
Estimating Sentiment via Probability and Information Theory
Kevin Labille, Sultan Alfarhood and Susan Gauch
Department of Computer Science and Computer Engineering, University of Arkansas, Fayetteville, AR 72701, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Lexicons, Sentiment Analysis, Data Mining, Text Mining, Opinion Mining.
Abstract:
Opinion detection and opinion analysis is a challenging but important task. Such sentiment analysis can be
done using traditional supervised learning methods such as naive Bayes classification and support vector ma-
chines (SVM) or unsupervised approaches based on a lexicon may be employed. Because lexicon-based senti-
ment analysis methods make use of an opinion dictionary that is a list of opinion-bearing or sentiment words,
sentiment lexicons play a key role. Our work focuses on the task of generating such a lexicon. We propose
several novel methods to automatically generate a general-purpose sentiment lexicon using a corpus-based
approach. While most existing methods generate a lexicon using a list of seed sentiment words and a domain
corpus, our work differs from these by generating a lexicon from scratch using probabilistic techniques and
information theoretical text mining techniques on a large diverse corpus. We conclude by presenting an ensem-
ble method that combines the two approaches. We evaluate and demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods
by utilizing the various automatically-generated lexicons during sentiment analysis. When used for sentiment
analysis, our best single lexicon achieves an accuracy of 87.60% and the ensemble approach achieves 88.75%
accuracy, both statistically significant improvements over 81.60% with a widely-used sentiment lexicon.
1 INTRODUCTION
Is this item worth buying ?” A friend may have asked
you this question before or you may have asked this
question yourself at some point. Asking someone
their opinion about an item we are considering buy-
ing has long been part of the human experience. We
often seek others’ opinions when we need to make a
decision (Liu, 2012). Until recently, we could only
ask those close to us, e.g., neighbors, friends, or fam-
ily for their thoughts. However, along with the rapid
growth of e-commerce, online retailers have made it
possible for customers to express their opinions about
products and items. However, it is hard to define ex-
actly what an opinion is; people will often disagree
on whether a statement is or is not an opinion rather
than a fact, (Kim and Hovy, 2006a), (Kim and Hovy,
2004)). Despite this, opinions can be useful not only
to online e-commerce but also in government intelli-
gence, business intelligence, and other online services
(Pang and Lee, 2008).
The number of online reviews has grown rapidly
and it is possible today to read the opinions of thou-
sands of people all over the Internet on movies,
restaurants, hotels, books, products, and profession-
als. The large amount of information available online
today allows researchers to study how individuals ex-
press opinions and to mine the collections of opin-
ions to identify trends and consensus. This new phe-
nomenon has given birth to two main tasks: opinion
summarization and opinion mining. Opinion summa-
rization consists of identifying and extracting prod-
ucts features from user’s reviews whereas opinion
mining consists of identifying the semantic orienta-
tion (positive/negative) of users’ reviews.
Sentiment analysis approaches are often divided
into two categories: corpus-based approaches and the
lexicon-based approaches. The first category consists
of building classifiers from labeled instances and is
often described as a machine-learning approach also
known as supervised classification. The latter uses
a dictionary of opinion-bearing words, that is, a list
of word associated with a sentiment orientation (posi-
tive/negative) that is often associated with a sentiment
strength as well. Thus, we can see the key role that the
opinion lexicon plays in the sentiment analysis task.
If the lexicon is missing words that are important in-
dicators of sentiment, or if it incorrectly assigns senti-
ment strengths to words, the accuracy of the resulting
sentiment analysis will be negatively impacted. An-
other advantage to creating a sentiment lexicon is that
it can be built from a large corpus and then used in
other applications where there may not be enough in-
formation to do corpus-based approaches.
Labille, K., Alfarhood, S. and Gauch, S.
Estimating Sentiment via Probability and Information Theory.
DOI: 10.5220/0006072101210129
In Proceedings of the 8th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2016) - Volume 1: KDIR, pages 121-129
ISBN: 978-989-758-203-5
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
121

In our work, we focus on the task of automati-
cally generating a sentiment lexicon from a corpus of
documents. We implement and evaluate two differ-
ent techniques to perform this task: (1) a probabilistic
approach; and (2) an information theoretic approach.
We then combine the best resulting lexicons using an
ensemble approach. Our approaches differ from the
traditional ones in several ways: (a) we generate a
lexicon using text mining with no a priori knowledge
rather than expanding a list of seed words; (b) un-
like most of the existing lexicons that contain only
adjectives (Taboada et al., 2011), our lexicon includes
words from all parts-of-speech; and (c) we use a large
diverse corpus rather than a domain-specific corpus.
We evaluate and demonstrate the effectiveness of
our methods by using the resulting lexicons to do sen-
timent analysis on Amazon product reviews. Similar
to (Hu and Liu, 2004a), we accumulate the sentiment
scores for each word of the review to compute an
overall sentiment score. If the score is positive then
the review is deemed to be positive; conversely, if
the resulting score is negative the review is deemed
to be negative. Results show that our lexicons per-
form well in the sentiment analysis task with accuracy
ranging from 87.30% to 88.75% versus a baseline of
81.60% for a widely-used lexicon. All of our lexicon
generation methods and the combination of them also
achieve good recall, precision, and F1-Scores.
The rest of the paper is organized as follow: In
Section 2, we present various existing work on senti-
ment analysis and lexicon generation. Section 3 de-
scribes the baseline that we use and both our systems
(1) and (2). Section 4 contains experimental evalua-
tion and results that we get, and Section 5 summarizes
our findings and highlights future work and improve-
ments.
