
Development of Domains and Keyphrases along Years
Yaakov HaCohen-Kerner and Meir Hassan
Department of Computer Science, Jerusalem College of Technology,
21 Havaad Haleumi St., P.O.B. 16031, 9116001 Jerusalem, Israel
Keywords: Development Concepts, Development Model, NLP Domains, Keyphrases, Trends, Word Bigrams and
Trigrams.
Abstract: This paper presents a methodology (including a detailed algorithm, various development concepts and
measures, and stopword lists) for measuring the development of domains and keyphrases along years. The
examined corpus contains 1020 articles that were accepted for full presentation in PACLIC along the last 18
years. The experimental results for 5 chosen domains (digital humanities, language resources, machine
translation, sentiment analysis and opinion mining, and social media) suggest that development trends of
domains and keyphrases can be efficiently measured. Top bigrams and trigrams were found as efficient to
identify general trends in NLP domains.
1 INTRODUCTION
Your Natural language processing (NLP) is the
research and application domain that investigates
how computers and software can be used to
successfully process natural language text or speech.
NLP contains a wide range of research fields, e.g.:
information extraction, information retrieval,
machine learning, machine translation, morphology,
natural language generation, phonology, semantics,
sentiment analysis, syntax, speech recognition, and
summarization.
NLP is a very active research domain. Many
conferences (e.g., ACL, CICLing, COLING,
CONLL, EMNLP, LREC, NAACL, and PACLIC)
are held in this area every one or two years.
Thousands of academic works are published every
year in various forums of NLP such as journals,
conferences, workshops, symposiums, Ph.D.
dissertations, M.Sc. theses, technical papers, and
working papers.
Among the research issues that are covered by
NLP is the investigation of the development of
various NLP's sub-domains in general and their
keyphrases in particular over the years. An example
for such a question is the analysis of the
development of domains and keyphrases in various
NLP’s conferences over the years.
The aim of this work is to explore a corpus of a
certain NLP conference and to analyze the
development of the NLP’s keyphrases and domains
along an interval of years. The chosen application
domain is the articles of the Pacific Asia Conference
on Language, Information and Computation
(PACLIC) that were accepted for full presentation
along the last 18 years (1998-2015). For this study
we decided to investigate five research domains: (1)
digital humanities, (2) language resources, (3)
machine translation, (4) sentiment analysis and
opinion mining, and (5) social media. These
domains were selected from the domain list that is
provided in PACLIC-2016 (http://paclic30.khu.ac.kr/
index.html).
The motivation of this research is to discover
important trends in various domains and keyphrases
in a given conference. The identification of such
trends is important in order to know which domains
are currently top or more important ones and which
domains are less or no longer important. The
findings might allow proper resource allocation on
the one hand and a choice of “hot” research topics
by researchers on the other hand. Furthermore, the
identification of NLP’s domains and their key-
phrases will enable automatic classification of
papers into NLP’s domains. Such a classification
can help journal editors and conference chairs to
automatically distribute papers to suitable reviewers.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 presents relevant background about
investigating research trends over years. Section 3
HaCohen-Kerner, Y. and Hassan, M.
Development of Domains and Keyphrases along Years.
DOI: 10.5220/0006077303750383
In Proceedings of the 8th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2016) - Volume 1: KDIR, pages 375-383
ISBN: 978-989-758-203-5
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
375

introduces various NLP’s domains and development
of domains and keyphrases. Section 4 describes the
model that enables the exploring of the development
of domains and keyphrases along the years. Section
5 presents the examined corpus, the experimental
results and their analysis. Finally, Section 6
summarizes the main findings and suggests future
directions.
2 INVESTIGATION OF
RESEARCH TRENDS
Investigation of research trends or domains was
conducted in a number of ways based on at least one
of the following elements: citations, topics,
keyphrases, and sentences.
