
An Efficient Approach for Capacity Savings using Load Balancing in
Dual Layer 3G Wireless Networks
Tiago Pedro
1,2
, Andr
´
e Martins
3
, Ant
´
onio Rodrigues
1,2
and Pedro Vieira
1,4
1
Instituto de Telecomunicac¸
˜
oes (IT), Lisbon, Portugal
2
Instituto Superior T
´
ecnico (IST), Lisbon, Portugal
3
Celfinet, Consultoria em Telecomunicac¸
˜
oes, Lisbon, Portugal
4
Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa (ISEL), Lisbon, Portugal
Keywords:
3G Wireless Access Networks, Traffic Forecasting, Load Balancing, Capacity Management, Geo-positioned
Indicators.
Abstract:
In order to survive in a highly competitive market, mobile network operators have to be as efficient as possible
in managing their resources. This is particularly relevant in what concerns the capacity available at their
sites. This work aims to give the operators a method to improve longevity of their sites. This was achieved
using a Load Balancing algorithm, which takes into consideration the Channel Element usage of sites and
sets an Received Signal Code Power threshold value for each one. Its evaluation is done by using a Traffic
Forecast algorithm, based on a fitting method, in order to obtain an estimate of when the sites’ capacity limit
is reached, before and after applying Load Balancing. The used input data consisted of real traffic statistics,
including geo-located indicators. During the course of this work it was possible to develop a semi-automatic
method for network optimization using geo-located data, thus making a contribute to the development of
national research on Self-Organizing Networks. This project was developed in collaboration with a Portuguese
telecommunications consulting company, Celfinet, which provided valuable supervision and guidance. Using
the suggested method it is predicted that, after a year of implementation, it is possible to achieve savings of
about 70% in capacity expansions in the network.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Telecommunications industry is subjected to
many expenses, coming either from day-to-day op-
eration costs, usually called Operational Expenditure
(OpEx), or from investments that need to be made
in order to improve the network, Capital Expenditure
(CapEx). Technological progress in the field, namely
the appearance of more powerful user devices such as
smartphones that allow higher bit rates, demands an
increase in network capacity. Just last year, the total
mobile data traffic grew 69% (Cis, 2014). Addition-
ally, it is expected that by the end of 2021 data traffic
will have increased ten-fold (Eri, 2015).
In order to keep CapEx, and also OpEx, to a mini-
mum, operators should make the most out of the avail-
able resources. Mobile operators need to be able to
define network capacity in terms of useful costumer-
centric Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), install ca-
pacity in the several network elements on a just-in-
time basis and exploit soft capacity properties of mod-
ern network technologies (Northcote, 2014).
Densification of the networks in order to meet
these traffic demands causes a greater level of com-
plexity when optimizing the network parameters. The
only way this optimization can be cost-efficient is
to have more automated and autonomous systems
such as Self-Organizing Networks (SON) (Ramiro
and Hamied, 2012). Implementing a SON allows sav-
ings in expenditure for operators, for example by de-
laying the need to upgrade the capacity of a site that
otherwise would be considered at its limit.
1.1 Objectives
In order to present a solution for the problems pre-
viously mentioned, it was decided to develop two al-
gorithms: a Traffic Forecasting algorithm, which will
allow the operator to know when to perform a capac-
ity upgrade, adding radio equipment hardware in base
stations in order to increase the traffic throughput of
a site; and a Load Balancing (LB) algorithm that will
Pedro, T., Martins, A., Rodrigues, A. and Vieira, P.
An Efficient Approach for Capacity Savings using Load Balancing in Dual Layer 3G Wireless Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0005971000630073
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2016) - Volume 6: WINSYS, pages 63-73
ISBN: 978-989-758-196-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
63

allow this moment to be delayed as most as possible.
This work is developed considering Third-
generation (3G) Wireless Access Networks, which
operates in two different frequency bands, 900 and
2100 MHz. Operators usually don’t distribute traffic
equally between these two bands, creating an over-
load in the 2100 MHz band. This band is usually
given a higher priority for connections, since the 900
MHz band is used mostly to assure site coverage. The
developed Load Balancing algorithm will try to cor-
rect this issue.
In order to develop a meaningful, realistic and
technically accurate solution, a collaboration with a
Portuguese telecommunications consulting company,
Celfinet, was established. Celfinet provided the nec-
essary input data for the development of this research
work as well as guidance and supervision throughout
the project. This allowed designing a semi-automatic
algorithm for network optimization, thus contributing
for the development of SONs in Portugal.
1.2 Related Work
Extensive work is being developed in both Traffic
Forecasting and Load Balancing algorithms in both
academia and industry environments. The studies
developed in (Cunha et al., 2015; Li et al., 2014;
Yu et al., 2013; Yu et al., 2010; Dawoud et al.,
2014) present several solutions for Traffic Forecasting
which were already tested, employing different meth-
ods such as fitting functions, entropy theory and Auto-
Regressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA). In
(Ramiro and Hamied, 2012) several theoretical meth-
ods and driving factors for Load Balancing are de-
tailed and in (Li et al., 2005), a practical example of
an algorithm using adaptive thresholds is presented.
