
A Hierarchical Magnification Approach for Enhancing the Insight in
Data Visualizations
Stavros Papadopoulos, Anastasios Drosou and Dimitrios Tzovaras
Information Technologies Institute, Centre for Research and Technology Hellas, Thessaloniki, Greece
Keywords:
Data Visualization, Hierarchical, Magnification.
Abstract:
Non-linear deformations are useful for applications where users face highly cluttered visual displays, either
due to large datasets, or visualizations on small screens, or a combination of both, that increases the density
of the data and makes the perception of patterns difficult. Non-linear deformations have been used to magnify
significant/cluttered regions in data visualization, for the purpose of reducing clutter and enhancing the per-
ception of patterns. General deformation methods (e.g. logarithmic scaling and fish-eye views) suffer from
several drawbacks, since they do not consider the prominent features that must be preserved in the visualiza-
tion. This work introduces a hierarchical approach for non-linear deformation that aims to reduce visual clutter
by magnifying significant regions, and lead to enhanced visualizations of two/three-dimensional datasets on
highly cluttered displays. The proposed approach utilizes an energy function, which aims to determine the
optimal deformation for every local region in the data, taking the information from multiple single-layer sig-
nificance maps into account. The problem is subsequently transformed into an optimization problem for the
minimization of the energy function under specific spatial constraints. The proposed hierarchical approach
for the generation of the significance map, surpasses current methods, and manages to efficiently identify
significant regions and achieve better results.
1 INTRODUCTION
According to Rosenholtz et al.(Rosenholtz et al.,
2005) clutter is defined as the state at which excess
items, or their representation or organization, leads to
a degradation of performance at some task. Visual
clutter(Ellis and Dix, 2007) can mislead users into de-
riving wrong conclusions, and increase the decision
confidence on erroneous decisions. It can be caused
when large data volumes are visualized on small dis-
play devices, which reduce the visualization space
and its information capacity.
Non-linear deformations have been used to mag-
nify highly cluttered regions, and thus, reduce the
total cluttering in visualizations (Ellis and Dix,
2007)(Wu et al., 2013)(Tao et al., 2014). The
most commonly used functions for non-linear trans-
formations and clutter reduction are the logarithmic
and square root mappings(Maciejewski et al., 2013),
which do not take into account the content of the vi-
sualizations. According to Ellis et al. (Ellis and Dix,
2007), other popular methods for clutter reduction in-
clude: sampling/filtering, changing the opacity of the
visual objects, and dimensional reordering. This work
focuses, only on non-linear transformations for clutter
reduction, since they can be used to create a general
approach that can be applied on multiple types of data
visualizations.
Towards reducing visual clutter on the visualiza-
tions, this work proposes a hierarchical magnification
approach for non-linear deformation. Building upon
the current state-of-the art, the proposed method en-
hances significant regions of the data based on an un-
derling significance map. It can be considered as a
focus+context technique, in which the focus points
are calculated automatically, based on their underly-
ing significance. The proposed approach distributes
the distortion of the input data to regions of low sig-
nificance, while significant neighboring regions are
uniformly magnified. In other words, although the de-
formation of all the cells in the grid is non-uniform,
small neighborhoods of significant regions that have
similar significance values, are magnified by a simi-
lar amount, i.e. uniformly. This procedure results in
a deformation of the visualizations that reduces the
visual clutter, and enhances the analytics potential of
the visualizations.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Sec-
Papadopoulos S., Drosou A. and Tzovaras D.
A Hierarchical Magnification Approach for Enhancing the Insight in Data Visualizations.
DOI: 10.5220/0006073400290039
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2017), pages 29-39
ISBN: 978-989-758-228-8
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
29

tion 2 presents the related work on visualization de-
formation. The proposed magnification approach is
presented in Section 3. Section 4 illustrates the appli-
cation of the Magnification approach onto different
types of visualizations, as well as its comparison with
existing approaches. Finally, the paper concludes in
Section 5.
2 RELATED WORK
Over the last decade, many researchers have focused
their efforts on reducing visual clutter(Ellis and Dix,
2007) and capturing important properties of the data,
for extracting meaningful information. In this di-
rection several techniques dealing with clutter have
been proposed, like non-linear deformation, adjust-
ment of sampling ratios (Bertini and Santucci, 2006),
etc. Still, spatial deformation has been identified as
one of the most popular antagonists for clutter reduc-
tion (Ellis and Dix, 2007). Thereby, the positions of
the visual objects (e.g. a node of a graph, or a word
in context preserving word clouds) are displaced on
the display, so as to accommodate for the better visu-
alization of data patterns.