2.1 Citations
There are many works that explored citations in
scientific papers. Garfield (1965) was the first to
publish an investigation of the issue of automatic
production of citation indexes, extraction, and
analysis of citations from documents. He found that
citation indices can also be used to analyze research
trends, identify emerging areas of science, and
determine the popularity of an article.
Nanba and Okumura (1999) defined the concept
of a citing area as the sequence of sentences that
appear around the location of a given reference in a
certain scientific paper. The authors also presented a
rule-based algorithm to identify the citing area of
any given reference. Later on, Nanba et al. (2000)
used their algorithm to identify the author’s reason
for citing a given paper.
Radev and Abu-Jbara (2012) investigated citing
sentences (a citing sentence is a sentence, which
appears in a scientific paper and contains an explicit
reference to another paper) that appear in the ACL
Anthology Network (AAN, http://clair.eecs.umich.
edu/anthology/), which is a comprehensive manually
curated networked corpus of citations and
collaborations in the field of computational
linguistics. In their paper, the authors used the AAN
in order to discover research trends and to
summarize previous discoveries and contributions.
In addition, they presented a few applications that
make use of citing sentences e.g., identifying
controversial arguments, identifying relations
between techniques, tools and tasks, and scientific
literature summarization.
Sim et al. (2012) presented a joint probabilistic
model of who cites whom in computational
linguistics, and also of how is the citing written.
Their model reveals latent factions, which are
groups of individuals whom we expect to collaborate
more closely within their faction, cite within the
faction using language distinct from citation outside
the faction, and be largely understandable through
the language used when cited from without. The
authors conducted an exploratory data analysis on
the ACL Anthology and they extended the model to
reveal changes in some authors’ faction
memberships over time.
Research trends in scientific literature have been
also investigated by many researchers (e.g.,
McCallum et al., 2006; Dietz et al., 2007; Hall et al.,
2008; and Gerrish and Blei, 2010) using topic
models such as the latent Dirichlet allocation (Blei et
al., 2003) and its variations.
2.2 Topics
Exploring of computational history using topic
models to analyze the rise and fall of research topics
to study the progress of science, has been performed
in general by Griffiths and Steyvers (2004) and more
specifically in the ACL Anthology by Hall et al.
(2008).
Anderson et al. (2012) developed a people-
centered computational history of science that tracks
authors over topics with application to the history of
computational linguistics. The authors identified the
topical subfields authors work on by assigning
automatically generated topics to each paper in the
ACL Anthology from 1980 to 2008. They identified
four different research periods. They analyzed the
flow of authors across topics to discern how some
subfields flow into the next, forming different stages
of ACL research. They claimed that the NLP’s sub-
domains become more integrated.
2.3 Keyphrases
Omodei et al. (2014A) presented a new method to
extract keywords from texts and classify these
keywords according to their informational value,
derived from the analysis of the argumentative goal
of the sentences they appear in. The method is
applied to the ACL Anthology corpus, containing
papers on the computational linguistic domain
published between 1980 and 2008. The analysis of
the ACL Anthology corpus is based on the identifi-
cation of keywords, which are classified according
to their informational status. The classification is
done according to a text zoning analysis of the
papers’ abstracts. The authors showed that coupling
keyword extraction with text zoning enable to
observe fine grained facts in the dynamics of a
scientific domain. Their approach allows to highlight
KDIR 2016 - 8th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
376

interesting facts concerning the evolution of the topics
and methods used in computational linguistics.
Daudaravičius (2012) employed collocation
segmentation to extract terms from the ACL
Anthology Reference Corpus. The results of his
research show that until 1986, the most significant
terms were related to formal/rule based methods.
Since 1987, terms related to statistical methods (e.g.,
language model, similarity measure, and text
classification) became more important. Since 1990,
terms related to newly released language resources
(e.g., Penn Treebank, Mutual Information, statistical
parsing, bilingual corpus, and dependency tree)
became the most important. There are some terms
such as “machine translation” and “machine
learning” that are significant throughout the whole
ACL ARC corpus and they are not significant for
any particular time period. That is to say, finding
shows that some terms can be globally significant
while some other terms are significant during part(s)
of the time and insignificant during other part(s) of
the time.
