
Context Specific, Networked and Feedback Enhanced
eTransformation Business Model
Ana Hol
Director of Academic Program, Computing / Information Systems, School of Computing Engineering Mathematics,
Western Sydney University, Locked Bag 1797, 1797, Penrith South DC, NSW, Australia
Keywords: eTransformation, Business Transformation, Context Specific Knowledge, Business Networks.
Abstract: Businesses have been transforming for centuries. Each era of civilisation brought in new innovations and new
technologies. Today we find ourselves surrounded by devices, services and applications that in some form
utilise technology. Individuals, utilise it to be more productive, groups exchange and manipulate data using it
and businesses run their day to day operations. Consequently, technology is been implemented to speed
operations, be more reliable and crate new revenues. Based on the scenario analysis of five new businesses
which utilise transformed renewed business model, this study investigates technology factors that drive new
business models and identifies roles that current technological advancements play in shaping the new models.
The study highlights that there is a direct relationship between open access technology platforms and current
technology trends. Furthermore, this study identifies that for the new business model to be established
definition of the specific domain problems and the importance of the access to the resource networks, such as
the network of context specific knowledge, either experts, or the individuals with knowledge and skills who
can provide timely context specific solutions and network of those who have interest in a the specific context
domain are paramount for the model to succeed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Business models and operations have been changing
and transforming for centuries. New implementations
often saw pioneers, however new inventions where
not always fully embraced into daily accepted
routines immediately. For example, when electricity
was discovered, its discovery brought in not just light
but fires, disasters and circuit shortages that had
detrimental effect in the early days of its use. It is only
much after that time that electricity has become a
second nature to day to day living.
Similar was noted when Information Technology
further advanced from personal productivity tools and
storages to more integrated systems and solutions.
The innovations were accepted much quicker than
those of the electricity, however introductions of new
systems to the business environments were not
always smooth. 2000 .com crash created a havocs
across the globe to a large number of businesses.
Sixteen years later businesses are surrounded by the
electronic transaction systems, tracking systems,
production and operation systems. Our lives today are
closely intertwined with the use of the information
systems on a daily basis.
However, even though today technology is an
integral part of many business operations, its full
potentials are still to be fully explored.
To understand how technological advancements
are currently shaping and impacting new innovative
business, a process of business transformation is
reviewed. eTransformation takes into the account that
businesses should never stand still and that to excel
each business needs to go through iterative review, so
that they can establish the most suitable resources,
objective and performance strategy. (Hol and Ginige,
2011). Therefore, when steam engines were invented
factories and transportation began to flourish, when
electricity started to be implemented working
conditions improved, electricity powered machines
started to be used and work became more productive.
This was the transformation of business environment
and the business models known up to that time.
Today, many changes within business
environments can be contributed to the technology
changes and improvements. To study
eTransformation in detail companies and industries
98
Hol, A.
Context Specific, Networked and Feedback Enhanced eTransformation Business Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0005967600980105
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2016) - Volume 2: ICE-B, pages 98-105
ISBN: 978-989-758-196-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

need to address a change across dimensions Strategy,
Structure, Tasks and Processes and Technology.
First, it is essential to take into the account
Strategy. It defines company’s direction, aims,
objectives, future outlook, expectations and
predictions. It is the guiding dimension that assures
company stays on the goal pathway. Next Structure is
reviewed. It identifies and defines company’s
organisational constitution, that can be bureaucratic,
hierarchical, linear, networked or ad-hoc – initiated
based on a need. After structure is set it is important
to define appropriate Tasks and Processes. These are
the activities that outline workload, production steps
and operations that need to be completed for the
products to be delivered to the customers or services
provided. Finally, Information Technology Tools and
Systems are reviewed. At this point it is important to
take into the account, software, hardware, online
presence, support systems, management,
maintenance, backup and security (Hol and Ginige,
2011).
