
A Distributed and Cooperative Verification Mechanism to Defend
against DODAG Version Number Attack in RPL
Firoz Ahmed and Young-Bae Ko
Department of Computer Engineering, Ajou University, Suwon, Republic of Korea
Keywords: RPL, DODAG Version Number Attack, Security, Distributed, Cooperative.
Abstract: To design a routing protocol for Low-power and Lossy Networks (LLNs), the IETF developed RPL
(Routing Protocol for Low-power and lossy network) which is novel, standard and light weight routing
protocol standardized for constrained environment and does not have the functionality like of traditional
routing protocols. Providing security in RPL is still challenging as the devices are connected to the
vulnerable Internet, limited resources, and the communication links are lossy. Therefore, an attacker can
easily exploit the functionalities of RPL protocol. RPL exposed to a variety of attacks. One of the most
inconsistency topological attacks is DODAG version number attack. In this paper, we proposed a distributed
and cooperative verification mechanism to securely defend against the DODAG version number attack with
low control overhead and high reliability. Simulation results show that the proposed approach defends
DODAG version number attack reliably and reduces control overhead significantly.
1 INTRODUCTION
The emergence of embedded device capable of
wireless communication is leading to a
materialization of an Internet of Things (IoT).
Recently, IoT has increasingly become a hot topic in
wireless sensor network (WSN) area with a lot of
promising applications. One of the most challenging
issues for IoT is to the connectivity of smart objects
to the Internet. Most of the core technology solution
for this issue has been conducted by IETF working
group 6LoWPAN (IPv6 over Low power Wireless
Personal Area Network) (Kushalnagar et al. 2007).
As part of the 6LoWPAN, the Routing Protocol
Low-power and lossy network (RPL) (Winter et al.
2012) has recently been standardized by IETF to
efficiently handle the layer 3 functions when
providing Internet connectivity for WSN. RPL has
been designed for constrained device and networks.
Due to their constrained nature RPL-based networks
may be exposed to a large variety of security attacks
(Tsao et al. 2015). An adversary can intercept, forge,
modify, inject and create messages in order to
interface with the operation of entire network.
Though the security functionalities have been
considered in RPL, they are based on the traditional
cryptographic solutions which provides
authentication, confidentiality and integrity,
nevertheless, cannot protect the network from
internal attackers. Therefore, we consider the case
where the attacker is a compromised node.
In this paper, we address the security attack,
referred to as a DODAG version number attack,
when RPL is employed for routing in network. In
DODAG version number attack, a malicious node
modifies DODAG version number by illegitimately
increasing the version number of the corresponding
field in DIO message when it forwards them to its
neighbour. Once nodes receive the DIO message
with increased version number, they start the
formation of new DODAG tree. This formation can
cause increased overhead, depletion of energy
reserves, channel availability issue and even loops in
the routing topology.
The RPL attacks (e.g., rank attack, topological
attack, inconsistency attack, etc) have been tackled
in various ways. Some focused on preventing to
publish an illegitimate rank (Dvir et al., 2011) and
other focused on monitoring and intrusion detection
systems architecture (Le et al., 2011), (Mayzaud et
al., 2015). Meanwhile, only a few methods have
been proposed to tackle the DODAG version
number attack. Version number and rank
authentication (VeRA) has been proposed to prevent
version number attack and rank attack using digital
Ahmed, F. and Ko, Y-B.
A Distributed and Cooperative Verification Mechanism to Defend against DODAG Version Number Attack in RPL.
DOI: 10.5220/0005930000550062
In Proceedings of the 6th International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems (PECCS 2016), pages 55-62
ISBN: 978-989-758-195-3
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
55

signature and MAC mechanism in (Dvir et al.,
2011). However, the control overhead of this scheme
will be increased because of using digital signature
and MAC operation. On the other hand, the authors
of (Mayzaud et al., 2014) only describe the version
number attack. However, they did not provide any
kind of defending mechanism to defend the attack.