1.3 Structure
This article is organized in five sections. The first in-
troduces the problem at hand and inserts it in the cur-
rent network situation. The second presents the so-
lution developed for Traffic Forecasting, along with
the corresponding prediction error analysis. The third
section presents the Load Balancing solution used to
solve the issue presented in the first section. In the
fourth section, an analysis is made combining the two
algorithms in order to know the obtained gained from
the Load Balancing algorithm. The final section sums
up the conclusions taken from this work and presents
some possible future improvements that can be made.
2 TRAFFIC FORECAST
As previously mentioned, the Traffic Forecast algo-
rithm was developed with the objective of providing
a tool for predicting when a site’s capacity limit is
reached. The chosen approach was to design a fore-
cast algorithm based on a fitting model. In order to
validate the algorithm, real traffic statistics and KPIs
were provided by a Portuguese telecommunications
operator. The data is from a total of 43 sites with dual
frequency band deployment and spans of the course
of 192 days with a daily sample frequency. Since this
data presents a strong weekly periodicity, it was de-
cided to also use as input for the algorithm a weekly
compression of the data using three different meth-
ods: weekly average, weekly peak value and weekly
90
th
percentile.
In order to be able to validate the algorithm, the
full length of the data set was divided into three equal
sub-sets, as detailed in Figure 1. The first two are
used as the input for the algorithm whereas the last
will be used to compare with the obtained forecast for
validation.
Figure 1: Splitting of input data into the 3 sets.
2.1 Stages
A fitting algorithm tries to fit the input data to a set
of functions and chooses the best fit to make a fore-
cast. The set of chosen functions should reflect typical
traffic behaviour in mobile networks. Taking into ac-
count this consideration, five different functions were
chosen to find the best fit, these are detailed in Equa-
tions (1) to (5), where x represents the time variable,
in either days or weeks, a, b and c are the function
parameters to be obtained in the fitting process, and
y will be the resulting forecast obtained through the
fitting process:
• Linear Function:
y = ax +b (1)
• Quadratic Function:
y = ax
2
+ bx + c (2)
WINSYS 2016 - International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems
64

• Power Function:
y = ax
b
+ c (3)
• Gaussian Function:
y = ae
−
(
x−b
c
)
2
(4)
• Logarithmic Function:
y = a + b log(x) (5)
This particular algorithm has three stages: fitting,
decision and validation. The overall view of the al-
gorithm is detailed in the flowchart of Figure 2. On
the first two stages, the algorithm takes as input data
the two first sub-sets mentioned earlier. In the fitting
stage, it fits the first sub-set to each of the five fitting
functions. Afterwards, in the decision stage, the al-
gorithm makes a forecast spanning over the duration
of the second sub-set. Then, it compares the obtained
forecast with the real data and finds the best fitting
function for it, minimizing the prediction error.
Figure 2: Overall flowchart of the Traffic Forecast algo-
rithm.
After obtaining the best fitting function for the
data and its parameters, it is possible to make a pre-
diction spanning for the last third of the input data in
order to validate the algorithm’s accuracy, by com-
paring the real data with the forecast. For this pur-
pose two different error functions were used: a Mean
Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) and a Normalized
Root Mean Squared Error (NRMSE). The NRMSE is
normalized with the real data’s mean value.
2.2 Results and Analysis
The developed forecast algorithm developed was ap-
plied to several Quality of Service (QoS) metrics and
statistics, including traffic volume, number of users
and Channel Element (CE) usage in both Uplink (UL)
and Downlink (DL). An example of the obtained pre-
diction can be seen in Figure 3. The input data used
in the example was the daily maximum UL CE us-
age in Site 2. In Figure 4 is illustrated an example for
the same site but now with a weekly input data using
the 90
th
percentile. From Figures 5 to 8 are exam-
ples of the forecast algorithm’s output when using the
remaining metrics as input data.
Figure 3: Example of a forecast used for validation.
Figure 4: Example of a forecast used for validation, with
weekly input data.
Figure 5: Example of a forecast used for validation, with
speech traffic as input data.
The detailed prediction error results obtained for
each case are presented in Tables 1 and 2, using
MAPE and NRMSE, respectively.
From the obtained results it is easily concluded
that the weekly compressed data sets provide much
better prediction errors, meaning it is easier to predict
the weekly behaviour of the sites than its daily be-
haviour. Moreover, for most cases of input data, the
90
th
Percentile is the better aggregation method, min-
imizing the prediction error. However, in the Max-
An Efficient Approach for Capacity Savings using Load Balancing in Dual Layer 3G Wireless Networks
65

Table 1: Average MAPE for the several input data types.