For the companies to make holistic and successful
decisions at each step of the journey, it was identified
by Hol in 2014 that eTransformation is not only
defined through eTransformation dimensions as
earlier thought (Hol and Ginige, 2011) but by also the
Domain in which activities are executed as well as the
Context which defines a situation in which certain
services or products are being sought such as time,
place and location (Hol, 2014). Therefore, the
Context Specific Framework takes into the account
carefully drafted analysis of required knowledge
origin, knowledge source essential for the delivery of
service or product and conditions under which such
products and / or services need to be delivered or
provided.
Thus, for the company to be able to successfully
transform, it is also essential to understand the
Domain Knowledge (Hol, 2014) that specifies data
about the industry and in detail defines products and
services being offered. Once Domain is understood,
it is crucial to gather Context specific data (Hol,
2014) about the customers, markets and identify
suitability of the location, time and the scope in which
decisions need to be made, so that company
operations can continue to seamlessly operate.
This study therefore builds upon Context Specific
eTransformation as a base of the investigation and it
further reviews:
- the guiding eTransformation models of 2010’s;
-defining characteristics of new model
companies;
- parameters that new successful companies that
are using technology as a base of their business
operation require to take into the account, so they can
successfully transform;
2 STUDY DESIGN
To test current Contextual eTransformation Model
and identify other characteristics that are impacting
emergence of newly eTransformed business model
companies and recent start-ups that have transformed
existing business models were in-depth analysed.
It was noted that new business models have in
recent times been transforming and even pushing the
boundaries of the previously known business models.
Therefore, the requirement for this study was to
select:
- new companies that have so far operated for a
minimum of three years;
- have purely been designed on the online
platforms where services are not owned by the
organisations, providing the services;
- where the organisations purely provides the
platform that can be utilised for networking, job
posting, expert sourcing, funds exchanges and service
and job reviews;
Five companies, namely well-known
international companies Skillshare, Airbnb and Uber
and two Australian based companies Airtasker and
Parkhound were selected for the study. Consequently,
for each source supporting data was identified. Next,
each case was reviewed, key points summarised and
based on those points scenarios created.
Scenarios were analysed, utilising scenario based
analysis (Di Giovanni et al, 2012). This allowed for
the storyline to be created and based on it most
important data extracted, so that characteristics
