
A Study on the Public Construction Project Cost-Saving Practice
Information Provision Service Method
Hyun Ok and Tae-Hak Kim
Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology, Goyang-si, Republic of Korea
Keywords: CODIL(COnstruction technology Digital LIbrary), CPIPS(Construction Project Information Portal System),
Design Value Engineering, Cost-Saving Practices, Public Construction Projects.
Abstract: Cost saving in construction projects consists in building structures with the most economical method while
satisfying the user requirements with regard to the features and quality. Cost saving through systematic cost
management is required to improve the competitiveness in line with the changing construction environment.
Organizations affiliated with the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport are striving to save on
construction costs by reviewing the economic efficiency of their designs, process management, and project
management when implementing public construction projects. They are sharing the design value engineering
(VE) results information among the public ordering agencies during the design stage, but the sharing of the
cost-saving practices in the construction stage is still insufficient. This study presented step-by-step
information systems development and service methods so that people can refer to and utilize cost-saving
practices in similar construction projects while carrying out public construction projects. The results of this
study are expected to contribute to more rational decision-making in and the higher investment efficiency of
public construction projects through the analysis and provision of cost-saving cases information for each stage
of the construction project life cycle, such as the planning, design, construction, and maintenance stages.
1 INTRODUCTION
It is difficult to estimate the profit and loss of
construction projects compared to the projects in
other fields or industries because there is a high
degree of uncertainty in the contract execution
process. Therefore, the cost of the whole process of a
construction project must be managed economically
within the specified budget through cost management
[1]. Cost saving consists in building structures with
the most economical method while satisfying the user
requirements with regard to the features and quality.
Cost saving through systematic cost management is
required to improve the competitiveness in line with
the changing construction environment. The Ministry
of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport (MOLIT) and
their affiliated organizations, such as corporations
and industrial complexes, are striving to save on
construction costs by reviewing the economic
efficiency of designs in the design stage (“Design
value engineering” or “Design VE”), as well as the
process and project management during the
construction stage. At present, the design VE results
information is being shared among the public
ordering agencies during the design stage, but the
sharing of cost-saving practices in the construction
stage is still insufficient.
This study was conducted to build an information
system for sharing cost-saving practice information
during the performance of public construction
projects, and to present an information service
method for utilization in the public and private
sectors. The results of this study will contribute to the
efficient execution of public construction projects
through the reference and utilization of related
information by the MOLIT-affiliated organizations,
local governments, public ordering agencies, and
construction companies.
2 STATUS ANALYSIS
2.1 Construction Management System
Status
The cost-saving practices of public construction
projects refer to success stories that enabled cost
savings in construction projects through technical
development and project management by MOLIT and
248
Ok, H. and Kim, T-H.
A Study on the Public Construction Project Cost-Saving Practice Information Provision Service Method.
DOI: 10.5220/0006083202480253
In Proceedings of the 8th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2016) - Volume 3: KMIS, pages 248-253
ISBN: 978-989-758-203-5
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

its affiliated organizations, local governments, public
ordering agencies, and construction companies [2].
MOLIT requires a review of the design VE during the
basic and working design stages for public
construction projects with a minimum total project
cost of 10 billion won, in accordance with the
"Enforcement Guideline for the Review of the
Economic Efficiency of Designs, Etc." Furthermore,
the results of the design VE are registered and
managed through the Design VE Madang in the
Construction Project Information Portal System, and
the design VE information is shared among the
MOLIT-affiliated organizations, local governments,
public ordering agencies, and construction-related
organizations. The design VE information is limited,
however, because it contains only the ideas and
improvements in the basic and working design stages
as well as summarized information regarding cost-
saving practices. The MOLIT-affiliated
organizations, such as corporations and industrial
complexes, are sharing information by publishing
their collections of cost-saving practices in the
planning, design, and construction stages. The
regional construction and management offices,
however, which are affiliated with MOLIT, are not
yet publishing or sharing their cost-saving practices.
