
Transitioning to a Javascript Voting Client for Remote Online Voting
Jordi Cucurull
1
, Sandra Guasch
1
and David Galindo
2
1
Scytl Secure Online Voting, Pl. Gal·la Placídia, 1-3, 1st floor, 08006, Barcelona, Spain
2
School of Computer Science, The University of Birmingham, Edgbaston, Birmingham, B15 2TT, U.K.
Keywords:
Remote Electronic Voting, Javascript Security, Implementation, Performance, Random Number Generation.
Abstract:
Voters in remote electronic voting systems typically cast their votes from their own devices, such as PCs
and smartphones. The software executed at their devices in charge of performing the ballot presentation,
navigation and most of the cryptographic operations required to protect the integrity and privacy of the ballot,
is referred to as the voting client. The first voting clients were developed as Java Applets. However, the use of
this technology has become relegated in front of web technologies such as Javascript, which provide a better
multi-platform user experience. This is the reason why in 2013 Scytl decided it was imperative to develop
a voting client purely based on Javascript. This industrial paper shows the implementation experiences and
lessons learned during the development and deployment of Javascript voting clients for our remote electronic
voting systems. The paper is complemented with a performance study of 1) the main cryptographic primitives
used in voting clients and 2) the voting casting process of one of the voting clients used in a real election.
1 INTRODUCTION
In remote electronic voting systems, voters are usu-
ally allowed to cast their votes from their own de-
vices, such as PCs, laptops, smartphones, etc. This
is specially suitable for voters who live abroad, who
are outside of their region during the election day, and
for impaired voters who may have mobility issues.
In general, remote electronic voting systems have
to fulfill a set of security requirements in order to be
used in electoral processes, which are focused on en-
suring that at least the same properties of traditional
voting scenarios are maintained, such as vote authen-
ticity and privacy, result accuracy, secrecy of interme-
diate results, verifiability and auditability, and unco-
ercibility and vote selling protection. In order to fulfill
such security requirements, remote electronic voting
systems use advanced cryptographic protocols (see
for example (Adida, 2008), (Gjosteen, 2013), (Juels
et al., 2010)). These protocols require to perform
some cryptographic operations both at the client and
server sides. The piece of software which is run in the
voter’s device, which is in charge of performing the
ballot presentation, navigation and most of the crypto-
graphic operations, is referred to as the voting client.
The first voting clients implemented in Scytl’s
products were developed as Java Applets. The usage
of Java enabled 1) the possibility to perform complex
cryptographic operations on a multiplatform setup
and 2) code and expertise reuse of the developers that
were already working on the backend. However, the
use of Java Applets implied a high price to pay in
terms of user experience and security. Voters’ devices
required a Java Runtime Environment (JRE), that was
not always present neither updated, being a source of
security vulnerabilities, not even supported in most
of mobile devices and with support recently removed
from the most popular browsers. In recent years, the
natural evolution of the World Wide Web standards
and the introduction of HTML5 have strengthened the
use of Javascript for increasingly complex operations,
reaching a point where performing cryptographic op-
erations in Javascript at the browser has become fea-
sible. Due to this feasibility and the advantages the
Javascript technology offered in terms of user expe-
rience and multi-platform compatibility (specially for
mobile devices), in 2013 Scytl decided it was imper-
ative to develop a voting client purely based on this
technology to replace the former Java-based versions.
Thus, the main contribution of this industrial pa-
per is to show the implementation experiences and
lessons learned, along with the whole process of de-
veloping and deploying Javascript voting clients used
in several real elections. The paper is organized in
seven sections: Section 2 describes a generic vot-
ing client and the cryptographic operations it may
Cucurull, J., Guasch, S. and Galindo, D.
Transitioning to a Javascript Voting Client for Remote Online Voting.
DOI: 10.5220/0005967301210132
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2016) - Volume 4: SECRYPT, pages 121-132
ISBN: 978-989-758-196-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
121

require; Sections 3 and 4 describe the challenges
to implement a Javascript-based voting client and
the solutions adopted; Section 5 explains the test-
ing of a pseudo-random number generator imple-
mented; Section 6 analyses the performance of cryp-
tographic primitives and a voting client implemented
in Javascript, and also explains some of the ap-
proaches followed to improve it; finally Section 7
presents the conclusions reached.
2 VOTING CLIENT
This section introduces the details of generic voting
clients used in remote electronic voting systems.
2.1 Remote Electronic Voting Systems
From a high level point of view, a remote voting sys-
tem is composed of two main components, the voting
servers and the voting client (see Figure 1). During
the election, the voting servers provide the back-end
services that allow voter authentication, ballot provi-
sion, and verification and storage of cast ballots in
the ballot box. During the counting phase, the vot-
ing servers decrypt and tally the votes providing the
election results, while protecting the voter’s privacy.
A usual approach for this is to use a mix-net (Chaum
and Pedersen, 1992) in order to shuffle and transform
the encrypted votes prior to decryption.
A good practice in remote electronic voting is
to cryptographically protect the vote by encrypting
and digitally signing it at the voter’s device, before
it is sent to the remote voting server for being stored.
Hence the privacy and the integrity of the vote are pro-
tected from the very beginning, right after the vote is
generated until it is processed at the counting stage.
This is commonly known as end-to-end encryption
and it is possible thanks to the voting client applica-
tion executed at the voter’s device.
The voting client is the front-end that allows the
voters to authenticate, navigate through the ballot, se-
lect their voting options, generate an encrypted and
signed ballot and cast it.
2.2 Basic Components
The voting client comprises a graphical user interface
and some underlying logics. These last ones can be
divided in several components:
• Authentication: This component authenticates
the voter in front of the voting system. The com-
ponent can be adapted for integration with the cus-
tomer infrastructure or totally replaced by a third-
party authentication system.
• Vote Generation: This component generates the
ballot to be cast, i.e. encoding the voting op-
tions selected by the voter, encrypting and digi-
tally signing the ballot containing them, and send-
ing the ballot to the remote voting server. Addi-
tionally, it may generate mathematical proofs to
prove the correctness of the operations performed.
• Cryptographic Library: The authentication and
ballot generation components require the usage of
cryptographic primitives that are not natively pro-
vided by the Javascript language. Thus they are
included as cryptographic libraries.
• Pseudo Random Number Generator and En-
tropy Collector: A module to generate sequences
of secure random numbers, required by some
cryptographic primitives, is included for the plat-
forms that do not possess a built-in generator.
2.3 Basic Voting Flow
The flow in the voting client depends on the spe-
cific voting protocol implemented each one provid-
ing different security properties under different as-
sumptions (Gharadaghy and Volkamer, 2010), (Puig-
galí et al., ). Despite this, a generic set of operations
can be defined: 1) The voter authenticates to the sys-
tem; 2) upon presentation of her ballot, she selects the
voting options that represent her voting intent; 3) after
the voter confirms her vote, the voting options are en-
coded and encrypted; 4) mathematical proofs of cor-
rect encryption are generated (if required by the pro-
tocol); 5) the encrypted voting options and the mathe-
matical proofs are digitally signed; 6) the vote is cast
to the remote server; 7) the server provides a confir-
mation receipt which is presented to the voter.
2.4 Cryptographic Functionalities
The following generic set of cryptographic function-
alities and algorithms, depending on the voting proto-
col implemented, may be required in the voting client:
• Hash Functions: they are used for computing
certificate fingerprinting and digital signatures.
