
A Fuzzy Modelling Approach of Emotion for Affective Computing
Systems
Charalampos Karyotis
1
, Faiyaz Doctor
1
, Rahat Iqbal
1
, Anne James
1
and Victor Chang
2
1
Faculty of Engineering, Environment and Computing, Coventry University, Priory Street, CV1 5FB, Coventry, U.K.
2
School of Computing, Creative Technologies & Engineering, Leeds Beckett University,
City Campus, Leeds, LS1 3HE, U.K.
Keywords: Adaptive Fuzzy Systems, Emotion Modelling, Affective Trajectories, Arousal Valence, Affective
Computing, Personalised Learning.
Abstract: In this paper we present a novel affective modelling approach to be utilised by Affective Computing
systems. This approach is a combination of the well known Arousal Valence model of emotion and the
newly introduced Affective Trajectories Hypothesis. An adaptive data driven fuzzy method is proposed in
order to extract personalized emotion models, and successfully visualise the associations of these models’
basic elements, to different emotional labels, using easily interpretable fuzzy rules. Namely we explore how
the combinations of arousal, valence, prediction of the future, and the experienced outcome after this
prediction, enable us to differentiate between different emotional labels. We use the results obtained from a
user study consisting of an online survey, to demonstrate the potential applicability of this affective
modelling approach, and test the effectiveness and stability of its adaptive element, which accounts for
individual differences between the users. We also propose a basic architecture in order for this approach to
be used effectively by AC systems, and finally we present an implementation of a personalised learning
system which utilises the suggested framework. This implementation is tested through a pilot experimental
session consisting of a tutorial on fuzzy logic which was conducted under an activity-led and problem based
learning context.
1 INTRODUCTION
The modern world calls for techniques which enable
the surrounding environment to behave in an
intelligent way in order to support and aid people in
their lives. Ambient Intelligence (AmI) has emerged
as a discipline promising to satisfy this need through
modifying our everyday environment by providing
intelligence to networks of electronic devices around
us. But how is it possible for this vision of AmI to
be realised through the development of truly
intelligent systems, if they do not possess a basic
understanding of core aspects of human behavior
such as emotions? Affective Computing (AC) is an
emerging scientific field that incorporates emotion
into the design of computing systems, in order to
bridge the gap between the emotional human and the
emotionally challenged computer application.
Affective Computing is defined in (Picard, 1999) as
"computing that relates to, arises from or
deliberately influences emotions". Emotions
influence almost every cognitive process of an
individual. Their influence in performance,
motivation, learning, communication, perception and
organization of memory, attention and many other
aspects of human life has been identified by
numerous studies (Nasoz, 2010). Therefore as
Rosalind Picard pointed out, if we wish to construct
an intelligent system with a higher level of human
machine interaction, we should allow them to
successfully recognize and model emotions, or even
enable them to express their own emotions. The
range of applications of AC is vast since emotion
plays a vital role in every aspect of human life. Since
the dawn of AC we have seen applications in
medicine (Lisetti, 2003), gaming (Mandryk, 2007),
learning (Graesser, 2005), driving (Nasoz, 2010) and
many others. This paper focuses especially on the
application of AC in learning by presenting a
personalised learning AC system. Emotion plays a
vital role in the learning process due to its close
relation to the levels of motivation and engagement
Karyotis, C., Doctor, F., Iqbal, R., James, A. and Chang, V.
A Fuzzy Modelling Approach of Emotion for Affective Computing Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0005945604530460
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Internet of Things and Big Data (IoTBD 2016), pages 453-460
ISBN: 978-989-758-183-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
453

of the learner. Therefore we can infer the need of
AC systems with the ability to take emotion into
account in order to aid in the educational process.
As proposed by Wu et Al in (Wu, 2010) an AC
system should consist of three basic elements. These
elements will be responsible for recognizing and
modelling affect, and finally making the necessary
shifts of user's affective states by outputting the
necessary control signals (figure 1). Wu's affective
loop is the basis of our proposed architecture.
Figure 1: Wu's affective loop.
