
Robust Index Code with Digital Images on the Internet
Minsu Kim
1
, Kunwoo Lee
1
, Katsuhiko Gondow and Jun-ichi Imura
Graduate School of Information Science and Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo, Japan
Keywords:
Bar Codes, Robustness, Digital Images, Image Databases, Image Color Analysis, Encoding.
Abstract:
A new color code which has high robustness is proposed, called Robust Index Code (RIC for short). RIC can
be used on digital images and link them with the database. There are several technologies embedding data into
images such as QR Code and Digital watermark. QR Code cannot be used on digital images because it does
not have robustness on digital images. Besides Digital watermark can be used on digital images, but embedded
data cannot be extracted 100% on damaged images. From evaluation using our implemented RIC encoder and
decoder, the encoded indexes can be extracted 100% on compressed images to 30%. We also implemented a
doubt color correction algorithm for damaged images. In conclusion, RIC has the high robustness on digital
images. Hence, it is able to store all the type of digital products by embedding indexes into digital images
to access database, which means it makes a Superdistribution system with digital images realized. Therefore
RIC has the potential for new Internet image services, since all the images encoded by RIC are possible to
access original products anywhere.
1 INTRODUCTION
With easily being able to retrieve digital contents on
cell phones, Internet services which focus on images
have been growing. Nowadays, over 350 million
images are uploaded to Facebook every day (inter-
net.org, 2013). In spite that the trend of mobile con-
tents continues to increase, the complete recoverable
data embedding method into digital images on the In-
ternet is not realized.
The techniques which can store data into printed
images were developed such as barcode, QR Code
and CQR Code (Nurwono and Kosala, 2009). How-
ever, these technologies have several problems for us-
ing on digital images. QR Code can only store data
up to 23,648 bits, which is very small in contrast to
digital contents and image size (Incorporated., 2008).
CQR Code is a color code which can store 9KB data
(Nurwono and Kosala, 2009). Still, 9KB data limit is
too small to store digital multiform contents.
Another problem is damage of data by random
degradation on the Internet. When images are up-
loaded typically on Facebook, they are resized or
compressed for the fast response. On image degrada-
tion, a stored data by QR Code get damaged so that it
cannot be extracted correctly. For this reason, digital
watermarking, a method to covertly embed some in-
1
Corresponding author of this paper.
formation in multimedia objects, has received signif-
icant attention. In spite that watermarking has many
different applications, watermarking schemes do not
work effectivelyfor all types of media and universally
for various diverse applications (Mintzer et al., 1997).
Its robustness is very high compared to QR Code, but
it is still not guaranteed that embedded images can be
100% extracted by digital watermarks (Mohanty and
Bhargava, 2008).
This paper proposes Robust Index Code called
RIC, which is a brand new color code that has high
robustness and can link with unlimited data. RIC
guarantees to restore 100% original embedded data in
the defined specification, which means an index of N-
bits to access to a remote database can also be safely
embedded into a RIC image so that we can link with
multiformed and unlimited data in the remote server.
We implemented RIC and evaluated its performance
and robustness through extensive experiments under
a range of settings on specific parameters. The result
shows that the data of RIC are extracted 100% on the
images over 420 pixels Resize and 30% JPEG Com-
pression.
From the result, according to RIC concept shown
in Figure 1, users can embed text, link, music, video,
VR contents into a digital image with high robust-
ness by RIC. As shown in Figure 1, only a database
index encoded with RIC is actually embedded in im-
28
Kim, M., Lee, K., Gondow, K. and Imura, J-i.
Robust Index Code with Digital Images on the Internet.
DOI: 10.5220/0005951400280037
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2016) - Volume 5: SIGMAP, pages 28-37
ISBN: 978-989-758-196-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Remote Database
Image
RIC
<Database
Index>
Text Link Music Video VR
Figure 1: RIC Concept.
ages. Moreover, we can expect a new Superdistribu-
tion system based on RIC which is not restricted by
any existing or new Internet platforms. Because the
RIC image is platform-independent, anyone can copy
and share it in all the ways, such as E-mail, SNS or
mobile messenger. In addition, the RIC library sup-
porting multiple platforms will be offered for free.
Hence, it is possible that any users instinctively ac-
cess to the embedded data in the RIC images very eas-
ily without restricting platforms. It is highly expected
that the Superdistribution system by RIC be one of
the fastest and strongest distribution routes of digital
products and communication, regardless of platforms
on the Internet.