The approaches of the version number attack
discussed above incur high overhead as well as
failure to address the attack. Therefore, we propose a
distributed and cooperative verification mechanism
that can defend a DODAG version number attack
effectively and reliably with low control overhead
while preserving the integrity of the RPL operation.
In this mechanism, when a node receives a DIO
message with increased DODAG version number
from its neighbour, instead of updating and sending
the DIO message, it rather verifies the neighbour's
identity whether or not the neighbour is malicious.
The node then initiates cooperative verification
process only if it receives increased version number
in DIO messages from its neighbours. Thus, it is of
great importance to devise an efficient and
dependable verification process. Simulation results
show that our mechanism can reduce control
overhead and judgment error for a malicious node
and normal node significantly.
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2
provides the RPL protocol to describe the operation
of the protocol. Related works is provided in Section
3 and the proposed distributed and cooperative
verification mechanism is described formally in
Section 4. The performance evaluation with various
simulation scenarios is given in Section 5 and is
followed by the concluding remarks in Section 6.
2 THE RPL PROTOCOL
RPL is a standardized routing protocol for the IoT.
The design of RPL is a combination of multiple
DODAG networks, each of these consider many
wireless sensor devices connected to a DODAG
root. RPL instance ID; DODAG ID; DODAG
version number; and rank values can differentiate
each and every DODAG in the network. In order to
establish and maintain DODAG as well as routing,
RPL utilizes new ICMPv6 control messages: DIO
(DODAG Information Object), DAO (Destination
Advertisement Object), and DIS (DODAG
Information Solicitation). DODAG root starts the
establishment of the DODAG graph and the
construction of upward routes by broadcasting the
DIO messages. Upon receiving the DIO message,
nodes select the parent to sender. Receiving node then
needs to inform other neighbour nodes by forwarding
the updated information in the next DIO, if it updates
its rank or preferred parent. Each node in DODAG
has a rank that indicates the position of a node relative
to other nodes and with respect to the DODAG root.
Finally, the node selects a preferred parent based on
its parent list which becomes the default gateway.
When a node wants to forward a message towards the
DODAG root, it first tries to send the message to the
preferred parent. If the transmission is unsuccessful, it
tries to forward the message to any of the non-
preferred parents, one after the other.
To optimize the network resources, instead of
sending DIO frequently, RPL uses the trickle
algorithm (Levis et al., 2004) for sending it
periodically. RPL allows each node in the network to
determine whether packets are to be forwarded
upward routes or downward routes. In order to
support downward routing either non-storing mode or
storing mode are used. To prevent loop creation, RPL
uses the rank rule that a node in the parent should
always have lower rank than its children. DODAG
loops may also appear when DODAG is no longer
acyclic. To prevent this, a leaving node must poison
its sub-DODAG by advertising an infinite rank. When
inconsistencies are detected (e.g., nodes disappearing
from a network due to lack of battery power or poor
link conditions), the RPL nodes trigger repair
mechanisms. There are two kinds of repair
mechanism available in RPL; (i) Global and (ii) Local
repair mechanism. The local repair mechanism
consists in finding an alternative path to route the
packets when the preferred parent is not available.
When the local repair mechanisms fail due to multiple
inconsistencies, the DODAG root can initiate a global
repair to rebuild the entire DODAG by incrementing
the version number of the DODAG graph. The
version number is carried in the DIO message. When
a node receives a DIO from its parent compares its
existing version number against the one received. If
the received version is higher, it must ignore its
current rank information. The node then reset trickle
timer and initiate a new procedure to join the
DODAG. Amounting to a reform of a new DODAG,
this global repair mechanism guarantees a loop free
topology. The RPL protocol defines some security
mechanisms that contribute to its security.
3 RELATED WORK
The four categories threats authentication,
confidentiality, integrity, and availability are
PEC 2016 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing
56
identified by Routing Over Low power and Lossy
network (ROLL) working group for potential
security issues in RPL networks and proposed their
countermeasures in (Tsao et al., 2015). To
overcome the attack from outsider, the above
security mechanisms work well. However, they are
not able to protect the network from insider.