2.2 Investigation and Analysis of the
Current Research Trends
The studies on the cost-saving practices of
construction projects have been mostly about the
application cases of design VE and the improvement
of the construction and engineering methods. Other
studies include those on the cost management and
saving methods for unit constructions as well as on
the construction types, cost-saving methods through
schedule management, and analysis of the factors
influencing the construction cost.
The analysis of the current research trends
revealed that there have been few studies on the cost-
saving practice information sharing and service
methods for improving the efficiency of public
construction projects. Therefore, research on
information sharing and service is required for the
integrated and systematic management and utilization
of cost-saving practices in the execution of public
construction projects in the future.
2.3 Analysis of Cases of FMMS-based
Bridge Inspection and Analysis
FMMS’s inspection and diagnosis menu consists of
planning in line with the above workflow,
management of the inspection history, inquiry about
the damage photos by member and about the maps of
damages by visual inspection, internal approval, and
confirmation of the inspection book. Fig. 1 shows
cases of the history of inspection and diagnosis.
3 INFORMATION SYSTEM
DEVELOPMENT AND
SERVICE METHODS
In this study, to develop a cost-saving practice
information system for construction projects, the
design changes, design standards, and operation
process revisions were analyzed based on the
"Collection of Expressway Design Work Practices"
published by Korea Expressway Corporation.
Furthermore, a database (DB) of cost-saving practices
and original data such as project outlines, status,
problems, improvements, and conclusions with
regard to construction cost-saving practices was
constructed through the preparation of metadata [2].
The construction project cost-saving practice DB
was designed to consist of four major types of
information: “cost-saving practices”, “cost-saving
practice application details”, “cost-saving practice
utilization plans”, and “cost-saving practice common
codes”. The cost-saving practice information includes
the general status information of construction
projects, including the project outlines. The cost-
saving practice application details consist in the
processing status and the results of requests for cost-
saving practices in public ordering agencies and
construction companies. The cost-saving practice
utilization plans allow the entry of a detailed
utilization plan to view or download cost-saving
practice information or attached files. The cost-saving
practice common codes define classification names,
classification types, and codes according to the
integrated construction information classification
system to improve the search and view convenience.
In this study, a step-by-step information system
development method was prepared for the utilization
and integrated management of cost-saving practice
information in the future by MOLIT and the regional
construction and management offices.