essential to eTransformation and /or new business
implementations can be studied in detail.
3 EMERGENCE OF
NETWORKED CONTEXT
SPECIFIC TRANSFORMATION
MODEL
Based on the studied sources, data for each company
was collated. Anlaysis was performed to identify:
- main services companies offered
- main benefits companies offered
- outcomes for the customers
- priviledges for workers
- main distingushing characteristics
Context Specific, Networked and Feedback Enhanced eTransformation Business Model
99
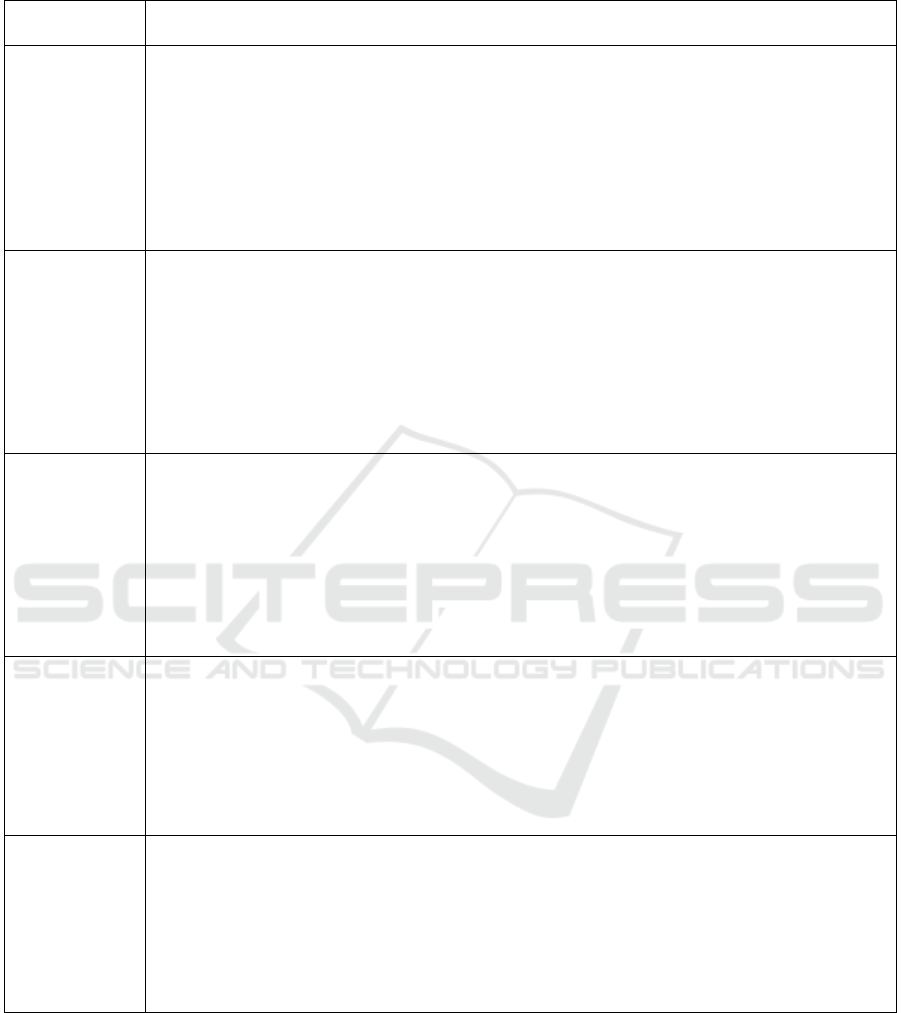
Table 1: Three Scenarios.
Compan
y
Name
Technology and Business Implementation
Skillshare, 2011
Education
(Empson, 2014;
Liu, 2015;
Tracy, 2016
Walgrove,
2014)
Skillshare business model opens its doors to all to participate. Anyone can teach skills they
have and anyone can subscribe to learn. The aim of the company is to assure that those who
require a skill in a certain time can easily obtain it. Focus is also placed on real time
information and data that is based on real life examples and projects.
There are no participation suitability criteria based on prior knowledge or education. Focus
is given to social interactions, engagement with other users, both teachers and students.
Initially teachers are required to market course to their own network. Only after they have
25 students enrolled and those students are providing satisfying results their courses are
advertised.
Airbnb, 2008
Hospitality
(Airbnb 2016a;
Airbnb 2016b;
Ting, 2016)
Airbnb allows anyone to offer their room, unit or a whole house to people who would like
to stay there for a certain time. Stays can range from very short to longer stays. The platform
allows registered users to state the service they offer and for those looking for the
accommodation to identify suitable locations where to spend time. The service utilises
geographical coordinates that allow users to identify exact locations of properties. The
system also incorporates fully feedback response where both providers of the service and
those who utilise the service provide reviews. This makes service in turn more reliable. Those
who gain better ratings in turn become more prone to being offered a service or a place where
to stay in the future. A number of legal and security issues are still to be fully resolved.
Uber, 2009
Transport
(ABC News,
2015;
Hullinger,
2016; Pullen,
2014)
Uber is a company that offers anyone to get transport from A to B and to act as a driver as
long as they meet set criteria, have a car, insurance and drivers licence. The service also
does not require users to have a taxi licence. All that is required to be a driver is for the
driver to be subscribed to a service, have access to the application and be able to collect
passengers that book a vehicles for transport. Both passengers and drivers get rated on their
performance which aids credibility.
Furthermore, Uber service often costs much less then taxi. It is convenient, easy to track and
utilise.