There are several kinds of attacks in RPL
protocol and their defending mechanisms have been
carried out in recent years. Rank attack (Le et al.,
2013), (Dvir et al., 2011), and (Perrey et al., 2013),
which is specific RPL internal threat aiming at its
rank property. A malicious node advertises a higher
rank value than the one it is supposed to have. It
then tries to attract child node for selecting as parent,
and attracts large traffic going toward the root.
The survey of the attacks against RPL and
6LowPAN in IoT and their security mechanisms
using different types of intrusion detection system
have been proposed in (Pongle and Chavan, 2015).
A novel intrusion detection system for the IoT has
also been proposed in (Raza et al., 2013). Authors
targeted routing attack such as sinkhole attack,
selective forwarding attack and spoofed or altered
information. However, the authors of (T Matsunaga
and K Toyoda 2015) identified two problems in
(Raza et al., 2013). The problems brought about high
false alarm rate that the sink mistakenly judges
nodes as attackers and which are mitigated by (T
Matsunaga and K Toyoda, 2015).
The authors of (Mayzaud et al., 2015) describe
topological inconsistency attack, in which a
malicious node manipulates the IPv6 header option
of data packets and forwards it to next hop to drop
the modifies packet. As a result, increases control
message overhead and energy consumption, and
reduce channel availability. To mitigate the attack,
they provide an adaptive and dynamic threshold
mechanism.
Network monitoring architecture and RPL
specification-based IDS with a finite state machine
have been proposed for malicious checking in each
monitor node in (Le et al., 2011). The authors in
(Chugh et al., 2012) investigated consequences of
black hole attacks in RPL networks and highlighted
specific measurable parameters to detect such
threats. Defence techniques against sink hole in RPL
networks were explored by Weekly and Pister
(Weekly and Pister 2012).
4 DISTRIBUTED AND
COOPERATIVE
VERIFICATION MECHANISM
In this paper, we propose a distributed and
cooperative verification mechanism which aims to
increase the malicious node detection rate and
reduce the corresponding control overhead. The
proposed scheme is assumed that the network is
dense and it is formed by a numbers of constrained
network devices with limited processing, memory,
and energy when they are battery operated. A
number of malicious nodes with a malicious
intension can intrude the network. However, the
malicious node starts their malicious behaviour after
forming the initial DODAG graph. Each node in the
network is required to evaluate if there is any
malicious node in its neighbourhood. A routing
protocol is used to establish a path between sources
to sink that want to communicate. The routing
protocol is implemented in this network is the RPL
protocol.
4.1 System Model
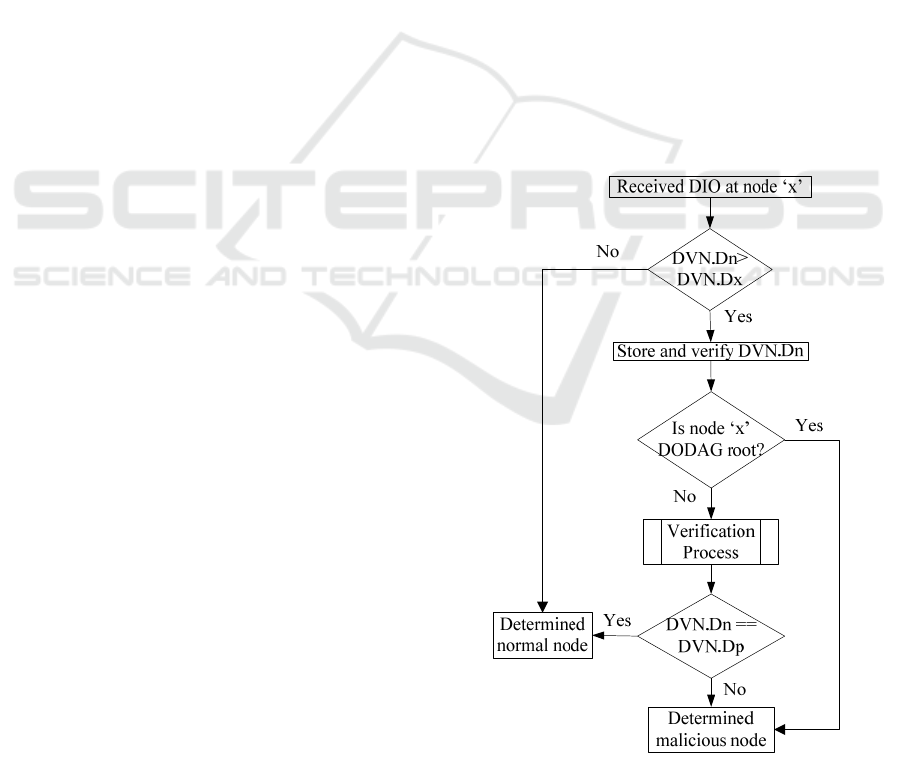
Figure 1: Flow diagram of the proposed scheme.