Omodei et al. (2014B) analyzed the evolution of
the computational linguistics domain between the
years of 1988 and 2012 using a quantitative analysis
of the ACL Anthology. They reconstructed the
socio-semantic landscape of the domain by inferring
a co-authorship and a semantic network from the
analysis of the corpus. Keywords were extracted
using a hybrid approach mixing linguistic patterns
with statistical information; then, the semantic
network was built using a co-occurrence analysis of
these keywords within the corpus. Combining tem-
poral and network analysis techniques, their model
is able to examine the main evolutions of the domain
and to identify the active subdomains over the years.
2.4 Sentences
Reiplinger et al. (2012) introduced a comparative
study of two approaches to extracting definitional
sentences from a corpus of scholarly discourse: one
based on bootstrapping lexico-syntactic patterns and
another based on deep analysis. Computational
linguistics was used as the target domain and the
ACL Anthology as the corpus. Definitional senten-
ces extracted for a set of well-defined concepts were
rated by domain experts. Results show that both
methods extract high-quality definition sentences
intended for automated glossary construction. The
majority of the extracted sentences provide useful
information about the domain concepts. The authors
claim that since both approaches use generic
linguistic resources and pre-processing (identity
extraction, name, POS-tagging, etc.) they can be
considered domain-independent.
3 NLP’S DOMAINS AND
KEYPHRASES AND THEIR
DEVELOPMENT
3.1 NLP’s Domains
There is no consensus among NLP’s researchers
about the division of NLP into research domains and
their definitions. Each NLP’s conference has its own
division to NLP’s sub-domains. PACLIC-2016
(http://paclic30.khu.ac.kr/index.html) presents the
following list of sub-domains:
Language Studies: Corpus linguistics,
Discourse analysis, Language acquisition,
Language learning, Language mind and
culture, Language theory, Morphology,
Phonology, Pragmatics/Sociolinguistics,
Semantics, Spoken language processing,
Syntax, Typology
Information Processing and Computational
Applications: Cognitive modeling of language,
Dialogue and interactive systems, Digital
humanities, Information retrieval/extraction,
Language resources, Machine learning/Data
mining, Machine translation, Multi-linguality
in NLP, NLP applications, Sentiment analysis
and opinion mining, Social media, Text
classification/summarization, Word
segmentation
3.2 Development of Domains and
Keyphrases
We plan to investigate the life of several research
domains in general and of several top frequent
keyphrases in these domains in particular throughout
the years of a certain conference. We would like to
define concepts such as birth/death/rise/decline and
to analyze their values for a certain conference.
Since our main research domain is NLP, we
decided to apply our plan to an NLP conference and
we chose to work on the articles that were accepted
to PACLIC for full presentation along the last 18
years (1998-2015).
The chosen keyphrases are bigrams and trigrams
(see Section 4 why unigrams are not regarded as
keyphrases that identify domains). We intend to
measure the development of a few selected domains
and part of the keyphrases over groups of three years
for each group. For this purpose, we defined the
following measures of development:
Birth of a Keyphrase – A keyphrase that did
not appear in the past and its current frequency
Development of Domains and Keyphrases along Years
377

is above the minimal threshold (two
appearances in a group of three years).
Death of a Keyphrase - keyphrase that
appeared in the past and its current frequency is
0.
Local Rise of a Keyphrase - keyphrase that its
value has increased relatively to its previous
value.
Global Rise of a Keyphrase - keyphrase that
its last value has increased relatively to its first
value.
Local Decline of a Keyphrase - keyphrase that
its value has decreased relatively to its previous
value.
Global Decline of a Keyphrase - keyphrase
that its last value has decreased relatively to its
first value.