2 RELATED WORK
Mining and summarizing online reviews to determine
sentiment orientation has become a popular research
topic. Opinion summarization is the task of identi-
fying and extracting product features from product’s
reviews in order to summarize them. Hu and Liu (Hu
and Liu, 2004a) proposed a method to find and extract
key features and the opinions related to them among
several reviews. In contrast, opinion mining consists
of analyzing a product’s review in order to determine
whether or not it reflects a positive or negative senti-
ment ((Kim and Hovy, 2006b); (Liu, 2010)). There
are traditionally two ways of doing sentiment analy-
sis, using either supervised learning techniques or un-
supervised learning techniques.
In the former approach, sentiment classification is
often seen as a two-class classification problem and
we typically use a naive Bayes classifier or build a
Support Vector Machine (SVM) that is trained on a
particular dataset ((Pang et al., 2002); (Pang and Lee,
2004); (Ng et al., 2006);(Liu et al., 2010);(Zhou et al.,
2010); (Li et al., 2009); (Gao et al., 2015)). This
approach generally performs well on the domain for
which it is trained. The latter approach, also referred
to as a lexicon-based approach, consists of computing
the semantic orientation of a review from the semantic
orientation of each word found in that review. It can
be seen as an unsupervised learning method ((Turney,
2002); (Taboada et al., 2011); (Ding et al., 2008); (Hu
and Liu, 2004b); (Khan et al., 2015); (Abdulla et al.,
2014)).
It is not uncommon to have reviews that are rated
within a range, e.g., from 1 to 5, to express a de-
gree of positiveness or negativeness. Sentiment rat-
ing prediction or rating-inference research focuses on
the task of predicting the rating rather than the senti-
ment orientation. Pang and Lee (Pang and Lee, 2005)
tackled this problem using an SVM regression ap-
proach and a SVM multiclass approach. Goldberg
and Zhu (Goldberg and Zhu, 2006) implemented a
graph-based semi-supervised approach and improved
upon the previous work.
While most of the cited work so far is done on
the document level, it is important to mention senti-
ment classification on a sentence level i.e., evaluating
the sentiment orientation of a single sentence. Here
again, both supervised learning and lexicon-based
approaches have been explored. Yu and Hatzivas-
siloglou (Yu and Hatzivassiloglou, 2003) used three
unsupervised statistical techniques to identify the po-
larity of a sentence. More recently, Davidov et al
(Davidov et al., 2010) studied the classification of
tweets using supervised learning on text, hashtags and
smileys.
Another application of sentiment analysis aims to
evaluate a particular aspect or feature of a review as
opposed to evaluating the sentiment of the whole re-
view. Ding et al. employed a sentiment lexicon in
their approach (Ding et al., 2008) whereas Wei and
Gulla (Wei and Gulla, 2010) modeled the problem
as a hierarchical classification problem and utilized
a Sentiment Ontology Tree.
Since sentiment lexicons are crucial for so many
sentiment classification tasks, it is important to accu-
rately capture the sentiment of each word in the lex-
icon. Sentiment lexicons can be generated (1) man-
ually; (2) using a dictionary; or (3) using a corpus
of documents. Dictionary-based approaches typically
use a few seed words for which the sentiment orienta-
KDIR 2016 - 8th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
122

tion is known. The list is then expanded by searching
within a dictionary for the synonyms and antonyms
of the seed words. The process is then repeated un-
til the lexicon has grown to a sufficient size.((Kamps
et al., 2004);(Mohammad et al., 2009);(Peng and
Park, 2004)). Corpus-based approaches can also use a
list of seed words that is expanded by using a domain
corpus rather than a dictionary. The second method
consists of adapting a general sentiment lexicon to a
domain-specific one by using a domain corpus as well
(Hatzivassiloglou and McKeown, 1997), (Choi and
Cardie, 2009) and (Kanayama and Nasukawa, 2006).
Relatively less work has focused on generating a
sentiment lexicon without a priori knowledge. Pal-
toglou and Thelwall (Paltoglou and Thelwall, 2010)
use information retrieval weighting schemes to es-
timate the score of a word. Their work extends
the SMART retrieval system and the BM25 proba-
bilistic model by introducing a delta (∆) variant and
smoothed delta variant of the idf. Kim et al. (Kim
et al., 2009) used a term weighting scheme based on
corpus statistics as well as contextual and topic related
characteristics. They evaluate the sentiment degree
of a document using a probabilistic approach. They
evaluate the likelihood of a query given a word using
Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) and Pointwise Mu-
tual Information (PMI). Additionally, they estimate
the probability of a document to generate a partic-
ular word using the Vector Space (VS) model, the
BM25 probabilistic model and Language Modeling
(LM) model.
Our method differs from the aforementioned work
by (1) introducing a new weighting scheme called
brtf.idf and (2) by using Bayes theorem for text clas-
sification as our probabilistic approach rather than us-
ing the BM25 or LM model. Taking a similar ap-
proach, Martineau and Finin (Martineau and Finin,
2009) introduced Delta tf.idf which basically calcu-
lates the difference of a word’s tf.idf score in the pos-
itive and negative training dataset. Our work extends
from this by estimating the score of a word in an un-
balanced dataset as rather than requiring a balanced
dataset. We also incorporate a parameter to allow us
to weight words occurring in more extreme reviews,
i.e., 1
∗
and 5
∗
, more highly.