Metric
Daily
Data [%]
Weekly
Average [%]
Weekly
Peak [%]
Weekly 90th
Percentile [%]
CE Usage
Maximum UL 24.46 13.52 11.69 10.92
Maximum DL 42.66 12.70 15.88 15.09
Average UL 32.80 18.93 16.88 17.57
Average DL 47.04 12.27 12.43 11.66
Traffic
Volume
Speech 58.98 18.11 15.29 15.87
HSDPA 57.22 39.48 43.72 41.82
EUL 71.37 39.72 57.65 56.97
R99 DL 48.29 34.58 43.25 40.21
R99 UL 98.70 54.90 90.59 83.20
Number
of Users
Speech 49.86 18.22 16.79 16.52
HSPA 36.05 24.83 23.88 23.99
R99 69.62 24.71 25.93 24.20
Table 2: Average NRMSE for the several input data types.
Metric
Daily
Data [%]
Weekly
Average [%]
Weekly
Peak [%]
Weekly 90th
Percentile [%]
CE Usage
Maximum UL 24.94 15.04 13.67 12.75
Maximum DL 35.59 14.58 19.63 18.48
Average UL 30.35 20.59 18.15 18.74
Average DL 36.88 13.88 14.17 13.40
Traffic
Volume
Speech 38.77 19.66 17.09 17.56
HSDPA 50.19 41.13 45.62 43.72
EUL 65.51 41.96 61.92 61.01
R99 DL 45.62 37.40 46.78 43.59
R99 UL 80.64 52.86 79.85 74.91
Number
of Users
Speech 38.16 19.62 18.48 18.08
HSPA 34.12 26.59 25.51 25.73
R99 45.87 25.77 27.56 25.64
Figure 6: Example of a forecast used for validation, with
HSPA traffic as input data.
imum DL CE usage, EUL and R99 DL Traffic Vol-
umes present a slightly different trend, not having the
90
th
Percentile as the best method for aggregation of
the input data. This may be due to the fact that these
metrics present low usage, such as R99 DL Traffic, or
highly irregular behaviour resulting in high prediction
errors, as can be seen in Figures 5 to 8. In fact, for
these three metrics the best aggregation method is a
Figure 7: Example of a forecast used for validation, with
R99 data traffic as input data.
weekly average, since this is more stable for irregular
data than the 90
th
Percentile.
It is also possible to verify that the CE usage data
is the easiest to predict, mainly because it is the most
stable indicator. After that, the most reliable indica-
tor is the number of users statistics. Where it comes
to traffic volume, the algorithm finds more difficulties
due to its highly irregular behaviour along the sam-
WINSYS 2016 - International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems
66

Figure 8: Example of a forecast used for validation, with
user number as input data.
pling window. However, the speech traffic and num-
ber of users statistics reveals itself as a good indicator,
having a considerably lower prediction error.
In order to evaluate the chosen functions’ usage
and performance, a statistical test was performed.
In Table 3, the usage of each function is presented,
grouped by data type as well as a global view, which
is an average of all input data cases. In Table 4, the
same analysis is presented for the prediction errors
(MAPE) obtained for each function.
From the previous tables it is possible to con-
clude that the logarithmic function is the most com-
mon choice of the forecast algorithm, whereas the
Quadratic is the least chosen function. In terms of
prediction error, the Quadratic function presents the
worst performance, opposed to the Gaussian func-
tion that presents the best performance. There is a
certain consistency between usage and performance,
since the worst performing function is the least cho-
sen and the best performing is the second most chosen
function.
Note that the most chosen function does not al-
ways provide the lower prediction error. This is due
to the fact that the fitting function is chosen in a way
that minimizes the error in section 2 of Figure 1, and
thus does not assure that it is the best choice for the
third section.
3 Load Balancing Algorithm
There are several factors that may be used as triggers
for a Load Balancing mechanism. In this work, the
used indicator will be the maximum UL CE usage,
since the CE resource availability in the UL baseband
pool is the restraining capacity factor.
For this algorithm, the input data will also be pro-
vided by the same Portuguese mobile operator, and
it consists of user traces, geo-located reports of Re-
ceived Signal Code Power (RSCP) with the corre-
sponding timestamps. These traces were positioned
through an algorithm developed by Celfinet (Vieira
et al., 2013; Vieira et al., 2014). The measurements
were made in a set of 40 sites, all belonging to the
same set as the one used in the previous section, and
spans over the course of one hour, from 10:00 to 11:00
AM on April 27th, 2015. The samples were collected
every second. However, the available data only in-
cludes one carrier in the 2100 MHz band, so the statis-
tics for the 900 MHz band will have to be estimated.
3.1 Imbalance Analysis
Before applying the load balancing algorithm to a site,
it is beneficial to know the degree of imbalance be-
tween the 900 MHz and 2100 MHz frequency bands
present in the site, which will be referred to as U900
and U2100 from here onwards. For this purpose, a
small routine was designed.