Similar concepts (birth/death/rise/decline) can be
defined for each domain based on the sum total
values of the domain’s top frequent n-grams.
4 THE DEVELOPMENT MODEL
The main stages of the development model are:
A. Creating a corpus including PDF-files
representing an NLP conference. We then used
a conversion program (http://www.squarepdf.
net/file/get/6463hkb5ergbvkwaiq663zijza) to
convert the PDF files of the source articles into
text files.
B. Filtering stopwords and finding the best n-
grams that represent each chosen domain using
most-cited related papers (not necessarily
PACLIC’s papers). We decided to work only
with 10 top bigrams and 3 top trigrams but
without unigrams. According to our
experiments, unigrams are not suitable for
domain identification because many of them
are ambiguous in the sense that they are
suitable for more than one domain. Examples
of such noisy unigrams are: “analysis”,
“corpus”, “data”, “feature”, “features”,
“sentence“, “text”, “texts”, “user”, “users”, and
“web”. Some of these unigrams can be added
to the “domain stopwords”. However, we did
not do that because some of these unigrams
might be parts of beneficial bigrams or
trigrams.
C. Finding the frequencies of the top five frequent
bigrams and the top frequent trigram for each
group of 3 years for the last 18 years of the
PACLIC’s conference (1998-2015).
D. Computing the development trends of each
chosen domain and its top n-grams over the
years using the total values of the selected
bigrams and trigram.
Analysis of the results of various bigrams,
trigrams, and domains.
Each main stage will be detailed separately, as
follows. In stage A, we selected five specific
domains in NLP. These domains were chosen from
the list of the domains that are belonging to the
“Information Processing and Computational
Applications” area. The five chosen domains are: (1)
Digital humanities (DH), (2) Language resources
(LR), (3) Machine translation (MT), (4) Sentiment
analysis and opinion mining (SA & OM), and (5)
Social media (SM).
For each domain, we extracted 50 papers via
Google Scholar (https://scholar.google.com/). We
downloaded only the 50 most-cited papers that
contained in their headlines the exact keyphrase of
their domain and we succeeded to achieve their
PDF-version. That is to say, we downloaded the 50
most-cited papers that contained in their headlines
“Digital humanities” and we were able to achieve
their PDF-version. For the domain of “Sentiment
analysis and opinion mining” we downloaded 25
papers that contained in their headlines “Sentiment
analysis” and 25 papers that contained in their
headlines “opinion mining”.
For each one of these five domains using the 50
downloaded papers, we have extracted the ten most
frequent bigrams and the three most frequent
trigrams excluding stopwords. We chose these
relatively low numbers of n-grams in order to avoid
unnecessarily large number of n-grams on the one
hand, and to avoid noisy n-grams that might be
related to more than one domain on the other hand.
We chose only 3 trigrams less than the number of
chosen bigrams (10) because according to our
experience there are much more frequent bigrams
than frequent trigrams both in numbers and their
frequencies. In other words, word bigrams are better
representative classifiers for domain classification
than word trigrams.
In stage B, we worked with PACLIC’s papers
using the top five frequent bigrams (out of the ten
bigrams extracted from Google Scholar’s papers)
and the most frequent trigram (out of the three
trigrams extracted from Google Scholar’s papers)
for each group of 3 years for each domain
separately. We did not work with all the top n-grams
that were extracted from Google Scholar because not
all of these n-grams were included in PACLIC’s
papers.
KDIR 2016 - 8th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
378

Table 1: General information about the corpus.
Total # of full papers
Total # of words
Avg. # of words
per paper
Median value of words
per paper
Std. of words
per paper
1020
5048544
4949.55
4905.5
1622.17
Table 2: General information about the corpus in units of groups of 3 years.
