
From Natural-language Regulations to Enterprise Data using Knowledge
Representation and Model Transformations
Deepali Kholkar, Sagar Sunkle and Vinay Kulkarni
Tata Consultancy Services, Pune, India
Keywords:
Formal Compliance Checking, Knowledge Representation, Knowledge Base, Fact-oriented Model, SBVR,
Model Transformation, Reasoning, Defeasible Logic, Enterprise Data Integration.
Abstract:
Enterprises today face an unprecedented regulatory regime and are increasingly looking to technology to
ease their regulatory compliance concerns. Formal approaches in research focus on checking compliance of
business processes against rules, and assume usage of matching terminology on both sides. We focus on
run-time compliance of enterprise data, and the specific problem of identifying enterprise data relevant to a
regulation, in an automated manner. We present a knowledge representation approach and semi-automated
solution using models and model transformations to extract the same from distributed enterprise databases.
We use a Semantics of Business Vocabulary and Rules (SBVR) model of regulation rules as the basis to arrive
at the necessary and sufficient model of enterprise data. The approach is illustrated using a real-life case study
of the MiFID-II financial regulation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Enterprises today face an unprecedented regulatory
regime (Reuters, 2016). Regulators have put in place
measures for ensuring greater transparency in deal-
ings of financial institutions and stricter oversight by
regulatory bodies, to prevent recurrence of financial
crises. Compliance is mandatory and non-compliance
is heavily penalized. In order to avoid millions of dol-
lars in fines and the associated loss of reputation, reg-
ulatory compliance has assumed critical importance
for enterprises.
Regulatory compliance is a manual process in cur-
rent industry practice, and heavily dependent upon
experts. Due to these reasons, costs of achieving
compliance are very high (English and Hammond,
2014). Enterprises are increasingly looking to tech-
nology and automation to contain costs and mitigate
the risk of non-compliance.
Taking a model-theoretic view
1
, the regulatory
compliance checking problem can be formally de-
fined as
EM |= R (1)
where EM denotes the model of an enterprise that
needs to satisfy the formally specified set of regula-
1
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: Model theory,
http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/model-theory/
Enterprise
operations
Compliance
Checker
Formal
Regulation
Rules R
Formal
Proof of
Compliance
Enterprise
Data EM
Natural-
language
Regulation
Text
…
Figure 1: Formal approach to compliance checking.
tion rules R. EM signifies the relevant enterprise de-
tails to be checked for compliance to R, as depicted in
Figure 1. If EM satisfies R, EM is a model of R, by
model theory.
Several approaches for formal compliance check-
ing have been proposed in literature (Governatori and
Rotolo, 2010; Awad et al., 2010; Kharbili et al.,
2008a; Governatori et al., 2009; Governatori, 2005;
Dimaresis, 2007). Each of these approaches uses a
formalism to encode R, and a reasoning engine to
check compliance of operational details of the enter-
prise EM, also encoded in the same formalism, to pro-
duce a proof of compliance, as depicted in Figure 1.
Encoding of both R and EM is done manually.
Most approaches in literature describe design-time
compliance checking (Governatori and Rotolo, 2010;
Awad et al., 2010; Kharbili et al., 2008a), where mod-
els of enterprise business processes are checked, with
the aim of detection and correction of non-compliance
60
Kholkar, D., Sunkle, S. and Kulkarni, V.
From Natural-language Regulations to Enterprise Data using Knowledge Representation and Model Transformations.
DOI: 10.5220/0006002600600071
In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Software Technologies (ICSOFT 2016) - Volume 2: ICSOFT-PT, pages 60-71
ISBN: 978-989-758-194-6
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

at the design stage, before actual enterprise systems
implement these business processes. Here, EM com-
prises business process paths. Design-time compli-
ance checking, thus, has a preventive focus. This,
although extremely important, is not sufficient. It is
imperative to institute run-time compliance checking
on enterprise systems, since that is where compliance
is desired and needs to be demonstrated by enterprises
on an ongoing basis.
Approaches for run-time compliance in literature
fall into two categories. The first category is, again,
a preventive approach that uses execution paths gen-
erated from business process models for compliance
checking. The other category does check running
enterprise systems, using business rule management
systems for production rule execution (Kharbili et al.,
2008a). However, in the latter approach, encoding of
regulation rules from natural-language (NL) regula-
tion text into the business rule management systems,
particularly, relating them to the exact enterprise data
on which they need to be executed, is a task left to
experts.
This aspect of relating the regulation to the enter-
prise, i.e. identifying the relevant EM to be checked
for compliance to R, is simplified in current ap-
proaches by assuming correspondence between labels
or terms used in specifications of R and EM. In real-
ity, there are several issues involved. One, the rela-
tion is not a direct mapping. The regulation uses a
conceptual information model at a different level of
abstraction from that used by the enterprise in its sys-
tems. The corresponding model of enterprise infor-
mation may span several enterprise systems and there-
fore, databases. Moreover, there is typically, an over-
lap between data in various systems. Finally, there is
no mapping or common enterprise-wide view of the
data. Currently, these issues are surmounted by ex-
perts with knowledge of the business and legal do-
mains as well as systems.
We focus specifically on this problem in run-time
compliance of enterprise data, viz. finding the ap-
plicability of the regulation to the enterprise, i.e., an-
swering the question: ’what is the enterprise data
EM
data
that should be checked, to ascertain the enter-
prise’s compliance to this regulation?’ We opine that,
there is a need for a method and tools that help auto-
mate to the extent possible, bridging of the concep-
tual gap between regulation text and enterprise data,
reducing the burden on experts. We believe that it is
necessary to construct a conceptual model of the reg-
ulation in order to be able to do this.
We present a knowledge representation (KR)
(Brachman and Levesque, 2004) approach and
model-driven engineering (MDE) solution to the
problem of identifying enterprise data relevant to a
regulation in an automated manner. Our specific con-
tributions are two-fold
1. A semi-automated method to arrive at the concep-
tual model of requisite enterprise data, from the
NL regulation text, by building a model of regu-
lation rules in the Semantics of Business Vocabu-
lary and Rules (SBVR)
2
formalism.
2. A semi-automated method to obtain the requisite
data (EM
data
) from enterprise data stores using the
above conceptual model for enterprise data inte-
gration (EDI).
Our overall approach is described in Section 2 and de-
tailed in Section 3, which also illustrates our method
using a real-life case study of the MiFID-II
3
financial
regulation. Section 4 discusses related work, and Sec-
tion 5 concludes the paper.
2 OVERALL APPROACH USING
KR AND MDE
Regulations are made available by regulators as NL
text. Our objective is to create a conceptual model of
the regulation, so as to be able to analyze regulation
rules, with the specific aim of understanding which
areas and entities of the enterprise they relate to. We
elect to treat this as a knowledge representation prob-
lem.
Knowledge representation (Brachman and
Levesque, 2004) is the construction of systems that
contain symbolic representations of information in a
problem space, such that the representations have the
following properties
1. they express propositions about the problem space
2. they capture the intentional stance or goals of the
problem space, and cause the system to behave in
accordance with these goals.
This definition is as per the Knowledge Representa-
tion Hypothesis (Smith, 1982).
Such systems are knowledge-based systems
(KBS) and the representations constitute knowledge
bases (KB) (Brachman and Levesque, 2004). Prop-
erty 2 is critical for a model to qualify as a knowl-
edge base. e.g. a knowledge-based system for play-
ing chess captures propositions about playing pieces
and allowed moves, as also the rules and goals of the
game.
