
Fuzzy Modeling and Control for Intention Recognition in Human-robot
Systems
Rainer Palm, Ravi Chadalavada and Achim J. Lilienthal
AASS, Dept. of Technology
¨
Orebro University SE-70182
¨
Orebro, Sweden
Keywords:
Fuzzy Control, Fuzzy Modeling, Human-robot Interaction, Human Intentions.
Abstract:
The recognition of human intentions from trajectories in the framework of human-robot interaction is a chal-
lenging field of research. In this paper some control problems of the human-robot interaction and their inten-
tions to compete or cooperate in shared work spaces are addressed and the time schedule of the information
flow is discussed. The expected human movements relative to the robot are summarized in a so-called ”com-
pass dial” from which fuzzy control rules for the robot’s reactions are derived. To avoid collisions between
robot and human very early the computation of collision times at predicted human-robot intersections is dis-
cussed and a switching controller for collision avoidance is proposed. In the context of the recognition of
human intentions to move to certain goals, pedestrian tracks are modeled by fuzzy clustering, lanes preferred
by human agents are identified, and the identification of degrees of membership of a pedestrian track to spe-
cific lanes are discussed. Computations based on simulated and experimental data show the applicability of
the methods presented.
1 INTRODUCTION
Dealing with interactions of humans and autonomous
robots in common working areas is a challenging re-
search field with regard to system stability and per-
formance and to human safety. Research results on
planning of mobile robot tasks, learning of repeated
situations, navigation and obstacle avoidance have
been published by (Mataric, 1990; Firl, 2014; Khatib,
1985; Palm and Bouguerra, 2013). When human
agents and robots share the same workspace, both of
them have to adapt their behavior, to either support
their cooperation, or to enable them to do their own
task separately. In this connection it is difficult to
predict the behavior, motions and goals of a human
agent. Even more it is important to predict the hu-
man behavior for a limited time horizon with a cer-
tain probability to enable the robot to perform ade-
quate reactions. One class of solutions to this prob-
lem is the building of models of the human behav-
ior by clustering methods (Mataric, 1990; F. Sadri
and Xafi, 2012; R. Palm and Kadmiry, 2009). Fur-
ther research activities focus on Bayesian networks
(Tahboub, 2006; Han and Pereira, 2013), Hidden
Markov Models (HMM) (M. Bennewitz and Thrun,
2005), Fuzzy logic or Fuzzy Cognitive Maps and re-
inforcement learning (Tahboub, 2006; A. Ciaramella
and Straccia, 2010). Heinze addresses human in-
tentions from the ontological point of view (Heinze,
2004). Another aspect is the (automatic) recognition
of human intentions to aim at a certain goal. Some
research on intention recognition describes human-
robot interaction scenarios and the ”philosophical and
technical background for intention recognition” (Tah-
boub, 2006). Further research deals with ”Intention
Recognition in Human-RobotCollaborativeSystems”
(Aarno, 2007; Krauthausen, 2012), human-robot mo-
tions initiated by human intentions (T. Fraichard
and Reignier, 2014), and socially inspired planning
(J.V. Gomez and Garrido, 2013). In practice, the iden-
tification of a human intention needs to predict the di-
rection of motion, the average velocity and parts of
the future trajectory. In this connection, Bruce et al
address a planned human-robot rendezvous at an in-
tersection zone (J. Bruce and Vaughan, 2015). Satake
et al (Satake et al., 2009) describe a social robot, that
approaches a human agent in a way that is acceptable
for humans. Further research on human intentions to-
gether with trajectory recognition and planning is pre-
sented by (A.F.Johansson, 2009; Chadalavada et al.,
2015). The modeling of pedestrian trajectories using
Gaussian processes is shown in (T. Ellis and Reid,
2009). In (Makris and Ellis, 2010) fuzzy methods,
probabilistic methods and HMM approaches for mod-
Palm, R., Chadalavada, R. and Lilienthal, A.
