
Near-duplicate Fragments in Simultaneously Captured Videos
A Study on Real-time Detection using CBVIR Approach
Andrzej Sluzek
ECE Department, Khalifa University, Abu Dhabi, U.A.E.
Keywords: Visual Surveillance, CBVIR, Real Time, Keypoint Matching, Keypoint Descriptors, MSER, SIFT.
Abstract: CBVIR approach to video-based surveillance is discussed. The objective is to detect in real time near-
duplicates (e.g. similarly-looking objects) simultaneously appearing in concurrently captured/played videos.
A novel method of keypoint matching is proposed, based on keypoint descriptions additionally
incorporating visual and geometric contexts. Near-duplicate fragments can be identified by keypoint
matching only. The analysis of geometric constraints (a bottleneck of typical CBVIR methods for sub-image
retrieval) is not required. When the proposed method is fully implemented, high-speed and good
performances can be achieved, as preliminarily shown in proof-of-concept experiments. The method is
affine-invariant and employs typical keypoint detectors and descriptors (MSER and SIFT) as the low-level
mechanisms.
1 INTRODUCTION
Content-based visual information retrieval (CVBIR)
is an important area of machine vision. Typical
applications, however, seem to focus on offline
tasks, e.g. image retrieval from a large visual
database. One of the most challenging problems is
the retrieval of near-duplicates, i.e. the returned
database images and the query should share some
visually similar fragments (similar objects) while the
remaining contents of images can be different (e.g.
Zhao and Ngo, 2009, Chum et al., 2009).
Real-time retrieval in video sequences of
contents similar to given images is a typical problem
of automatic visual surveillance. It can be noted that
such a task is conceptually similar to CVBIR
applications. In visual surveillance, each frame is
actually a query that should be quickly processed
and matched against a very small “database” (of
images depicting the object of interest). Thus, the
underlying mechanisms are almost the same even
though computational requirements and timing
constraints are rather different. Some works on
CBVIR actually use retrieval in videos as case
studies (e.g. Sivic and Zisserman, 2003 or Zhao et
al., 2007). In fact, the original work by Sivic and
Zisserman, 2003, proposed the concept of visual
words for video search, although the real-time object
retrieval was not possible because of computational
costs. Nevertheless, examples of real-time
surveillance systems which apply CBVIR algorithms
are known (e.g. Sluzek and Paradowski, 2010).
The goal of this paper is to further explore this
approach. Generally, our objective is to evaluate
feasibility of CBVIR-based systems which
continuously acquire video signals from several
sources and detect in real time cases of near-
duplicate fragments (objects) simultaneously
appearing in at least two of these videos. No pre-
existing knowledge about the contents and topics of
the videos is assumed. Therefore, the employed
algorithms and mechanisms should allow an
immediate switch from one domain to another
without retraining.
From the perspective of CBVIR, this is a system
with a small, dynamically modified database (a
number of frames simultaneously captured from
several cameras) where each element of the database
is also used as a query.
In Section 2, the problem’s challenges are
discussed. Section 3 presents recent algorithmic
tools to be applied. The core idea is to incorporate
properties of neighbourhoods in the feature
descriptors (a generalization of feature bundling, e.g.
Romberg et al., 2012) so that semi-local visual
similarities can be easily established.
Section 4 presents a limited-scale proof-of-
concept verification of these tools and estimates the
232
Sluzek, A.
Near-duplicate Fragments in Simultaneously Captured Videos - A Study on Real-time Detection using CBVIR Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0005971902320237
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2016) - Volume 2, pages 232-237
ISBN: 978-989-758-198-4
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

overall performances of a complete system. The
concluding remarks are given in Section 5.
2 BACKGROUND WORKS
2.1 Keypoint Detection and Description
In order to build a surveillance system based on the
concept of sub-image retrieval, keypoint detection,
description and matching should be applied as the
low-level tools. Therefore, real-time performances
of keypoint detection and description are core
requirements to deploy such a system.
Numerous keypoint detectors exist (e.g.
Tuytelaars and Mikolajczyk, 2008) but affine-
invariant ones are recommended because of their
robustness and repeatability under perspective
distortions. Therefore, our choice is MSER detector
(Matas et al., 2002) which is apparently the only
affine-invariant keypoint detector with hardware
implementations reported (e.g., Kristensen and
MacLean, 2007, and Salahat et al., 2014). In the
subsequent sections of this paper we can assume,
therefore, that real-time MSER detection is
achievable.