Some expected examples are cited as follows. For
instance, many talented artists may embed their con-
tents and information of themselves, and retail shops
may embed the links for their e-commerce system or
promotion information into the their attractive images
to collect traffic on the Internet. The media is also eas-
ily expected to embed the recent issues in the intrigu-
ing pictures to attract people. In case of software com-
panies, the relatively big size contents such as games,
VR contents, and so on are expected. Subsequently,
those digital products embedded in the RIC images
spread out by the honest needs and judgment of typi-
cal users to personally consume them on the Internet,
not on the existing platforms. It means the quality
and the prices of the products are only the consider-
ations of selection and purchase without any existing
interference and it is a relatively desirable system for
both owners and recipients. Ultimately, this proposal
aims to improve the rights of product owners and con-
sumers, by the renovation of a distribution process
and profit structure on the Internet.
2 RELATED WORK
There are more than 20 types of conventional 2D
codes: QR Code (Incorporated., 2008), Color Quick
Reference Code (Nurwono and Kosala, 2009), Mi-
crosoft’s High Capacity Color Barcode (HCCB) (Re-
search, 2010), etc. The papers (Grillo et al., 2010;
Hao et al., 2012; Liu et al., 2008; Yeh and Chen,
1998) provide examples of 2D codes. The main dif-
ference among the presented codes is the limited data
size. Because they are targeting on mainly off-line
printed images, the capacity of data is one of the main
challenges of them (Grillo et al., 2010). In Addition,
the finder pattern boxes on existing Codemark can be
easily damaged by Resize. Therefore, in spite of high
recognitionrate on printed images, the data embedded
by the presented codes get damaged on image degra-
dation such as Resize, JPEG Compression. They are
not suitable for digital images on the Internet.
Digital watermark is another data embedding
method on images which has high robustness on im-
age degradation. The data embedded by watermark-
ing algorithms are not damaged by JPEG Compres-
sion, Gaussian noise, Cropping and Resize (Woo
et al., 2005; Jiansheng et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2007).
But due to the purpose of digital watermark which is
ownership evidence or fingerprinting, the watermark
detection does not succeed 100% (Woo et al., 2005;
Jiansheng et al., 2009), which means that everyone
who downloads an embedded image cannot see the
same data. The paper (Jiang and Armstrong, 2002)
tries to embed indexes into images using digital wa-
termark. Despite its large encoded size, data loss oc-
curs by JPEG Compression. Steganography similar
to Digital watermark has high robustness too, but also
embedded data can not be detected fully (Liu et al.,
2011; Provos and Honeyman, 2001).
3 ROBUST INDEX CODE
Robust Index Code, named RIC in this paper, is a new
color index code which has high robustness. The idea
is to develop a new color code which embeds not real
digital products but a database index. Hence, RIC
should not be damaged by sharing Internet services
such as E-mail, Messanger, SNS. When users obtain
an image from the Internet service, there is high pos-
sibility that the image got damaged by Resize and
JPEG Compression for the fast response on the ser-
vice. So RIC focuses on Resize and JPEG Compres-
sion. In addition, to link with unlimited data, RIC
embeds only 50-bit index into each digital image, as-
suming a server on the Internet to store its content
Robust Index Code with Digital Images on the Internet
29

data. About 350 million images are uploaded to Face-
book every day (internet.org, 2013). So 50-bit index
is reasonably enough for index size.
Our concept is to design a new color code which
has high robustness so that we can embed an index
key of a remote database which stores lots of data.
In addition, an encoded image should be able to be
decoded on every device which can access on the In-
ternet such as a mobile phone and PC browser. For
this reason, we developed a C++ encoder / decoder
prototype library to be deployed on iOS, Android
and Chrome Extension. By using a mobile phone or
Chrome browser on PC, users can easily and directly
see the contents of an encoded image on the Internet.
There is an example of the RIC library, which is ex-
plained in Appendix.
RIC consists of encoding and decoding parts. This
section describes encoding part with the design of
RIC and decoding part with a new algorithm.
3.1 Robust Index Code Design
Our goal is to design a color code which has robust-
ness on the most common image degradation on the
Internet like Resize and JPEG Compression. The rea-
son why QR Code gets damaged by Resize or JPEG
Compression is that data pixels are infected by other
pixels. These are due to the quantization step of the
JPEG Compression (Furht, 1995). To solve those
problems, a data pixel should be larger than other
codes and the distance between data pixels should be
long enough not to be infected by neighbor pixels. So
we propose a circle of a fixed size, which radius is r
pixel, for inserting bit data and the distance between
two circles is longer than a constant d pixel which is
shown in Figure 2. The idea of embedded spot is simi-
lar to CQR Code (Nurwono and Kosala, 2009), which
is 24-bit RGB color. On each circle, 3 bits data can be
embedded by 1 bit to R, 1 bit to G and 1 bit to B with
converting 0 to color D
0
and 1 to color D
1
. Figure 2 is
an example of setting D
0
= 80 and D
1
= 255.
r r
d
R= 80 → 0
G= 80 → 0
B=255 → 1
Figure 2: Example of RIC circle.