In AC one of the most important design
dilemmas is the selection of the appropriate machine
learning technique for modelling affect relations,
and mapping low level values, such as sensory
inputs, to values of affective states. Our selected
machine learning and affect modelling approach is
based on Fuzzy Logic. Fuzzy logic systems are very
efficient in dealing with uncertainties concerning
emotion (Wu, 2012). Different people may perceive
or express the same emotion differently
(interpersonal uncertainty), while even the same
individual may have uncertainty about the same
emotion in different times or in a different context
(intrapersonal uncertainty). Moreover through
employing fuzzy logic we can construct
interpretable rule bases to illustrate the existing
relations. This is fundamental for our research since
we aim to be able to reveal the underlying affect
relations while building an effective AC system.
Modelling and understanding emotion is a very
difficult task, heavily debated by psychologists. In
the early days of psychology the prominent view
was that the labels we use to describe our affective
state are in direct relation to underlying discrete
affective states. Paul Ekman for example identified
six basic emotions (anger, disgust, fear, happiness,
sadness and surprise) by using cross-cultural facial
expressions experiments (Ekman, 1975). A different
approach called psychological constructivism,
suggests that emotion is constructed from the
combination of more basic elements. Examples of
constructivist theories are the Arousal Valence (AV)
model (Russell, 1980) and the Affective Trajectories
(AT) Hypothesis (Kirkland, 2012). The arousal
valence model suggests that emotions can be
represented as points in a two-dimensional space
where the first axis is valence, and it ranges from
unpleasant to pleasant, and the second axis is
arousal, and it ranges from passive to active (figure
2). For example anger can be defined as a high
arousal and negative valence state. The AT
hypothesis on the other hand states that an emotional
experience can be created from the combination of a
person's evaluation of their current state, their
predictions about the future, and their evaluations of
the outcome they have experienced (Kirkland,
2012). With this approach anger could be defined as
a state where the outcome of a process is bad and
unexpected. In (Karyotis, 2015) was shown that this
approach can be used within the context of
education and that individual differences play a part
in the construction of different affective states.
Meaning that every individual utilizes the AT's basic
elements but may do so in a personalised manner.
In our research the use of the combination of
these two models is suggested in order to
differentiate more successfully between the emotion
labels we use to describe our affective state. More
specifically we propose a two stage (prediction-
outcome) modelling approach. In the first stage an
emotion is constructed from the combination of the
person's arousal, valence and predictions of the
future, while in the second stage we utilize the
combination of the person's arousal, valence and
evaluation of an outcome. As an example flow can
be described as a state of medium-high arousal
where one makes a positive prediction about the
future, while excitement is a state of positive
valence, high arousal and is mostly related with a
better than expected outcome. The AV and AT
models have already been used in AC applications
(Mandryk, 2007), (Karyotis, 2015) thus it would be
interesting to explore the performance of this mix-
modelling approach in AC systems.
Figure 2: Russell's Affect Grid.
In the following sections we aim to highlight the
potential efficacy of this model, and introduce an
appropriate AC system's architecture able to utilize
our model beyond context constraints. In section 2
RAIBS 2016 - Special Session on Recent Advancement in IoT, Big Data and Security
454

the proposed fuzzy rule extraction and adaptation
method is presented, aiming to harvest the necessary
information in order to create personalized emotion
models. Obtained results, using data collected from a
previous study, are also included in this section,
demonstrating the stability of our method. The
proposed AC system architecture is outlined in
section 3. In section 4 a personalised learning system
utilising the suggested architecture, fuzzy method
and affect modelling approach is presented. In
section 5 we test the proposed system with the help
of a tutorial session on fuzzy logic and we present
the corresponding results. In section 6 conclusions
and research directions are being discussed.
2 METHODOLOGY
Our proposed fuzzy modelling approach comprises
of three stages. Firstly user data is collected using an
online survey as described in section 2.1. Then the
fuzzy membership functions (MF) are extracted, and
the fuzzy rule-bases are being constructed from the
data by using the approach outlined in section 2.2.
Finally the general rule base extracted is adapted to a
specific participant by utilizing the fuzzy adaptation
method presented in section 2.3.