Numerous hardware-based implementations of
keypoint descriptors have been reported as well.
They are usually discussed in conjunction with
keypoint detection (e.g. Cornelis and Van Gool,
2008) but in Suzuki, 2012, the keypoint description
component can be run independently.
Altogether, we can conclude real-time MSER
detection and the corresponding SIFT description are
available. Even if additional modules are needed to
convert MSER regions into the best-fit ellipses (and
the subsequent circular normalization) these are
relatively straightforward operations for which
hardware solutions have been reported as well, e.g.
Paschalakis et al., 2003, Salahat et al., 2014, etc.
2.2 Keypoint Matching
Keypoint matching can be done by using either
descriptor vectors or descriptors quantized into
visual words. However, individual keypoint matches
are virtually useless for sub-image matching (even if
large vocabularies or the most credible matching
schemes are used). For example, our unpublished
study shows that in a collection of 135,460 pairs of
random-content images, where 511 pairs contain the
same object(s), precision of keypoint matching is
around 0.1% (depending on the matching scheme,
the size of visual vocabulary, etc.). Numerical
results are given in the first row of Table 1, and two
illustrative examples (where no significant
differences between a relevant pair and an irrelevant
pair of images can be noticed) are shown in Fig. 1.
(a)
(b)
Figure 1: Exemplary matches between affine-invariant
keypoints (using SIFT descriptors): (a) for a pair of
images sharing a similar object and (b) for a pair of image
without similar objects.
Because of that, most reported techniques for
sub-image retrieval are based on the hypothesize-
and-verify paradigm. Various approaches can used
to verify validity of preliminarily matched
keypoints, e.g. RANSAC and its derivatives (Sivic
and Zisserman, 2003), Hough transform, hashing
(e.g. Chum et al., 2009), entropy (e.g. Zhao and
Ngo, 2009), etc. Eventually, similarly looking
fragments are identified as groups of matching
keypoints for which a consistent mapping between
both images has been found. This approach (in spite
of major improvements in the verification methods)
is not fully scalable to real-time applications because
of the complexity issues.
Additionally, some of typical assumptions of
CBVIR have to be reformulated in the context of
real-time detection of similar fragments from
simultaneously acquired videos:
a) High precision of retrieval is more critical than
recall. Errors of low recall can be corrected by
repeatable detection in subsequent frames. If
precision is too low, the errors cannot be
corrected.
b) The costs of assigning words to the keypoints are
comparable (or higher) to the costs of descriptor
matching (unless the words are assigned
hierarchically, e.g. Nister and Stewenius, 2006).
Thus, both approaches can be alternatively used.
c) Image pre-retrieval is usually not needed because
the numbers of image pairs to be matched are
Near-duplicate Fragments in Simultaneously Captured Videos - A Study on Real-time Detection using CBVIR Approach
233

rather small (e.g. 15 image pairs for 6 cameras,
45 image pairs for 10 cameras, etc.).
d) Computational costs of consistency verification
are the bottleneck of the retrieval process. Even
though systems performing such a verification in
real time have been reported (e.g. Paradowski,
2010) the approach is generally not scalable to
larger numbers of video-cameras.
Thus, in this paper we present an alternative
approach. The main novelty consists in the modified
keypoint description. Original descriptors are
enriched by the neighbourhood data so that
individual keypoint matches become credible
indicators that the compared images contain similar
fragments.
3 DETECTION OF
NEAR-DUPLICATE
FRAGMENTS
The significance of keypoint context has been
recognized and exploited from the early days of
CBVIR. For example, Schmid and Mohr, 1997,
verified credibility of keypoint matching by
considering additional matches within the
corresponding neighbourhoods. Other examples
include geometric min-hashing (Chum et al., 2009),
feature bundling (e.g. Romberg et al., 2012), etc.
