
Evaluation of Handwriting Characteristic
for Two-factor Authentication Interface on Touch-pad Panel
Moe Sasaki and Masaki Inamura
Informatics, Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Graduate School of Tokyo Denki University,
Ishizaka, Hiki-gun, Hatoyama-machi, Saitama, Japan
Keywords: Authentication, Two-factor Authentication, Identification, Biometrics, Handwriting, Touch-pad.
Abstract: Frequencies of user authentication increase and spread of smartphone and tablet advances rapidly in recent
years. However, it is a great challenge that password authentication is easy to be attacked and must be solved.
We assume authentication, which use touch panel and handwriting as an authentication element in this paper.
As far as we know, there have few papers about generating a digital data from handwriting. Therefore, our
contribution of this paper is to define handwriting characteristics of a letter that can convert into a digital data
and evaluate possibility of the conversion.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, with spreading smartphone and tablet,
it is possible to be easily connected to Internet. In
addition, frequencies of user authentication increase
when users use service on Internet. Password
authentication accounts for approximate 80% of user
authentications (Symantec Corporation, 2013).
However, it is thought that users set a password that
is easy to be guessed in user authentication because
of difference of security awareness of users. By the
reasons that I mentioned above, assailants can easily
attack such as dictionary attack, which enters from
beginning to end in all of words.
Two-factor authentication is known as solution to
problem of password authentication. A security token
is used as an authentication element to use together
with a password in two-factor authentication.
However, users must have it. In contrast, users don’t
have to have it in the case of biological information.
In addition, touch-pad panel, which device have
become widespread. Therefore, we use handwriting
as a authentication element with a password in two-
factor authentication in this paper.
Because it is thought that an input pattern is not
the same digital data every time, general handwriting
authentication apply pattern matching of handwriting
and measure similarity by comparing an input
handwriting pattern with a handwriting pattern
registered beforehand. On the other hand, digital data
are considered to be password and can be introduced
into an existing authentication protocol(Masaki,
2015). If digital data which are different each
individual can be output every time by a handwriting
pattern, they can be used generating of key for
authentication. Handwriting authentication can be
implemented by an existing authentication protocol
without implementing a new protocol for handwriting
authentication and can be expected cost reduction.
Therefore, our contribution of this paper is to
define handwriting characteristics of a letter, which
can convert into a digital data and evaluate possibility
of conversion. We suggest differences of
characteristics of the handwriting inputted by the
application and examine whether to convert it into
{0,1}
n
.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows.
In section 2, we denote examples of user authentication
and its problems. In section 3, we describe the
characteristic of a handwriting which convert into a
binary digit. In section 4, we denote procedures in the
experiment to collect handwriting. We provide a
conclusion and a discussion in section 5.
2 USER AUTHENTICATION
In section 2.1, we denote challenge response method in
password authentication and problem of password
106
Sasaki, M. and Inamura, M.
Evaluation of Handwriting Characteristic for Two-factor Authentication Interface on Touch-pad Panel.
DOI: 10.5220/0005992501060111
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2016) - Volume 2: ICE-B, pages 106-111
ISBN: 978-989-758-196-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
authentication. We denote two-factor authentication in
section 2.2, and physical characteristic in section 2.3.
2.1 Password Authentication
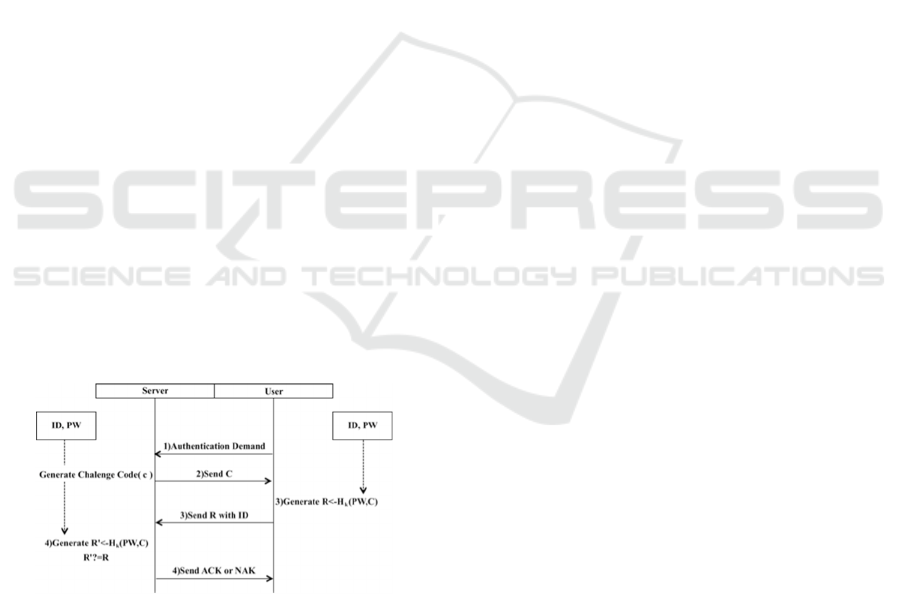
2.1.1 Challenge Response
Challenge response is proved that third party can’t
obtain password of users because a response code,
that is encrypted and a challenge code, that is
generated by random number generator are delivered
on packet on network (Atsuko and Hiroaki, 2003).