First, the construction project cost-saving practice
information system was set up in such a way that it
can be serviced from CODIL (Construction
Technology Digital Library), which corresponds to a
unit system of the Construction Project Information
System, one of MOLIT’s operation systems. CODIL
is easily accessible by the MOLIT-affiliated
A Study on the Public Construction Project Cost-Saving Practice Information Provision Service Method
249
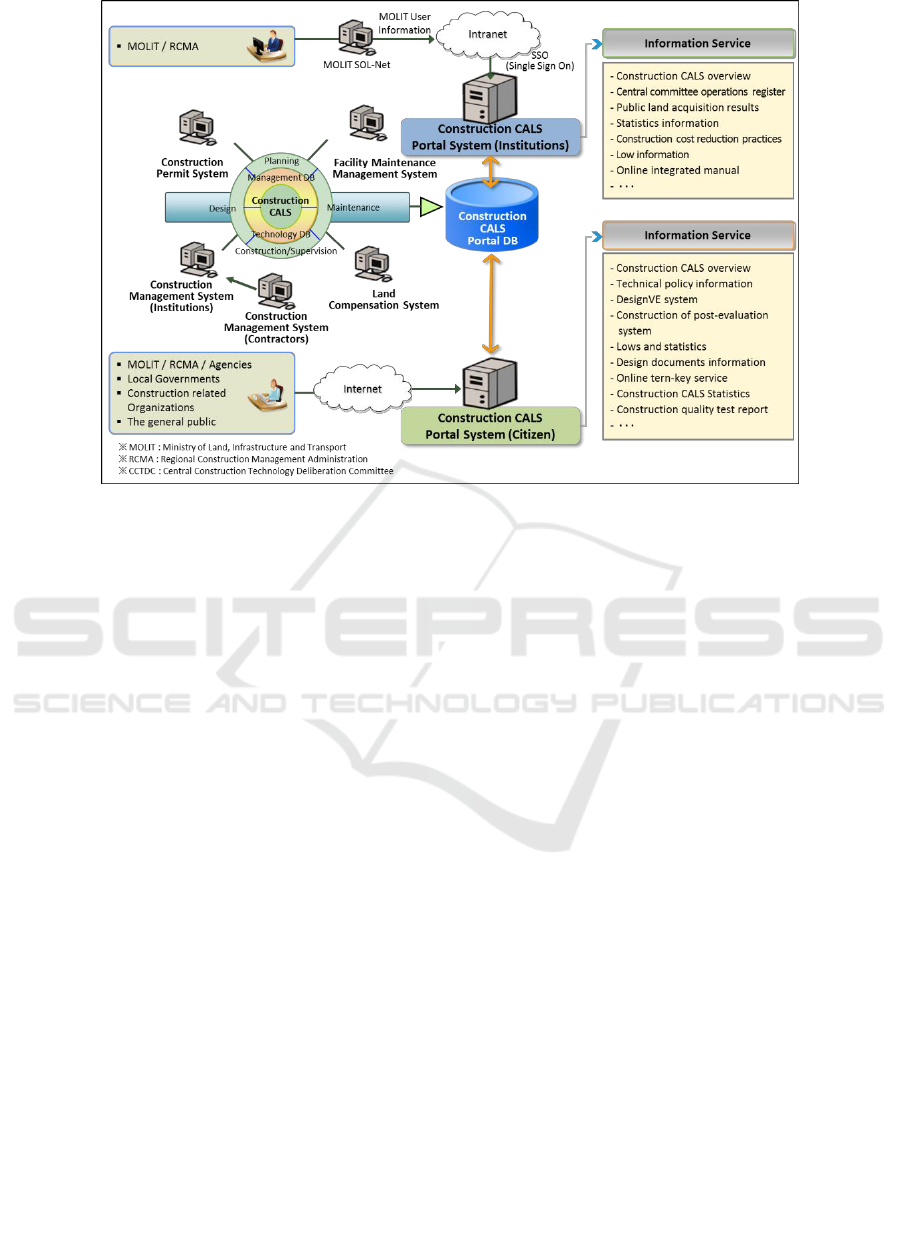
Figure 1: Concept diagram of the CPIPS (Construction Project Information Portal System).
organizations, local governments, public ordering
agencies, and construction companies because it is
located on the Internet. When MOLIT and the
regional construction and management offices,
however, which are on the organization network
(internal network), want to view cost-saving
practices, they must change from the organization
network to the Internet before logging on to CODIL,
which is inconvenient.
To address this problem, an upgrade plan was first
established for the development of the cost-saving
practices view feature on the Construction Project
Information Portal System (for agencies/public) and
for service provision in connection with CODIL, and
for later enabling integrated management through the
development of management features for cost-saving
practices in the future.
The construction project information portal
system is a gateway to the construction project
information system. It works as a single-access
window and performs public services by integrating
the information from each construction project
information unit system and their operating
environments. The system enables the sharing of
diverse construction information. The figure below is
a concept diagram of the said system. The
construction project information portal system
consists of the agency portal system, which is used by
the MOLIT headquarters and subagencies, such as
five regional construction and management
administrations, and the public portal system, which
is used by the MOLIT subagencies, other
departments, municipalities, construction companies,
and the general public. The agency portal system has
10 major functions, including the operation of the
central committee, and the public portal system has
10 major functions, including the post-evaluation of
construction projects, design VE square, online
turnkey square, design drawing information square,
and cost reduction cases of construction projects. For
the development of the view feature for construction
project cost-saving practices, a DB of cost-saving
practices will be developed and managed in CODIL
before developing OpenAPI. Next, for the public
portal system, a metadata collection feature for cost-
saving practices will be developed for linking with
CODIL. Lastly, information linking with the public
portal system will be developed so that the MOLIT
users can access the agency portal system to search
and view cost-saving practices [3]. The following
figure shows a conceptual diagram for the
development of a cost-saving practices view feature
[4].