In order to detect an encoded area on an image,
RIC includes a square wrapping data circles. The
square’s background color is light gray for not infect-
ing data circles. For more accurate detection, the bor-
der of square is added with light black color like (Ong
et al., 2008). Assuming r to 4, d to 2, D
0
to 80 and
D
1
to 255, the final design is shown in Figure 3 used
in encoding, decoding and evaluating.
b
s
p
Figure 3: Example pattern of RIC.
From our design, the capacity of RIC is shown in
the following formula:
capacity(bit) = 3N
c
s.t. 0 < N
c
≤ (
s+ d− 2p
2r+ d
)
2
(1)
where s is a side pixel of the square without the bor-
der, p is padding pixels of the square (assumed to 6)
and N
c
is the number of circles. Figure 3 contains 22
circles, for the design reason to represent P, so that 66
bits can be embedded. It is enough capacity to embed
database index, which size is 50 bits.
To determine RIC is correctly encoded, RIC has
a checksum algorithm. On RIC, a checksum is in-
serted on c bits and an index is inserted on the rest of
bits. The algorithm is simple that a checksum value is
the remainder when an index is divided into 2
c
. That
means we can determine true RIC with 1/2
c
proba-
bility. In this paper, we decide on the bit length of
checksum as 16.
3.2 Robust Index Code Decoder
Decoding RIC consists of three main parts, determin-
ing the data square, extracting bit data on data circles
with damage check, validating extracted data. The
progress of decoding is shown in Figure 4.
Decoding
Square
Exist?
Not Encoded
Image
Damaged
?
No
Yes
No
Yes
Checksum
Validate?
Yes
Success
Attacked Image or
Not Encoded Image
No
Too Damaged
Image
DB Index
Check?
Yes
Not Original
Image
No
Extract data
of one circle
Doubt Color
Correction
Extract all
circles?
Yes
No
Figure 4: Decoding process.
• Step 1: A data square can be determined with
High-pass filter and Low-pass filter. Because the
border of a square could be uneven by image
degradation, a square itself is used for detecting.
Still, when the square cannot be extracted, the im-
age is regarded as not RIC image or extremely
SIGMAP 2016 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
30

indexList := new List();
indexList.add(new int[circles.size()*3]);
For
i
=0 To circles.size()-1 Dd
//
i
: 0
→
R, 1
→
G, 2
→
B
For
j
=0 To 2 Do
// Check
j
Color damaged
bool damaged :=
isColorDamaged(circles[
i
],
j
);
For
k
=0 To indexList.size()-1 Do
int *original := indexList[
k
];
If damaged =
true
Then
// add both possibilities to the list
int *cloned := original.clone();
original[
i
*3+
j
] := 0;
cloned[
i
*3+
j
] := 1;
indexList.add(cloned);
Else
// add extracted bit to the list
original[
i
*3+
j
] :=
extractBinary(circles[
i
],
j
);
End If
End For
If indexList.size()
> N d
Then
Print "Too Damaged Image";
End If
End For
End For
Figure 5: Doubt Color Correction Algorithm.
damaged image which means out of specification
for the performance cost.
• Step 2: Bit data is extracted from the center of
data circles. Although D
0
or D
1
color circles are
drawn on Encoding process, there is a high pos-
sibility that the color is not D
0
or D
1
by image
degradation. Therefore we propose a new algo-
rithm for color damage checking, doubt color cor-
rection algorithm in Figure 5.
When an extracted color from a data circle is far
from D
0
and D
1
, we cannot determine the origi-
nal bit data was 0 or 1. Hence, the algorithm adds
both 0 and 1 for that doubtable color into possible
index list, called doubt list in this paper,so that ac-
tual original index is always included in the doubt
list. In addition, the algorithm puts on the limit of
the size of the doubt list, N
d
. If the size oversteps
the limit, the decoder recognizes the image as a
too damaged image and stop decoding. With this
algorithm, the decoder can recover damaged RIC.
• Step 3: From the second step, the decoder extracts
multiple indexes, which is the doubt list. To ex-
tract exactly the original index, RIC decoder need
to validate the doubt list. In this step, RIC de-
coder checks two algorithms. One is validating
checksum value of extracted data. The other is to
check image’s inclinations matching up with orig-
inal image’s attributes of the database with the ex-
tracted index, such as Brightness, Histogram, Ra-
tio, Keypoints based on several image processing
theories. At last, a few validated-extracted data
remains. We expect the size of the last remained
doubt list is only one. If it’s more than one, the
user picks the data.