Although the standard for SHA-3 has already
been published (NIST, 2015), the previous stan-
dard SHA-2 (NIST, 2012) (specifically, SHA-
256) has been considered due to compatibility is-
sues.
• Digital Signature Functions: they are used for
digitally signing the vote and for verifying the dig-
ital signatures of the information received from
SECRYPT 2016 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
122

Figure 1: Remote electronic voting system.
the remote voting server. The RSA algorithm with
the hash variant (RSA Full Domain Hash signa-
ture scheme (RSA-FDH) (Bellare and Rogaway,
1993)) has been considered.
• Encryption Algorithms: they are used for en-
crypting the voting options. RSA and ElGa-
mal encryption algorithms (Menezes et al., 1996),
and the AES encryption algorithm (NIST, 2001),
are considered for public key and symmetric key
cryptography respectively.
• Zero-Knowledge Proofs of Knowledge
(ZKPK): they (Damgaard, 2010) are used
to prove a certain statement without revealing any
other information than the statement is true. For
example the Schnorr Signature (Schnorr, 1991)
can prove knowledge of the randomness used for
encrypting a message, providing assurance of the
originator of an encrypted vote, and preventing
vote copying (Cortier and Smyth, 2011).
• Pseudo-random Number Generators (PRNG):
these are used for generating the random values
required by the cryptographic algorithms.
• Password-based Key Derivation Functions: in
the voting client they are used to derive keys for
the authentication of the voter and to access pri-
vate data. The PBKDF2 (RSA Laboratories, b)
algorithm is the one selected.
• Functionalities for Parsing and Opening Key-
stores: these are used for providing private
signing and encrypting keys to the voters.
PKCS#12 (RSA Laboratories, a) or equivalent
key containers are used.
• Reading, Parsing and Validation of Digital
Certificates: these are used to check the valid-
ity of the cryptographic keys and X509v3 (RFC-
5280, 2008) certificates used in the application.
3 CHALLENGES
The implementation of a voting client in Javascript
implied several challenges on cryptography, security
and performance.
3.1 Cryptography
3.1.1 Availability of Cryptographic Primitives
JavaScript does not implement the cryptographic
functionalities required by the voting client. An anal-
ysis of existing third party libraries was done to deter-
mine which of the required functionalities were pro-
vided by each library. The following factors were
considered: functionality provided, in order to know
if the library provided exactly what was needed, or if
it required some modification; confidence level, the
popularity of the library and the maintenance of the
code; license, to analyse if the license terms were
compatible with the license of the voting client ap-
plication. In our particular context we preferred BSD,
MIT or LGPL licensed libraries.
The results of the analysis, updated on April 2015,
are shown on Table 1. The conclusion was the Forge
1
library is one of the best alternatives to implement a
voting client. It provides functions for parsing and
opening PKCS#12 containers, as well as managing
digital certificates and public key cryptography. Be-
sides this, it has a strong developer support and up-
dates are made constantly. Both SJCL
2
(Stark et al.,
2009) and jsbn
3
are also broadly used in other soft-
ware. Specifically, jsbn is used in other of the ana-
lyzed libraries to provide BigInteger support (Forge,
1
http://digitalbazaar.com/forge
2
http://crypto.stanford.edu/sjcl
3
http://www-cs-students.stanford.edu/˜tjw/jsbn
Transitioning to a Javascript Voting Client for Remote Online Voting
123
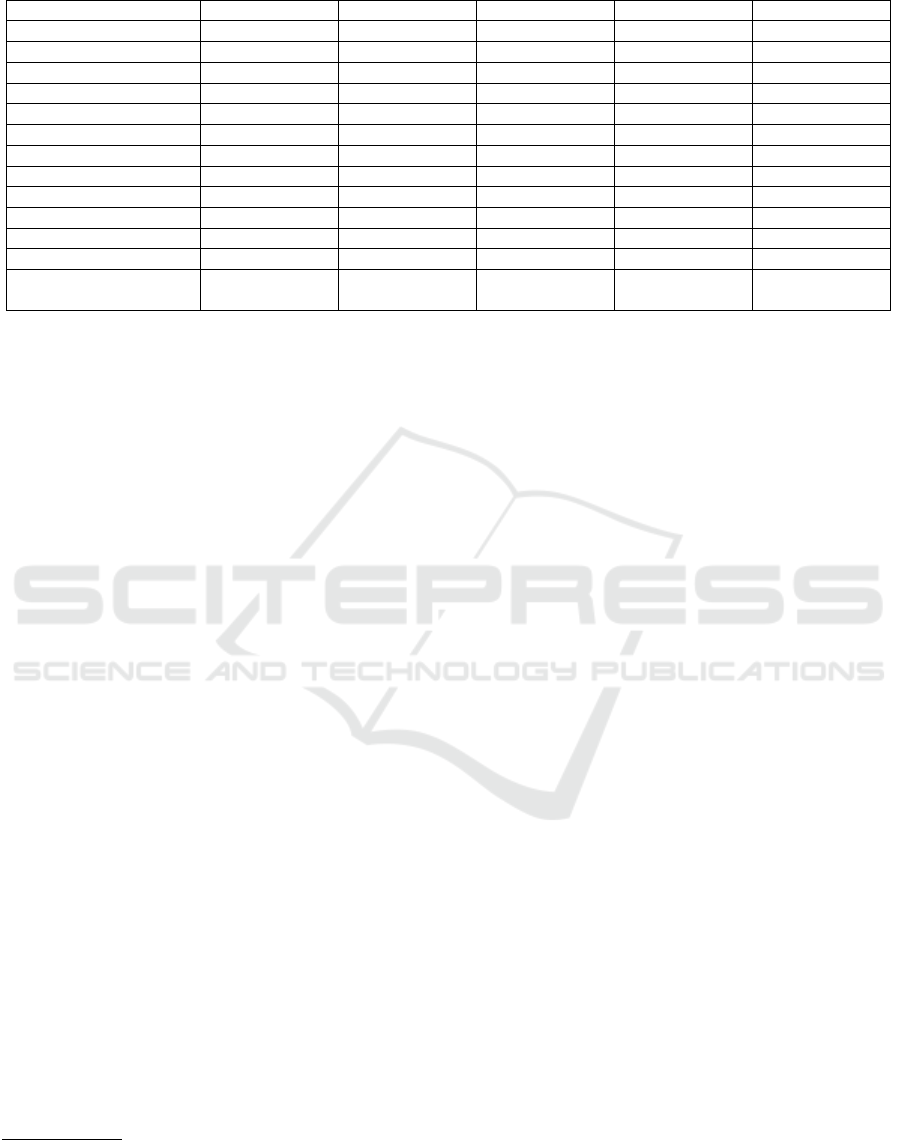
Table 1: Cryptographic functionalities provided by third party libraries.
Functionality SJCL Forge jsbn jsrsasign CryptoJS
SHA-256
√ √
X
√ √
RSA signature with SHA-256 X
√
X
√
X
RSA encryption X
√ √
X X
ElGamal encryption (over Zp) X X X X X
AES encryption
√ √
X X
√
Schnorr Signature or ZKPKs X X X X X
BigInteger support
√ √ √ √
X
PRNG
√ √ √
X X
Parsing PKCS#12 containers X
√
X X X
Parsing X.509 certificates X
√
X
√
X
PBKDF2
√ √
X
√ √
Confidence level Maintained Maintained No updates Few updates Few updates
License BSD, GPL-2.0 BSD 3-Clause,
GPL-2.0
BSD MIT BSD
jrsasign
4
), and in the Helios voting system (Adida,
2008). SJCL is a library developed by highly recog-
nized cryptographers. Therefore it was worth to con-
sider it for some of the needed functionalities, such
as secure random generation or hash algorithms. jsr-
sasign and CryptoJS
5
did not seem to provide enough
support from the point of view of maintenance and
use, as well as functionalities. Considering the anal-
ysis performed, the Forge library was selected. The
functionalities missing in the library were imple-
mented on top of it (see Section 4.1.1).