Next, the development of cost-saving practice
management features is identical to the development
of the cost-saving practices view feature, but first, a
public portal system-CODIL cost-saving practices
synchronization process must be developed. Next, the
cost-saving practices search, view, entry, and
modification features through the agency portal
system will be developed for the MOLIT users.
KMIS 2016 - 8th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
250
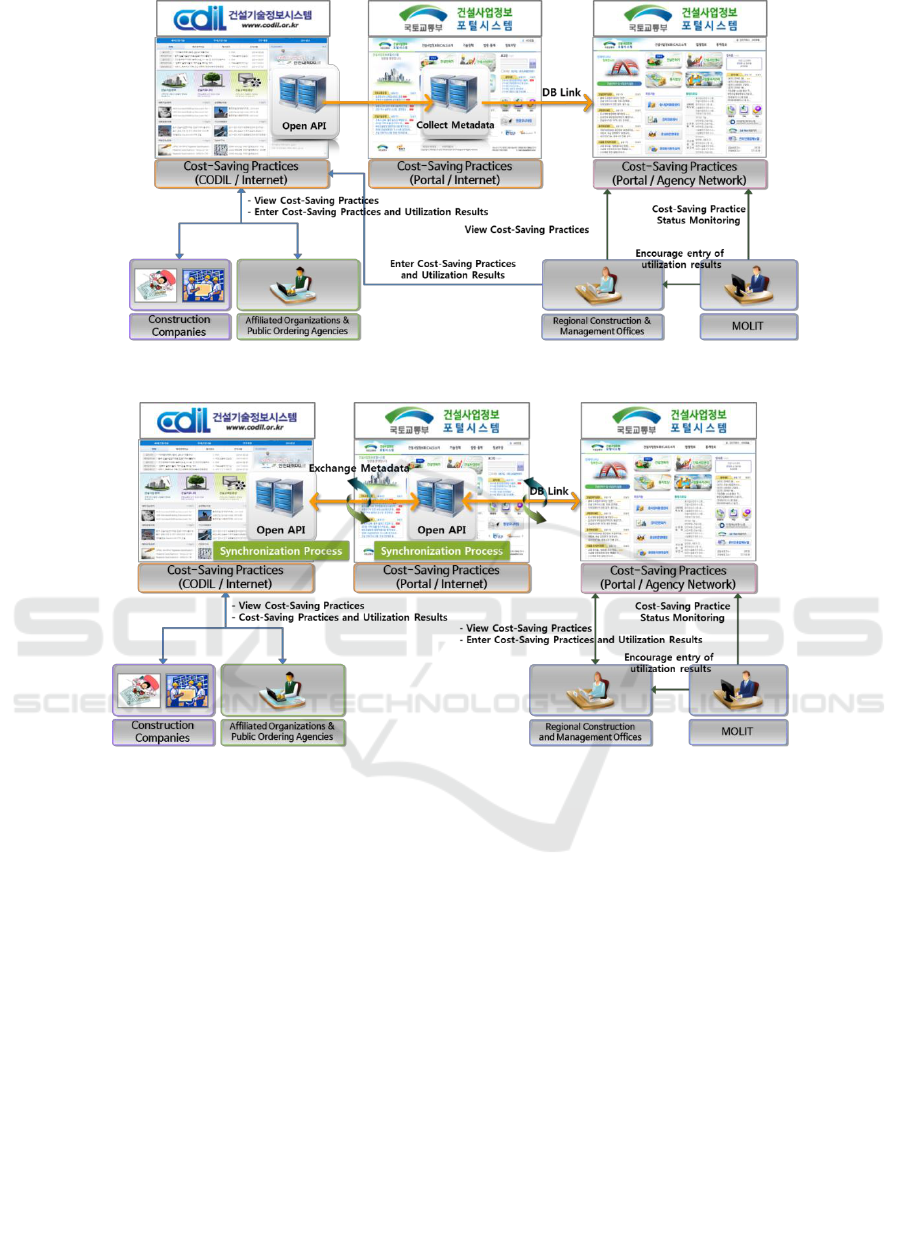
Figure 2: Development of a view feature for construction project cost-saving practices.