3 LEXICON GENERATION
3.1 Probability-based
Our first approach is based on Baye’s theorem (Bayes
and Price, 1763) that calculates the posterior proba-
bility defined as the probability of an event A happen-
ing given that event B has happened. We define the
probability-based score of a word w, Score
prob
(w), to
be the difference between its probability of being pos-
itive, p(pos|w), and its probability of being negative,
p(neg|w), as follows:
Score
prob
(w) = p(pos|w) − p(neg|w)
where:
p(pos|w) =
p(pos) × p(w|pos)
p(w)
p(neg|w) =
p(neg) × p(w|neg)
p(w)
p(pos) =
∑
w
0
∑
r∈R
pos
n
w
0
r
p(neg) =
∑
w
0
∑
r∈R
neg
n
w
0
r
p(w) =
∑
r∈R
n
wr
p(pos) is the prior probability of the positive class,
i.e., the proportion of words that belongs to the pos-
itive class; p(neg) is the proportion of words that
belongs to the negative class; and p(w) is the total
number of occurrences of w; p(w|pos) is the prob-
ability to observe a word w given the positive class;
and p(w|neg) is the probability to observe w given the
negative class. This yields scores in the range from -
1 to 1, with -1 indicating that the a word is entirely
negative, +1 that a word is entirely positive, and 0 in-
dicating a neutral word.
We propose 3 different ways of calculating the
probability that a given word w belongs to the posi-
tive or negative class. The first is the simplest:
p(w|pos) =
p(w
pos
)
p(pos)
p(w|neg) =
p(w
neg
)
p(neg)
(P1)
where p(w
pos
) is number of times word w appears in
the positive class; p(pos) is the proportion of words
that belong to the positive class; p(w
neg
) is the num-
ber of times w appears in the negative class; and
p(neg) is the proportion of words that belong to the
negative class. Because this formula does not take
into account unbalanced datasets, and we have many
more positive reviews than negative ones, we do not
expect this formula to perform well.
Our second approach is influenced by Frank and
Bouckaert (Frank and Bouckaert, 2006) who studied
the problem of using Baye’s theorem for text classi-
fication with unbalanced classes and proposed a so-
lution. Based on their work, the second method esti-
Estimating Sentiment via Probability and Information Theory
123

mates the probability of word w to be positive or neg-
ative as follows:
p(w|pos) =
∑
r∈R
pos
n
wr
∑
w
0
∑
r∈R
pos
n
w
0
r
+ 1
k
pos
+ 1
p(w|neg) =
∑
r∈R
neg
n
wr
∑
w
0
∑
r∈R
neg
n
w
0
r
+ 1
k
neg
+ 1
(P2)
where:
∑
r∈R
pos
n
wr
= n
w5
∗
+ n
w4
∗
∑
r∈R
neg
n
wr
= n
w1
∗
+ n
w2
∗
In this approach,
∑
r∈R
pos
n
wr
is the number of
times word w appears in the positive class (i.e., the
number of times it appears in each positive review r
in corpus R);
∑
r∈R
neg
n
wr
is the number of times w
appears in the negative class;
∑
w
0
∑
r∈R
pos
n
w
0
r
is the
number of occurrences of every word in the positive
class; and
∑
w
0
∑
r∈D
neg
n
w
0
r
the number of occurrences
of every words in the negative class.
Our third probability-based method computes
p(w|pos) and p(w|neg) similarly to (2). The only dif-
ference is that we add a weight factor γ to take into
account the frequency of the words within the 1
∗
and
5
∗
review classes. Our intuition is that, since 1
∗
re-
views are more negative than 2
∗
reviews and 5
∗
are
more positive than 4
∗
reviews, word occurrences in
these more extreme reviews should count for more.
Thus,
∑
r∈R
pos
n
wr
and
∑
r∈R
neg
n
wr
in our third method
become:
p(w|pos) =
∑
r∈R
pos
n
wr
∑
w
0
∑
r∈R
pos
n
w
0
r
+ 1
k
pos
+ 1
p(w|neg) =
∑
r∈R
neg
n
wr
∑
w
0
∑
r∈R
neg
n
w
0
r
+ 1
k
neg
+ 1
(P3)
where:
∑
r∈R
pos
n
wr
= γ n
w5
∗
+ n
w4
∗
∑
r∈R
neg
n
wr
= γ n
w1
∗
+ n
w2
∗
In experiments not presented here, a value of 4 for γ
gave the best results.
3.2 Information Theory-based
These methods are based on a traditional information
theoretic technique called TF-IDF (Term Frequency-
Inverse Document Frequency)(Salton and McGill,
1986), that assesses the importance of a word when
representing the content of a document. The overall
score of a word w is the difference between its posi-
tive score and its negative score times its inverse doc-
ument frequency and is defined as follows:
Score
IT
(w) =
pos(w) − neg(w)
× IDF(w)
where :
IDF(w) = log
N
d f
w
We propose 3 formulae to compute the positive
and negative score of word w. The first uses the tra-
ditional relative term frequency of a word and is in-
spired by (Martineau and Finin, 2009)
(
pos(w) = rt f (w
5
∗
) + rt f (w
4
∗
)
neg(w) = rt f (w
1
∗
) + rt f (w
2
∗
)
(I1)
where:
rt f (w
x
∗
) =
∑
r
x
∈R
n
wr
|r|
Here, rt f
wr
is the relative term frequency of word
w in review r; N
neg
is the total number of negative re-
view; N
pos
is the total number of positive reviews; N is
the total number of reviews. For example, rt f (w
5
∗
) is
the relative term frequency of w in the 5-star reviews;
and |r| is the size of the review.