Similarly to these works, we define the keypoint
context as a collection of other keypoints within a
reasonably sized neighbourhood. Formally, the
context of K keypoint (represented by E ellipse) is
defined as a set of at most N closest keypoints
{K
1
,…, K
N
} with {E
1
,…, E
N
} ellipses, which satisfy:
1. The Mahanalobis distance D
M
(K, K
i
) < 1.5 and
D
M
(K, K
i
) > 0.7 (where the unit distance is
defined by the ellipse E), i.e. keypoints which are
too far or too close to K are excluded.
2. E
i
ellipses have sizes comparable to E, e.g.
0.5 ( ) ( ) 2 ( )
i
area E area E area E≤≤ .
The proposed value of N is 12 (which
compromises complexity and performances).
3.1 Description of Keypoint Context
Assuming that an individual MSER keypoint K is
represented by a visual word (e.g. SIFT word)
SW(K), the keypoint neighbourhood (context) can be
defined by a bag of words BoW
1
( ) { ( ),..., ( )}
N
BoWK SWK SWK=
(1)
Then, two keypoints K and L would be matched
if they are assigned the same word (i.e. SW(K) =
SW(L)) and their BoW’s sufficiently overlap, i.e.
() ()BoWK BoWL M∩≥
(2)
Performances of such an approach (which was
used, for example, in Schmid and Mohr, 1997, and
Romberg et al., 2012) are rather limited.
The experiment reported in Table 1 indicates that
even the optimum values of M have unacceptably
low performances (precision in particular). Again,
the same dataset of 135,460 image pairs is used.
Table 1: Keypoint matching and image pair retrieval by
using MSER keypoints and their contexts. M = 0 means
that the keypoint context is not used at all.
M
Precision
of
keypoint
matching
Retrieved
image
pairs
(correct)
Comment
0 0.11%
135,460
(511)
Poor precision. (ALL
image pairs retrieved).
2 0.36%
131,683
(499)
Almost the same as
above.
6 16.55%
2285
(381)
Optimum (still not
satisfactory)
11 20.19% 257 (89)
Too few correct
image pairs retrieved.
3.2 Extended Description of Keypoint
Context
The proposed improvements in keypoint context
description combine the ideas presented in Sluzek,
2012 and 2014. First, the SIFT descriptors of
neighbouring keypoints {K
1
,…, K
i
,... K
N
} (and,
subsequently, their visual words) are computed over
E
i
ellipses of these keypoints using (,)
i
K
K
vectors
as the reference orientations (as illustrated in Fig. 2)
instead of the dominant orientations established by
the SIFT algorithm. Thus, we use symbols SIFT
K
(K
i
)
for so calculated SIFTs, and SW
K
(K
i
) for the
corresponding words.
In this way, the bag of words
{
1
(),..., ( )
K
KN
SW K SW K } at least partially reflects
geometry of the keypoint neighbourhoods.
Then, more specific geometric relations between
a keypoint and its context are as follows (see also
Fig. 3): Given ellipses around the K keypoint and a
K
i
keypoint of its context, four triangles Δ(A,B,C),
Δ(A,B,K
i
), Δ(A
i
,B
i
,C
i
) and Δ(A
i
,B
i
,K) are
unambiguously defined by shapes and relative
locations of both ellipses.
