
Gait Transition in Artificial Locomotion Systems using Adaptive Control
Jonas Kr¨aml and Carsten Behn
Department of Technical Mechanics, Technical University of Ilmenau, Max-Planck-Ring 12, 98693 Ilmenau, Germany
Keywords:
Bio-inspired Locomotion System, Gait Transition, Adaptive Control, Uncertain System, Gait Generation.
Abstract:
This paper deals with the modeling, analysis and controlled gait transitions of terrestrial artificial locomotion
systems. These systems are inspired by the motion of earthworms and are firstly moving unidirectionally. In
contrast to the analyzed systems in literature, the mechanical model in this paper consists of a chain of 10
discrete mass points. The theory is not restricted to a specified number of mass point, just to a fixed, but
arbitrary number. Recent results from literature present investigations of short worms (n < 4). The movement
of the whole system is achieved by shortening and lengthening of the distances between consecutive mass
points, while they can only move in forward direction. To inhibit the backward movement, a spiky contact
to the ground using ideal spikes – preventing velocities from being negative – are attached to every mass
point realizing the ground contact. The changes of the distances combined with the ground contact results in
a global movement of the system, called undulatory locomotion. But, to change the distances, viscoelastic
force actuators link neighboring mass points and shall control desired distances in using adaptive control
strategies. Specific gaits are required to guarantee a controlled movement that differ especially in the number of
resting mass points and the load of actuators and spikes. To determine the most advantageous gaits, numerical
investigations are performed and a weighting function offers a decision of best possible gaits. Using these
gaits, a gait transition algorithm, which autonomously changes velocity and number of resting mass points
depending on the spike and actuator force load, is presented and tested in numerical simulations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Worm-like locomotion systems play an increasing
role in current mechanics literature, see for example
(Miller, 1988), (Hirose, 1993), (Ostrowski and Bur-
dick, 1996), (Vaidyanathan et al., 2000), (Liu et al.,
2006), and find their place in teaching and educa-
tion of students, see textbooks (Zimmermann et al.,
2009) and (Steigenberger and Behn, 2012). These
systems have the advantage of little space require-
ments due to their unidirectional motion. Hence, they
are used in narrow places. Possible applications are,
e.g., minimally invasive surgery (Dario et al., 1996),
service and maintenance robots (Fatikow and Rem-
bold, 1997) or drilling robots (Kubota et al., 2007).
Previous publications deal with worm-like loco-
motion systems with 3 or 4 mass points (Schwebke
and Behn, 2013). This paper supplements the knowl-
edge of the dynamic behavior of worm-like locomo-
tion systems with 10 mass points with the goal to ex-
pand the gained results to snake-like locomotion sys-
tems in further works.
Firstly, the mechanical model of a worm-like lo-
comotion system and the adaptive control scheme
are presented. Afterwards, the generation of suit-
able gaits considering current literature is introduced.
These gaits are used by a gait transition algorithm that
changes velocity and number of resting mass points
depending on the load of spikes and actuators, like the
biological paradigm does (Merz and Edwards, 1998).
Finally, simulations are carried out to demonstrate the
functionality of the scheme.
2 MODELING & CONTROL
Modeling: The model is identical to (Steigenberger
and Behn, 2012). The kinematic model comprises
a chain of discrete mass points m
i
as shown in Fig-
ure 1, where x
i
(t)(i = 0, n) are the coordinates of the
mass points (single degree of freedom). The distance
of neighboring mass elements is l
j
(t) := x
i−1
(t) −
x
i
(t). To inhibit backward movement, ideal spikes are
mounted at each segment.
A segment here is a mass point, but it can
also appear as balloon-like or bellows-like elements
(possibly fluid filled), see (Slatkin et al., 1995),
Kräml, J. and Behn, C.
Gait Transition in Artificial Locomotion Systems using Adaptive Control.
DOI: 10.5220/0006003001190129
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2016) - Volume 2, pages 119-129
ISBN: 978-989-758-198-4
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
119

Figure 1: Chain of mass points with spikes, due to (Schwe-
bke and Behn, 2013).
(Vaidyanathan et al., 2000), (Meier et al., 2004) and
(Liu et al., 2006).
To allow a movement of the worm, the distances
between the mass points have to be shortened and
lengthened. This can be done in adjusting their longi-
tudinal or radial dimensions (Nakamura et al., 2006)
or, as here, the distances between adjacent elements
(Behn and Zimmermann, 2011a) and (Behn and Zim-
mermann, 2011b). For this purpose, viscoelastic ac-
tuators are assumed between the segments in the dy-
namic model. The applied forces on a mass point are:
• Spring Forces F
c,i
= c
i
(x
i−1
− x
i
− l
0,i
) and
−F
c,i+1
= −c
i+1
(x
i
− x
i+1
− l
0,i+1
), where l
0,i
and
l
0,i+1
are the detensioned lengths of the springs;
• Damping Forces F
d,i
= d
i
( ˙x
i−1
− ˙x
i
) and
−F
d,i+1
= −d
i+1
( ˙x
i
− ˙x
i+1
);
• Actuator Forces u
i
and −u
i+1
;
• Spike Forces F
Z,i
;
• Weight F
Gx,i
in x-direction;
• Friction Force F
R,i
= 0.