2
SBVR: http://www.omg.org/spec/SBVR/1.2/
3
MiFID: http://ec.europa.eu/finance/securities/isd/index en.
htm
From Natural-language Regulations to Enterprise Data using Knowledge Representation and Model Transformations
61
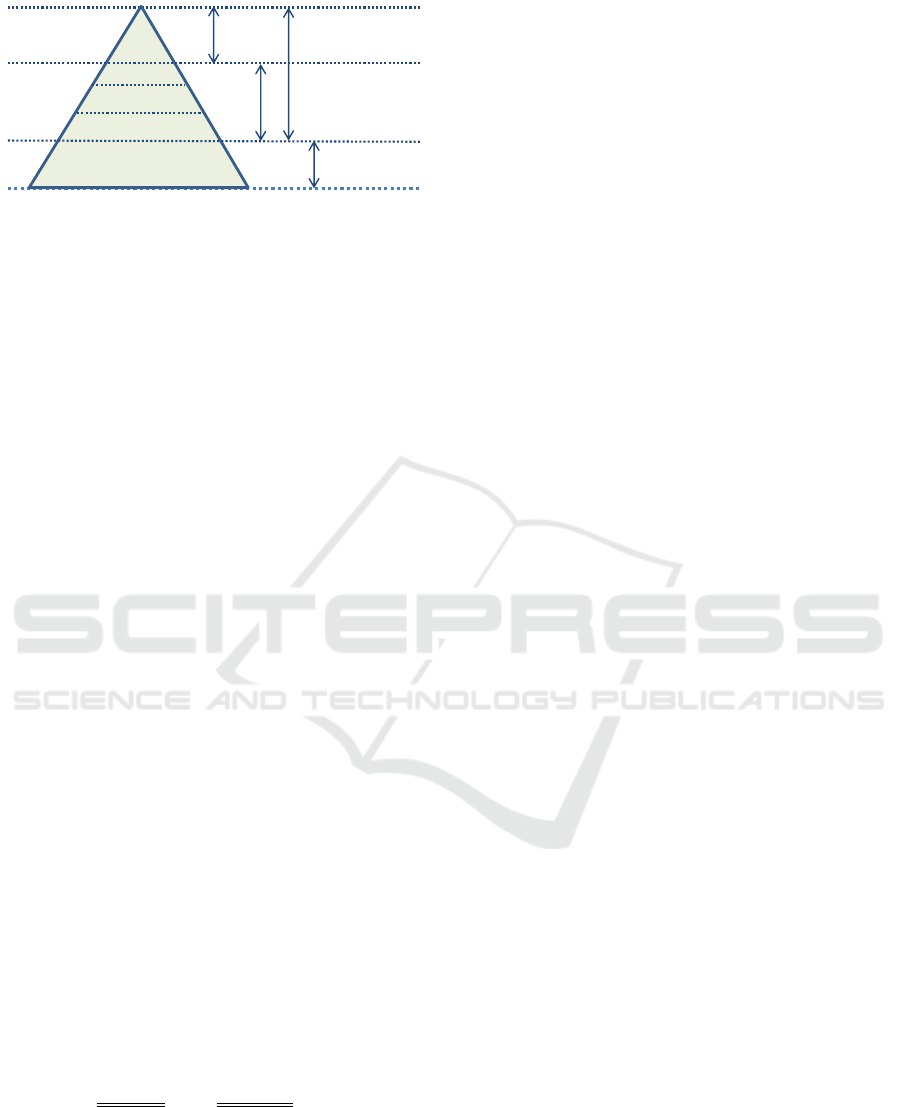
Conceptual
schema
SBVR Meta-
model
Enterprise
data as facts
Generic
layer
Domain-
specific
layer
Fact
population
Ground
facts
Knowledge
Meta-
knowledge
Regulation
model
Rules
Fact Types
Concepts
Figure 2: Layers of a fact-oriented model.
We proceed to build a knowledge base of regula-
tion rules, referred henceforth as regulation KB. It can
be easily seen that the goals of a regulation KB are, to
be able to
• Goal1: establish compliance to regulation rules
• Goal2: identify requisite data EM
data
, to check for
compliance to the rules
This means the representations of the regulation KB
a) express propositions about the problem domain of
the regulation and b) satisfy the above stated goals.
We need to pick a language to represent the reg-
ulation KB. We choose the fact-oriented modeling
(FOM) paradigm (Nijssen, 2007; Halpin, 2007), and
briefly describe the rationale for this choice in the next
sub-section.
2.1 Fact-oriented Modeling
The fact-oriented formalism captures knowledge
about the universe of discourse in the form of facts.
Facts, also called fact types, are propositions about
things in the universe of discourse e.g. Customer
holds account, account has balance. Customer, ac-
count and balance are concepts, or things in the
universe of discourse. Rules are built by imposing
modalities onto compositions of fact types. e.g. It is
obligatory that account has balance if customer holds
account.
The fact-oriented model thus represents knowl-
edge in three layers: concepts, fact types based upon
concepts, and rules based upon fact types, as shown
in Figure 2. FOM supports reasoning with data pro-
vided as a population of ground facts, shown by the
fact population layer in Figure 2. E.g. for the fact
type customer holds account, a population of ground
facts would give data of accounts held by specific cus-
tomers e.g. Cust001 holds AC10076.
FOM is therefore well-suited to meet our above
stated goals for the regulation knowledge base due to
the following specific properties
• Regulation rules can be modeled as FOM rules.
• Representation of rules in terms of fact types and
concepts identifies the concept model on which a
rule depends.
• Given a fact population for EM
data
, a reasoning
engine can reason about the truth of a set of rules
R, as given by Equation 1.
• FOM maps naturally to NL text as well as first-
order logic. It is thus useful both for creating the
regulation KB from NL text as well as for transla-
tion to logic form.
We employ SBVR as the fact-oriented modeling lan-
guage for our approach. The SBVR meta-model thus
defines the generic or meta-knowledge layer in our
model, shown in Figure 2. The next sub-section de-
scribes our approach.
2.2 Our Approach
We create the regulation KB as a fact-oriented model
of regulation rules, with the aim of explicating rules
in a structured manner, iteratively, until all the depen-
dencies become explicit. The fact types on which the
rules are based, denote the propositions whose truth
value must be determined in order to evaluate whether
the rule holds. The set of fact types on which rules
are based, therefore constitute the necessary and suf-
ficient model of information needed from the enter-
prise, for determining compliance. This is a concep-
tual model of required enterprise data, since it is ex-
pressed in terms of concepts from regulation vocabu-
lary. This addresses Goal2 of creating the regulation
KB.
The enterprise can provide data as ground facts
corresponding to this conceptual model. These can
be checked for compliance to the rules by a reasoning
engine, addressing Goal1. e.g. for the simplistic rule
about customer account, the fact types customer holds
account, and account has balance denote the model of
information needed to check compliance to the rule,
for which the enterprise has to provide ground facts,
say Cust001 holds Acct101, Cust002 holds Acct102,
Acct101 has Rs 2000, as data.
Rules in regulation text are expressed in terms of
concepts at a high level of abstraction. When creating
the regulation KB, we make the design choice to ex-
plicate the high-level concepts from regulation rules
using propositions obtained from definitions or data
descriptions within the regulation text, or knowledge
from the domain. We continue the process of expli-
cation until the leaf-level concepts are simple atomic
concepts that need not be explicated further. This cre-
ates a hierarchy of concepts. This is how we design
the representations of the regulation KB to specifi-
cally address Goal2. The fact types at the leaf level
constitute the model of required enterprise data, as we
illustrate in the case study section.