A Distributed and Cooperative Verification Mechanism to Defend against DODAG Version Number Attack in RPL
57

The proposed scheme consists of two
progressive steps, checking step and verification
step. As illustrate in Figure 1. In the first step, when
a node receives DIO messages from its neighbouring
nodes, the receiving node compares and checks
whether or not the DODAG version number in DIO
message (DVN.Dn) is higher than the version
number of the receiving node (DVN.Dx). If the
version number is higher in receiving DIO, the
system then invokes a cooperative verification
procedure to verify the identity of the neighbouring
node. For verification, a verification node obtains a
current DODAG version number from two-hop
neighbouring nodes (DVN.Dp) efficiently.
If a malicious node stays near (one-hop away)
DODAG root and tries to sends DIO messages with
increased version number to its neighbour, in this
case it is very easy to detect the malicious node by
DODAG root. Upon receiving fake DIO message
from malicious node, root node compares the
version number contains in receiving DIO message
with its own version number. It detects anomaly in
DODAG version number field of the incoming DIO
message because the intension of the malicious node
always sends DIO message with higher version
number to its neighbour to attract them. Upon
comparing the version number of malicious node,
the root node can easily determine the malicious
node. On the other hand, when a node (either
malicious node or normal node) stays far (at least
more than one-hop away) from DODAG root and
tries to send DIO messages with increased version
number to its neighbours, the neighbours then verify
the message to check whether or not the node is
malicious. We describe the verification procedure as
the section below.
4.2 Cooperative Verification Procedure
Even though any malicious node joins a network, if
a node sends DIOs without spoofing its version
number field or other malicious behaviour, the
network works safely. The way that a node
determines neighbour's reliability depends on the
behaviour of the neighbour. Every node observes the
communication behaviours of its neighbours by
checking the DODAG version number in DIO
message sent from its neighbours. One simple way
that decides the reliability of a node is to know
whether or not the node has sent the DIO message
with correct version number to its neighbours.
Initially, every node is reliable to each other. A node
is said to be reliable if previously it sent DIOs
without increasing its version number. Therefore, if
a node has received DIOs without spoofing version
number from its neighbour before, the neighbour is
reliable.
When a node receives DIO messages from its
neighbouring nodes it first checks the DODAG
version number field in the corresponding messages.
If the receiving DIO contains higher version number
than the receiving node has, the receiving node is
then becoming a verification node, would initiate the
verification procedure to analyze whether the
neighbouring node is a malicious node. In order to
verify the version number, the verification node
temporarily stores the version number instead of
updating and sending DIO message to its
neighbours. The cooperative verification procedure,
as presented in Figure 2 and its corresponding table
is shown in Table 1, starts with the verification node.
It selects two-hop neighbours as a destination
through the intermediate node of the verification
node such as parent, alternative parent and sib-link
as cooperative nodes to cooperatively participate in
the decision process confirming whether the
neighbour node in question is malicious one. It then
sends out a CVQReq (cooperative verification query
request) = (destination node address, verification
node address, timestamp) message to get their
current DODAG version number. Upon receiving a
CVQReq message, two-hop neighbours of the
verification node replies CVQRep (cooperative
verification query reply) = (verification node
address, destination node address, timestamp,
current DODAG version number) message via the
cooperative intermediate nodes to the verification
node. Accordingly the verification node may receive
the number of reply from two-hop neighbours.