At this stage of investigations, the assumed zero fric-
tion force is only a special case. The interaction to
the ground is modeled via ideal spikes. In future
work, we have to replace these spikes by anisotropic
Coulomb friction, see also (Steigenberger and Behn,
2012).
According to (Steigenberger and Behn, 2012), the
ideal spikes have to fulfill these conditions:
˙x
i
≥ 0, F
Z,i
≥ 0, ˙x
i
· F
Z,i
= 0 (1)
These conditions can be fulfilled by the following
equation, where F
i
is the sum of all remaining applied
forces:
F
Z,i
= −
1
2
(1− sign( ˙x
i
)) · (1− sign(F
i
)) · F
i
(2)
Now, the coupled differential equations for movement
of the segments can be formulated:
m
i
¨x
i
= +c
i
(x
i−1
− x
i
− l
0,i
)
− c
i+1
(x
i
− x
i+1
− l
0,i+1
)
+ d
i
( ˙x
i−1
− ˙x
i
) − d
i+1
( ˙x
i
− ˙x
i+1
)
+ u
i
− u
i+1
+ F
Z,i
+ F
Gx,i
+ F
R,i
(3)
with c
0
= c
n+1
= d
0
= d
n+1
= u
0
= u
n+1
= 0. The
DoF of the system is N.
To influence the system, acuators have to apply
forces on the mass points. They serve as inputs to the
crawling system to control the distances between the
segments.
Control: To follow a given motion pattern, to react to
changes of the environment and to deal with unknown
or uncertain system parameters, an adaptive controller
is used that generates necessary actuator forces on its
own. The forces depend on the error e
j
(t):
• l
j
(t) := x
j−1
(t) − x
j
(t), the distance between
neighboring mass points, which are the system
outputs;
• l
ref, j
(t), the predefined time-variant reference dis-
tance functions;
• e
j
(t) := l
j
(t) − l
ref, j
(t), error of the output.
The used controller is described in (Behn, 2013). It
contains regular PD-control, which adapts the gain of
P and D elements depending on the 2-norm of the er-
ror ke(t)k. The controller’s goal is to track a reference
function of the outputs and to keep the error within a
certain tolerance λ-tube. This kind of λ-tracking in
combination with an adaptive controller is described
in (Behn and Loepelmann, 2012):
e(t) := l(t) −l
ref
(t)
u(t) = k(t) e(t) +k(t)κ
˙
e(t) = k(t) · (e(t) + κ
˙
e(t))
˙
k(t) =
γ· (ke(t)k−λ)
2
, ke(t)k ≥ λ +1
γ· (ke(t)k−λ)
0.5
, λ+1 > ke(t)k ≥ λ
0, (ke(t)k < λ)
∧(t − t
E
< t
d
)
−σk(t), (ke(t)k < λ)
∧(t − t
E
≥ t
d
)
k(t
0
) = k
0
(4)
with γ > 1, κ > 0, σ > 0, t
d
≥ 0, λ ≥ 0, k
0
> 0,
determined in pre-simulations and set in Table 2.
It is obvious that the proposed controller is based
on the availability of the error velocity. This is some-
times quite hard to arrange, therefore, see (Behn,
2011) and (Ye, 1999) for controllers without deriva-
tive measurement of the output.
ICINCO 2016 - 13th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
120

Controller (4) works as follows: if the error norm
is higher than λ, k(·) increases either quadratic or with
a square-root function depending on the amount of ex-
ceeding. The variable t
E
is the point in time, when the
error norm latest entered the λ-tube. If the error norm
is smaller than λ and t
E
is smaller than the parameter
t
d
, k(·) is staying constant. Ift
E
is bigger than t
d
, there
is an exponential decrease of k(·).
3 GENERATION OF GAITS
Firstly, it is demonstrated for a system of N = 3 mass
points, how the controller works and that suitable
gaits are necessary. Suitable means some kind of op-
timality with respect to resting phases of mass points
and speed of the whole system. Therefore, arbitrar-
ily chosen reference distance functions l
ref, j
(t) and
their time derivatives
˙
l
ref, j
(t) are defined according to
(Schwebke, 2012):
l
ref,1
(t) = l
0
+
1
4
l
0
sin(ωt)
l
ref,2
(t) = l
0
+
1
4
l
0
sin
ωt +
π
2
˙
l
ref,1
(t) =
1
4
l
0
ωcos(ωt)
˙
l
ref,2
(t) =
1
4
l
0
ωcos
ωt +
π
2
(5)
Figure 2 shows, how the gain k(t) behaves de-
pending on the error norm ke(t)k . Regarding the
worm movement x
i
(t), the system is able to move for-
ward successfully. However, the velocities of the seg-
ments ˙x
i
(t) are non-uniform,which results in different
resting times of the mass points. It is not possible to
create a defined gait with a certain sequence of active
spikes (i.e., resting mass points) by using this kind of
reference distance functions (5), which is important
for gait transition. Moreover, due to the arbitrarily
chosen gait, the speed of the worm system is rather
low (keep this in mind for the upcoming simulations,
where the speed of the system is increased in using
appropriate developed gaits).