Uber model has also risen concerns about security for customers and service providers alike.
Airtasker, 2012
Multiple
industry
professionals
(Airstriker,
2016, Powell,
2015)
Airtasker allows anyone to post a job and search for people who would be able to complete
it.
Airtasker utilises a review system that allows both sides service expert and customer to
review each other and based on it build a community of respected operators and customers.
It is the responsibility of the service provide to ensure that they are able to conduct the work
is done by the qualified personnel. Airtasker only provides a technical platform that allows
customers and the service providers to meet, communicate, exchange funds and provide
reviews.
Parkhound,
2013
Service –
parking
(Parkhound,
2016, Dillon,
2014)
Operates very similar to Airbnb. In this case owners advertise their parking spots, carports
and garages. This service provides a platform for customers to search for the available
parking nearby based on the geographical coordinates. People who have and are at certain
times not using their parking spots may advertise them on the site and allow others to rent
them for a fee. Fees range based on the type of spot available, security and a location. Spots
can be rented for an hour to a month or even longer.
Consequently, stories for each company were
drafted. It is important to note, that stories were
generated based on the series of available online data.
4 NETWORKED, CONTEXT
SPECIFIC ETRANSFORMED
BUSINESS MODEL
Based on data collected and reviewed in Table 1, it
can be see that there are certain characteristics that
ICE-B 2016 - International Conference on e-Business
100

prevail and are crucial for successful business
operations.
Considering it was identified that in order for the
companies to operate successfully Domain and origin
of the problem, the gap or the requirement of the
service needs to be known.
Next, it is essential to identify Context, time and
place where such problems or services may need to
be provided. This also helps define the environment
in which company is to interact with its customers and
stakeholders.
Following the assessment of the problems, gaps
or generally the requirements for services and
solutions, it is important to identify specific Context
based Knowledge. Such knowledge may come from
books, brochures, experts and even those who self-
select that they have a particular skill, so that
solutions can be smoothly delivered when required.
For the knowledge to be effectively delivered it is
essential to ensure that such knowledge is provided
for the particular circumstances, in a given time and
place for the certain conditions; as it is only valid
under those circumstances.
Furthermore, knowledge, or solutions provided or
services delivered are then subjected to feedback,
where both those offering services as well as those
receiving services are able to provide reviews and
based on the received reviews their credibility is
being measured.
Consequently, a detailed scenario assessment for
the five companies is given below, stating
characteristics essential at each level of decision
making:
Domain
Review of Airbnb identifies that the company
specialises in renting spare rooms, units and homes
and providing accommodation for guests.
Assessment of Uber identifies that they provide
service to customers who require transport from one
location to the other.
Skillshare allows everyone to promote a course,
teach it and learn from the courses others offer.
Airtasker specialises in job advertisements where
individuals can post a task or a job and seek for a
suitable worker. Employees can also be matched to
the roles based on the listed skills.
Finally, Parkhound is similar to Airbnb however
it offers parking spots instead of the accommodation.
Consequently, each of the five assessed
companies is providing a service within the set
industries.
Context
Based on the Context assessment Airbnb
company is in Hospitality sector and it specialises in
providing accommodation to people who are looking
for a place where to stay for a short period of time.
They operate across the world. Based on
availabilities, owners post information and clearly
state dates when the property and or room is
available. Furthermore, properties are also plotted on
the map which allows the users to see exactly where
the accommodation is located.
Uber belongs to the industry of Transport. The
role of the Uber driver is to provide quick and
responsive service based on customer needs and
transport them to a certain location. Furthermore,
customers are able to identify when and where the
cars currently are and based on the map location
identify where they could hail the car from/
Skillshare is an Education based company. It
allows anyone with a skill to teach and share that skill
with those who would like to learn and excel within
the field.
Airtasker is a part of the Service industry. The
company allows individuals to advertise jobs and to
claim jobs creating a network between those who
require services and those who can provide them.
