
R
isk Management of Information Technology Outsourcing based on
Cobit
ChunMei Wang
Linyi University School of Automation and Electrical Engineering,276000,China
Keywords: COBIT standard; information technology outsourcing; risk management.
Abstract: At present, more and more enterprises outsource their information technology, which causes various risks.
The first part of this paper is the brief introduction of COBIT, second part is the detailed analysis of
COBIT-based outsourcing related risks of information technology, and the final part is a series of risk
management measures related to the risks. This paper is expected to provide some information and advices
to the relevant enterprises.
1 INTRODUCTION
At this stage, in this context of the rapid
development of the market economy, the
development of enterprises’ information technology
faces more stringent requirements. In this
environment, information technology outsourcing
has gradually developed. However, enterprises’
mode of information technology outsourcing has
both advantages and disadvantages for the
development of the enterprise itself, on the one hand
it could meet the needs of information technology
very well, but on the other hand it also brings the
risks to enterprises’ business operation. To make full
use of the maximum value of information
technology outsourcing, IT project management
must be reasonably used (Qianglin Z,2010).
Strengthening risk management of information
technology outsourcing based on COBIT, could
effectively control the risks, promote the application
of information technology, so as to promote the
successful implementation of the outsourcing
projects, and ensure the normal operation of
enterprises, what's more which is beneficial to the
progress and development of the whole social
information technology (Kun H,2010).
2 COBIT OVERVIEW
ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control
Association) represents the information systems
audit and Control Association in the United States,
COBIT (Control Objectives Information and Related
Technology) refers that, based on the control target
system before, according to currant relevant
international standards and industry standards,
control objectives system established by optimizing
them, which is the world's most authoritative, most
advanced information technology management
standard (Dejian W,2007). COBIT is applied to the
audit staff’s information technology outsourcing
control work, and which could provide a certain
reference. According to the information system
cycle, COBIT can be divided into four areas of
planning and organization, acquisition and
implementation, delivery and support, monitoring
and evaluation, as shown in figure 1 (Lei H 2013).
362
362
Wang C.
Risk Management of Information Technology Outsourcing based on Cobit.
DOI: 10.5220/0006450503620366
In ISME 2016 - Information Science and Management Engineering IV (ISME 2016), pages 362-366
ISBN: 978-989-758-208-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
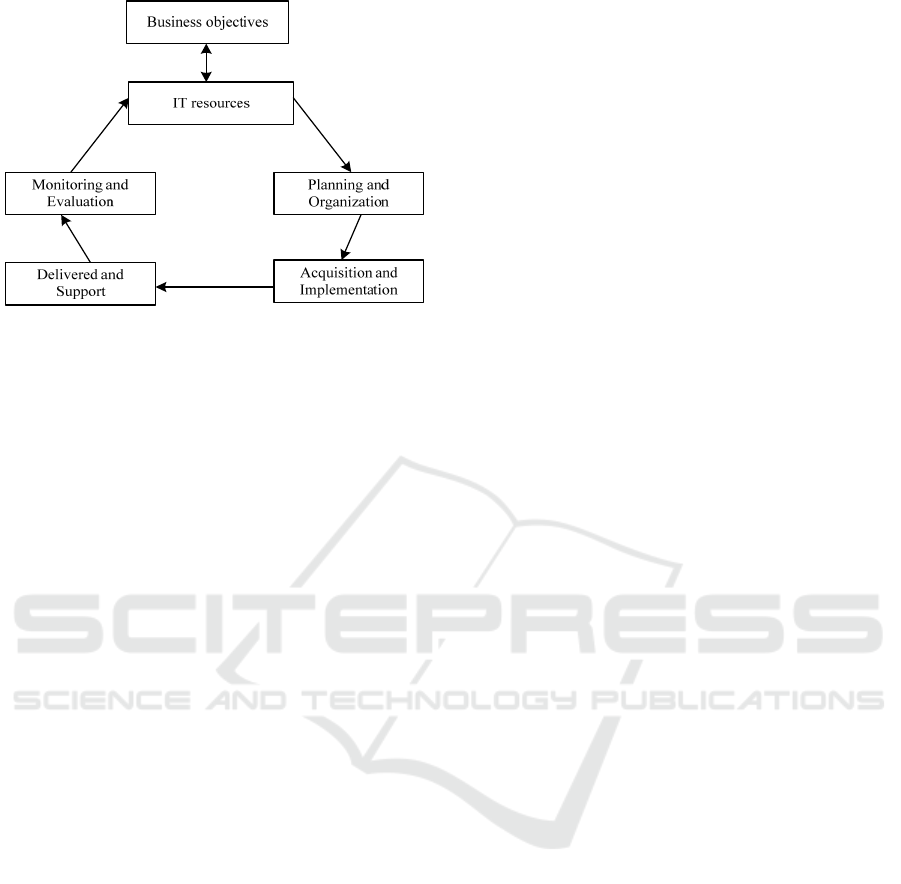
Figure 1: Overall framework of COBIT
First, the part of planning and organization
involves the enterprises’ strategies and tactics,
mainly focuses on searching for how IT making the
best contributive channel for completing business
tasks. Second, acquisition and implementation, in
order to complete the IT strategy of the enterprise, it
is needed to identify, purchase and implement the IT
solution of the supplier and at the same time
integrate the solution into the business of the
enterprise organically. In addition, this area also
involves the situation of maintaining and changing
of current system used, so as to ensure the continuity
