
Self-Organizing Maps in the Design of Anti-spam Filters
A Proposal based on Thematic Categories
Ylermi Cabrera-León
1
, Patricio García Báez
2
and Carmen Paz Suárez-Araujo
3
1
Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria (ULPGC), Canary Islands, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain
2
Departamento de Ingeniería Informática y de Sistemas, Universidad de La Laguna,
Canary Islands, San Cristóbal de La Laguna, Spain
3
Instituto Universitario de Ciencias y Tecnologías Cibernéticas, ULPGC,
Canary Islands, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain
Keywords:
Anti-spam, Spam, Ham, Artificial Neural Networks, Self-Organizing Maps (
SOM
s), Thematic Category, Term
Frequency, Inverse Category or Class Frequency.
Abstract:
Spam, or unsolicited messages sent massively, is one of the threats that affects email and other media. Its
high volume generates substantial time and economic losses. A solution to this problem is presented: a
hybrid anti-spam filter based on unsupervised Artificial Neural Networks (
ANN
s). It consists of two steps,
preprocessing and processing, both based on different computation models: programmed and neural (using
Kohonen
SOM
). This system has been optimized using, as a data corpus, ham from “Enron Email” and spam
from two different sources: traditional (user’s inbox) and spamtrap-honeypot. It has been proved that thematic
categories can be found both in spam and ham words. 1260 system configurations were analyzed, comparing
their quality and performance with the most used metrics. All of them achieved
AUC > 0.90
and the best 204
AUC > 0.95
, despite just using 13 attributes for the input vectors of the
SOM
, one for each thematic category.
Results were similar to other researchers’ over the same corpus, though they make use of different Machine
Learning (
ML
) methods and a number of attributes several orders of magnitude greater. It was further tested
with datasets not utilized during design, obtaining 0.77 < AUC < 0.96 with normalized data.
1 INTRODUCTION AND
BACKGROUND
Nowadays, the use and importance of telecommunica-
tion has increased, primarily due to the rise of Informa-
tion and Communications Technology (
ICT
). Among
the multiple ways to make such communication, email
can be highlighted, mainly because it has been used
extensively for decades. Unfortunately, this popular-
ity has brought with it the appearance of threats such
as hoaxes, cyber-attacks, computer viruses and, to a
greater extent, spam.
Although there are many different ways of defining
the word “spam” (Subramaniam et al., 2010), in this
paper spam refers to any message, mostly email but
other media are affected too, sent massively without
the recipients having requested or desired it. The char-
acteristic of “massive” must be highlighted because,
for years, both spam volume and overall spam rate (in
other words, the quantity of spam and the percentage of
spam relative to all messages, respectively) have been
extremely high: in 2008 about 62 trillion unwanted
messages (McAfee and ICF International, 2009) and
less than 1 out of 10 emails could be considered as
ham (legitimate or desired messages), fortunately im-
proving to 4 out of 10 in 2014 (Statista, 2016).
Considering that, in most cases, their content is
offensive or questionable - e.g. scam, phishing, il-
legal drugs, pornography, replicas. . . (Cabrera León
et al., 2015) - it can be asserted that spam is a great
scourge, creating quite substantial, both temporary and
economic, losses: annually, American firms and con-
sumers experience costs of near $20 billion due to
spam whereas spammers (people or companies that
send spam) and spam-advertised firms collect $200
million worldwide (Rao and Reiley, 2012). This oc-
curs, mainly, due to sending spam being easy and
having low cost, and that the recipient carries the bulk
of the cost, in contrast to what happens with more
traditional or off-line unsolicited marketing methods
(Lieb, 2002).
There have been a wide variety of proposals to
solve the problem of email spam detection so far, and
Cabrera-León, Y., Báez, P. and Suárez-Araujo, C.
Self-Organizing Maps in the Design of Anti-spam Filters - A Proposal based on Thematic Categories.
DOI: 10.5220/0006041400210032
In Proceedings of the 8th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2016) - Volume 3: NCTA, pages 21-32
ISBN: 978-989-758-201-1
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
21

therefore there is a huge proliferation of papers in this
regard, as it will be discussed in Subsection 1.1. In
this paper another solution to this problem is presented:
a hybrid spam filtering system. It can be considered
hybrid not only because its two main stages, prepro-
cessing and processing, are based on different com-
puting models - programmed and neural computation,
respectively - but also because in the processing one
the
SOM
, an unsupervised
ANN
, is followed by a
non-neural supervised labeling part.
This system has been optimized using, as a data
body, ham from “Enron Email” (Cohen, 2004) and
spam from two different sources: obtained through tra-
ditional ways (user’s inbox), or through spamtraps and
honeypots. Its quality and performance have been ana-
lyzed on several different datasets with both Kohonen
maps’ most used quality measures, Mean Quantiza-
tion Error (
MQE
) and Topographic Error (
TE
), and the
most common performance metrics for classifiers such
as Receiver Operating Characteristic (
ROC
) curves
and AUC, among others.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows. In Subsection 1.1 some of the numerous related
works developed throughout the last decades are de-
scribed. Through Section 2 the dataset and methods
are explained. Section 3 shows the experimental re-
sults, followed by a discussion of them. Finally, the
conclusions can be found in Section 4.
1.1 Related Works
As it is common to defensive and security systems
in all areas (such as pathogenic diseases, armament,
crime and predation), attackers (spammers in our case)
are always one step ahead of defenders (Postini, Inc,
2004), therefore, in this area, the latter need to con-
tinuously face new threats and counter shortcomings,
weaknesses and security flaws that the former have
found, and later exploited, in anti-spam filters, other
software or hardware (Spammer-X et al., 2004). Ac-
tually, this evolution explains the proliferation of mul-
tiple anti-spam techniques developed over the past
decades (Wang et al., 2013).
Anti-spam methods may filter during any of the
network hierarchical levels (mostly in the Application,
Transport and Network layers of the TCP/IP model),
i.e. in any of the steps involved with sending emails: in
the sender device, en route and in the recipient. Along-
side this manner, spam classifiers can also be grouped
by these two ways: based on the design method, and
based on the source of information. This section’s
scope has been reduced by just choosing user-level
and administrator-level filters, whose techniques be-
long to any of the two previous groups, due to the fact
that a user-level filtering system was developed here.
1.1.1 Based on the Design Method
There are two subgroups in this group, the latter being
the most popular one:
Manual:
easier to implement and more useful for
email administrators. Despite their slow adapta-
tion to changes in spam, whitelists and blacklists
(respectively, lists of good and bad mail servers
and ISPs) achieve just 1% of False Positives (
FP
)
and False Negatives (
FN
) (Erickson et al., 2008).
Furthermore, greylisting blocks email delivery tem-
porarily with unrecognized senders, forcing re-
sending, something not usually done by spammers
(Kucherawy and Crocker, 2012). It reduces band-
width waste at the expense of delaying ham too
(Harris, 2003).
Based on ML:
it is the largest subgroup (Guzella and
Caminhas, 2009), where filters can be classified, at
the same time, depending on the kind of architec-
ture used (neural or not), or the quantity of human
interaction required (supervised, semi-supervised
or unsupervised). Making use of the latter, we
could classify some anti-spam techniques as fol-
lows:
•
Supervised: the most popular non-neural one
is the Bayesian (Meyer and Whateley, 2004;
Sahami et al., 1998), and, therefore, the most
attacked by spammers through Bayesian poi-
soning (Lowd and Meek, 2005; Sprengers and
Heskes, 2009; Wittel and Wu, 2004).
(Metsis et al., 2006) must be described sepa-
rately from other Bayesian filters because this
paper’s dataset was built from theirs and later
compared with, as explained in Section 2. Their
system performs very well (with average sensi-
tivity of 0.9753 and specificity of 0.9726, and
quite-near-perfection
ROC
curves) when 3000
attributes, the greatest number they tested, are
used.
Nowadays, other popular non-neural one, due to
its performance, is the Support Vector Machine
(
SVM
) (Drucker et al., 1999; Xie et al., 2009),
which is greatly kernel-dependent (Chhabra
et al., 2010) and offers better results when sev-
eral are combined with a voting strategy (Blanco
et al., 2007).