2.1 Data Collection
In order to acquire the necessary data a user study
was conducted to gather data relating to the
construction of emotions from the proposed basic
structural elements. The user study comprises of a
survey including stories which describe common
real life situations and are context specific (i.e.
education). During the survey the user is asked to
read the scenario and imagine that they are taking
part in the story described. Each story consists of
two stages. In the first stage, the starting point of the
story is described (e.g. "you are attending a
mandatory seminar which you predict isn't going to
be useful to you"). In the second part of the story,
which follows consequently, the ending of the story
is presented to the user (e.g. "the seminar proves to
be extremely interesting"). In the first stage, the user
is asked to provide ratings of their valence, arousal
and prediction while in the second stage the user is
asked to rate their valence, arousal and evaluation of
the experienced outcome. In both stages, after
providing the corresponding values, the user rates
the degree to which each of the emotional words
(flow, excitement, calm, boredom, stress, confusion,
frustration and neutral state) fit their affective state
in the story. Every variable is rated using sliders and
ranges from 0 to 100. Valence ranges from
unpleasant (0) to pleasant (100), arousal from
deactivated (0) to activated (100), prediction from
very negative (0) to very positive (100) and the
degree the emotions fit the story from not at all (0)
to perfectly (100). As a result our data samples have
3 inputs and 8 outputs. The inputs for the first stage
are valence, arousal and prediction, and those for the
second stage are valence, arousal and outcome. The
outputs in both stages are values of the eight
emotions.
2.2 Fuzzy MFs and Fuzzy Rule Base
Extraction
In order to extract the necessary MFs from the data,
it is essential that we originally define the number of
fuzzy sets we require, in order to cover the input-
output space. Subsequently we utilize the FCM
algorithm and compute the same number of fuzzy
sets' centers. Finally we define the corresponding
fuzzy set to have triangular MFs with degree of
membership equal to one, at the previously
computed by the FCM center. The support is the
space defined between the projections of the
previous center and the next center on the horizontal
axis. Figure 3 displays the extracted fuzzy sets for
the prediction element.
Figure 3: Prediction element's MFs.
The fuzzy rule extraction method is based on the
method presented in (Wang, 2005) by Wang.
According to this method, initially every data
sample is converted to a fuzzy rule. The extracted
fuzzy rules are afterwards organized to groups, each
group containing the rules with the same if-part. A
single rule is then extracted for every group by
computing the weighted average of the consequents
of the all the rules in the group and by mapping the
extracted value to the corresponding output fuzzy
set. These fuzzy rules are utilised in our system by
two fuzzy classifiers, for stage 1 and 2 respectively,
in order to map values of arousal, valence,
prediction and outcome to values of the targeted
emotions.
A Fuzzy Modelling Approach of Emotion for Affective Computing Systems
455

2.3 Adaptation
As shown in (Karyotis, 2015) for the AT hypothesis
every person uses the basic elements in a
personalized way in order for them to select the
appropriate emotion label. For this to be accounted
in our model we implement a modified version of
the Adaptive Online Fuzzy Inference System
(AOFIS) (Doctor, 2005) as proposed in (Karyotis,
2015). With this method the user can provide new
emotion values if they aren’t satisfied with the
output of the system, also resulting in changes to the
fuzzy rule base. This will allow the system to adjust
its general rule base to a specific user, making it
more accurate and user-friendly. To achieve this,
when the user provides new values, a new training
sample is formed, and fed into the system. This new
data sample is used by the system to identify the
rules that fired and alter the consequent of the rule
with the highest activation value. This is
accomplished by calculating the optimal position of
the output fuzzy set's center of the highest activation
value rule, given the contribution of all the other
fired rules, and by mapping this value to the
corresponding output fuzzy set. Finally we propose
that the data samples collected offline from the
responses of a specific user at the online survey
described before to be presented one by one to the
system. This way the system will make all the
necessary changes to the fuzzy rule base, thus
creating a more personalised system before the user
starts using it in a real time setting.
