
From UML/MARTE Models of Multiprocessor Real-time Embedded
Systems to Early Schedulability Analysis based on SimSo Tool
Amina Magdich, Yessine Hadj Kacem, Adel Mahfoudhi and Mohamed Abid
CES laboratory, National School of Engineers of Sfax (ENIS), Sfax, Tunisia
Keywords:
MARTE, MDE, Model Transformation, SimSo, Semi-partitioned Scheduling, Global Scheduling.
Abstract:
The increasing complexity of Real-Time Embedded Systems (RTES) should be met with equally sophisticated
design methods. The recent Unified Modeling Language (UML) profile for Modeling and Analysis of Real-
Time Embedded systems (MARTE) is well adapted for systems modeling. However along with the variety
of schedulability analysis tools, bridging the gap between design models and meta-models of the documented
scheduling analysis tools becomes an important issue.
In this paper, we discuss a Model To Text (M2T) transformation for enabling the derivation of schedulability
analysis models from UML/MARTE models. The generated model for schedulability analysis represents an
input for an analysis tool. As a proof of concepts, we present the implemented code and experimental results.
1 INTRODUCTION
The spread of technology and the industry re-
quirements have pushed designers to switch from
simple monoprocessor architectures to more complex
parallel multiprocessor architectures. Considering
multiprocessor systems leads to an increasing trend of
RTES design, which requires rigorous methodologies
to reduce the designer’s effort and avoid systems
failures. A prominent effort has been focused on the
use of Model Driven Engineering (MDE) (Schmidt,
2006) and high-level modeling languages such as
UML/MARTE profile (OMG, 2008) to automate the
design flows and raise the abstraction level.
On the other hand, designers are interested in verify-
ing the temporal correctness of their studied systems
at early design stages to be reassured that no deadline
may be missed. In this context, the schedulability
analysis is used to validate the temporal behavior of
systems scheduled using monoprocessor or multipro-
cessor scheduling approaches.
Regarding multiprocessor scheduling, three ap-
proaches are available in the literature; the partitioned
scheduling approach, the global scheduling approach
and the semi-partitioned one (Dorin et al., 2010).
The partitioned scheduling approach consists on
statically assigning each task to be executed on only
one processor. Using this strategy comes to using
monoprocessor scheduling approach, since each
task may be allocated to only one processor. In a
partitioned scheduling context, tasks are not allowed
to migrate inter-processors.
While adopting a global scheduling approach, tasks
are dynamically allocated to processors and they
are allowed to migrate inter-processors improving
then Central Processing Units (CPUs) occupation.
While using this approach, a full migration of tasks is
allowed. Consequently, an attention must be given to
the cost of preemption and context switching as well
as the number of cache misses due to the transferring
of tasks from one computing resource to another one.
Under the semi-partitioned scheduling approach,
most tasks are assigned to be executed on speci-
fied processors like in the partitioned scheduling
approach. Nevertheless, tasks that may not be
assigned to a single processor are allowed to migrate
inter-processors. This approach enables a restricted
task migration to maximize CPU occupation and
reduce context switching costs.
Regardless the used scheduling approach, the
schedulability analysis has always been an important
issue that has been widely studied during the last
years. Nevertheless, there are still many open issues
regarding this context. In fact, due to the variety of
schedulability analysis tools coupled with the ever
growing complexity of RTES, there is still a need
to automate the early schedulability analysis step to
reduce designers’ effort. Researchers’ attention has
been then focused on the transformation of systems
models into analysis tools meta-models to analyze
202
Magdich, A., Kacem, Y., Mahfoudhi, A. and Abid, M.
From UML/MARTE Models of Multiprocessor Real-time Embedded Systems to Ear ly Schedulability Analysis based on SimSo Tool.
DOI: 10.5220/0005982902020209
In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Software Technologies (ICSOFT 2016) - Volume 1: ICSOFT-EA, pages 202-209
ISBN: 978-989-758-194-6
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

systems, which are scheduled using monoprocessor
and multiprocessor scheduling approaches.