As in the case with our initial probability formula,
P1, this formula does not account for an unbalanced
dataset. Thus, since we have many more positive re-
views than negative reviews in our datasets, we do not
expect this formula to perform well.
Our second information-theoretic formula adapts
to unbalanced data sets by introducing a factor, the
balanced relative term frequency of a word. brtf com-
putes a word’s frequency relative to the type of review
it is, that is, a positive or negative review. If a word
w belongs to a negative review, the brtf is defined as
follows:
brt f (w
c
) =
rt f
wr
N
neg
× N
Conversely, if w belongs to a positive review the brtf
of w becomes the following:
brt f (w
c
) =
rt f
wr
N
pos
× N
The positive score, pos(w), and negative score,
neg(w) of a word become:
(
pos(w) = brt f (w
5
∗
) + brt f (w
4
∗
)
neg(w) = brt f (w
1
∗
) + brt f (w
2
∗
)
(I2)
KDIR 2016 - 8th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
124

Finally, based on the same intuition as with the
probabilistic approaches, we add a weight factor γ to
take into account the frequency of the words within
the more extreme review classes 1
∗
and 5
∗
. In this
case, the positive score and negative scores of a word
are now calculated as follows:
We first introduce a new term called balanced rel-
ative term frequency of a word that is a modified rel-
ative term frequency that takes into account the un-
balanced factor of a word in the dataset. balanced
relative term frequency, brt f , computes a word’s fre-
quency relative to the type of review it is, that is, a
positive or negative review. If a word w belongs to a
negative review the brtf is defined as follow:
(
pos(w) = γ brt f
c
(w
5
∗
) + brt f
c
(w
4
∗
)
neg(w) = γ brt f
c
(w
1
∗
) + brt f
c
(w
2
∗
)
(I3)
Based on experiments not reported here, we employ 4
for γ.
3.3 Ensemble
Since our probabilistic approach uses the global fre-
quency of a word, it gives importance to the distribu-
tion of that word on a corpus level while our infor-
mation theoretic approach uses the balanced relative
term frequency as well as the Inverse Document Fre-
quency of a word granting more importance to that
word on the document level.
In order to benefit from both methods, we com-
bine the best probabilistic approach with the best in-
formation theoretic approach into what we call an en-
semble approach. The score of a word w is calculated
as the average of both the Score
prob
and Score
IT
of
that word. Thus, the final score of a word w is calcu-
lated as follow:
Score(w) =
Score
prob
(w) + Score
IT
(w)
2
4 EXPERIMENT
4.1 Experimental Setup
Since our lexicon is built for a general purpose,
we need to have a large and diverse dataset. We
use Amazon products reviews ((McAuley et al.,
2015b);(McAuley et al., 2015a)) from 15 different
categories to ensure the diverseness of the data. We
use reviews from January 2013 through July 2014
from each of the 15 datasets merged into one large
and diverse dataset. The resulting dataset contains
11,129,382 reviews which are rated from 1 to 5. We
randomly split our dataset into two subsets, using
80% for training and the remaining 20% for test pur-
poses. Table 1 presents some statistics about both
datasets.
Table 1: Training and test dataset statistics.
Training dataset Test dataset
# reviews 8,903,505 2,225,877
# negative reviews 1,062,522 265,914
# positive reviews 7,063,481 1,766,132
# 1* reviews 622,970 155,688
# 2* reviews 439,552 110,226
# 4* reviews 1,693,861 422,946
# 5* reviews 5,369,620 1,343,186
Throughout the rest of our experiment, we con-
sider a review to be positive if it is rated with either 4
or 5 stars, conversely, a review is considered negative
if it is rated either with 1 or 2 stars. 3-star reviews are
considered neutral and are ignored during the experi-
ments.
Additionally, we evaluate our results against a
baseline lexicon built from the free lexical resource
SentiWordNet (Baccianella et al., 2010) ,ignoring part
of speech. SentiWordNet is constructed using state-
of-the-art techniques and it assigns three sentiment
scores to each word whereas our sentiment lexicons
provides only one single score per word. To account
for that, we use Petter Tonberg’s sentiment value ap-
proximation to approximate the score of a word with
its POS tag. Furthermore, we average each word’s
score across all POS tags to provide a single senti-
ment score.
We evaluate the sentiment lexicons built from
the training subset using a basic sentiment analysis
method on the 2,225,977 Amazon products reviews in
the test dataset. We compute a reviews score by sum-
ming up each words score in the lexicon and normal-
izing for length. If the resulting score is positive then
the review is deemed to be positive, conversely, if the
resulting score is negative then the review is deemed
to be negative.