ICSOFT-PT 2016 - 11th International Conference on Software Paradigm Trends
62
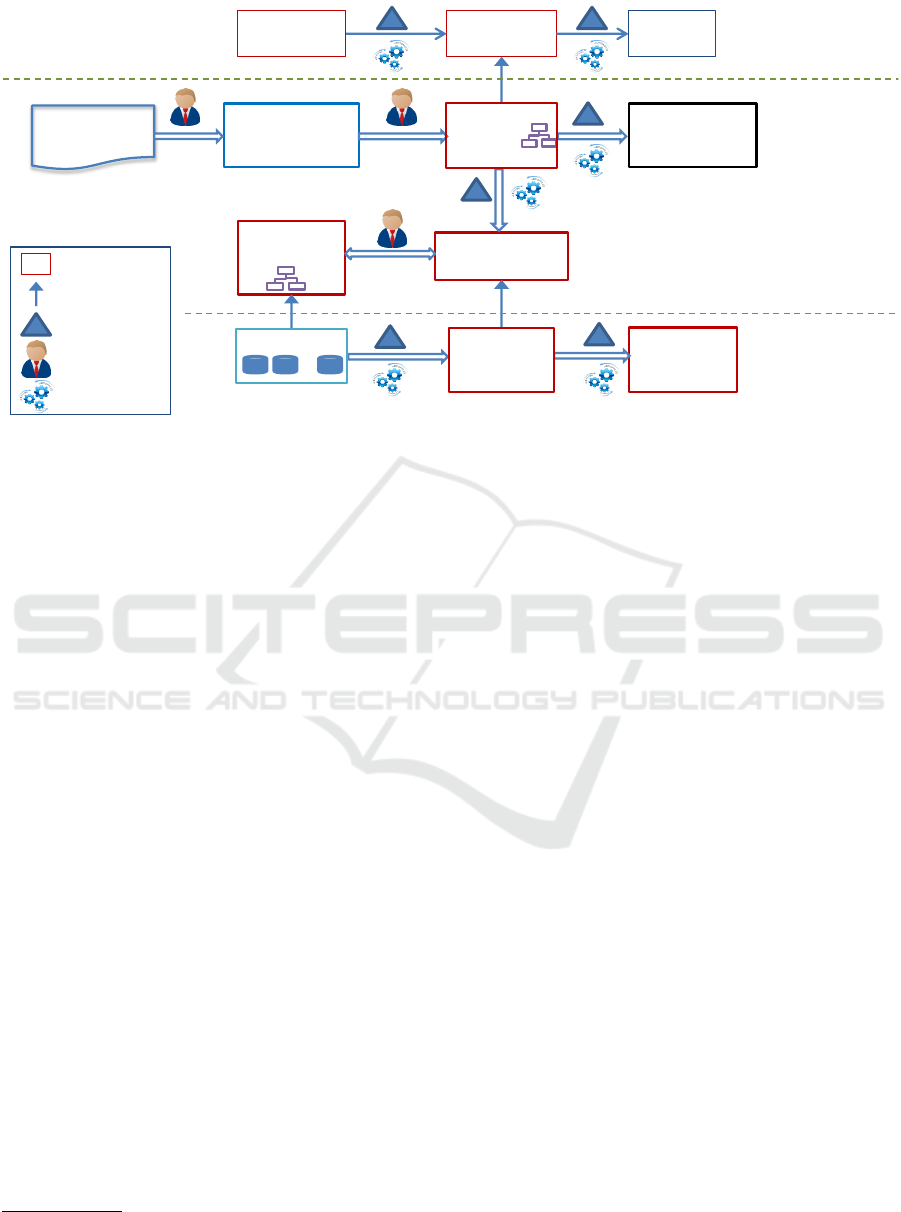
Natural-
language
regulation text
Controlled
natural-language
rules (SBVR SE)
Formal
regulation rules
R (DR-Prolog)
SBVR
EMF
editor
Pen ‘n’
paper
Enterprise data
(RDBMS)
Enterprise
Data as Facts
EM
Enterprise
Data Model
Conceptual data
model (SBVR)
Mapping
using EDI
tool
SBVR MOF
Meta model
SBVR Ecore
Meta model
SBVR EMF
editor
Enterprise
regulation-
specific data
…
Transformation
Automated task
Manual task
Instance of
Model
Automated
query
Meta-model
transformations
Model
transformations
Instance-model
transformations
Regulation
knowledge
base (SBVR)
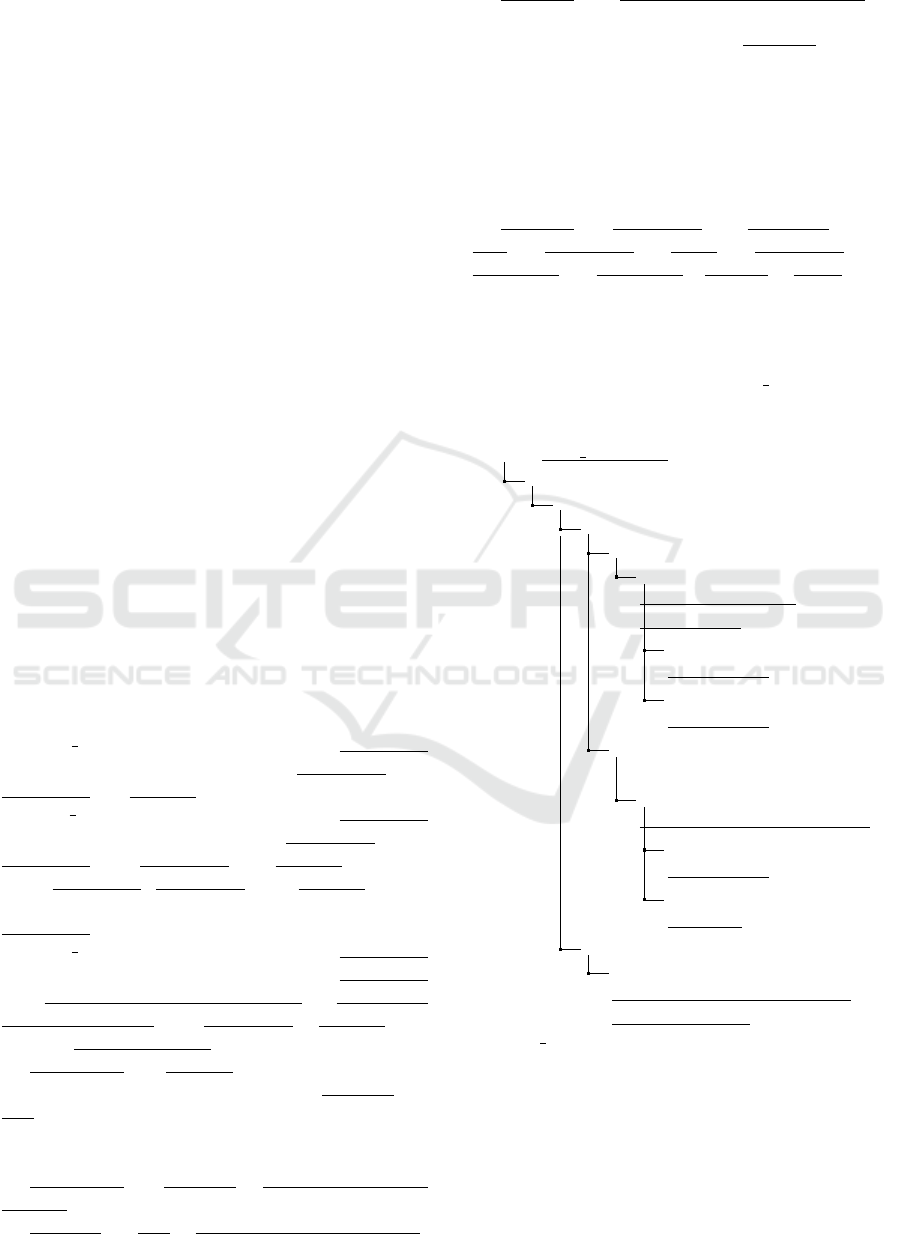
Figure 3: Model chain from NL regulations to enterprise data extraction.
We employ a chain of models and model trans-
formations at multiple levels, in order to reach from
regulation NL text to extraction of enterprise data, de-
picted in Figure 3, listed below, and described in de-
tail in the next section.
1. Meta-model Level: In order to create the reg-
ulation KB as an SBVR model, we build an
SBVR editor by importing the MOF-compliant
OMG SBVR meta-model into Eclipse Modeling
Framework (EMF)
4
Ecore format and use of EMF
model-to-text tools to generate editor code, as
shown in the top layer of Figure 3.
2. Model Level: The model-level transformations
for transforming NL rules to regulation KB to
conceptual model, as well as model mappings
from conceptual model to enterprise physical
model, constitute this middle layer in Figure 3,
comprising the following steps
(a) Express regulation rules from NL text in
SBVR’s controlled natural-language (CNL)
syntax.
(b) Create the regulation KB as an SBVR model
from the CNL rules.
(c) Extract the conceptual model of data from the
regulation KB, by model-to-model transforma-
tion.
(d) Translate rules from the KB into defeasible
logic rules R by model-to-model transforma-
tion. Although we have implemented the trans-
4
Eclipse Modeling Framework: http://www.eclipse.org/
modeling/emf/
lation, detailed description of this aspect is out-
side the scope of this paper.
(e) Map the conceptual model of data to the enter-
prise physical data model.
3. Model Instance Level: The requisite enter-
prise data EM
data
for checking compliance is ex-
tracted from enterprise data stores, by model-
to-model transformation from enterprise physical
data model to conceptual data model to facts, as
shown in the data layer or model instance layer of
Figure 3.
The next section describes the above steps in greater
detail, using a case study of the MiFID-II regulation.
3 DETAILED APPROACH
We use SBVR to create the regulation KB as the piv-
otal first step, as illustrated in the subsection below.