of this solution and meet the requirements of the
business objectives (Zongbin Y,2013). Third,
delivery and support, the focus of this area is the
actual delivery situation of the service needed,
which contains user support services, security and
continuity management, etc. Fourth, the part of
monitoring and evaluation represents that enterprises
need to do regular assessment for the quality and
control degree of the IT process. In this field,
internal supervision and performance management,
legalization and standardization will be mainly
explained (Juan L,2012).
3 RISKS OF INFORMATION
TECHNOLOGY
OUTSOURCING
In the level of enterprise management, information
technology outsourcing service refers to the strategic
use of enterprises’ external resources: it is kind of
management mode that users effectively integrate
and use the enterprises’ external ideal IT specialized
resources, so as to promote the cost reduction, work
efficiency and the core competitiveness of
enterprises. In essence, the information technology
outsourcing service mainly refers to a model that for
achieving a goal the user (outsourcing subject)
outsources its original all, part, or planned
information technology service to professional
companies by signing the contract and to service
under the operation of specialized companies and
personnel (Hanmi L,2010).
The main reasons for enterprises’ outsourcing: 1.
cost, adopting information technology outsourcing,
can greatly reduce the non-core business, and then
achieve the costs reduction of enterprises’ operation.
2. Technology, technical outsourcing could cleverly
use supplier's technical strength to meet their own
information technology needs. 3. Core competence,
outsourcing non-core business of the enterprise can
promote the development of core business. 4.
Business process, outsourcing can promote the
process design optimization of enterprises’ business,
information, and management (Xiaowen L,2009).
3.1 Risks of planning and organization
First, the risks caused by blind outsourcing. The
enterprise does not carry out scientific analysis on
outsourcing, does not fully understood the specific
scope and necessity of outsourcing, and does know
its own business objectives and positioning
systematically, in this case the information
technology outsourcing will have certain risks.
Second, the risk of information positioning, the
enterprise should reasonably evaluate its own
informationization degree, so as to fully grasp its
own information technology needs, should not
blindly seek and apply the latest information
technology, if ultimately its development status
could not adapt to the information technology, in
turn it will affect the improvement of enterprise’s
work efficiency. Third, the risks caused by
outsourcing cooperation mode and content. We all
know that the companies are very different, which
makes the outsourcing process particular and
complex, and there are obvious differences in terms
of security and confidentiality, process supervision,
division of rights and responsibilities.
3.2 Risks in acquisition and
implementation
First, risks in choosing the outsourcing service
providers. Supplier plays a key role in outsourcing,
and we must pay attention to the choice for suppliers
to ensure that the supplier has high qualification and
advanced technology. Enterprises should carry out
Risk Management of Information Technology Outsourcing based on Cobit
363
Risk Management of Information Technology Outsourcing based on Cobit
363

reasonable and objective evaluation for outsourcing
service providers, and fully understand the level of
its information technology, corporate reputation,
specific financial situation and enterprise culture.
