
Engineering a Stable Synaptogenic Extracellular Matrix
Laila Al-Alwan
1
, Markus Hellmund
2
, Rainer Haag
2
and Timothy Kennedy
1
1
Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University, 3801 Univerity Street, Montreal, Canada
2
Chemistry and Biochemistry Institute, Freie University Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Keywords: Neural Biocompatibility, Synthetic Synapse, Neural Prosthetic, Biomimetic Functionalised Surfaces,
Polymer Chemistry, Synaptogenic Protein.
Abstract: Synapses are specialized sites of asymmetric cell – cell contact that mediate information transfer between
neurons and their targets. Many proteins involved in the recruitment, organization and maintenance of
synapses have been identified. Surprisingly, synaptic differentiation does not require a biological membrane
surface. Instead, synaptic specializations can form quickly at sites of neurite adhesion to microspheres
(beads) coated with synaptogenic proteins or even poly-lysine, a synthetic cationic polypeptide, raising the
possibility that functional hemi-synaptic connections could be formed onto designer engineered surfaces.
Previous studies examining the stability of synapses formed in brain onto poly-lysine coated beads found
they were unstable, degraded, and ultimately replaced by a glial scar. Here, we address the capacity of an
extreme biomimetic of poly-lysine, PGB50, a dendritic polyglycerol (dPG)-amine soft matter nanoparticle,
to enhance synapse formation in long-term cultures of rat cortical neurons. Microbeads coated with PGB50
exhibit substantially enhanced synaptogenesis and synapse stability compared to poly-lysine. We propose
that synaptogenic extracellular matrices could be used to engineer synaptogenic electrodes with enhanced
neural-compatibility, reducing glial scaring and inflammation, and allowing for bi-directional
communication with neurons through the formation of stable of synaptic specializations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Deficits due to neurodegeneration or injury-induced
brain diseases are, ultimately, a direct reflection of
the loss of functional synapses. Synapses are
specialized sites of asymmetric cell – cell contact
that mediate information transfer between neurons
and their targets. Many proteins involved in the
recruitment, organization, and maintenance of
synapses have been identified and the molecular
biology of synaptic adhesion is increasingly well
understood. Furthermore, neural activity can now be
read out to activate muscles or control the movement
of robotic limbs (Hochberg et al., 2012; van den
Brand et al., 2012). In spite of these advances,
contemporary microelectrodes, made of metal or
glass, present fundamentally invasive surfaces that
neural cells isolate by enclosing in a glial scar.
Synaptic specializations can assemble rapidly
following axon – dendrite contact. Surprisingly, the
formation of an active pre-synaptic terminal does not
require a biological post-synaptic membrane surface.
Instead, pre-synaptic specializations can form
quickly at sites of axonal adhesion to microspheres
(beads) coated with specific lipids or proteins,
including the synthetic poly-cationic polypeptide
poly-lysine (PLL) (Burry, 1982; Lucido et al., 2009;
Gopalakrishnan et al., 2010; Goldman et al., 2013;
Suarez et al., 2013).
PLL is a naturally occurring polymer that is
susceptible to degradation by several common
secreted proteases, including trypsin and cathepsins.
Consistent with this, presynaptic specializations
formed onto PLL coated beads in vivo were not
stable but completely degraded within two weeks,
replaced by an astrocytic glial scar that isolated the
bead (Burry, 1983, 1985). PDL, a protein
biomimetic enantiomer of PLL, was developed to
resist protease degradation, and thereby enhance its
utility as a cell culture substrate. Here, using long-
term cultures of embryonic rat cortical neurons we
address the capacity of an extreme biomimetic of
PLL, PGB50, an ~75 kDa dendritic polyglycerol
(dPG)-amine soft matter nanoparticle based on a
highly stable and biocompatible polyglycerol
scaffold (Hellmund et al., 2015), to enhance synapse
formation.
We propose that synaptogenic extracellular
matrices may be engineered to enhance biocompati-
Al-Alwan, L., Hellmund, M., Haag, R. and Kennedy, T.