3.1 Creation of SBVR Model of
Regulation Rules
The necessary and sufficient subset of Object Man-
agement Group (OMG)s SBVR meta-model, that we
use to capture our FOM of regulation rules, is shown
in Figure 4. The three sections of the meta-model are
• Meaning Vocabulary: This is the meta-model for
capturing concepts. Noun concepts denote enti-
ties, while verb concepts signify relations or fact
types. Fact types take the form role verb role,
From Natural-language Regulations to Enterprise Data using Knowledge Representation and Model Transformations
63
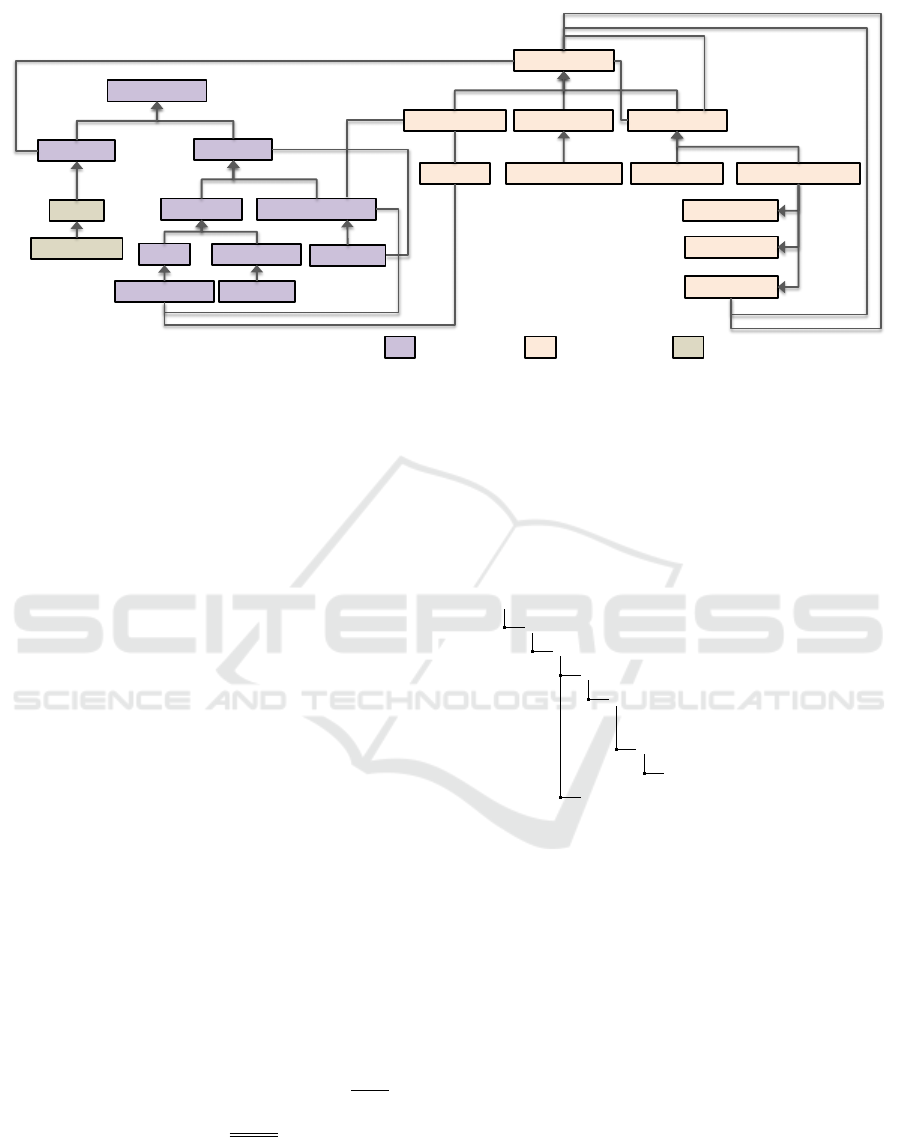
Meaning
Concept
Noun concept Fact Type/ Verb concept
Characteristic
incorporates
Logical Formulation
Modal Formulation
Obligation Formulation
Logical Operation
logicalOperand
isBasedOn
embeds
Proposition
General Concept
Concept Type
isMeantBy
Legend Meaning vocabulary
Logical Formulation of
Semantics vocabulary
Rule vocabulary
Rule
Definitional Rule
Role
Verb Concept Role
Logical Negation Binary Logical Operation
Conjunction
Disjunction
Implication
Atomic Formulation
Role Binding
rolebinding
role
rolebinding
antecedent
consequent
Figure 4: SBVR meta-model for capturing rules.
where each role stands for a noun concept. Gen-
eral concepts and concept types specialize con-
cepts and help create concept hierarchies. At-
tributes of a concept are captured as characteris-
tics.
• Logical Formulation of Semantics Vocabulary:
This section comprises logical formulations of
fact types, on which rules are based. Compound
logical formulations viz. conjunctions, implica-
tions, negations are composed of atomic formula-
tions. Each atomic formulation is based on a fact
type.
• Rule Vocabulary: We use rules to denote obli-
gations and definitional rules to denote necessity
formulations. A rule inherits from proposition,
that is meant by a logical formulation that for-
mally expresses the rule in terms of fact types.
We build the SBVR model of regulation rules in the
following steps, first expressing NL rule statements in
an intermediate CNL form.
1. A domain expert is required to mark in the NL
regulation text, the statements representing rules
to be checked, definitions of terms used in the
rules, and data descriptions relevant to the rules.
2. Each NL rule statement is then written in CNL, in
our case SBVR Structured English (SE). SBVR
SE is written using a restricted English vocabu-
lary, and specific font styles, viz. the term font
for designating noun concepts, general concepts,
concept types and roles; Name font for individual
concepts or names; verb font for designations of
fact types; and keyword font for other words in
definitions and statements.
3. SBVR SE statements map to SBVR meta-model
constructs. However, SBVR SE being a CNL, al-
lows ambiguities that render the automated trans-
lation to an SBVR model as not straightforward,
and is part of our ongoing explorations. We there-
fore create the SBVR rule model corresponding to
the SE statements manually, by instantiating the
following part of the SBVR meta-model using the
SBVR editor.
Rule
isMeantByÝObligationFormulation
embedsÝImplication
antecedentÝLogicalFormulation
logicalOperandÝ
AtomicFormulation
isBasedOnÝFactType
roleÝVerbConceptRole
consequentÝAtomicFormulation
The italicized labels with arrows Ý indicate associa-
tions to be created from the parent object to the child
object.
We have thus described the construction of the
regulation KB using SBVR. We now explain extrac-
tion of the conceptual model of enterprise data from
the regulation KB.
3.2 Extraction of Conceptual Model of
Enterprise Data
The fact types and concepts on which rules are built,
constitute the conceptual model for data expected
from the enterprise, as discussed in Section 2.2. The
meta-model for concepts and fact types in the SBVR
model, is the section shown in blue in Figure 4, except
for the entity Proposition.