Nevertheless, considering the multiprocessor
scheduling, the documented automatic schedulability
analysis approaches have addressed only the parti-
tioned and global scheduling approaches.
In this context, we propose an automatic schedula-
bility analysis for systems that are scheduled using
semi-partitioned and global scheduling approaches.
MDE is used in this context to raise the abstraction
level and automate the schedulability analysis step.
The remainder of this paper starts with motivation
and related works in section 2. Section 3 gives an
overview of high-level methodologies and analysis
tools for early schedulability analysis. In section 4,
the proposed process for automatic schedulability
analysis at early design stages is highlighted. To
validate our proposal, a case study is performed in
section 5. Finally, conclusions and future works are
given in section 6.
2 MOTIVATION AND RELATED
WORK
Checking if RTES meet their timing requirements at
early design stages is extremely important to avoid
systems failures. In this context, a wide number of re-
search works have been proposed (Zhang and Burns,
2009)(Abdeddaïm et al., 2014)(Lee and Shin, 2013).
On the other hand, along with the variety of schedula-
bility analysis tools, the schedulability analysis is still
considered as an important issue that needs to be man-
aged properly at a high-level of abstraction to reduce
designers’ effort.
In fact, each schedulability analysis tool is based on
an input meta-model that encloses all the required in-
formation for schedulability analysis step.
An input meta-model may be defined using UML,
SysML, MARTE, XML, etc.
Since input meta-models differ from one analysis tool
to another, some research works have been focused
on the building of specific models that represent in-
put for the adopted analysis tools such as in (Jensen,
2009). In this proposal, authors have used MARTE
to build a specific model that represents an input for
MAST tool. This methodology has been used to sup-
port only monoprocessor systems. Moreover, the con-
struction of input models for analysis tools has been
done manually. With this regard, other research works
have been focused on the automatic built of analysis
models through a transformation of systems models
to schedulability analysis meta-models.
This model transformation offers automatic schedu-
lability analysis step and fosters the independence of
the design flow towards the used analysis tools.
In this context, a Model To Model (M2M) transfor-
mation has been performed in (Hagner and Huhn,
2008) to establish an early schedulability analysis of
systems using SymTA/S tool (Henia et al., 2005).
MARTE profile has been used in this context to an-
notate models with timing requirements. Activity
diagrams annotated through Schedulability Analysis
Modeling (SAM) have been transformed to SymTA/S
tool meta-model. In the same context, OPTIMUM
methodology has been provided in (Mraidha et al.,
2011) for early schedulability analysis of systems
modeled using MARTE sub-profiles mainly Generic
Resource Modeling (GRM) and SAM.
The models transformation that has been proposed
in this methodology enables generating concurrency
models that may be analyzed and validated using
COTS schedulability analysis tools. OPTIMUM has
been tested in the case of monoprocessor systems.
In (Medina and Cuesta, 2011), the MARTE profile
has been used to model temporal requirements of
multiprocessor systems. Built models are then trans-
formed to cheddar tool meta-model to establish an
early schedulability analysis for multiprocessors sys-
tems while considering partitioned scheduling.
In the same context, a model to model transformation
from an activity diagram to Petri Net tool has been
proposed in (HadjKacem et al., 2012) to establish an
early schedulability analysis of RTES. MARTE/SAM
sub-profile has been used to annotate the dynamic
view. The multiprocessor scheduling regarding the
partitioned scheduling approach has been supported.
In (Naija et al., 2015), an early schedulability anal-
ysis for real-time systems has been proposed while
using MDE concepts. To perform this step, a model
to model transformation has been performed to trans-
form an activity diagram annotated with SAM to Petri
Nets tool meta-model. Only the partitioned schedul-
ing has been supported in this proposal.