4.2 Experimental Results
Table 2 presents the evaluation of each of the de-
scribed methods. We report the True Positive Rate
(TPR) that measures the proportion of positive re-
views that are correctly identified as positive, the True
Negative Rate (TNR) that measures the proportion of
negative reviews that are correctly identified. We also
report the Predicted Positive Value (PPV) as well as
the Predicted Negative Value (NPV) that measures the
proportion of positive results that are true positive and
Estimating Sentiment via Probability and Information Theory
125
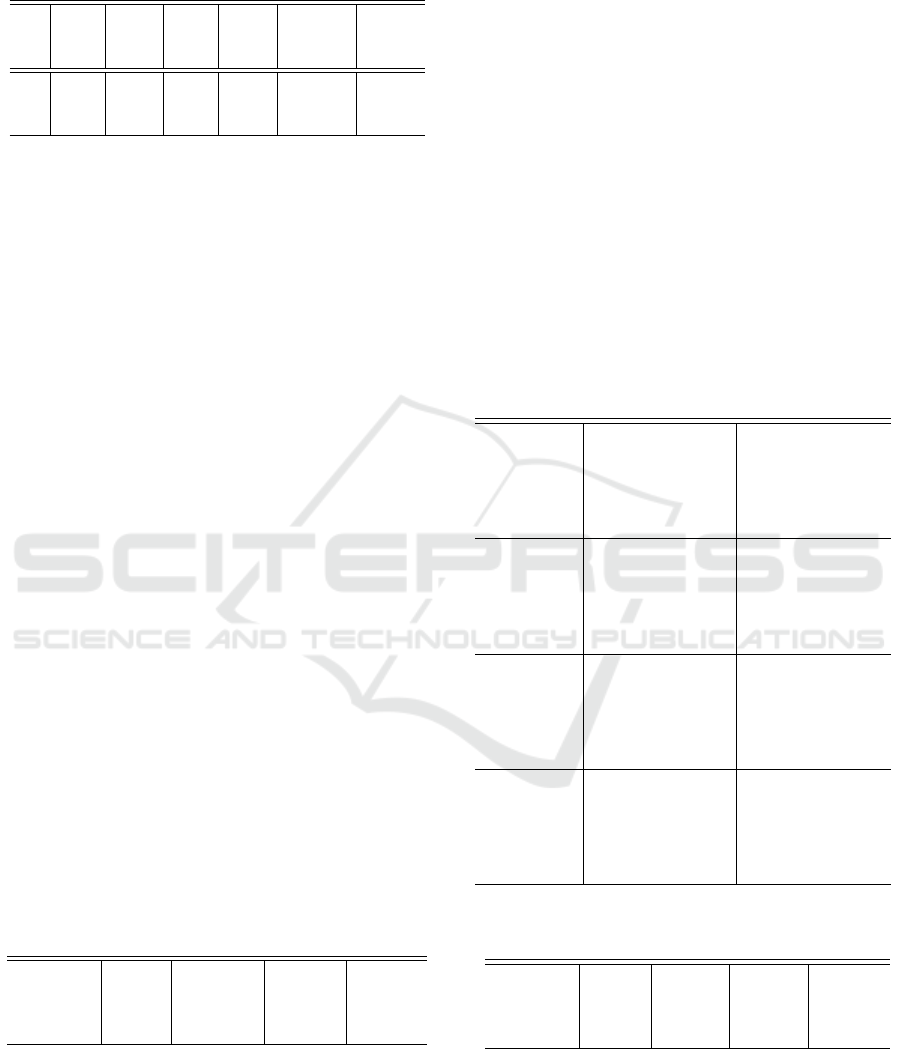
Table 2: Performances of the different formulae.
TPR TNR PPV NPV F-Score Acc
P1 1.0 0.0 0.86 0.0 0.92 86.9%
P2 0.69 0.94 0.98 0.31 0.81 72.6%
P3 0.89 0.79 0.96 0.51 0.92 87.6%
I1 1.0 0.0 0.86 0.0 0.92 86.9%
I2 0.75 0.86 0.97 0.34 0.84 76.6%
I3 0.90 0.68 0.95 0.51 0.92 87.3%
the proportion of negative results that are true neg-
ative, respectively. We also report the F-Score and
Accuracy for each of the different methods.
As shown in the table, P1 and I1 achieve a high ac-
curacy overall, each achieving 86.9% accuracy. How-
ever, they are not able to correctly identify negative
reviews as evidenced by the 0.0 TNR each produces.
We attribute this to the high proportion of positive
reviews in the training dataset. Because P2 and I2
include factors to accommodate unbalanced datasets,
they are able to identify negative reviews. How-
ever, their high TNR is offset by a decreased TPR
and overall they achieve a lower accuracies of 76.6%
and 72.6%, respectively. However, when we include
the factor gamma that weights extreme reviews more
highly, we achieve our highest the accuracy, 87.3%-
87.6%, while still correctly classifying both positive
and negative reviews.
We compare our best performing individual ap-
proaches to an ensemble approach and our baseline.
Since P3 is our best probabilistic approach and I3
is our best information-theoretic approach, these are
the two that the ensemble approach combines. Ta-
ble 3 presents this comparison using Precision, Re-
call, F1-Score, and Accuracy. As we can see, all of
our lexicons outperform the baseline lexicon in terms
of all metrics used. Our best lexicon, the ensemble,
achieves an accuracy of 88.75%, which is an improve-
ment of 7.15% over the baseline lexicon that achieves
81.60% accuracy. This result is statistically signifi-
cant (p < 0.05) based on the paired student t-test.
Table 3: Evaluation of the different approaches.
Recall Precision F-Score Acc.
P3 0.89 0.96 0.92 87.60%
I3 0.90 0.95 0.92 87.30%
Ensemble 0.91 0.96 0.93 88.75%
Baseline 0.86 0.92 0.89 81.60%
The ensemble approach also achieves a better re-
call and precision than the baseline, suggesting that
the resulting lexicon could be more exact and com-
plete than the baseline lexicon. Likewise, the ensem-
ble approach performs better than both the informa-
tion theoretic and probabilistic approaches, meaning
that the combination of both approaches works better
than each of them used individually.
4.3 Discussion
To give an intuitive feel for the lexicons produced by
the different approaches, Table 4, shows the 5 most
positive and 5 most negative words from our lexicons
in addition to the baseline lexicon. As table 5 shows,
all the lexicons classified the word good as positive.