3.1.2 Secure Random Numbers and Entropy
Several cryptographic primitives require the use of
random values. The quality of the random val-
ues (in the sense of their unpredictability) determine
the security offered by these primitives (for exam-
ple, non-random values can lead to weak encryp-
tions). Although Javascript has a native method
for random number generation, Math.random() (EC-
MAScript, 2011), its implementation is not consid-
ered cryptographically secure (Klein, 2008). Alter-
natively, there is a W3C standardization initiative for
a JavaScript API for performing basic cryptographic
operations (W3C, b). This includes a Pseudo Ran-
dom Number Generator (PRNG) suitable for cryp-
tographic uses, window.crypto.getRandomValues(),
which uses the browser’s host system entropy, but is
only implemented in recent versions of the browsers
and not for all mobile devices’ browsers
6
.
Some of the cryptographic libraries analized have
their own PRNG implementations. Specifically, SJCL
and Forge implement the Fortuna PRNG by Schneier
4
http://kjur.github.com/jsrsasign
5
http://code.google.com/p/crypto-js
6
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-
US/docs/DOM/window.crypto.getRandomValues
and Ferguson (Ferguson and Schneier, 2003). This
PRNG is intended to be used in long-term systems,
such as servers, and provides measures for collect-
ing randomness from the system events, and mixing
it in order to provide secure random values. How-
ever, web sessions in which Javascript cryptography
may be used can be very different from a server sys-
tem, and therefore the same approaches taken in the
design of the Fortuna algorithm may not be the best
choice. For example, web sessions have a short life
time, and the sources of entropy in a browser or in
a server are not the same. Current implementations
from SJCL and Forge of Fortuna have modifications
regarding the original scheme (Stark et al., 2009).
However, they still have some limitations regarding
the entropy sources they use to generate the random
numbers. Thus a custom PRNG, based on the Fortuna
PRNG, has been implemented (see Section 4.2).
3.2 Security
3.2.1 Code Authenticity
One of the challenges to develop a Javascript voting
client is to ensure the authenticity of the code to be
executed in the voter’s device. A modification of this
code by an attacker could have severe implications in
the security of the solution, for example compromis-
ing the integrity and secrecy of the votes.
A classical solution to ensure the authenticity of
the code consists of signing it using public key cryp-
tography and enforcing the validation of this signature
in the browser. However, as opposed to other tech-
nologies such as Java Applets, there is no standard to
sign and verify the Javascript code delivered to the
browsers. There only exists a proprietary, and depre-
SECRYPT 2016 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
124

cated, solution
7
, implemented in Mozilla and, for-
merly, Netscape Communicator 4.x, browsers. This
solution was based on packaging the Javascript and
HTML code within a signed Jar file, that was verified
by the browser when accessed. More promising is the
new Candidate Recommendation W3C Subresource
Integrity (W3C, a) that enables the HTML code to in-
clude fingerprints of the Javascript code it refers. De-
spite this ensures the integrity of the included third
party code, it does not guarantee the integrity of the
HTML files that contain the hashes. Thus, it is not
a complete solution for the authenticity of the whole
code of the voting client. Finally, there exist proposals
ensuring end to end integrity, but they require the in-
stallation of browser plugins (Karapanos et al., 2016).
Given the current lack of support for guaranteeing
the JS code authenticity, the following approaches, to
detect code manipulation, have been implemented: 1)
TLS communications to guarantee the code transport
authenticity (preventing man-in-the-middle attacks);
2) Regular checks of file integrity in the server, in-
cluding the Javascript voting client code against a
baseline, e.g. using software scanning tools such as
AIDE
8
; 3) Running a Javascript remote integrity val-
idation service, i.e an externally executed service to
remotely download a selected set of Javascript code
from the server as a regular user and check if it
matches a previously generated baseline. This service
has been implemented and used within the context of
an election, but still not to check a voting client code.
3.2.2 Third Party Code
Javascript allows the inclusion of third party code and,
more important, the dynamic loading of scripts from
different servers. However, embedding third party
code dynamically loaded from external servers inside
the voting application’s website can pose a serious
security risk and it is totally unadvised, as this code
could access any variable or method of the voting ap-
plication. A server that does not belong to the elec-
tion realm may not fulfill the same security policies,
potentially becoming a weak point of attack. Any le-
gitimate external server acting as code source must be
secured as the main code server is.
An example of this is the vulnerability (Halder-
man and Teague, 2015) that a team of researchers dis-
covered in the Javascript voting client that we imple-
mented for the State General Elections 2015 of New
South Wales
9
. In this case a third party code owned
7
http://www.mozilla.org/projects/security/components/
signed-scripts.html
8
http://aide.sourceforge.net
9
http://www.vote.nsw.gov.au
by Piwik, used by monitoring purposes, was included
on behalf of NSW. A manipulation of this code, ex-
ploiting the FREAK vulnerability present in the ex-
ternal Piwik server that hosted the code, could poten-
tially allow a sophisticated attacker to alter the voting
client code running on the voter’s browser and mod-
ify the intended voting options. From the point of
view of the secrecy and integrity of the vote, the re-
ported vulnerability’s potential damage was similar to
that of having malware installed in the voter’s device.
This possibility was already considered in the design
of iVote 2015, and the defence against it (regarding
the integrity of the vote) was the inclusion of a voice
verification mechanism using the DTMF phone input.
Thus, we do not recommend including third party
code from external servers. But, this may change if
the W3C Subresource Integrity (W3C, a) candidate
recommendation becomes an adopted standard.
3.3 Performance
The computational performance of Javascript is con-
stantly improving, but still below the one obtained by
native applications. In addition, the Javascript appli-
cations can be executed in a myriad of devices with
very different computational capabilities, e.g. smart-
phones, laptops, etc. Some existing voting client
implementations (Adida, 2008) combined Javascript
with the usage of Java for certain primitives that re-
quired higher performance using a technology called
LiveConnect. However, this alternative could not be
considered because the aim was to completely elimi-
nate the dependency with the Java Virtual Machine.
As cryptographic operations are computationally
expensive, an efficient implementation was required
and several optimizations had to be performed at
the cryptographic protocol level (see Sections 4.1.1
and 4.3) to provide reasonable voting times.
4 IMPLEMENTATION
EXPERIENCE
During 2013-2015, most of the Scytl voting systems
were transitioned to use a Javascript voting client.
This section describes the most relevant aspects of the
implementation of them considering the challenges
previously described.
4.1 Cryptographic Library
Scytl provides different voting systems with different
cryptographic protocols, thus several variants of the
Transitioning to a Javascript Voting Client for Remote Online Voting
125

Javascript voting client were implemented. As a con-
sequence, a cryptographic library containing a large
amount of primitives was developed:
4.1.1 Basic Primitives
The basic cryptographic primitives are the most
widely used in standard web applications and, there-
fore, present in some of the libraries studied. For ex-
ample, SHA-256 hash functions, RSA digital signa-
ture, AES symmetric encryption, key derivation func-
tions such as PBKDF2, and support for X.509 certifi-
cates and PKCS#12 containers. These primitives have
been wrapped in our library from the Forge library.