Among the many received CVQRep message, the
verification node records the address of intermediate
node, destination node, and corresponding version
number into the storing table (ST) shown in Table 1.
The confirmation of a malicious node is then
determined by checking the version number of the
storing table with the temporarily stored version
number in verification node. In case, if the
verification node receives two different version
numbers from the same destination, it then checks
the two intermediate nodes from storing table. The
cooperative intermediate node is judged to be
malicious which forward the higher version number
than the other intermediate node. The detail
algorithm is giving in Algorithm 1.
Note that, it is possible any destination node
(two-hop destination) can be a malicious node and
can reply a fake CVQRep message with a higher
version number through the intermediate node to the
PEC 2016 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing
58

verification node. The version number is either the
same as the neighbour of the verification node
(stored version number) or it is bigger than that. In
that case the initiation of a particular detection
process may fail. However, since our algorithm is
distributed in nature some other nodes may find the
anomaly behaviour of the same node and similar
process would be started with appropriate detection
node.
In the following we demonstrate how the
verification process works with an example. Refer to
the following Figure 2, suppose that node 5 receives
increased version number from node 2. Node 5 then
becomes a verification node and selects the
cooperative intermediate node 3 and 6 to reach the
two-hop destination node 1, 3, 4 and 6. Node 5 then
sends CVQReq message to all two-hop destination
node through the cooperative nodes 3 and 6. After a
while node 5 receives a numbers of reply from
destination node 1, 3, 4 and 6 via node 3 and 6 and
store them in storing table (ST) of node 5 as shown
in Table 1. Finally, node 5 compares the increased
version number received from node 2 with the
version number in ST.
Figure 2: Cooperative verification procedure.
Table 1: Storing table of node 5.
I
ntermediate node
D
estination node
V
ersion numbe
r
3 1 2
3 4 2
3 6 2
6 4 3
6 3 3
In order to reduce the impact of the bandwidth-
limited network, we use limited range of cooperative
verification query messages within two-hop. For
example, the cooperative detection procedure uses
cooperative verification query messages to two-hop
destination through cooperative intermediate node.
With this mechanism, the control overhead greatly
reduced.
4.3 Dropping of Verification Messages
Even though any malicious node (it can be either
cooperative intermediate nodes or two-hop
destination nodes) drops the verification messages
deliberately or fails to forward a verification
messages due to link failure or the hidden terminal
problem, the proposed scheme will work smoothly.
The reason is that the verification node will receive
other verification messages from the destination via
cooperative intermediate node other than the
malicious node. In order to dense network
alternative intermediate cooperative node may exist
in verification procedure. Every node on the path has
to take an explicit transmission action when it
receives a verification message. Thus, if any node
does not take any action, it can be determined to be
malicious. However, if a node on the path meets link
failure, it cannot take the transmission action. To
cope with this problem, it is required to send an error
message to the verification node.
Algorithm 1: Cooperative verification algorithm.
