
Enhancing Community Detection in Social Network using Ontology
Salma Khattab, Abeer ElKorany and Akram Salah
Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Computer and Information, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt
Keywords: Ontology, Semantic User Profile, Similarity, Modularity, Community Detection.
Abstract: In recent years, social networks have been spread widely. Within social network, people tend to form
communities in order to have more chances to share opinions, experiences and expertise. Users in social
networks belong to the same community according to their behaviour and common interest. This paper
presents a semantic approach for community extraction based on identifying the interest of user in order to
group them into communities. An ontological user profile is created indicating user interest that is associated
with items domain ontology. A set of experiments was applied using real dataset (BookCrossing) to measure
the accuracy of the proposed semantic-based framework.
1 INTRODUCTION
Currently, with the appearance of social web sites like
Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn, a pool of users with
different interests, from different geographical
regions, topics, opinions and feelings is created.
Users within social networks share their interest and
feeling in different area like marketing, politics,
science, sports, movies and other. With the evolution
of social network, users tend to belong different
communities. Community is a collection of users who
share the same interest(s) and interact with each other
most likely than other users in the network.
Discovering hidden communities is considered as one
of the valuable research area as it allows extraction
useful knowledge from this rich pool of information.
Community discovery helps to connect people with
common interests and encourages people to
contribute and share more contents. Furthermore, it
gives insights about the dynamics within each
community and provides a good indicator about the
status of the whole network and its health. The
capability to extract hidden communities based on
user interest is becoming vital for a wide variety of
applications such as product recommendation,
marketing, elections, stock index and computer
science.
This research aims to find people who share the
same interests no matter whether they are connected
by a social graph or not. The proposed model assumes
that users could be connected together if they have
common interest. For example, in book domain if two
users read the same topic(s) without necessarily being
friends they could belong to the same community
based on their tie which is calculated using their
interests in this topic. Therefore, the proposed model
focus on detecting community among people within
the social network based on their interests.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2
presents the related works used infer semantic in
community detection. In Section 3, our framework to
utilize ontology in community detection process is
illustrated. Section 4 describes the process of building
ontology. Section 5 provides the experimental steps
using real dataset from BookCrossing dataset. Section
6 presents the conclusion.
2 RELATED WORKS
One of the most important works in community
detection was a research done by Newman and
Girvan which is used for comparison in this paper as
bassline technique in community detection. It
proposed a divisive algorithm that uses edge
betweenness as a metric to identify the boundaries of
communities also they introduced modularity as an
objective function (Newman and Girvan, 2004).
Furthermore, several works have been done to
apply semantic in community detection over social
networks. In this section, a brief review about recent
works in this area is presented
The work proposed by (H.A.Abdelbary, 2013)
depends on analysis the user comments and posts in
150
Khattab, S., ElKorany, A. and Salah, A.
Enhancing Community Detection in Social Network using Ontology.
DOI: 10.5220/0006067801500156
In Proceedings of the 8th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2016) - Volume 2: KEOD, pages 150-156
ISBN: 978-989-758-203-5
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

social network. It divided users into communities
depend on the topics of interest. It represents the user
in form of vector contain deferent words and each
word in the vector refer to specific topic if the user
comments and post contain this word the word in the
vector take 1 else it takes 0. As a user can share more
than one topic, he/she could be found in more than
one community. This technique depended on
calculating similarity degree between different users
using their topics of interest and ignored other
features like number of posts in the same topic as well
as frequency of interaction between users. This work
utilized the WordNet as one of the widely used
ontology, however in the proposed framework, we
have created the required ontology to serve the
specific domain (in our case study book).
Another work proposed by (Zhan Bu., 2014)
analysis the comments between network users by
count the number of the opposing and supportive
words for every user comments. The comment
analysis done using the regular expression and every
word take a rate from 0 to 1 depending on word tone
then the technique start to calculate the trust degree
between the users. This technique has different
limitations which yield to make the trust value
between users not accurate as it depended on the tone
of emotional words in the user comments and the
number of emotional words in the comments not the
number of the comments itself between user.
