
Local Ozone Prediction with Hybrid Model
Dejan Gradiˇsar
1
, Boˇstjan Graˇsiˇc
2
, Marija Zlata Boˇznar
2
, Primoˇz Mlakar
2
and Juˇs Kocijan
1,3
1
Joˇzef Stefan Institute, Jamova 39, SI-1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia
2
MEIS d.o.o, Mali Vrh pri
ˇ
Smarju 78, SI-1293
ˇ
Smarje - Sap, Slovenia
3
University of Nova Gorica, Vipavska 13, SI-5000 Nova Gorica, Slovenia
Keywords:
Air Pollution, Ozone, Prediction of Ozone Concentration, Statistical Modelling.
Abstract:
Tropospheric ozone in high concentrations can cause health problems. A reliable alerting system is needed.
In this paper we present the hybrid model that can be used for ozone forecasting in urban microlocations.
The hybrid model is combined from meteorological and air-quality models (covering large geographical 3-
dimensional space), and empirical model (offering good local forecasts), implemented as a Gaussian-process
model. Prediction model for the city of Koper in Slovenia that has Mediterranean climate and problems with
the ozone pollution is presented and used for improved one-day-ahead forecasting of the maximum hourly
value within each day. The model validation results show that hybrid model improves ozone forecasts and
provides better alert systems for the selected location.
1 INTRODUCTION
Tropospheric ozone is an air pollutant that causes
health problems. Therefore, the EU directives were
established that regulate standards of air quality that
guarantee the protection of human health as well the
thresholds of ozone for informing and alerting the
public when they are violated. For this reason the
forecasting of the ozone is necessary.
In order to provide good forecast of ozone con-
centration, air-quality and meteorological models are
necessary. These models can be developed using
a variety of methods that contain the scientific un-
derstanding of the physical processes involved in air
quality and meteorology, i.e. first principles models
(Im et al., 2015). These models provide prognostic
time- and spatially-resolved concentrations for vari-
ous scenarios (including atypical ones) and, above all,
provide insights into pollutant formation processes
(Zhang et al., 2012). Due to their complete spatial
coverage, these models also provide forecasts in loca-
tions which are not monitored (
ˇ
Zabkar et al., 2015).
While air-quality and meteorological models cover
large geographical 3-dimensional space, their local
resolution is often not satisfactory. This is a disadvan-
tage in the case of topographically complex terrain.
On the other hand, models can be developed
empirically, using statistical methods that describe
the non-linear dynamics of air-quality components,
formed from available measurement data only. When
these models are developed correctly and well, they
provide forecasts of higher accuracy and with better
computational efficiency than first principles models
(Zhang et al., 2012). Nevertheless, the physical pro-
cesses involved in air quality and meteorology can-
not be seen transparently in empirical models. Vari-
ous empirical models are used for air-quality forecast-
ing, ranging from Principal Component Regression to
Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy models, e.g., (Al-Alawi et al.,
2008), (Petelin et al., 2013), (Mlakar and Boˇznar,
2011).
The present paper deals with improving the ozone
forecasting in a selected micro-location, the city of
Koper in Slovenia, for the purpose of giving alerts,
which, in general, has a complex and geographically
diverse terrain (
ˇ
Zabkar et al., 2015). Presented work
is part of extensive efforts to develop air-quality fore-
casting system for Slovenia. The main contribution
of the present work is the combination of first prin-
ciples and empirical model as presented in (Gradiˇsar
et al., 2015) on the case of neural-network models,
while in this paper empirical model is developed us-
ing Gaussian-process (GP) model (Kocijan, 2016).
The integration of first principles and empirical mod-
els for forecasting ozone with the aim of uniting ’the
best of both worlds’ in modelling, is to overcome the
problem of the low resolution of first principles mod-
els while retaining their advantages.
262
Gradišar, D., Graši
ˇ
c, B., Božnar, M., Mlakar, P. and Kocijan, J.
Local Ozone Prediction with Hybrid Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0005980002620269
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH 2016), pages 262-269
ISBN: 978-989-758-199-1
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

The idea of using the hybrid model, i.e., the com-
bination of first principles and empirical models is not
a novel one. It is quite common in fields like process
engineering, e.g., (von Stosch et al., 2014). GP mod-
els may complement first principles models as a sup-
plement for parts of a model, e.g., in (Schmitt et al.,
2008), as a model of stochastic input, known as Latent
Force Model (LFM), e.g., in (
´
Alvarez et al., 2009), or
as a model of residuals from first principles models,
e.g., in (Chen et al., 2013). However, hybrid mod-
els have rarely been employed in atmospheric science.
Applications in (Pelliccioni and Tirabassi, 2006) and
(Goyal and Kumar, 2012) are examples of integrating
first principles and empirical models for the elimina-
tion of system errors in diagnostic investigation of the
air quality in flat terrain case studies and for so-called
tracer experiments using nonreactive gasses.
The present report is structured as follows. The
problem is described in the next section. The pro-
posed methodology is introduced in Section 3. Sec-
tion 4 describes and discusses the results of the exper-
iments to showthe feasibility of the proposed method-
ology. The conclusions are drawn at the end.
2 PROBLEM DESCRIPTION
The problem considered in this paper is to improve
ozone forecasting and consequentlyto increase the re-
liability of alerts for the city of Koper. The location
is an urban location, and this is the kind of location
where alerts based on EU directives are necessary.