However, the word okay is classified as negative in
our three lexicons built via text mining whereas the
baseline lexicon has it classified as positive. Like-
wise, the word refund appears to have a negative con-
notation in our methods whilst it is a positive word in
the baseline lexicon. These differences are due to the
nature of our training dataset of online reviews.
Table 4: Top 5 words for each lexicon.
Approach Top pos. words Top neg. words
P3 perfectible garbaged
marvellously junkiest
oustanding refundable
lushness misadvertised
grogginess defectively
I3 great not
love waste
easy money
perfect return
well disappointed
Ensemble great waste
love money
easy not
perfect refund
loved return
Baseline wonderfulness angriness
fantabulous henpecked
congratulations lamentable
excellent motormouth
bliss shitwork
Table 5: Various words and their score.
good refund okay speaker
P3 0.0524 -0.7050 -0.0421 0.0079
I3 0.4384 -0.2422 -0.0421 -0.0075
Ensemble 0.2454 -0.4736 -0.0619 0.0000
Baseline 0.4779 0.0000 0.2500 0.0000
Table 6 shows snippets of how sentiment analysis
is done on an entire review using each of the differ-
ent approaches. As shown in the table, the baseline
approach takes into account only a few words within
the review. These words are usually only adjectives
whilst our approach can score nearly every words of
KDIR 2016 - 8th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
126
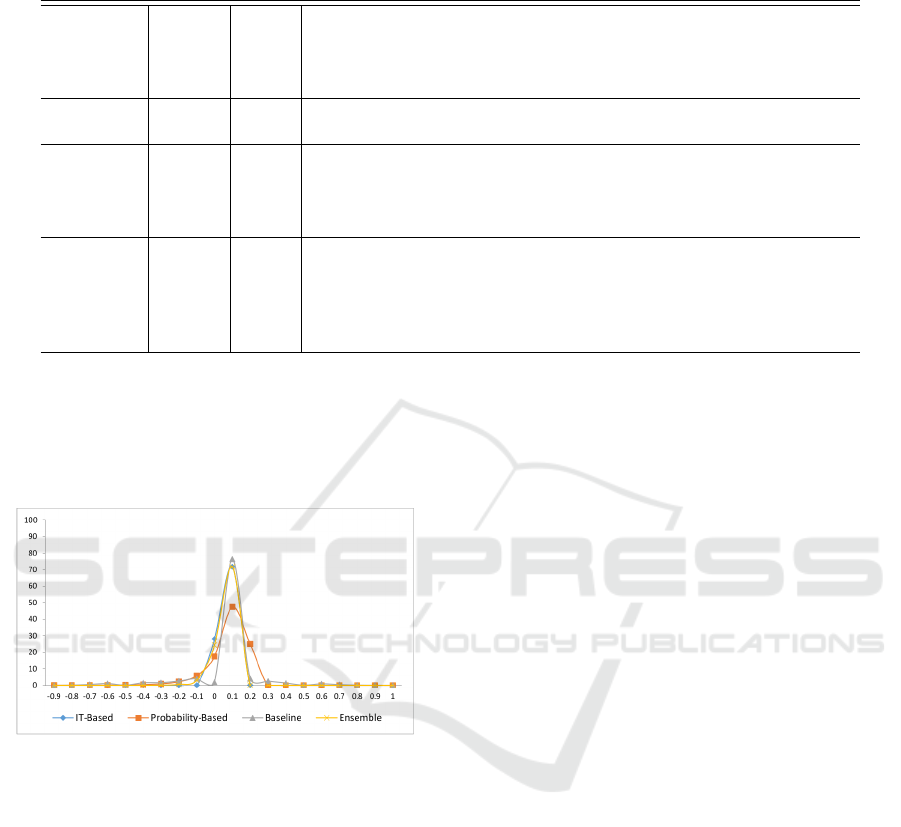
Table 6: Snippets of rated reviews.
Approach Rating Score Review
P3 5* 0.15 excelente(0.15)
1* -0.38 waste(-0.68) waste(-0.68) waste(-0.68) awaste(0.0)
waste(-0.68) waste(-0.68) time(0.003) money(-0.27)
stay(-0.09) away(-0.03) ordering(-0.005)
I3 5* 1.00 great(1.0)
1* -0.62 not(-0.91) work(-0.32)
Ensemble 5* 0.55 great(0.55)
1* -0.41 waste(-0.80) money(-0.76) try(-0.08) something(-0.10)
else(-0.05) waste(-0.80) money(-0.76) waste(-0.80)
money(-0.76) waste(-0.80) money(-0.76) throw(-0.04) away(-0.10)
Baseline 5* 1.0 secrets(0.0) vine(0.0) devotional(0.0) breaking(0.0)
abundance(0.0) bruce(0.0) wilkinson(0.0) excellent(1.0)
companion(0.0) booklet(0.0) author(0.0)
1* -0.75 purchased(0.0) based(0.0) reviews(0.0) crappy(-0.75)
worked(0.0) two(0.0) days(0.0)
the review. This major difference could explain the
higher accuracy achieved by our lexicons. Indeed, al-
though some words are not adjectives, they can still
carry a sentiment orientation and it may be important
to take them into account.
Figure 1: Score distribution from the different approaches.