Firstly, it evaluates two factors: the percentage
of capacity used by each band and the ratio between
the allocated capacity in each band. Then, it checks
how far from perfect balance the site is. This is done
by comparing the imbalance factor of used capacity
(I
usage
) and the imbalance factor of the allocated ca-
pacity (I
capacity
), originating the imbalance differen-
tial (∆I). Ideally, this differential should be equal to
zero, but most times it is bigger since the U2100 band
is usually overloaded.
The 3 factors are detailed in Equations (6), (7) and
(8), where n
CE
U900
and n
CE
U2100
represent the average
CE usage reported on the corresponding day for both
frequency bands and n
CE,lim
U900
and n
CE,lim
U2100
rep-
resent the allocated capacity in both frequency bands.
These values were taken from the traffic statistics file
used in the previous section, for the forecasting algo-
rithm.
I
usage
=
n
CE
U900
n
CE
U2100
+ n
CE
U900
× 100[%] (6)
I
capacity
=
n
CE,lim
U900
n
CE,lim
U2100
+ n
CE,lim
U900
× 100[%] (7)
∆I = I
capacity
− I
usage
(8)
It was decided that a site must have an imbalance
differential larger than 10% to be a candidate for im-
provement. This means that a site is overloaded in the
U2100 band while there is still considerable capacity
available on the U900 band. From the 43 initial sites
23 were selected. There are a few sites with negative
imbalance differential, only one with a factor greater
than 10%, but these sites will not be considered since
the objective of this research work is to offload the
U2100 band.
An Efficient Approach for Capacity Savings using Load Balancing in Dual Layer 3G Wireless Networks
67

Table 3: Usage of each function in the forecast algorithm.
Function Daily [%]
Weekly
Average [%]
Weekly
Peak [%]
Weekly 90th
Percentile [%]
Global
View [%]
Linear 23.49 14.53 13.84 12.56 16.10
Quadratic 6.16 3.37 8.84 8.95 6.83
Power 10.12 12.56 13.14 13.37 12.30
Gaussian 22.67 28.26 23.02 24.30 24.56
Logarithmic 37.56 41.28 41.16 40.81 40.20
Table 4: Prediction error associated with each function chosen by the forecast algorithm.
Function Daily [%]
Weekly
Average [%]
Weekly
Peak [%]
Weekly 90th
Percentile [%]
Global
View [%]
Linear 48.41 24.00 26.00 25.88 33.70
Quadratic 85.63 52.37 64.31 58.80 65.84
Power 53.70 30.98 30.27 29.77 35.13
Gaussian 44.58 22.09 25.15 22.31 28.05
Logarithmic 62.66 30.74 37.45 36.66 41.42
3.2 U900 Band Parameter Estimation
Before the Load Balancing algorithm can be applied it
is necessary to estimate the traces of this band. Since
its objective will be to offload the U2100 band, it is
not necessary to know exactly where the trace data
is generated but only the number of events that are
expected to occur in the U900 band.
To estimate this value we take the usage imbal-
ance factor obtained earlier and calculate the expected
number of events considering that it is proportional
to CE usage. This is, of course, assuming that the
used capacity depends only on the number of events
recorded in each band and that each event has the
same weight in the total CE usage of the site. The
estimate for this parameter is then given by Equation
(9), where N
events
represents the number of reported
events in each band.
N
events
U900
= N
events
U2100
I
usage
100 − I
usage
(9)
3.3 Strategy
In the following sections, the strategy taken to per-
form the load balancing for the selected sites will be
detailed. Firstly, the site is analysed to check if it is a
viable candidate, which was already done in Section
3.1. Afterwards, a target for the number of events in
both bands is calculated based on the imbalance fac-
tors. Finally, the required threshold to achieve the tar-
get load distribution is calculated.
After having a threshold estimate, the new distri-
bution of the load can be made. This stage will be
important to obtain an objective evaluation of the ef-
fectiveness of the Load Balancing algorithm.
3.3.1 Target Number of Events
The target number of events is calculated based on the
capacity imbalance factor, since this value is the op-
timal load distribution for each site. Taking the total
CE usage and multiplying by the imbalance factor we
obtain the target usage for the U900 band. The target
number of events for the U900 band is rounded down
to the closest integer in order to eliminate fractions of
events from the calculations. Afterwards, the U2100
band usage is simply the remaining from the total us-
age. This process is detailed in Equations (10), (11)
and (12).
N
events
total
= N
events
U2100
+ N
events
U900
(10)
N
target
U900
=
N
events
total
I
capacity
100
(11)
N
target
U2100
= N
events
total
− N
target
U900
(12)
3.3.2 RSCP Threshold
Originally, all cells have an admission threshold of -
115 dBm. This means that only UEs with a higher
or equal RSCP value may connect to the cell. The
output of this Load Balancing algorithm will be a
suggested RSCP threshold value in order to achieve
a better load distribution between the two frequency
bands. This is illustrated by Equation (13). Note
that n = N
events
U2100
, which means it is the number of
WINSYS 2016 - International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems
68

events in the U2100 band before the Load Balancing
is applied.