Instances of this meta-model represent the con-
cepts used in the regulation KB. The concepts at the
ICSOFT-PT 2016 - 11th International Conference on Software Paradigm Trends
64
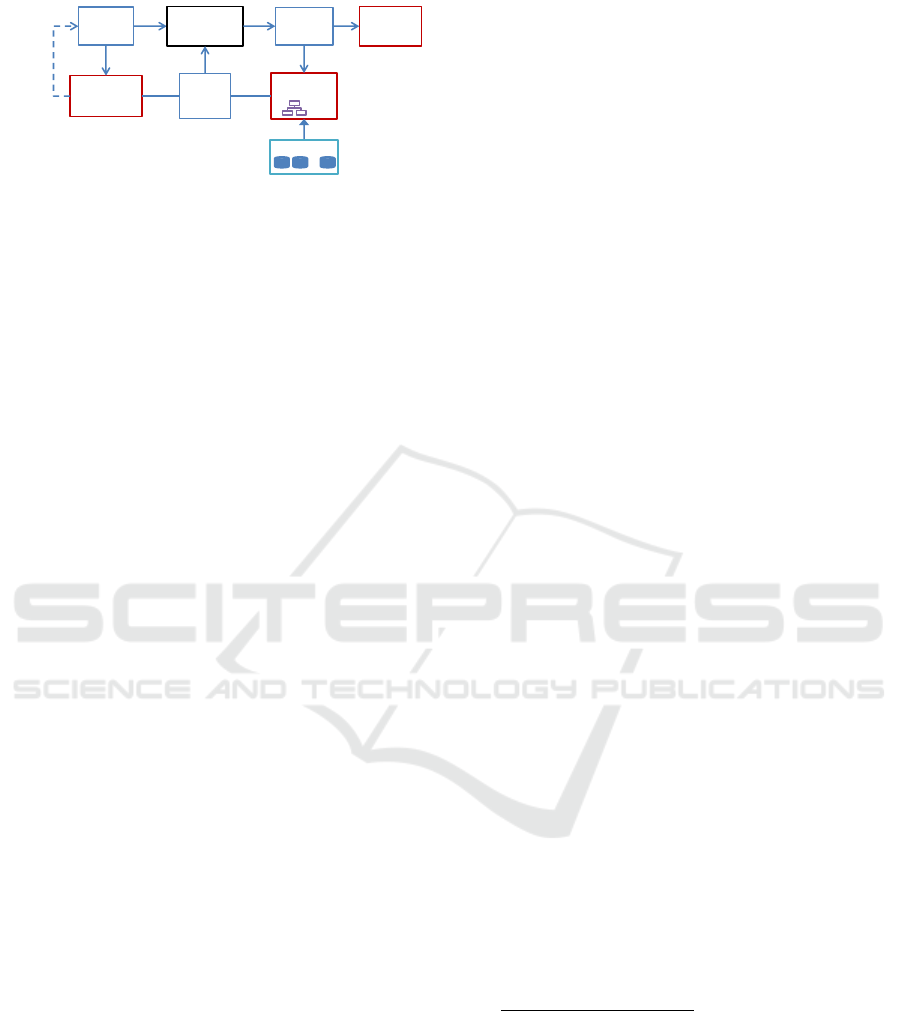
Automated
query
generation
Enterprise data
(RDBMS)
Enterprise
Data Model
Conceptual
data model of
Regulation
Mapping
using EDI
tool
Enterprise
regulation-
specific data
…
Query on
regulation
model
Query
translator
Query on
enterprise
model
Figure 5: Query translation using EDI tool.
leaf level represent the conceptual model of data ex-
pected from the enterprise. We extract this subset pro-
grammatically using EMF-generated functions, and
use this conceptual model to retrieve enterprise data
as described in the next subsection.
3.3 Retrieval of Enterprise Data
In industry practice of compliance, compliance ex-
perts, enterprise operations and systems experts are
required to analyze the regulation text and interpret
its vocabulary in the context of enterprise systems to
identify the data mapping for a regulation. Since en-
terprise data relevant to a regulation is typically dis-
tributed across several enterprise systems, with no
mapping or enterprise-level view of data, data inte-
gration is needed in order to map data to the regula-
tion. Extraction of data for compliance checking thus
becomes a schema integration problem, and we tackle
it as such.
We use an in-house EDI tool (Reddy, 2010) for
schema integration. It allows mapping of multi-
ple physical database schemas to a single conceptual
schema. It also facilitates queries to be written on
the conceptual schema that are translated to queries
on the enterprise physical database schemas using the
mapping.
We provide the conceptual schema obtained from
the regulation KB to the domain expert, who maps its
concepts and characteristics to appropriate tables and
columns from multiple enterprise database schemas.
Currently, the enterprise physical database schema
descriptions are manually obtained and entered into
the EDI tool, but this step can be easily automated,
and is part of our ongoing work.
We then generate queries on the conceptual data
model, in an automated manner, for retrieval of req-
uisite data corresponding to each concept and fact
type in the conceptual model. These are translated
by EDI to queries on enterprise physical tables using
the above mapping, as depicted in Figure 5.
The translated queries on execution fetch the re-
quired data to be checked for compliance, by model-
to-model transformation from enterprise physical data
model to the regulation conceptual data model. A
simple fact generator program formats the fetched
data rows into ground facts in the syntax of DR-
Prolog (Dimaresis, 2007), the compliance checking
engine we use. We thus obtain the requisite data
EM
data
to check for compliance to regulation rules R.
In the next subsection, we illustrate our approach us-
ing a case study of the MiFID-II regulation.
3.4 MiFID-II Regulation Case Study
Example
MiFID-II (Markets in Financial Instruments Direc-
tive) is a financial regulation that lays down specific
obligations on financial institutions for reporting mar-
ket trades carried out by them. MiFID-II has a com-
plex set of rules regarding the types of transactions to
be included/ excluded in reporting, and a large num-
ber of data fields that must be reported. We chose a
subset of the transaction inclusion/ exclusion rules of
MiFID-II for our case study.
For the enterprise data needed for our experimen-
tation, we collaborated with our financial domain ex-
pert colleagues from the capital markets practice unit.
They selected a bank with trading systems represen-
tative of the typical real-world scenario, comprising
multiple subsystems, with data spread across multiple
physical databases. We needed to apply the MiFID-
II reporting rules to transaction data residing in these
databases. The team shared database schema details
after suitably masking field and system names.
We carried out the case study in our lab by ap-
plying our method described in Section 2. The next
few subsections illustrate the case study artefacts cor-
responding to each step of the method.
3.4.1 NL Regulation Text
The excerpt from the inclusion and exclusion rules,
identified by the domain expert from the original
MiFID-II regulation text, that we used as the NL reg-
ulation text for our case study, is shown below.
Meaning of Transaction
1. For the purposes of Article 26 of Regulation (EU)
No 600/2014, the conclusion of an acquisition or
disposal of a financial instrument shall constitute
a transaction.
2. An acquisition referred to in paragraph 1 shall in-
clude:
(a) a purchase of a financial instrument;
(b) entering into a derivative contract in a financial
instrument.
From Natural-language Regulations to Enterprise Data using Knowledge Representation and Model Transformations
65
3. A disposal referred to in paragraph 1 shall in-
clude:
(a) sale of a financial instrument;
(b) closing out of a derivative contract in a finan-
cial instrument.
4. A transaction for the purposes of Article 26 of
Regulation (EU) No 600/2014 shall not include:
(a) a securities financing transaction as defined
in Regulation [Securities Financing Transac-
tions]
(b) a contract arising exclusively for clearing or
settlement purposes;
(c) an acquisition or disposal that is solely a result
of custodial activity.
The next subsection illustrates these regulation rules,
written in CNL.
3.4.2 MiFID Regulation KB
We write the inclusion and exclusion rules 1 and 4
respectively, from the regulation text, in SBVR SE as
obligations, since they are binding on enterprises.
It may be mentioned here, that we did the writing
of SE statements for the case study; however, in prac-
tice, domain experts would need to be trained to write
statements in SBVR SE, which is easy, since it just a
restricted NL form with a few keywords and sentence
patterns to be followed. The SBVR SE rules, written
in the notation described in Section 3.1, are shown
below.
Rule Inclusion: It is obligatory that transaction
is included in MiFID reporting if the transaction is an
acquisition or a disposal.
Rule Inclusion is built upon fact types transaction
is included in MiFID reporting, transaction is an
acquisition, and transaction is a disposal, and con-
cepts transaction, acquisition, and disposal; is in-
cluded in MiFID reporting is a characteristic of a
transaction.
Rule Exclusion: It is obligatory that transaction
is excluded from MiFID reporting if the transaction
is a securities financing transaction or clearing or
settlement contract or an acquisition or disposal aris-
ing from custodial activity.
Acquisition and disposal are high-level concepts
defined in terms of other concepts, e.g. purchase and
sale, in the rules 2 and 3 in the regulation text. These
definitions are captured as definitional rules in SBVR
SE, as follows
Acquisition is a purchase or entering a derivative
contract.
Disposal is a sale or closing a derivative contract.
Purchase and entering a derivative contract are
further explicated to the extent possible, in accor-
dance with our design choice. Purchase is shown
here, defined by domain experts in terms of propo-
sitions on elements such as buyer and seller defined
in the data description section in the regulation, as
well as concepts such as trade type from their own
knowledge of the domain. The data description sec-
tion excerpts are not included here owing to space
constraints.
Purchase is a transaction with trade type equal to
Buy and transaction has buyer and transaction trades
instrument and instrument is equities or bonds.
The leaf-level concepts and fact types obtained in
this lowest-level definition, constitute the conceptual
model of data for which ground facts are needed from
the enterprise.
The SBVR rule model for Rule Inclusion corre-
sponding to these SBVR SE rule statements is shown
in the listing below.