In (Rubini et al., 2013), an early schedulability anal-
ysis from AADL models is performed while using
cheddar tool. In this proposal, cheddar has been ex-
tended to support global scheduling, but it stills does
not support semi-partitioned scheduling.
In previous cited research works for automatic
schedulability analysis at early design stages, mono-
processor and multiprocessor scheduling have been
supported. Nevertheless, considering the multipro-
cessor scheduling, only the partitioned or global
scheduling approaches have been addressed. No
attention has been given to the semi-partitioned
scheduling approach. With this regard, we propose in
this paper an early schedulability analysis for semi-
From UML/MARTE Models of Multiprocessor Real-time Embedded Systems to Early Schedulability Analysis based on SimSo Tool
203

partitioned and global scheduling. Our proposal is
based on the use of MDE concepts and UML/MARTE
profile for a high-level automatic schedulability anal-
ysis. Our main goal is to establish models transforma-
tion in order to reduce the gap between systems mod-
els and schedulability analysis tools meta-models.
3 HIGH-LEVEL
METHODOLOGIES AND
SCHEDULABILITY ANALYSIS
TOOLS FOR AUTOMATIC
SCHEDULABILITY ANALYSIS
OF MULTIPROCESSOR
SYSTEMS
While dealing with complex systems, the use of high-
level languages and techniques reduces designers’ ef-
fort and overcomes the design challenges.
In this section, we give an overview of the used lan-
guages, techniques and tools to establish a high-level
schedulability analysis step.
3.1 MDE
The Model Driven Engineering (Schmidt, 2006) is a
software development methodology considered to be
an effective solution that simplifies the design pro-
cess since it focuses on the abstract representation
of domains rather than on computing concepts such
as algorithmic concepts. The promoted idea of the
MDE paradigm is to use models at different level of
abstraction while designing systems to raise the ab-
straction level of systems specification and increase
the automation of their development. MDE is based
on three main concepts which are meta-model, model
and model transformation.
A model is often specified using Domain Specific
Language (DSL) that can be graphical or textual such
as UML, MARTE, etc. In fact, different transforma-
tion techniques are available in the literature such as
M2T and M2M.
The M2T type, which represents a mapping from
a model to a text, is based on existing parsers
(such as XML/XSLT) that are based on pro-
gramming languages (JAVA) or mapping templates
(JET/ACCELEO). Regarding the M2M technique, it
uses mapping languages (ATL or Kermeta) to trans-
late a meta-model to another meta-model while adopt-
ing a syntactic and semantic analysis.
In our proposal, we adopt the M2T transformation
to transform the system model into a schedulability
analysis meta-model and then establish an automatic
schedulability analysis at early design stages.
In this context, we have implemented an ACCELEO
template (ECLIPSE, 2008) to perform this transfor-
mation.
3.2 MARTE
MARTE is a profile adopted by the Object Manage-
ment Group (OMG) to replace the UML Profile for
Schedulability, Performance and Time (SPT) (OMG,
2002). This profile defines foundations to support
specification, design and verification of RTES. It pro-
vides a common way of modeling both hardware and
software aspects. MARTE is considered as one of the
most commonly used high-level language for com-
plex systems modeling. Considerably, it models prop-
erly temporal requirements of RTES.
MARTE encloses different sub-profiles providing a
big set of stereotypes and attributes to annotate mod-
els with data, which are required to establish specific
analysis. Among these sub-profiles, we cite Generic
Resource Modeling (GRM), Software Resource Mod-
eling (SRM), Hardware Resource Modeling (HRM),
Generic Quantitative Analysis Modeling (GQAM),
Performance Analysis Modeling (PAM), SAM, etc.
What is worthwhile to note is that originally
MARTE supported only monoprocessor and parti-
tioned scheduling.
In this context, extensions of MARTE have been doc-
umented to support both semi-partitioned and global
scheduling (Magdich et al., 2012)(Magdich et al.,
2013a)(Magdich et al., 2013b). These extensions are
used in this paper to model the studied system.