Hence, gaits haveto be designed systematically, as
described in (Steigenberger and Behn, 2011). For fur-
ther algorithms relying on binary segment states (con-
tracted, extended), see (Slatkin et al., 1995), (Chen
et al., 1999a), (Chen et al., 1999b) and (Chen et al.,
2001).
First of all, gaits differ in the number of active
spikes a ∈ {1, . . . ,n}. Furthermore, there is a peri-
odic sequence of active spikes A(t), e.g., for a sys-
tem with N = 3 mass points a possible sequence is
A(t) = {0} → {1} → {2}. With this information,
0
5
10
15
20
0
100
200
300
time [s]
gain k [N/m]
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
error norm kek [m]
gain
error norm
λ-tube
(a) Gain and error norm.
0
5
10
15
20
−2
0
2
4
6
time [s]
worm movement x
i
[m]
mass point m
0
mass point m
1
mass point m
2
(b) Worm movement.
0
5
10
15
20
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
time [s]
velocity ˙x
i
[m]
(c) Worm velocity.
Figure 2: Worm-like locomotion of a system with 3 mass
points: arbitrary distance functions (5).
it can be deduced whether a distance l
j
(t) has to be
shortened or lengthened at a certain point of time.
Following the recommendation from (Steigenberger
and Behn, 2011), the sequence of active spike should
move to left or to the right (only by one segment)
like the worm does. A possible sequence is A(t) =
{0, 1} → {1, 2} → {2, 3} → {3, 0} for a system with
N = 4 segments, while A(t) = {0, 1} → {2, 3} →
{1, 2} → {3, 0} is not recommended. Hence, allowed
gaits can be described explicitly by the beginning se-
quence A
0
of the resting mass points of a time pe-
riod and the direction dir of the wave of active spikes,
which can be ”l” for left or ”r” for right.
The reference distance functions are built as de-
scribed in (Steigenberger and Behn, 2011). The time
intervals are defined as:
Gait Transition in Artificial Locomotion Systems using Adaptive Control
121

t ∈
p
T
N
, (p+ 1)
T
N
, p ∈ N
0
.
To ensure a smooth movement of the system, i.e.,
there are no jerks to the mass points, we use sin
2
(·)-
functions to describe the link lengths of the mass
points, while τ = t − p
T
N
:
˙
l
j
(τ) = εl
0
2N f sin
2
(πfNτ)
l
j
(τ) = l
0∗
+ εl
0
N fτ−
1
2π
εl
0
sin(2π fNτ) ,
(6)
• |ε| ∈ (0;1) is the relative factor of the maximum
distance change,
• f is the frequency of the A(t)-sequence with its
periodic time T =
1
f
, chosen in simulation to
avoid a rigid-body-movement of the whole worm
system,
• l
0
> 0 is the initial distance (detensioned spring),
• l
0∗
is the distance at the beginning of the time
interval (τ = 0), depending on the previous
interval either l
0
, l
0
(1+ε) or l
0
(1−ε) (Schwebke
and Behn, 2013).
The allowed gaits also differ in their load of the spikes
and actuators. To find the most advantageous (i.e.,
lowest load of actuators and spikes) gaits for transi-
tion, numerical simulations are executed. Gaits with
equal number of active spikes a (i.e., equally quick)
are rated with a weighting function:
W
S,g
:=w
1
k
max,S
2
+ w
2
n
∑
i=0
F
Z,i,max,S
2
+ w
3
n
∑
j=1
u
j,max,S
2
W
T,g
:=w
1
k
max,T
2
+ w
2
n
∑
i=0
F
Z,i,max,T
2
+ w
3
n
∑
j=1
u
j,max,T
2
W
S,g,sc
:=
W
S,g
W
S,min
; W
T,g,sc
:=
W
T,g
W
T,min
W
g,tot
:=
W
T,g,sc
+W
S,g,sc
2
+
W
T,g,sc
W
S,g,sc
+
W
S,g,sc
W
T,g,sc
(7)
Because of transient effects at the beginning of the
simulation, this function considers firstly the maxi-
mum load of actuators u
j
(·) and spikes F
Z,i
(·), and the
maximum gain parameter k(·) for a transient interval
W
T,g
as well as a stationary intervalW
S,g
. The weight-
ing factors are chosen as w
1
= 1.0m/N, w
2
= 4.0N
−1
,
w
3
= 4.0N
−1
to have a bigger influence of the load of
actuators and spikes. Afterwards, the values W
S,g
and
W
T,g
are scaled to the minimum value W
S,min
respec-
tively W
T,min
within the gaits with equal number of
active spikes a. Finally, transient and stationary parts
are weighted against each other. The minimum value
W
g,tot
within gaits with equal number of active spikes
a identifies the most advantageous gait.