Fuzzy Modeling and Control for Intention Recognition in Human-robot Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0006015400670074
In Proceedings of the 8th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2016) - Volume 2: FCTA, pages 67-74
ISBN: 978-989-758-201-1
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
67
eling of human trajectories are compared. In addition
to the recent research mentioned above and as an ex-
tension of our work described in (R. Palm and Lilien-
thal, 2016), this paper concentrates on the recognition
of human intentions to move along certain trajecto-
ries. The method is based on observations of early
trajectory parts, plus a subsequent extrapolation. The
here discussed control principles of interaction be-
tween human and robot mainly deal with trajectory
planning and external sensor feedback on a higher
level of the control hierarchy. Furthermore, the time
schedule of the information flow and the kinematic re-
lationship of a human-robot system in motion is con-
sidered. The observation of the human agent by the
robot supplies motion data that are Kalman-filtered to
cope with uncertainties and noise. This leads to an es-
timation of the velocity vector of the human relative to
the robot which is depicted in a ”compass dial”. From
this, a set of fuzzy rules is extracted that results in a
possible reaction of the robot either to prevent a col-
lision or enable a cooperation. Our case is somehow
different from the usual case of avoidance of moving
obstacles due to the uncertainty to predict human in-
tentions. A special issue is the case of unchanged di-
rections of a motion both of the human and the robot
that should be distinguished from a common obstacle
avoidance methods (Khatib, 1985). This is tackled by
a switching robot controller that computes the time
for possible collisions at the intersections. According
to this knowledge the controller changes the robot’s
speed which helps to prevent collisions at intersec-
tion of the planned paths. Due to uncertainties in the
observations and to measurement noise the intersec-
tion points are extended to intersection areas which
must not be entered at the same time neither by the
human nor by the robot. Since this operation com-
prises only the first part of the human motion the sub-
sequent extrapolations are updated at each time step
in order to avoid larger errors. Another essential issue
is the identification of lanes from trajectories usually
preferred by human agents in an open area or at a fac-
tory work floor. This is motivated by the need for an
early reaction of the robot to the human’s intention to
walk, and to plan either a collision avoidance or a co-
operation action. In this paper we concentrate on the
fuzzy modeling of pedestrian tracks, the identification
of lanes preferred by the human agents, and the iden-
tification of a membership of a pedestrian track (or
parts of it) to a specific lane.
The paper is organized as follows. In Section 2
we address the interaction between human and robot
from the control structure point of view and the time
schedule of the information flow. Section 3 deals with
the kinematic and geometric relations between human
and robot. A ”compass dial” with the relative veloci-
ties and the corresponding fuzzy rules is presented in
Sect. 4. Section 5 deals with avoidance strategies at
intersections. Section 6 addresses the fuzzy modeling
of sets (bundles) of pedestrian tracks and the identifi-
cation of the membership of a single track to a certain
lane. Section 7 presents results based on simulations
and experimental data, and Sect. 8 ends with a dis-
cussion and conclusions.
2 INTERACTION BETWEEN
HUMAN AND ROBOT
In a shared working environment, human and robot
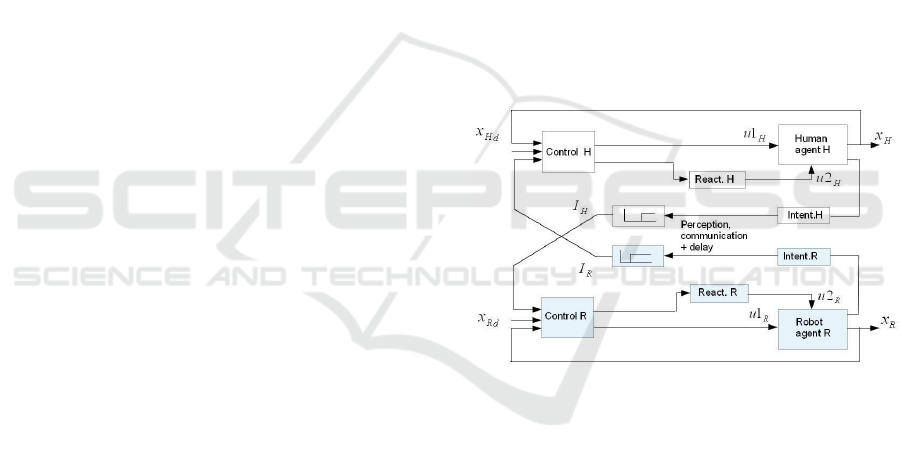
are constituted by a common control system shown in
Fig. 1. Both human and robot are driven by their in-
dividual goals (desired trajectories) x
H
d
and x
R
d
. Ac-
tions and reactions are represented by desired states
x
H
d
(t
i
) and x
R
d
(t
i
). From the interaction of the two
agents we obtain observable states x
H
(t
i
) and x
R
(t
i
).
Figure 1: Human-robot interaction, control scheme.
Intentions I
H
and I
R
are signals (e.g. information
about parts of trajectories) transmitted to/observed by
the other agent. The dynamic equations can formally
be written as
˙x
H
= f
H
(x
H
,u1
H
,u2
H
); ˙x
R
= f
R
(x
R
,u1
R
,u2
R
)
u1
H
= g1
H
(x
H
d
,x
H
);u1
R
= g1
R
(x
R
d
,x
R
)
u2
H
= g2
H
(I
R
,x
H
);u2
R
= g2
R
(I
H
,x
R
)
I
H
= h
H
(x
H
,x
R
,x
H
d
);I
R
= h
R
(x
R
,x
H
,x
R
d
) (1)
The 1-st two lines of (1) denote the individual dy-
namics of human and robot, where the next two lines
denote the ’crosswise’ influence of intention and reac-
tion between human and robot. The functions in (1)
are highly nonlinear hybrid functions with continuous
and switching attributes. A good example for model-
ing human-robot dynamics can be found in (P. Leica
FCTA 2016 - 8th International Conference on Fuzzy Computation Theory and Applications
68

and Carelli, 2015). Recall here that the control prob-
lems discussed here deal with the higher control level
of external sensory and trajectory generation. Fur-
thermore the feasibility of the desired trajectory x
R
d
and its possible variations should be guaranteed be-
cause of the nonholonomic kinematics of the robot.
