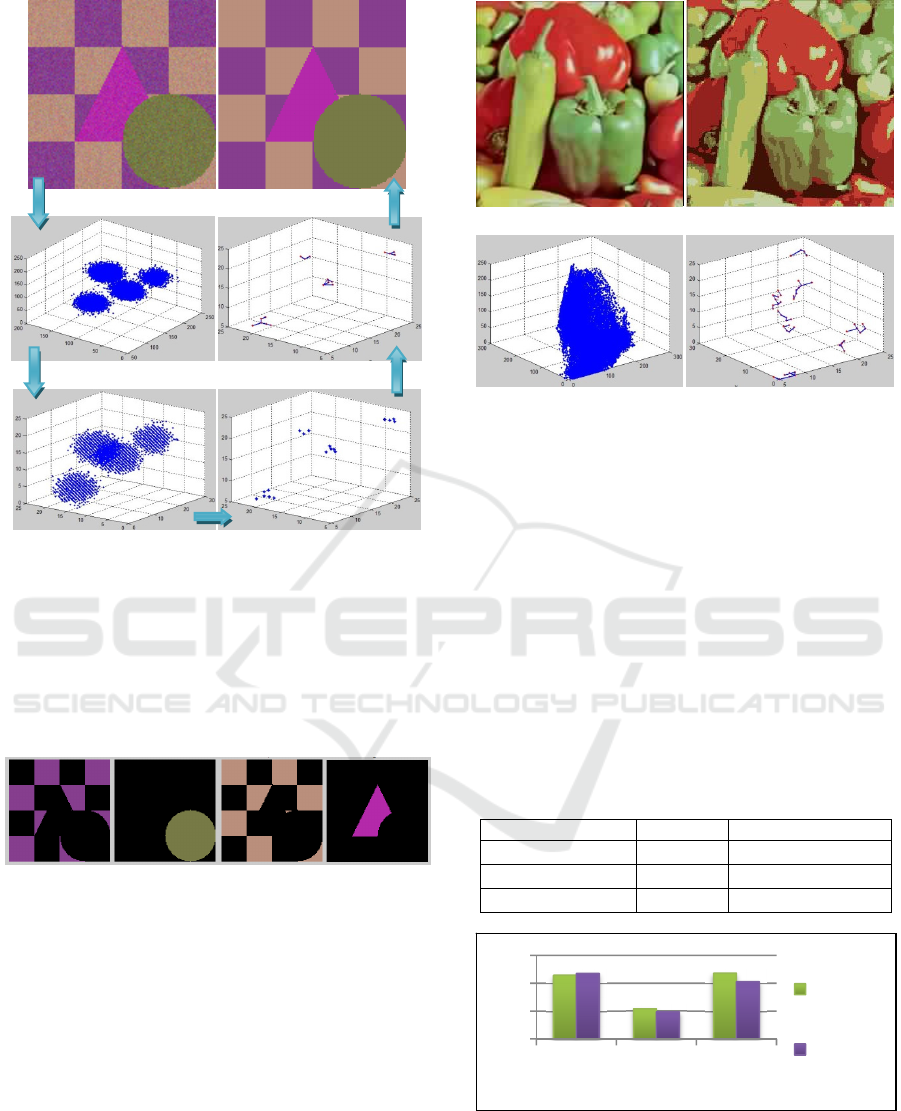
(a) (f)
(b) (e)
(c) (d)
Figure 3: (a) Original color image; (b) Pixels in the RGB
color space; (c) Estimation of the underlying pdf; (d)
Prototypes in the RGB color space; (e) Prototypes
connected by edges; (f) Segmented color image.
This figure provides the clear idea about the
different steps of the proposed method. Below we
illustrate separately the 4 classes of the image:
Figure 4: the four classes of the image.
As shown, the proposed technique success to
detect the four groups of connected neurons
presenting the four classes in the image (fig. 3(e))
and have been used to get the segmented image (fig.
3(f)).
Now, we will apply the approach on a real color
image, with a significant overlapping degree,
constituted of five homogeneous regions with
different shapes:
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Figure 5: (a) Original pepper image; (b) Segmented pepper
image; (c) Pixels in the RGB color space; (d) Prototypes
connected by edges defining 8 classes in 8 iterations.
Despite the difficulty of the treatment of this
image where the various clusters present a
significant overlapping degree in the RGB color
space ( fig.5(c)), the use of the Mahalanobis Metric
as criterion of resemblance, allows the proposed
approach to give more powerful results compared to
the Neuromemetic approach.
In order to prove the approach’s efficiency more,
we evaluate the homogeneity in the image compared
to K-means result applying on the same image by
the experimental parameters exposed below:
Table 1: Statistical parameters of the two methods.
Parameters K-Means Proposed method
avg voxel intensity
45.764
47.0573
Std Dev
21.6
19.3433
Coeff Var
47.21%
41.106%
Figure 6: Comparison of statistical parameters.
The image segmented by the suggested
procedure is most consistent because of its lower
standard deviation and higher average voxel
0
20
40
60
avg voxel
intensity
Std Dev Coeff Var
K-Mean
s
Propose
d
method
Color Image Segmentation upon a New Unsupervised Approach using Amended Competitive Hebbian Learning
209

intensity, which is clearly proved by its lower
coefficient of variance compared to the K-means
result. Hence, the proposed procedure demonstrates
its accuracy in color image segmentation, knowing
that this method has all advantages of artificial
neural network mentioned before.