This leads to the result shown in Table 1 for a sys-
tem with N = 10 mass points:
Table 1: Most advantageous gaits.
a
gait
1 A
0
= {1}, dir = r
2
A
0
= {2, 3}, dir = r
3 A
0
= {0, 1, 2}, dir = r
4
A
0
= {6, 7, 8, 9}, dir = l
5 A
0
= {2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, dir = l
6
A
0
= {5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0}, dir = l
7 A
0
= {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}, dir = l
8
A
0
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}, dir = l
9 A
0
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, dir = l
These gaits are used for gait transition.
4 GAIT TRANSITION
Changes of the environment, e.g., change of the slope,
malfunction of an actuator or failing of spikes, lead
to different loads of (the remaining) actuators and
spikes. To react to such circumstances, the system has
to change the gait and its frequency autonomously,
i.e., on its own. This is addressed to the following
investigations. Analogous example: driving a car –
increasing the frequency can be compared to acceler-
ating while gait changing is similar to gear shifting.
The frequency shall only be changed after con-
cluding a single period, i.e., when a part of the se-
quence A(t) is finished. Changing the frequency has
a great influence on the loads of actuators and spikes.
To affect their amount, a P-controller is used for the
frequency adjustment. Additionally, it is possible to
weight the load of actuators and spikes against each
other with the factors w
Fz
and w
u
:
f
1
=
w
Fz
f
0
(1+ k
p,Fz
(F
z,set
− F
z,act
))
w
Fz
+
w
u
f
0
(1+ k
p,u
(u
set
− u
act
))
w
u
, (8)
with k
p,Fz
and k
p,u
as the gain parameters for spikes
and actuators, f
0
as the previous frequency and f
1
as
the newly adjusted frequency. The setpoints F
z,set
and
u
set
are predefined, while the actual values are within
a single period:
ICINCO 2016 - 13th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
122

0 10 20 30 40
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
time [s]
frequency f [Hz]
0
1
2
number of active spikes a [-]
frequency active spikes
(a) Frequency and number of active spikes.
0 10 20 30 40
0
300
600
900
time [s]
gain k [N/m]
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
error norm kek [m]
gain
error norm
λ-tube
(b) Gain and error norm.
0 10 20 30 40
−10
0
10
20
time [s]
worm movement x
i
[m]
(c) Worm movement.
Figure 3: Worm-like locomotion of a system with 10 mass
points: without transition (part 1).
F
z,act
= max{F
z,0
, F
z,1
, ..., F
z,9
}
¯u
j
=
1
T
e
t
Z
t−T
e
u
j
(τ)dτ
u
act
= max{ ¯u
1
, ¯u
2
, ..., ¯u
9
}
(9)
The value for the frequency has to be limited to f
max
.
According to (Steigenberger and Behn, 2012), there
would occur rigid-body-movement, if the frequency
exceeded f
max
. The system would be uncontrollable.
The maximum frequency, from a kinematical theory
according to (Steigenberger and Behn, 2012), is given
by:
0 10 20 30 40
0.00
0.25
0.50
0.75
1.00
1.25
time [s]
mean velocity x
m
[m/s]
(a) Mean velocity.
0 10 20 30 40
−100
−50
0
50
100
time [s]
actuator forces u
j
[N]
(b) Actuator forces.
0 10 20 30 40
0
20
40
60
80
100
time [s]
spike forces F
Z,i
[N]
(c) Spike forces.
Figure 4: Worm-like locomotion of a system with 10 mass
points: without transition (part 2).
f
max
(a) =
s
gsin(α)
2πεl
0
N(N − a)
(10)
The system changes the number of active spikes after
finishing a total period T, i.e., when the sequence of
active spikes would start again. The model upshifts
(decrease the number of active spikes), if the maxi-
mum frequency f
max
of a gait is reached. It down-
shifts (increases the number of active spikes), if the
current reference velocity (11), according to (Steigen-
berger and Behn, 2012), is also reachable with the
next slower gait without exceeding the maximum fre-
quency of the slower gait:
¯v
ref
(a, f ) = (N − a)εl
0
f (11)
Gait Transition in Artificial Locomotion Systems using Adaptive Control
123

0 10 20 30 40
50
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
0.50
time [s]
frequency f [Hz]
0
2
4
6
8
10
number of active spikes a [-]
frequency active spikes
(a) Frequency and number of active spikes.