ICINCO 2016 - 13th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
234
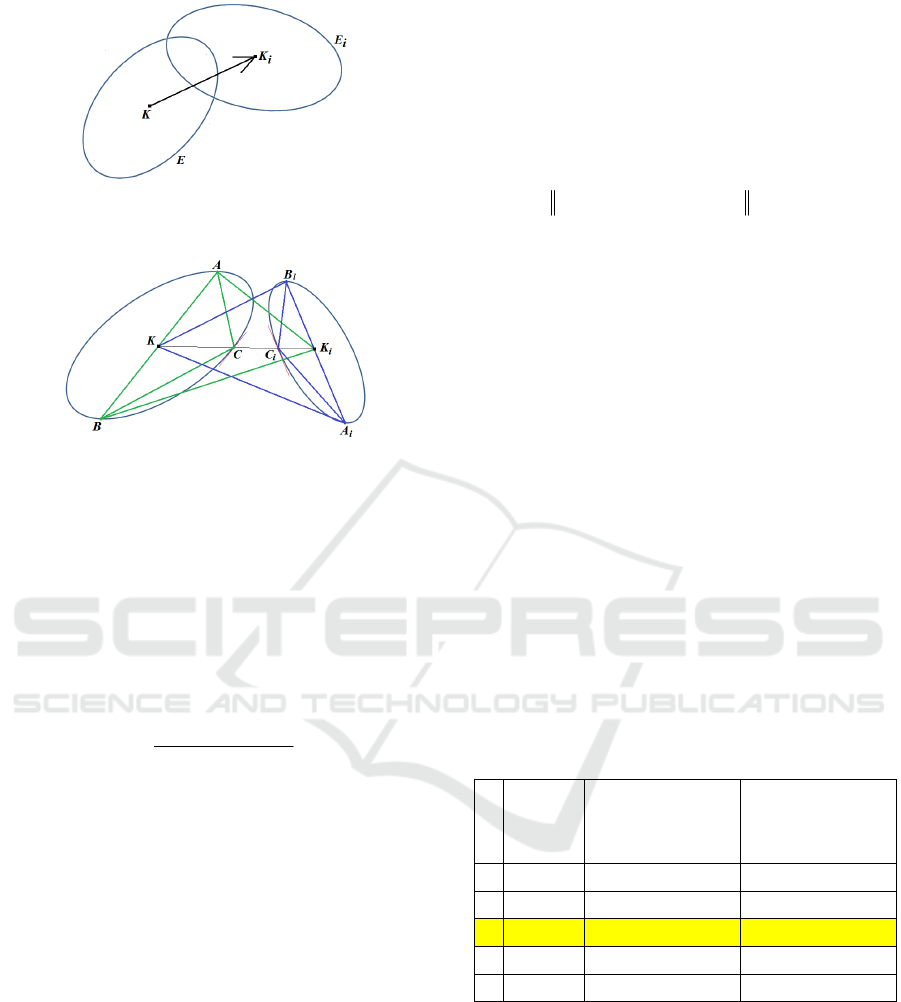
Figure 2: A configuration of a main keypoint K and its
neighbour K
i
for computing SIFT descriptor of the latter.
Figure 3: A configuration of two ellipses with four
triangles defined by shapes and locations of the ellipses.
When two ellipses are jointly transformed by an
affine mapping, the geometry of triangles changes
correspondingly. Since all triangles are equivalent
under affine transformations, we chose pairs of
triangles to identify pairs of keypoints which are
covariantly transformed.
The simplest affine-invariant moment expression
(see Flusser and Suk, 1993)
2
20 02 11
4
00
4
M
MM
Inv
M
−
=
(3)
is applied to three additive unions of triangle pairs to
form a 3D invariant descriptor MPT (Moments over
Pairs of Triangles) representing geometry of the
keypoint K and its neighbour K
i
:
1123
(, ) ( ), ( ), ( ),MPT K K Inv PT Inv PT Inv PT=
(4)
where (a)
()( )
11
,, ,,PT A B C A B K=Δ ∪Δ ;
(b)
()()
2111 11
,, ,,PT A B C A B K=Δ ∪Δ
and
(c)
()( )
3111
,, , ,PT A B K A B K=Δ ∪Δ .
MPT descriptors can also be quantized into a
finite number of MW words. Eventually, the
keypoint neighbourhood is described by a bag of
pairs of words BoPW, where each pair consists of a
SW
K
(K
i
) word and a
1
(, )
M
WKK word:
{
}
11
( ) [ ( ), ( , )],...
...,[ ( ), ( , )] .
K
KN N
BoPW K SW K MW K K
SW K MW K K
=
(5)
With the proposed extended descriptions,
keypoints can be matched straightforwardly. Two
keypoints K and L are considered a match if:
(1) They share the same SIFT words (i.e. SW(K) =
SW(L)), and
(2) Their bags of pairs of words BoPW sufficiently
overlap, i.e.
() ()BoPW K BoPW L M∩≥
(6)
3.3 Performance Evaluation
Preliminary evaluation has been performed on the
same dataset of 135,460 pairs of random-content
images, where 511 pairs contain identically looking
object(s). MSER keypoints are represented by SIFT
descriptors quantized into 2048 words. The number
looks small compared to typical CBVIR systems
(e.g. Stewenius et al., 2012) but the actual
vocabulary size is 2048
2
= 4,194,304 because the
words are used in conjunction with the words of
neighbours (Eqs 5 and 6) so that sufficiently good
precision can be achieved.