Third, the risks caused by lack of restraint
mechanism. In the process of signing the
outsourcing contract, if the supplier does not give
clear and obvious regulations and restrictions for the
standard of service, fault reaction time, it will cause
certain risks to enterprise’s own economic interests
and initiative (Shizhong A,2011).
3.3 Risk in delivery and support
In this part, if the service fitting in with the actual
demand is the first risk. If in the process of the
project execution, outsourcing service providers
could not ensure to provide information technology
services meeting the enterprise’s needs, when the
project begins to run, it is bound to face the hidden
risks. Second, risks caused by outsourcing ideas. By
information technology outsourcing, the flexibility
and control force for its own information technology
of enterprises decrease significantly. The
implementation of outsourcing requires the
cooperation between enterprises and outsourcing
service providers, if the enterprise is too dependent
on outsourcing service providers, it is bound to bring
some risks for their own normal management
(Xufeng L,2014).
3.4 Risks in monitoring and assessment
When the information technology outsourcing
delivery is complete, although there is the signed
outsourcing contract, the enterprise can use the
relevant provisions of the contract to stringently
constrain the outsourcing service providers, but if
the completion effect of the project is successful, if
the outsourcing supplier can complete the intended
target, enterprises need to evaluate the project in
every stage, stringently monitor the specific effect of
project implementation. The monitoring and
evaluation method can encourage enterprises to use
their own initiatives to effectively avoid the project
out of control and reduce the economic losses of
enterprises.
4 MANAGEMENT MEASURES
FOR OUTSOURCING RISKS
4.1 Risk management in planning and
organization
System planning activity is the first step of the
process of information technology outsourcing, this
part relates to enterprises’ strategic target, technical
indicators study and internal policies and
regulations; original construction mode and
construction target; information organization,
personnel management and function structure;
benefit research and implementation plan of
information technology outsourcing. The scientific
planning of the project has very important impact on
the construction of outsourcing projects.
The overall goal of the whole information
system is to enhance the work efficiency, promote
the comprehensive service and coordination function
of the enterprise, and promote the optimization of
the core business process of the enterprise. The
corresponding planning needs to meet the following
requirements: first, the planning should be simple
and accurate to ensure vast majority of enterprises
staff could understand and recognize. Planning
needs to be fully licensed by the leading group;
planning objectives should be measurable; planning
should be drawn up based on the full investigation of
internal and external information (Guoyan L,2015).
4.2 Risk management in acquisition
and implementation
System analysis is the deep analysis for the
enterprise’s internal management and information
processing situation based on the comprehensive,
systematic research. System analysis involves
complex data, business, personnel, information, and
the workload of specific implementation is huge. At
the same time in the actual work, the enterprise’s
informatization cannot be confirmed by one time,
and it keeps changing; in addition, the information
technology contractors do not know the specific
business of every department, and there are always
deviations in understanding in the actual work, thus
the modeling errors. So, the system analysis needs to
fully meet the requirements of validity, integrity,
unity, reality and so on. Then, based on the system
analysis, enterprise should repeatedly discuss and
analyze the specific operability of the outsourcing
program provided by the contractor, and then
determine the corresponding technical standards and
specific implementation rules.
ISME 2016 - Information Science and Management Engineering IV
364
ISME 2016 - International Conference on Information System and Management Engineering
364

4.3 Risk management in service and
support
The demand of the enterprise is not immutable and
frozen, the business objectives change along with its
own development, the contractors need to carry out
the efficient data tracking, meet the needs of
enterprises as far as possible in the premise of
ensuring feasibility, timely improve and optimize the
related issues in the development plan. First,
tracking the level of outsourcing services, the
business organizations of the enterprise sign relevant
agreements with outsourcing service providers, thus
to ensure that enterprise and service provider to
maintain consistency in business needs, priorities
and other aspects. The service level agreement
relates to the specific expectations of the business
organization for the system, in detail, the agreement
makes clear provisions on the service level
reporting, service level measurement, the cost and
other performance levels. Signing operation level
agreement with suppliers is to ensure that each
organization can obtain the most advanced
technology, so as to better meet the needs of the
service level. Enterprises need to organize regular
inspection activities to check the accuracy of the
service level agreement, so as to ensure the relevant
contents could effectively adapt to changes of
demand. Second, the continuous management for
outsourcing services, developing IT continuity plans
to prevent business disruptions due to system crash.