Rule Rule Inclusion
isMeantByÝObligationFormulation
embedsÝImplication
antecedentÝDisjunction
logicalOperandÝAtomicFormulation
isBasedOnÝFactType
transaction is an
acquisition
roleÝVerbConceptRole
transaction
roleÝVerbConceptRole
acquisition
logicalOperandÝ
AtomicFormulation
isBasedOnÝFactType
transaction is a disposal
roleÝVerbConceptRole
transaction
roleÝVerbConceptRole
disposal
consequentÝ AtomicFormulation
isBasedOnÝFactType
transaction is included in
MiFID reporting
Rule Exclusion is similarly encoded as an SBVR
model.
The SBVR model for the entire set of SBVR SE
statements for the regulation constitutes the source
from which the conceptual model of the regulation is
extracted. The conceptual model of the MiFID-II reg-
ulation subset of our case study is shown in the next
subsection.
ICSOFT-PT 2016 - 11th International Conference on Software Paradigm Trends
66
tradedAt
trades
Transaction
TransRef
TradingVenue
TransIdCode
TradeType
ReportingStatus
TradingDateTime
TradingCap
Qty
QtyCcy
Price
PriceCcy
NetAmt
Instrument
Instrument ID
Instrument type
Instrument name
Instrument
classifn
Underlying inst
code
Trading
Venue
Country
Cntry code
executedBy
buyer
Seller
Seller ID
Seller DOB
Buyer
Buyer ID
Buyer DOB
uses
Executing Firm
Exec Entity ID
CntryBrnchMbrship
Currency
Ccy code
seller
cntry
Conceptual model
from regulation
ccy
Deal
TransID
Venue
TradeType
InstActionCode
TrdDateAndTime
TrdCap
TradeQty
QuanCcy
TradePrice
PriceCurrency
TransNetAmount
Security Master
InsIdCode
InsName
InsClassif
UnInsCode
Country
CountryCd
deal
buyer
Client
Master
ClientRefNum
ClientName1
Clientname2
transacts
Trans
TransID
PTSTransCode
TransType
BuyerRefNum
SellerRefNum
SecId
Currency
Ccy code
seller
cntry
Enterprise physical
model
Deal subsystem
Securities
subsystem
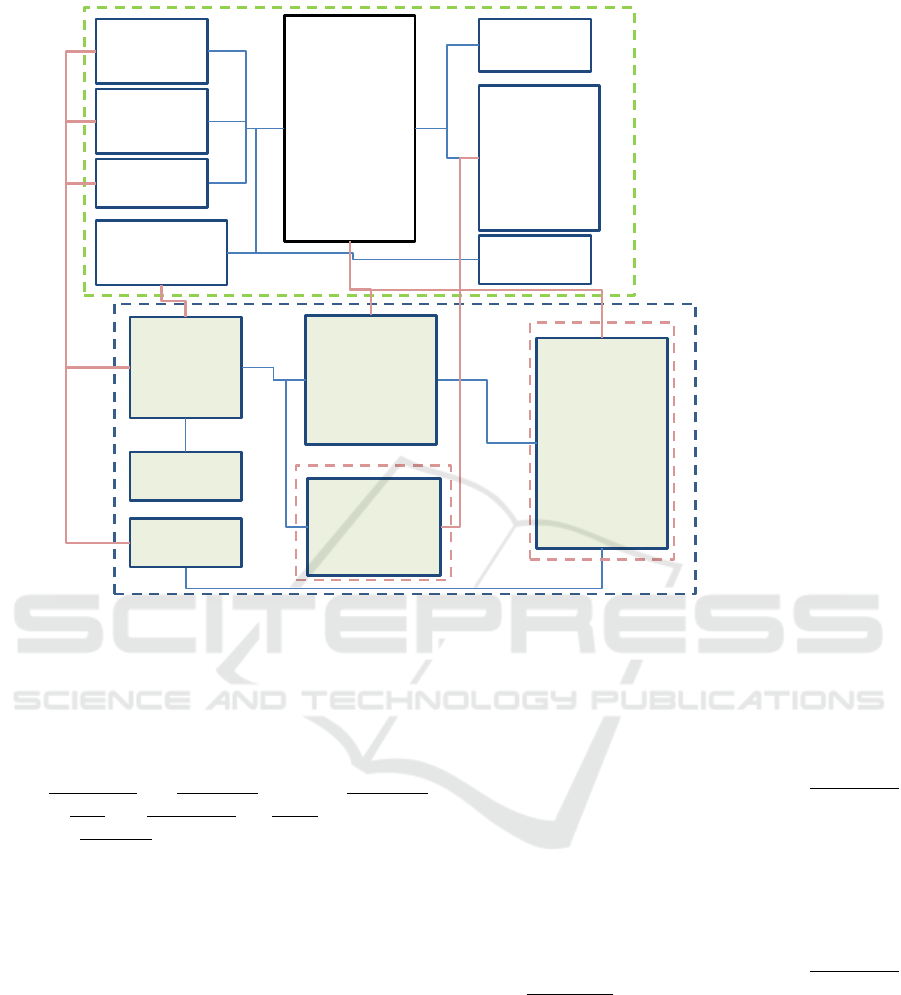
Figure 6: Conceptual to physical data mapping in EDI.
3.4.3 Extracted Conceptual Data Model
The conceptual data model of the MiFID-II regulation
comprises leaf-level concepts and fact types from all
of the detailed definitions and rules, such as the con-
cepts transaction and trade type, and facts trade type
equal to Buy, and transaction has buyer from the def-
inition of purchase above.
The conceptual model automatically extracted
from the SBVR rule model is shown in the upper half
of Figure 6. The list of characteristics within each
concept is an illustrative subset, the exhaustive list not
shown due to space constraints. Mapping of this con-
ceptual model to the bank’s physical data model is
illustrated in the subsection below.
3.4.4 Enterprise Data Extraction
The enterprise physical schema comprises several
sub-schemas from component sub-systems, such as
Deal and Securities sub-systems seen in Figure 6. Do-
main experts perform the mapping of concepts from
the MiFID regulation conceptual schema to the bank’s
physical database schema, shown in Figure 6.
The Transaction concept from the regulation
schema maps to the Trans and Deal tables from the
enterprise Deal sub-system database, while Instru-
ment maps to the Security Master table from the
Securities sub-system. Buyer, Seller and Executing
Firm entities from the conceptual schema map to the
Client Master table of the enterprise database. Indi-
vidual characteristics of concepts such as transaction
are mapped to columns of corresponding tables, in
this case Trans and Deal.
Two of the sample queries we generate automat-
ically, for retrieving data for Transaction and Instru-
ment tables in the conceptual schema, are shown here.
Queries for fact types that relate concepts mapping to
different tables are translated as joins, such as query
2 below, corresponding to the fact type transaction
trades instrument.
1 1 ) SELECT ∗ FROM T r a n s a c t i o n ;
2 2 ) SELECT ∗ FROM I n s t r u m e n t i ,
T r a n s a c t i o n t
3 where i . I n s t r u m e n t I D = t .
I n s t r u m e n t I D ;
These queries are translated by the EDI tool into
queries on corresponding enterprise tables 1) Trans
and Deal, and 2) Securities respectively. The trans-
lated query corresponding to query 1) is shown below
From Natural-language Regulations to Enterprise Data using Knowledge Representation and Model Transformations
67

1 SELECT t 1 . Tra nsI D ,
2 t 1 . TradeType ,
3 t 1 . I ns t A c t i o n C o d e ,
4 t 1 . TrdDateAndTime ,
5 t 1 . TrdCap ,
6 t 1 . TradeQ ty ,
7 t 1 . QuanCcy ,
8 t 1 . T r a d e P r i c e ,
9 t 1 . P r i c e C u r r e n c y ,
10 t 1 . Trans Ne tA mount ,
11 t 2 . t r a n s T y p e ,
12 t 2 . P TS T r a ns a c t io n C o de ,
13 t 1 . Venue ,
14 t 2 . Se cI d ,
15 t 2 . BuyerRefNum ,
16 t 2 . Se l l er R efN u m
17 FROM DealSchema . Dea l t 1 , Tra deSc hema
. T r a n s t 2
18 WHERE t 1 . Tr a nsI D = t 2 . T ra n sID
The translated query, on execution, transforms data
from Trans and Deal enterprise tables into data corre-
sponding to the
transaction concept from the concep-
tual schema. The retrieved data rows are formatted by
our fact generator into DR-Prolog transaction ground
facts.