0 10 20 30 40
50
0
200
400
600
800
time [s]
gain k [N/m]
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
error norm kek [m]
gain
error norm
λ-tube
(b) Gain and error norm..
0 10 20 30 40
50
−10
0
10
20
time [s]
worm movement x
i
[m]
(c) Worm movement.
Figure 5: Worm-like locomotion of a system with 10 mass
points: with transition (part 1).
This downshift frequency f
min
is:
¯v
min,a
= ¯v
max,a+1
(N − a)εl
0
f
min
= [N − (a+ 1)]εl
0
f
max,a+1
f
min
=
N − (a+ 1)
N − a
f
max,a+1
(12)
To guarantee the same velocity before and after a gait
transition, the frequency has to be adapted. The anal-
ogy to car driving is the adaption of the engine speed.
The frequency after the transition is:
¯v
new
= ¯v
old
(N − a
new
)εl
0
f
new
= (N − a
old
)εl
0
f
old
f
new
=
N − a
old
N − a
new
f
old
(13)
0 10 20 30 40
50
0.00
0.25
0.50
0.75
1.00
time [s]
mean velocity x
m
[m/s]
(a) Mean velocity.
0 10 20 30 40
50
−100
−50
0
50
100
time [s]
actuator forces u
j
[N]
(b) Actuator forces.
0 10 20 30 40
50
0
20
40
60
80
100
time [s]
spike forces F
Z,i
[N]
(c) Spike forces.
Figure 6: Worm-like locomotion of a system with 10 mass
points: with transition (part 2).
5 SIMULATIONS
Example 1: Worm System with Constant Slope
without Gait Transition: First of all, a simulation
without transition and frequency controlling is pre-
sented to get familiar with the basic functionality of
the system. The worm crawls up a ramp with a slope
of 30
◦
with the maximum frequency f
max
= 0.147Hz
according to (10) of the fastest gait with a = 1. The
used parameters for each simulations are shown in Ta-
ble 2.
One can clearly see in Figure 3(c) a typical worm
movement with the reference functions according
to (6), the first mass point travels 18m in 40s. The
adaptive controller works reliably; the gain parameter
reaches its stationary state after 7s and oscillates
ICINCO 2016 - 13th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
124

0
50
100
150
200
250
300
0.00
0.12
0.24
0.36
0.48
0.60
time [s]
frequency f [Hz]
0
2
4
6
8
10
number of active spikes a [-]
frequency active spikes
(a) Frequency and number of active spikes.
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
0
400
800
1,200
time [s]
gain k [N/m]
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
error norm kek [m]
gain
error norm
λ-tube
(b) Gain and error norm.
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
−20
0
20
40
60
80
time [s]
worm movement x
i
[m]
(c) Worm movement.
Figure 7: Worm-like locomotion of a system with 10 mass
points: with transition and changing slope (part 1).
around a value of 700N/m, see Figure 3(b). The max-
imum spike force is 98.3N, see Figure 4(c), while the
maximum actuator force is 90.3N, see Figure 4(b).
Thus, the maximum values F
Z,max
respectively u
max
are set as 100N for the spike force and 90N for the
actuator force for the upcoming simulations with gait
transitions.
Example 2: Worm System with Constant Slope
and with Gait Transition: Now, the system will
change the gait and the frequency, while the weighing
factors in (8) are w
Fz
= w
u
= 1. The worm crawls up
a ramp with a slope of 30
◦
again.
As expected, the gait is changed depending on the
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
0.00
0.25
0.50
0.75
1.00
time [s]
mean velocity x
m
[m/s]
(a) Mean velocity.
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
−100
−50
0
50
100
time [s]
actuator forces u
j
[N]
(b) Actuator forces.
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
0
30
60
90
120
time [s]
spike forces F
Z,i
[N]
(c) Spike forces.
Figure 8: Worm-like locomotion of a system with 10 mass
points: with transition and changing slope (part 2).
Table 2: Parameters for simulations.
t
end
= 40s m
i
= 1.0kg
c
j
= 10.0N/m d
j
= 5.0kg/s
l
0
= 1.0m ε = 0.4
λ = 0.05m κ = 1s
t
d
= 2.0s γ = 500
σ = 0.2s
−1
k
0
= 10N/m
k
p,Fz
= 0.02N
−1
k
p,u
= 0.02N
−1
g = 9.806m/s
2
α = 30
◦
loads, see Figure 5(a). Due to changing only one gait,
it takes a long time until the system finds a suitable
gait. E.g., the system requires 40s to change from
a = 9 to a = 1. To solve this problem, we restrict the
usable number of gaits from 9 to 3 afterwards.
Gait Transition in Artificial Locomotion Systems using Adaptive Control
125

0
50
100
150
200
250
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
0.50
time [s]
frequency f [Hz]
0
2
4
6
8
10
number of active spikes a [-]
frequency active spikes
(a) Frequency and number of active spikes.