Engineering a Stable Synaptogenic Extracellular Matrix.
In Extended Abstracts (NEUROTECHNIX 2016), pages 11-13
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
11
bility and promote the stable formation of synaptic
specializations onto manufactured surfaces in vivo.
Our goal is to engineer synaptogenic electrodes with
enhanced neural-compatibility that reduce glial
scaring and inflammation, and allow for bi-
directional communication with neurons.
2 METHODS
Cell cultures were prepared from cerebral cortex of
embryonic day 17–18 (E17–E18). Cells were plated
at high density (∼40,000 cells/cm
2
) and maintained
for 14-25 days in vitro (DIV) in Neurobasal medium
containing 1% B27, 2 mM glutamax and 0.5% N2.
Microspheres (7.3 μm polystyrene; Bangs Beads)
were washed 3× in PBS (sterile, pH 7.4) before use,
then incubated overnight with (50 μg/ml) PLL, PDL
and PGB50. Beads were then washed in PBS,
pelleted by centrifugation, 7 min at 6500 rpm, and
resuspended in culture medium before addition to
cultures. Control beads were treated similarly,
without coating. Beads were added to cultures at 11
DIV and maintained for an additional 3, 7 or 14 days
of incubation (DOI). All images were captured using
an Olympus FV1000 confocal microscope. At least
60 Beads were quantified per condition using
ImageJ. Corrected total cell fluorescence intensity
(CTCF) was calculated for both bead and neurite as:
Integrated Density - (Area of selected cell X Mean
fluorescence of background), and fold changes in
CTCF of bead/neurite plotted. Data are mean ±
SEM, Two-way ANOVA followed by a post hoc test
was used to calculate p values.
3 RESULTS
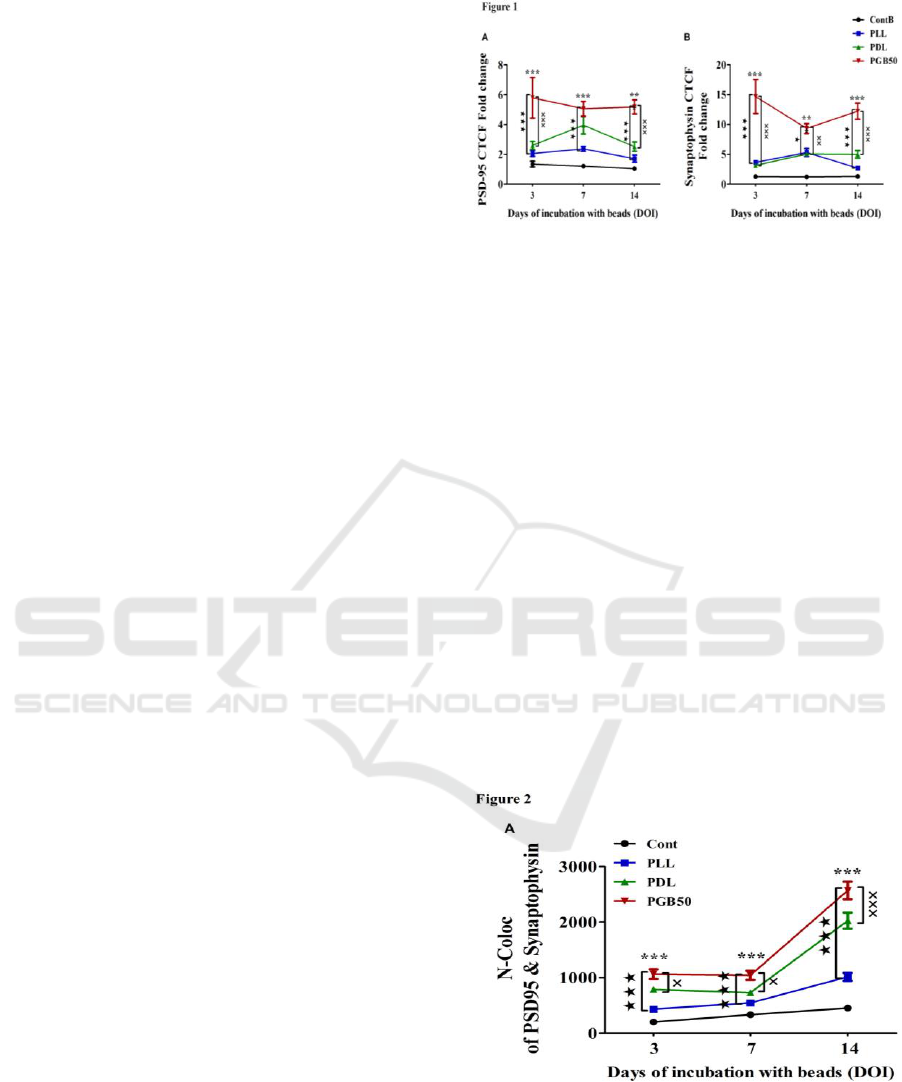
3.1 PGB50 Enhances Synapse
Formation
Using long-term cultures of embryonic rat cortical
neurons, we tested and compared the efficacy of
beads coated with PLL, PDL or PGB50 to induce
synapse formation and promote synapse stability.
Immunoreactive CTCF for synaptophysin and PSD-