Parkhound is Service based Hospitality oriented
organisation that offers accommodation for cars.
Customers based on their location are able to identify
the most suitable place where to park their car.
Current Knowledge within Domain
Potential customers of Airbnb are also able identify
other accommodation information, including data
about hotels.
Potential customers of Uber can also reach the
required location by utilising other types of transport-
Taxi, public transport or a combination.
Potential customers of Skillshare can search for
courses that they would like to study. Often they have
a particular goal in mind when selecting courses,
however alternatively such skills can be gained via
online classes, colleges, universities and industry
offered courses.
Airtasker allows for the jobs to be advertised and
based on who enquires about them offers them to
those with skills to complete them. Airtasker also acts
as a recruitment site that matches individuals’ skills
to particular jobs. Alternatively customers can also
search Yellow pages or trade websites to identify
adequate workers or search sites like seek.com.au to
identify suitable job adds.
Parkhound offers a unique service that allows
customers to find parking nearby usually much
cheaper then offered by garages. Alternatively
customers may search for parking either on the streets
or in garages at the locations near the destination.
Context Specific, Networked and Feedback Enhanced eTransformation Business Model
101

Contextual Knowledge - Knowledge specific to
problem, time and place
Once Contextual data is reviewed the specific data
that potential customers may generate is that possibly
staying with Airbnb is much more affordable then for
example staying at a hotel, however that staying with
Airbnb may be riskier than staying at a hotel. To
counteract this scenario new business model
integrates a feedback loop.
The contextual data for Uber is similar to that of
Airbnb. Uber is quicker to hail and is cheaper in many
parts of the world then taxi. Hoverer, Uber cars do not
necessarily meet the same requirements that taxis are
required to meet, their cars are not of a specific fleet
and their drivers are not specifically trained. They do
however provide the service customers require,
nevertheless Uber’s safety as well as legal regulations
under which they operate are not of the same standard
as those of taxis.
Skillshare introduces a very different educational
model. It allow everyone regardless of their
certification and experiences to teach, share
knowledge and learn. It ensures that there are no pre-
set barriers to further learning. Therefore, anyone
with a particular interest is able to participate and is
able to act as a class participant and/or educator. This
also allows for the quick, almost ad-hoc, role swap,
where one person can be a teacher for one field, and
in the other class they may be a student.
Airtasker allows anyone to advertise for jobs and
anyone to claim the jobs. This system raises issues of
security. Airtasker provides security as the insurance
however does not guarantee jobs quality.
Parkhound allows those searching for parking to
review places prior to leaving their cars at the location
however again provokes issues of safety, standards
and security. Parkhound often provides cheaper
parking particularly in busy cities when compared to
parking stations. Also, it is often easier and quicker to
search for the availabilities, particularly for the longer
stays via Parkhound.
Feedback Loop – Knowledge Acceptance and New
Knowledge Generation
It can be seen that the Contextual Knowledge within
Domain alone is not sufficient. For the system to
operate seamlessly three scenarios need to be met.
First is the application to real problem. In Airbnb case
it is the ability to stay at the identified location and
pay for the stay online. Second is the ability to
confirm whether in fact a stay like this is seen as safe
and whether this option is in fact able to meet the
customer’s requirements. Therefore, system
implements feedback and rating from both those who
stay at locations as well as owners of properties who
are able to rate guests. Each in return receive
feedback. This process vets the model and also
provides a continuous loop that allows for the
services to be checked, confirmed and if suitable rated
highly, therefore making them more likely choices in
the future. If either of the parties receives negative
reviews, this acts as a warning sign to new potential
guests / owners when accepting them. Therefore, for
a healthy system operation, it is essential that both
hosts and guests act in accordance to regulations.
Consequently with Uber there is a feedback loop
created. Customers who call Uber cars are able to rate
drivers and many articles highlight that in fact rating
of a driver is the one that carries more waiting then
rating of the user. However, as with Airbnb customers
of Uber can also be rated which also builds credibility
and provides feedback to future drivers.