0
50
100
150
200
250
0
400
800
1,200
time [s]
gain k [N/m]
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
error norm kek [m]
gain
error norm
λ-tube
(b) Gain and error norm.
0
50
100
150
200
250
−20
0
20
40
60
80
time [s]
worm movement x
i
[m]
(c) Worm movement.
Figure 9: Worm-like locomotion of a system with 10 mass
points: limitation of actuator forces (part 1).
Example 3: Worm System with Changing slope
and with Gait Transition: Here, the worm also
crawls up a ramp with a slope of 30
◦
, but when the
worm covered the mean distance of 25m, there is
a change of it to 60
◦
for each segment (in the plots
marked with a red vertical line). After a distance
of 50m, it is changed to 30
◦
again (also marked
with a red vertical line). To get the setpoints F
Z,set
respectively u
set
for actuator and spike force, the
maximum values F
Z,max
and u
max
are multiplied from
now on with a safety factor s = 0.8.
The system adapts the frequency and gait after the
change of the slope to reduce/increase the loads of
actuators and spikes, see Figure 7(a). Similiar to
0
50
100
150
200
250
0.00
0.25
0.50
0.75
1.00
time [s]
mean velocity x
m
[m/s]
(a) Mean velocity.
0
50
100
150
200
250
−100
−50
0
50
100
time [s]
actuator forces u
j
[N]
(b) Actuator forces.
0
50
100
150
200
250
0
30
60
90
120
time [s]
spike forces F
Z,i
[N]
(c) Spike forces.
Figure 10: Worm-like locomotion of a system with 10 mass
points: limitation of actuator forces (part 2).
Example 2, it takes too much time to adjust the gait.
E.g., the system requires 53s to change from a = 1
to a = 9. Furthermore, there occur values above the
maximum permissible values F
Z,max
and u
max
due to
slope of 60
◦
, see Figure 8(b) and 8(c). This problem
is faced below.
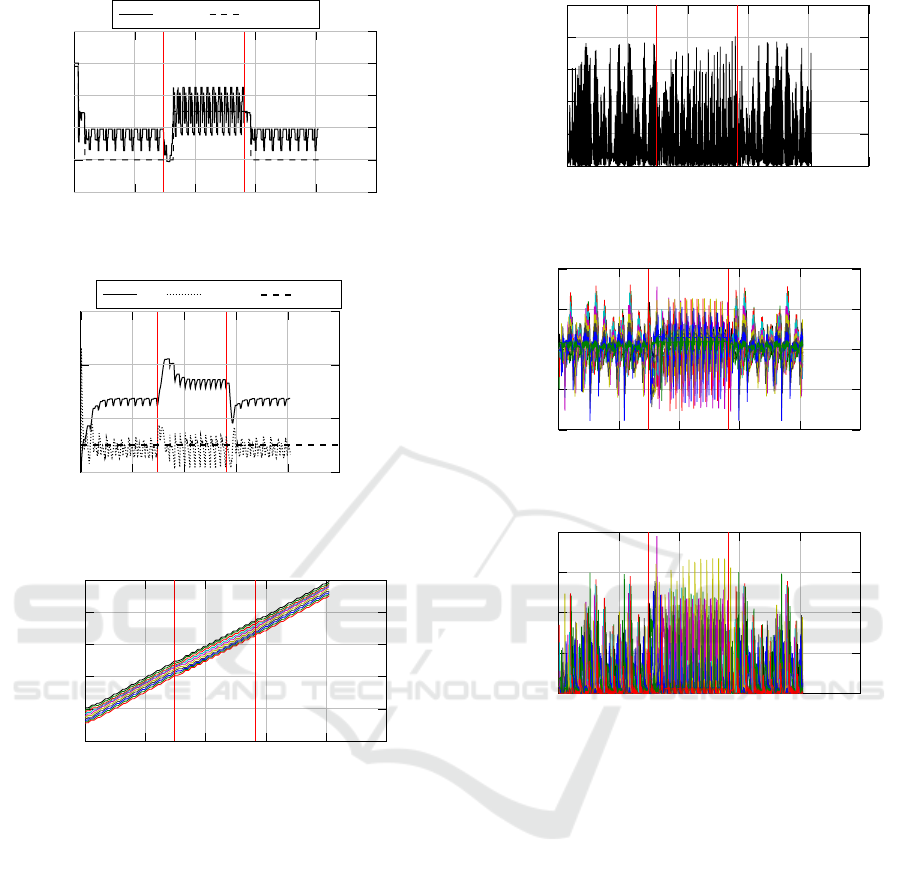
Example 4: Worm System with Changing Slope
and with Gait Transition for Limitation of Actu-
ator Forces: To limit the actuator forces, a limita-
tion factor l = 0.99 is used, that is multiplied with
the maximum actuator force u
max
. Actuators are now
not able to exceed this value. In practice, this could
be realized with a current limit function. In contrast,
the spike forces cannot be limited by any function and
hence, the spike load has to be estimated.