4.1.2 ElGamal and ZKPK Primitives
Other primitives such as ElGamal encryption or
ZKPKs are more specific to cryptographic protocols
such as those for e-voting. Therefore, they are not in-
cluded in the existing libraries. A custom implemen-
tation of these primitives has been built.
ElGamal encryption scheme has homomorphic
properties that are essential in electronic vot-
ing (Adida, 2008), (Gjosteen, 2013), (Galindo et al.,
2015). However, the usage of modular exponenti-
ations with large integers is computationally expen-
sive. Therefore, two modifications were performed to
the original scheme to improve its efficiency:
• ElGamal Encryption with Short Exponents:
This is a well-known optimization (Gennaro,
2005; van Oorschot and Wiener, 1996) consisting
of using shorter exponents (e.g. of about 256 bits)
than those defined by the cyclic group used in the
scheme (which may be of about 2048 bits). This
reduces the cost of the modular exponentiations
without posing at risk the security of the scheme
in practice (Koshiba and Kurosawa, 2004).
• ElGamal Encryption with Multiple Keys:
When the number of plaintexts to be encrypted is
higher than one, an optimization consists of re-
ducing the number of exponentiations to compute
by using a different public key for computing each
ciphertext, but the same randomness for all them.
This does not affect the security of the encryption
scheme (Gjosteen, 2013; Kurosawa, 2002).
In order to maximize the code reuse and reduce
the likelihood of errors, we used the Maurer frame-
work (Maurer, 2009), which generalizes the imple-
mentation of ZKPKs for different statements. Thus
a unique base code is used for all the ZKPK vari-
ants of our voting systems. The Java-like BigInteger
functionalities required to operate with the large mag-
nitude integers used in these primitives were reused
from the existing libraries.
4.2 Pseudo-random Number Generator
A pseudo-random number generator (PRNG) is an
algorithm that generates a sequence of numbers
which is cryptographically indistinguishable from a
sequence of true random numbers. PRNGs gener-
ate the sequence of numbers in a deterministic man-
ner. The unpredictability of the values generated by
a PRNG is given by the unpredictability of the value
with which it is initialized, which is called the seed.
In order to provide high quality random values for the
cryptographic primitives, the PRNG is seeded with
entropy (random data) from the system events and in-
formation.
We have implemented a custom PRNG to be
used in the voting client. Its design has taken into
account requirements and particularities of voting
clients, specifically a short runtime life and strong
unpredictability of the random values produced. The
following principles were followed in the design and
use: 1) the collection of entropy to seed the PRNG
had to start as soon as possible, preferably as soon
as the voter started interacting with the system. The
implemented PRNG provides methods to start the
entropy collection task before the protocol-specific
functions have to be called; 2) in order to collect en-
tropy as fast as possible, user-driven events from an
extense set of sources were collected; 3) entropy es-
timation mechanisms were included in order to es-
timate how much entropy can be attributed to each
type of information collected in the browser. These
mechanisms ensure that enough entropy is collected
for seeding the PRNG and starting generating secure
random values.
The PRNG functionality implemented is com-
posed by several parts (see Figure 2) detailed in the
following sections.
Entropy Collection Mechanism. Collects infor-
mation available in the browser, as well as events gen-
erated by web navigation and user interaction:
• Sources of information available in the browser or
in the voting application.
– Random numbers from Javascript crypto-
graphic API if available in the used browser
– Browser information (e.g. User Agent string)
– Date
– Regular random numbers from the standard
Math library
SECRYPT 2016 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
126
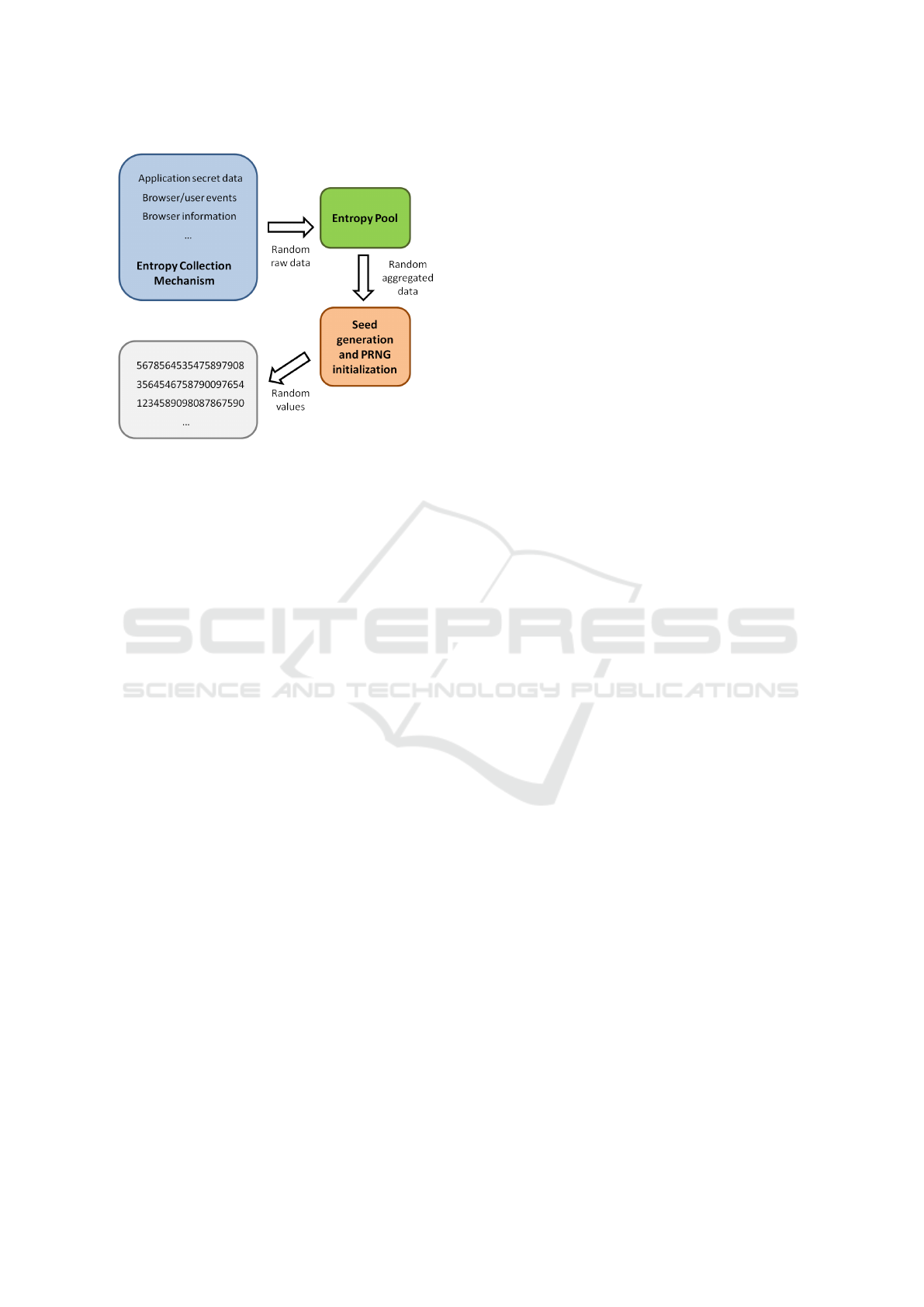
Figure 2: Diagram of the Pseudo-Random Number Gener-
ator.