The solution shall circumvent a real-life problem that
is caused by the low resolution of the meteorologi-
cal and air-quality models, something which becomes
problematic at microlocations in complex terrain.
The on-line forecasting model is aimed at pre-
dictions of the daily maximum ozone concentrations
one-day ahead of the target day. The daily maximum
value is, in our case, defined as the maximum value
of the hourly average ozone concentrations obtained
between 1 and 24 hours on a particular day. The pre-
dictions of the model for the next day are to be made
at 24:00 hours on the day before the target day.
3 METHODOLOGY
Our goal is to develop an hybrid ozone-forecasting
model, composed of first principles and empirical
models. Such a model allows us to use the advan-
tages of both and produce more accurate forecasts.
Two first principles models are used in our study: one
for air-quality predictions and another to predict the
meteorological variables. Besides those, we use a
database with various historical meteorological and
air-quality values measured in the city of Koper for
the training of the empirical model.
Three sets of ozone-concentrationpredictions will
be developed for the selected location. Two first prin-
ciples models are used in our study: one to predict air
quality (QualeAria) and the other for meteorological
forecasts (WRF model). Prediction model based only
on these two models is denoted by Model 1. Predic-
tions based on an empirical model, i.e., a GP model
that has been developed based on air-quality and me-
teorological measurements for the target day. This
model is highly accurate for the microlocation from
where the measurements have been sampled. How-
ever, it is unrealistic, because in reality, the meteoro-
logical regressors for the time of prediction can be
based on meteorological forecasts only. Neverthe-
less, the predictions of such a model are in our case
used for comparison with the other model’s accuracy,
and the model will be referred to as the idealistic GP
model and denoted by Model 2. Predictions based on
an hybrid model for each of the selected microloca-
tions, which will integrate all available information,
i.e., the history of air-quality and meteorological mea-
surements from that specific location, and air-quality
and meteorological forecasts from the first principles
models available for that region. The aim of the hy-
brid model, denoted by Model 3, is to attain the pre-
diction quality of the idealistic GP model and at the
same time retain the transparency of the first princi-
ples model.
3.1 The Air-quality Model—QualeAria
Air quality predictions for selected locations are
obtained with the QualeAria forecasting system.
QualeAria implements three-dimensional state-of-
the-art models to describe the emission, dispersion,
and transformation of pollutants in the atmosphere. It
is based on the Flexible Air quality Regional Model—
FARM, a 3D Eulerian model simulating the disper-
sion and chemical reactions of atmospheric pollutants
(Kukkonen et al., 2012). The model is operationally
run by the ARIANET and is coupled with the mete-
orological model RAMS, (AriaNet Srl. and ENEA,
2015). It is part of the MINNI Italian national mod-
elling system (Zanini et al., 2005) and is based on the
same meteorological and air-quality models.
The QualeAria system is currently configured on
two nested computational grids, the wider one cover-
ing Europe at a horizontalresolution of 48 km, and the
smaller one covering Italy and its near neighbourhood
at 12 km resolution. Slovenia is placed in the inner
Local Ozone Prediction with Hybrid Model
263

part of the second modelling domain, far enough from
the domain’s border so that the results for Slovene ter-
ritory are not heavily affected by the boundary condi-
tions. QualeAria produces air pollution forecasts for
Slovenia for up to two days in advance at 1 h time
resolution and also at 12 km spatial resolution. The
predictions of the main pollutants from this configu-
ration are validated in (Boˇznar et al., 2014) and are
available on-line on a daily basis on the KOoreg web-
site (MEIS d.o.o., 2015).
3.2 The Meteorological Model—WRF
Meteorological predictions for selected locations are
obtained with the Weather Research & Forecast—
WRF model (Skamarock et al., 2008). The WRF
model is a numerical weather prediction system that is
used for operational forecasting and for atmospheric
research. The WRF model was developed coopera-
tively by the US institutions (NCEP and NCAR), and
the meteorological research community. There are
two dynamics solvers in the WRF software frame-
work: ARW and NNM, where the ARW solver, pri-
marily developed and maintained by NCAR, is used
in this study.
ARW model, which runs permanently on daily ba-
sis at the MEIS company,calculate predictionson two
geographical domains. A larger domain (central Eu-
rope) is covered with 101 by 101 cells in a resolution
of 12 km per 3 hours and a smaller domain (Slovenia
with surroundings) covered with 76 by 76 cells in a
resolution of 4 km per 30 min. The horizon of pre-
diction is two days and three hours. The model is run
at 5:00 UTC. The simulation runs for three to four
hours, and it is run again at 17:00 UTC. The model
with a given configuration running over the terrain of
Slovenia was validated in (Boˇznar et al., 2012).
3.3 The Gaussian-process Model
GP models are probabilistic, non-parametric models
based on the principles of Bayesian probability. GPs
actually provide a Bayesian interpretation to the ker-
nel methods (Rasmussen and Williams, 2006). This
means that with a GP model we do not try to approxi-
mate the modelled system by fitting the parameters of
the selected basis functions, but rather we search for
the relationship among the measured data. The mod-
elling properties of GP models are reviewed in (Ras-
mussen and Williams, 2006), (Kocijan, 2016), (Shi
and Choi, 2011).