Parkhound provides a very similar feedback loop
for parking places and rates renters and service
providers.
Skillshare has a very closely integrated feedback
loop. Before a teacher is able to share their skill with
general public, they are required to network and share
the content with their network circle. Following this
they are required to look for adequate marketing
avenues. This initial group is a testbed that is acting
as a review group to a course offered. Teachers are
payed only after they have 25 students, which in fact
allows only for the well-developed courses to move
ahead, be listed and be open to recruiting new
students. Furthermore, teachers can learn from their
students and can improve. All teachers and student
belong to a network, where they can form new
collaborations and partnerships. They can also initiate
online discussions, track each other’s progress and
when suitable even be able to organise face to face
meetings.
Airtasker provides the ability for both customers
and those completing jobs to leave feedback. Some
work does require certifications, however it is up to
customer and the company to assure this is followed
as required. Both customers and service providers are
rated which also gives reputation to those who are
performing well.
5 CONTEXT SPECIFIC,
NETWORKED AND
FEEDBACK ENHANCED
ETRANSFORMATION MODEL
Based on the analysis of the data presented in the
section above, it can be see that over the time
ICE-B 2016 - International Conference on e-Business
102

business models have been changing and that
different innovations and discoveries brought new
inventions. Initially computers software
applications and user productivity. Next
developments sow the rise of web applications and
tools that allowed for data exchanges and
information systems to be implemented. Next
innovation was the invention of applications and
social media technologies that is now allowing users
to network with their friends, seek for people with
same interests provide feedback, answer questions,
follow interests and rate those who are performing
well.
Therefore, five companies are based on principles
defined by social networking that assures
communication, technically well integrated
platforms, ability to exchange and review data and
means to make decisions. Detailed analysis is
presented below:
Open Access to All (Strategy)
Open access means that all system users can equally
participate, their education and/or past experiences
and involvements are not at all pre-determining
factors of their success. Therefore, anyone can
provide service and anyone can seek for a specific
service. Initially access to such network is open,
however to stay as valued members of the network
participants are required to follow certain terms and
conditions.
Also, strategy in new model companies needs to
take into the account services and products that are to
be provided and delivered. Furthermore, it is also
important to focus on enabling electronic platforms
suitable for data sharing.
Open Service Platform (Structure, Technology)
Service and operation are provided via the technology
platform. Platform is just a medium via which
specific skill / goods can be provided. As it can be
seen from the reviews of the five companies, they are
all technology based service oriented organisations
and have no knowledge of particular trades. They are
however designed in a way that attracts customers or
people searching for jobs, training or locations to
engage. Skills are purely a domain of service /
product providers, not the main organisations’
running the business.
Domain, Context Specific Knowledge Provided
(Tasks and Processes)
This identifies knowledge that is being delivered via
credible sources, or from experts themselves.
However, for the knowledge to be delivered,
following needs to be taken into the account:
- Context – the Industry sector, specific time and
location or a condition where service and or
knowledge is needed. Location, may also be a guiding
factor in how solution is being delivered.
Furthermore, the organisation may need to deploy
parameters required for the technology company to
operate seamlessly which forms the first base layer of
the company. Second layer allows for the services
offered to be mapped, so that the company can attract
certain type of customer or providers.
- Network - needs to be present. It allows those
seeking solutions and /or services to interact.
Furthermore, such Network opens doors to
sourcing specific Skills or Services. During
interaction network participants can learn from one
another, can collaborate and can also provide
feedback that can lead to future changes and
improvements.
Figure 1: Networked, feedback enhanced eTransformation model.
Context Specific, Networked and Feedback Enhanced eTransformation Business Model
103

From Fig. 1 it can be seen that there are many
domains, however that for a particular knowledge to
be sourced Domain Context needs to be defined. Such
Context specifies types of products and /or services
that need to be provided and / or offered.