• Events triggered by JavaScript or Ajax calls, as
well as user events.
– Mouse: mousemove, mousedown, mouseup,
wheel
– Keyboard: keydown, keyup
– Touch: touchstart, touchmove, touchend, ges-
turestart, gesturechange, gestureend
– Device accelerometer/compass: devicemotion,
deviceorientation
– Page loads and other AJAX calls
Since the Javascript cryptographic API is a source
of cryptographically strong random values, this col-
lector is defined to be the first one to be called. In user
events the following information is collected when
possible: relative position to the window and to the
screen, key/button, date, angle (only for compass) and
acceleration components (x,y,z) (only for accelerom-
eter in smartphones, tablets and alike). Each event
collected has been assigned with an estimated entropy
value, thus it is possible to estimate the amount of en-
tropy gathered by the entropy collector. Most of the
estimated entropy values were obtained from existing
analysis (Stark et al., 2009).
Seed Generation and Initialization. The data
gathered by the entropy collection mechanism is ac-
cumulated into an entropy pool, and at the same time
an entropy counter is increased with the estimated en-
tropy. The entropy collection starts at the very begin-
ning after downloading the voting client. Every time
new data is collected, there is the possibility to check
if a minimum amount of entropy required by the ap-
plication has been reached. After collecting enough
entropy the collector mechanism is stopped and the
PRNG is seeded. An amount of 128 bits of entropy is
enough for initializing the PRNG.
Pseudo-random Values Generation. The PRNG
generates sequences of pseudo-random values suit-
able for cryptographic purposes. Our implementa-
tion is based on the Fortuna PRNG (Ferguson and
Schneier, 2003) and the random values are obtained
from an AES cipher in counter mode. The PRNG
output has been tested against statistical analysis tools
(see Section 5) to guarantee its robustness.
4.3 Vote Generator
The Javascript implementation of the voting client has
influenced the voting protocols because the computa-
tional efficiency is limited and the trust of the under-
lying platform cannot be guaranteed. An overview of
the main considerations is shown below.
Pre-computations. The idea behind this is to pre-
compute some cryptographic operations’ values while
the voter selects the voting options, so that when the
voter decides to cast the vote the number of remaining
computations is small and the time the voter has to
wait for the ballot to be cast is considerably shorter.
The amount of operations that can be pre-computed
can account up to 95% in certain voting protocols.
Cast as Intended Validation. Since the voter de-
vice cannot be trusted, e.g. it may be infected by
malware, some of the voting protocols implemented
provide validation mechanisms that allow the voter
to check the integrity of the vote cast. For exam-
ple, in the Norwegian project eValg2013 (Gjosteen,
2013) secret codes received via SMS allowed voters
to check that the votes cast contained the voting op-
tions they selected. In the Neuchâtel e-voting plat-
form (Galindo et al., 2015), the same approach was
followed with the difference that the codes were re-
turned by the same voting client. This option was pos-
sible in this case because multiple voting was not al-
lowed, thus the voting client could not learn the codes
and vote again with manipulated voting options.
Defense Against User Manipulation. Develop-
ment tools provided by browsers make the manipula-
tion of the code easier for a regular user than in other
languages. A non honest voter could take advan-
tage of this by manipulating the processes that happen
on her browser to disrupt the election. As a general
rule, it is recommended to make at server-side some
pre-processing over the data received from the voting
Transitioning to a Javascript Voting Client for Remote Online Voting
127
client prior to passing it to further layers of the pro-
tocol. In addition, voting protocols must be designed
to cope with these cases, e.g. including ZKPKs to be
verified at the voting server when the vote is received.
5 TEST OF THE PRNG
Since the PRNG is required to produce values with
strong randomness, we tested its output against a sta-
tistical analysis tool. The tests proved that the im-
plemented PRNG provides random values of the exp-
tected quality.
5.1 Testing Tool
Dieharder (Brown et al., 2009) was the tool selected
to perform the statistical analysis, a random number
generator testing suite, intended to test generators. It
includes tests from the original Diehard Battery of
Tests of Randomness (Marsaglia, 1996), as well as
tests from the Statistical Test Suite (STS) (Rukhin
et al., 2010) developed by the National Institute
for Standards and Technology (NIST) and tests de-
veloped by the author of the Dieharder test suite.
Dieharder is well known and highly reputed due to
the broad characteristics of random number genera-
tors that are evaluated in its tests.
5.2 Test-bed Setup
In order to test the PRNG, most of the tests available
in the Dieharder suite have been performed, except
those which need an overwhelming quantity of data
(more than 4GB).
Most of the discarded tests overlapped with other
tests, thus it was considered not to affect the quality
of the testing. Tests which supported different con-
figurations were performed using different input pa-
rameters, thus in total an amount of 78 statistical tests
were performed.
In order to have a reference of what should be
expected from the tests on the implemented Scytl
PRNG, two other PRNGs have also been evaluated
in the same way: a Flawed PRNG which is known
to generate sequences of correlated random numbers,
and the AES_OFB generator as the Gold Standard
PRNG, which is a commonly known good PRNG.
A set of datasets were generated for each of the
PRNGs to test (11 datasets for the Scytl PRNG, 5
datasets for the Gold Standard PRNG and 3 datasets
for the Flawed PRNG). Each dataset contained 256
million random unsigned 32-bit integers, which was
composed of 400 sets of 640.000 values that were
Table 2: Dieharder tests performed.
Dieharder tests performed
Gold
PRNG
Scytl
PRNG
Flawed
PRNG
Diehard Birthdays Test X X X
Diehard 32x32 Binary Rank Test X X X
Diehard 6x8 Binary Rank Test X X X
Diehard Bitstream Test X X X
Diehard OPSO X X X
Diehard OQSO Test X X X
Diehard DNA Test X X X
Diehard Count the 1s (stream) Test X X X
Diehard Count the 1s Test (byte) X X X
Diehard Parking Lot Test X X X
Diehard Min. Dist. (2d Circle) Test X X X
Diehard 3d Sphere (Min. Dist.) Test X X X
Diehard Squeeze Test X X X
Diehard Sums Test X X X
Diehard Runs Test X X X
Diehard Craps Test X X X
STS Monobit Test X X X
STS Runs Test X X X
STS Serial Test (Generalized) X X X
RGB Bit Distribution Test X X X
RGB Generalized Min. Dist. Test X X X
RGB Permutations Test X X X
RGB Lagged Sum Test X X X
RGB Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test Test X X X
generated with a different PRNG instance and seed.
These values composed the input of the Dieharder
test suite. Values generated with the PRNG initial-
ized with different seeds have been used in order to
test, not only that the values sequentially generated by
a PRNG instance have the expected properties (corre-
sponding to a sequence of random numbers), but also
to test that different instances of the PRNG (initial-
ized with different seeds) generate uncorrelated ran-
dom numbers.
5.3 Results
All the tests have been successfully passed by the im-
plemented Scytl PRNG, as well as by the Gold Stan-
dard PRNG (see Table 2). On the other hand, the
Flawed PRNG has failed most of the tests.
In order to determine the quality of a PRNG,
Dieharder tests the null hypothesis, which is that the
sequence of numbers generated by the random num-
ber generator under test is trully random. Dieharder
computes certain statistics over the random values
generated by the PRNG, which ultimately lead to the
p-value. This value denotes the probability that a true
random number generator would produce a sequence
of similar characteristics. That is, it summarizes the
evidence against the null hypothesis: if the p-value
is lower than a certain significance level, the null hy-
pothesis is rejected and the PRNG under test is not
accepted as a good one. For other p-values, the null
hypothesis is not accepted, but it fails to be rejected
for this particular test. In fact, for good PRNGs, p-
values extracted from different rounds of each test are
SECRYPT 2016 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
128

expected to be uniformly distributed. More informa-
tion about the null hypothesis and the p-values can be
found in (NIST, 2010) and the Dieharder manuals
10
.