Figure 1 shows the word sentiment score distribu-
tion for each of the approaches. As you can see, in
all lexicons words score tend to fall in the range -0.25
to 0.25. There are also many words with the positive
scores versus those with negative scores.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, a new method is presented that gener-
ates a sentiment lexicon using the combination of a
probabilistic approach and an information theoretic
approach. Our new method can generate a lexicon
using text mining with no a priori knowledge rather
than expanding a list of seed words as in traditional
techniques. Furthermore, our lexicon includes words
from all part-of-speech rather than being exclusive to
adjectives. Our approaches are unique in that we use
a large diverse corpus rather than a domain-specific
corpus and, unlike other approaches, we work with
unbalanced datasets. Finally, we achieve the best re-
sults when we weight words appearing in the more
extreme reviews, i.e., 1
∗
and 5
∗
, more highly.
We evaluate the effectiveness of our methods by
using the resulting lexicons to do sentiment analysis
on Amazon product reviews. Our experimental re-
sults indicate that our lexicons perform well in the
sentiment analysis task with accuracy ranging from
87.30% to 88.75% versus a baseline of 81.60% for a
widely used lexicon. Our best probabilistic approach
achieves an accuracy of 87.60% versus 87.30% for
our best information theoretic approach. However,
the ensemble approach improved on the single lexi-
cons, achieving 88.75% accuracy. Our lexicon gener-
ation methods also achieve good recall, precision, and
F1-Scores.
In the future, we will evaluate our approaches in
domain-specific datasets to measure their effective-
ness across different domains. In addition, since on-
line reviews tend to be rated within a range (e.g. typi-
cally from 1 to 5) to express a degree of negativeness
or positiveness, a sentiment rating prediction might be
experimented using our lexicons instead of doing sen-
timent analysis. Finally, we will investigate the use of
deep learning to create the sentiment lexicons.
REFERENCES
Abdulla, N. A., Ahmed, N. A., Shehab, M. A., Al-Ayyoub,
M., Al-Kabi, M. N., and Al-rifai, S. (2014). Towards
improving the lexicon-based approach for arabic sen-
timent analysis. International Journal of Information
Estimating Sentiment via Probability and Information Theory
127

Technology and Web Engineering (IJITWE), 9(3):55–
71.
Baccianella, S., Esuli, A., and Sebastiani, F. (2010). Sen-
tiwordnet 3.0: An enhanced lexical resource for sen-
timent analysis and opinion mining. In LREC, vol-
ume 10, pages 2200–2204.
Bayes, M. and Price, M. (1763). An essay towards solv-
ing a problem in the doctrine of chances. by the late
rev. mr. bayes, frs communicated by mr. price, in a let-
ter to john canton, amfrs. Philosophical Transactions
(1683-1775), pages 370–418.
Choi, Y. and Cardie, C. (2009). Adapting a polarity lex-
icon using integer linear programming for domain-
specific sentiment classification. In Proceedings of
the 2009 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natu-
ral Language Processing: Volume 2-Volume 2, pages
590–598. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Davidov, D., Tsur, O., and Rappoport, A. (2010). Enhanced
sentiment learning using twitter hashtags and smileys.
In Proceedings of the 23rd international conference
on computational linguistics: posters, pages 241–249.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Ding, X., Liu, B., and Yu, P. S. (2008). A holistic lexicon-
based approach to opinion mining. In Proceedings of
the 2008 international conference on web search and
data mining, pages 231–240. ACM.
Frank, E. and Bouckaert, R. R. (2006). Naive bayes for text
classification with unbalanced classes. In European
Conference on Principles of Data Mining and Knowl-
edge Discovery, pages 503–510. Springer.
Gao, D., Wei, F., Li, W., Liu, X., and Zhou, M. (2015).
Cross-lingual sentiment lexicon learning with bilin-
gual word graph label propagation. Computational
Linguistics.
Goldberg, A. B. and Zhu, X. (2006). Seeing stars when
there aren’t many stars: graph-based semi-supervised
learning for sentiment categorization. In Proceedings
of the First Workshop on Graph Based Methods for
Natural Language Processing, pages 45–52. Associa-
tion for Computational Linguistics.
Hatzivassiloglou, V. and McKeown, K. R. (1997). Predict-
ing the semantic orientation of adjectives. In Proceed-
ings of the eighth conference on European chapter of
the Association for Computational Linguistics, pages
174–181. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Hu, M. and Liu, B. (2004a). Mining and summarizing
customer reviews. In Proceedings of the tenth ACM
SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge dis-
covery and data mining, pages 168–177. ACM.
Hu, M. and Liu, B. (2004b). Mining opinion features in
customer reviews. In AAAI, volume 4, pages 755–760.
Kamps, J., Marx, M., Mokken, R. J., Rijke, M. d., et al.
(2004). Using wordnet to measure semantic orienta-
tions of adjectives.
Kanayama, H. and Nasukawa, T. (2006). Fully auto-
matic lexicon expansion for domain-oriented senti-
ment analysis. In Proceedings of the 2006 conference
on empirical methods in natural language processing,
pages 355–363. Association for Computational Lin-
guistics.
Khan, A. Z., Atique, M., and Thakare, V. (2015). Com-
bining lexicon-based and learning-based methods for
twitter sentiment analysis. International Journal of
Electronics, Communication and Soft Computing Sci-
ence & Engineering (IJECSCSE), page 89.
Kim, J., Li, J.-J., and Lee, J.-H. (2009). Discovering the dis-
criminative views: measuring term weights for senti-
ment analysis. In Proceedings of the Joint Conference
of the 47th Annual Meeting of the ACL and the 4th
International Joint Conference on Natural Language
Processing of the AFNLP: Volume 1-Volume 1, pages
253–261. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Kim, S.-M. and Hovy, E. (2004). Determining the sentiment
of opinions. In Proceedings of the 20th international
conference on Computational Linguistics, page 1367.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Kim, S.-M. and Hovy, E. (2006a). Extracting opinions,
opinion holders, and topics expressed in online news
media text. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Senti-
ment and Subjectivity in Text, pages 1–8. Association
for Computational Linguistics.