GP models can be used for regression, where
the task is to infer a mapping from a set of N D-
dimensional regression vectors represented by the re-
gression matrix X = [x
1
,x
2
,...,x
N
]
T
to a vector of
output data y = [y
1
,y
2
,...,y
N
] forming the data D =
{(x
i
,y
i
)|i = 1,... ,N} = {(X,y)}. The outputs are
usually assumed to be noisy realisations of the under-
lying function f(x
i
). A GP model assumes that the
output is a realisation of a GP with a joint probabil-
ity density function p(y) = N (m,K), with the mean
m and covariance K being functions of the inputs x.
Usually, the mean function is defined as 0, while the
covariance function or kernel K
ij
= C(x
i
,x
j
) defines
the characteristics of the process to be modelled, i.e.,
the stationarity, smoothness, etc. The value of the
covariance function C(x
i
,x
j
) expresses the correla-
tion between the individual outputs f(x
i
) and f(x
j
)
with respect to the inputs x
i
and x
j
. The covari-
ance function can be any function that generates a
positive, semi-definite covariance matrix. Assuming
the stationary data is contaminated with white noise,
the most commonly used covariance function is the
composition of the square exponential (SE) covari-
ance function with ‘automatic relevance determina-
tion’ (ARD) hyperparameters (MacKay, 1998) and a
constant covariance function assuming white noise.
The ARD property means that hyperparameters indi-
cate the importance of individual inputs. Description
of this and further covariance functions suitable for
various applications can be found in, e.g., (Kocijan,
2016).
The common aim of regression is to predict the
output y
∗
in an unobserved test location x
∗
given the
training data, a known mean function and a known co-
variance functionC. The posterior predictivedistribu-
tion can be obtained by constructing the joint poste-
rior distribution using the Bayes’ rule. The computa-
tion of posterior distribution integrals can be difficult
due to the intractable nature of the non-linear func-
tions. In the case of GP inference a frequently used
approximate solution to the problem of intractable in-
tegrals is to estimate the hyperparameters with the
maximising of the marginal likelihood from Bayes’
rule (Rasmussen and Williams, 2006).
A prediction of the GP model, in addition to the
mean value, also provides information about the con-
fidence of the prediction using the prediction vari-
ance. Usually, the confidence in the prediction is
interpreted with a 2σ interval, which corresponds to
about 95% of the confidence interval. The confidence
interval highlights the areas of the input space where
the prediction quality is poor, due to the lack of data
or noisy data, by indicating a wider confidence inter-
val around the predicted mean.
SIMULTECH 2016 - 6th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
264

3.4 Validation Methodology
The proposed hybrid model (Model 3) will be com-
pared to (i) the existing QualeAria system (Model 1)
and (ii) the idealistic GP model trained with inputs
based on measurements only (Model 2).
Koper is an industrial and port town on the Adri-
atic coast with a Mediterranean climate, with its air
quality strongly influenced by the river Po and the in-
dustrial Friuli region in Italy.
Both empirical models, including the hybrid mod-
els, have been trained on measurements from a period
of one year and tested on measurements from the pe-
riod of the two subsequent years. This was done for
the purpose of demonstrating the performance of the
forecasting models for a longer period.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Measurements
The meteorological and air-quality variables at the se-
lected location were measured and then elaborated on
an hourly basis. The measured data in this study were
acquired for all the available variables for a period of
three years (from the beginning of 2012 to the end of
2014). Available variables’ measurements are: ozone
concentration (O
3
), solid particles (PM10), nitrogen
oxides concentration (NO
x
), nitrogen dioxide concen-
tration (NO
2
), carbon monoxide (CO), air tempera-
ture (AirTemp), relative humidity (RelHum), global
solar radiation (GlSolRad), wind speed (WindSpd),
wind direction (WindDir), air pressure (Pressure) and
precipitation (Precip).
Besides the measurements, one-day ahead pre-
dictions of meteorological variables obtained from
the WRF modelling system, and air-quality variables
forecast by the QualeAria system for the same period
of time are available.
4.2 Regressor Selection
To gain a credible ozone forecast, the model needs in-
put data of all influential variables. However, with the
number of available variables and their lagged values,
the size of the regression vector or input features and,
consequently, of the model, increases noticeably. For
this reason it is necessary to select only the regres-
sors that add the most information to the prediction.
Various methods for the selection of the regressors or
features are available.
In this paper, we use the same regressors as
they were used in similar neural-network based study
(Gradiˇsar et al., 2015). The method used in this study
was introduced in (Kocijan et al., 2016) and is as fol-
lows. It combines various regressor-selection algo-
rithms, where the rankings achieved are first averaged
for various locations in Slovenia and these are later
grouped to obtain the final sequence of regressors,
ordered in terms of their importance. In the second
stage, we determine how many of regressors should
be used in order to produce the best prediction, us-
ing 10-fold cross-validation. Note that the models in
the second stage were GP models. Further note, that
the hybrid model uses one additional regressor: the
value of ozone from the QualeAria system for the tar-
get day (O3(k+ 1)). As prediction for NO
x
needed in
hybrid model is not available from QualeAria model,
NO
2
is used instead which is a reasonable substi-
tute for NO
x
. In the case that there are no measure-
ments for some regressors, the training and prediction
are performed without that time interval. The first 9
regressors from the final selection give the best re-
sults on average on all tested locations and measures.