In our case, intentions are functions of desired and
actual states. The robot controllers g1
R
and g2
R
can
be designed based on the knowledge about the system
dynamics (R.-E.Precup and Preitl, 2009) whereas the
human controllers g1
H
and g2
H
, which have been in-
troduced due to formal reasons, cannot be designed in
the same way. The same is true for the formal descrip-
tion f
H
of the human behavior which is usually only a
rough approximation of the reality. Since a modeling
especially of the human’s behavior is quite difficult,
the modeling of both the robot and the human by TS
fuzzy models from motion data is worth mentioning.
In this case each of the nonlinear functions of (1) split
up into n local functions like
f
H
=
n
∑
i=1
w
i
(x
H
) · f
H
i
(x
H
,u1
H
,u2
H
) (2)
f
R
=
n
∑
i=1
w
i
(x
R
) · f
R
i
(x
R
,u1
R
,u2
R
)
where w
i
are membership functions. Let furthermore
the robot controllers u1
R
,u2
R
either be designed as
weighted combinations of local controllers
u1
R
=
n
∑
i=1
w
i
(x
R
) · g1
R
i
(x
R
d
,x
R
) (3)
u2
R
=
n
∑
i=1
w
i
(x
R
) · g2
R
i
(I
H
,x
R
)
or as Mamdani expert rules formulated in Sect. 4.
On the other hand, human controllers u1
H
,u2
H
are
also expressed as Mamdani expert rules which are the
counterparts of the robot expert rules. A switching
robot controller for collision avoidance is presented
in Sec. 5. An intention may become observable in
an early part of the human trajectory x
H
(t
k
|k = 1...m)
where m is the time horizon on the basis of which
the robot should recognize the human’s intention to
move. This information is sent to the robot with a de-
lay T
d
H
. After that the robot starts its intention recog-
nition and starts to plan/compute a corresponding re-
action x
R
d
(t
i
). The intention to react is realized as
a part of the trajectory of the robot x
R
(t
k
|k = j...n)
where (n − j) is the corresponding time horizon on
the basis of which the human tries to recognize the
robot’s intention to move. Then this intention is trans-
mitted to the human.
The sampling time of the whole process is T
tot
.
Robot and human can control the mutual cooperation
only if T
tot
meets certain requirements regarding the
time constants of the system. There are two time con-
stants involved, the time constant τ
H
of the human and
the time constant τ
R
of the robot. Let the total process
time constant be the sum of the two
τ
tot
= τ
H
+ τ
R
(4)
A rule of the thumb says that the sample time T
tot
should be 5...30 times shorter than the largest time
constant of the process ((Ed.), 1995).
3 KINEMATIC RELATIONS OF
HUMAN AGENTS AND
MOBILE ROBOTS IN A
COMMON WORKSPACE
The analysis of the mutual observations between
human and robot requires the formulation of rela-
tive positions/orientations and velocities in the lo-
cal coordinate systems C
H
(human) and C
R
(robot)
and the global coordinate system C
B
(basis). First,
let us assume a sufficient knowledge of the posi-
tions/orientations of robot and human both in their lo-
cal systems C
H
, C
R
and in the basis system C
B
. The
relation between two coordinate systems C
A
and C
B
is then defined by the transformation Figure 2 shows
the kinematic relations between the coordinate sys-
tems C
R
, C
H
, and C
B
: T
HB
between human and ba-
sis, T
RB
between robot and basis, T
HR
between human
and robot. The orientation, of human and robot are
chosen so that the y axis is pointing in the direction
of motion. Next an additional coordinate system C
˜
H
is defined whose y-axis points from the center of C
H
to the center of C
R
. This coordinate system is nec-
essary for the formulation of the heading angle from
human to robot. The distance between C
H
(and C
˜
H
)
andC
R
is denoted by d
HR
. In the following we assume
parts of the intended trajectory x
HR
(t
i
) of the human
to be measurable by the robot from which the velocity
Figure 2: Transformations between frames.
Fuzzy Modeling and Control for Intention Recognition in Human-robot Systems
69

˙x
HR
(t
i
), the orientation angle φ
HR
(t
i
) and the trans-
formation matrix T
HR
(t
i
) can be estimated. Since the
robot is assumed to know its own trajectory x
RB
(t
i
)
and the transformation matrix T
RB
(t
i
) we can compute
the transformation matrix: T
HB
(t
i
) = T
RB
(t
i
) · T
HR
(t
i
).
Then we measure the distance d
HR
between C
H
and
C
R
, and the relative angle α
˜
HR
between the line C
H
– C
R
and the y-axis of C
R
. Finally we compute the
heading angle φ
˜
HH
= π − (α
˜
HR
+ φ
H
R) between C
˜
H
and C
H
which is necessary for the qualitative relation
between human and robot. Now we have all informa-
tion to formulate a set of qualitative fuzzy rules for
human-robot interactions.