4 EVALUATION
The evaluation of the RIC algorithm is involved with
robustness. We used a Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio
(PSNR) as a comparison parameter between a dam-
aged image and an original image. The bigger value
of PSNR implies the less damaged image and the in-
finity value of PSNR implies the original image (Jian-
sheng et al., 2009; Hore and Ziou, 2010). We exper-
imented the prototype of RIC encoder/decoder with
Figure 3 pattern, developed by C++ using OpenCV (It-
seez, 2000). The experiments are simulated by watch-
ing the success number of decoding attacked images
with assuming r to 4, D
0
to 80, D
1
to 255, p to 6,
N
c
to 22, N
d
to 2
12
. The process consists of encod-
ing 10,000 pictures, attacking the images and decod-
ing the attacked encoded images. We used 9,850 pri-
vate images, which mainly pictured with landscapes,
foods and people, and 150 downloaded images from
free photo archivesmorgueFile(Connors et al., 1996),
which width is 1280 px. Also, to check DB index
in this paper, on encoding step, the original images’
attributes are saved on the memory. So on decoding
step, decoder checked the extracted index and image’s
ratio matching up the data saved above. In this ex-
periment, we exclude detecting and matching image’s
inclination.
4.1 Distance of Circles
We experimented on finding proper d (the distance of
circles). The distance evaluation was done by assum-
ing d to 0, 1, 2, 3, 7, 9 pixels. Also for measuring how
much the distance is related with damage, validating
DB index and image’s ratios process are not included
on this experiment. To evaluate robustness, before de-
coding images, we attack the encoded images by 30%
JPEG Compression. The result is shown in Table 1.
The distance of circles is related highly with the
decoding performance. Table 1 shows that the longer
distance of circles makes the size of doubt list con-
verge 1, which means RIC is not easily damaged.
While long distance makes the accuracy of decoding
RIC high, we want to make RIC area smaller with op-
timized performance. Also more image attacks could
widen the size of doubt list difference. For this rea-
Robust Index Code with Digital Images on the Internet
31

Table 1: Distance Experiment Result.
Distance
Success
Rates
Size Avg of
Doubt List
Decode
Time Avg
0 1.0000 1.1613 0.0497s
1 1.0000 1.1267 0.0531s
2 1.0000 1.0555 0.0590s
3 1.0000 1.0228 0.0569s
7 1.0000 1.0000 0.0714s
9 1.0000 1.0045 0.0789s
son, we choose to set d to 2 in this paper among the
shortest distance for the size of doubt list to be smaller
than 1.1.
4.2 Robustness
For evaluating RIC’s robustness, the experiment in-
cludes various attack types. Robustness experiment
has been held with experiment cases on Table 2.
JPEG Compression is one of the common compres-
sion attacks on digital images (Woo et al., 2005). Re-
sizing is another common attack on digital images. In
addition, combining Resize with JPEG Compression
is also considered. Figure 6 shows a sample RIC of
experiment case No.9 on Table 2. Table 3 shows the
result of experiment cases.
Table 2: Robustness Experiment Case.
No Attack Type
1 No Attack
2 50% JPEG Compression
3 30% JPEG Compression
4 Resize to 2000px
5 Resize to 2000px × 50% JPEG Compres-
sion
6 Resize to 2000px × 30% JPEG Compres-
sion
7 Resize to 420px
8 Resize to 420px × 50% JPEG Compres-
sion
9 Resize to 420px × 30% JPEG Compres-
sion
10 No. 9 × Resize to 1280px × 30% JPEG
Compression
11 No. 10 × Resize to 450px
12 No. 11 × 30% JPEG Compression
13 No. 12 × Resize to 2000px
14 No. 13 × 30% JPEG Compression
15 No. 14 × Resize to 400px
16 No. 15 × Resize to 420px
In the experiment cases, RIC of images over
420px Resize were detected successfully. Also, the
Figure 6: Resize 420px and 30% JPEG Compression of Fig-
ure 3.
size average of doubt list converged to 1, which
proves that RIC decoder detects mostly only one orig-
inal data with the doubt color correction algorithm.
On the performance evaluation of RIC decoder, it
took less than one second. Table 2 and 3 show that
decoding time is in direct proportion to image’s size
and degradation.
4.3 Comparing with Related Work
In this experiment, there are seven attack types used
to compare the proposed system with QR Code (In-
corporated., 2008) and Robust watermark (Yesilyurt
et al., 2013). Three methods embed a database in-
dex into an image. QR Code, embedded a database
index with the high error correction level, is embed-
ded on an image’s left-bottom area with same pixel
size of RIC. On the other hand, on Robust water-
mark, the two images of 400px and 640px are filled
with a redundant index by the DCT Based watermark-
ing method using Luminance component. The result
is regarded as success when an extracted data is the
same as an embedded data. The experiment process
is cited as follows. Table 4 shows the result of this
experiment.
• Step 1 : Generate a random database index.
• Step 2 : Pick an image and embed the generated
index to it by QR Code, Watermark and RIC.
• Step 3 : Attack embedded images by Resize or
JPEG Compression.
• Step 4 : Extract the index from attacked images
and check matching up with the original index.