Period of years
# of full papers
Total # of words
Avg. # of words
per paper
Median value of words
per paper
Std. of words
per paper
1998-2001
115
540113
4696.63
4506
1662.96
2002-2004
128
547378
4276.39
4223.5
1370.26
2005-2007
139
599036
4309.61
4110
1780.36
2008-2010
205
1031467
5031.55
4821
1299.6
2011-2013
239
1222014
5113.03
5152
1558.72
2014-2015
194
1108536
5714.10
5715
1586.77
The following procedure was applied in stage B:
1. All appearances of stopwords for general texts
(called general stopwords) are deleted.
2. All appearances of stopwords for texts in NLP
(called domain stopwords) are deleted.
3. All possible continuous N-gram words (for N
=2, 3) are created, provided that the all the
words in a certain N-gram are in the same
sentence.
4. The frequency of each N-gram feature in the
corpora is counted.
5. The bigram and trigram features (each group
alone) are sorted in descending order.
There are 386 general stopwords, e.g., "a", "an",
"and", "another", "any", "are", "aren't", "as", and
"at". There are 606 domain stopwords, e.g.,
"abstract", "annual", "association", "chapter",
"process", “processes", and "publishers".
Measures Dealing with Development of
Keyphrases
We defined three measures to estimate the
development of keyphrases. These measure will be
described and discussed in the following paragraphs.
Measure1 = # of occurrences of a certain
keyphrase in a certain period of time
The disadvantage of measure1 is that it does not
take into account the # of papers that might be
enlarged over the years. Assuming each period of
time lasts one years, and for instance the # of a
certain keyphrase can be increased from 50 to 60
in two consecutive years while the # of papers can
be increased from 50 to 80 in the same two
consecutive years. In other words, although it seems
as if the frequency of a certain keyphrase has been
increased, the truth is that the frequency of this
certain keyphrase was decreased relatively to the
increase of # of papers. Therefore, we thought about
normalizing measure1 by the # of papers in the
discussed year. This thought led to the definition of
measure2.
Measure2 = measure1 in a certain period of time /
# of papers in the same period of time
Measure2 has also a serious disadvantage. It does
not take into account specific situations. For
example, a certain conference can decide that from a
certain year the # of available pages for an accepted
paper will be increased in two (e.g., from 8 to 10
pages). Thus, we thought about normalizing
measure1 by the # of words included in all of the
papers in the discussed period of time (call it the # of
words in the discussed period of time). This thought
led to the definition of measure3 as follows.
Measure3 = 10000 * measure1 in a certain period
of time / # of words in the discussed period of time
Measure3 is much more objective than the two
previous measures. Thus, we decided to carry out
our experiments using this measure. Since the results
we received were very small numbers we decided to
multiply each result by 10000.
5 CORPUS AND
EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
The examined corpus contains the articles of the
Pacific Asia Conference on Language, Information
and Computation (PACLIC) that were accepted for
full presentation along the last 18 years (1998-2015).
The PDF-versions of these papers were downloaded
from the ACL Anthology web site. Table 1 presents
general information about this corpus. Table 2
introduces various statistics while looking at the
corpus in units of groups of 3 years for each group.
Development of Domains and Keyphrases along Years
379

From Table 1 we see that along the last 18 years
there were 1020 full papers and their average length
is around 4950 words (very close to the median
value ~ 4906 words). From Table 2 we see that in
general the # of full papers is rising over the years
starting from 115 papers in the first three years
(1998-2000) and ending with 194 papers in the last
three years (2013-2015). Also the average length of
a paper in words in general is rising over the years
starting from around 4500 words per paper in the
first three years (1998-2000) and ending with around
5700 words per paper in the last three years (2013-
2015).
Figure 1 introduces the experimental results
regarding the development of the five chosen
domains according to the top five bigrams and the
top first trigram for each domain along groups of 3
years. Figures 2-6 present the development of all the
five selected domains; the development of each
domain is presented alone based on its top five
bigrams and its top first trigram. Figure 2 introduces
the experimental results regarding the development
of the DH domain according to its top five bigrams
and its top first trigram along groups of 3 years.