3.3 Schedulability Analysis Tools for
Multiprocessor Scheduling
To validate temporal requirements of critical applica-
tions, various tools for scheduling analysis have been
documented in the literature such as MAST (Gonza-
lez Harbour et al., 2001), Cheddar (Singhoff et al.,
2004), (Rubini et al., 2013), RealtssMP (Ramirez
et al., 2012), STORM Simulation TOol for Real-time
Multiprocessor scheduling (Urunuela et al., 2010),
Colored Petri Nets (CPN) tools (cpn, 2015), etc.
The cited scheduling analysis tools may be used to
analyze systems which are scheduled using monopro-
cessor or multiprocessor scheduling approaches.
Considering multiprocessor scheduling approaches,
only the partitioned and global scheduling approaches
are supported by these tools. On the other hand, these
tools are designed to validate, test and analyze sys-
tems without handling with direct overheads such as
ICSOFT-EA 2016 - 11th International Conference on Software Engineering and Applications
204

Figure 1: Early schedulability analysis methodology based on MDE and Simso tool.
scheduling overheads and context switching.
To deal with this issue, SimSo tool for Simula-
tion of Multiprocessor Scheduling with Overheads
(Chéramy et al., 2014) has been proposed. This open
source tool is used in our proposal since it supports
both semi-partitioned and global scheduling. The in-
put of the considered tool is an XML file that encloses
all the needed criteria for temporal verification.
Consequently, the challenge addressed in this paper
is the transformation of a MARTE model supporting
semi-partitioned or global scheduling to SimSo meta-
model for early and automatic schedulability analysis.
4 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
FOR AUTOMATIC
SCHEDULABILITY ANALYSIS
AT AN EARLY STAGE
The proposed methodology enables automatic
schedulability analysis of RTES at early design
stages while supporting both semi-partitioned and
global scheduling approaches. Figure 1 shows the
different steps adopted by our methodology to check
the temporal correctness of RTES.
To validate temporal correctness of RTES, SimSo
tool that accepts only XML file as input is used in our
proposal.
Given a system model annotated through MARTE
profile and mainly using GRM and GQAM (Step1),
a M2T transformation must be performed to translate
the system properties from the MARTE model to the
meta-model of SimSo tool. In this context, we have
implemented an ACCELEO template (Figure 2) to
support this transformation (Step2).
This template implements transformation of MARTE
concepts to SimSo meta-model concepts.
The execution of the implemented template allows
the generation of an XML file, which contains the
system properties (Step3).
This file will be entered to the SimSo tool for
schedulability analysis check (Step4). In case of
non schedulability, a feed-back has to be done for
MARTE model rectification. Table1 shows some of
transformation concepts from MARTE to SimSo.
Table 1: MARTE to SimSo transformation concepts.
MARTE SimSo
Processor
stereotypes
«HwProcessor» processor
and
annotations
«HwComputing
Resource»
«name» name
«speedFactor» speed
Tasks
stereotypes
and
annotations
«SwSchedulable
Resource»
task
«isPreemptable» preemptible
«type» task_type
«periodElements» period
Scheduler
stereotypes
«GaExecHost» sched
and
annotations
«Scheduler»
«otherSchedPolicy» class
For example, a class annotated through the stereotype
«HwProcessor» or «HwComputingResource» (or
both of them) models a processor. It is transformed
to an element named processor.
«speedFactor» is an attribute of the stereotypes
«HwProcessor» and «HwComputingResource». It is
transformed to the element name.
«SwSchedulableResource» is used to annotate a class
which models a task. It is transformed to the element
task. «isPreemptible» is a MARTE attribute that is
used to specify whether a task may be interrupted. It
is transformed to the element preemptible.
The stereotypes «GaExecHost» and «Scheduler» are
used to annotate a class, which models a scheduler.