Furthermore, the process of analysis the content
of user content is not accurate due to having language
and grammar mistakes.
3 PROPOSED FRAMEWORK
The proposed framework depends on semantically
grouping social network users based on their field of
interest. Therefore, the framework builds semantic
user profile based on the interest of user in specific
domain. Then, use this interest to calculate degree of
similarity between users in order to group them. The
framework consists of the following components as
shown in figure 1:
Data Storage
User Profile
Similarity Engine
Community Detection engine
3.1 Data Storage
"Data Storage" component is divided to two sub
Figure 1: Proposed framework.
components the first one is the social network user
database which contains the required data entered by
the social network users. The second component is
the "Interest Ontology". This component use
ontology to describe the concept in the interest and
will be explained in next sections.
3.2 User Profile
The framework stores two different data about the
user in the network:
3.2.1 Static Profile
It called "login data" as it stores the data which the
user enter to create account on the network such
name, age, address and set of interests user interested
in which the user choose from the "Interest Ontology
" in the framework. It consists of attributes that
represents user interest for special item.
3.2.2 Behavioural User Profile
It is a semantic user profile that the framework infers
for each user in the network. This semantic profile
represents the interest of user which changes with
respect to the behaviour of the user on the network.
Considering the book domain which is used as a case
study, user degree of interest represents the type of
book that the user read and the rate the user will give
for each book. Accordingly, whenever the user reads
or rates a new book, the profile is updated according
to the category of this new book. Behavioural user
Enhancing Community Detection in Social Network using Ontology
151

profile for each user is represented in this framework
in form of vector.
3.3 Similarity Engine
Similarity engine is used to measure the degree of
similarity between users in the network. In the
proposed framework it consists of three components:
Semantic User Matching
Identify User Interest
Measuring Similarity Degree
3.3.1 Semantic User Matching
Figure 2: Hierarchal representation for domain interests.
Depending on ontology hierarchal representation of
book domain represented in figure 2, each user is
linked with type of books she/he interested in.
Accordingly, user similarity measurement could be
divided based on degree of matching between users
in social network as follows:
Full Matching Users: this level of interest will
contain the entire system users who are
interested in same category and sub-category
in the interest ontology (in our case book
ontology).
Semi Matching Users: this level of interest
will contain the entire system users who are
interested in common super category in the
interest ontology although they do not share
same interest in sub- concepts.
No Matching Users: this level of interest will
contains the entire system users who do not
share any interests.
The basic idea of applying semantic user
matching as a first component in similarity engine is
to divide users in the network to small communities
depending on the matched interests between the users
will speed up the process of grouping later in the
engine.
3.3.2 Identify User Interest
This component calculates the degree of user interest
in specific domain depending on the behaviour of the
user in the system. As indicated above, user is
represented in form of vector which is shown in figure
3. Each cell in this vector represents degree of user
interest in specific category. Considering book
domain which is represented in form of ontology that
expresses category of books, degree of interests of
user in each category is calculated based on number
of books the user read as well as the rate the user give
for each book such that the engine can use one of
these items or both of them to calculate degree of
interest for each category using equation 2 which will
be explained in detailed in section 4.2.
Figure 3: Vector user representation.
3.3.3 Measuring Similarity Degree
After building the vector represents each user. The
engine will start to measure the similarity degree
between users which works on measuring the strength
of links or relationships between users in the social
network using the cosine similarity function. The
inputs to the cosine similarity function is the vector
created in the "identify user interest".