It can be seen on Table 4 that the embedded data
using QR Code or Robust watermark do not have
robustness on Resize and JPEG Compression. On
the other hand, the data embedded by our proposed
method is correctly extracted over the 420px. Hence,
RIC is the only image-embed method to digital im-
ages on the Internet.
SIGMAP 2016 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
32
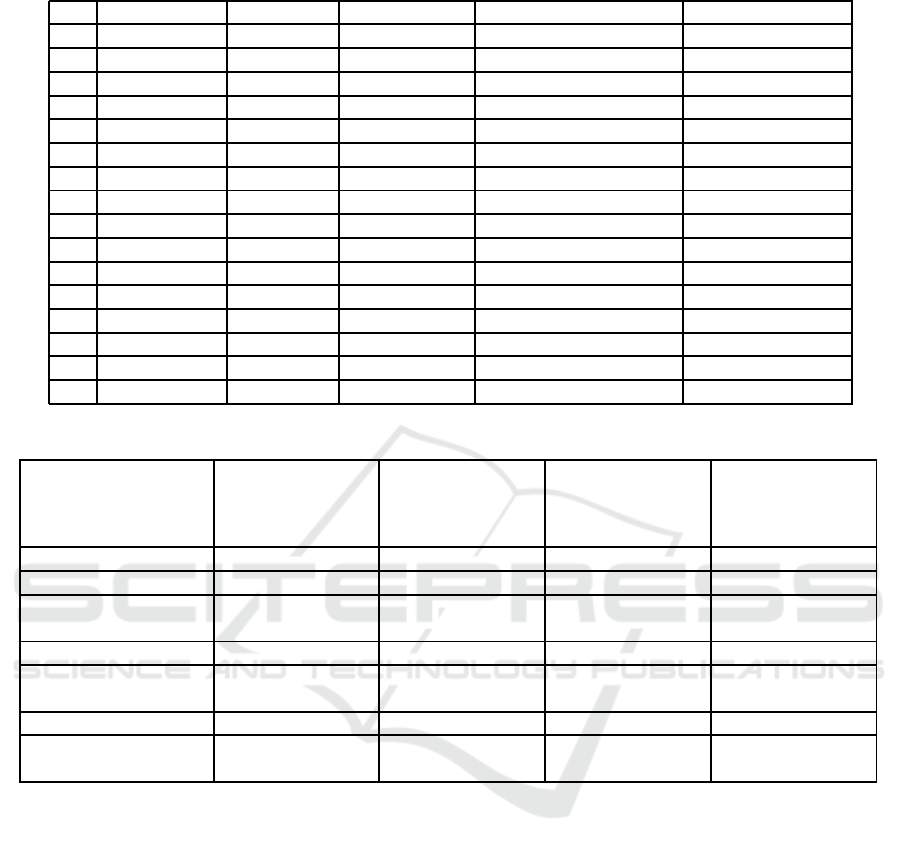
Table 3: Robustness Experiment Result.
No RIC Size(px) PSNR Avg Success Rates Size Avg of Doubt List Decode Time Avg
1 204×205 ∞ 1.0000 1.0000 0.0630s
2 204×205 33.76 1.0000 1.0000 0.0562s
3 204×205 32.22 1.0000 1.0000 0.0572s
4 313×314 42.33 1.0000 1.0000 0.0810s
5 313×314 37.58 1.0000 1.0000 0.0781s
6 313×314 35.81 1.0000 1.0000 0.0715s
7 73×74 31.74 1.0000 1.0000 0.0176s
8 73×74 29.47 1.0000 1.0000 0.0649s
9 73×74 28.64 1.0000 1.0000 0.4000s
10 204×205 27.71 1.0000 1.0000 0.4200s
11 77×78 27.50 1.0000 1.0000 0.4301s
12 77×78 27.47 1.0000 1.0000 0.4152s
13 313×314 27.22 1.0000 1.0000 0.4872s
14 313×314 27.10 1.0000 1.0000 0.4565s
15 70×71 28.02 0.9999 1.0000 0.4210s
16 73×74 27.90 0.9998 1.0000 0.7228s
Table 4: Comparison Experiment Result.
Attack Type
QR Code (Incor-
porated., 2008)
Success Rates
Watermark (Yesi-
lyurt et al., 2013)
Success Rates
(400px)
Watermark (Yesi-
lyurt et al., 2013)
Success Rates
(640px)
Proposed Method
Success Rates
No Attack 0.9700 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000
Resize to 450px 0.7421 0.9999 1.0000 1.0000
Resize to 450px ×
30% JPEG Comp.
0.5291 0.0594 0.0000 1.0000
Resize to 420px 0.0926 1.0000 0.9978 1.0000
Resize to 420px ×
30% JPEG Comp.
0.2723 0.0278 0.0000 1.0000
Resize to 400px 0.9416 1.0000 0.9998 1.0000
Resize to 400px ×
30% JPEG Comp.