Following this, it is important to source a network
of interested participants. Individual skills within the
network domain can range from expert to novice to
those that just require services and / or products.
Consequently, data gathered needs to be filtered,
so it can meet specific parameters such as time,
location and circumstances where certain decisions or
services are required. This for example can be done
utilising the geographical coordinates to map exactly
where opportunities for services are, and which
providers are closest in proximity and can offer them
in a timely manner. Once service is being delivered
and requirements of the customer attended to, system
has an inbuilt feedback loop that require all
participants to provide it.
Feedback helps define quality, remove
redundancies and acknowledge those who act in
accordance to the requirements. Consequently, a
feedback loop crates valued network chains and helps
stream traffic in a direction where value is being
created (positive reviews).
Actors or participants new to the market often are
required to spend additional efforts marketing their
services, so that they can become a valued node
within the network.
Therefore, the system mimics characteristics of
the organic system. Such systems source resources
for survival from those who can provide them. Its
wellbeing or usability depends on a number of people
that interact within and across its value networks.
As members of the networks interact they are
being rated and their performance acknowledged.
Members of networks learn, provide feedback and
teach those who require skills.
The only drawback of the network like this is that
it corresponds to the “historic cave times” where
those who were able to hunt were rewarded (those
who provide services) and those who did not got
killed (get extracted from the network, either due to
not participating or due to not behaving in accordance
to regulations).
During “the cave times” there were no legal
regulations that were governing operations. Tribe
chiefs or the tribes themselves, in the electronic case
the followers of specific services or providers,
determine future of participants (both those requiring
service as customers and those providing services). It
is expected however that in the future there will be
strictly determined policies and legal regulations that
will seamlessly help drive and support electronic
network driven exchanges.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In the future it can be noted that there will be many
new business models that will be based and delivered
purely on a technology platforms. It can be noted that
companies as Uber, Airbnb, Skillshare, Airtasker,
Parkhound have all been started by technology gurus,
not industry experts. None of these companies have
experts in hospitality, education, transport, parking
nor services.
Inventors in each of the five cases were able to
identify a demand in a sector, identify gaps in current
services and propose solutions that are helping fill
current known operation gaps.
Solutions proposed therefore identify that we live
in a networked world, where most working
individuals in developed countries are connected
24/7.
Considering, inventors identify that anyone with
the skill or resources can for a fee provide a service
or deliver a product utilising a technology platform as
a medium commonly used for social networking
exchanges.
By doing so, they remove any entrance barriers
and regulations, strict check procedures and
educational pre-requisites. They do however provide
certain terms and condition that do cover some
insurance.
All five companies’ systems operate organically.
They give those who are effective rewards and shame
those who are not providing suitable services or
behave inappropriately. Consequently, systems run as
a semi-open loop, keeping and rewarding those who
are performing well, acknowledging new entrants
who have reached certain standards and providing
negative feedback to those who are not meeting the
expectation.
Systems like these are mimicking natural
selection. Those who are successful and well
supported by their networks are regarded highly, are
continuously engaged and are also based on the
reviews more likely to be selected by the new
entrants. For those with poor ratings it is becoming
harder and harder to prove their worth and stay
competitive.
Future studies are required to study organically
behaving transformed organisational systems. It is
expected that future studies will look into how
organic systems could become more robust and how
in the future they may be able to incorporate stricter
ICE-B 2016 - International Conference on e-Business
104

but more streamlined and system embedded check
points, user confirmations, qualification checks and
more comprehensive global legal regulations and
policies, so that systems can automatically warrant
security and safety of the network and the
participants.