These are: O3(k), GlSolRad(k+ 1), AirTemp(k+ 1),
AirTemp(k), GlSolRad(k), RelHum(k+ 1), NOx(k+
1), Pressure(k+1) and Pressure(k). All listed regres-
sors have been used for the empirical as well as for the
hybrid model, but forecasts are used instead of mea-
surements when necessary according to the type of
model.
This procedure makes it possible to obtain a sin-
gle uniform regression vector for a larger area, in our
case the urban parts of Slovenia, and to avoid having
to select the regressors every time we include a new
location.
4.3 Prediction Quality
In this section we compare all three different mod-
els used for one-day-ahead predictions of 1h O
3
daily
maxima in the selected location. The predictions
are validated with the following performance mea-
sures, which are described in the Appendix: the root
mean square error (RMSE), the standardised mean-
squared error (SMSE), the mean standardised log loss
- MSLL, Pearson’s correlation coefficient (PCC), the
mean fractional bias (MFB), and the factor of the
modelled values within a factor of two of the obser-
vations (FAC2).
Firstly, we analyse the prediction quality of the
QualeAria system. As described in subsection 3.1, its
spatial resolution is 12 km. Therefore, we can expect
that its predictions are not equally accurate in every
location. The resulting performance measures for the
observed location are listed in Table 1.
Next, we introduce the idealistic GP model. The
Local Ozone Prediction with Hybrid Model
265
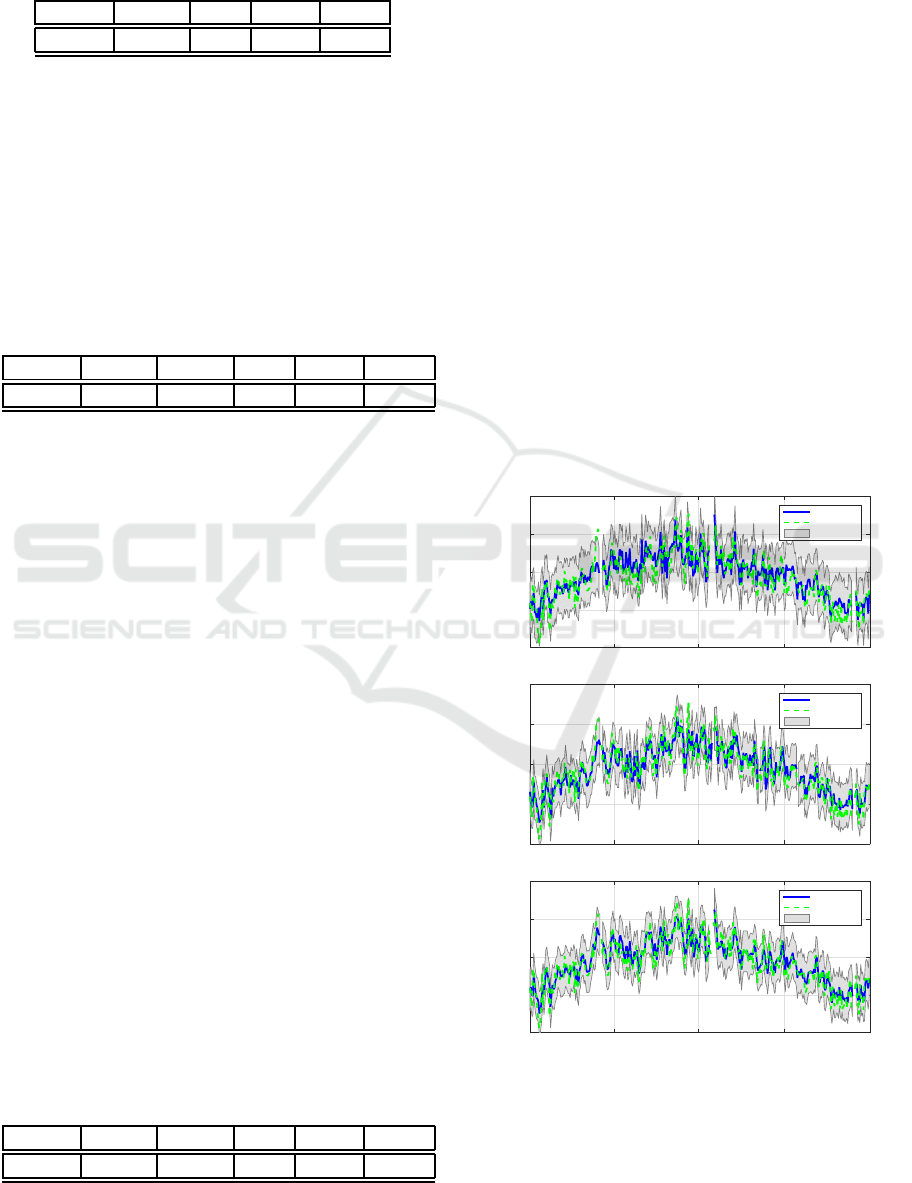
Table 1: Performance measures for predictions of daily
maximum O
3
concentrations: QualeAria predictions
(Model 1).