Figure 3: Development of construction project cost-saving practice management features.
Furthermore, the downloading feature for the
attached files regarding cost-saving practices will be
developed in such a way that the downloading of such
files will be allowed only after a utilization plan is
entered [3]. The following figure shows a conceptual
diagram of the development plan for the cost-saving
practice management features.
A cost-saving practice icon was added to the initial
screen of the Construction Project Information Portal
System for agencies so that it can be used to view the
same information as the cost-saving practices entered
in CODIL [4].
The initial screen of the agency portal system was
developed in such a way that selecting the
construction project cost-saving practice icon on the
initial screen will show the list of cost-saving
practices, and selecting an item in this list will allow
the user to download the details of and the attached
files regarding the selected cost-saving practice [4].
The MOLIT-affiliated organizations, local
governments, public ordering agencies, and
construction-related organizations such as associa-
tions should maintain a cooperation system for the
continuous expansion of the cost-saving practice DB
for public construction projects in the future.
Furthermore, the services must be increased and the
features must be upgraded so that construction sites
and workers can frequently refer to the cost-saving
practice DB [2]. In particular, such issues as double
management of data and synchronization between
CODIL and the Construction Project Information
Portal System could arise due to the development of
the construction project cost-saving practice
management features. Therefore, the integrated
information service of the construction project cost-
saving practices requires the preparation of system
upgrade plans considering the efficient management
of the computing resources.
A Study on the Public Construction Project Cost-Saving Practice Information Provision Service Method
251
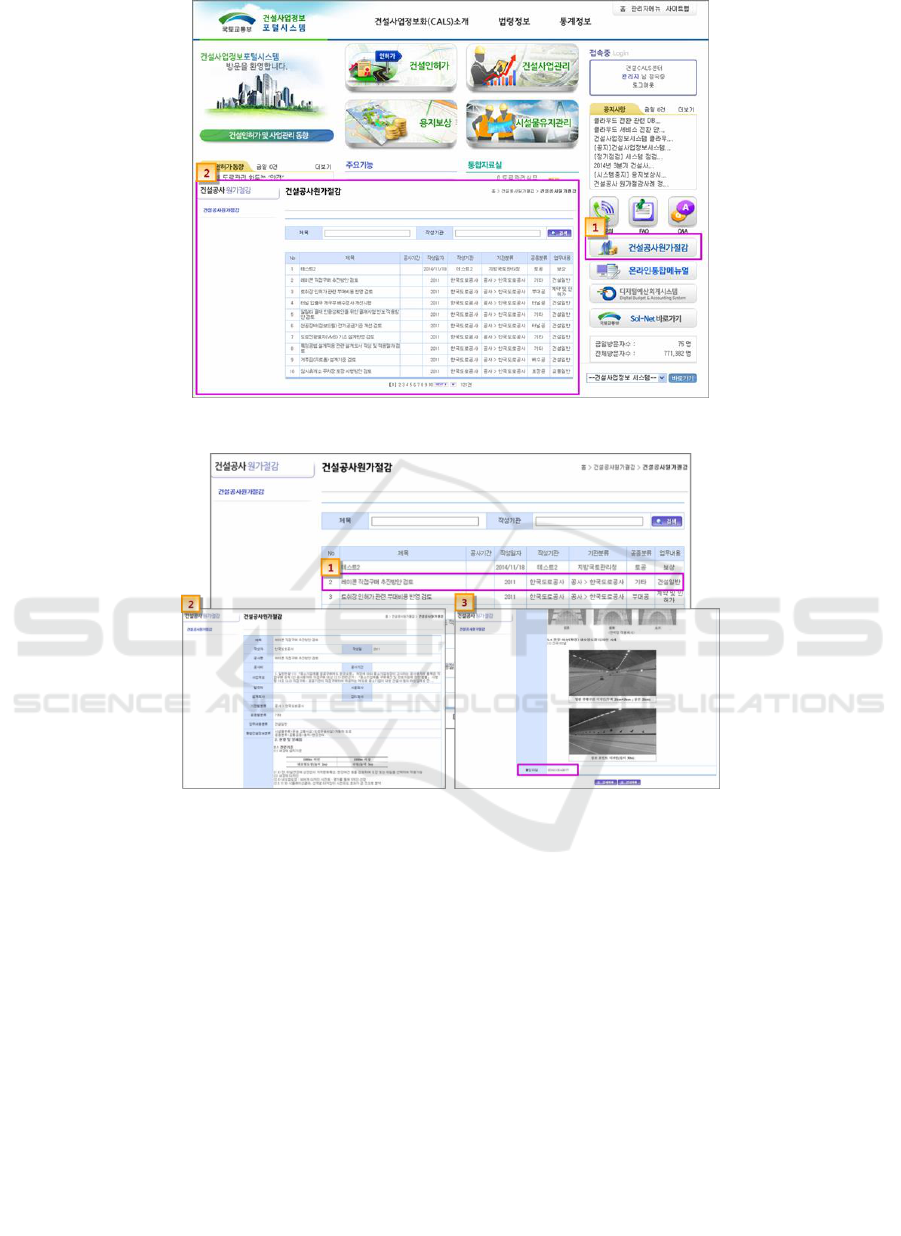
Figure 4: Initial screen of the construction project cost-saving practice portal system for agencies.