More explicitly, in order to determine whether a
test succeeds or fails, Dieharder internally calculates a
set of p-values performing several executions of each
test with different data. If the p-values of a given test
are smaller than the significance level (usually values
in the range of 0.1 to 0.001), then the test fails. In
addition, the set of p-values obtained are tested with
the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test to check the null
hypothesis is not rejected. The result of this check is
a number between 0 and 1.
Since several datasets were generated for each
PRNG, each Dieharder test was repeated a few times
for each PRNG. In order to test the different runs of
each test, we have treated the KS test values output
for each test as p-values. Then, we have set a sig-
nificance level of 0.005 and we have considered the
test failed if any of the values were below this thresh-
old. Another issue to be considered is that these val-
ues are random variables and, as such, the same test
over different datasets should produce noticeably dif-
ferent values. This is why we compared the difference
between the maximum and minimum values, and con-
sidered the test failed if this difference was smaller
than 0.1. Both Scytl ’s and the Gold Standard PRNG
succeed with this test as well, in particular such differ-
ence was much bigger than 0.1 for all the tests. On the
other hand, the flawed PRNG had many similar val-
ues, and as a consequence it failed most of the tests.
6 PERFORMANCE
A good performance of the voting client application is
important to guarantee a smooth user experience. The
next sections study the timing associated to the voting
client and its cryptographic operations.
6.1 Cryptographic Operations
A benchmarking application was developed to mea-
sure the speed of some cryptographic operations. The
benchmarks were performed on a PC with several op-
erating systems and browsers and on two smartphones
based on Android and iOS operating systems. The re-
sults obtained (see Table 3) are product of one exe-
cution of the benchmark application on each of the
systems detailed. The time shown for each opera-
tion is the average of 1000 executions for the SHA-
256, HMACwithSHA256 and AES-128 operations,
10
http://manpages.ubuntu.com/manpages/precise/man1/
dieharder.1.html
100 executions for the PBKDF2 operation, and 10 ex-
ecutions for the rest of operations respectively. Fur-
thermore, the PBKDF2 is setup with 1000 iterations
and computes a key of length 256 bits. ElGamal and
RSA algorithms are tested with 2048-bit keys.
Several conclusions can be extracted from the re-
sults. First, the performance is heavily influenced by
the type of device, i.e. regular PC or mobile device,
and browser. As expected, the regular PC performs
faster since it is more powerful than a mobile de-
vice. There is also a huge difference between different
browsers, e.g. Google Chrome and Firefox perform
certain operations more than 6 times faster than Inter-
net Explorer. The operating system does not have a
strong impact on the results, e.g. similar results are
obtained in Linux and Windows. Regarding the op-
eration types, hashing is much faster than asymmetric
encryption and decryption, as expected. The results
also show a 5-7 times speedup in the optimized El-
Gamal encryption based on short exponents (see Sec-
tion 4.1), reaching a speed closer to RSA.
6.2 Voting Client Application
The performance of the voting client may present a
high variability depending of:
• Voting Protocol: defines the cryptographic prim-
itives and communication handshakes performed
with the server.
• Election and Cryptographic Parameters: The
election parameters define the number of candi-
dates, parties and contests of an election, implying
different vote lengths and number of encryptions.
The cryptographic parameters define the length of
the keys and algorithms used, which influences
the timings of the cryptographic primitives.
• Browser: Certain browser Javascript engines are
much more efficient than others executing the
cryptographic operations implemented.
• Device: Voter device’s processor and memory
considerably affect the performance.
The tests performed were focused on measuring
the user experience in different browsers and devices
for a given voting protocol and set of election param-
eters. The results reflect the time passed since the
voter requests the cast of the vote until the process
finishes. Pre-computed operations are not considered
since they are executed before the mentioned process.
6.2.1 Neuchâtel e-voting Protocol
The selected voting protocol is the one used in a re-
cent election in Neuchâtel e-voting platform (Galindo
Transitioning to a Javascript Voting Client for Remote Online Voting
129
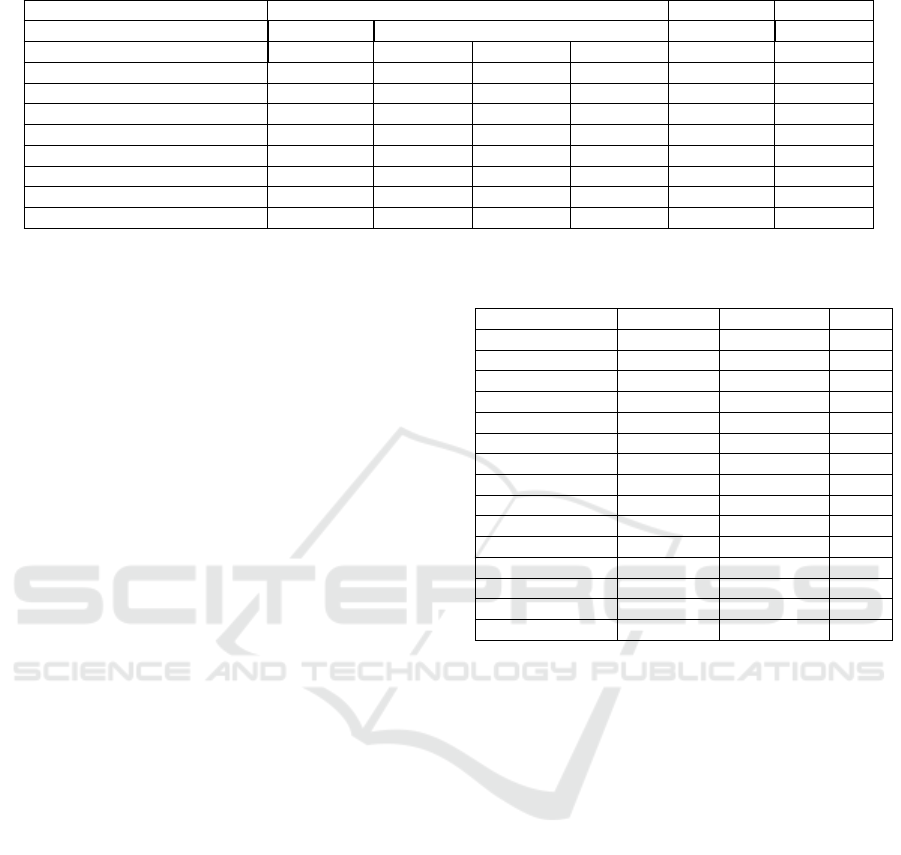
Table 3: Cryptographic operations performance (time in ms).