2.4 Results
Since data collection is still ongoing, we used the
data collected for (Karyotis, 2015) in order to
demonstrate the stability of the system and
interpretability of the rules obtained from the fuzzy
method discussed above. The results acquired are
promising and can be improved and extended upon
completion of the data collection and processing
phase of the new user study described in the
previous section. In (Karyotis, 2015) the data were
collected following the method described in section
2.1. However this data do not account for the values
of arousal since the survey was aimed at modelling
the AT theory. We have inferred some arousal
values from the provided emotional values by using
the Affective Norms for English Words (ANEW)
(Bradley, 2010) database. The values we used for
valence correspond to the values of "current state" as
used in (Karyotis, 2015), since this variable was
used to describe how positive or negative valenced
the user was. To follow the aforementioned
methodology arousal, valence and prediction values
are considered as inputs for the first stage
classification systems. While for the second stage
classification systems, the inputs are: arousal,
valence and outcome values. For both stages the
outputs are values of the educational context specific
emotions: flow, excitement, calm, boredom, stress,
confusion, frustration and the neutral state. For a
chosen number of five fuzzy sets for both input and
output space we have computed the Normalized
Root Mean Square Error (NRMSE) using ten-fold
cross validation for stage 1 and stage 2 classifiers of
our proposed model (AV-AT) and of the model
proposed in (Karyotis, 2015) (AT) . For the adaptive
versions (Adaptive AT and Adaptive AV-AT) we
considered the values given from a specific
participant as changes they have provided during
their interaction with the system. The results are
shown in table 1.
To demonstrate the ability of the proposed fuzzy
approach to produce easily interpretable fuzzy rules,
we quote some examples of the rules extracted using
this method on the data from (Karyotis, 2015) for
excitement and flow.
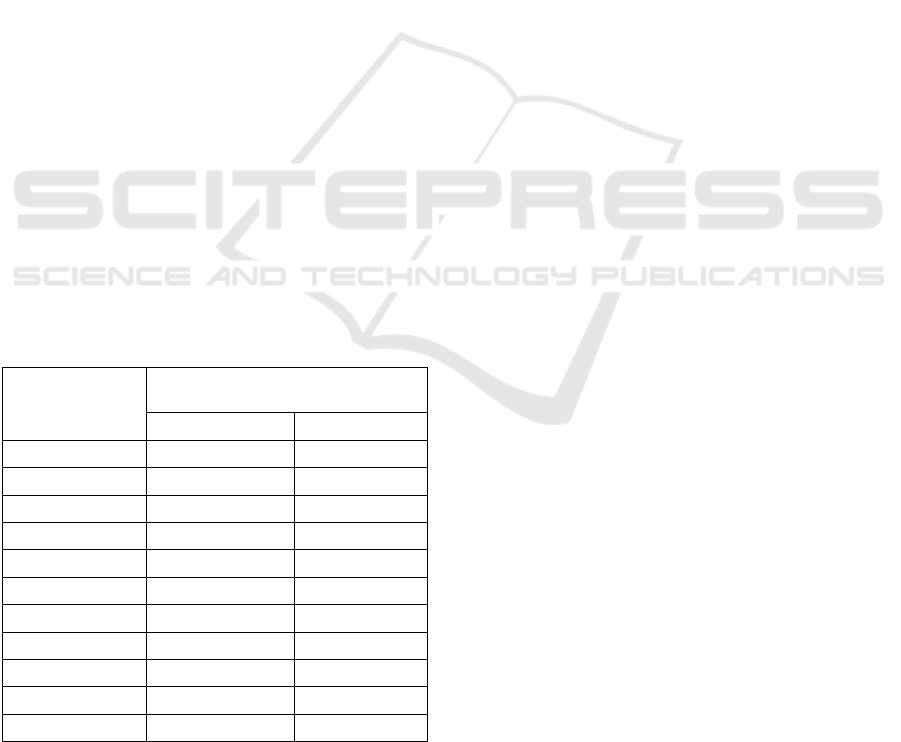
Table 1: NRMSE of AT and AV-AT models using the proposed fuzzy method.