From UML/MARTE Models of Multiprocessor Real-time Embedded Systems to Early Schedulability Analysis based on SimSo Tool
205
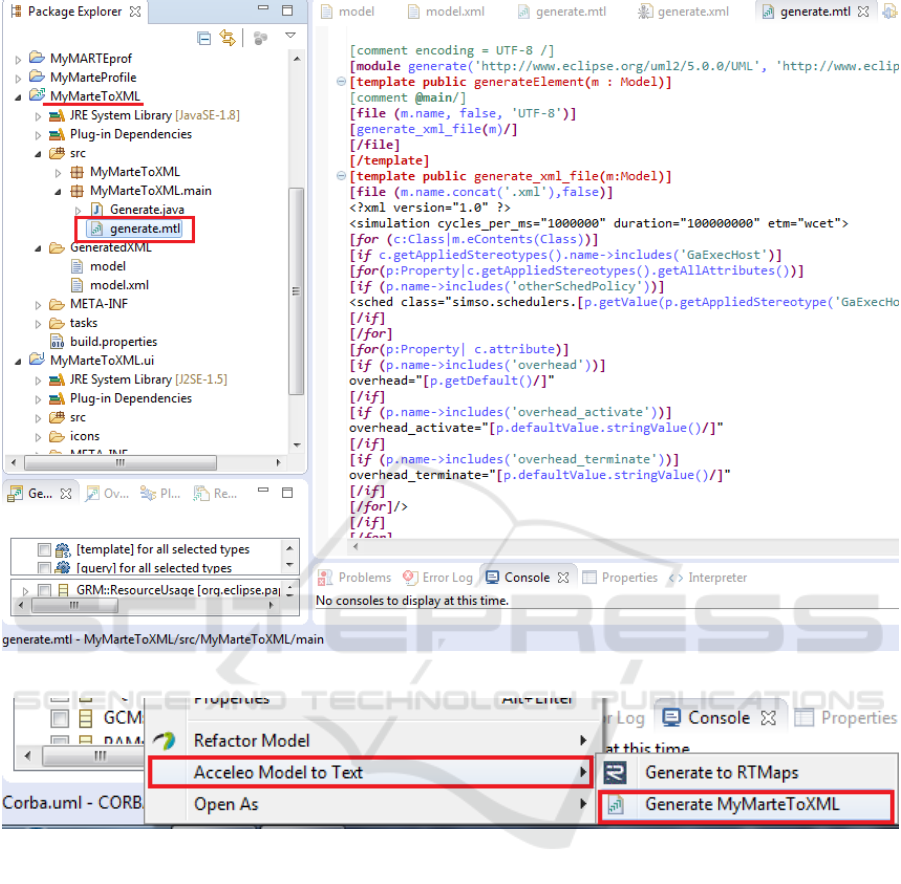
Figure 2: ACCELEO template for MARTE to XML transformation.
Figure 3: ECLIPSE plugin for automatic MARTE to XML transformation.
These stereotypes are transformed to the element
sched. The attribute «otherSchedPolicy» is used
to specify the name of the scheduling policy. It
is transformed to the element class. To automate
any model to text transformation from MARTE to
XML model, we have transformed the implemented
ACCELEO code into an ECLIPSE plugin (Figure3).
5 CASE STUDY
To evaluate the proposed methodology for early
schedulability analysis, we have considered the Real-
Time CORBA avionics application (Madl, 2009). The
system application is composed of eleven periodic
and independent tasks such that every task is charac-
terized by a WCET (Worst Case Execution Time), a
period, a priority and a deadline (Table 2).
These parameters will be used as input for the schedu-
lability analysis step. Thus, they have been specified
in the MARTE model of CORBA system.
These properties must be entered in the tasks classes
annotated through «SwSchedulableResource» stereo-
type. Other parameters, such as the scheduling type
(static or dynamic scheduling), must also be speci-
fied to handle this step. The considered application
is mapped to a preemptive execution platform com-
posed of three identical processors running at 4GHz
using 6GB three-channel RAM. The modeling of the
studied system using UML/MARTE is exposed via
Figure 4. As specified in Table 2, Gps task is peri-
odic, which is indicated through the attribute «type:
ICSOFT-EA 2016 - 11th International Conference on Software Engineering and Applications
206

Table 2: Tasks parameters for CORBA application.