similarity = cos
(
θ
)
=
A .B
‖
A
‖
‖B‖
(1)
4 BUILDING ONTOLOGY
In order to evaluate the proposed framework,
BookCrossing
1
(BookCrossing, 2014) dataset will be
used to represent the domain of interest for users in
social networks. It is significant to mention that the
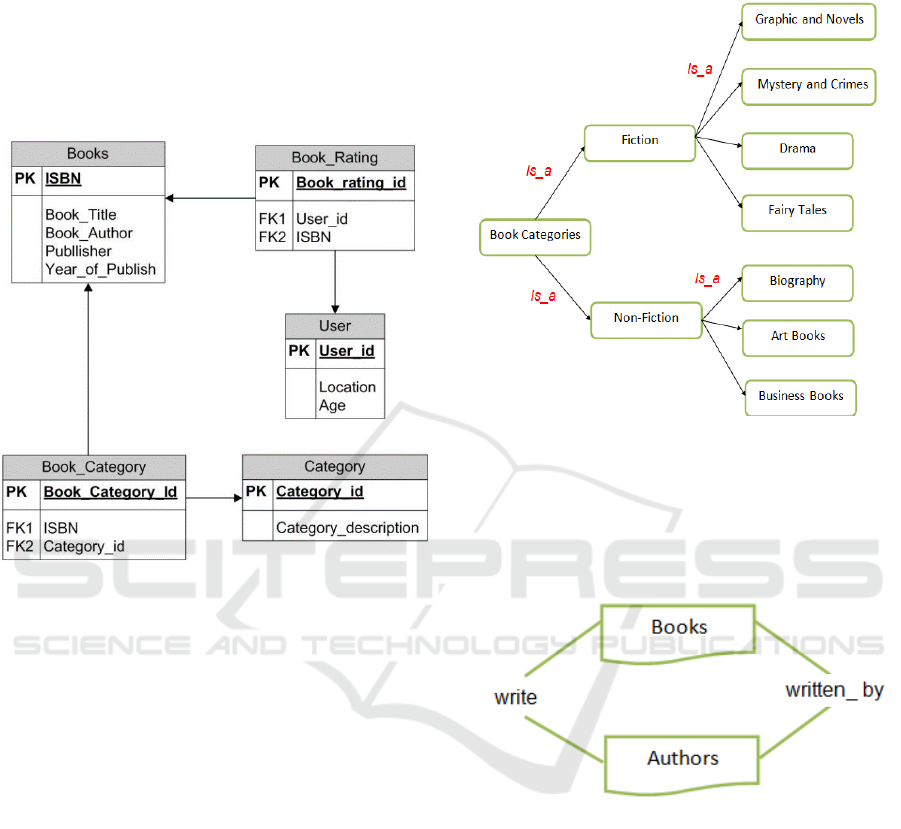
Figure 4: BookCrossing tables.
1
http://www.bookcrossing.com
KEOD 2016 - 8th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
152
proposed framework is generally applicable for any
domain of interest. Therefore, Book-Crossing data is
used as field of interest which contains 278,858users
providing 1,149,780 ratings to 271,379 books.
The dataset contains three tables Books, Users and
Book-Ratings.
However, the dataset doesn’t contain the book
category which is essential to represent user interest.
Figure 5: Refined bookcrossing tables.
Therefore, "google book" has been used as
external knowledge resource to extract the category
of each book in order to be used and stored in
database to be used by developed ontology using the
book ISBN. ISBN is used as a key to extract book
category from google book and then store it in
database as shown in figure 5.
Accordingly, ISBN is used as reference to extract
book category and then store it in database as shown
in figure 5.
4.1 Ontology Refinement
The next step is building the ontology for book
domain using both refined bookcrosing database as
well as google book categories. First, book categories
obtained from google have been divided into
hierarchal form using another online source (Barnes
and Noble, 2014). This source provides a simple
hierarchal for book categories as shown in figure 6.
The main problem in this step is how to solve the
mismatching between the exact names of categories
as extracted from google book and that exist in Barnes
and Noble. In order to solve this problem, WordNet
has been used to align category names with the same
meaning.
Figure 6: Ontological representation for book categories.