The following procedure is CHAP (Challenge
Handshake Authentication Protocol) (Simpson,
1996), which is used challenge response method in
password authentication. A password is encrypted by
hash function with the key in challenge response
method. Just for information, hash function link hash
value and digital data that is called for private key and
calculate it.
1. Users send a server authentication demand.
2. The server generates challenge code (hereinafter
it is called C) by random number generator and
sends the user it.
3. The user encrypts C with a password (hereinafter
it is called PW) that the user has by hash function
with the key (hereinafter it is called R ←
H
K
(PW,C)) and sends the server it with user’s ID.
4. The server encrypts C with administered PW
bound to the ID, verifies whether generated value
and received value in procedure 3 are identical or
not (“ACK” means success of this verification,
and “NAK” means failure of this verification),
and notifies the user of result of this verification.
Figure 1: Procedure of CHAP.
2.1.2 Problems
Password authentication is a user authentication that
use password bound to user’s ID as an authentication
element. Password authentication accounts for
approximate 80% of user authentications (Symantec
Corporation, 2013). However, it is thought that users
set a password that is easy to be guessed such as
user’s birthday in user authentication because of
difference of security awareness of users. In addition,
there are a lot of the users who use a same password
in plural sites because remembering plural passwords
is a burden for the users (Information-technology
Promotion Agency Japan, 2014).
From the above a reason, assailants obtain lists of
user’s ID and password bound to user’s ID and try
login using it illegally (Information-technology
Promotion Agency Japan, 2015). As a result,
information leaks occur frequently.
2.2 Two-factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication is a user authentication,
that uses two authentication elements in three
authentication elements shown below (SOPHOS,
2014).
1) Information that users memorize
(E.g. password, personal identification number)
2) Objects which users possess (e.g. IC card, token)
3) Characteristics that users have
(E.g. handwriting, fingerprints)
The problem that was described in 2.1.2 needs a
solution. Therefore, a goal of this study is to
strengthen security of password authentication by
adding one authentication element.
Handwriting is used for an authentication element
with a password in this paper and the reason is
denoted in 3.1.
2.3 Behavioral Characteristic
First, biological information is classified in two types.
The first of two types is physical features such as iris
and fingerprint, and the second of two types is
behavioral characteristics such as handwriting and
walking (Atsuko and Hiroaki, 2003). Using
biological information for an authentication element
has advantages for users. We denote advantages and
defects of the two types as follows.
Possibility of the authentication that use physical
features accept another persons is extremely low
(Information-technology Promotion Agency Japan,
2012). However, changing physical features that are
used for an authentication element is difficult when
physical features leaked out. On the other hand, users
feel less resistance to authentication that use
behavioral characteristics (Kensuke et al., 2015) and
can easily change behavioral characteristics
(Information-technology Promotion Agency Japan,
2015).
Evaluation of Handwriting Characteristic for Two-factor Authentication Interface on Touch-pad Panel
107
3 HANDWRITING FOR
SAMPLING DIGITAL DATA
As described in section 2.3, authentication that uses
behavioral characteristics has many advantages.
Device with touch-pad panel are widely diffused.
Therefore, we focus on handwriting that can be
inputted by touch-pad panel.
A few authentication systems that use
handwriting are proposed (Hitachi Systems, 2002;
Witswell, 2012). However, few studies have focused
on possibility of conversion from handwriting to
digital data. Therefore, we discuss using handwriting
not only for an authentication element with password
but also for private key. As a previous step, we define
handwriting characteristics of a letter to convert into
digital data and evaluate possibility of the conversion
in this paper.