Emotions
NRMSE
Stage1 Stage2
AT AV-AT Adaptive AT Adaptive AV-AT AT AV-AT Adaptive AT Adaptive AV-AT
Flow 0,2559 0,2478 0,1823 0,2098 0.2359 0,2379 0,1724 0,1813
Excitement 0,2432 0,2292 0,1766 0,1770 0.2081 0,2094 0,1654 0,1712
Calm 0,2763 0,2502 0,2175 0,1810 0.2857 0,2573 0,1882 0,1820
Boredom 0,2386 0,2180 0,2057 0,1658 0.2199 0,2102 0,1413 0,1274
Stress 0,2689 0,2284 0,2134 0,2120 0.2473 0,2522 0,1652 0,1591
Confusion 0,2145 0,2063 0,1512 0,1376 0.2331 0,2311 0,1366 0,1375
Frustration 0,2174 0,2175 0,1428 0,1512 0.2001 0,1910 0,1455 0,1862
Neutral 0,2209 0,2215 0,1682 0,1442 0.2064 0,2057 0,1278 0,1186
Overall 0,2420 0,2273 0,1822 0,1723 0.2296 0,2243 0,1554 0,1579
RAIBS 2016 - Special Session on Recent Advancement in IoT, Big Data and Security
456
If valence is neutral, and arousal is medium, and
prediction is positive, then flow is medium.
If valence is positive, and arousal is high, and
outcome is better than expected, then excitement is
high.
3 PROPOSED AC
ARCHITECTURE
In this section we will outline the architecture of an
AC system utilizing the proposed approach. This
approach can be applied in different contexts by
simply adjusting the output emotions to context
specific ones. For example the output emotions of a
system installed in a car aiming to aid the driver,
could comprise of: panic, fear, frustration, anger,
boredom, fatigue (Nasoz, 2010), while for an
affective learning system a suitable set of target
emotions would be the one used in (Karyotis, 2015).
Nevertheless no matter the context of the
application, it is necessary to have separate sessions
where the start and end points can be clearly
defined, so that we can acquire the user's prediction
and his evaluation of the experienced outcome. For
example in a driving application, a driving session
could include a journey, where the driver is able to
provide a prediction for the journey ahead when
entering the vehicle, and an evaluation of the
outcome when leaving the vehicle.
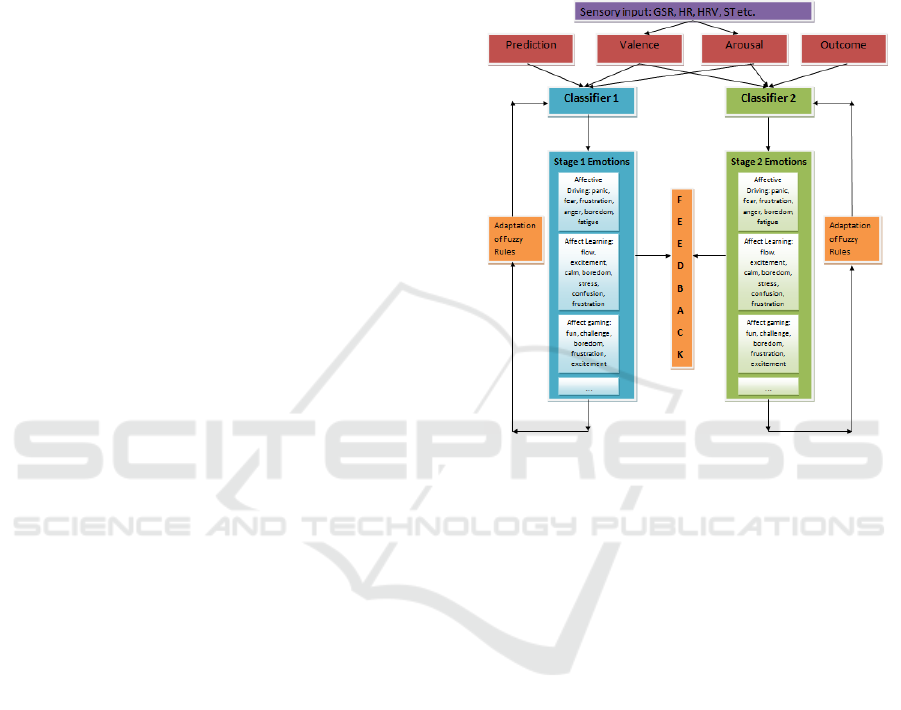
In figure 4 an overview of the proposed
architecture can be found. The design encompasses
the two-stage classification approach described in
section 2. The inputs comprise of the user’s arousal,
valence, and estimate of prediction for the first
stage, while for the second stage the inputs used
include: arousal, valence, and evaluation of the
outcome. These inputs are fed to the appropriate
classifiers in order to be mapped to the context
related emotion values. The classification systems
also include the adaptation mechanism (described in
section 2.3) in order to account for individual
differences and make the necessary changes to the
fuzzy rule base when the user is not happy with the
results and provides new values for the targeted
emotions. Valence and arousal have been found to
have close relations to different physiological
signals. For example, a person’s heart rate (HR)
(Rainville, 2006) can increase when he is presented
with positive stimuli; the galvanic skin response
signal (GSR) (Dawson, 2007) is in close relation to
their arousal levels and their skin temperature (ST)
changes according to their affective state
(McFarland, 1985). As a result values of arousal and
valence can be acquired either explicitly, by asking
the user, or implicitly, by computing estimates of
their values using physiological sensors. This can be
achieved with the help of non obtrusive wearable
devices such as the Autosense, the Empatica E3, or
E4 sensors and others.