On the other hand, for a long time, the per-
ceptron, neural, has dominated as anti-spam
(Kufandirimbwa and Gotora, 2012; Sculley
et al., 2006) but the raise of Bayesian and
SVM
changed this.
Other supervised
ANN
is the Learning Vec-
tor Quantization (
LVQ
) with whom (Chuan
NCTA 2016 - 8th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
22

et al., 2005) built a quite good filter (96.20%
F-measure, 98.97% precision and 93.58% sensi-
tivity) if enough iterations, at least 1500, were
made.
•
Unsupervised: because no previous data la-
beling process is needed, emails should oc-
cupy less disk space and be more recent (Cabr-
era León and Acosta Padrón, 2011). Among
non-neural filters, we could find: the Spam-
CampaignAssassin (Qian et al., 2010) based on
the detection of spam campaigns, one based on
the alienness or searching of similarities in sub-
strings (Narisawa et al., 2007), and other which
uses suffix trees (Uemura et al., 2008).
On the other hand, there are also unsuper-
vised neural techniques. The
SOM
Based Se-
quence Analysis (Luo and Zincir-Heywood,
2005) makes use of a double hierarchical-
leveled
SOM
, where the second
SOM
is con-
nected a posteriori with a k-Nearest Neigh-
bors (
k-NN
) for categorization and sequence
analysis.
(Vrusias and Golledge, 2009a; Vrusias and
Golledge, 2009b) should be introduced sepa-
rately from others due to their importance for
this paper’s research. They compare their
SOM
-
based system with what they consider to be the
best spam classifiers: the Multinomial Naïve
Bayes Boolean,
SVM
and Boosted Decision
Trees. It is a 10x10
SOM
, sequentially trained
for 1000 cycles, whose input vectors have 26
or 500 attributes, and where keywords were
grouped (just when 26 attributes were used) and
identified with Term Frequency
·
Inverse Docu-
ment Frequency (
TF·IDF
) and weirdness. The
main differences between their filters and this
paper’s are: larger
SOM
, smaller input vectors,
other learning algorithm and a similar way of
identifying keywords were used here, as de-
scribed in Section 2. They also used datasets
based on the “Enron-Spam” corpus from (Met-
sis et al., 2006).
•
Semi-supervised: not many labeled data, due to
high costs (Chapelle et al., 2006), with a lot of
unlabeled examples. Regularized Discriminant
Expectation-Maximization (Gao et al., 2009)
combine both transductive (for labeling unla-
beled data) with inductive (to make a model in
order to classify new data) methods, obtaining
91.66% detection rate and 2.96% FP.
Learning with Local and Global Consistency, of
which there is a variant proposed by (Pfahringer,
2006), obtains better results than with
k-NN
and
SVM (Santos et al., 2011; Zhou et al., 2004).
Although SpamAssassin (Mason, 2009) is gen-
erally considered supervised, it can also utilize a
semi-supervised learning rule (Xu et al., 2009).
A semi-supervised version of
SVM
also exists,
Transductive Support Vector Machine (Shunli
and Qingshuang, 2010; Zhou et al., 2007),
which sometimes performs worse than
SVM
as
an anti-spam (Mojdeh and Cormack, 2008).
1.1.2 Based on the Source of Information
These methods, which use any part of an email i.e.
envelope, header and body (P. Resnick, 2008), can
also be subdivided in the next three assortments:
Content of the Email:
the most prevalent way, either
using the whole message (Cormack and Mojdeh,
2009) or just selecting parts with different meth-
ods: rules (Malathi, 2011), detecting anchored
parts (Pitsillidis et al., 2010) or spam campaigns
(Qian et al., 2010), signatures of messages (Kolcz
et al., 2004), or combining several techniques, such
as in SpamAssassin (Mason, 2009; The Apache
SpamAssassin Project, 2014) and CRM114 (Yer-
azunis et al., 2010) popular anti-spam filters.
User Feedback:
in spite of users being considered
the most reliable and robust anti-spam method, spe-
cially against content obfuscation made by spam-
mers, (Graham-Cumming, 2006) find out that they
have up to 2% of classification errors, due to ham
being very similar to spam - a.k.a. “hard ham”
(Feroze et al., 2015) - or the presence of “grey
cases” (Bruce, 2012), where categorization has an
important subjective factor.
Information Relative to the System:
they fre-
quently take the advantage on the inherent
difficulty for spammers to change the message
headers and produce valid ones (Ramachandran
and Feamster, 2006). This can be detected
by checking fields of some network protocols,
specially the ones which contain the sender’s IP
and port, and the local sending time (countless
emails sent during sender’s sleeping time may
indicate that sender’s device belongs to a botnet).
On the other hand, they can also detect the
presence or absence of specific characteristics in
the message, such as only images (usually no text
at all, hence called “image spam”) (Fumera et al.,
2006; Gao et al., 2009), and attached files, prone
to be malware-infected.
Self-Organizing Maps in the Design of Anti-spam Filters - A Proposal based on Thematic Categories
23
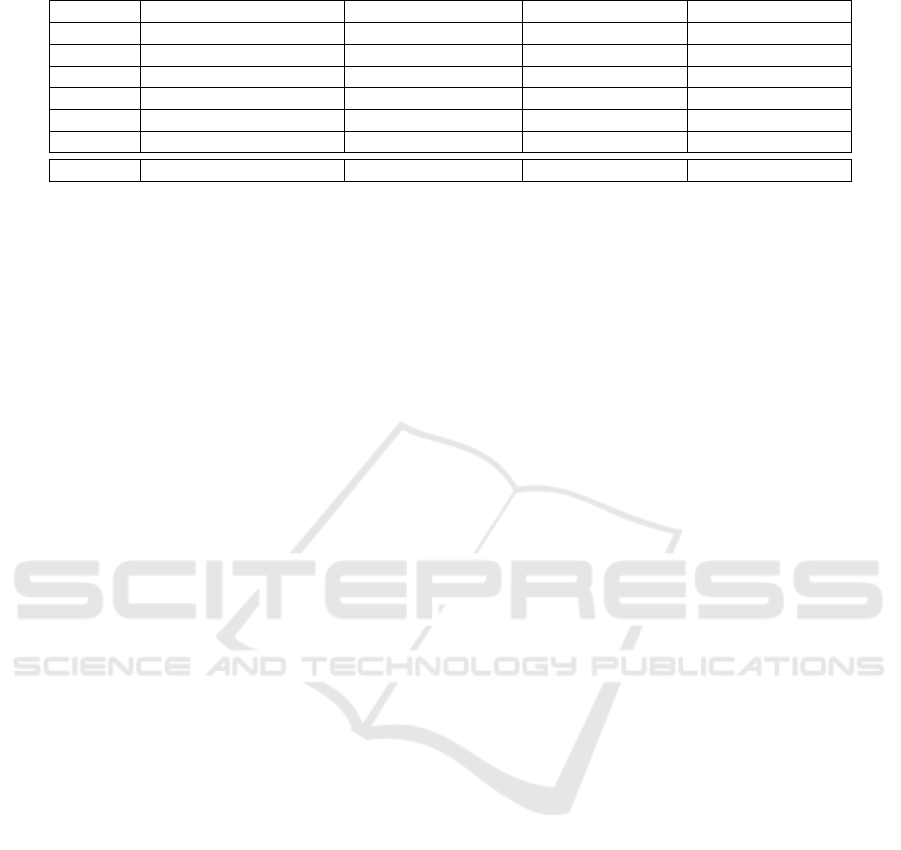
Table 1: Original email corpus. In bold our datasets.
FOLDER HAM–SPAM ORIGINS NO. OF HAM-SPAM HAM DATES SPAM DATES
E1 farmer-d – GP 3672 - 1500 12/1999 - 01/2002 12/2003 - 09/2005
E2 kaminski-v – SH 4361 - 1496 12/1999 - 05/2001 05/2001 - 07/2005
E3 kitchen-l – BG 4012 - 1500 02/2001 - 02/2002 08/2004 - 07/2005
E4 williams-w3 – GP 1500 - 4500 04/2001 - 02/2002 12/2003 - 09/2005
E5 beck-s – SH 1500 - 3675 01/2000 - 05/2001 05/2001 - 07/2005
E6 lokay-m – BG 1500 - 4500 06/2000 - 03/2002 08/2004 - 07/2005
SA2 easy_ham_2 – spam_2 1400 - 1397 02/2003 02/2003
2 DATASET AND METHODS
2.1 Dataset
In order to work with
ANN
s effectively, it is crucial
to have a broad and representative dataset, i.e. a set
of emails where both spam and ham are widely rep-
resented (Borovicka et al., 2012). Most email corpus
are both restricted and costly in order to keep their
users’ privacy and obstruct spammers’ countermea-
sures. In spite of this, several corpus are freely avail-
able nowadays (Cabrera León et al., 2015; Guzella and
Caminhas, 2009).