Figure 1: Domains’ development along the years.
Figure 1 shows that in general there is a global
rise for all the five domains because the last value of
measure3 (years 13-15) of each domain is higher
than the first value of measure3 (years 98-00).
However, the values of the first three domains (LR,
SA&OM, and MT) are significantly higher than the
values of the last two domains (DH, and SM). This
means that the first three domains (especially MT)
are much more popular from the viewpoint of their
top chosen features along the years than the last two
Figure 2: Development of the DH domain.
domains, especially over the last years. Moreover,
the global rise of the first three domains is
significantly higher in absolute values along the
years than the last two domains. There are also
several local declines. Most of them belong to the
LR domain.
Figure 2 shows that only one bigram “social
media” has a relative significant rise compared to
the other top keyphrases. The values of most other
keyphrases are close to zero over most of the years.
These findings indicate that DH is not a popular
research domain among PACLIC’s full papers.
Three keyphrases present a late birth during 07-09
(i.e., they had zero frequencies until 07).
Figure 3: Development of the LR domain.
Figure 3 introduces the experimental results
regarding the development of the LR domain
KDIR 2016 - 8th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
380
according to its top five bigrams and its top first
trigram. Figure 4 introduces the experimental results
regarding the development of the MT domain
according to its top five bigrams and its top first
trigram along groups of 3 years.
Figure 3 shows that the LR domain is a
heterogeneous domain from the viewpoint of its top
chosen n-grams. There are three keyphrases
(“machine translation”, “language resources”, and
“human language technologies”) that present a
global rise over the years; while the other three
keyphrases (“speech recognition”, “sign language”,
and “spoken language”) present a global decline
over the years. Moreover, the “sign language”
keyphrase presents “death”. The most impressive
rise was observed for the bigram “machine
translation”, which is the name of another domain.
Based on Figures 1 and 3, the LR domain seems as
an important and unstable domain with a general
increase over the years characterized also by a few
declines in different periods of years.
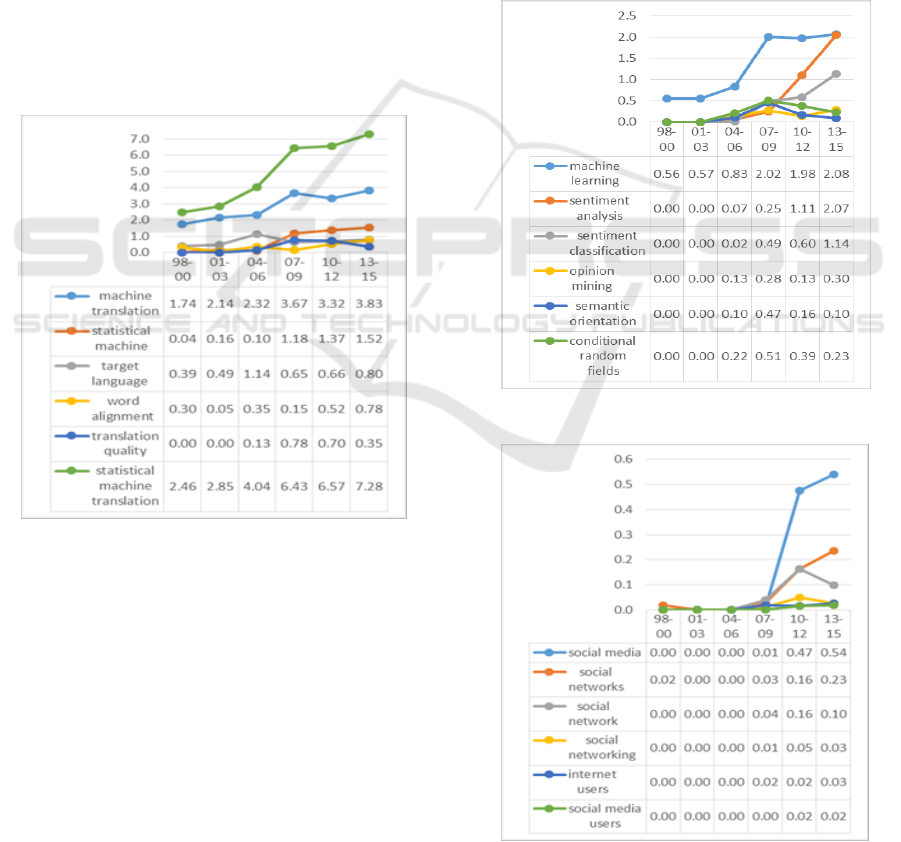
Figure 4: Development of the MT Domain.