Figure 4: Proposed AC system architecture.
Given the output emotion values and the context
of the application, the system delivers the
appropriate feedback to the user. More specifically
in the context of an affective driving application the
system could suggest a break to the driver, or
choose a designated favourite radio station on the
car's entertainment system, when it detects high
levels of frustration. Another example would be
affective gaming, where the difficulty level could be
adjusted to match the output emotion values. This
could be achieved by raising the difficulty level of
the game to make the session more challenging, or
by decreasing the level to make the game more
appealing to novice users. Moreover it would be
useful to store the input values of the basic elements
along with the system's output values, and the values
provided from the user in order to retrain the system,
in a future time, when enough data have been
accumulated, thus resulting to a rule-base which is
more tailored to the user.
.
A Fuzzy Modelling Approach of Emotion for Affective Computing Systems
457

4 PERSONALISED LEARNING
SYSTEM
In this section we will present the basic
implementation (using Matlab) of a personalized
learning system based on the architecture described
above. The suggested system aims to aid the student
during collaborative, and activity led learning tasks.
As mentioned before it is vital for our system to
have predefined starting and end points so that the
prediction and outcome elements could be provided.
In this case the entire learning session would consist
of a number of different activities. These activities
may include: a lecture, a presentation, a lab exercise,
a class game, a discussion etc.
The step by step implementation of the system
for a single activity is described below. This process
will be repeated for every activity of a specific
learning session. At the beginning of the activity the
user is explicitly asked to provide a value of his
prediction concerning the upcoming activity. At this
point of the research, arousal, and valence values are
also acquired by explicitly asking the participant.
The arousal, valence, and prediction values obtained
are used from the system's first stage classifier to
provide values for flow, excitement, calm, boredom,
stress, confusion, frustration and neutral. The
calculated emotional values are presented to the
student with the use of bar charts. If a student is not
happy with the results they can provide their own
values for any of the emotions. These new values
will be used by the adaptation mechanism to make
the necessary changes to the fuzzy rule base. The
system will provide feedback to the student in the
form of tips, by taking into account the values of the
targeted emotions and the way these emotion
influence student's performance. Feedback appears
in the form of short motivational quotes or advice
("It appears you have high levels of stress, please try
to discuss your concerns with your tutor or take a
break"). The average values from every emotion
category are also calculated and shown to the tutor,
in the form of bar charts. As a result the tutor is able
to observe their classes' overall affective state, and
thus they are able to adjust their teaching style or
classroom conditions, to suit their students' needs.
At the end of the activity the student is asked to
provide a value rating of what happened (outcome)
in respect to their prediction in the beginning of the
activity. Student's valence, arousal and outcome
values will be given to the second classifier which
would be now responsible for providing the
necessary results. The feedback and adaptation
mechanism is the same as in the previous stage. It is
important to note that the system could be used to
observe the student's affective state during activities
spanning multiple learning sessions. These student's
affective trajectories are stored and can be shown to
the student when required, allowing them to reflect
on their learning performance. For example in figure
5 we can observe the user's affective trajectory for a
session containing 4 activities (8 points).
This AC system has a very low computational
burden and can offer its services instantly and
without requiring any complex and expensive
equipment. A standard laptop or smart phone would
be a more than adequate device to run the system
along with its adaptive mechanism, which
contributes to making the system more user-friendly
and accurate.
Figure 5: Recorded affective trajectory of a student.