RMSE SMSE PCC MFB FAC2
16.40 0.26 0.86 0.033 0.987
regressors as selected in subsection 4.2 are used for
training and prediction of the ozone concentration
level. In this case we assume the ideal case, where
also the regressors corresponding to the time of pre-
diction (the target day) are taken from the database
of measurements as surrogates for a perfect forecast.
The evaluation of the model predictions is presented
in Table 2.
Table 2: Performance measures for predictions of daily
maximum O
3
concentrations: idealistic GP model using
measured data only (Model 2).
RMSE SMSE MSLL PCC MFB FAC2
13.06 0.17 -0.89 0.91 0.019 0.99
It can be seen from the table that the predictions
of the idealistic GP model are much better than those
from Table 1. Nevertheless, the idealistic model can-
not provide insights into the pollutant formation pro-
cesses.
Finally, we present the evaluation results for the
hybrid model (Model 3). The idea of the hybrid model
is to enhance the predictions from the first principles
model with the empirical model. This can be seen
as the serial connection of the first principles model
and the empirical model. This way, the addition of
the GP to the first principles model compensates for
the model mismatch in microlocations due to resolu-
tion inaccuracies. The values of performance mea-
sures in this study exhibit slightly better results from
those presented in study (Gradiˇsar et al., 2015).
The hybrid model also uses predicted air-quality
regressors, including the ozone concentration, pro-
vided by the QualeAria forecast system. Conse-
quently, the regressors are combined from the his-
torical measured data of air-quality and meteorolog-
ical variables, from predicted meteorological regres-
sors obtained from the WRF model, and predicted air-
quality regressors for O
3
and NO
x
from the QualeAria
model for the target day.
The evaluation of the hybrid model predictions is
given in Table 3 and confirms the improvement in the
Table 3: Performance measures for predictions of daily
max. concentrations: hybrid model predictions (Model 3).
RMSE SMSE MSLL PCC MFB FAC2
12.67 0.16 -0.92 0.92 0.026 0.99
quality of the predictions.
The results show that in our case the first prin-
ciples air-quality models can be upgraded and their
results enhanced with a properly trained empirical
model. It is clear also that the predictions of the hy-
brid model are better than those of the idealistic GP
model, as it has additional information about ozone
prediction from first principles air-quality model.
It is important to note that any suitable first prin-
ciples and any properly trained empirical nonlinear
model can be used to pursue the proposed modelling
and forecasting method for complex terrain. The se-
lection at hand was conditioned by the availability of
the data and need to evaluate the prediction using GP
models.
Next, a visual comparison of the models’ predic-
tions, employing time responses and scatter plots, will
be given for the considered microlocation. In Figure
1, time-series plots of the measured and predicted val-
ues for one year (2014), out of two years that are used
for validation, are shown. It can be observed that the
predictions by the QualeAria forecasting system are
not up to the predictions of the hybrid model.
01-Jan-2014 01-Apr-2014 01-Jul-2014 01-Oct-2014 01-Jan-2015
Ozone [µg/m
3
]
0
50
100
150
200
Model 1: QualeAria
prediction (µ )
measurement
µ ± 2σ
01-Jan-2014 01-Apr-2014 01-Jul-2014 01-Oct-2014 01-Jan-2015
Ozone [µg/m
3
]
0
50
100
150
200
Model 2: GP model (measurements)
prediction (µ )
measurement
µ ± 2σ
01-Jan-2014 01-Apr-2014 01-Jul-2014 01-Oct-2014 01-Jan-2015
Ozone [µg/m
3
]
0
50
100
150
200
Model 3: Hybrid model
prediction (µ )
measurement
µ ± 2σ
Figure 1: Time-series plot of predictions for daily max-
imum ozone concentrations for Koper for year 2014:
QualeAria predictions (Model 1), GP using measured data
(Model 2) and hybrid model (Model 3).