0.5469 0.0131 0.0000 0.9999
5 SUPERDISTRIBUTION
SYSTEM
Superdistribution system (Mori and Kawahara, 1990)
is an ideal proposal to distribute digital products in
which software is made available freely and with-
out restriction but is protected from modifications and
modes of usage not authorized by its vendor, and nor-
mally there are three principal functions (Wikipedia,
2013) :
• A Cryptographic wrapper for digital products that
cannot be removedand remains in place whenever
the product is copied.
• A digital rights management system for tracking
usage of the product and assuring that any usage
of the product or access to its code conforms to
the terms set by the product owner.
• An arrangement for secure payments from the
product’s users to its owner.
The idea above is the most optimized architecture
for both product owners and recipients for the reason
that there is no restraint or additional expense through
several distribution channels. Unfortunately, the com-
plete concept of Superdistribution systems barely ex-
ists in the reality, but there are several partial Su-
perdistribution systems which intend to make a mas-
sive profit from the distribution process on the Inter-
net. In other words, massive platform companies have
built up their own ecosystem to make a profit from
both product owners and recipients. For example, Ap-
ple app store is a huge cash cow for Apple taking a flat
Robust Index Code with Digital Images on the Internet
33
Product
Owner
<Embed digital products
into an image>
<Set Security Policy>
<Cryptographically
wrap>
RIC Image
Database
index
<Recursively
spread out>
Internet
service
RIC Decoder
Extract the
embedded
index
Fetch the
original
product data
Recipient
Embed the
database
index using
RIC
Show the
original
data
<Pay directly
to the owner>
RIC Encoder
Save digital
products and
image’s
inclination
Embed the
database index
into the image
Remote Server
Remote
Database
1
2
3
4
I
II III
5
Fetch a
database
index
IV
Figure 7: New Superdistribution System Architecture.
30% cut of all App Store transactions, earning Apple
over 10 billions USD in revenue in a year (Applein-
sider, 2014).
To the best of our knowledge, there has not been
a complete Superdistribution system. To design the
desired system, we need the new source as a Crypto-
graphic wrapper which is able to embed safely both
digital products and security, payment arrangement
from a product owner, and barely damaged by all the
expected degradation on the Internet, and also recur-
sively spread out through Internet services.
For the reasons above, we considered three basic
conditions for the wrapper of the new Superdistribu-
tion system. The digital image has received signifi-
cant attention for the first condition, and the concept
of RIC has been designed for the second and third
condition in the first place.
• Intriguing sources for recipients, which spread out
easily, regardless of platforms
• An almost unlimited capacity for diverse types of
contents, and low risk for security issues
• Extremely high robustness against degradation on
distribution process on the Internet
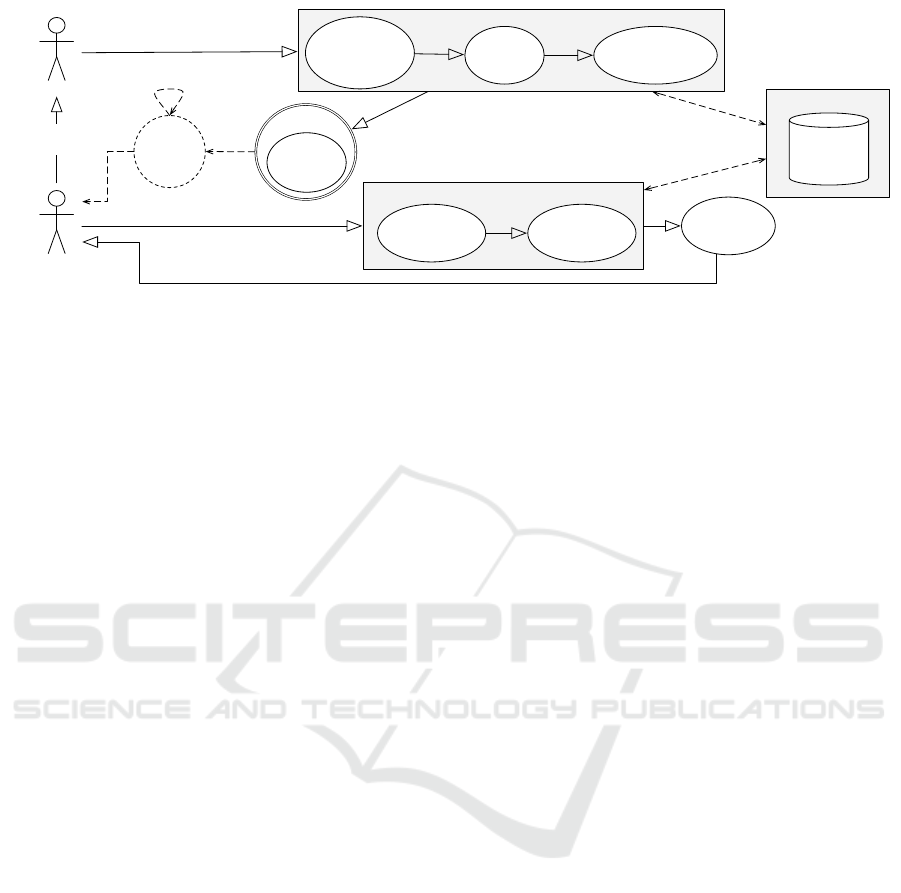
Product owners embed their digital products, se-
curity or payment policy into a digital image by RIC
Encoder. RIC Encoder preferentially extracts incli-
nation which shows the features of the digital image,
such as Brightness, Histogram, Ratio, Keypoints and
so on, and save them with digital products into a re-
mote database. Subsequently, the index of the address
to access the data is embedded on the image by RIC.