4 FUZZY RULES FOR
HUMAN-ROBOT
INTERACTIONS
In the center of C
˜
H
a so-called compass dial
is introduced that expresses the qualitative rela-
tionship of the human intentions seen from the
robot. These comprise 8 human motions rela-
tive to the robot: ’APP=approach’, ’AVR=avoid
right’, ’MOR=move right’, ’RER=recede right’,
’REC=recede’, ’REL=recede left’, ’MOL=move
left’, ’AVL=avoid left’.
Figure 3: Compass dial for human actions.
To identify the trajectory of the human relative to
the robot it is enough to know the heading angle φ
˜
H
H
and the relative velocity ∆v = |˙x
HB
− ˙x
RB
| = |˙x
HR
|.
Since ∆v is an invariant it becomes clear that it can be
computed in each arbitrary coordinate system. Ones
the heading angle φ
˜
HH
is computed one can deter-
mine a qualitative relation between human and robot
according to the compass dial in Fig. 3. A fuzzy la-
bel is attached to each motion direction of the human
agent. A crisp heading angle φ
˜
HH
is fuzzified with re-
Figure 4: Fuzzy sets for human motions.
spect to the corresponding fuzzy sets for ’approach’,
’avoid right’ etc (see Fig. 4). From α
˜
HR
, φ
˜
HH
, ∆v and
the distances |∆x| = |x
HR
| the response of the robot to
the human’s intention is computed in an early state of
the human action. However, because of the uncer-
tain nature of the data (system/measurement noise)
one obtains estimates of positions and velocities by
an appropriate Kalman filter. Noise on velocity and
measurement are filtered out leading to a smooth tra-
jectory (or part of trajectory) from which the velocity
vector is estimated. The variables to be processed are
α
˜
HR
, φ
˜
HH
, the distance |∆x| = |x
HR
|, and the relative
velocities |∆v|. For |x
HR
| and |∆v| fuzzy sets ’Small’,
’Medium’, and ’Large’ of Gaussian type are defined
and appropriate fuzzy rules are formulated
IF α
˜
HR
= A
i
φ
˜
HH
= P
i
AND
|∆x| = DX
i
AND |∆v| = DV
i
(5)
THEN ACT
rob
ACT
rob
: φ
HR
rob
= PH
i
AND |v|
rob
= VR
i
i - rule number
α
˜
HR
- relative angle between C
˜
H
and C
R
A
i
- fuzzy set for the relative angle
φ
˜
HH
- heading angle between C
˜
H
and C
H
P
i
- fuzzy set for the heading angle
|∆x| - distance between C
H
and C
R
DX
i
- fuzzy set for the distance
|∆v| - relative velocity between C
H
and C
R
DV
i
- fuzzy set for the relative velocity
φ
HR
rob
- steering angle of robot
PH
i
- fuzzy set for the steering angle
|v|
rob
- desired velocity of the vehicle
VR
i
- fuzzy set for the desired velocity
However, not every combination makes sense. There-
fore ”pruning” of the set of rules and intelligent hier-
archization can solve this problem. A simple set of
rules for α
˜
HR
> 0 to avoid a collision between human
and robot contains only the heading angle φ
˜
HH
and
the steering angle φ
HR
rob
like:
IF φ
˜
HH
= APP THEN φ
HR
rob
= TR (6)
where TR=turn right, TL=turn left, MS=move
straight ahead, MSSD=move straight ahead/slow
down.
FCTA 2016 - 8th International Conference on Fuzzy Computation Theory and Applications
70
5 SWITCHING CONTROLLER
FOR COLLISION AVOIDANCE
5.1 Early Observation of Trajectories
From measured robot/human positions taken at an
early point in time Kalman filtered sequences of robot
and human positions x
RB
(t
i
) and x
HR
(t
i
) are gained
from which the velocities v
H
and v
R
are estimated.
Then the distance d
HR
between C
H
and C
R
and the
relative angle α
˜
HR
are measured and the angle φ
HR
computed.
Despite of existent traffic rules a collision be-
tween human agent and robot may occur especially
in the cases AVR,MOR,RER or AVL,MOL,REL of
the compass dial. Therefore at a certain distance the
robot controller switches from the ’normal mode’ to
a ’prediction mode’ to compute an ’area of intersec-
tion’ and the time to reach it. After having reached
this area the controller switches back to the ’normal
mode’ keeping its latest velocity constant.