5 SYSTEM EVALUATION
In order to test the performance of the developed
system we carried out a practical experimental
session, comprising of a tutorial on fuzzy logic,
where the participants were utilizing the proposed
system. A total of twenty one participants took part
in the tutorial. All the participants had completed the
online survey in order to provide the necessary data
for the construction of a more personalised learning
system. The structure of the tutorial was congruent
with the limitations of the model and followed an
activity led learning based approach. The tutorial
comprised of 2 separate sessions which contained 4
activities each. The first session included an
introductory lecture on fuzzy logic, a class game
designed to introduce the students to the basic fuzzy
logic concepts, a discussion on famous quotes
concerning the subject and finally a small quiz. The
second session included a lecture focused on fuzzy
logic as an machine learning approach, example lab
exercises using Matlab's fuzzy toolbox, a group
project where the students were asked to utilize what
RAIBS 2016 - Special Session on Recent Advancement in IoT, Big Data and Security
458
they have learned to solve a basic machine learning
problem, and finally the students made a short
presentation of their work to the class. All the
participants used their personal laptops where the
system was previously installed. Upon entering the
class the participants were divided into groups of
three students.
We tested the performance of the system in terms
of the emotion recognition accuracy it provided for
stage 1 and stage 2 of the emotional model
respectively. More specifically we tested the
recognition accuracy in terms of the NRMSE error
for all emotion categories, and we also calculated the
dominant emotion accuracy (DEA) for the AV-AT
model in comparison to the accuracy provide it by
another affective system if it used the AV model of
emotion. As dominant emotion for our system we
defined the emotion for which the system provided
the highest value. In order to calculate the dominant
emotion values for the AV model we initially
utilized the Affective Norms for English Words
(ANEW) (Bradley, 2010) database in order to define
clusters in arousal valence space representing each
of the eight emotions (flow, excitement, calm,
boredom, stress, confusion, frustration and neutral).
The arousal and valence values of those words in the
database were used in order to define the cluster
centers. Afterwards we utilized the arousal and
valence values provided from the participant, and
the dominant emotion was defined by calculating the
minimum Euclidian distance from each clusters'
centers. The results are shown in table 2.
Table 2: NRMSE and DEA results for the tutorial session.
Emotions
NRMSE and DEA for fuzzy
Tutorial
Stage 1 Stage2
Flow 7.3253 8.8728
Excitement 8.3177 7.1235
Calm 9.3274 8.1050
Boredom 7.2292 9.6106
Stress 10.8370 6.5552
Confusion 6.1300 9.6812
Frustration 7.6439 9.5817
Neutral 5.5270 8.6740
Overall 7.7922 8.5253
AV-AT DEA 88.10% 80.95%
AV DEA 58.93% 60.12%
The results from table 2 show that the
performance of the proposed model outperforms the
survey results for both stages. This is to be expected
due the adaptation process of the system which
allowed for a more successful representation of
individual differences. Individual differences play a
major role in the construction of emotions using the
AT theory (Karyotis, 2015) as a result they play a
major role in the AV-AT model which is an
extension of the AT. The AV-AT emotional model
also provides a more efficient emotional modelling
approach than the AV model for both stages. This is
obvious from the dominant emotion accuracy
results. The AT-AV model scored 88.10% for stage
1 and 80.95% for stage2 respectively, while the AV
scored around 60% for both stages. These are very
logical results since the arousal valence model is not
dependant of stages.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we introduced an emotional modelling
approach which combines the Arousal Valence
model of emotion, and the Affective Trajectories
Hypothesis. We provided a framework in which this
model can be utilised in Affective Computing and
presented an example of a personalised learning
system which uses this architecture. The proposed
system is responsible for recognizing and recording
the affective state of a student through time, offering
in the same time appropriate feedback to aid in the
learning process. This system utilizes the suggested
novel emotional modelling approach by using an
adaptive fuzzy logic mechanism.
Our preliminary results demonstrate the potential
of this model, and highlight the applicability of the
implemented fuzzy method. By using the data from
a previous study we observed that the fuzzy
approach used, proves to be stable, promising and in
the same time it is able to capture individual
differences and preferences through its adaptive part.
Additionally the rule base extracted, using this
method, contains easily interpretable fuzzy rules.