The new embedded image is called RIC Image, and
used as a Cryptographic wrapper in this architecture,
shown in Figure 7.
The RIC image is exposed to recipients by being
recursively copied and spreading out on the Internet
by existing Internet services like SNS. Afterwards the
recipients are able to extract the products, security or
payment policy of product owners easily, if RIC De-
coder Library is implemented in their devices. More-
over, even if a codemark is deleted from an image, the
original products remain on a remote database so that
recipients are able to access the data from other RIC
images.
Compared to the existing distribution process, the
main difference is that all the data which productown-
ers intend can be easily distributed, regardless any
existing platforms, and recipients consume the data
by the policy arranged from the product owner, not
platformers, because the image contains the products.
For instance, talented artists embed their music con-
tents and concert information of themselves into the
their attractive images, which means they get RIC im-
ages linked with their contents. The thing they only
have to do for advertising themselves is uploading
RIC images to SNS like Facebook, Twitter, LINE,
KakaoTalk, WhatsApp and so on. Users who find the
RIC image can easily access to the original contents
like right clicking the image on the Google Image
Search on PC. Hence, RIC is the only method target-
ing digital images on the Internet so that the new pro-
posed Superdistribution system can be only realized
by RIC. When the RIC library becomes a middleware
on the Internet construction, the proposed Superdis-
tribution system will be realized.
6 CONCLUSION
This paper presented the design and implementation
of the extremely high robustness codemark technol-
ogy, named RIC. We have determined that a digital
image is one of the most desirable sources, for reasons
that users already get used to use it for communica-
tion, and it is relatively easy to be copied and shared.
RIC has the apparent advantage to link a digital im-
age with unlimited digital data, and also guarantees
most cases of degradation occurred on the Internet, so
SIGMAP 2016 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
34

that the strengths of digital images above can be max-
imized. Our experiments validate the robustness of
RIC.
To our knowledge, there is no digital image ser-
vice using embedding data technologies into images.
RIC is mainly designed for digital images for chal-
lenging to open a new Superdistribution system, com-
pared to the existing ecosystems provided by platform
companies. Using RIC, it is possible that RIC images
can spread out in any sharing way, such as E-mail,
SNS, chat-app, and the original embedded digital data
can be easily extracted by end recipients on any Inter-
net services, regardless of platforms. We had already
implemented RIC to iOS, Android, Chrome browser
extension, and so on to confirm that RIC can be oper-
ated across diverse platforms.
In spite that high robustness of RIC is realized,
the performance of RIC, such as extracting time is
not completely considered. For example, the doubt
color correction algorithm helps detect damaged im-
ages, but it is highly likely that decoding process of
terribly damaged images takes relatively long time
when N
d
is big. We keep trying the way of optimizing
a doubt color correction algorithm with a small value
of N
d
. In addition, research for image’s inclination
matching is also critically important for security pol-
icy, and we are still trying several additional image
matching features. These future works will upgrade
the completeness and stability of the system, which
also means RIC will possibly be able to be operated in
the worse conditions than the currently defined speci-
fication.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Tokyo Institute of Tech-
nology and Pulit Inc. The authors would like to ap-
preciate the anonymous reviewers for their valuable
suggestions and comments.
REFERENCES
Appleinsider (2014). Apple’s App Store gener-
ated over $10 billion in revenue for devel-
opers in record 2014. [Online]. Available:
http://appleinsider.com/articles/15/01/08/apples-
app-store-generated-over-10-billion-in-revenue-for-
developers-in-record-2014.
Connors, K., Connors, M., and Seemann, J.
(1996). morgueFile. [Online]. Available:
http://www.morguefile.com.
Furht, B. (1995). A Survey of Multimedia Compression
Techniques and Standards. Part I: JPEG Standard.
Real-Time Imaging, 1(1):49–67.
Grillo, A., Lentini, A., Querini, M., and Italiano, G. (2010).