95, marking pre- and post-synaptic specializations,
was significantly enhanced for PGB50-coated beads
when compared to Control, PLL- and PDL-coated
beads (Figures 1A and 1B). These results reveal
more effective induction of long-term stable
synaptic specializations by PGB-50 compared to
either PLL or PDL.
Figure 1: PGB50 Enhances Synapse Formation.
Quantification of corrected total cell fluorescence intensity
(CTCF) of A. The post-synaptic marker; PSD-95 and B.
The pre-synaptic marker; Synaptophysin. Neuronal
cultures were incubated with control, PLL-, PDL- or
PGB50-coated beads for 3, 7 and 14 days of incubation
(DOI). ***p < 0.001 vs. control, p < 0.05, p <
0.001 vs. PLL, xx p < 0.01, xxx p < 0.001 vs. PDL.
3.2 PGB50 Enhances Synaptic
Specialization
The formation of synaptic specializations, with a
post-synaptic bouton localized adjacent to its pre-
synaptic counterpart, is essential for synapse
formation, maturation and function. To test whether
PGB50, PLL and PDL promote local synapse
formation, we quantified the overlap of presynaptic
synaptophysin with postsynaptic PSD-95, within a
3D volume around the beads (voxels).
The overlap of PSD-95 and synaptophysin was
enhanced by all coatings compared to control beads
(Figure 2). PGB50-coated beads exhibited signify-
cantly higher numbers of voxels positive for both
Figure 2: PGB50 Enhances Synaptic Specialization.
Quantification of number of co-labeled voxels (N-Coloc)
of the post-synaptic marker; PSD-95 and the pre-synaptic
marker; Synaptophysin. Neuronal cultures were incubated
with control, PLL-, PDL- or PGB50- coated beads for 3, 7
and 14 days of incubation (DOI). ***p < 0.001 vs. control,
p < 0.001 vs. PLL, x p < 0.05, xxx p < 0.001 vs.
PDL.
NEUROTECHNIX 2016 - 4th International Congress on Neurotechnology, Electronics and Informatics
12

PSD-95 and synaptophysin at all time points
examined. These results suggest a greater capacity
of PGB50 compared to PLL and PDL to initiate and
support the local formation of synapses.