The size of MPT vocabulary is also small, i.e. 9
3
(some alternatives are given in Table 2 as well).
Both SIFT and MPT vocabularies are built using
the statistical approach (instead of standard k-means
technique) so that quantization of descriptors into
words can be done instantaneously.
Table 2: Retrieval of relevant (sharing the same objects)
pairs of images using extended description of keypoint
context. The size of SIFT vocabulary is constant (2048).
M
Size of
MPT
voc.
Precision and recall
of image retrieval.
Avg. no of matches
found in relevant
(irrelevant) pairs of
images.
3 729 (9
3
) p=20.5%; r=70.1% 2.417 (0.036)
4 27 (3
3
) p=12.4%; r=76.3% 3.337 (0.104)
4 729 (9
3
)
p=76.1%; r=57.1%
1.683 (0.003)
5 125 (5
3
) p=24.7%; r=61.5% 1.593 (0.014)
6 27 (3
3
) p=23.5%; r=60.3% 1.675 (0.018)
In general, very few keypoint correspondences
are found by the proposed method (see the last
column of Table 2). Thus, a pair of images is
matched (i.e. presumably containing the same
object(s)) if at least one correspondence between
keypoints from both images is found.
Near-duplicate Fragments in Simultaneously Captured Videos - A Study on Real-time Detection using CBVIR Approach
235

Figure 4: Exemplary ambiguities in the interpretation of
keypoint matching.
The variant highlighted in Table 2 provides the
best precision, while recall is only moderately
lower. As mentioned in Section 2.2, precision is
more important in matching simultaneously captured
videos. Therefore, we decided to use the highlighted
settings in the preliminary experiments on the actual
videos (see Section 4).
Finally, some ambiguities in the interpretation of
keypoint matching should be mentioned. Examples
in Fig. 4 show matches which are semantically
incorrect (keypoints are found in different objects)
but correct from a purely visual perspective (the
indicated fragments are near-duplicate).
4 PRELIMINARY EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Setup
Proof-of-concept experiments have been conducted
using a small collection of indoor-captured videos of
VGA resolution (exemplary frame sequences are
shown in Fig. 5). The system is implemented in two
separate Matlab modules. The first module (which
could be eventually replaced by the hardware-based
solutions, see Section 2.1) detects MSER keypoints
and describes them by the extended descriptors
according to Section 3.2.
In the second module, frames from two videos
(represented by descriptions built in the 1
st
module)
are matched at 5 frames/sec rate. We believe that
much higher frame rates can be achieved after
converting the module to C++.
4.2 Exemplary Results
Figs 6 and 7 show exemplary results (for the
sequences from Fig. 5). The examples are selected to
illustrate some limitations of the method.
In Fig. 6, one pair of frames is undetected, and
one pair contains two incorrectly matched keypoints.
Pairs of frames in Fig. 7 are not supposed to be
matched but, nevertheless, one keypoint
correspondence is actually found.
A
B
C
Figure 5: Exemplary sequences of frames with complex
contents. Sequences (A) and (B) contain the same object.
Incorrect keypoint matches appear rather
incidentally (see statistics in Table 2) and randomly,
so that we use a simple majority voting (the results
from the most recent 4 frames) to decide whether the
videos contain near-identical objects. In case of a
draw, the decision is postponed until the next frames
are processed. Thus, in both examples shown in the
figures, the final decisions are correct.
Figure 6: Matching results for sequences (A) and (B) from
Fig. 5. Note an undetected pair of frames and two
incorrect keypoint correspondences.
Finally, it should be noted that a single match
actually indicates several matches between a few
keypoints from the corresponding contexts. If
ICINCO 2016 - 13th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
236

necessary, those keypoints can be identified and
used to estimate more accurately sizes and shapes of
the detected near-duplicate fragments.
Figure 7: Results for sequences (A) and (C) from Fig. 5.
One incorrect keypoint correspondence can be seen.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The paper demonstrates that CBVIR techniques are a
feasible option for a multi-camera video
surveillance. It is shown that near-duplicates
simultaneously seen by several cameras can be fairly
reliably detected. Limited performances of the
approach can be rectified by combining results from
a number of subsequent frames. No assumptions
about the image backgrounds and the type/number
of objects are required.