The actuator forces do not exceed their maximum
ICINCO 2016 - 13th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
126
0
50
100
150
200
250
0.00
0.08
0.16
0.24
0.32
0.40
time [s]
frequency f [Hz]
0
2
4
6
8
10
number of active spikes a [-]
frequency active spikes
(a) Frequency and number of active spikes.
0
50
100
150
200
250
0
600
1,200
1,800
time [s]
gain k [N/m]
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
error norm kek [m]
gain
error norm
λ-tube
(b) Gain and error norm.
0
50
100
150
200
250
−20
0
20
40
60
80
time [s]
worm movement x
i
[m]
(c) Worm movement.
Figure 11: Worm-like locomotion of a system with 10 mass
points: transition with three gaits (part 1).
value, see Figure 10(b). However, the spike forces
are still exceeded, see Figure 10(c). Spikes have
to be designed adequately solid and should not be
overstrained in practice.
Example 5: Worm System with Changing Slope
and with Gait Transition using Only Three
Gaits: As mentioned above, the number of gait
transitions has to be reduced. For this purpose, the
system can change only three gaits at a time. Pos-
sible gaits are now those with a = 2, 5, 8 from Table 2.
The number of transitions can be reduced signifi-
cantly with this solution, see Figure 11(a). The sys-
tem is able to find a suitable gait more quickly. The
0
50
100
150
200
250
0.00
0.25
0.50
0.75
1.00
1.25
time [s]
mean velocity x
m
[m/s]
(a) Mean velocity.
0
50
100
150
200
250
−100
−50
0
50
100
time [s]
actuator forces u
j
[N]
(b) Actuator forces.
0
50
100
150
200
250
0
30
60
90
120
time [s]
spike forces F
Z,i
[N]
(c) Spike forces.
Figure 12: Worm-like locomotion of a system with 10 mass
points: transition with three gaits (part 2).
loads of spikes and actuators are not influenced by this
method.
6 CONCLUSION & OUTLOOK
The main focus of the presented work was laid on the
design of an artificial worm-like locomotion system
with 10 mass points using adaptive control for gait
transition and performing simulations with it. There-
fore, gaits had to be generated, which differ in the load
of actuators and spikes. In order to find those with the
smallest load for gait transition, a weighting function
was used that considers stationary and transient parts.
After determining these most advantageous gaits, a
scheme for frequency-control and gait transition was
presented. The frequency-controlleruses actuator and
Gait Transition in Artificial Locomotion Systems using Adaptive Control
127

Figure 13: Prototype of a cascaded locomotion system consisting of 4 mass points on a conveyor belt with changing slope,
(Otterbach, 2016).
spike forces as input, which can be weighted against
each other. A foregoing simulation without transi-
tion proved the suitability of the adaptive controller
for this system and also served to determine the max-
imum forces for actuators and spikes for the follow-
ing simulations. With this, a gait transition simulation
was performed. The system changed the frequency
and gait depending on the actuators’ and spikes’ load.
However, the maximum values for actuator and spike
force were exceeded. So, a limitation of the actua-
tor forces was implemented, which prevents the ac-
tuator forces of exceeding, but cannot keep the spike
forces below their maximum value. Also, the system
requires too much time to reach the suitable gait. To
deal with this problem, the number of gaits was re-
duced to three. This solution reduces the number of
gait transitions successfully.
Future work shall be directed to find a solution to
limit the spike forces; consideration of sliding fric-
tion; experimental verification of these theoretical in-
vestigations; expand the system to a 2D-snake-like-
movement based on (Behn et al., 2015), which deals
only with the adaptive movement without gait transi-
tion.
Furtheron, we have to focus on experimental re-
sults, because the working principle of the gait ad-
justing algorithm is just validated by numerical sim-
ulations. For this, we developed a prototype of (until
now) 4 mass points moving on a conveyor belt whose
slope can be controlled/pre-adjusted, see Figure 13.
Experimental results will be generated in near future.
REFERENCES
Behn, C. (2011). Adaptive control of straight worms with-
out derivative measurement. Multibody System Dy-
namics, 26(3):213–243.
Behn, C. (2013). Mathematical modeling and control of
biologically inspired uncertain motion systems with
adaptive features. Habilitation, Dept. of Mechanical
Engineering, TU Ilmenau, Germany.
Behn, C., Heinz, L., and Kr¨uger, M. (2015). Kine-
matic and dynamic description of non-standard snake-
like locomotion systems. IFAC Mechatronics.
doi:10.1016/j.mechatronics.2015.10.010.
Behn, C. and Loepelmann, P. (2012). Adaptive vs. fuzzy
control of uncertain mechanical systems. Interna-
tional Journal of Applied Mechanics (IJAM), 4.