Figure 4 shows rises for all five MT’s
keyphrases. The most impressive rise was observed
for the trigram “statistical machine translation”
starting from 2.46 and ending with 7.28; values
higher the compatible values of all the five top
bigrams over all the years. Moreover, the values
obtained by the MT’s top three keyphrases (above
1.0) are higher than the values obtained by all the
other keyphrases from all the other four domains
(Figures 2, 3, 5, and 6). The same finding can be
seen in Figure 1, where the values of MT’s
keyphrases are much higher than those of all other
four domains. Figure 5 introduces the experimental
results regarding the development of the fourth
domain SA & OM according to its top five bigrams
and its top first trigram. Figure 6 introduces the
experimental results regarding the development of
the SM domain according to its top five bigrams and
its top first trigram.
Figure 5 shows rises for all five SA&OM’s
keyphrases likewise the MT domain (Figure 4).
While three keyphrases (“opinion mining”,
“semantic orientation”, and “conditional random
fields”) present relatively small increases, the
“machine learning” keyphrase presents an
impressive jump from 04-06 to 07-09 and the two
sentiment keyphrases “sentiment analysis” and
“sentiment classification” present impressive
increases over the last 6-9 years.
Figure 5: Development of the SA&OM domain.
Figure 6: Development of the SM Domain.
Development of Domains and Keyphrases along Years
381

Figure 6 shows very small rises for three SM’s
keyphrases (“social networking”, “internet users,
and “social media users”). Only two keyphrases
“social media” and “social networks” show
relatively nice rises. It is interesting to point that
four out of the five keyphrases include the word
“social”, which is also the dominate word included
in the domain name. The relatively low values of all
the five keyphrases are compatible with the low
scores of this domain in Figure 1.
6 SUMMARY AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, we present a methodology (including a
detailed algorithm, various development measures,
and suitable stopword lists) for measuring the
development of domains and keyphrases. The
experimental results suggest that development trends
of domains and keyphrases can be efficiently
measured using measure3.
The main findings are: (1) The investigation of
the five NLP sub-domains found that three domains:
LR, SA&OM, and especially MT are much more
popular especially over the last years, while DH and
SM are significantly less explored; (2) Top bigrams
and trigram(s) are enough to identify general trends
in NLP domains while unigrams are noisy and
therefore were avoided; and (3) As expected the
name of the domain was one of the top keyphrases
in each one of the tested domain.
Future research proposals are: (1) Use extended
definitions of keyphrases (not only bigrams and
trigrams) and apply more sophisticated methods to
automatically learn and extract keyphrases (e.g.,
HaCohen-Kerner et al, 2005; HaCohen-Kerner et al,
2007); (2) Apply additional keyphrases’ measures,
which are more complex and informative such as
PWI “probability-weighted amount of information’’
and TF-IDF ‘‘Term frequency–inverse document
frequency’’; (3) Perform additional experiments on
other kinds of intervals of years (e.g., every one
year, every five years); (4) Apply this development
model to other types of NLP domains and
conferences as well as to other domains in other
fields; and (5) Investigation of additional concepts
regarding development of domains and concepts
such as merge of two concepts (domains) to one
concept (domain), and split of one concept (domain)
to several concepts (domains).