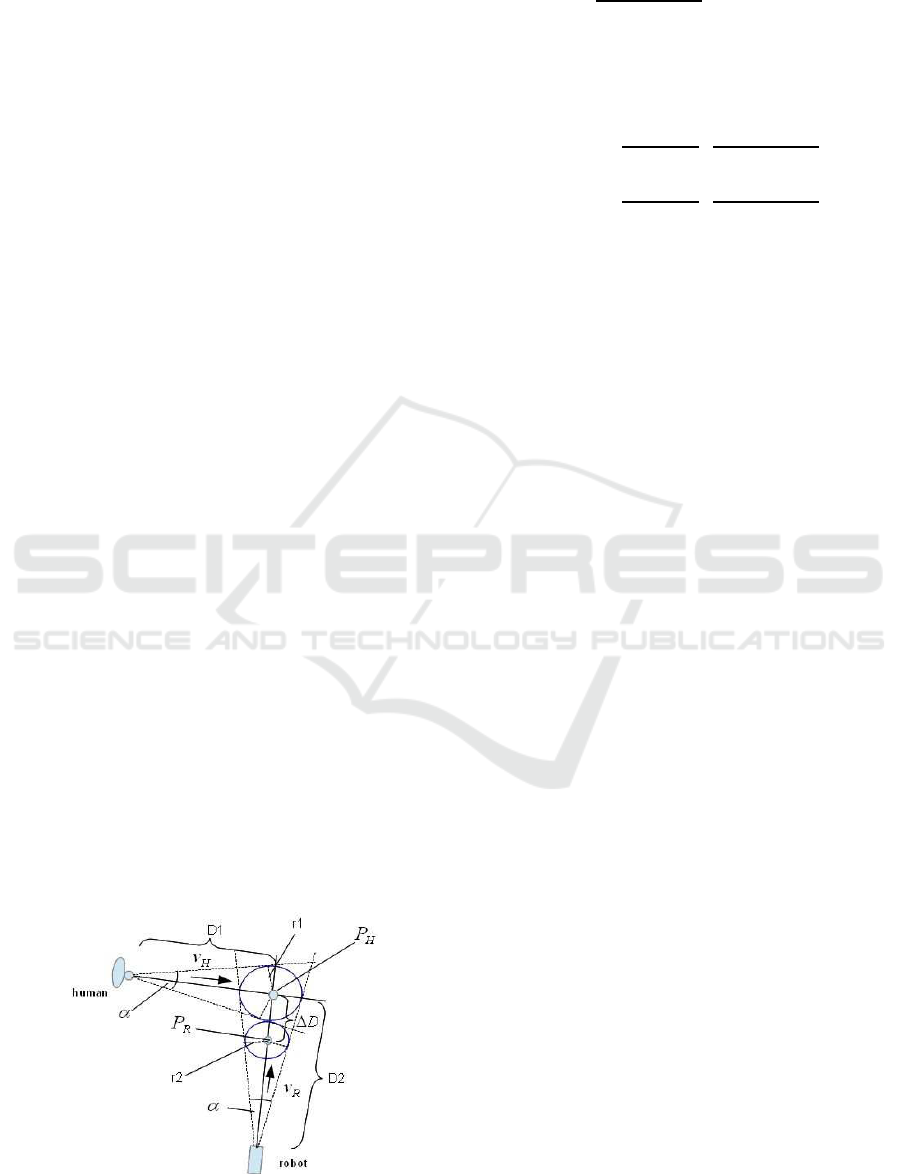
5.2 Uncertainty in Measurements
Uncertainties in measurements and unexpected
changes in directions and velocities lead to deviations
in the calculations of possible crossing points. From
simulations and experiments circular areas of possi-
ble collisions can be designed. Figure 5 shows the
relations for the ”1 human - 1 robot” case. Let P
H
be
the crossing point of human and robot and α the an-
gle of uncertainty for both human and robot at a spe-
cific time t
i
. A circle with the radius r
1
= D
1
· sinα/2
describes the uncertainty area A
H
of the human to
be avoided by the robot. On the other hand, the
robot has its own circular uncertainty area A
R
that
should not overlap with A
H
. Let the distance between
robot and crossing point be ∆D then the radius of A
R
is r
2
= (D
1
− ∆D) · sinα/2. From the requirement
A
H
∩A
R
=
/
0 we obtain ∆D ≥ r
1
+r
2
. For ∆D = r
1
+r
2
Figure 5: Crossing areas.
we obtain
r
2
=
sinα/2
(1+ sinα/2)
(D
2
− r
1
) (7)
and finally the velocity v
r
for the robot to reach the
distance point P
R
in the time t
HR
that the human would
need to get to P
H
(see (8 a))
a : v
R
opt
=
(D
2
− r
1
)
t
HR
·
1
(1+ sinα/2)
(8)
b : v
R
opt
=
(D
2
+ r
1
)
t
HR
·
1
(1− sinα/2)
(8 a) is valid for the case when the human passes the
crossing point before the robot. To be on the safe side
one should require v
R
≤ v
R
opt
. For the case when the
human passes the crossing point after the robot we get
(8 b)
with v
r
≥ v
R
opt
.
6 INTENTION RECOGNITION
BASED ON LEARNING OF
PEDESTRIAN LANES
6.1 Fuzzy Modeling of Lanes
A good option to identify/recognize human intention
to aim at a specific goal is to learn from experience.