Task WCET Deadline Period Priority
Gps 21 100 5 41
Airframe 53 100 15 42
Pilot_waypoints 37 100 5 43
Routes 18 100 10 44
Display_device 26 150 10 47
Af_monitor 33 120 5 49
Nav_display 14 80 5 48
Nav_steering 69 100 5 46
Navigato _navsteering _points 42 150 10 45
Pilot _control 43 100 20 50
Tactical _steering 38 80 10 51
Figure 4: The static view of the CORBA application.
ArrivalPattern» that is set to «periodic(5,ms)».
The priority of Gps task is 41, which is spec-
ified through the attribute «priority:NFP_Integer
[0..*] =priority». The deadline and period of
Gps task are respectively specified through «dead-
line:NFP _Duration[0..*] = deadline» and «pe-
riod:NFP_Duration[0..*]= period» such that the dead-
line and the period are respectively set to (100,ms)
and (5,ms).
The activation date of Gps is set to 0 ms through «ac-
tivationDate:NFP_ Duration [0..*]=(0,ms)». The re-
quired scheduling type is static, which is mentioned
by setting the value of «isStaticSchedulingFeature»
to «true». The used scheduling algorithm is EDZL
(Lee and Shin, 2013). Using our ECLIPSE plugin for
MARTE to XML transformation, the MARTE model
for CORBA application has been transformed into an
XML file that will be entered to SimSo tool. Figure
5 shows the contents of the generated XML file under
ECLIPSE. The generated XML file has been entered
From UML/MARTE Models of Multiprocessor Real-time Embedded Systems to Early Schedulability Analysis based on SimSo Tool
207
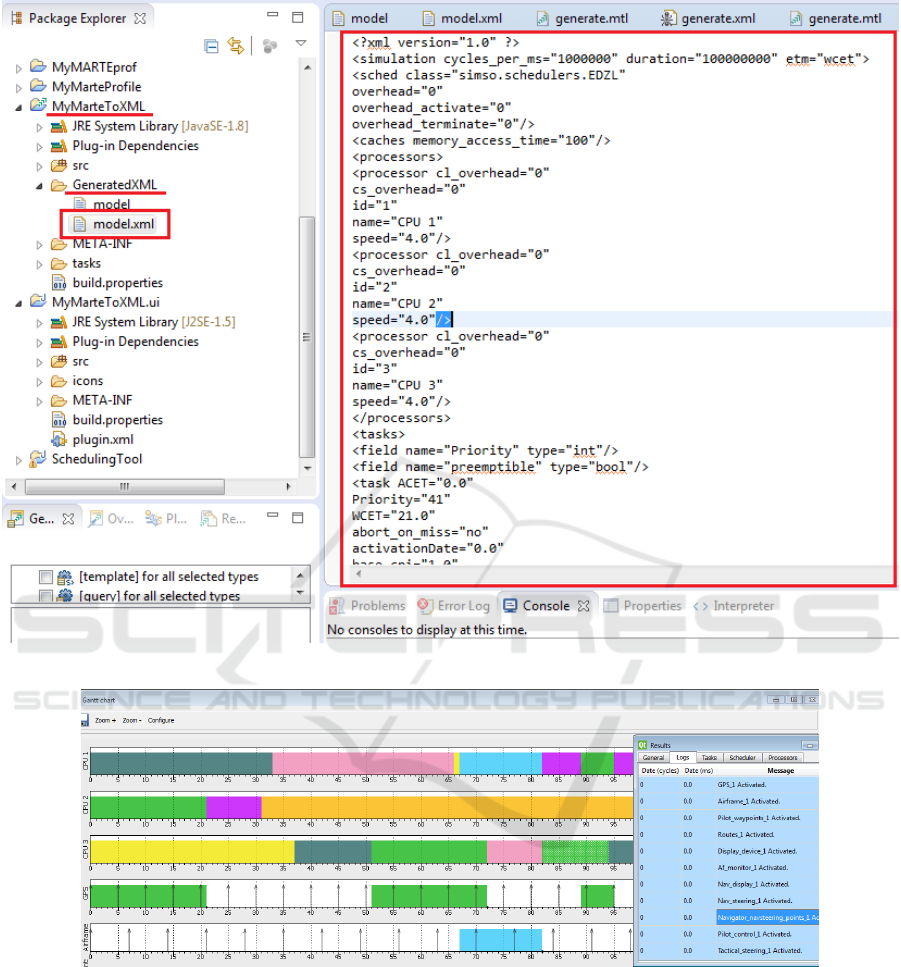
Figure 5: Generated XML file after a M2T transformation.