T
RSCP
= RSCP
i
, i = n − N
target
U2100
(13)
3.3.3 New Load Distribution
After having a suggested threshold, the number of
events in each band (N
result
) is calculated, as well as
the new imbalance factor (I
result
) obtained in order to
understand what is the impact of the algorithm in the
site capacity.
To calculate these parameters we have to check
how many events have a reported RSCP value equal
or superior to the obtained threshold for the U2100
band (RSCP
event
≥ T
RSCP
). These events will remain
in the U2100 band, whereas the rest will now switch
to the U900 band. The new number of U2100 events
will be designated as N
result
2100
. Equation (14) shows
the taken approach to find the number of U900 events.
N
result
U900
= N
events
total
− N
result
U2100
(14)
Having the resulting number of events for both
bands, it is possible to calculate the new imbalance
factor. The new imbalance differential (∆I
result
) is also
relevant to understand the effectiveness of the algo-
rithm. Equations (15) and (16) detail how these fac-
tors are calculated.
I
result
=
N
result
U900
N
result
U900
+ N
result
U2100
× 100[%] (15)
∆I
result
= I
capacity
− I
result
(16)
If the algorithm is to be considered effective, then
the new imbalance factor should be close to the ca-
pacity imbalance factor, thus obtaining the perfect
balance. This means that the imbalance differential
should be close to zero. The analysis of the factor
∆I
result
will then be the validation method for the Load
Balancing algorithm.
3.4 Results and Analysis
In Table 5, the obtained values for the imbalance dif-
ferential before (∆I) and after (∆I
result
) Load Balanc-
ing are presented, as well as the RSCP threshold val-
ues obtained in dBm for each selected site. In Figure
9 these results are illustrated next to the old imbalance
values.
The results show a significant change in the ∆I pa-
rameter, which had values greater than 10% for the se-
lected sites and now have an average value of 1.78%.
This value demonstrates a good effectiveness for the
Figure 9: Imbalance factors for all sites, before and after
Load Balancing.
Table 5: Summary of Load Balancing results.
Site I
result
[%] ∆I
result
[%] T
RSCP
[dBm]
1 41.42 0.05 -98
4 32.65 0.11 -100
5 22.84 0.97 -104
7 37.90 0.56 -96
9 30.95 2.38 -103
10 21.39 0.04 -109
18 34.47 0.01 -104
19 36.68 1.15 -103
20 56.95 0.19 -96
21 30.93 0.99 -103
23 42.84 1.02 -100
24 48.48 1.52 -99
25 13.48 16.52 -115
26 45.41 0.01 -100
27 36.78 0.36 -99
28 41.93 0.93 -93
34 40.65 0.38 -105
36 37.50 0.96 -91
37 32.14 1.19 -102
39 29.63 6.73 -114
40 42.26 0.60 -105
42 40.00 2.86 -108
43 51.16 0.84 -96
Load Balancing algorithm since it comes close to the
specified target of zero for the perfect balancing of
each site.
However, Site 25 presents a value much higher
than desired. This is due to a huge number of events
with a low RSCP value, more specifically -115 dBm.
This fact makes it very hard for the algorithm to de-
cide on a suitable threshold for the site, since a higher
value than the original -115 dBm will cause a capac-
ity overload situation in the U900 band. Because of
this, it decides to keep the original value unchanged.
In order to better understand how the Load Bal-
ancing algorithm affects the load distribution the
before and after Cumulative Distribution Function
An Efficient Approach for Capacity Savings using Load Balancing in Dual Layer 3G Wireless Networks
69

(CDF) of the imbalance differentials (∆I) is presented
in Figure 10. It can easily be concluded that after the
Load Balancing about 95% of the sites show a good
load distribution, opposing to the previous 45%.
Figure 10: Imbalance differential CDF before and after
Load Balancing.
4 Capacity Limit Estimation
The objective of this part of the work is to quan-
titatively determine the effect of the Load Balanc-
ing algorithm. Estimating when the capacity limit is
reached before and after the Load Balancing and com-
paring the results it will be possible to determine the
real gain. This gain can be presented according to
several methods, such as site longevity or overall CE
and economic savings.
In this part of the work, the necessary input data
will be the CE usage statistics, more specifically the
UL usage since this will be the limiting factor for the
capacity of the sites (Cunha et al., 2015). However,
since this data is only available before the use of Load
Balancing, an estimate of the CE usage statistics after
Load Balancing must be calculated.