The semantic behaviour of the user is calculated
based on the number of books user read and the rate
for each book provided by the user. Each book is
identified by its topic as well as its author as shown
in figure 7.
Figure 7: Relation between book and authors before
refinement.
In order to be able to correctly represent the user
interest, we not only consider the favourite books that
the user either rate or read, but authors who wrote in
the same theme are also considered. Therefore,
depending on the ontological representation of book
categories, each sub-category is associated with two
other concepts:
The list of books which belongs to
subcategories.
The authors which writing the theme in
subcategories.
The refined relation between books, authors, and
category is now represented as shown in figure 8.
Enhancing Community Detection in Social Network using Ontology
153

Figure 8: Relation between book and authors after
refinement.
4.2 Calculating Degree of Interest
User can rate the book on rate scale from 0 to 1.This
scale will be describe in three fuzzy ranges
Low Range where rate is ≥ 0 and ≤ 3
Medium Range where rate is ≥ 4 and ≤ 7
High Range where rate is ≥ 8 and ≤ 10
Each range takes a rate value to represent the
range let's assume low range with value 0.1 and
medium with value 0.2 and high with value 0.3.
As mentioned earlier, the degree of interest of
each user represents the number of books the user
read in each sub-category and the rate the user for
each book which will be measured using equation 2
UID =
(
∑
𝑟
𝑛
0
)
∗ 𝑟𝑏
𝑡𝑏
(2)
Where:
UID is user degree of interest in subcategory
related to book attribute
r is book rate range value user reads in
subcategory
rbno. of books user reads in subcategory
tb no. of books in subcategory.
Another type of attribute could be used to measure
user interest, which is the author. Since readers tends
to read books that are written by the same author. The
framework could be extended to detect the
communities for users depend on the user interest
toward different attribute like authors. The similarity
degree between users will be measured in the same
way like measuring similarity using books. However,
in this paper experiments are limited to consider
books only.
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULT
In following, a set of experiments is described and
each is used to validate the effectiveness of the
proposed community detection framework.
Modularity is an objective function used to evaluate
the quality of the particular division of a network into
communities. It is a scale value between -1 and 1 that
measures the density of edges inside communities to
edges outside communities (Barber, M. J., 2007;
Newman, M. E., 2006).
5.1 Experiment Setup
The main problem here is the huge number of users
which affects in the execution time. The set of users
selected by considering the number of books the user
reads. Accordingly, a set of users has been selected
based on the number of books they read and rate
which yielded to selecting top 600 users in the list.
This will guarantee that the domain of the selected
users will cover almost all the subcategories in the
ontology. In the following experiments modularity is
measured using gephi
2
.
5.2 Experiment 1
The main purpose of the experiment is to study the
effectiveness of the community detection framework
by measuring the similarity between the selected set
of users in the dataset and measure the modularity
afterwards.In this experiment, similarity between
users is measured using the refined ontology which
contains 4 levels of sub-categories. As shown in
figure 9, the value of modularity is almost 0.5 which
is considered a high value.
Figure 9: The modularity value measured by gephi and
number of communities created depends on 4th level of the
refined ontology.