Figure 6: Simso tool schedulability analysis report.
into SimSo for schedulability analysis of CORBA
application. Results have shown that the system is
schedulable (Figure 6).
6 CONCLUSIONS
Throughout this paper, we have proposed an MDE-
based automatic schedulability analysis at early de-
sign stages. Based on a M2T transformation from
MARTE model to SimSo tool meta-model, prop-
erties of the studied system were translated from
MARTE model to an XML file representing the input
of SimSo. A main key of this proposal is that is sup-
ports analysis of systems, which are scheduled using
semi-partitioned and global scheduling approaches.
ICSOFT-EA 2016 - 11th International Conference on Software Engineering and Applications
208

REFERENCES
(2015). Cpn tools http://cpntools.org/.
Abdeddaïm, Y., Chandarli, Y., Davis, R. I., and Masson, D.
(2014). Schedulability analysis for fixed priority real-
time systems with energy-harvesting. In Proceedings
of the 22Nd International Conference on Real-Time
Networks and Systems, RTNS ’14, pages 311:311–
311:320, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Chéramy, M., Hladik, P.-E., and Déplanche, A.-M. (2014).
Simso: A simulation tool to evaluate real-time multi-
processor scheduling algorithms. In The 5th Interna-
tional Workshop on Analysis Tools and Methodologies
for Embedded and Real-time Systems, WATERS.
Dorin, F., Yomsi, P. M., Goossens, J., and Richard, P.
(2010). Semi-partitioned hard real-time scheduling
with restricted migrations upon identical multiproces-
sor platforms. CoRR, abs/1006.2637.
ECLIPSE (2008). Acceleo http://wiki.eclipse.org/acceleo.
Gonzalez Harbour, M., Gutierrez Garcia, J., Palen-
cia Gutierrez, J., and Drake Moyano, J. (2001). Mast:
Modeling and analysis suite for real time applications.
In Real-Time Systems, 13th Euromicro Conference on,
2001., pages 125–134.
HadjKacem, Y., Mahfoudhi, A., Magdich, A., Karamti, W.,
and Abid, M. (2012). Using mde and priority time
petri nets for the schedulability analysis of embed-
ded systems modeled by uml activity diagrams. In
the 19th Annual IEEE International Conference and
Workshops on the Engineering of Computer Based
Systems (ECBS), pages 316–323.
Hagner, M. and Huhn, M. (2008). Tool support for a
scheduling analysis view. In The workshop "Model-
ing and Analysis of Real-Time and Embedded Systems
with the MARTE UML profile" at DATE’08 (Design,
Automation & Test in Europe).
Henia, R., Hamann, A., Jersak, M., Racu, R., Richter, K.,
and Ernst, R. (2005). System level performance anal-
ysis - the symta/s approach. Computers and Digital
Techniques, IEE Proceedings -, 152(2):148–166.
Jensen, K. E. (2009). Schedulability analysis of embed-
ded applications modelled using MARTE. PhD thesis,
Technical University of Denmark.