A novel affine-invariant description of keypoints
(incorporating the keypoint contexts) is a core
element of the method. By using such descriptions,
similar image fragments can be identified by
individual keypoint correspondences, i.e.
verification of configuration constraints (required in
typical retrieval algorithms) is not needed.
REFERENCES
Zhao, W-L., Ngo, C-W., 2009. Scale-rotation invariant
pattern entropy for keypoint-based near-duplicate
detection. IEEE Trans. Image Proc., 18(2): 412-423.
Chum, O., Perdoch, M., Matas, J., 2009. Geometric min-
hashing: Finding a (thick) needle in a haystack. Proc.
IEEE Conf. CVPR’09: 17–24.
Sivic, J., Zisserman. A., 2003. Video Google: A text
retrieval approach to object matching in videos. Proc.
9th IEEE Int. Conf. ICCV’03: 1470-1477.
Zhao, W.-L., Ngo, C.-W., Tan, H.-K. and Wu, X., 2007.
Near-duplicate keyframe identification with interest
point matching and pattern learning. IEEE Trans.
Multimedia, 9(5): 1037–1048.
Paradowski, M., Sluzek, A., 2010. Real-time retrieval of
near- duplicate fragments in images and video-clips.
Proc. ACIVS 2010 (LNCS 6474): 18-29.
Romberg, S., August, M., Ries, Ch.X. and Lienhart, R.,
2012. Robust Feature Bundling. Proc. PCM 2012
(LNCS 7674): 45-56.
Tuytelaars, T., Mikolajczyk, K., 2008. Local inavariant
feature detectors: A survey, Now Publishers Inc.
Matas, J., Chum, O., Urban, M. and Pajdla, T., 2002.
Robust wide baseline stereo from maximally stable
extremal regions, Proc. BMVC’02: 384–393.
Kristensen, F., MacLean, W.J., 2007. Real-time extraction
of maximally stable extremal regions on an FPGA,
Proc. IEEE Symp. ISCAS’07: 165-168.
Salahat, E., Saleh, H., Sluzek, A., Al-Qutayri, M.,
Mohammed, B., and Ismail, M., 2016. Architecture
and method for real-time parallel detection and
extraction of maximally stable extremal regions
(MSERs), U.S. Patent 9,311,555.
Cornelis, N., Van Gool, L., 2008. Fast scale invariant
feature detection and matching on programmable
graphics hardware, Proc. IEEE Conf. CVPR’08
Workshop: 1-8, 2008.
Sluzek, A., 2012. Large vocabularies for keypoint-based
representation and matching of image patches, Proc.
ECCV’12 W&T (LNCS 7583): 229–238.
Suzuki, T., 2012. SIFT-based low complexity keypoint
extraction and its real-time hardware implementation
for full-HD video, Proc. APSIPA’12 Annual Summit
and Conf.: 1-6.
Paschalakis, S., Lee, P. and Bober, M., 2003. An FPGA
system for the high speed extraction, normalization
and classification of moment descriptors, Proc. 13 Int.
Conf. FPL’03 (LNCS 2778): 543-552.
Nister, D., Stewenius, H., 2006. Scalable recognition with
a vocabulary tree, Proc. IEEE Conf. CVPR’06: 2161-
2168.
Jegou, H., Douze, M. and Schmid, C., 2010. Improving
bag-of-features for large scale image search, Int. J.
Comp. Vision 87(3): 316–336.
Schmid, C., Mohr, R., 1997. Local grayvalue invariants
for image retrieval. IEEE Trans PAMI 19(5): 530–534.
Sluzek, A., 2014. Extended keypoint description and the
corresponding improvements in image retrieval, Proc.
ACCV 2014 Workshops, (LNCS 9008): 698-709.
Flusser, J., Suk, T., 1993. Pattern recognition by affine
moment invariants, Pattern Recognition 26: 167–174.
Stewenius, H., Gunderson, S., Pilet, J., 2012. Size matters:
Exhaustive geometric verification for image retrieval.
Proc. ECCV’12 (LNCS 7573): 674-687.
Near-duplicate Fragments in Simultaneously Captured Videos - A Study on Real-time Detection using CBVIR Approach
237