The proposed system has been developed using a
free and gratis one: a subset of emails from a corpus
created by (Metsis et al., 2006) known as “Enron-
Spam”. Our dataset was built using only “Enron1”
(
E1
) and “Enron5” (
E5
) folders, Table 1. By doing
this, we have worked with a balanced dataset (5172
ham and 5175 spam) from the preprocessed version of
their corpus, wherein:
•
Ham belonged to the “Enron Email Corpus”,
which has been widely used with different pre-
processing techniques applied on it (Cohen, 2004;
Skillicorn, 2013; Styler, 2011). In fact, (Metsis
et al., 2006) use ham from 6 out of 7 Enron users’
inboxes from the preprocessed version of (Bekker-
man et al., 2004), as seen in the column with the
ham origin in Table 1.
•
Spam came from two different sources: received
in a traditional way by one of the authors of the
mentioned corpus, Georgios Paliouras (GP); and
through spamtraps (The Apache SpamAssassin
Project, 2013) and honeypots (SH), which are anti-
spam techniques intended, respectively, to lure
spam, and to bait, investigate and punish spam-
mers. Unwanted messages from Bruce Guenter’s
“Spam Archive” (BG) (Guenter, 1998) were not
used in our case, unlike (Metsis et al., 2006).
Our dataset was subsequently partitioned in the
following balanced sets: 80% for training-validation
the
ANN
and 20% for testing the system over data
never seen before.
Apart from
E1
and
E5
(
E1E5
) used during the de-
sign of the system, other datasets which came from
different email corpora were utilized to test the design
more independently, in order to evaluate in a more
realistic way the methodology of the system: both pre-
processing and processing stages. Thus, the system
was further tested on two additional balanced datasets,
Table 1: the “Enron2” (
E2
) and “Enron4” (
E4
) combi-
nation,
E2E4
hereafter, which is similar to
E1E5
but
with ham from other Enron users and different quanti-
ties of spam from same sources, and “SpamAssassin_2”
(
SA2
), built choosing the newest ham and spam folders
from the SpamAssassin dataset, which differ consid-
erably from our previous datasets in terms of content,
topics, origins and dates (The Apache SpamAssassin
Project, 2013).
2.2 Methods
The proposed intelligent anti-spam system consisted
of two different computing stages or modules, Figure
1, and it can be considered hybrid because each of
them was based on a different computing scheme. The
first one was the preprocessing stage, Subsection 2.2.1,
which was based on programmed computation (i.e.
digital electronic computing together with stored pro-
grams) whereas the second one, the processing stage,
Subsection 2.2.2, made use of a neural computing
scheme. The preprocessing module was responsible
for obtaining a semantic and compact representation
of the information environment, a set of feature vec-
tors for emails to analyze. These vectors were the
input data for the subsequent hybrid processing mod-
ule, where the detection of spam by a
SOM
-based,
unsupervised
ANN
, system was performed, followed
by a non-neural supervised labeling method which
worked with the outputs of the SOM.
2.2.1 Preprocessing Module
The preprocessing stage is quite important (Hovold,
2005; Zhang, 2012), especially with unsupervised
NCTA 2016 - 8th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
24

Figure 1: Anti-spam filtering system scheme.
methods due to the fact that no kind of corrective
signals nor correct outputs are provided. The main
purposes of this stage were: reducing the dimensional-
ity of the vocabulary, and only making use of the most
relevant words. Three key concepts - thematic cate-
gories, Inverse Category or Class Frequency (
ICF
) and
Top k% of words - were used, which will be explained
in the next paragraphs.
This preprocessing is founded on the premise that
there are several spam thematic categories (Cabrera
León et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2013), ergo, based on
this, detection and differentiation from ham would be
feasible. The most common thematic categories fre-
quently found in spam and ham, which were expected
to exist within our dataset, have been encountered and
the most similar ones were lumped together in only
13 thematic categories, Table 2. Email words can be-
long to more than one category at the same time (e.g.:
obfuscation & medicine, links & trading. . . ). Initially,
our words categorization in thematic categories was
made manually, keeping in mind the word’s use and
context. Later and based on this, this process was au-
tomatized. Manual words categorization brought with
it two useful advantages:
•
No lemmatization nor stemming were required
(Porter, 1980), common in many anti-spam filters.
•
Robust against words deliberately obfuscated, a
countermeasure frequently applied by spammers
to deceive or defeat anti-spam techniques (Freschi
et al., 2006; Liu and Stamm, 2007).
The existence of the aforementioned thematic cate-
gories directed this research to the usage of
ICF
, which
is recommended by some authors when categories
or classes exist in the data (Wang and Zhang, 2013),
rather than using Inverse Document Frequency (IDF).
Both
ICF
and
IDF
are used for similar purposes: re-
duce the importance/weight given by Term Frequency
(
TF
) to “stop words” i.e. extremely common words
in categories or documents, respectively. The three
different variants of
ICF
described by (Lertnattee and
Theeramunkong, 2004) have been checked, which are
defined by Equations 1, 2 and 3, where
C
is the total
number of categories, and
f
t
is the number of cate-
gories where token t happens.
ICF
Log
= log(
|C|
f
t
) (1)
ICF
Linear
=
|C|
f
t
(2)
ICF
Sqrt
=
s
(
|C|
f
t
) (3)
Another interesting aspect in this process was to
know if using all the words within a thematic cate-
gory was better than using less, so the system was
tested with different number of words in each one.
This number is given by some percentage, k, which
means that we chose the k% of the words with greater
T F
category
· ICF, that is, the Top k% of words.
Our preprocessing stage could be divided in four
phases, executed in the indicated sequential order as
they are interdependent:
Phase 0:
batch extraction of subject line and body of
all emails-files in a path. Also, non alphanumeric
characters were inserted between blank spaces to
ease next phases.
Phase 1:
only keeping selected words, that is, with
length
>
2, not very rare and also not too frequent
as they might be “stop words” (Zeimpekis et al.,
2011). Each email was reduced to a text line, fol-
lowing the bag-of-words model i.e. several pairs of
selected word next to its raw
TF
in this document:
T F
document
. At the end of each line two labels were
added: spam/ham (not used during training) and
the original, alphanumeric, email ID.
Phase 2:
previously making the described manual
words categorization. Building a 13-dimensional,
integer, array where each element, accumulator,
represents the sum of the raw
T F
document
of all the
words belonging to a thematic category, by looking
up the word in every category. At the end of each
line the same two labels were inserted.