The fact schema for each concept comprises its
characteristics. e.g. the fact schema for transaction
is fact(transaction(TransRef, TradingVenue, Tran-
sIdCode, TradeType, ReportingStatus, TradingDate-
Time, TradingCap, Qty, QtyCcy, Price, PriceCcy, Ne-
tAmt)).
The schema for each fact type, e.g. transaction
trades instrument comprises unique key fields of the
concepts being related, i.e. TransRef for transaction
and InstrumentID for instrument.
The listing of two sample sets of ground facts, for
a purchase and a closing a derivative contract transac-
tion is shown below.
1 /∗ Set 1 : Purchase t r a n s a c t i o n ∗ /
2 f a c t ( t r a n s a c t i o n ( ’ 1010000023TATA ’ , ’ ’ , ’
Buy ’ , ’NEWT ’ , ’ 2015−11−06T09
:16: 36:14 3232 ’ , ’MTCH ’ , 2500 , , 150 ,
’ INR ’ , 375000) ) .
3 f a c t ( i n s t r u me n t ( ’ INE467B01029 ’ , ’ESXXXX ’ )
) .
4 f a c t ( cu rr e nc y ( ’ INR ’ , , ’ A c t i ve ’ ) ) .
5 f a c t ( t ra de dA t ( ’ 1010000023TATA ’ , ’XXXX ’ ) ) .
6 f a c t ( t r a d es ( ’ 1010000023TATA ’ , ’
INE467B01029 ’ ) ) .
7
8 /∗ Set 2 : Cl os ing out o f D e r i v a t i v e
Co nt ra ct ∗ /
9 f a c t ( t r a n s a c t i o n ( ’ 000CMEC000 ’ , ’ AB4 ’ , ’
S e l l ’ , ’NEWT ’ , ’ 2015−11−06T09
:11: 36:14 3232 ’ , ’DEAL ’ , 5 , , 7 5 .43 ,
’GBP ’ , 377150) ) .
10 f a c t ( h a s Se l l e r ( ’ 000CMEC000 ’ , ’
AFXS5XCH7N0Y05NIXW17 ’ ) ) .
11 f a c t ( h as Un de r l y in gI ns tr um en t ( ’ 000CMEC000
’ , ’ GB0008706128 ’ ) ) .
12 f a c t ( i n s t r u me n t ( ’ GB000 8706128 ’ , ’ FFICNX ’ )
) .
13 f a c t ( cu rr e nc y ( ’GBP ’ , , ’ I n a c t i v e ’ ) ) .
We thus complete the process of discovering the con-
ceptual model in the MiFID regulation text and map-
ping it to the physical data model of the bank, as well
as automated extraction of the relevant data from the
bank’s databases in the form of facts, for checking
compliance to the regulation.
The next section discusses related work.
4 RELATED WORK AND
DISCUSSION
Most formal compliance checking approaches check
business process models for compliance against reg-
ulations (Governatori and Rotolo, 2010; Awad et al.,
2010; Governatori et al., 2009; Governatori, 2005).
Various approaches have been developed for relating
regulations to enterprise business processes such as
constructing an execution trace as in (Sadiq et al.,
2007), finding paths in process structure tree as in
(Awad et al., 2009), or labels placed manually on a
business property specification language diagram as
in (Liu et al., 2007). Domain experts are assumed to
take care of formal encoding of rules, and labels from
business processes in such traces, paths, or other rep-
resentations are presumed to map to labels used in the
formal models of rules. Business rule management
systems too, widely used to check run-time compli-
ance, need rules to be encoded using the same labels
as physical data or need mapping to the same.
In reality, since mapping of not just labels but of
conceptual models at different levels of abstraction on
the regulation and enterprise side is needed, our ap-
proach of knowledge representation gives a structured
method to elicit the regulation conceptual model from
the NL rules. A conceptual model of the regulation
is a necessary first step for computing its impact on
the enterprise, storing, and in future, even performing
the mapping to enterprise data in an automated man-
ner. Use of CNL is targeted at helping domain ex-
perts build the model without being familiar with the
details of underlying logic. Building a model of the
regulation and using a structured method to build the
model enables automation, creates a rule repository,
and increases the accuracy of the process, since there
is a way to track rules being checked and chances of
missing rules are minimized. Automation is crucial
to correctness, repeatability, and cost savings, consid-
ering that compliance checks have to be run on large
ICSOFT-PT 2016 - 11th International Conference on Software Paradigm Trends
68

datasets repeatedly, to demonstrate compliance on an
ongoing basis.
A system for defeasible logic representation of
regulations and compliance checking is presented in
(Dimaresis, 2007) that we use as the compliance en-
gine in our work. In our earlier works, the problem of
semantic disparity between regulations and enterprise
has been tackled (Sunkle et al., 2015c; Sunkle et al.,
2015d), and a mapping between vocabularies on both
sides is proposed. Generation of NL proof explana-
tions of (non-) compliance, and handling regulatory
change have been described in (Sunkle et al., 2015a)
and (Sunkle et al., 2015b) respectively, while an end-
to-end model-based method has been introduced in
(Sunkle et al., 2016). These works however, do not
cover identification of a conceptual model of the data
needed by the regulation, and mapping to or extrac-
tion of this data from enterprise physical databases.
A model that enables traceability of delegation
of obligations from regulations and their refinement
into software requirements is given by (Breaux et al.,
2009). A language for modeling norms and their
inter-relations and analysis of various compliance al-
ternatives is described in (Ingolfo et al., 2013; In-
golfo et al., 2014), that performs goal-oriented analy-
sis based on effects of norms on one another. Ontolo-
gies are suggested in (Kharbili et al., 2008b) to tackle
semantic disparity. A conceptual model of the reg-
ulatory compliance management process and activi-
ties involved is used as basis to survey and rank busi-
ness process compliance management frameworks in
(Kharbili, 2012). We address some of the recom-
mendations from this work such as making compli-
ance requirement specification amenable to business
users and extending use of logic to the business con-
text, through the use of CNL and SBVR for capturing
rules. These are relatively easy formats for business
users to understand.
Another classification of compliance checking
based on the granularity of checks, i.e., whether
business processes, tasks, attributes or pure data is
checked, and finally whether checking takes place
by making use of an inference engine and/or queries
to models of enterprise information is presented in
(Kharbili et al., 2008a). Existing business process
based compliance management approaches are sur-
veyed for generalizability and applicability in (Becker
et al., 2012), reporting that available frameworks sup-
port only a single model specification, do not check
entire regulations but only excerpts, and lack evalua-
tion. Although we have only described mapping to
enterprise physical databases in this paper, our ap-
proach can be applied to map to a data model that
could be sourced from the enterprises business pro-
cesses, tool repositories or indeed any other source.
The reasoner we use (Dimaresis, 2007), scales to very
large fact and rule-bases. We have tested this on large
sets of data and rules in the MiFID case study.
SBVR has been used for capturing legal rules in
(Johnsen and Berre, 2010; Kamada et al., 2010), to
precisely define rules and reveal inconsistencies and
translate to Formal Contract Logic (FCL), a propri-
etary defeasible logic language with special operators
for non-monotonic reasoning, respectively. Semi-
automated natural-language processing approaches to
generate SBVR formulations are presented in (Bajwa
et al., 2011; Levy and Nazarenko, 2013; Njonko and
Abed, 2012). Interpretation and expression of anti-
money laundering rules in SBVR is described in (Abi-
Lahoud et al., 2013). Our principal objective in using
SBVR is to create a knowledge base of the regulation
rules, such that its representations are usable for both
compliance checking and identifying enterprise data,
as listed in the goals in Section 2. We use the SBVR
model as a means to build and automatically extract
the conceptual data model for an NL regulation.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
We described enterprises’ critical need to comply
with regulations at run-time and to cut costs and miti-
gate risk using technology and automation. We chose
to focus on the problem of relating the regulation to
relevant enterprise details, i.e. data to be checked
for compliance, in an automated manner. We pre-
sented a knowledge representation approach to relate
the regulation to the enterprise, given the NL regu-
lation text, by building a knowledge base of regula-
tion rules using SBVR. We provided a model-driven,
semi-automated solution to obtain first the conceptual
model, then the physical model of requisite data, and
finally the actual enterprise data from distributed en-
terprise databases, using a series of model-to-model
transformations and enterprise data integration.