Figure 5: Detailed screen of the construction project cost-saving practice portal system for agencies.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This study aimed to improve the efficiency of
construction project execution through the sharing
and propagation of cost-saving practice information
among public ordering agencies, such as the
organizations affiliated with the Ministry of Land,
Infrastructure, and Transport (MOLIT), by building a
database (DB) and providing information services
based on the cost-saving practices of the affiliated
organizations, such as Korea Expressway
Corporation, for public construction projects. For this
purpose, step-by-step information development and
cost-saving practice information service methods
were presented so that cost-saving practices can be
referred to and utilized for similar public construction
projects.
The analysis and provision service of cost-saving
practice information by life cycle stage of public
construction projects, such as the planning, design,
construction, and management stages, are expected to
contribute to more rational decision-making in, and
the higher investment efficiency of, public constru-
ction projects in the future.
REFERENCES
H. P. Woo, “A study of cost management and reduction
strategy in construction work [master’s thesis]”,
University of ULSAN, pp.1-3, (2012).
KMIS 2016 - 8th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
252

Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs
(MOLIT), “15 Operation of Construction Technology
Knowledge Information Database and Service System,
final report”, Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and
Building Technology (KICT), pp.79-118, (2015).
MOLIT, “ 14 Operation and Technical Improvement of
Construction CALS System (Ⅱ) final report”, KICT,
pp.208-212, (2014).
MOLIT, “ 15 Operation and Technical Improvement of
Construction CALS System (Ⅱ) final report”, KICT,
pp.64-67, (2015).
CPIPS(Construction Project Information Portal System),
http://www.calspia.go.kr
CODIL(Construction Technology Digital Library),
http://www.codil.or.kr
A Study on the Public Construction Project Cost-Saving Practice Information Provision Service Method
253