Phase 3:
automatizing words categorization (email
words are counted using accumulators as in Phase
2 and associated to, by default 1, the winner
thematic category) and weighting words with
T F
category
· ICF
so extremely common words were
given less importance. Ordering categories us-
ing those values permitted the obtainment of sev-
eral Top k% of words to be tested. Building a
Self-Organizing Maps in the Design of Anti-spam Filters - A Proposal based on Thematic Categories
25
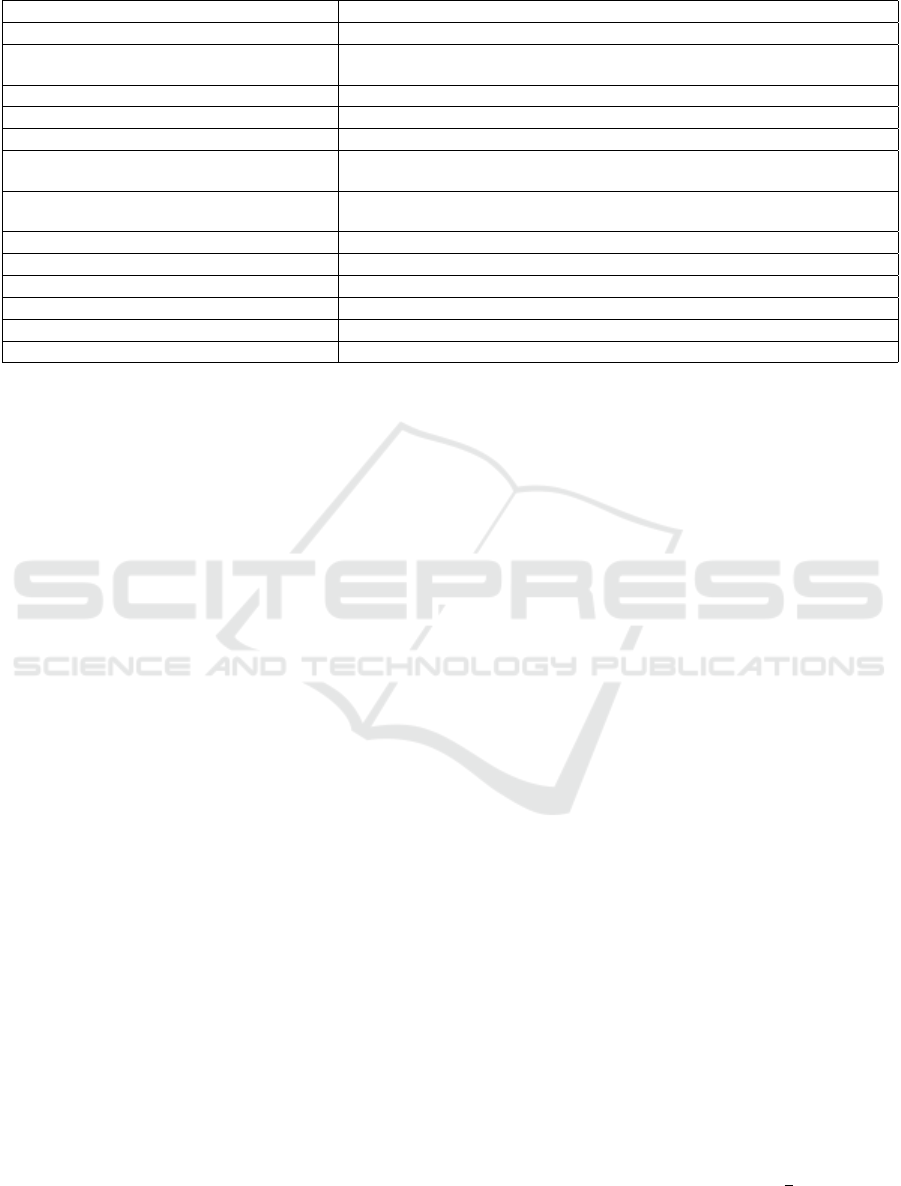
Table 2: Description of the 13 thematic categories within our spam and ham words.
THEMATIC CATEGORY DESCRIPTION
Sex & Relationships Mostly pornography, casual sex and dating websites
Medicine, Drugs & Body
Selling medicines or illegal drugs. Includes words related with body parts,
and surgical procedures and tools
Betting, Gambling & Divination Includes lotto, sports betting, casino, tarot, etc.
Banking, Investment, Insurance & Trading Commerce, offers, funds, stock markets. . .
Links & Email addresses
Parts of links to websites and emails, mainly web extensions and domains
Other languages Most of the emails were written in English but some were in Spanish,
German, French, Dutch and Turkish, among others
Obfuscation
Very common. Words badly written on purpose by spammers to interfere
with most content-based anti-spam filters
Business, Companies & Government Name of firms, governmental agencies and analogous
Internet & Technology ICT vocabulary
Documents & Paperwork CV, diplomas, business documents, etc.
Names & Family Names and surnames, also family members
Tourism & Regions Countries, cities, holidays. . .
Attached files Several file extensions and words related with “attach”
13-dimensional, floating point, array where each el-
ement represented the sum of the
T F
document
· ICF
,
similar to Phase 2 but now weighted, of all words
belonging to certain thematic category. Same two
labels at the end of each line-email.
2.2.2 Processing Module
The system’s processing stage has as its information
environment the feature vectors obtained in the prepro-
cessing stage. It is hybrid as the first part was based
on a type of
ANN
s, the well known Kohonen Self-
Organizing Maps (Kohonen, 2001), whereas the sec-
ond one was non-neural. Both parts will be explained
below.
SOM
, as an unsupervised neural architecture, is a
very appropriate method for facing the problem to be
solved. It quantifies the input space in different regions
represented by a specific number of output neurons,
a.k.a. detectors. In our case, there are two types of
detectors: spam detectors and ham detectors.
Moreover,
SOM
s might be used as a visualiza-
tion tool of high-dimensional data by projections over
lower-dimensional maps (Rojas, 1996). During this
projection process akin to multidimensional scaling,
it is easily seen that
SOM
s try to extract the features
of the input space in order to preserve its topological
properties, similar to the idea of topographic maps
that exist in the brains of highly developed animals
(Haykin, 1999).
Its structure is made of an input layer fully intercon-
nected, by excitatory connections, with the neurons
in the output layer. The latter is organized in a m-
dimensional space, the most common being the 2D
matrix. Within this matrix there is a neighborhood re-
lationship between its nodes that is usually defined by
an hexagonal or rectangular lattice. Also, the matrix
shape can vary, the sheet one being the most common.
All neurons within the output layer simultaneously
present inhibitory lateral connections among neural
neighbors as well as excitatory self-connections. Their
neurodynamic is simplified by computing the least
(more frequently Euclidean and hence used in this
work) distance between the inputs and a model (Ko-
honen, 2001), which is a parametric real vector, that
can be considered as the weight vector in the neural
architecture. The winning neuron, a.k.a. Best Match-
ing Unit (
BMU
), will be the one with the minimum
distance value.
The learning process belongs to a winner-take-all,
unsupervised and competitive training paradigm. The
main variations are seen in the modification of the
synaptic weights, which not only affects the winning
neuron but also, to a lesser extent, the set of neurons
in the winners’ neighborhood
N
(thus,
SOM
training
can be considered cooperative too), and consequently
being able to generate topological relations, Equation
4. During the training period, the neighborhood rela-
tionship between nodes
h
ji
decreases both in time and
distance (commonly a Gaussian function), affecting
only the
BMU
during the final phase. The learning
rate
α
normally decreases with time, usually beginning
near the unity and finishing close to zero during the
fine tuning done in the last training cycles, although a
fixed value may be utilized but not recommended (Tan
and George, 2004).
∆w
li
=
(
α(x
i
− w
li
) if i ∈ N = argmin
k
{net
k
(x)}
0 otherwise
(4)
SOM
s can use two different learning methods: se-
quential and batch, Equation 5, where
x
j
is the mean
of the elements in a list of weights updates;
h
ji
, the
NCTA 2016 - 8th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
26

neighborhood function; and
n
i
, the number of elements
in that list. Batch learning method, which can be bet-
ter and converges faster (Kohonen, 2013), has been
employed in this article.
w
j
(n + 1) =
∑
i
n
i
· h
ji
· x
j
∑
i
n
i
· h
ji
(5)
The second part of the processing stage was a non-
neural supervised classification method, which was
appended after the
SOM
, Figure 1. Its main aim was
to label the results obtained by the
SOM
, that way
classifying in spam or ham the emails inputted into the
anti-spam filter. It was based on confidence thresholds,
which are based on the minimum percentage from
which consider an email as spam. These confidence
thresholds, which were empirically chosen, will allow
us to adjust the system relative to the
FP
, an important
factor in this kind of filters. In a nutshell, an email was
labeled as ham if the spam ratio
#spam
#spam + #ham
was lesser
than this threshold, or as spam otherwise, Equation 6.
label
email
=
spam if
#spam
#spam + #ham
≥ threshold
ham otherwise
(6)
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
MATLAB was the main development environment for
our anti-spam filter, using the
SOM
Toolbox (Vesanto
et al., 2000) for the
SOM
architecture and visualiza-
tion tools, and the Parallel Computing Toolbox (Math-
Works, 2014) to reduce the high computational costs
of the experiments.