We argued that building a knowledge base of reg-
ulation rules, with the explicit goals of compliance
checking and identification of requisite data, results
in the design of representations that pave the way for
automated generation of formal specification of both
rules R and requisite data EM
data
, hitherto a manual
process. We have shown how to generate EM
data
. It
is possible to also generate the formal specification
of rules R from the regulation KB. We have imple-
mented the same to generate a defeasible logic spec-
ification in DR-Prolog, however, its detailed descrip-
tion is outside the scope of this paper. Formal au-
From Natural-language Regulations to Enterprise Data using Knowledge Representation and Model Transformations
69

tomated compliance checking if implemented, can
greatly enhance accuracy and cost savings.
We plan to extend this approach with semantic
similarity techniques, to aid the expert with sugges-
tions during schema mapping. We are also working
towards automating population of the knowledge base
from NL regulation text. Also ongoing is our work
on translating SBVR SE statements into an SBVR
model.
The case study described in this paper although
using a real-world problem and enterprise data, was
conducted in a laboratory setting. We plan to extend
the case study scope, conduct a rigorous experimental
validation of our approach, and present a comparison
with other similar approaches. We also plan to ap-
ply our approach in an industry setting, with domain
experts to use it as well as evaluate the results.
REFERENCES
Abi-Lahoud, E., Butler, T., Chapin, D., and Hall, J. (2013).
Interpreting regulations with SBVR. Fodor, P., Ro-
man, D., Anicic, D., Wyner, A., Palmirani, M., Sot-
tara, D., Lvy, F., eds.: Joint Proceedings of the 7th
International Rule Challenge, the Special Track on
Human Language Technology and the 3rd RuleML
Doctoral Consortium, Seattle, USA, July 11 -13,
2013. Volume 1004 of CEUR Workshop Proceedings.,
CEUR-WS.org.
Awad, A., Smirnov, S., and Weske, M. (2009). Resolution
of compliance violation in business process models:
A planning-based approach. OTM Conferences (1)
2009: 6-23.
Awad, A., Weidlich, M., and Weske., M. (2010). Consis-
tency checking of compliance rules. In BIS 2010:
106-11.
Bajwa, I., Lee, M., and Bordbar, B. (2011). Sbvr business
rules generation from natural language specification.
AAAI Spring Symposium: AI for Business Agility.
pp. 28. AIII.
Becker, J., Delfmann, P., Eggert, M., and Schwittay,
S. (2012). Generalizability and applicability of
model-based business process compliance-checking
approaches a state-of-the-art analysis and research
roadmap. BuR Business Research Journal, Vol. 5, No.
2, pp. 221-247, November 2012.
Brachman, R. J. and Levesque, H. J. (2004). Knowledge
Representation and Reasoning. Elsevier.
Breaux, T. D., Antn, A. I., and Spafford, E. H. (2009). A
distributed requirements management framework for
legal compliance and accountability. Computers &
Security 28(1-2): 8-17.
Dimaresis, N. (2007). A system for modal and deontic de-
feasible reasoning. In Int. J. Cooperative Inf. Syst.
14(2-3): 181-216.
English, S. and Hammond, S. (2014). Cost of compliance
2014.
Governatori, G. (2005). Representing business contracts in
ruleml. In Int. J. Cooperative Inf. Syst. 14(2-3): 181-
216.
Governatori, G., Hoffmann, J., Sadiq, S., and Weber, I.
(2009). Detecting regulatory compliance for busi-
ness process models through semantic annotations. In
Ardagna, D., Mecella, M., Yang, J., eds.: Business
Process Management Workshops. Volume 17 of Lec-
ture Notes in Business Information Processing. 517.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Governatori, G. and Rotolo, A. (2010). A conceptually rich
model of business process compliance. In APCCM
2010: 3-12.
Halpin, T. (2007). Fact oriented modeling past, present
and future. In Conceptual Modelling in Information
Systems Engineering, J.Krogstie, A. L. Opdahl, and
S. Brinkkemper (eds.) pp. 19-38. Berlin Heidelberg:
Springer-Verlag.
Ingolfo, S., Jureta, I., Siena, A., Perini, A., and Susi, A.
(2014). Nmos 3: Legal compliance of roles and re-
quirements. ER 2014: 275-288.
Ingolfo, S., Siena, A., Susi, A., , A. P., and Mylopoulos, J.
(2013). Modeling laws with nomos 2. Requirements
Engineering and Law (RELAW), Sixth International
Workshop on , vol., no., pp.69,71, 16-16 July 2013.
Johnsen, A. and Berre, A. (2010). A bridge between legis-
lator and technologist - formalization in sbvr for im-
proved quality and understanding of legal rules. In-
ternational Workshop on Business Models, Business
Rules and Ontologies, Bressanone, Brixen, Italy.
Kamada, A., Governatori, G., and Sadiq, S. (2010). Trans-
formation of sbvr compliant business rules to exe-
cutable fcl rules. RuleML 2010: 4th International Web
Rule Symposium. Number 6403, Springer (2010)
153161.
Kharbili, M. (2012). Business process regulatory compli-
ance management solution frameworks: a compara-
tive evaluatio. Asia-Pacific Conference on Concep-
tual Modelling (APCCM 2012) Melbourne, Australia.
CRPIT, 130. Ghose,A. and Ferrarotti,F. Eds., ACS.
23-32.
Kharbili, M., de Medeiros, A., Stein, S., and van der Aalst,
W. (2008a). Business process compliance checking:
Current state and future challenges. P. Loos, M.
Nuttgens, K. Turowski, and D. Werth, editors, MobIS,
volume 141 of LNI, pages 107-113.
Kharbili, M. E., Stein, S., Markovic, I., and Pulvermller, E.
(2008b). Towards a framework for semantic business
process compliance management. The Impact of Gov-
ernance, Risk, and Compliance on Information Sys-
tems (GRCIS). Volume 339 of CEUR Workshop Pro-
ceedings., Montpellier, France (June 17 2008) 115.
Levy, F. and Nazarenko, A. (2013). Formalization of natural
language regulations through sbvr structured english
(tutorial). Morgenstern, L., Stefaneas, P., Levy, F.,
Wyner, A., Paschke, A. (eds.) RuleML 2013. LNCS,
vol. 8035, pp. 19-33. Springer, Heidelberg.
Liu, Y., Mller, S., and K.Xu (2007). A static compliance-
checking framework for business process models.
IBM Systems Journal 46(2): 335-362.
ICSOFT-PT 2016 - 11th International Conference on Software Paradigm Trends
70

Nijssen, G. (2007). Sbvr: Semantics for business.
Njonko, P. and Abed, W. E. (2012). From natural language
business requirements to executable models via sbvr.
Systems and Informatics (ICSAI), 2012 International
Conference on. IEEE.
Reddy, S. (2010). A model driven approach to enterprise
data integration. In COMAD 2010: 202.
Reuters, T. (2016). State of regulatory reform 2016: A spe-
cial report.
Sadiq, S., Governatori, G., and Namiri, K. (2007). Mod-
eling control objectives for business process compli-
ance. BPM 2007: 149-164.
Smith, B. C. (1982). Reflection and Semantics in a Proce-
dural Language. PhD thesis.
Sunkle, S., Kholkar, D., and Kulkarni, V. (2015a). Expla-
nation of proofs of regulatory (non-)compliance using
semantic vocabularies. In RuleML 2015: 388-403.
Sunkle, S., Kholkar, D., and Kulkarni, V. (2015b). Model-
driven regulatory compliance: A case udy of know
your customer regulations. In MoDELS 2015: 436-
445.
Sunkle, S., Kholkar, D., and Kulkarni, V. (2015c). Solv-
ing semantic disparity and explanation problems in
regulatory compliance- a research-in-progress report
with design science research perspective. In BMMD-
S/EMMSAD 2015: 326-341.
Sunkle, S., Kholkar, D., and Kulkarni, V. (2015d). Toward
better mapping between regulations and operations of
enterprises using vocabularies and semantic similarity.
In CSIMQ 5: 39-60.
Sunkle, S., Kholkar, D., and Kulkarni, V. (2016). Toward
(semi-) automated end-to-end model-driven compli-
ance framework. In ModSym+SAAAS@ISEC 2016:
33-38.
From Natural-language Regulations to Enterprise Data using Knowledge Representation and Model Transformations
71