5.3 Experiment 2
The aim of this experiment is to compare the accuracy
of the proposed framework with another research for
community detection like "Newman and Girvan"
algorithm using the same set of users from
experiment 1. The "Newman and Girvan" is one of
the basic community detection algorithm used to
detect communities by progressively removing
2
https://gephi.org/
KEOD 2016 - 8th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
154
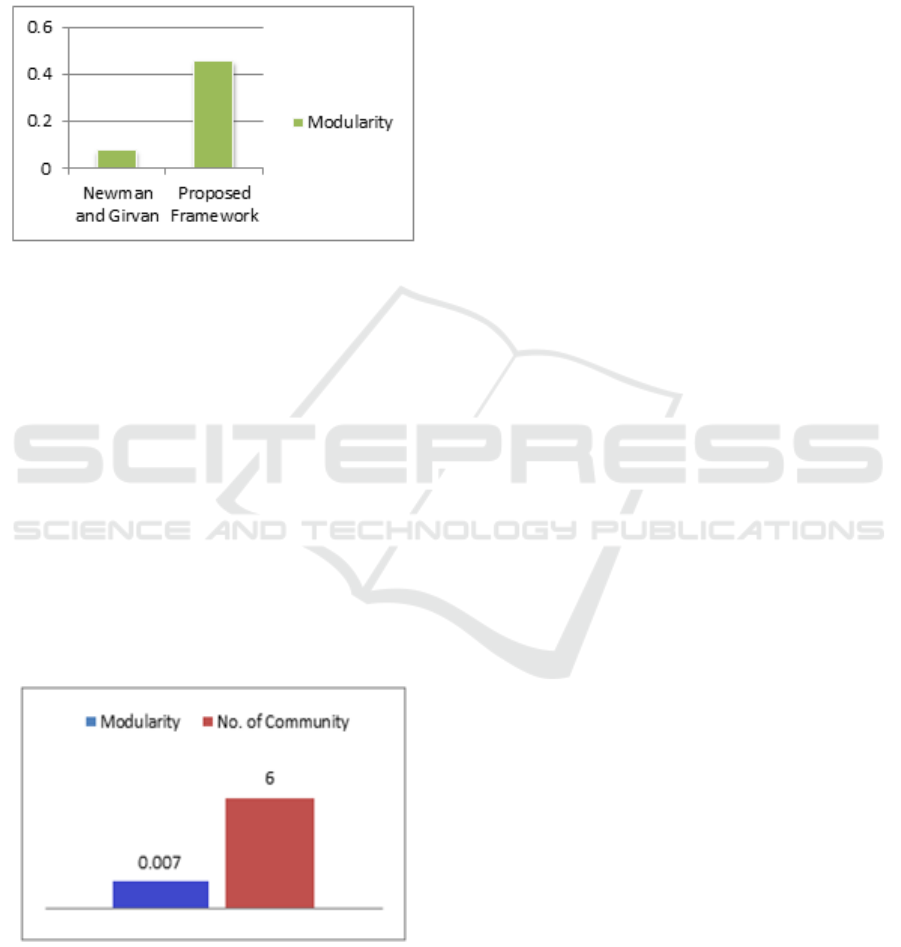
edges from the original network. The experiment
show that the modularity of the proposed frameworks
is higher than the "Newman and Girvan" algorithm
which means the strength of the relation between the
generated communities using the proposed frame
work stronger than the current "Newman and Girvan"
algorithm.
Figure 10: Comparison between modularity for Newman
and Grivan algorithm and the proposed framework.
5.4 Experiment 3
The aim of this experiment is to study the effect of
changing the number of hierarchal levels in the
reference ontology on the efficiency of the detection
process. In this experiment, two different level of
hierarchy were used to measure similarity between
users and accordingly, detects the communities. As
shown in figure 11, increasing the level of hierarchy,
leads to increase the accuracy of community detection
which is measured by the modularity. Therefore,
modularity at level 3 hierarchies is dramatically less
than level 4 which means that semantic relation
positively affects the accuracy of community
detection algorithm.
Figure 11: The modularity value measured by gephi and
number of communities created depends on 3rd level of the
refined ontology.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper represents a new framework for
community detection in social network utilizing the
semantic behaviour of the user and the ontology
concept to enhance the quality and the accuracy for
the detection process. The experiments used a real
dataset obtained from BookCrossing. The used
dataset was refined to build the ontology
representation for interests. The experiments clarify
the effects of using ontology by measuring the
performance on different level of the built ontological
data.
As future work, we plan to include several
semantic relations that would enhance community
discovery process such as link influence and trust
relationship.
Furthermore, other knowledge could be added
about user interest and could be extracted from other
social network such as Facebook.
REFERENCES
A. El-Korany, "Society in hand: toward community service
through social network", International journal of
computer application, 2012.