The plan needs to involve every key function of the
system, as well as the recovery priority of each
function, recovery methods and damage tolerance.
Information technology corresponds to kinds of
contract content and methods, such as the
development of information system, completion of
system delivery, the enterprise should be able to
independently ensure the orderly operation of the
system, etc. But if it comes to some special
industries, such as the financial sector, once the
system is in trouble, and even if only a very short
period of time, it still will cause incalculable
damage.
4.4 Risk management in supervision
and evaluation
After the implementation of information technology
outsourcing project, the security and availability of
the system has to be ensured, the information related
to the system is the valuable resource in the process
of enterprise’s operation. The internal audit is the
audit agency of information system built by the
enterprise in its interior, internal auditors can strictly
inspect and evaluate the security and stability of
electronic information system, and timely report the
final evaluation results to the management of the
enterprise. Internal audit institution of information
system is independent from every functional
department of the enterprise. The establishment of
COBIT-based management and audit model of
information system could help people to better
analyze and understand the information system, play
an important guidance role in building relevant
mechanism for people, and place all of the
construction of information system and application
in a certain control range. It can help the investment
and management staff of information system to
achieve the balance of investment and risk in
unpredictable conditions. By the management
control and audit, etc. it could provide effective
security and service activities for staff using
information systems. As for the auditor, it could
provide strong help and support on the audit trail, so
that the identification of the audit staff could be
more persuasive.
5 CONCLUDING REMARKS
In summary, we have known that, in the background
of current rapid development of information
technology, the demand of enterprise for information
technology continues to increase, in order to better
carry out various business work, enterprises could
choose to outsource the information technology,
which could not only effectively meet the
enterprises’ constantly updated needs for
information technology, but also reduce their own
business workload, so that it can focus more on the
core business activities. We deeply analyzed the
risks of COBIT-based information technology
outsourcing, and finally put forward the risk
management measures for specific risk, which are
expected to effectively meet the needs of enterprise
for information technology, and promote the further
development of the enterprise.
REFERENCES
Qianglin Z., Liping S., Risk management Information of
technology outsourcing based on COBIT. Technology
and Innovation Management. (5)572-575, 2010
Kun H., Risk management of whole life cycle of
information technology outsourcing project. Social
Science. (12) 44-49,2010
Risk Management of Information Technology Outsourcing based on Cobit
365
Risk Management of Information Technology Outsourcing based on Cobit
365

Dejian W., The application of COBIT standard in risk
management of IT outsourcing business. Market
Modernization. (32) 75-76,2007
Lei H., Risk management of enterprise’s information
technology outsourcing project. Spacecraft
Environment Engineering. (4)446-451,2013
Zongbin Y., Haixia L., Analysis on the risk management
strategy of bank information technology outsourcing.
Digital Technology and Application, 9(21-22),2013
Juan L., Research on risk of information technology
outsourcing based on the life cycle. Enterprise guides
print, (14) 199-199,2012
Hanmi L., Yan Q., Research on risk management of
information technology outsourcing based on the
suppliers' perspective. Journal of Commercial
Economics, (9) 92-94,2010
Xiaowen L., Kejin H., Research on management
framework of enterprise IT outsourcing relationship,
Journal of Intelligence. 28 (3) 113-116,2009
Shizhong A., Yonghui S., Yan X., Analysis of influencing
factors of IT outsourcing knowledge transfer--
empirical research based on relationship quality,
Studies in Science of Science, (8)1216-1222,2011
Xufeng L., Shizhong A., Empirical study on the
influencing factors of enterprise performance in IT
outsourcing, Chinese Journal of Management Science,
22 (2) 142-148,2014
Guoyan L., Heqing Z., Performance Analysis of Hybrid
Cooperation in Asymmetric Fading Channels, Journal
of Communications, 10(1)9-15, 2015.
ISME 2016 - Information Science and Management Engineering IV
366
ISME 2016 - International Conference on Information System and Management Engineering
366