High Capacity Colored Two Dimensional codes. In
Proc. Int. Multiconference on Computer Science and
Information Technology (IMCSIT), pages 709–716.
Hao, T., Zhou, R., and Xing, G. (2012). COBRA: Color
Barcode Streaming for Smartphone Systems. In Proc.
10th Int. Conf. on Mobile Systems, Applications, and
Services, MobiSys ’12, pages 85–98. ACM.
Hore, A. and Ziou, D. (2010). Image Quality Metrics:
PSNR vs. SSIM. In 20th Int. Conf. on Pattern Recog-
nition (ICPR), pages 2366–2369.
Incorporated., D. W. (2008). About QR Code. [Online].
Available: http://www.qrcode.com/.
internet.org (2013). A Focus on Efficiency. [Online]. Avail-
able: http://internet.org/efficiencypaper.
Itseez (2000). OpenCV. [Online]. Available:
http://opencv.org.
Jiang, J. and Armstrong, A. (2002). Data hiding approach
for efficient image indexing. Electronics Letters,
38(23):1424–1425.
Jiansheng, M., Sukang, L., and Xiaomei, T. (2009). A
Digital Watermarking Algorithm Based On DCT and
DWT. In Proc. Int. Symposium on Web Information
Systems and Applications, WISA ’09, pages 104–107.
Academy Publisher.
Liu, Q., Sung, A. H., and Qiao, M. (2011). Neighboring
Joint Density-based JPEG Steganalysis. ACM Trans.
Intell. Syst. Technol., 2(2):16:1–16:16.
Liu, X., Doermann, D., and Li, H. (2008). A Camera-
based Mobile Data Channel: Capacity and Analysis.
In Proc. 16th ACM Int. Conf. on Multimedia, MM ’08,
pages 359–368. ACM.
Mintzer, F., Braudaway, G., and Yeung, M. (1997). Effec-
tive and ineffective digital watermarks. In Proc. 3rd
Int. Conf. on Image Processing, volume 3, pages 9–
12.
Mohanty, S. P. and Bhargava, B. K. (2008). Invisi-
ble Watermarking Based on Creation and Robust
Insertion-extraction of Image Adaptive Watermarks.
ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl.,
5(2):12:1–12:22.
Mori, R. and Kawahara, M. (1990). Superdistribution: The
Concept and the Architecture. The Trans. of the IE-
ICE, 73(7):1133–1146.
Nurwono, K. A. H. and Kosala, R. (2009). Color Quick
Response Code for Mobile Content Distribution. In
Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on Advances in Mobile Computing
and Multimedia, MoMM ’09, pages 267–271, New
York, USA. ACM.
Ong, S. K., Chai, D., and Tan, K. (2008). The Use of Border
in Colour 2D Barcode. In Int. Symp. on Parallel and
Distributed Processing with Applications, ISPA ’08,
pages 999–1005.
Provos, N. and Honeyman, P. (2001). Detecting Stegano-
graphic Content on the Internet. Technical report, In
ISOC NDSS02.
Robust Index Code with Digital Images on the Internet
35

Research, M. (2010). High Capacity Color Barcodes. [On-
line]. Available: http://research.microsoft.com/en-
us/projects/hccb/.
Wang, C., Ni, J., Huang, J., Zhang, R., and Huang, M.
(2007). Robust and High Capacity Image Watermark-
ing Based on Jointly Coding and Embedding Opti-
mization. In Information Hiding, volume 4567 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 65–79.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Wikipedia (2013). Superdistribution. [Online]. Available:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Superdistribution.
Woo, C.-S., Du, J., and Pham, B. (2005). Performance
Factors Analysis of a Wavelet-based Watermarking
Method. In Proc. 2005 Australasian Workshop on
Grid Computing and e-Research - Volume 44, ACSW
Frontiers ’05, pages 89–97. Australian Computer So-
ciety, Inc.
Yeh, C.-T. and Chen, L.-H. (1998). A system for a new two-
dimensional code: Secure 2D code. Machine Vision
and Applications, 11(2):74–82.
Yesilyurt, M., Yalman, Y., and Ozcerit, A. T. (2013). A
New DCT Based Watermarking Method Using Lumi-
nance Component. Electronics & Electrical Engineer-
ing, 19(4):47–52.
APPENDIX
This appendix describes an example of the prototype
iOS application of the RIC library. Figure 8 shows a
RIC image linked with the food information. When
users open the image in the app, they can see gray
spots which contain information like Figure 9. With
tapping a spot, food name, description, location and
so on will be displayed shown in Figure 10.
Figure 8: Example of the RIC image.
Figure 9: Open Figure 8 in the Application.
SIGMAP 2016 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
36

Figure 10: Detail information of the RIC image in the Ap-
plication.
Robust Index Code with Digital Images on the Internet
37