Table 3: Modified characteristics and their tested values for
all the 1260 configurations.
CHARACTERISTIC TESTED VALUES
Normalization Scenario 1 (None) or
Scenario 2 (Variance
is normalized to one,
linear operation)
ICF log, linear & sqrt
Top k% of words
100, 95, 90, 75, 50, 25,
10
SOM size 13x13, 20x20, 25x25,
40x40 & 50x50
SOM training algorithm batch
Number of epochs 100, 500, 1000, 3000,
5000 & 8000
Neighborhood function gaussian
SOM shape sheet
Lattice hexagonal
Weight initialization linear
The experiments have been performed using origi-
nal (non-normalized) and normalized data, which are
indicated as Scenario 1 and Scenario 2 respectively.
1260 different system configurations were developed,
which differed between them by varying several char-
acteristics related to the information environment and
the SOM structure, Table 3.
The efficiency and quality of the proposed anti-
spam system were determined through the usage of
two different families of metrics:
• Quality of the SOM map (Tan and George, 2004):
MQE
and
TE
, which measure the map resolution
(how accurately the inputs are reflected in the out-
put space) and the topology preservation (the order
of the map), respectively.
•
On-use performance measures such as F-score,
accuracy, precision, specificity, sensitivity,
ROC
curve and
AUC
. All of them can be expressed
in term of the elements of the confusion matrix:
True Positives (
TP
),
FP
, True Negatives (
TN
) and
FN
. Also, it might be included in this group one
simple and low cost metric found out during this
research that measures the least Euclidean distance
between the
ROC
curve and the point of perfect
classification in (0, 1).
For evaluation purposes and comparison with other
researchers’, the best considered performance mea-
sures are
ROC
curves
1
and
AUC
(Fawcett, 2004;
Metz, 1978; Slaby, 2007).
Relative to
E1E5
dataset, results obtained with all
metrics were quite positive. All the 1260 analyzed
configurations obtained
AUC > 0.90
, and even 204
got
AUC > 0.95
which can be described as “excellent”
classifiers in the anti-spam context. Additionally, most
metrics’s results were quite similar between config-
urations, even more if comparing same scenario. It
has been observed that all pairs Top 100% and Top
95% configurations, with identical rest of parameters,
shared the same results. Consequently, Top 95% ones
were preferred because of their faster learning due to
using a smaller vocabulary. Furthermore, none of the
best classifiers for each scenario used the biggest
SOM
sizes, 50x50, but smaller-sized ones. Besides, it was
found out that normalized data behaved better, which
usually happens with Kohonen networks. Obtained
MQE
and
TE
with normalized data are on the same
range of values as other authors’ (Cabrera León et al.,
2015).
Comparing our results in Table 4 with other re-
searchers’ in Table 5, the proposed system achieves
worse than desired
FP
and
FN
(around 7% and 3%,
1
Each
ROC
curve was drawn with 102 specificity and
sensitivity values, given by the same number of confidence
thresholds, for enhanced ROC curve detail.
Self-Organizing Maps in the Design of Anti-spam Filters - A Proposal based on Thematic Categories
27

Table 5: Results obtained by some researchers, indicating dataset, methodology and metric utilized.
RESEARCH DATASET METHOD BEST RESULTS
(Metsis et al., 2006) Enron-Spam Bayesian (several) Sensitivity = [0.9232 - 0.9753]
(Vrusias and Golledge, 2009b) Enron-Spam SOM Precision = 0.992867
Sensitivity = 0.920067
(Chuan et al., 2005) SpamAssassin LVQ Precision = 0.9897
Sensitivity = 0.9358
(Holden, 2004) SpamAssassin Bayesian (several, commercial) Precision = [0.328 - 1]
Sensitivity = [0.837 - 0.988]
(Kufandirimbwa and Gotora, 2012) SpamAssassin Perceptron algorithm Precision = 0.97149
Sensitivity = 0.77859
(Luo and Zincir-Heywood, 2005) Ling-Spam Two-level SOMs + k-NN Precision = [0.933 - 1]
Sensitivity = [0.675 - 0.975]
(Shunli and Qingshuang, 2010) ECML-PKDD 2006 Transductive SVM AUC = 0.9321
(Xie et al., 2009) PU1 & PU2 SVM (several) Accuracy (PU1) = [0.926 - 0.941]
Accuracy (PU2) = [0.932 - 0.945]
Table 4: Results of the anti-spam filter for each scenario
(testing phase) with E1E5 (20%, 2069 emails) dataset.
E1E5 (20%)
PERFORMANCE
MEASUREMENTS
Scenario 1 Scenario 2
AUC 0.970809 0.977740
Discrete AUC
(threshold)
0.924172
(38)
0.944499
(37)
Accuracy 0.924595 0.944726
Precision 0.898782 0.928571
F-score 0.927915 0.946385
Specificity 0.889344 0.924103
Sensitivity 0.959000 0.964895
TP 959 962
FP 108 74
TN 868 901
FN 41 35
% FP 10.44% 7.15%
% FN 3.96% 3.38%
Distance to (0, 1) 0.118007 0.083623
SOM MAP QUALITY Scenario 1 Scenario 2
MQE 39.592070 0.452661
TE 0.118567 0.078204
respectively), which should be the correction priority
in future works, while good and comparable values
with performance metrics. Still, it should be noted
that this comparison would have been more realistic
if exactly the same emails and preprocessing methods
had been tested with other processing techniques. This
is expected to be done in future works, together with a
more advanced system.
The optimal system configuration used normalized
data (Scenario 2), Top 95% of words,
ICF
sqrt, gaus-
sian neighborhood, hexagonal lattice, 20x20 sheet-
shaped map, and trained for 8000 epochs [with the
batch algorithm]. It overcame the Scenario 1’s oppo-
nent that used data without any kind of normalization
applied to it, Top 25% of words,
ICF
log, gaussian
neighborhood, hexagonal lattice, 20x20 sheet-shaped
map, and was trained for 100 epochs, Table 4 and
Figure 2(a)).
The proposed anti-spam filter was further tested
with other datasets, which are different from the one
used during the design of the anti-spam (
E1E5
). In-
deed, the datasets were mixed in order to analyze both
best configurations in a more realistic situation (i.e.
with emails from diverse origins and in different pro-
portions):
• E2E4
: from different folders of the same email
corpus, “Enron-Spam”.
• E2E4
+
SA2
: a mix of emails from “Enron-Spam”
and “SpamAssassin_2”.
• E1E5
+
E2E4
+
SA2
: an even more realistic mix
of the three datasets used, including unseen emails
from the dataset utilized during the design (
E1E5
),
and without taking into account the mail distribu-
tion among them, using the whole set of emails.
Regarding to Scenario 2 as it has been the one
that achieved better performance, obtained results for
the previous dataset mixtures vary from having an
excellent performance -
AUC
over
0.964
and
0.906
,
respectively - with
E2E4
and
E1E5
+
E2E4
+
SA2
to a satisfactory one -
AUC > 0.778
- with
E2E4
+
SA2
, as seen in Table 6 and Figure 2(b)). These values
reflect a coherent behavior and a good performance of
the proposed system.
When the analyzed emails share similar character-
istics (e.g. content, topics and origins) with the dataset
used for design, training, performance is excellent. But
the system is still able to have good and very good per-
formance with new received emails, whose attributes
are highly dissimilar. These differences fully justify
the results in each case, Tables 4 and 6. At the same
time, results are quite promising and indicative of the
goodness of the proposed methods.