Lee, J. and Shin, I. (2013). Edzl schedulability analysis in
real-time multicore scheduling. IEEE Transactions on
Software Engineering, 39(7):910–916.
Madl, G. (2009). Model-based Analysis of Event-driven
Distributed Real-time Embedded Systems. PhD the-
sis, Long Beach, CA, USA.
Magdich, A., Hadj Kacem, Y., Mahfoudhi, A., and Abid,
M. (2013a). Reducing uml/sam modeling view size
for schedulability analysis. In The 1st IEEE interna-
tional conference on Computer Applications Technol-
ogy (ICCAT). IEEE.
Magdich, A., Kacem, Y. H., and Mahfoudhi, A. (2013b).
Extending uml/marte-grm for integrating tasks migra-
tions in class diagrams. In Lee, R. Y., editor, 11th In-
ternational Conference on Software Engineering Re-
search, Management and Applications SERA (selected
papers), volume 496 of Studies in Computational In-
telligence, pages 73–84. Springer.
Magdich, A., Kacem, Y. H., Mahfoudhi, A., and Abid, M.
(2012). A MARTE extension for global scheduling
analysis of multiprocessor systems. In the 23th IEEE
International Symposium on Software Reliability En-
gineering (ISSRE), pages 371–379.
Medina, J. L. and Cuesta, A. G. (2011). From composable
design models to schedulability analysis with uml and
the uml profile for marte. SIGBED Rev., 8(1):64–68.
Mraidha, C., Tucci-Piergiovanni, S., and Gerard, S. (2011).
Optimum: A marte-based methodology for schedula-
bility analysis at early design stages. SIGSOFT Softw.
Eng. Notes, 36(1):1–8.
Naija, M., Ahmed, S. B., and Bruel, J. (2015). New
schedulability analysis for real-time systems based on
MDE and petri nets model at early design stages. In
ICSOFT-EA 2015 - Proceedings of the 10th Interna-
tional Conference on Software Engineering and Ap-
plications, Colmar, Alsace, France, 20-22 July, 2015.,
pages 330–338.
OMG (2002). Uml profile for schedulability, performance
and time.
OMG (2008). A uml profile for marte: Modeling and anal-
ysis of real-time embedded systems.
Ramirez, A. D., Valenzuela, D. K. O., and Mejía-Alvarez, P.
(2012). A multiprocessor real-time scheduling simu-
lation tool. In 22nd International Conference on Elec-
trical Communications and Computers, CONIELE-
COMP 2012, Cholula, Puebla, Mexico, February 27-
29, 2012, pages 157–161.
Rubini, S., Fotsing, C., Singhoff, F., Tran, H. N., and Dis-
saux, P. (2013). Scheduling analysis from architec-
tural models of embedded multi-processor systems.
EWiLi Workshop.
Schmidt, D. C. (2006). Model-driven engineering. IEEE
Computer, 39.
Singhoff, F., Legrand, J., Nana, L., and Marcé, L. (2004).
Cheddar: A flexible real time scheduling framework.
In Proceedings of the 2004 Annual ACM SIGAda In-
ternational Conference on Ada: The Engineering of
Correct and Reliable Software for Real-time &Amp;
Distributed Systems Using Ada and Related Technolo-
gies, SIGAda ’04, pages 1–8, New York, NY, USA.
Urunuela, R., Déplanche, A. M., and Trinquet, Y. (2010).
Storm a simulation tool for real-time multiprocessor
scheduling evaluation. In Emerging Technologies and
Factory Automation (ETFA), 2010 IEEE Conference
on, pages 1–8.
Zhang, F. and Burns, A. (2009). Schedulability analysis for
real-time systems with edf scheduling. IEEE Transac-
tions on Computers, 58(9):1250–1258.
From UML/MARTE Models of Multiprocessor Real-time Embedded Systems to Early Schedulability Analysis based on SimSo Tool
209