In spite of that, The Mahalanobis Distance has a
higher execution time than Euclidian Distance
because of its processing complexity but the nearest-
neighbor search can be performed in only O(LogN)
instead of O(N) time by exploiting the Delaunay
triangulation (Knuth, 1973). Also, with this so
reduced number N of neurons, the proposed
detection of modes procedure stays faster than this
phase in both Neuromimetic and
Neuromorphological procedures (Timouyas et al.,
2014). Although, our aim to further minimize the
execution time of the new approach in overall.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, a new approach of unsupervised color
image segmentation has been introduced, based
essentially on neural network concepts.
In order to conceive an unsupervised
classification procedure, we have searched to
connect the detected local maxima, by CNN, in such
away, every connected set of neurons represents a
class, using the Competitive Hebbian Learning.
The proposed procedure permits good
unsupervised image color segmentation without
resorting to any thresholding and does not require
any priori information about the number of classes
nor about the structure of their distributions in the
sample.
REFERENCES
Delaunay, B. (1934). Sur la Sphère vide. Bulletin of the
Academy of Sciences USSR,VII, pp.793-800.
Devijver, P.A., & Kittler, K. (1982) ‘Pattern recognition:
A statistical approach’, Englewood Cliff, NJ, Prentice-
Hall international.
Eddarouich, S., & Sbihi, A. (2007) ‘Neural Network for
Modes Detection in Pattern Classification’. ICTIS’07,
Morocco, Fez, 3-5 pp. 300-303.
Fritzke, B. (1995) ‘ A growing neural gas network learns
topologies’, In G. Tesauro, D. S. Touretzky, & T. K.
Leen (Eds.), Advances in neural information
processing systems: 7. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press,
pp. 625_632.
Fukunagal, K., & Hostler, D. (1975). The estimation of the
gradient of a density function with applications in
pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, vol. IT-
21, n°1, p 32-40.
Gray, R.M. (1984) ‘Vector Quantization’, ASSP Magazine,
IEEE (Vol 1, Issue 2 ), ISSN :0740-7467, 1984, pp. 4–29.
Hammouche, K. Diaf, M. and Postaire, J.-G. (2005) ‘A
clustering method based on multidimensional texture
analysis’, Pattern Recognition, pp. 1-13.
Hebb, D. (1949) ‘Organisation of Behavior’, Wiley, New
York.
Knuth, D. E. (1973) ‘The art of computer programming’,
Volume III: Sorting and searching. Reading, MA:
Addison-Wesley.
Martinetz, T.M. (1993) ‘Competitive Hebbian learning
rule forms perfectly topology preserving maps’,
(ICANN), Gielen S. and Kappen B. (eds), Springer,
Heidelberg, pp. 427_434.
Martinetz, T., & schulten K. (1994). Topology
Representing Networks. Neural Networks. Vol. 7, No
3, pp. 507-522.
Mizoguchi, R., & Shimura, S. (1976). Nonparametric
learning without a teacher based on mode estimation.
IEEE Trans. Comput., C-25(11), pp.1109-1117.
Moussa. A, Sbihi. A and Postaire. J-G, (2008) ‘A Markov
random field model for mode detection in cluster
analysis’. Patt. Recog. Letters 29, pp. 1197–1207.
Muthanna, A. H.,Touahni, R., Sbihi, A., & Messoussi, R.
and Eddarouich, S. (2010) ‘Détection des modes d’une
distribution de données multidimensionnelles par
réseau de neurones et morphologie mathématique’,
Journées d'optique et du traitement de l'information.
Parzen, E. (1962) ‘An Estimation of a Probability Density
Function and Mode’, Ann. Math. Stat., vol. 33, pp.
1065-1076.
Postaire, J.-G., & Vasseur, C. P. A. (1982) ‘A fast
Algorithm for non Parametric Probability Density
Estimation’, IEEE, Trans. on Pattern Anal. and
Machine Intel. PAMI-4, n°6, pp. 663-666.
Timouyas, M., Eddarouich, S., & Hammouch, A. (2012).
A new approach of classification for non-Gaussian
distribution upon competitive training, (ICCS’12),
Agadir, Morocco, pp.1-6.
Timouyas, M., Eddarouich, S., Hammouch, A, Touahni,
R. & Sbihi, A. (2014)‘Unsupervised Neural-
Morphological Colour Image Segmentation Using the
Mahalanobis as Criteria of Resemblance’, ICMCS’14,
Marrakech, Morocco, pp.314–320.
Uchiyama, T., & Arbib, M. A. (1994) ‘Color image
segmentation using competitive learning’, IEEE
Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, Vol. 16, n 12, pp. 1197-1206.
Vasseur, C. P. A. & Postaire, J-G. (1980) ‘A connexity
testing method for cluster analysis’ I.EEE Trans. Syst.
Man. Cyber, vol SMC-10, n°3, p 145-179.
Verikas, A., Malmqvist, K., & Bergman, L. (1997). Colour
image segmentation by modular neural network. Pattern
Recognition Letters, Vol 18, Issue 2, pp. 173–185.
Yeo, N.C., Lee, K.H., Venkatesh, Y.V. and Ong, S.H.
(2005) ‘Colour image segmentation using the self-
organizing map and adaptive resonance theory’, Image
and Vision Computing 23, pp. 1006-1079.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
210