Still, a generalization of thematic categories, of
the words inside them or a mix of both might be one
of the potential solutions in order to improve even
NCTA 2016 - 8th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
28
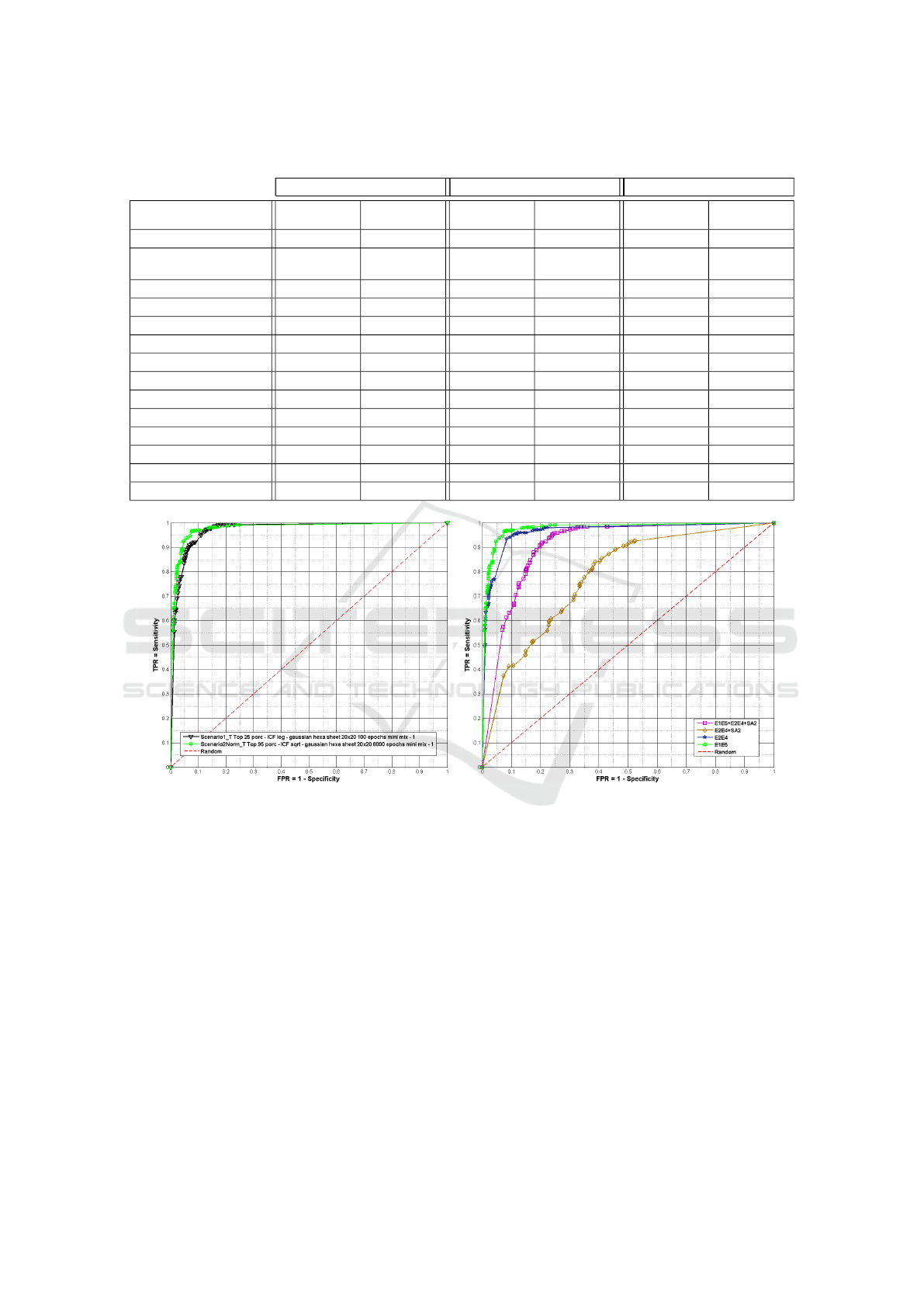
Table 6: Results of the anti-spam filter for each scenario (testing phase) with
E2E4
(2000 random emails),
E2E4
+
SA2
(2000
random, 50% each) and E1E5 + E2E4 + SA2 (20% of E1E5, all E2E4 and SA2, 16719 emails) datasets.
E2E4 E2E4 + SA2 E1E5 + E2E4 + SA2
PERFORMANCE
MEASUREMENTS
Scenario 1 Scenario 2 Scenario 1 Scenario 2 Scenario 1 Scenario 2
AUC 0.951306 0.964116 0.730900 0.778584 0.886687 0.906290
Discrete AUC
(threshold)
0.890036
(71)
0.925391
(48)
0.709345
(71)
0.726712
(27)
0.835745
(71)
0.856466
(48)
Accuracy 0.889952 0.925509 0.707214 0.724960 0.835752 0.856403
Precision 0.897137 0.918835 0.646072 0.677951 0.802223 0.816712
F-score 0.890995 0.927034 0.752889 0.750601 0.844410 0.864702
Specificity 0.895135 0.915401 0.516667 0.612735 0.780211 0.794249
Sensitivity 0.884937 0.935381 0.902023 0.840689 0.891279 0.918684
TP 846 883 847 781 7001 7174
FP 97 78 464 371 1726 1610
TN 828 844 496 587 6127 6215
FN 110 61 92 148 854 635
% FP 9.97% 8.01% 46.44% 37.13% 20.80% 19.11%
% FN 10.71% 5.94% 9.19% 14.78% 10.13% 7.53%
Distance to (0, 1) 0.155679 0.106454 0.493164 0.418753 0.245208 0.221237
(a) (b)
Figure 2: a)
ROC
curve of the anti-spam filter for each scenario (testing phase - “E1E5” dataset). b) Comparison of the
ROC
curves obtained by the proposed system for Scenario 2 with several datasets.
more the performance of the proposed system when
dealing with any email type. Another solution might
be updating the filter periodically with new messages
(i.e. providing it with online-learning capabilities)
to both counteract the evolution of spam and ham
content and topics. The latter phenomenon is known
as “topic drift” (Wang et al., 2013) and it is related
with the general problem of “concept drift” in
ML
:
unexpected variations of the statistical properties of
the target variable over time, which usually imply
increasingly inaccurate predictions over the course
of time (Gama et al., 2014; [Pleaseinsertintopream-
ble]liobait[Pleaseinsertintopreamble] et al., 2015).
Comparing with the anti-spam filters proposed by
(Metsis et al., 2006), from whom most of the datasets
used in this paper were obtained, our results in Table 4
are comparable to theirs, Table 5, and our
ROC
curves
in Figure 2(a)) are similar to their separated curves for
“Enron1” and “Enron5” folders: specificity = 0.94433
and sensitivity = 0.96436 (average and for only those
two folders). The main difference is that their filters
make use of a non-neural methodology with super-
vised learning strategy and up to 3000 attributes while
our proposal is a
SOM
-based system which used only
13 for analogous results. Consequently, we could infer
that we utilized both appropriate preprocessing meth-
ods, that let us obtain smaller yet more informative
input vectors, and a powerful processing tool, which
is able to work with such unlabeled vectors.
Self-Organizing Maps in the Design of Anti-spam Filters - A Proposal based on Thematic Categories
29

4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper a hybrid and modular anti-spam filter-
ing system based on Kohonen Self-Organizing Maps
and supervised non-neural computing has been pre-
sented. It has been proved that thematic categories
can be found in spam and ham so, accordingly, both
spam and ham words have been classified in the 13 cat-
egories found. The proposed system is robust to word
obfuscation, quite frequent in spam, and it is also inde-
pendent of the need to use stemming or lemmatization
algorithms, unlike other anti-spam filters.
All the studied configurations obtained good re-
sults with all metrics with
E1E5
, the dataset used dur-
ing the design of the system. Results were identical
when using the whole set, Top 100%, of keywords
from each of the 13 categories or just the Top 95%,
something that also brought lower runtime along. Our
optimal configuration was attained with normalized
data, which is usual with Kohonen
SOM
s. Obtained re-
sults were similar to other researchers’ over the same
corpus (Metsis et al., 2006), though they use input
vectors with a dimensionality several orders of mag-
nitude greater than ours, up to 3000, and a number of
Bayesian methods.
The developed anti-spam filter was additionally
tested with data that were completely different from
the ones used during its design, achieving important
findings. Results with
E2E4
dataset were similar but
worse with the non-Enron
SA2
. Testing with a mix of
the previous three datasets in different number and pro-
portion confirmed that the filter’s detection power got
affected when newer and off-topic spam and ham were
encountered. This is common to other offline-training
anti-spam solutions because topics drift along the time
as both spam and spammers’ techniques evolve (Wang
et al., 2013). This situation can be solved with periodic
retraining (as in online-training filters) or, on the other
hand, improving the generalization of the system or
the thematic categories.