We denote handwriting skill in section 3.1 and
standard for converting handwriting into a digital data
in section 3.2.
3.1 Handwriting Skill
We convert handwriting into a digital data based on
difference of a handwriting characteristic.
It has been proposed that individual difference of
handwriting is caused by difference of handwriting
skill (Yoshikazu and Junichi, 1994). Table 1 shows
classification of handwriting skill (Yoshikazu and
Junichi, 1994). Therefore, we define handwriting
characteristics based on handwriting skill.
Table 1: Category of Handwriting skill.
3.2 Data Judgment by Difference in
Handwriting Letter
Image data of handwriting are collected in the
experiment. Therefore, molding method was referred
as standard for evaluation in handwriting skill
because handwriting characteristics are easy to be
distinguished in image data.
Molding method is constitution of length and
direction of points and lines in a letter, or constitution
of how lines in a letter cross. We choose how lines in
a letter cross on the basis of standards of handwriting
characteristics in molding method because it is easy
to convert it into a binary digit such as 0 or 1.
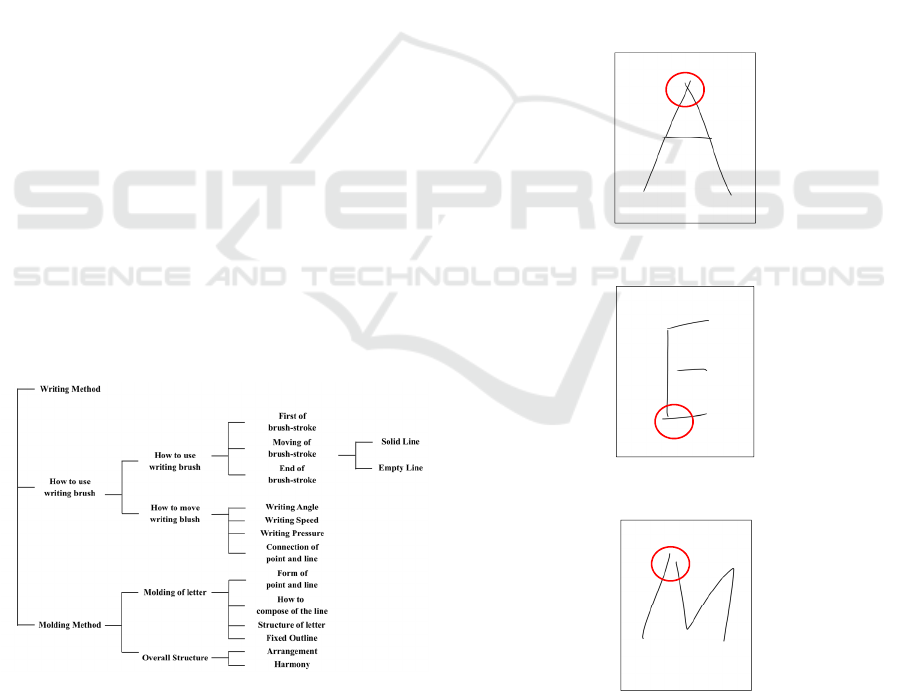
We define three handwriting characteristics in a
letter that can convert into a digital data.
The first handwriting characteristic in this paper
is whether two lines protrude in other words; two
lines intersect in a part that the two lines contact in
normal situation. A binary digit becomes 1 when two
lines intersect in the part in a letter. A binary digit
becomes 0 when the two lines contact in the part.
Figure 2 shows “A” of a capital letter of alphabet as
an example of the first handwriting characteristic in
this paper.
Figure 2: Example of two lines intersect.
Figure 3: Example of one line protrudes.
Figure 4: Example of two lines don’t contact.
The second handwriting characteristic in this
paper is whether one line of two lines protrudes in a
part that the two lines contact in normal situation. A
ICE-B 2016 - International Conference on e-Business
108
binary digit becomes 1 when one line of two lines
protrudes in the part in a letter. A binary digit
becomes 0 when two lines contact in the part. Figure
3 shows “E” of a capital letter of alphabet as an
example of the second handwriting characteristic in
this paper.
The third handwriting characteristic in this paper
is whether two lines don’t contact in a part that the
two lines contact in normal situation. A binary digit
becomes 1 when two lines don’t contact in the part in
a letter. A binary digit becomes 0 when two lines
contact in the part. Figure 4 shows “M” of a capital
letter of alphabet as an example of the third
handwriting characteristic in this paper.