REFERENCES
ABC News, 2015. Fact check: Does Uber need the law to
change? Available: http://www.abc.net.au/news/2015-
10-16/does-uber-need-the-laws-to-change-fact-
check/6846512 [Accessed 9. December, 2015]
Airbnb 2016a. How do reviews work? Available:
https://www.airbnb.com.au/help/article/13/how-do-
reviews-work [Accessed 6. March 2016]
Airbnb, 2016b, https://www.airbnb.com.au/ [Accessed 6
March, 2016]
Airstriker, 2016, Terms, Available: https://www.airtasker.
com/terms/ [Accessed 30. May,]. 2016]
Di Giovanni, P., Romano, M., Sebillo, M., Tortora, G.,
Vitiello, G., Ginige, T., De Silva, L., Goonethilaka, J.,
Wikramanayake, G. & Ginige, A. User centered
scenario based approach for developing mobile
interfaces for Social Life Networks. Usability and
Accessibility Focused Requirements Engineering
(UsARE), 2012 First International Workshop on, 2012.
IEEE, 18-24.
Dillon, S. 2014, New online marketplace for car parking
spaces Parkhound could make trawling the streets of
Sydney for a spot a thing of the past, The Daily
Telegraph, Available http://www.dailytelegraph.
com.au/news/nsw/new-online-marketplace-for-car-
parking-spaces-parkhound-could-make-trawling-the-
streets-of-sydney-for-a-spot-a-thing-of-the-past/story-
fni0cx12-1226827324077 [Accessed 27. May. 2016]
Empson, R., 2014. A Year from Launch, Skillshare Lands
$6M From USV, Spark To Double Down On Its Project-
Based, Online Classes, Techcrunch, Available:
http://techcrunch.com/2014/02/28/a-year-from-launch-
skillshare-lands-6m-from-usv-spark-to-double-down-
on-project-based-online-classes/ [Accessed 2. March.
2016]
Hol, A. and Ginige, A. 2011, A case study approach : eT
guide - assisting the eTransformation journey,
International Journal On Advances in ICT for Emerging
Regions, vol 4, no 3.
Hol, A. 2014. Context Specific eTransformation Decision
Making Framework” in ICIS 2014: International
Conference on Information Systems, Venice, Italy
November, 13-14, 2014.
Hullinger, J. 2016. 16 Things You Might Not Know About
Uber and Its Drivers, Available
http://mentalfloss.com/article/67010/16-things-you-
might-not-know-about-uber-and-its-drivers [Accessed
23. February, 2016]
Liu, T, 2015. Skillshare, Harvard Business Review,
Available: https://rctom.hbs.org/submission/skillshare-
the-future-belongs-to-the-curious/ [Accessed 10.
March 2016]
Tracy, A., 2016. Skillshare: Redesigning Education for the
Masses, INC. Available: http://www.inc.com/abigail-
tracy/35-under-35-skillshare-online-education-
platform.html [Accessed 7. March, 2016]
Parkhound, 2016, Available https://www.parkhound.com.
au/about-parkhound [Accessed 7. April, 2016]
Powell R., 2015 Startup War Story: How Airtasker survived
furious clients and angry friends, Sydney Morning
Herald, 15
th
July, 2015.
Available http://www.smh.com.au/business/startup-war-
story-how-airtasker-survived-furious-clients-and-
angry-friends-20150720-gig1fa.html [accessed 1. June
2016]
Pullen, J. P. 2014, Everything You Need to Know About
Uber, Times Magazine, Available http://time.com/
3556741/uber/ [Accessed 8. March, 2016]
Ting, I., 2016, How Airbnb is taking over Sydney, one beach
at a time, Available: http://www.smh.com.au/nsw/how-
airbnb-is-taking-over-sydney-one-beach-at-a-time-
20160104-glzfbg.html [Accessed: 2. March, 2016]
Walgrove, A., 2014. The Content Strategies, Available:
https://contently.com/strategist/2015/11/02/is-
skillshare-the-next-big-content-marketing-platform/
[Accessed: 2. March, 2016]
Context Specific, Networked and Feedback Enhanced eTransformation Business Model
105