Obtained results confirmed the goodness and high
quality of the proposed system. The usage of compu-
tational intelligence methods and hybrid schemes for
designing anti-spam filtering systems were quite ben-
eficial. Both facts encourage us to continue research
over these topics. A big upgrading step might be the
use of some powerful hybrid neural architectures such
as the Counterpropagation network or the Hybrid Un-
supervised Modular Adaptive Neural Network (Suárez
Araujo et al., 2010).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank all six reviewers for
their valuable commentaries, which led to the improve-
ment of this article.
REFERENCES
Bekkerman, R., McCallum, A., and Huang, G. (2004). Auto-
matic categorization of email into folders: Benchmark
experiments on Enron and SRI corpora. Technical
Report IR-418, Center for Intelligent Information Re-
trieval - University of Massachusetts Amherst.
Blanco, Á., Ricket, A. M., and Martín-Merino, M. (2007).
Combining SVM classifiers for email anti-spam filter-
ing. In Sandoval, F., Prieto, A., Cabestany, J., and
Graña, M., editors, Computational and Ambient Intel-
ligence, volume 4507 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science. 9th International Work-Conference on Artifi-
cial Neural Networks, IWANN 2007, pages 903–910.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg, San Sebastián, Spain.
Borovicka, T., Jirina Jr., M., Kordik, P., and Jirina, M. (2012).
Selecting Representative Data Sets. In Karahoca, A.,
editor, Advances in Data Mining Knowledge Discovery
and Applications. InTech.
Bruce, J. (2012). Grey Mail: The New Email Nuisance To
Hit Your Inbox.
Cabrera León, Y. and Acosta Padrón, O. (2011). Spam: Def-
inition, statistics, anti-spam methods and legislation.
Course project, Politechnika Wroclawska, Wroclaw,
Poland.
Cabrera León, Y., Suárez Araujo, C. P., and García Báez, P.
(2015). Análisis del Uso de las Redes Neuronales Artifi-
ciales en el Diseño de Filtros Antispam: una Propuesta
Basada en Arquitecturas Neuronales No Supervisadas.
Final project, Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Ca-
naria, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria.
Chapelle, O., Schölkopf, B., and Zien, A. (2006). Semi-
Supervised Learning, volume 2. MIT Press, Cam-
bridge, MA, USA.
Chhabra, P., Wadhvani, R., and Shukla, S. (2010). Spam Fil-
tering using Support Vector Machine. In Special Issue
of IJCCT Vol.1 Issue 2, 3, 4; 2010 for International
Conference [ACCTA-2010], pages 166–171.
Chuan, Z., Xianliang, L., Mengshu, H., and Xu, Z. (2005). A
LVQ-based neural network anti-spam email approach.
ACM SIGOPS Operating Systems Review, 39(1):34–39
(6).
Cohen, W. W. (2004). Enron Email Dataset.
Cormack, G. V. and Mojdeh, M. (2009). Machine learning
for information retrieval: TREC 2009 web, relevance
feedback and legal tracks. In The Eighteenth Text RE-
trieval Conference Proceedings (TREC 2009), pages
1–9, Gaithersburg, MD, USA.
Drucker, H., Wu, D., and Vapnik, V. N. (1999). Support
Vector Machines for spam categorization. IEEE Trans-
actions on Neural Networks, 10(5):1048–1054.
Erickson, D., Casado, M., and McKeown, N. (2008). The
Effectiveness of Whitelisting: A User-Study. In Proc.
of Conference on Email and Anti-Spam, pages 1–10.
NCTA 2016 - 8th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
30

Fawcett, T. (2004). ROC graphs: Notes and practical consid-
erations for researchers. Machine Learning, 31(1):1–
38.
Feroze, M. A., Baig, Z. A., and Johnstone, M. N. (2015). A
Two-Tiered User Feedback-based Approach for Spam
Detection. In Becker Westphall, C., Borcoci, E., and
Manoharan, S., editors, ICSNC 2015: The Tenth Inter-
national Conference on Systems and Networks Commu-
nications, November 15-20, 2015, Barcelona, Spain,
pages 12–17. Curran Associates, Inc, Red Hook, NY.
Freschi, V., Seraghiti, A., and Bogliolo, A. (2006). Filtering
obfuscated email spam by means of phonetic string
matching. In Advances in Information Retrieval, pages
505–509. Springer.
Fumera, G., Pillai, I., and Roli, F. (2006). Spam filtering
based on the analysis of text information embedded
into images. The Journal of Machine Learning Re-
search, 7:2699–2720.
Gama, J., Žliobait
˙
e, I., Bifet, A., Pechenizkiy, M., and
Bouchachia, A. (2014). A Survey on Concept Drift
Adaptation. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 46(4):1–
37.
Gao, Y., Yan, M., and Choudhary, A. (2009). Semi Super-
vised Image Spam Hunter: A Regularized Discrimi-
nant EM Approach. In International Conference on
Advanced Data Mining and Applications, pages 152–
164. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Graham-Cumming, J. (2006). SpamOrHam. Virus Bulletin,
pages 22–24.
Guenter, B. (1998). SPAM Archive: Email spam received
yearly, since early 1998.
Guzella, T. S. and Caminhas, W. M. (2009). A review of
machine learning approaches to Spam filtering. Expert
Systems with Applications, 36(7):10206–10222.
Harris, E. (2003). The Next Step in the Spam Control War:
Greylisting.
Haykin, S. S. (1999). Neural Networks. A Comprehen-
sive Foundation. Prentice-Hall International, Ontario,
Canada, 2nd edition.
Holden, S. (2004). Spam Filtering II: Comparison of a
number of Bayesian anti-spam filters over different
email corpora.
Hovold, J. (2005). Naive Bayes Spam Filtering Using Word-
Position-Based Attributes. In CEAS.
Kohonen, T. (2001). Self-Organizing Maps. Springer-Verlag
New York, Secaucus, NJ, USA, 3 edition.
Kohonen, T. (2013). Essentials of the self-organizing map.
Neural Networks, 37:52–65.
Kolcz, A., Chowdhury, A., and Alspector, J. (2004). The
impact of feature selection on signature-driven spam
detection. In Proceedings of the 1st Conference on
Email and Anti-Spam (CEAS-2004), pages 1–8.
Kucherawy, M. and Crocker, D. (2012). RFC 6647 - Email
Greylisting: An Applicability Statement for SMTP.
Proposed standard.
Kufandirimbwa, O. and Gotora, R. (2012). Spam Detection
Using Artificial Neural Networks (Perceptron Learning
Rule). Online Journal of Physical and Environmental
Science Research, 1(2):22–29.
Lertnattee, V. and Theeramunkong, T. (2004). Analysis of
inverse class frequency in centroid-based text classifi-
cation. volume 2, pages 1171–1176. IEEE.
Lieb, R. (2002). Make Spammers Pay Before You Do.
Liu, C. and Stamm, S. (2007). Fighting Unicode-obfuscated
spam. In Proceedings of the Anti-Phishing Working
Groups 2nd Annual eCrime Researchers Summit, pages
45–59. ACM.
Lowd, D. and Meek, C. (2005). Good Word Attacks on
Statistical Spam Filters. In Proceedings of the Second
Conference on Email and Anti-Spam (CEAS), pages
1–8.
Luo, X. and Zincir-Heywood, N. (2005). Comparison of
a SOM based sequence analysis system and naive
Bayesian classifier for spam filtering. In Neural Net-
works, 2005. IJCNN’05. Proceedings. 2005 IEEE In-
ternational Joint Conference on, volume 4, pages 2571–
2576.
Malathi, R. (2011). Email Spam Filter using Supervised
Learning with Bayesian Neural Network. Computer
Science, HH The Rajah’s College, Pudukkottai-622,
1:89–100.
Mason, J. (2009). Filtering Spam With SpamAssassin.
MathWorks (2014). Parallel Computing Toolbox for Matlab
R2014a - User’s Guide.
McAfee and ICF International (2009). The Carbon Footprint
of Email Spam Report. Technical report.
Metsis, V., Androutsopoulos, I., and Paliouras, G. (2006).
Spam Filtering with Naive Bayes - Which Naive
Bayes? In CEAS 2006 - Third Conference on Email
and Anti-Spam, pages 27–28, Mountain View, Califor-
nia, USA.