A. L. Gentile, V. Lanfranchi, S. Mazumdar, and F.
Ciravegna," Extracting Semantic User Networks From
Informal Communication Exchanges", Department of
Computer Science,University of Sheffield,Sheffield,
United Kingdom.
Abdelbary, Hassa, and Abeer El-Korany. "Semantic Topics
Modeling Approach for Community Detection."
International Journal of Computer Applications Vol.
81, No. 6 ,2013:50-58. . DOI 10.5120/14020-2177
Alan Mislove, BimalViswanath, Krishna P. Gummadi and
Peter Druschel , "You Are Who You Know:Inferring
User Profiles in Online Social Networks"
Ali, G. and ElKorany,A.,2014. Semantic-based
Collaborative Filtering for Enhancing
Recommendation. In KEOD (pp. 176-185).
Barber, M. J. ,2007. Modularity and community detection
in bipartite networks. Physical Review E, 76(6),
066102.
BookCrossing Dataset website[online], Available at:
www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~cziegler/BX/ [Last
accessed: May, 2014].
Borgatti, Stephen P., Mehra, Ajay, Brass and Daniel J.
Labianca, "Network Analysis in the Social Sciences",
2009.
David LibenNowell and Jon Kleinbergy, "The Link
Prediction Problem for Social Networks", 2004.
Eyharabide, V. and Amandi, A. , "Ontology-based user
profile learning", 2012.
Enhancing Community Detection in Social Network using Ontology
155

Girvan, M. and Newman," Community structure in social
and biological network", Proceedings of the National
Academy of Sciences,2002.
Jilin Chen, Werner Geyer, Casey Dugan , Michael Muller
and Ido Guy ,“Make New Friends, but Keep the Old –
Recommending People on Social Networking Sites".
Lada A. Adamic and EytanAdar ,"Friends and neighbors on
the web. Social Networks", July 2003.
Lindamood, J., Heatherly, R., Kantarcioglu, M. and
Thuraisingham, B.,"Inferring private information using
social network data", the 18th international conference
on World wide web, ACM, 2009
Mislove, A., Viswanath, B., Gummadi, K. P. and Druschel,
P."You are who you know: inferring user profiles in
online social networks", the 3rd ACM international
conference on Web search and data mining. ACM
,2010.
Natalya F. Noy and Deborah L. McGuinness," Ontology
Development 101: A Guide to Creating Your First
Ontology",Stanford University, Stanford.
Newman, M. E. ,2006. Modularity and community
structure in networks.Proceedings of the national
academy of sciences, 103(23), 8577-8582..
Quercia, D., Kosinski, M., Stillwell, D. and Crowcroft, J.,"
Our Twitter profiles, our selves: Predicting personality
with Twitter",the 3rd IEEE international conference on
social computing, IEEE Press ,2011.
Robert A. Hanneman ," Introduction to Social Network
Methods". Department of Sociology,University of
California, Riverside, 1998.
Tim Finin, Li Ding and Lina Zou, ” Social Networking on
the Semantic Web”,2005.
Wasserman, Stanley; Faust, Katherine ,"Social Network
Analysis in the Social and Behavioral Sciences",1994.
Zhan Bau and ZhengyouXia , "Community detection based
on semantic network" , 2013.
Zhao, Z., Feng, S., Wang, Q., Huang, J.Z., Williams, G.J.,
Fan, J.,2012. Topic oriented community detection
through social objects and link analysis in social
networks. Knowl.Based Syst. 26, 164–173.
Ziegler, C.-N., McNee, S.M., Konstan, J.A., Lausen, G.,
2005.Improving recommendation lists through topic
diversification.In:Proceedings of the 14th International
Conference on World WideWeb. Publishing, pp. 22–32
Barnes and Noble, 2014. Barnes and Noble website
[online],Available at: www.barnesandnoble.com
KEOD 2016 - 8th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
156