These rules will allow us to visualize how an
individual combines the basic elements to choose an
emotional label, thus enabling us to create both
general and personalised emotional models.
Ongoing work focuses on the collection and
processing of data through the online survey
described, in order to reveal and model the
underlying affect relations. Upon the completion of
this process we aim to explore the performance and
effectiveness of the proposed emotional model,
fuzzy technique and personalized learning system by
using the system in a series of practical learning
sessions which utilize collaborative and activity led
A Fuzzy Modelling Approach of Emotion for Affective Computing Systems
459

learning tasks. Providing a novel computational
methodology to model emotion, will enhance our
understanding of the incorporation of emotion in the
design of computing systems, resulting in the
improvement of services provided by those systems
to their users.
REFERENCES
Bradley, M.M. & Lang, P.J. (2010). Affective Norms for
English Words (ANEW): Instruction manual and
affective ratings. Technical Report C-2, Gainesville,
FL.The Center for research in Psychophysiology,
University of Florida.
Dawson, M.E., Schell, A. M., and Filion, D. L. (2007) The
electrodermal system, In Cacioppo, J. T., Tassinary, L.
G., Berntson, G. (eds),Handbook of Psychophysiology.
Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Doctor, F., Hagras, H., Callaghan, V. (2005) A Fuzzy
Embedded Agent-Based Approach for Realizing
Ambient Intelligence in Intelligent Inhabited
Environments. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man
and Cybernatics- Part A: Systems and Humans, 35(1),
55-56.
Ekman, P., and Friesen, W. V. (1975) Unmasking the
Face: A Guide to Recognizing Emotions from Facial
Expressions. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New
Jersey, NJ.
Graesser, A., Chipman, P., Haynes, B. and Olney, A.
(2005) AutoTutor: An Intelligent Tutoring System
with Mixed-Initiative Dialogue. IEEE Transactions on
Education 48(4), 612-618.
Karyotis, C., Doctor, F., Iqbal, R., and James, A. (2015)
An Intelligent Framework for Monitoring Students
Affective Trajectories Using Adaptive Fuzzy Systems.
IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, 2-5
August 2015, Istanbul, Turkey.
Kirkland, T., and Cunningham, W. A. (2012) Mapping
Emotions Through Time: How Affective Trajectories
Inform the Language of Emotion. Emotion, 12(2),
268–282.
Lisetti, C., Nasoz, F., LeRouge, C., Ozyer, O. and
Alvarez, K. (2003) Developing multimodal intelligent
affective interfaces for tele-home health care.
Internarional Journal of Human-Computer Studies,
59(1-2), 245–255.
Mandryk, R.L., Atkins, M.S. (2007) A Fuzzy
Physiological Approach for Continuously Modelling
Emotion during Interaction with Play Technologies.
International Journal of Human-Computer Studies,
65, 329- 347.
McFarland, R. A. (1985) Relationship of skin temperature
changes to the emotions accompanying music.
Biofeedback and Self-regulation, 10(3), 255–267.
Nasoz, F., Lisetti, C., and Vasilakos A. (2010) Affectively
intelligent and adaptive car interfaces. Information
Sciences, 180, 3817–3836.
Picard, R. (1997) Affective Computing. The MIT Press,
Cambridge MA.
Rainville, P., Bechara, A., Naqvi, N., and Damasio, A. R.
(2006) Basic emotions are associated with distinct
patterns of cardiorespiratory activity. International
Journal of Psychophysiology, 61(1), 5–18.
Russell, J. A. (1980) A Circumplex Model of Affect.
Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 39(6),
1161–1178.
Wang, L. X. (2003) The MW method completed: A
flexible system approach to data mining. IEEE
Transactions Fuzzy Systems, 11(6), 768–782.
Wu, D. et al. (2010) Using Physiological Signals: Virtual
Reality Stroop Task. IEEE Transactions on Affective
Computing, 1(2), 109–118.
Wu, D. (2012) Fuzzy sets and systems in building closed-
loop affective computing systems for human-computer
interaction: Advances and new directions, IEEE World
Congress on Computational Intelligence, Brisbane,
Australia.
RAIBS 2016 - Special Session on Recent Advancement in IoT, Big Data and Security
460