The prediction values are shown also in scatter
SIMULTECH 2016 - 6th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
266
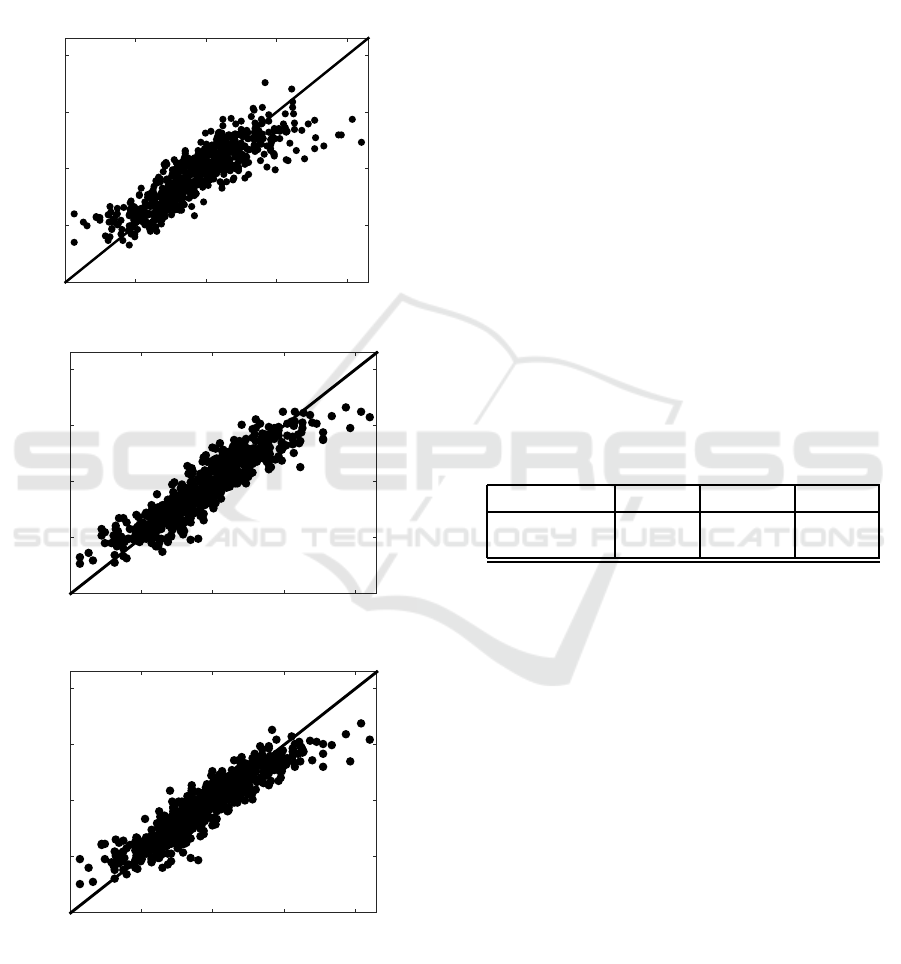
plots in Figure 2. The figures compare the predicted
and measured values. It can be seen that the predic-
tion quality for the location of interest improves when
GP models are used that use the information gained
from measurements at the location. It can be seen that
all developed models don’t provide good predictions
for higher values of ozone.
Measurements [µ g/m
3
]
0 50 100 150 200
Predictions [µg/m
3
]
0
50
100
150
200
Model 1: QualeAria
Measurements [µg/m
3
]
0 50 100 150 200
Predictions [µg/m
3
]
0
50
100
150
200
Model 2: GP model (measurements)
Measurements [µg/m
3
]
0 50 100 150 200
Predictions [µg/m
3
]
0
50
100
150
200
Model 3: Hybrid model
Figure 2: Predicted values versus observation values for
daily maximum ozone concentrations for Koper: QualeAria
predictions (Model 1), GP using measured data (Model 2),
hybrid model (Model 3).
The main purpose of the ozone-concentration
forecasting is to predict when concentration values
violate the prescribed thresholds. The European
Union’s Air Quality Directive sets four standards (Eu-
ropean Parliament and Council of the EU, 2010) to re-
duce air pollution by ozone and its impacts on health:
(i) information threshold: 1-hour average ozone con-
centration of 180 µg/m
3
, (ii) alert threshold: 1-hour
average ozone concentration of 240 µg/m
3
, (iii) long-
term objective: the maximum daily 8-hour mean con-
centration of ozone should not exceed 120 µg/m
3
, (iv)
target value: long-term objective (120 µg/m
3
) should
not be exceeded on more than 25 days per year, aver-
aged over three years.
We have analysed how successful our prediction
models would be when used to alert about cases of
1-hour ozone concentration. It never occurs that the
alert threshold (240 µg/m
3
) is violated in the observed
years. In Table 4, the number of information thresh-
old violations (180 µg/m
3
) is given, together with
the number of violations of additional—lowered—
informative threshold (140 µg/ m
3
). This threshold is
added in order to show the prediction capabilities of
our models.
In Table 4, all violations detected in 2013–2014
are listed, i.e., actual (correctly/failed forecasts).
Table 4: No. of threshold violations (Actual alarms/Correct
forecasts/False alarms).
Thr. [µg/m
3
] QA GP Hybrid
≥ 140 52/11/9 52/30/10 52/26/7
≥ 180 5/0/0 5/0/0 5/0/0
From the presented results it is clear that the de-
veloped hybrid model, based on local measured data
together with the available predictive meteorological
and air-quality values, predicts ozone concentrations
better than the currently available QualeAria system.
However, future work is needed in order to develop
methodologies, that would provide better predictions
for higher values of the ozone concentrations.
5 CONCLUSIONS
An application of an hybrid model for improving
ozone forecasting in the city of Koper, Slovenia is de-
scribed in the paper. Forecasting models have been
developed and validated for a period of three years.
The resulting model for this city is the com-
bination of the QueleAria air-quality model, the
WRF meteorological model, and empirical GP model.
QualeAria and WRF models do not provide enough
accurate ozone predictions for the purpose of issuing
alerts for this microlocation, because its horizontal
Local Ozone Prediction with Hybrid Model
267

resolution is too low and it misses a fair amount of
details. The integration of first principles and empir-
ical model enables the combined model to maintain
the scientific insights into pollutant formation pro-
cesses and prognostic abilities for atypical scenarios,
but have an improved forecasting ability for the mi-
crolocation.
The analysis shows that the hybrid model under
realistic conditions provides improved forecasting re-
sults than used first-principles models. An effective
methodology for the development of a model with an
increased reliability of ozone forecasting that can be
used for alerting the inhabitants according to regula-
tions has been demonstrated.