The framework of ”programming by demonstration”
focusses on the recognition of human grasp pattern
by fuzzy time clustering and modeling (R. Palm and
Kadmiry, 2009). Likewise for the intention recogni-
tion it is a matter of pattern recognition, when a model
is used that has been built on the basis of recorded
pedestrian trajectories. For this purpose we used the
”Edinburgh Informatics Forum Pedestrian Database”
which consists of a large set of walking trajectories
that has been measured over a period of months (edi,
2010) (see Fig. 6). The idea is to identify lanes that
people normally use in a specific working area. In our
case the models are built by fuzzy time clustering as
follows:
1. From the whole set of data select 12 trajectories
and divide them into 3 ”bundels”.
2. Make a clustering of each trajectory separately
with c = 10 time clusters C
i,k,l
∈ R
2
k-number of set; l-number of trajectory in the set; i -
number of time cluster
3. Compute the mean values of the time clusters in
each set: C
k,i
= 1/m
k
·
∑
m
k
l=1
C
i,k,l
m
k
- number of trajectories in set k. C
i,k
= (c
x
,c
y
)
T
i,k,l
are the x, y coordinates of the i-th cluster centers in the
Fuzzy Modeling and Control for Intention Recognition in Human-robot Systems
71

k-th set. The connections of C
i,k
i = 1...c represent fi-
nally the lanes k = 1...3. Fig.7 shows the results for
all 3 sets.
Figure 6: Edinburgh pedestrian data.
Figure 7: Lanes 1...3, average trajectories.
6.2 Recognition of Intentions to Follow
Certain Lanes
In order to recognize the intention of a human agent to
aim at a certain goal, the membership of his trajectory
(or part of it) to one of the lanes is to be computed.
The membership of a point x = (x,y)
T
to a cluster
center C
i,k
is here defined by
w
i,k
=
1
∑
c
j=1
(
d
i,k
d
j,k
)
2
m
proj
−1
(9)
where d
i,k
= (x−x
i,k
)
T
(x−x
i,k
), x
i,k
- i-th cluster cen-
ter in the k-th lane, m
proj
> 1 - fuzziness parameter
(Runkler and Palm, 1996). The algorithm works as
follows:
1. Compute the closest distances d
i
min
,k
= min
j
(|x−
x
j,k
|) to the cluster centers C
j,k
(j = 1...c,k = 1...m
k
)
2. Compare the membership functions w
i
min
,k
and se-
lect the lane with the highest membership:
(w
i
min
,k
)
max
= max(w
i
min
,k
), k = 1...m
k
or
k
max
= argmax(w
i
min
,k
).
However, only one data point is obviously not suffi-
cient for intention recognition. Therefore moving av-
erages ( ¯w
i
min
,k
)
max
over a predefined number of time
steps n are computed
( ¯w
i
min
,k
)
max
(t
j
) =
1
n
n−1
∑
i=0
(w
i
min
,k
)
max
(t
j
− i) (10)
With this the influence of noise is further reduced and
the degree of membership of a human trajectory to a
particular lane is reliably identified.
7 SIMULATION RESULTS
7.1 Collision Avoidance at Intersections
In the 1st simulation the ”1 human - 1 robot” case
is considered where the estimations of the crossing
points are made during motion. This experiment is
a combination of real human walking data from the
Edinburgh Data and a simulated robot. At each time
point the crossing points of the two tangents along the
velocity vectors are computed and the robot velocity
will be adjusted according to eq.(8 a). Figure 8 shows
the plot before the crossing point and Fig. 9 shows
the time schedule before and after the crossing point.
In the case of stationarity the velocity is limited at a
−2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
−2
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
tangents
robot
human
crossing point
distance point
y, m
x, m
Figure 8: Motion before crossing, case 1.
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0
5
10
15
DHR2ed, m
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0
5
10
15
DR2Hed, m
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0
0.5
1
1.5
t, 10s
vR2, m/s
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0
1
2
3
vH, m/s
t, 0.1s
human
velocity, robot
distance to intersection, human
distance to intersection, robot
velocity
Figure 9: Time schedule before and after crossing, case 1.
FCTA 2016 - 8th International Conference on Fuzzy Computation Theory and Applications
72

predefined distance between robot and actual crossing
point in order to prevent from too high robot veloci-
ties. Fig. 9 shows that after 3s the robot has reached a
velocity that guarantees the human to pass the cross-
ing point 1.5 second before the robot. Case 2 (eq.(8
b)) is shown in Figs. 10 and 11. Here the robot passes
the intersection before the human with a time differ-
ence of 2.5 seconds.
−2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
−2
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
human
robot
crossing point
distance point
tangents
y, m
x, m
Figure 10: Motion before crossing, case 2.
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0
5
10
15
DHR2ed,m
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0
5
10
15
DR2Hed,m
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
1.5
t, 10s
vR2, m/s
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0
1
2
3
t, 10s
vH, m/s
human
robot
robot
human
Distance to intersection
Distance to intersection
velocity
velocity
Figure 11: Time schedule before and after crossing, case 2.