The post Load Balancing estimate is based on the
obtained imbalance factors, which are presented in
Table 5. Taking the total CE usage in a site, i.e. sum-
ming the two frequency bands’ usage, and multiply-
ing it by the imbalance factor an estimate of the U900
band, CE usage is obtained. To get the same data for
the U2100 band we simply have to subtract the previ-
ous value from the total. This process is set in Equa-
tions (17), (18) and (19), where n
CE
is the vector con-
taining the CE usage statistics before Load Balancing
and n
CE,LB
is the vector containing the estimates for
CE usages after Load Balancing.
n
CE,total
= n
CE
U900
+ n
CE
U2100
(17)
n
CE,LB
U900
= n
CE,total
∆I
result
(18)
n
CE,LB
U2100
= n
CE,total
− n
CE,LB
U900
(19)
In order to find an estimate of the capacity limit,
the full set of available data was used, spanning from
November 28th of 2014 to June 4th of 2015. More-
over, since it produced lower prediction errors, a
weekly conversion of the data was made, more specif-
ically using the weekly 90
th
Percentile. In this case,
the Forecast algorithm skips the validation stage, and
only executes the fitting and decision stages.
4.1 Improved Forecasting
Since the input data for the Forecast algorithm is
known in detail, it is possible to improve the algo-
rithm in order to increase its accuracy. This improve-
ment is done by dismissing one or several fitting func-
tions, since they produce greater prediction errors.
In order to decide which functions are to be re-
moved, the Forecast algorithm is ran for all U2100
Nodes and for the designated input data, i.e., weekly
90th percentile of the maximum UL CE. In Table 6
the results are grouped by fitting function chosen by
the algorithm. It is evident that the Quadratic func-
tion produces the worse results in terms of prediction
error. Due to this fact, this function will be removed
from the analysis.
Table 6: Prediction error grouped by the chosen fitting func-
tion.
Function Average Error
Linear 2.45%
Quadratic 15.79%
Power 7.75%
Gaussian 4.01%
Logarithmic 7.19%
All 7.69%
Afterwards, the Forecast algorithm is ran again
only with the designated input data and it is validated
by using the same method described in Section 2. The
output is once again the prediction error, calculated
with MAPE, for each site. Moreover, a sequential
analysis is done by splitting the validation window
into three equal parcels (28 days each) and calculat-
ing the prediction error for each section. This allows a
better perception of how the error behaves with time.
In Table 7 the prediction error averaged over all the
analysed sites is presented. It is easy to conclude
this approach lowered the obtained prediction error
in about 2%.
Based on the results obtained in Table 7 it is pos-
sible to extrapolate the error obtained in predictions
made farther in the future. In Figure 11 this is de-
tailed. Day 0 is considered to be the first day of avail-
WINSYS 2016 - International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems
70
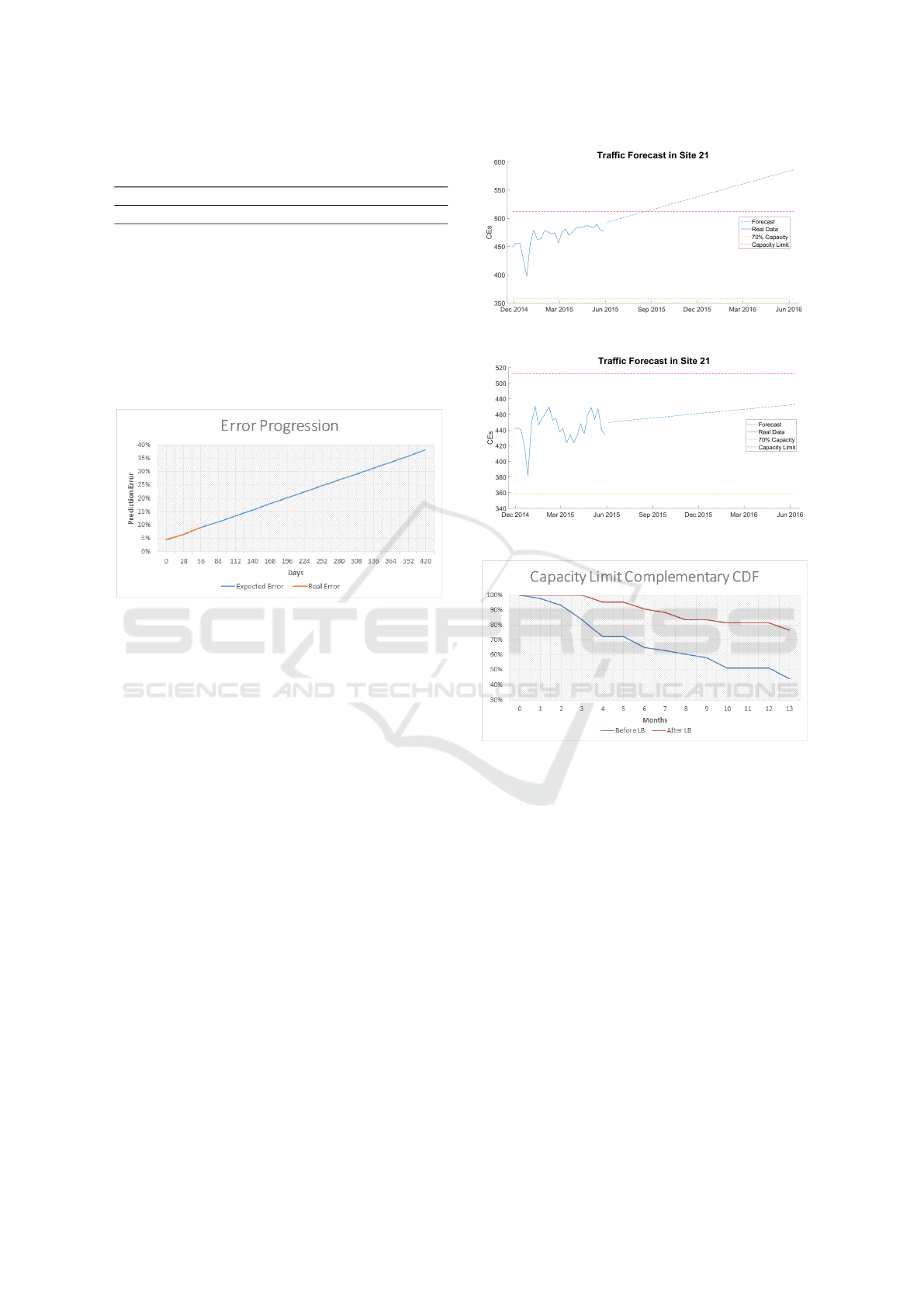
Table 7: Prediction error for improved Forecasting algo-
rithm.