Work on improved alerts based on on-line air-
quality model will be continued for obtaining better
air-quality forecasting models using other strategies
on prediction.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Slovenian Research
Agency with Grant Development and Implementa-
tion of a Method for On-Line Modelling and Fore-
casting of Air Pollution, L2-5475 and Grant Systems
and Control, P2-0001. The Slovenian Environment
Agency provided part of the data.
REFERENCES
Al-Alawi, S. M., Abdul-Wahab, S. A., and Bakheit, C. S.
(2008). Combining principal component regression
and artificial neural-networks for more accurate pre-
dictions of ground-level ozone. Environ Modell Softw,
23:396–403.
´
Alvarez, M. A., Luengo, D., and Lawrence, N. D. (2009).
Latent force models. In 12th Int. Conf. on Artificial
Intelligence and Statistics, volume 5, pages 5–9.
AriaNet Srl. and ENEA (2015). Qualearia - forecast system
for the air quality in italy and europe. http://www.aria-
net.eu/QualeAria.
Boˇznar, M. Z., Mlakar, P., and Graˇsiˇc, B. (2012). Short-
term fine resolution WRF forecast data validation in
complex terrain in Slovenia. International journal of
environment and pollution, 50(1-4):12–21.
Boˇznar, M. Z., Mlakar, P., Graˇsiˇc, B., Calori, G., D’Allura,
A., and Finardi, S. (2014). Operational background
air pollution prediction over Slovenia by QualeAria
modelling system - validation. International journal
of environment and pollution, 54(2-4):175–183.
Chen, N., Qian, Z., Meng, X., and Nabney, I. (2013).
Short-term wind power forecasting using Gaussian
processes. In International joint conference on Ar-
tificial Intelligence IJCAI’13, pages 1771–1777.
European Parliament and Council of the EU (2010). Direc-
tive 2008/50/EC on ambient air quality and cleaner
air for Europe. Number L 152. Official Journal of the
European Union, Brussels.
Goyal, P. and Kumar, A. (2012). Air quality forecasting
throught integrated model using air dispersion model
and neural network. In Latest advances in systems sci-
ence and computational intelligence, pages 219–224.
WSEAS.
Gradiˇsar, D., Graˇsiˇc, B., Boˇznar, M., Mlakar, P., and Koci-
jan, J. (2015). Improved local-ozone forecasting using
the integrated model. Technical Report DP - 11958,
Jozef Stefan Institute, Ljubljana.
Im, U., Bianconi, R., Solazzo, E., Kioutsioukis, I., Badia,
A., Balzarini, A., , Bar, R., Bellasio, R., Brunner,
D., Chemel, C., Curci, G., Flemming, J., Forkel, R.,
Giordano, L., Jimnez-Guerrero, P., Hirtl, M., Hodzic,
A., Honzak, L., Jorba, O., Knote, C., Kuenen, J. J.,
Makar, P. A., Manders-Groot, A., Neal, L., Prez,
J. L., Pirovano, G., Pouliot, G., Jose, R. S., Savage,
N., Schroder, W., Sokhi, R. S., Syrakov, D., Torian,
A., Tuccella, P., Werhahn, J., Wolke, R., Yahya, K.,
ˇ
Zabkar, R., Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., Hogrefe, C., and
Galmarini, S. (2015). Evaluation of operational on-
line-coupled regional air quality models over Europe
and North America in the context of AQMEII phase
2. Part I: Ozone. Atmospheric Environment, 115:404–
420.
Kocijan, J. (2016). Modelling and Control of Dynamic Sys-
tems Using Gaussian Process Models. Springer Inter-
national Publishing, Cham.
Kocijan, J., Gradiˇsar, D., Boˇznar, M. Z., Graˇsiˇc, B., and
Mlakar, P. (2016). On-line algorithm for ground-level
ozone prediction with a mobile station. Atmospheric
Environment, 131:326–333.
Kukkonen, J., Olsson, T., Schultz, D. M., Baklanov, A.,
Klein, T., Miranda, A. I., Monteiro, A., Hirtl, M.,
Tarvainen, V., Boy, M., Peuch, V.-H., Poupkou, A.,
Kioutsioukis, I., Finardi, S., Sofiev, M., Sokhi, R.,
Lehtinen, K. E. J., Karatzas, K., San Jos´e, R., Astitha,
M., Kallos, G., Schaap, M., Reimer, E., Jakobs,
H., and Eben, K. (2012). A review of operational,
regional-scale, chemical weather forecasting mod-
els in Europe. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,
12(1):1–87.
MacKay, D. J. C. (1998). Introduction to Gaussian pro-
cesses. NATO ASI Series, 168:133–166.
MEIS d.o.o. (2015). KOoreg regional air pollution control
prognostic and diagnostic modelling system.
Mlakar, P. and Boˇznar, M. Z. (2011). Advanced air pollu-
tion, chapter Artificial neural networks: a useful tool
in air pollution and meteorological modelling, pages
495–508. InTech, Rijeka.
Pelliccioni, A. and Tirabassi, T. (2006). Air dispersion
model and neural network: A new perspective for inte-
grated models in the simulation of complex situations.
Environmental Modelling & Software, 21(4):539–546.
Petelin, D., Grancharova, A., and Kocijan, J. (2013). Evolv-
ing Gaussian process models for the prediction of
ozone concentration in the air. Simulation Modelling
Practice and Theory, 33(1):68–80.