7.2 Recognition of Lanes While
Tracking
From 11 trajectories of the Edinburgh-data 3 differ-
ent lanes were identified beeing used in both direc-
tions with different velocities. Lanes 1, 2, and 3 are
modeled off line on the basis of 4, 5, and 2 trajec-
tories, respectively. The modeling results are repre-
sentative trajectories/paths of bundles of similar tra-
jectories. In our example, 3 from 20 test trajectories
(tracks) were selected from the Edinburgh-data which
have not been used for modeling but whose entry/exit
areas coincide with those of the modeled lanes (see
Fig. 12). During motion the degrees of membership
(see Fig. 13) for each track are computed accord-
ing to (9) and (10) with a moving average about 10
time steps. Here, from the membership degrees in
Figs.14-16 one can see, that from only a few samples
the membership of a track to a lane can be recognized.
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
x
y
lane 1
lane 2
track 1
track 2
track 3
lane 3
Figure 12: Lanes 1-3, test tracks.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
x
w
x1
x2
x3
cluster centers
lane 1
lane 2
lane 3
Figure 13: Membership
functions.
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
time step i
w(i)
lane 1
lane 2
lane 3
Figure 14: Memberships
track 1.
8 CONCLUSIONS
The problem of the recognition of human intentions
is part of a control task for human-robot interaction
and cooperation. A prominent role plays the pre-
diction of human motions to plan corresponding on
line reactions and maneuvers. The time schedule for
the information exchange and the kinematic relations
have been discussed, a general scheme of regarding
fuzzy control rules for the human-robot interaction
is presented and collision avoidance and optimization
strategies are discussed. Another method to recognize
intentions is the fuzzy modeling of pedestrian tracks,
the identification of lanes preferred by human agents,
and the identification of a membership of a pedestrian
track to a specific lane. Examples with both simu-
lated and real data show the applicability of the meth-
ods presented, whereas - because of the lack of space
- we confined ourself to the switching controller and
the recognition of lanes.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This research work has been supported by the AIR-
Fuzzy Modeling and Control for Intention Recognition in Human-robot Systems
73
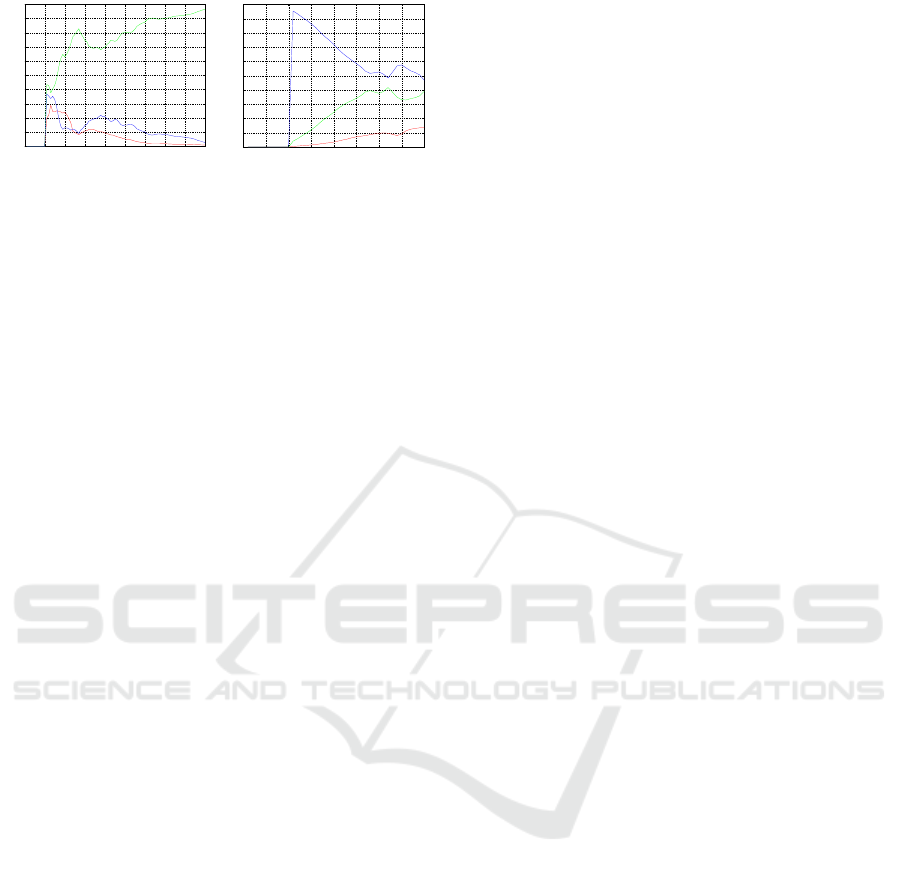
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
time step i
w(i)
lane 2
lane 3
lane 1
Figure 15: Memberships
track 2.
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
time step i
w(i)
lane 3
lane 2
lane 1
Figure 16: Memberships
track 3.
project, Action and Intention Recognition in Human
Interaction with Autonomous Systems.
REFERENCES
(2010). Edinburgh informatics forum pedestrian
database. http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/
FORUMTRACKING/.
A. Ciaramella, M.G.C.A.Cimino, F. M. and Straccia, U.
(2010). Combining fuzzy logic and semantic web
to enable situation-awareness in service recommenda-
tion. Database and Expert Systems Applications, Lec-
ture Notes in Computer Science., Volume 6261:31–45.