Device PC i5-2450M CPU 2,50GHz, 4GB RAM LG G2 iPhone 5s
OS Ubuntu 14.10 Windows 7 Android 4.4.2 iOS 8.2
Browser Chrome 42 Chrome 42 Firefox 37 IE 11 Chrome 42 Safari
SHA-256 0,053 0,042 0,051 0,040 0,114 0,127
HMACwithSHA256 0,065 0,041 0,040 0,042 0,150 0,204
Generate PBKDF2 with SHA256 9,480 9,510 12,780 23,880 31,620 4,541
AES-128 Enc / Dec 0,031 / 0,017 0,031 / 0,015 0,045 / 0,024 0,179 / 0,008 0,197 / 0,097 0,146 / 0,072
ElGamal Enc / Dec (Normal Exp) 343 / 180 354 / 183 285 / 154 1.888 / 940 1.002 / 500 1.505 / 790
ElGamal Enc / Dec (Short Exp) 48 / 29 49 / 29 47 / 23 252 / 139 160 / 105 213 / 134
Schnorr Proof Gen / Ver (Short Exp) 24 / 47 24 / 48 21 / 40 137 / 288 68 / 135 108 / 213
RSA Enc / Dec 2 / 48 2 / 48 2 / 45 8 / 259 7 / 156 8 / 213
et al., 2015) (March 2015). A test election was setup
where the voters had to vote for two contests. In the
first contest the voter had to choose one party and 5
candidates, whereas in the second contest the voter
had to choose one party and 41 candidates. The oper-
ations computed by this voting protocol are summa-
rized here:
1. Encryption of the Selected Voting Options: the
voting options selected of both contests are mul-
tiplied together and the result is encrypted into
one ciphertext. The ciphertext is computed using
the ElGamal encryption algorithm, which requires
2 exponentiations which have been pre-computed
while the voter navigates through the application
(see Section 4.3).
2. Computation of Partial Return Codes: these
are codes used to provide cast as intended ver-
ifiability (see Section 4.3). The computation of
partial return codes requires one exponentiation of
each voter selection to a voter-specific secret key,
which in the test election sums up to 47 exponen-
tiations. Every time the voter selects an option,
the corresponding partial return code is computed.
Therefore, these operations are already done when
the voter pulses the send button. Thus this time is
not included in the presented test results.
3. Encryption of Partial Return Codes: the par-
tial return codes are encrypted using the ElGamal
encryption algorithm, under the public key of the
server, in order to protect their privacy during their
transmission from the voting client to the server.
The variant with multiple key encryption, as de-
scribed in Section 4.1.1, is used. The required ex-
ponentiations, which sum up to 47, are also pre-
computed while the voter navigates through the
application.
4. Generation of Cryptographic Proofs (ZKPKs):
two ZKPKs are computed. The first, based on the
Schnorr (Schnorr, 1991) identification protocol,
proves the encrypted ballot is well-formed. The
second, based on the Chaum-Pedersen (Chaum
Table 4: Vote casting performance in a HP Intel Core i5-
3470 3.2 GHz PC, with Windows 7 Professional OS.
Device OS Browser Time
PC Windows 7 IE10 22 sec
PC Windows 7 IE11 5 sec
PC Windows 7 Firefox 35 5 sec
PC Windows 7 G. Chrome 39 5.5 sec
PC Ubuntu Firefox 35 5 sec
PC Ubuntu G. Chrome 39 6 sec
Mac Mac OS 10.8 Firefox 35 5.5 sec
Mac Mac OS 10.8 G. Chrome 39 5.5 sec
Mac Mac OS 10.8 Safari 6 sec
HTC Desire 610 Android 4.4 G. Chrome 39 43 sec
Nokia Lumia 730 W. Phone 8.1 IE Mobile 11.0 29 sec
iPhone 5C iOS 8.1.2 Safari 8.0 18 sec
S. Galaxy Tab3 Android 4.2.2 G. Chrome 39 23 sec
Enc. M. WT7-C-100 Windows 8.1 IE 11 14 sec
iPad Air iOS 8.1.2 Safari 7.0 11 sec
and Pedersen, 1992) protocol, prove to the server
that the partial return codes match the voting op-
tions of the encrypted ballot. For the first proof
1 exponentiation, which can be pre-computed, is
required. For the second proof, 7 exponentiations
are required, of which 5 can be pre-computed.
Thus, in total 8 exponentiations are computed dur-
ing the proof generation process, from which 6
can be pre-computed.
5. Signature of the Computed Values: all the com-
puted values are digitally signed using the RSA
digital signature algorithm.
The ElGamal encryption and the RSA signature
algorithms use 2048 bit keys. The approach described
in Section 4.1.2 for using short exponents (256-bit ex-
ponents instead of 2047-bit ones) in ElGamal is used
for the encryption of the voting options, for the en-
cryption of partial return codes, and for the Schnorr
and plaintext equality proofs.
6.2.2 Results Obtained
The results (see Table 4) are aligned with the ones
obtained for the cryptographic primitives, where the
SECRYPT 2016 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
130

platforms chosen have a strong influence on them.
But what it is more relevant is that in most of the
tested devices the time needed for casting a vote is
always below 45 seconds, and usually much less,
clearly demonstrating the Javascript technology is ap-
propriate for implementing a voting client.
6.3 Performance Challenges
During the development, one of the first points that
arose was that, the execution of cryptographic prim-
itives could be slow on certain browsers and/or plat-
forms. This generated two effects: a) the browser pre-
sented a pop-up indicating the script was not respond-
ing and b) the time to generate the encrypted ballot
was too long. Two solutions were applied to the first
issue. The HTML5 Web Workers
11
were used if avail-
able. This prevented the script from blocking the view
of the page and no pop-up was presented to the user.
For browsers no compatible with this technology, the
solution implemented consisted of dividing the costly
operations in smaller operations, thus avoiding ex-
ceeding the timeout associated to the pop-up. For
the second issue, the overall time taken to generate
a ballot, the primitive optimizations described in Sec-
tion 4.1, i.e. ElGamal encryption with short expo-
nents and multiple keys, and the pre-computation of
part of the cryptographic operations described in Sec-
tion 4.3 were applied. A second point was related to
the generation of random numbers. The amount of
entropy we initially required to seed the PRNG was
128 bits. This is recommended, in order to ensure
that the random generation is strong enough (i.e. the
random values generated are unpredictable). Never-
theless, in order to prevent usability issues due to ex-
ceptional cases where the minimum entropy cannot
be reached, a minimum amount of entropy collection
was not enforced in production. Instead, the entropy
estimation mechanism was used only during develop-
ment time to perform tests that ensured a minimum
level of entropy was reached before the first random
values were requested.
7 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have described our experience and
lessons learnt on implementing a Javascript voting
client in an industrial environment, focusing on the
main challenges encountered, implementation details
and performance results obtained.
11
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/
Web_Workers_API/Using_web_workers
In comparison to Java implementations, the over-
all security of Javascript voting clients is similar,
whereas the user experience and interoperability is
largely better since these clients are much lighter and
multi-platform than the Java ones. A browser with
Javascript support is the only usage requirement. The
fact that there is no dependency with the Java Run-
time Environment (JRE) has extensively reduced the
usability and interoperability problems, as well as the
exposure to critical security bugs, associated to the
former Java implementations. Regarding the security,
the only disadvantage is the Javascript implementa-
tion lacks the support for signing the code. However,
additional security measures mitigate this issue, e.g.
remote code integrity validation services and use of
verifiable voting protocols allowing the voter to verify
the vote cast with independence of the voting client
logics. In addition, we also reported on the usage of
the client in real elections, with a positive outcome.
Further work is being peformed to deal with the
Javascript weaknesses, mostly the lack of code signed
support. On the one hand, an intelligent application
for remote code integrity validation service is being
implemented. This application issues requests, which
should not distinguishable from regular requests is-
sued by real voters, to retrieve and validate the code
served. On the other hand, the development of spe-
cific voting client apps for the most popular mobile
platforms is studied, since these provide code in-
tegrity mechanisms for their applications.