;upward(x) is the parent or alternative parent of x
;downward(x) is the child of x
;nigh(x) is the neighbors of x; VN = Verification node
;IN
1
= Intermediate node; INC = Increased
;DVN = DODAG version number; DST = Destination
At node x that receives DIO with INC version
number from node y:
1: if node y is DODAG root then
2: x performs normal operation;
3: else
4: x becomes VN, stores and verifies DVN;
5: end if
At node x that receives CVQReq from y:
6: if node x is two-hop DST then
7: x sends CVQRep towards the VN;
8: else
9: forwards CVQReq towards two-hop DST;
10: end if
At node x that receives CVQRep from y:
11: if node x is VN then
12: checks DVN according to the DST in ST
13: if (DST
1
.DVN.IN
1
> DST
1
.DVN.IN
2
) then
14: x determines IN
1
is malicious
15: end if
16: checks DVN in ST with INC DVN in nigh(x)
17: if (INC DVN in nigh(x) > DVN in ST) then
18: x determines neighboring node is malicious;
19: else
20: x determines neighboring node is normal;
21: end if
22: else
23: forwards CVQRep to downwards(x) toward VN
24: end if
A Distributed and Cooperative Verification Mechanism to Defend against DODAG Version Number Attack in RPL
59

5 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
5.1 Simulation Environment and
Performance Metrics
In this section, we present the simulation
environment and performance metrics for
experiment. The Contiki 2.7 (Dunkels et al., 2004)
operating system and its simulator Cooja (Österlind
et al., 2006) was chosen in order to perform an
evaluation of the proposed scheme against standard
RPL and RPL with malicious nodes. Contiki is open
source, multi-tasking operating system for wireless
sensor network, and its release 2.7 provide
contikiRPL, designed to connect contiki’s IPv6 stack
with underlying MAC and radio duty cycling
protocol (Dunkels 2011). Cooja is flexible simulator
designed for simulating networks of sensor running
the Contiki operating system.
Tmote sky nodes are deployed on a plane square
and are considered motionless. Each node has a
communication range of 50 meter and the
interference range is 100 meter. The topology is set
up so that every node can have (multi-hop)
communication with the sink. One sink is assumed
in these simulations. Each node periodically sends
data packets to the sink. The simulation for each
scenario was performed 15 times and then the
average value for each metric was presented. The
simulation parameters and their values are given in
Table 2.
In order to evaluate the performance of the
proposed scheme, we use some performance metrics
such as packet delivery rate (PDR), control overhead
(CO), true positive rate (TPR), and false positive
rate (FPR),
Table 2: Simulation parameters and its values.
Parameter Value
Radio medium model
Unit Disk Graph
Medium (UDGM):
Distance Loss
Size of deployment area 100m x 100m
Number of nodes 10 to 50
Number of malicious nodes Up to 25%
Physical layer IEEE 802.15.4
Objective function Hop count and ETX
5.2 Simulation Result and Discussion
Figure 3 and Figure 4 show packet delivery rate, and
control overhead with the varying number of nodes
while 10 percent of the total nodes are malicious
nodes. As shown in Figure 3, the packet delivery
rate of all schemes goes down when the number of
nodes increases. This is obvious because packets
drop in the dense network more than the sparse
network by various reasons such as packet collision,
link broken etc. The figure also shows that RPL has
better performance when there is no malicious node
in the network, however, effect of 10% malicious
node the packet delivery rate of RPL dramatically
drops since malicious node hinders data packets to
reach the destination. On the other hand, the
proposed scheme seems to be effective in reducing
the attack effect because it performs well in the
presence of malicious node. Referring to Figure 4,
the control overhead of all schemes increases when
the number of nodes increases since the more
number of nodes produce more control message to
make a path, thus increasing the control overhead.
However, the control overhead of RPL with 10%
malicious node increased more because of the
characteristics of version number attack. When the
attacker node produces DIOs with increased version
number and send it to its neighbours, neighbours
then broadcast DIOs to rebuild the DODAG graph.
As a result, in the presence of malicious node the
control overhead of RPL is increased more. On the
other hand, in the presence of malicious node the
proposed scheme hinders broadcasting the
suspicious DIOs to rebuild DODAG. Therefore, the
control overhead of proposed scheme is much lower
than the RPL with 10% malicious nodes. However,
the proposed scheme also increased control
overhead slightly than RPL without malicious nodes
because the scheme uses some kind of extra message
to identify malicious nodes.
Figure 5 and Figure 6 show packet delivery rate
and control overhead with the varying percentage of
malicious nodes. The packet delivery rate of the both
schemes performs well in case of no malicious node
(i.e., it is higher than 99 percent). A notable result is
that the delivery rate of RPL dramatically drops
from 99 percent to 38 percent while 5 percent of
total nodes are malicious node and it becomes worse
as the percentage of malicious node increases.