4 EXPERIMENT METHOD
We assume authentication that use touch-pad panel
because of spread of smartphone or tablet, and
accessibility for users in this paper.
Therefore, we make an android application that
saves image data of letters that is written with a
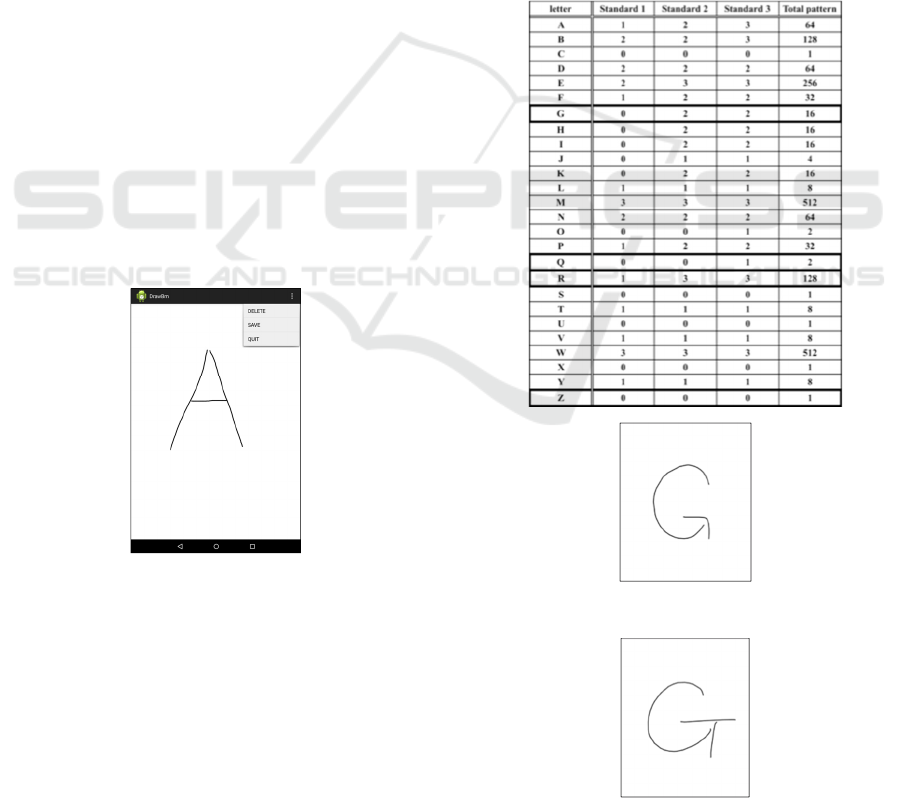
finger. Figure 5 shows a screen shot of collecting
letters. The application collected image data of capital
letters of alphabet from 22 subjects (All Japanese).
Capital letters of alphabet was chosen because it was
desirable that there were many letters that were
comprised of straight lines on using the three
handwriting characteristics.
Figure 5: Screen shot of collecting image data.
5 EVALUATION
We collected image data of letters by the experiment
shown in section 4 and evaluated every letter. We
denote result of evaluation of letters in section 5.1 and
show consideration of the result of evaluation in
section 5.2.
5.1 Result of Evaluation
Table 2 shows result of evaluation of letters. Standard
1 or 2, 3 correspond to handwriting characteristics
shown in section 3.2. Total pattern is the maximum
number of bit that a letter can express and is an object
for comparison in this paper. To give an actual
example, “A” has six characteristic points. Therefore,
total pattern of “A” is 2
6
= 64.
Letters that were surrounded with bold frame have
individual difference of form of the letters in table 2.
Explanation every letter is below.
Firstly, there are subjects who write after the
second of stroke order of G such as Figure 6 or Figure
7. As a factor of the result, we expect difference in
form of ‘G’ that subjects write.
Table 2: Result of evaluation.
Figure 6: Example1 of “G”.
Figure 7: Example2 of “G”.
Evaluation of Handwriting Characteristic for Two-factor Authentication Interface on Touch-pad Panel
109

Secondly, there were subjects who write “R” or
“Q” in block letters or in cursive letters, they were
mixed. As a factor of the result, we expect that
difference in form of the letters that subjects write is
big because English is not native language for the
subjects.
Figure 8: Example of “Z”.
Thirdly, there are subjects who add one line to “Z”
such as Figure 8 or don’t add one line to “Z”. As a
factor of the result, it is thought that there are subjects
who add one line to “Z” to distinguish number of 2
from it.