REFERENCES
Adida, B. (2008). Helios: Web-based open-audit voting. In
van Oorschot, P. C., editor, USENIX Security Sympo-
sium, pages 335–348. USENIX Association.
Bellare, M. and Rogaway, P. (1993). Random oracles are
practical: A paradigm for designing efficient proto-
cols. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM Conference on
Computer and Communications Security, CCS ’93,
pages 62–73, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Brown, R. G., Eddelbuettel, D., and Bauer, D. (2009).
Dieharder: A random number test suite. Duke Uni-
versity Physics Department.
Chaum, D. and Pedersen, T. P. (1992). Wallet databases
with observers. In Brickell, E. F., editor, Advances
in Cryptology - CRYPTO ’92, 12th Annual Interna-
tional Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, Cali-
fornia, USA, August 16-20, 1992, Proceedings, vol-
ume 740 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages
89–105. Springer.
Cortier, V. and Smyth, B. (2011). Attacking and fixing He-
lios: An analysis of ballot secrecy. In Proceedings of
the 24th IEEE Computer Security Foundations Sym-
posium, CSF 2011, pages 297–311. IEEE Computer
Society.
Transitioning to a Javascript Voting Client for Remote Online Voting
131

Damgaard, I. (2010). On σ-protocols. Cryptologic Protocol
Theory, CPT 2010, v.2.
ECMAScript (2011). ECMAScript
R
Language Specifica-
tion 5.1 Edition.
Ferguson, N. and Schneier, B. (2003). Practical Cryptogra-
phy. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY, USA,
1 edition.
Galindo, D., Guasch, S., and Puiggalí, J. (2015). 2015
Neuchâtel’s cast-as-intended verification mechanism.
In Haenni, R., Koenig, R. E., and Wikstro
¨
m, D., ed-
itors, E-Voting and Identity, volume 9269 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 3–18. Springer In-
ternational Publishing.
Gennaro, R. (2005). An improved pseudo-random genera-
tor based on the discrete logarithm problem. J. Cryp-
tology, 18(2):91–110.
Gharadaghy, R. and Volkamer, M. (2010). Verifiability
in electronic voting - explanations for non security
experts. In Krimmer, R. and Grimm, R., editors,
Electronic Voting 2010, EVOTE 2010, 4th Interna-
tional Conference, Co-organized by Council of Eu-
rope, Gesellschaft für Informatik and E-Voting.CC,
July 21st - 24th, 2010, in Castle Hofen, Bregenz, Aus-
tria, volume 167 of LNI, pages 151–162. GI.
Gjosteen, K. (2013). The norwegian internet voting proto-
col. ePrint. eprint.iacr.org/2013/473.pdf.
Halderman, J. A. and Teague, V. (2015). The new south
wales ivote system: Security failures and verification
flaws in a live online election. In Haenni, R., Koenig,
E. R., and Wikström, D., editors, E-Voting and Iden-
tity: 5th International Conference, VoteID 2015, Bern,
Switzerland, September 2-4, 2015 Proceedings, pages
35–53. Springer International Publishing.
Juels, A., Catalano, D., and Jakobsson, M. (2010).
Coercion-resistant electronic elections. In Chaum, D.,
Jakobsson, M., Rivest, R. L., Ryan, P. Y. A., Benaloh,
J., Kutylowski, M., and Adida, B., editors, Towards
Trustworthy Elections, New Directions in Electronic
Voting, volume 6000 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, pages 37–63. Springer.
Karapanos, N., Filios, A., Popa, R. A., and Capkun, S.
(2016). Verena: End-to-end integrity protection for
web applications. In 2016 IEEE Symposium on Secu-
rity and Privacy (to appear), pages 895–913.
Klein, A. (2008). Temporary user tracking in major
browsers and Cross-domain information leakage and
attacks. September-November, 2008, Trusteer.
Koshiba, T. and Kurosawa, K. (2004). Short exponent
diffie-hellman problems. In Bao, F., Deng, R. H.,
and Zhou, J., editors, Public Key Cryptography - PKC
2004, 7th Int. Workshop on Theory and Practice in
Public Key Cryptography, volume 2947 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 173–186. Springer.
Kurosawa, K. (2002). Multi-recipient public-key encryp-
tion with shortened ciphertext. In Naccache, D. and
Paillier, P., editors, Public Key Cryptography, 5th Int.
Workshop on Practice and Theory in Public Key Cryp-
tosystems, PKC 2002, volume 2274 of Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, pages 48–63. Springer.
Marsaglia, G. (1996). Diehard: a battery of tests of random-
ness.
Maurer, U. (2009). Unifying zero-knowledge proofs of
knowledge. In Preneel, B., editor, Progress in Cryp-
tology AFRICACRYPT 2009, volume 5580 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 272–286. Springer
Berlin Heidelberg.
Menezes, A. J., Vanstone, S. A., and Oorschot, P. C. V.
(1996). Handbook of Applied Cryptography. CRC
Press, Inc., Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1st edition.
NIST (2001). Federal Information Processing Standard
(FIPS) 197, Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
Technical report, U.S. Department Of Commerce.
NIST (2010). A Statistical Test Suite for the Validation
of Random Number Generators and Pseudo Random
Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications,
NIST Special Publication 800-22rev1a. Technical re-
port, U.S. Department Of Commerce.
NIST (2012). Federal Information Processing Standard
(FIPS 180-4), Secure Hash Standard. Technical re-
port, U.S. Department Of Commerce.
NIST (2015). Federal Information Processing Standard
(FIPS) 202, SHA-3 Standard: Permutation-Based
Hash and Extendable-Output Functions. Technical re-
port, U.S. Department Of Commerce.
Puiggalí, J., Chóliz, J., and Guasch, S. Best practices in in-
ternet voting. In NIST: Workshop on UOCAVA Remote
Voting Systems. Washington DC, August 2010.
RFC-5280 (2008). Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure
Certificate and Certificate Revocation List Profile.
RSA Laboratories. PKCS #12: Personal Information Ex-
change Syntax Standard.
RSA Laboratories. PKCS #5: Password-Based Cryptogra-
phy Standard.
Rukhin, A., Soto, J., Nechvatal, J., Barker, E., Leigh, S.,
Levenson, M., Banks, D., Heckert, A., Dray, J., Vo,
S., Rukhin, A., Soto, J., Smid, M., Leigh, S., Van-
gel, M., Heckert, A., Dray, J., and Iii, L. E. B. (2010).
NIST Special Publication 800-22 Rev 1a: Statistical
test suite for random and pseudorandom number gen-
erators for cryptographic applications.
Schnorr, C. P. (1991). Efficient signature generation by
smart cards. J. Cryptol., 4(3):161–174.
Stark, E., Hamburg, M., and Boneh, D. (2009). Symmetric
cryptography in JavaScript. In ACSAC, pages 373–
381. IEEE Computer Society.
van Oorschot, P. C. and Wiener, M. J. (1996). On diffie-
hellman key agreement with short exponents. In Mau-
rer, U. M., editor, Advances in Cryptology - EURO-
CRYPT ’96, Int.l Conf. on the Theory and Application
of Cryptographic Techniques, volume 1070 of Lecture
Notes in Computer Science, pages 332–343. Springer.
W3C. W3C Subresource Integrity. W3C Candidate Rec-
ommendation, November, 2015.
W3C. Web Cryptography API. W3C Candidate Recom-
mendation, December, 2014.
SECRYPT 2016 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
132