4 DISCUSSION
Studies carried out in the 1980s, addressing the
function of synaptogenic poly-cationic polymers,
found that simple beads coated with PLL had the
capacity to direct the formation of presynaptic
specializations in vitro and in vivo, but the synapses
formed did not persist, and within a few days in vivo
were displaced by an astrocytic scar (Burry, 1983,
1985). Although these findings supported the idea
that non-neuronal surfaces, when decorated with the
“correct” chemical signals could induce the forma-
tion of synaptic specializations, the short lifetime of
the synapses formed was fundamentally problematic
for translational applications. Here, we provide evi-
dence for enhanced synapse formation and stability
induced by the dendritic polyglycerol PGB50, a
highly stable non-protein molecular biomimic of
poly-lysine.
Our ongoing studies aim to enhance the function
and stability of synapses formed onto modified
synaptogenic surfaces in vivo, and develop
approaches to stimulate and record from these
surfaces. We aim to promote the formation of
adhesive contacts by axons and dendrites that will be
inherently more stable and better positioned to
record neuronal activity than is currently possible
using conventional electrodes. Our findings suggest
that the hemi-synaptic specializations formed onto
the dendritic polyglycerol surface will in turn induce
synapse formation by adjacent axons and dendrites,
resulting in the development of a dense local web of
synaptic connections surrounding the electrode.
Ultimately such an implant would achieve functional
integration into the neuronal network. We envision
that such implanted synaptogenic interfaces would
be broadly applicable to extend the function of the
injured or diseased human nervous system.
REFERENCES
Burry RW (1982) Development of apparent presynaptic
elements formed in response to polylysine coated
surfaces. Brain research 247:1-16.
Burry RW (1983) Postnatal rat neurons form apparent
presynaptic elements on polylysine-coated beads in
vivo. Brain research 278:236-239.
Burry RW (1985) Protein synthesis requirement for the
formation of synaptic elements. Brain research
344:109-119.
Goldman JS, Ashour MA, Magdesian MH, Tritsch NX,
Harris SN, Christofi N, Chemali R, Stern YE,
Thompson-Steckel G, Gris P, Glasgow SD, Grutter P,
Bouchard JF, Ruthazer ES, Stellwagen D, Kennedy
TE (2013) Netrin-1 promotes excitatory synapto-
genesis between cortical neurons by initiating synapse
assembly. The Journal of neuroscience : the official
journal of the Society for Neuroscience 33:17278-
17289.
Gopalakrishnan G, Thostrup P, Rouiller I, Lucido AL,
Belkaid W, Colman DR, Lennox RB (2010) Lipid
bilayer membrane-triggered presynaptic vesicle
assembly. ACS chemical neuroscience 1:86-94.
Hellmund M, Achazi K, Neumann F, Thota BN, Ma N,
Haag R (2015) Systematic adjustment of charge
densities and size of polyglycerol amines reduces
cytotoxic effects and enhances cellular uptake.
Biomaterials science 3:1459-1465.
Hochberg LR, Bacher D, Jarosiewicz B, Masse NY,
Simeral JD, Vogel J, Haddadin S, Liu J, Cash SS, van
der Smagt P, Donoghue JP (2012) Reach and grasp by
people with tetraplegia using a neurally controlled
robotic arm. Nature 485:372-375.
Lucido AL, Suarez Sanchez F, Thostrup P, Kwiatkowski
AV, Leal-Ortiz S, Gopalakrishnan G, Liazoghli D,
Belkaid W, Lennox RB, Grutter P, Garner CC,
Colman DR (2009) Rapid assembly of functional
presynaptic boutons triggered by adhesive contacts.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of
the Society for Neuroscience 29:12449-12466.
Suarez F, Thostrup P, Colman D, Grutter P (2013)
Dynamics of presynaptic protein recruitment induced
by local presentation of artificial adhesive contacts.
Developmental neurobiology 73:98-106.
van den Brand R, Heutschi J, Barraud Q, DiGiovanna J,
Bartholdi K, Huerlimann M, Friedli L, Vollenweider I,
Moraud EM, Duis S, Dominici N, Micera S, Musienko
P, Courtine G (2012) Restoring voluntary control of
locomotion after paralyzing spinal cord injury. Science
336:1182-1185.
Engineering a Stable Synaptogenic Extracellular Matrix
13