However, the proposed scheme seems to be effective
in reducing the version number attack effect. It
shows the packet delivery rate of the proposed
scheme is better than RPL in the presence of
malicious node because it can detect malicious node
more correctly by verifying the suspicious node. The
verification node does not make a valid path to the
root node via the suspicious node until the
suspicious node is judged to be a normal node. In the
later case, if the suspicious node is judged as a
PEC 2016 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing
60

Figure 3: Packet delivery rate vs.
Number of nodes.
Figure 4: Control overhead vs. Number
of nodes.
Figure 5: Packet delivery rate vs.
Percentage of malicious nodes.
Figure 6: Control overhead vs.
Percentage of malicious nodes.
Figure 7: True positive rate vs.
Percentage of malicious nodes.
Figure 8: False positive rate vs.
Percentage of malicious nodes.
malicious then the verification node uses another
valid path to send the packet to the root node. Figure
6 shows that the control overhead of RPL sharply
increases while 5 percent of total nodes are
malicious and it becomes worse as the percentage of
malicious nodes increases. This is because the
characteristic of version number attack. However,
the control overhead of the proposed scheme is not
sensitive to the percentage of malicious nodes since
the proposed scheme hinders the DIOs broadcasting
operation that broadcast to rebuild the DODAG. As
a result, the control overhead is much lower than the
original RPL with malicious nodes.
Figure 7 and Figure 8 show true positive rate and
false positive rate with varying percentage of
malicious nodes. According to Figure 7, true
positive rate decreases when the percentage of
malicious nodes increase. This is because when the
percentage of malicious nodes increase they may
colluding each other, therefore, if a cooperative
intermediate node and two hop destination node both
are the malicious node then it can be given a wrong
judgment. The figure also shows that the proposed
scheme performs well and its true positive rate is
near about 95 percent while the percentage of
malicious node is 25. This is due to the fact that it
can determine a malicious node effectively by using
cooperative intermediate node. Even if a node fails
to determine the malicious node, the malicious node
can be determined by other nodes because the
algorithm is distributed. Figure 8 shows that the
false positive rate increases as the percentage of
malicious nodes increases. This is because if there is
no sufficient intermediate cooperative neighbour to
verify the verification process then the verification
node cannot judge properly whether the node is
malicious or normal. Therefore a normal node may
judge to be a malicious node and it increases when
the percentage of malicious node increases.
6 CONCLUSIONS
An efficient distributed and cooperative verification
mechanism is proposed to effectively and reliably
defend against DODAG version number attack in
routing protocol for low power and lossy networks.
It can pin down DODAG version number attack by
employing a distributed and cooperative verification
approach. The verification process is initiated
conditionally and the cooperative verification query
messages are routed to the maximum two-hop away
through parent, alternative parents and sib-link along
the path toward the DODAG root. The proposed
A Distributed and Cooperative Verification Mechanism to Defend against DODAG Version Number Attack in RPL
61

approach not only reduces control overhead, but also
identify malicious node more reliable. Future work
includes modifying our verification approach for
colluding malicious node. To cope with colluding
malicious node, we will consider designing the new
verification method to accurately measure their
effects on overall performance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by Basic Science
Research Program through the National Research
Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry
of Education (NRF-2015R1D1A1A01059049)
REFERENCES
Chugh, K., Lasebae, A. and Loo, J., 2012. Case Study of a
Black Hole Attack on 6LoWPAN-RPL. SECURWARE
2012, The Sixth International Conference on
Emerging Security Information, Systems and
Technologies, (c), pp.157–162.
Dunkels, A., 2011. The ContikiMAC Radio Duty Cycling
Protocol. SICS Technical Report T2011:13 , ISSN
1100-3154, pp.1–11. Available at: http://dunkels.com
/adam/dunkels11contikimac.pdf.
Dunkels, A., Grönvall, B. and Voigt, T., 2004. Contiki - A
lightweight and flexible operating system for tiny
networked sensors. Proceedings - Conference on
Local Computer Networks, LCN, pp.455–462.