Kim, S.-M. and Hovy, E. (2006b). Identifying and analyz-
ing judgment opinions. In Proceedings of the main
conference on Human Language Technology Confer-
ence of the North American Chapter of the Associ-
ation of Computational Linguistics, pages 200–207.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Li, T., Zhang, Y., and Sindhwani, V. (2009). A non-negative
matrix tri-factorization approach to sentiment classifi-
cation with lexical prior knowledge. In Proceedings
of the Joint Conference of the 47th Annual Meeting of
the ACL and the 4th International Joint Conference on
Natural Language Processing of the AFNLP: Volume
1-Volume 1, pages 244–252. Association for Compu-
tational Linguistics.
Liu, B. (2010). Sentiment analysis and subjectivity. Hand-
book of natural language processing, 2:627–666.
Liu, B. (2012). Sentiment analysis and opinion mining.
Synthesis lectures on human language technologies,
5(1):1–167.
Liu, F., Wang, D., Li, B., and Liu, Y. (2010). Improv-
ing blog polarity classification via topic analysis and
adaptive methods. In Human Language Technologies:
The 2010 Annual Conference of the North American
Chapter of the Association for Computational Lin-
guistics, pages 309–312. Association for Computa-
tional Linguistics.
Martineau, J. and Finin, T. (2009). Delta tfidf: An improved
feature space for sentiment analysis. ICWSM, 9:106.
McAuley, J., Pandey, R., and Leskovec, J. (2015a). In-
ferring networks of substitutable and complementary
products. In Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD
International Conference on Knowledge Discovery
and Data Mining, pages 785–794. ACM.
McAuley, J., Targett, C., Shi, Q., and van den Hengel, A.
(2015b). Image-based recommendations on styles and
substitutes. In Proceedings of the 38th International
ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Develop-
ment in Information Retrieval, pages 43–52. ACM.
Mohammad, S., Dunne, C., and Dorr, B. (2009). Generat-
ing high-coverage semantic orientation lexicons from
KDIR 2016 - 8th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
128

overtly marked words and a thesaurus. In Proceedings
of the 2009 Conference on Empirical Methods in Nat-
ural Language Processing: Volume 2-Volume 2, pages
599–608. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Ng, V., Dasgupta, S., and Arifin, S. (2006). Examining
the role of linguistic knowledge sources in the auto-
matic identification and classification of reviews. In
Proceedings of the COLING/ACL on Main conference
poster sessions, pages 611–618. Association for Com-
putational Linguistics.
Paltoglou, G. and Thelwall, M. (2010). A study of informa-
tion retrieval weighting schemes for sentiment anal-
ysis. In Proceedings of the 48th Annual Meeting of
the Association for Computational Linguistics, pages
1386–1395. Association for Computational Linguis-
tics.
Pang, B. and Lee, L. (2004). A sentimental education:
Sentiment analysis using subjectivity summarization
based on minimum cuts. In Proceedings of the 42nd
annual meeting on Association for Computational
Linguistics, page 271. Association for Computational
Linguistics.
Pang, B. and Lee, L. (2005). Seeing stars: Exploiting class
relationships for sentiment categorization with respect
to rating scales. In Proceedings of the 43rd annual
meeting on association for computational linguistics,
pages 115–124. Association for Computational Lin-
guistics.
Pang, B. and Lee, L. (2008). Opinion mining and senti-
ment analysis. Foundations and trends in information
retrieval, 2(1-2):1–135.
Pang, B., Lee, L., and Vaithyanathan, S. (2002). Thumbs
up?: sentiment classification using machine learn-
ing techniques. In Proceedings of the ACL-02 con-
ference on Empirical methods in natural language
processing-Volume 10, pages 79–86. Association for
Computational Linguistics.
Peng, W. and Park, D. H. (2004). Generate adjective sen-
timent dictionary for social media sentiment analy-
sis using constrained nonnegative matrix factoriza-
tion. Urbana, 51:61801.
Salton, G. and McGill, M. J. (1986). Introduction to modern
information retrieval.
Taboada, M., Brooke, J., Tofiloski, M., Voll, K., and Stede,
M. (2011). Lexicon-based methods for sentiment
analysis. Computational linguistics, 37(2):267–307.
Turney, P. D. (2002). Thumbs up or thumbs down?: se-
mantic orientation applied to unsupervised classifica-
tion of reviews. In Proceedings of the 40th annual
meeting on association for computational linguistics,
pages 417–424. Association for Computational Lin-
guistics.
Wei, W. and Gulla, J. A. (2010). Sentiment learning on
product reviews via sentiment ontology tree. In Pro-
ceedings of the 48th Annual Meeting of the Associ-
ation for Computational Linguistics, pages 404–413.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Yu, H. and Hatzivassiloglou, V. (2003). Towards answering
opinion questions: Separating facts from opinions and
identifying the polarity of opinion sentences. In Pro-
ceedings of the 2003 conference on Empirical meth-
ods in natural language processing, pages 129–136.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Zhou, S., Chen, Q., and Wang, X. (2010). Active deep
networks for semi-supervised sentiment classification.
In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference
on Computational Linguistics: Posters, pages 1515–
1523. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Estimating Sentiment via Probability and Information Theory
129