5.2 Discussion
5.2.1 Handwriting Characteristic
We compared three handwriting characteristics
shown in section3.2. The mean value of total pattern
that is the maximum number of bit that a letter can
express was used for comparison. The following is a
result of comparison.
Standard 1 < Standard 2 < Standard 3
Standard 1 is whether two lines intersect, Standard
2 is whether one line of two lines protrudes, and
Standard 3 is whether two lines don’t contact.
Standard3 had a mean value that was bigger than
mean values that the others standards had.
As a factor of the result, a part that lines received
for the subject’s finger writing letters was hard for
subjects to be seen because line weight that is used in
the application which the subjects wrote letters with a
finger was thin. Therefore, future issue is to change
line weight that is used in the application and test it.
5.2.2 Evaluation of Letter
We found that there are differences of form of the
letters that subjects write shown in section 5.1. These
differences of form of the letters are future issues.
The number of the letters that is valid as an
authentication element is shown below. Standard that
was chosen is that the maximum number of bit that a
letter can express is more than two patterns. As a
result, 21 of 26 characters are valid. In other words,
approximate 80% of alphabet of capital letter is valid.
In addition, the mean of the maximum of bit that
alphabet of capital letter can express was 90 patterns.
(The decimal value was cut off.)
Evaluation in this paper is only whether
conversion from the three handwriting characteristics
to a binary digit is possible and comparison of the
maximum number of bit that a letter can express.
Therefore, future issues are combination of the letters
and the number of digits of bit that is used for an
authentication element.
6 CONCLUSION
We define handwriting characteristics of a letter to
convert into digital data and evaluate possibility of
the conversion. As a result, the present result
suggested validity of converting the handwriting
characteristics into digital data. Future topics of
discussion are line weight that subjects write letters
with a finger and individual difference of form of
letters.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We wish to thank Mr. Hashimoto, who studies at
Tokyo Denki University, for supporting our study.
REFERENCES
Miyazi, A., Kikuchi, H., 2003. Information Security,
Ohmsha, Ltd., Tokyo.
Hitachi Systems, Ltd, 2002. Handwriting signature
certification solution, https://www.hitachi-
systems.com/news/2002_j/download/020926.pdf
Information-technology Promotion Agency Japan, 2012.
Trend of the use and the utilization of the biometrics
authentication technology in the United States,
https://www.ipa.go.jp/files/000001952.pdf
Information-technology Promotion Agency Japan, 2014.
Fact-finding paper of the online person certification
method, https://www.ipa.go.jp/files/000040778.pdf
Information-technology Promotion Agency Japan, 2015.
Guidelines for biometrics authentication introduction
and use, http://www.ipa.go.jp/files/000013804.pdf
Information-technology Promotion Agency Japan, https://
www.ipa.go.jp/security/vuln/10threats2016.html.
Sakata, K., Takahashi, D., Okamoto, N., 2015. One
discussion about handwriting collation using the note
taking with the finger in the three-dimensional space. In
ICE-B 2016 - International Conference on e-Business
110

ITE Technical Paper. Vol.39, No.8, ME2015-45, pp.
37-40.
Inamura, M., 2015. Expansions of CHAP -
Modificationless on Its Structures of Packet and Data
Exchange, In ICISSP’15, International Conference on
Information Systems Security and Privacy. pp.213-220.
Simpson, W. A., 1996. PPP challenge handshake
authentication protocol (CHAP), Request for
Comments 1994.
SOPHOS. Merit of Two-factor Authentication ~ Knowing
Two-factor Authentication. https://www.sophos.com/
ja-jp/press-office/press-releases/2014/02/jpn-ns-the-
power-of-two-all-you-need-to-know-about-2fa.aspx
Symantec Corporation. Attitude survey about the password
management of an individual and the company.
http://internet.watch.impress.co.jp/docs/news/2013103
1_621665.html
Witswell Consulting & Solutions Inc. Security / signature
certification / cyber SIGN. http://www.witswell.co.jp/
cybersign/
Nakamura, Y., Toyoda, J., 1994. An Extraction of
Individual Handwriting Characteristics Based on
Calligraphic Skill. In The Institute of Electronics,
Information and Communication Engineers. Vol.J77-
D-II, No.3, pp.510-518.
Evaluation of Handwriting Characteristic for Two-factor Authentication Interface on Touch-pad Panel
111