Behn, C. and Zimmermann, K. (2011a). Straight worms un-
der adaptive control and friction - part 1: Modeling, in
iutam symposium on dynamics modeling and interac-
tion control in virtual and real environments. IUTAM
Bookseries, 30:57–64.
Behn, C. and Zimmermann, K. (2011b). Straight worms
under adaptive control and friction - part 2: Adap-
tive control, in iutam symposium on dynamics mod-
eling and interaction control in virtual and real envi-
ronments. IUTAM Bookseries, 30:65–72.
Chen, I.-M., Yeo, S., and Gao, Y. (1999a). Gait generation
for inchworm-like robot locomotion using finite state
model. Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE International
Conference on Robotics & Automation.
Chen, I.-M., Yeo, S., and Gao, Y. (1999b). Locomotion gait
generation for mutli-segment inchworm. Proceedings
of the 10th World Congress on the Theory of Machines
and Mechanisms.
Chen, I.-M., Yeo, S., and Gao, Y. (2001). Locomotive gait
generation for inchworm-like robots using finite state
approach. Robotica, 19:535–542.
Dario, P., Carrozza, M., Allotta, B., and Guglielmelli, E.
(1996). Micromechatronics in medicine. IEEE/ASME
Transactions on Mechatronics, 1:137–148.
ICINCO 2016 - 13th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
128

Fatikow, S. and Rembold, U. (1997). Microsystem technol-
ogy and microrobotics. Springer-Verlag.
Hirose, S. (1993). Biologically Inspired Robots: Snake-
like Locomotors and Manipulators. Oxford University
Press, Oxford, 3rd edition.
Kubota, T., Nagaoka, K., Tanaka, S., and Nakamura, T.
(2007). Earth-worm typed drilling robot for subsur-
face planetary exploration. IEEE International Con-
ference on Robotics and Biomimetics, pages 1394–
1399.
Liu, W., Menciassi, A., Scapellato, S., Dario, P., and
Chen, Y. (2006). A biomimetic sensor for a crawl-
ing minirobot. Robotics and Autonomous Systems,
54:513–528.
Meier, P., Dietrich, J., Oberth¨ur, S., Preuß, R., Voges, D.,
and Zimmermann, K. (2004). Development of a peri-
staltically actuated device for the minimal invasive
surgery with a haptic sensor array. Micro- and Nanos-
tructures of Biological Systems, pages 66–89.
Merz, R. A. and Edwards, D. R. (1998). Jointed setae - their
role in locomotion and gait transitions in polychaete
worms. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and
Ecology, 228:273–290.
Miller, G. (1988). The motion dynamics of snakes and
worms. Computer Graphics, 22:169–173.
Nakamura, T., Kato, T., Iwanaga, T., and Muranaka, Y.
(2006). Peristaltic crawling robot based on the lo-
comotion mechanism of earthworms. Proceedings
4th IFACSympos on Mechatronic Systems, pages 513–
528.
Ostrowski, J. and Burdick, J. (1996). Gait kinematics for a
serpentine robot. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robotics and
Autom.
Otterbach, J. (2016). Entwicklung von kaskadierten
Lokomotionssystemen und Implementierung von
Reglungsalgorithmen (Development of cascaded lo-
comotion systems and implementation of control al-
gorithms). Master Thesis, Dept. of Mechanical Engi-
neering, TU Ilmenau, Germany.
Schwebke, S. (2012). Contributions to adaptive control
strategies of biomimetic, worm-like locomotion sys-
tems and their use for gait shifting. Bachelor Thesis,
Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, TU Ilmenau, Ger-
many.
Schwebke, S. and Behn, C. (2013). Worm-like robotic
systems: Generation, analysis and shift of gaits us-
ing adaptive control. Artificial Intelligence Research
(AIR), 2:12–35.
Slatkin, A., Burdick, J., and Grundfest, W. (1995). The
development of a robotic endoscope. Proc. Int. Conf.
Intell. Robots and Systems, 2.
Steigenberger, J. and Behn, C. (2011). Gait generation
considering dynamics for artificial segmented worms.
Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 59:555–562.
Steigenberger, J. and Behn, C. (2012). Worm-like locomo-
tion systems: an intermediate theoretical approach.
Oldenbourg Verlag.
Vaidyanathan, R., Chiel, H., and Quinn, R. (2000). A hy-
drostatic robot for marine applications. Robotics and
Autonomous Systems, 30:103–113.
Ye, X. (1999). Universal λ-tracking for nonlinearly-
perturbed systems without restrictions on the relative
degree. Automatica, 35:109–119.
Zimmermann, K., Zeidis, I., and Behn, C. (2009). Mechan-
ics of Terrestrial Locomotion - With a Focus on Non-
pedal Motion Systems. Springer, Berlin.
Gait Transition in Artificial Locomotion Systems using Adaptive Control
129