Dvir, A., Holczer, T´. and Buttyan, L., 2011. VeRA -
Version number and rank authentication in RPL. In
Proceedings - 8th IEEE International Conference on
Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Systems, MASS 2011.
IEEE, pp. 709–714. Available at: http://ieeexplore.ieee
.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=6076674
[Accessed May 8, 2016].
Kushalnagar, N. C., Montenegro, G. (Microsoft C. and
Schumacher, C.A., 2007. RFC4919: IPv6 over Low-
Power Wireless Personal Area Networks
(6LoWPANs): Overview, Assumptions, Problem
Statement, and Goals. Request for Comments: 4919,
pp.1–12. Available at: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc
4919 [Accessed May 8, 2016].
Le, A. et al., 2011. Specification-based IDS for securing
RPL from topology attacks. In 2011 IFIP Wireless
Days (WD). IEEE, pp. 1–3. Available at:
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?
arnumber=6098218 [Accessed May 8, 2016].
Le, A. et al., 2013. The impact of rank attack on network
topology of routing protocol for low-power and lossy
networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 13(10), pp.3685–
3692. Available at: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/ep
ic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=6525333 [Accessed May
8, 2016].
Levis, P. et al., 2004. Trickle: a self-regulating algorithm
for code propagation and maintenance in wireless
sensor networks. Proceedings of the 1st conference on
Symposium on Networked Systems Design and
Implementation - Volume 1, pp.2–2.
Mayzaud, A. et al., 2014. A study of RPL DODAG
version attacks. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science
(including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial
Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics).
Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 92–104. Available at:
http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-662-43862-6_
12 [Accessed May 8, 2016].
Mayzaud, A. et al., 2015. Mitigation of topological
inconsistency attacks in RPL-based low-power lossy
networks. International Journal of Network
Management, 25(5), pp.320–339. Available at:
http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/nem.1898 [Accessed
May 8, 2016].
Österlind, F. et al., 2006. Cross-level sensor network
simulation with COOJA. In Proceedings - Conference
on Local Computer Networks, LCN. IEEE, pp. 641–
648. Available at: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs
/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=4116633 [Accessed
May 8, 2016].
Perrey, H. et al., 2013. TRAIL: Topology Authentication
in RPL. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer
Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS),
pp.73–74. Available at: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lp
docs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=6970745
[Accessed May 8, 2016].
Pongle, P. and Chavan, G., 2015. A survey: Attacks on
RPL and 6LoWPAN in IoT. 2015 International
Conference on Pervasive Computing: Advance
Communication Technology and Application for
Society, ICPC 2015, 00(c), pp.0–5.
Raza, S., Wallgren, L. and Voigt, T., 2013. SVELTE:
Real-time intrusion detection in the Internet of Things.
Ad Hoc Networks, 11(8), pp.2661–2674. Available at:
http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S15708705
13001005 [Accessed May 8, 2016].
T Matsunaga, K Toyoda, I.S., 2015. Low false alarm
attackers detection in RPL by considering timing
inconstancy between the rank measurements. IEICE
Communications Express, 4(2), pp.44–49.
Tsao, T. et al., 2015. A Security Threat Analysis for the
Routing Protocol for Low-Power and Lossy Networks
(RPLs). , (7416). Available at: http://www.ietf.org/r
fc/rfc7416.txt [Accessed May 8, 2016].
Weekly, K. and Pister, K., 2012. Evaluating sinkhole
defense techniques in RPL networks. In Proceedings -
International Conference on Network Protocols,
ICNP. IEEE, pp. 1–6. Available at: http://ieeexplore
.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=64599
48 [Accessed May 8, 2016].
Winter, T. et al., 2012. 01 RFC6550 RPL: IPv6 Routing
Protocol for Low-Power and Lossy Networks. Internet
Engineering Task Force (IETF), Request for
Comments : 6550, ISSN:2070-1721, pp.1–157.
Available at: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/rfc6550/.
PEC 2016 - International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing
62