Parcel 1 Parcel 2 Parcel 3 Total
Average 4.56% 6.51% 9.05% 6.22%
able data, so between Day 0 and 56 the values pre-
sented are the values obtained in Table 7, and from
there on is illustrated an expectation of the prediction
error for the next 390 days using a linear regression.
At the end of these 390 days, expected error is almost
40%, and this progression will be considered when
calculating the longevity of the sites in the following
section.
Figure 11: Prediction error distribution for selected data in-
put.
4.2 Results and Analysis
Using both cases, before and after Load Balancing, as
input for the Forecast algorithm it is possible to obtain
an estimate of when the capacity limit will be reached
in a site. In Figures 12 and 13 an example of how the
Load Balancing algorithm affects the capacity limit of
sites is presented. In Figure 12 the forecast obtained
for the U2100 band of Site 21 before the Load Bal-
ancing process was applied, whereas in Figure 13 the
forecast obtained after the Load Balancing is consid-
ered. It is clear that on the first case, the site is on the
verge of reaching its capacity limit, but after the Load
Balancing algorithm is applied, this instant is delayed
for a considerable amount of time.
The output of the algorithm is presented using the
corresponding complementary CDF, in terms of site
longevity, see Figure 14. The graph shows that, before
Load Balancing, 80% of the sites analysed had a pre-
dicted longevity of more than 3 months, whereas after
the Load Balancing process the predicted longevity is
greater than 1 year for the same amount of sites. An-
other way of interpreting is realizing that, before load
balancing, only about 50% of the sites had a longevity
greater than one year. After Load Balancing, this fig-
ure rises to 80%.
Figure 12: Example of Forecast before Load Balancing.
Figure 13: Example of Forecast after Load Balancing.
Figure 14: Capacity Limit complementary CDF.
However, a more practical approach is to estimate
the amount of CEs that the Load Balancing process
allows to save after a certain amount of time. Figure
15 illustrates the amount of CEs needed for expan-
sion in all sites for a time duration of up to one year.
It also includes a confidence interval for the forecast,
obtained by considering the mean value of the ex-
pected prediction error for each month. The dotted
lines represent this interval for both cases.
In one year, before Load Balancing, the operator
would need to expand the sites in about 1400 CEs.
After Load Balancing this value drops to around 400
CEs, representing a gain of about 1000 CEs. In terms
of time this would save the operator between 6 and
7 months before having to make an expansion of just
400 CEs.
An Efficient Approach for Capacity Savings using Load Balancing in Dual Layer 3G Wireless Networks
71

Figure 15: CEs needed for expansion of all sites over one
year.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper is presented a solution regarding the op-
timization of Capacity Management in 3G Wireless
Access Networks. This was done using a Load Bal-
ancing algorithm, which takes into consideration the
CE usage of sites and sets an RSCP threshold value
for each one. Its evaluation is done by using a Traffic
Forecast algorithm, based on a fitting method, in or-
der to obtain an estimate of when the sites’ capacity
limit is reached, before and after applying Load Bal-
ancing. After applying the algorithm it was concluded
that the amount of sites with longevity of at least one
year is raised in about 30% and that after a single year
it is possible to obtain savings of about 1000 CEs, or
70%, in capacity expansions of sites, which means a
reduction of costs for the operator.
In terms of future improvements, several ap-
proaches may be explored:
• Longer Input Data Period: Having traffic statis-
tics from a longer period of time it is possible to
make more accurate predictions. Network oper-
ators have a vast amount of traffic statistics they
can use to have a better idea of the longevity of
their sites.