SIMULTECH 2016 - 6th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
268

Rasmussen, C. E. and Williams, C. K. I. (2006). Gaussian
Processes for Machine Learning. MIT Press, Cam-
bridge, MA.
Schmitt, K., Madsen, J., Anitescu, M., and Negrut, D.
(2008). A Gaussian process based approach for han-
dling uncertainty in vehicle dynamics simulation. In
International Mechanical Engineering Congress and
Exposition (IMECE), volume 11, pages 617–628.
Shi, J. Q. and Choi, T. (2011). Gaussian process regression
analysis for functional data. Chapman and Hall/CRC,
Taylor & Francis group, Boca Raton, FL.
Skamarock, W. C., Klemp, J. B., Dudhia, J., Gill, D. O.,
Barker, M., Duda, K. G., Huang, X. Y., Wang, W., and
Powers, J. G. (2008). A description of the advanced
research WRF version 3. Technical report, National
Center for Atmospheric Research.
von Stosch, M., Oliveira, R., Peres, J., and de Azevedo, S. F.
(2014). Hybrid semi-parametric modeling in process
systems engineering: Past, present and future. Com-
puters & Chemical Engineering, 60:86 – 101.
ˇ
Zabkar, R., Honzak, L., Skok, G., Forkel, R., Rakovec, J.,
Ceglar, A., and
ˇ
Zagar, N. (2015). Evaluation of the
high resolution wrf-chem (v3.4.1) air quality forecast
and its comparison with statistical ozone predictions.
Geoscientific Model Development, 8(7):2119–2137.
Zanini, G., Pignatelli, T., Monforti, F., Vialetto, G., Vi-
tali, L., Brusasca, G., Calori, G., Finardi, S., Radice,
P., and Silibello, C. (December, 2005). The MINNI
project: An integrated assessment modeling system
for policy making. In Proceedings of MODSIM05,
International Congress on Modelling and Simulation,
Melbourne, Australia.
Zhang, Y., Bocquet, M., Mallet, V., Seigneur, C., and Bak-
lanov, A. (2012). Real-time air quality forecasting,
part i: History, techniques, and current status. Atmo-
spheric Environment, 60:632 – 655.
APPENDIX
The following are performance measures used in the
study.
• The root-mean-square error - RMSE,
RMSE =
s
1
N
N
∑
i=1
(E(ˆy
i
) − y
i
)
2
, (1)
where y
i
and ˆy
i
are the observation and the predic-
tion in the i-th step, respectively, E(·) denotes the
expectation, i.e., the mean value, of the random
variable, and N is the number of used observa-
tions.
• The standardised mean-squared error - SMSE
(Rasmussen and Williams, 2006):
SMSE =
1
N
∑
N
i=1
(E(ˆy
i
) − y
i
)
2
σ
2
y
, (2)
where σ
2
y
is the variance of the observations.
• The mean standardised log loss - MSLL (Ras-
mussen and Williams, 2006):
MSLL =
1
2N
N
∑
i=1
ln(σ
2
i
) +
(E(ˆy
i
) − y
i
)
2
σ
2
i
−
1
2N
N
∑
i=1
"
ln(σ
2
y
) +
(y
i
− E(y))
2
σ
2
y
#
,
(3)
where σ
2
i
is the prediction variance in the i-th step,
and E(y) is the expectation, i.e., the mean value,
of the vector of the observations.
• The Pearson’s correlation coefficient - PCC:
PCC =
∑
N
i=1
(E(ˆy
i
) − E(
ˆ
y))(y
i
− E(y))
Nσ
y
σ
ˆy
, (4)
where E(
ˆ
y) is the expectation, i.e., the mean
value, of the vector of predictions, and σ
y
,σ
ˆy
are
the standard deviations of the observationsand the
predictions, respectively.
• The mean fractional bias - MFB:
MFB =
1
N
N
∑
i=1
E(ˆy
i
) − y
i
1
2
(E(ˆy
i
) + y
i
)
. (5)
• The factor of the modelled values within a factor
of two of the observations - FAC2:
FAC2 =
1
N
N
∑
i=1
n
i
with
n
i
=
(
1 for 0.5 ≤ |
E( ˆy
i
)
y
i
| ≤ 2,
0 else.
(6)
RMSE and SMSE are frequently used measures for
the accuracy of the predictions’ mean values, which
are 0 in the case of perfect model. SMSE is the
standardised measure with values between 0 and 1.
MSLL is a standardised measure suited to predictions
in the form of random variables. It weights the pre-
diction error more heavily when it is accompanied by
a smaller prediction variance. The MSLL is approx-
imately zero for the simple models and negative for
the better ones. PCC is a measure of associativity and
is not sensitive to bias. Its value is between -1 and
+1, with ideally linearly correlated values resulting in
a value 1. MFB is the measure that bounds the max-
imum bias and gives additional weight to underesti-
mations and less weight to overestimations. Its value
is between -2 and +2, with the value 0 in the case of
a perfect model. FAC2 indicates the fraction of the
data that satisfies the condition from Equation (6). Its
value is between 0 and 1, with the perfect model re-
sulting in a value of 1.
Local Ozone Prediction with Hybrid Model
269