Metz, C. E. (1978). Basic principles of ROC analysis. In
Seminars in Nuclear Medicine, volume 8, pages 283–
298. Elsevier.
Meyer, T. A. and Whateley, B. (2004). SpamBayes: Effec-
tive open-source, Bayesian based, email classification
system. In CEAS. Citeseer.
Mojdeh, M. and Cormack, G. V. (2008). Semi-supervised
spam filtering: Does it work? In Proceedings of the
31st Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on
Research and Development in Information Retrieval,
pages 745–746, Singapore. ACM.
Narisawa, K., Bannai, H., Hatano, K., and Takeda, M. (2007).
Unsupervised spam detection based on string alien-
ness measures. In Discovery Science, pages 161–172.
Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
P. Resnick, E. (2008). RFC 5322 - Internet Message Format.
Draft standard.
Pfahringer, B. (2006). A semi-supervised spam mail detector.
pages 1–5, Berlin, Germany.
Pitsillidis, A., Levchenko, K., Kreibich, C., Kanich, C.,
Voelker, G. M., Paxson, V., Weaver, N., and Savage, S.
(2010). Botnet judo: Fighting spam with itself. In Sym-
posium on Network and Distributed System Security
(NDSS), pages 1–19.
Porter, M. F. (1980). An algorithm for suffix stripping. Pro-
gram, 14(3):130–137.
Postini, Inc (2004). The shifting tactics of spammers: What
you need to know about new email threats. White
paper.
Qian, F., Pathak, A., Hu, Y. C., Mao, Z. M., and Xie,
Y. (2010). A Case for Unsupervised-Learning-based
Spam Filtering. volume 38, pages 367–368. ACM.
Self-Organizing Maps in the Design of Anti-spam Filters - A Proposal based on Thematic Categories
31

Ramachandran, A. and Feamster, N. (2006). Understanding
the network-level behavior of spammers. In ACM SIG-
COMM Computer Communication Review, volume 36,
pages 291–302.
Rao, J. M. and Reiley, D. H. (2012). The Economics of Spam.
Journal of Economic Perspectives, 26(3):87–110.
Rojas, R. (1996). Kohonen Networks. In Neural Networks:
A Systematic Introduction, pages 391–412. Springer-
Verlag, Berlin.
Sahami, M., Dumais, S., Heckerman, D., and Horvitz, E.
(1998). A Bayesian Approach to Filtering Junk E-
mail. AAAI Technical Report WS-98-05, Madison,
Wisconsin.
Santos, I., Sanz, B., Laorden, C., Brezo, F., and Bringas, P. G.
(2011). Computational Intelligence in Security for In-
formation Systems: 4th International Conference, CI-
SIS 2011, Held at IWANN 2011. Torremolinos-Málaga,
Spain.
Sculley, D., Wachman, G., and Brodley, C. E. (2006). Spam
Filtering Using Inexact String Matching in Explicit
Feature Space with On-Line Linear Classifiers. In
TREC.
Shunli, Z. and Qingshuang, Y. (2010). Personal Spam Filter
by Semi-supervised Learning. In Proceedings of the
Third International Symposium on Com Puter Science
and Computational Technology (ISCSCT ’10), pages
171–174, Jiaozuo, P. R. China.
Skillicorn, D. (2013). Other versions of the Enron data
(preprocessed).
Slaby, A. (2007). ROC Analysis with Matlab. In Infor-
mation Technology Interfaces, 2007. ITI 2007. 29th
International Conference on, pages 191–196. IEEE.
Spammer-X, Posluns, J., and Sjouwerman, S. (2004). Inside
the SPAM Cartel. Syngress - Elsevier, 1 edition.
Sprengers, M. and Heskes, T. T. (2009). The Effects of Dif-
ferent Bayesian Poison Methods on the Quality of the
Bayesian Spam Filter ‘SpamBayes’. Bachelor thesis,
Radboud University Nijmegen.
Statista (2016). Global spam volume as percentage of total
e-mail traffic from 2007 to 2014.
Styler, W. (2011). The EnronSent Corpus. Technical Report
01-2011, University of Colorado at Boulder Institute
of Cognitive Science.
Suárez Araujo, C. P., García Báez, P., and Hernández Tru-
jillo, Y. (2010). Neural Computation Methods in the
Determination of Fungicides. In Fungicides. INTECH
Open Access Publisher, odile carisse edition.
Subramaniam, T., Jalab, H. A., and Taqa, A. Y.
(2010). Overview of textual anti-spam filtering tech-
niques. International Journal of the Physical Science,
5(12):1869–1882.
Tan, H. S. and George, S. E. (2004). Investigating Learning
Parameters in a Standard 2-D SOM Model to Select
Good Maps and Avoid Poor Ones. In Australasian
Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pages 425–
437. Springer.
The Apache SpamAssassin Project (2013). Index of the
SpamAssassin’s Public Corpus.
The Apache SpamAssassin Project (2014). SpamAssassin
v3.3.x: Tests Performed to Determine Spaminess and
Haminess of a Message.
Uemura, T., Ikeda, D., and Arimura, H. (2008). Unsuper-
vised spam detection by document complexity estima-
tion. In Discovery Science, pages 319–331.
Vesanto, J., Himberg, J., Alhoniemi, E., and Parhankangas, J.
(2000). SOM Toolbox for Matlab 5. Technical Report
Report A57, Helsinki University of Technology.
Vrusias, B. L. and Golledge, I. (2009a). Adaptable Text
Filters and Unsupervised Neural Classifiers for Spam
Detection. In Proceedings of the International Work-
shop on Computational Intelligence in Security for
Information Systems CISIS’08, volume 53 of Advances
in Soft Computing, pages 195–202. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
Vrusias, B. L. and Golledge, I. (2009b). Online Self-
Organised Map Classifiers as Text Filters for Spam
Email Detection. Journal of Information Assurance
and Security (JIAS), 4(2):151–160.
Wang, D., Irani, D., and Pu, C. (2013). A Study on Evolu-
tion of Email Spam Over Fifteen Years. pages 1–10,
Atlanta, Georgia (USA). IEEE.
Wang, D. and Zhang, H. (2013). Inverse-Category-
Frequency Based Supervised Term Weighting Schemes
for Text Categorization. Journal of Information Sci-
ence & Engineering, 29(2):209–225.
Wittel, G. L. and Wu, S. F. (2004). On Attacking Statistical
Spam Filters. In CEAS.
Xie, C., Ding, L., and Du, X. (2009). Anti-spam Filters
Based on Support Vector Machines. In Advances in
Computation and Intelligence. 4th International Sym-
posium, ISICA 2009, volume 5821 of Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, pages 349–357. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg, Huangshi, China.
Xu, J.-M., Fumera, G., Roli, F., and Zhou, Z.-H. (2009).
Training SpamAssassin with Active Semi-supervised
Learning. In Proceedings of the 6th Conference on
Email and Anti-Spam (CEAS’09), pages 1–8. Citeseer.
Yerazunis, W., Kato, M., Kori,, M., Shibata, H., and Hacken-
berg, K. (2010). Keeping the Good Stuff In: Confiden-
tial Information Firewalling with the CRM114 Spam
Filter & Text Classifier. White Paper for Black Hat
USA, pages 1–18.
Zeimpekis, D., Kontopoulou, E. M., and Gallopoulos, E.
(2011). Text to Matrix Generator (TMG).
Zhang, Y. (2012). Lecture for Chapter 2 - Data Preprocess-
ing.
Zhou, D., Bousquet, O., Lal, T. N., Weston, J., and
Schölkopf, B. (2004). Learning with local and global
consistency. Advances in neural information process-
ing systems, 16:321–328.
Zhou, D., Burges, C. J. C., and Tao, T. (2007). Transductive
link spam detection. In Proceedings of the 3rd Interna-
tional Workshop on Adversarial Information Retrieval
on the Web, pages 21–28.
Žliobait
˙
e, I., Pechenizky, M., and Gama, J. (2015). An
overview of concept drift applications. In Japkowicz,
N. and Stefanowski, J., editors, Big Data Analysis:
New Algorithms for a New Society, volume 16 of Stud-
ies in Big Data, pages 91–114. Springer International
Publishing.
NCTA 2016 - 8th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
32