• Larger Site Sample: Having a higher number of
sites with traffic statistics may be helpful to define
some traffic behaviour patterns depending factors
such as location, seasonality or rare events. This
would also help increase the accuracy of the Fore-
cast algorithm by characterizing sites in several
categories and having different prediction meth-
ods for each category.
• Multi-technology Extrapolation: In the current
setting of wireless access networks various tech-
nologies co-exist, namely 2G, 3G and 4G tech-
nologies. This means that the developed Load
Balancing algorithm may be used for evenly dis-
tribute traffic among the different technologies
and frequency bands available, allowing an even
greater increase in the longevity of sites. This ap-
proach may also be explored for the future deploy-
ment of 5G.
• Dynamic Thresholds: This Load Balancing al-
gorithm’s output is a suggested admission thresh-
old calculated with only one hour of trace data.
Having a real-time dynamic system, such as the
current wireless access networks, the thresholds
can be updated along the day, enabling a greater
efficiency for the algorithm. For example, the al-
gorithm can evaluate the traffic statistics in each
hour and decide on a threshold for the following
hour, or choose an even smaller update frequency.
• Event Differentiation: By knowing exactly how
each event impacts capacity usage of a site, it is
possible to develop an even more efficient solu-
tion for the Load Balancing algorithm, as opposed
to the solution obtained which considers that all
events have the same impact.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Instituto de
Telecomunicac¸
˜
oes (IT) and the Portuguese Founda-
tion for Science and Technology (FCT) under project
PEst-OE/EEI/LA0008/2013. The authors would like
to thank Celfinet for providing the data necessary to
the development of this work as well as its invaluable
supervision and guidance.
REFERENCES
(2014). Cisco Visual Networking Index: Global Mobile
Data Traffic Forecast Update, 20142019 [White Pa-
per]. Technical report, Cisco.
(2015). Ericsson Mobility Report [White Paper]. Technical
report, Ericsson.
Cunha, T., Martins, A., Vieira, P., Rodrigues, A., Silva,
N., and Varela, L. (2015). Energy Savings in 3G Us-
ing Dynamic Spectrum Access and Base Station Sleep
Modes. In URSI Atlantic Radio Science Conference
(URSI AT-RASC), Maspalomas, Spain.
Dawoud, S., Uzun, A., Gondor, S., and Kupper, A. (2014).
Optimizing the Power Consumption of Mobile Net-
works based on Traffic Prediction. In 38th Annual
International Computers, Software and Applications
Conference, pages 279–288, V
¨
aster
˚
as, Sweden.
Li, J., Fan, C., Yang, D., and Gu, J. (2005). UMTS Soft
Handover Algorithm with Adaptive Thresholds for
Load Balancing. In IEEE 62nd Vehicular Technology
Conference, volume 4, pages 2508–2512.
WINSYS 2016 - International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Systems
72

Li, R., Zhao, Z., Zhou, X., and Palicot, J. (2014). The Pre-
diction Analysis of Cellular Radio Access Network
Traffic: from Entropy Theory to Networking Practice.
IEEE Communications Magazine, 52(6):234–240.
Northcote, B. (2014). TEMS Capacity Manager: Cost-
Efficient Mobile Network Dimensioning [White Pa-
per]. Technical report, Ascom.
Ramiro, J. and Hamied, K. (2012). Self-Organizing Net-
works: Self-Planning, Self-Optimization and Self-
Healing for GSM, UMTS and LTE. John Wiley &
Sons, Ltd, first edition.
Vieira, P., Silva, N., Fernandes, N., Rodrigues, A., and
Varela, L. (2014). Improving Accuracy for OTD
Based 3G Geolocation in Real Urban/Suburban Envi-
ronments. In 2014 International Symposium on Wire-
less Personal Multimedia Communications (WPMC),
pages 362–366, Sydney, Australia.
Vieira, P., Varela, N., Fernandes, N., Guedes, N., Varela,
L., and Ribeiro, N. (2013). A SON Enhanced Algo-
rithm for Observed Time Differences Based Geoloca-
tion in Real 3G Networks. In 16th International Sym-
posium on Wireless Personal Multimedia Communi-
cations (WPMC), pages 1–5, Atlantic City, USA.
Yu, Y., Song, M., Fu, Y., and Song, J. (2013). Traffic Pre-
diction in 3G Mobile Networks Based on Multifrac-
tal Exploration. Tsinghua Science and Technology,
18(4):398–405.
Yu, Y., Wang, J., Song, M., and Song, J. (2010). Net-
work Traffic Prediction and Result Analysis Based on
Seasonal ARIMA and Correlation Coefficient. In In-
ternational Conference on Intelligent System Design
and Engineering Application (ISDEA), pages 980–
983, Changsha, China.
An Efficient Approach for Capacity Savings using Load Balancing in Dual Layer 3G Wireless Networks
73