Aarno, D. (2007). Intention recognition in human machine
collaborative systems. Licentiate Thesis Stockholm,
Sweden., pages 1–104.
A.F.Johansson (2009). Data driven modeling of pedestrian
crowds. Doctoral Thesis., pages 1–185.
Chadalavada, R. T., Andreasson, H., Krug, R., and Lilien-
thal, A. J. (2015). That’s on my mind! robot to human
intention communication through on-board projection
on shared floor space. European Conference on Mo-
bile Robots (ECMR).
(Ed.), W. L. (1995). The control handbook. page 316.
F. Sadri, W. W. and Xafi, A. (2012). Intention recognition
with clustering. Ambient Intelligence., Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, 7683:379–384.
Firl, J. (2014). Probabilistic maneuver recognition in traffic
scenarios. Doctoral dissertation, KIT Karlsruhe,.
Han, T. A. and Pereira, L. (2013). State of the art of
intention recognition. AI Communications., Volume
26:237–246.
Heinze, C. (2004). Modelling intention recognition for in-
telligent agent systems. Research Report, Air Opera-
tions Division.
J. Bruce, J. W. and Vaughan, R. (2015). Human-robot ren-
dezvous by co-operative trajectory signals. pages 1–2.
J.V. Gomez, N. M. and Garrido, S. (2013). Social path plan-
ning: Generic human-robot interaction framework for
robotic navigation tasks. Workshop of the IEEE/RSJ
Intern. Conf. on Int. Rob. and Syst. (IROS’13).
Khatib, O. (1985). Real-time 0bstacle avoidance for ma-
nipulators and mobile robots. IEEE Int. Conf. On
Robotics and Automation,St. Loius,Missouri, 1985,
page 500505.
Krauthausen, P. (2012). Learning dynamic systems for in-
tention recognition in human-robot-cooperation. Doc-
toral dissertation, University report, Karlsruhe.
M. Bennewitz, W. Burgard, G. C. and Thrun, S. (2005).
Learning motion patterns of people for compliant
robot motion. The International Journal of Robotics
Research., vol. 24 no. 1:31–48.
Makris, D. and Ellis, T. (2010). Spatial and probabilistic
modelling of pedestrian behaviour. In Proc. ICRA,
page 39603965. IEEE.
Mataric, M. (1990). A distributed model for mobile robot
environment-learning and navigation. Technical Re-
port., pages 1–139.
P. Leica, M.Toibero, F. R. and Carelli, R. (2015). Switched
control to robot-human bilateral interaction for guid-
ing people. Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Sys-
tems,DORDRECHT. Argentina. 77. 1., pages 73–93.
Palm, R. and Bouguerra, A. (2013). Particle swarm opti-
mization of potential fields for obstacle avoidance. In
Proceeding of RARM 2013, Istanbul, Turkey. Volume:
Scient. coop. Intern. Conf. in elect. and electr. eng.
R.-E.Precup, M. T. and Preitl, S. (2009). Fuzzy logic con-
trol system stability analysis based on lyapunov’s di-
rect method. In International Journal of Computers,
Communications and Control,vol. 4, no. 4, pages 415–
426.
R. Palm, B. I. and Kadmiry, B. (2009). Recognition of
human grasps by time-clustering and fuzzy model-
ing. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, Vol. 57, No.
5.:484–495.
R. Palm, R. C. and Lilienthal, A. (2016). Recognition of
human-robot motion intentions by trajectory observa-
tion. In 9th Intern. Conf. on Human System Interac-
tion, HSI2016. IEEE.
Runkler, T. and Palm, R. (1996). Identification of nonlinear
system using regular fuzzy c-elliptotype clustering. In
Proc. FUZZIEEE 96, pages 1026–1030. IEEE.
Satake, S., Kanda, T., Glas, D. F., Imai, M., Ishiguro, H.,
and Hagita, N. (2009). How to approach humans?-
strategies for social robots to initiate interaction. 13th
Intern. Symp. on Experimental Robotics, pages 109–
116.
T. Ellis, E. S. and Reid, I. (2009). Modelling pedes-
trian trajectory patterns with gaussian processes. In
2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Com-
puter Vision, Workshops (ICCV Workshops), pages
1229–1234. IEEE.
T. Fraichard, R. P. and Reignier, P. (2014). Human-robot
motion: Taking attention into account . Research Re-
port, RR-8487.
Tahboub, K. A. (2006). Intelligent human-machine interac-
tion based on dynamic bayesian networks probabilis-
tic intention recognition. Journal of Intelligent and
Robotic Systems., Volume 45, Issue 1:31–52.
Takagi, T. and Sugeno, M. (1985). Identification of sys-
tems and its applications to modeling and control.
IEEE Trans. on Syst., Man, and Cyb., Vol. SMC-15.
No.1:116–132.
FCTA 2016 - 8th International Conference on Fuzzy Computation Theory and Applications
74