REFERENCES
Anderson, A., McFarland, D., Jurafsky, D., 2012. Towards
a computational history of the ACL: 1980-2008. In
Proceedings of the ACL-2012 Special Workshop on
Rediscovering 50 Years of Discoveries (pp. 13-21).
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Blei, D. M., Ng, A. Y., Jordan, M. I., 2003. Latent
dirichlet allocation. The Journal of machine Learning
research, 3, 993-1022.
Daudaravičius, V., 2012. Applying collocation
segmentation to the ACL Anthology Reference
Corpus. In Proceedings of the ACL-2012 Special
Workshop on Rediscovering 50 Years of Discoveries
(pp. 66-75). Association for Computational
Linguistics.
Dietz, L., Bickel, S., Scheffer, T., 2007. Unsupervised
prediction of citation influences. In Proc. of ICML.
Garfield, E. 1965. Can citation indexing be automated? In
Statistical association methods for mechanical
documentation, Symposium Proceedings, Washington
edited by M. Stevens. (National Bureau of Standards,
Miscellaneous Publication 269, Dec 1964, 15, 1965).
Gerrish, S., Blei, D. M., 2010. A language-based approach
to measuring scholarly impact. In Proc. of ICML.
Griffiths, T. L, Steyvers. M., 2004. Finding scientific
topics. Proc. of the National Academy of Sciences of
the United States of America, 101(Suppl 1):5228.
HaCohen-Kerner, Y., Gross, Z., Masa, A., 2005.
Automatic extraction and learning of keyphrases from
scientific articles. In Proc. of CICLing (pp. 657-669).
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
HaCohen-Kerner, Y., Stern, I., Korkus, D., Fredj, E.,
2007. Automatic machine learning of keyphrase
extraction from short html documents written in
Hebrew. Cybernetics and Systems: An International
Journal, 38(1), 1-21.
Hall, D., Jurafsky, D., Manning, C. D., 2008. Studying the
history of ideas using topic models. In Proc. of
EMNLP.
Mann, G. S., Mimno. D., McCallum, A., 2006.
Bibliometric impact measures leveraging topic
analysis. In Proc. of the 6
th
ACM/IEEE-CS joint
conference on Digital libraries. ACM, 2006. p. 65-74.
Omodei, E., Guo, Y., Cointet, J. P., Poibeau, T., 2014A.
Social and semantic diversity: Socio-semantic
representation of a scientific corpus. EACL 2014, 71.
Omodei, E., Cointet, J-P., Poibeau, T., 2014B. Mapping
the natural language processing domain: experiments
using the ACL anthology. LREC 2014, the Ninth
International Conference on Language Resources and
Evaluation, May 2014, Reykjavik, Iceland. ELRA, pp.
2972-2979.
Radev, D., Abu-Jbara, A., 2012. Rediscovering ACL
discoveries through the lens of ACL anthology
network citing sentences. In Proc. of the ACL-2012
Special Workshop on Rediscovering 50 Years of
Discoveries (pp. 1-12). Association for Computational
Linguistics.
KDIR 2016 - 8th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
382

Reiplinger, M., Schäfer, U., Wolska, M., 2012. Extracting
glossary sentences from scholarly articles: A
comparative evaluation of pattern bootstrapping and
deep analysis. In Proceedings of the ACL-2012
Special Workshop on Rediscovering 50 Years of
Discoveries (pp. 55-65). Association for Computatio-
nal Linguistics.
Sim, Y., Smith, N. A., Smith, D. A., 2012. Discovering
factions in the computational linguistics community.
In Proc. of the ACL-2012 Special Workshop on
Rediscovering 50 Years of Discoveries (pp. 22-32).
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Development of Domains and Keyphrases along Years
383