Regarding spatial deformation of the position/size
of the visual objects, Keim et al. (Keim et al., 2010)
presented the generalized scatterplots, a method to de-
form the positions of the points on the scatterplots and
reduce visual clutter. The authors also made use of
point displacement around the initial point of refer-
ence, in order to further reduce visual clutter in high
density areas. In the field of flow visualization, Tao et
al. (Tao et al., 2014) proposed the utilization of a 3D
deformation method, based on an entropy significance
map. The proposed approach magnifies regions with
high entropy in the flow visualizations, and reduces
visual clutter. Similarly, Wang et al. (Wang et al.,
2011) proposed a method for Focus+Context visual-
ization of volumetric data based on 3D grid deforma-
tion. The authors utilized a significance map in or-
der to magnify important regions at the expense of re-
ducing the size of less significant regions. The previ-
ous methods were only adjusted for specific visualiza-
tions, and they did not take the human perception for
clutter reduction into consideration. Based on these
limitations, Wu et al. (Wu et al., 2013) presented a
general visualization resizing framework, in order to
scale every visualization approach on small displays.
The authors utilized a clutter and a degree of interest
map in order to generate a 2-dimensional significance
map. The positions of the data objects (i.e. scatterplot
point positions, graph layout, and word positions on a
context preserving word cloud) are distorted in order
to allow for the visualization of significant visualiza-
tion areas on small screen sizes. The limitations of
the aforementioned approaches, are that they utilize
significance maps created taking only one grid layer
with a specific resolution into account, and thus, they
lose important information. The introduction of the
hierarchical significance map in this work is able to
more efficiently identify significant regions, and pro-
vides better results.
The aforementioned methods deal only with
the spatial visual variables, which refer to the
size/position/shape of the visual objects. Very few
approaches have been proposed for non-spatial visual
variables, such as the color. For example, Thompson
et al. (Thompson et al., 2013) proposed a method for
color mapping that takes the input data distribution
into account. The authors produced palettes utiliz-
ing perceptual color distance, in order to emphasize
prominent values in the data. They also introduced
two different color mappings, one for the visual detec-
tion of large differences in data values, and one for the
visual detection of similar values, so that small differ-
ences can be detected. Eisemann et al. (Eisemann
et al., 2011) proposed the use of a simple projection
technique based on angular interpolation, in order to
distort the dataset before mapping its values to col-
ors. The user of the visualization can select the de-
sired distortion factor. Maciejewski et al. (Maciejew-
ski et al., 2013) utilized Box-Cox transformations for
transforming the distribution data, as close to a nor-
mal distribution as possible, before applying a color
scheme for choropleth maps. Unlike previous meth-
ods, the approach proposed in this paper is applied on
both spatial and non-spatial visual variables.
Towards the direction of reducing visual clutter,
this paper presents an extension of the previous works
on deformation, using Focus+Context techniques. In
particular, the current paper extends the work of Wu
et al. (Wu et al., 2013), via the introduction of a hi-
erarchical approach for the generation of the signif-
icance map. The latter manages to retrieve informa-
tion from multiple levels (i.e. layers) of abstraction
of increasing granularity, and facilitates, thus, a sig-
nificantly more efficient detection of, a more accurate
focusing on and a more effective preservation of sig-
nificant patterns or objects. The proposed approach
results in less distortion of significant objects, when
compared to previous methods, leading to better re-
sults. Additionally, unlike previous approaches, the
magnification method is applied on both spatial and
non-spatial visual variables.
IVAPP 2017 - International Conference on Information Visualization Theory and Applications
30

3 MAGNIFICATION APPROACH
An overview of the proposed visualization magnifica-
tion approach is presented in Figure 1. Taking into ac-
count the input dataset, the first step is the generation
of the hierarchical significance map, which defines re-
gions of the input space that are important and need
to be magnified. Independent of the type of the input
data that can be either N-dimensional points, or word
clouds, multiple grid resolutions are defined, while a
significance map is generated for each such resolu-
tion. The significance maps are afterwards combined
for the generation of the hierarchical significance map
that includes both small and large significant regions,
or in other words includes both small and large data
patterns.
The second step is the generation of the multi-
resolution grid, which assigns a larger number of
hyperrectangles in the regions of the input space
with high significance. The hyperrectangles are N-
dimensional representations of rectangles. Each hy-
perrectangle represents a cell in the grid. In the case
of 2 dimensions each cell is a rectangle, and in 3 di-
mensions each cell is a rectangular cuboid. The ad-
vantage of the multi-resolution grid, when compared
to the uniform grid, is that it results in better local
pattern preservation in the deformed space. Further-
more, the optimization space (number of variables) of
the multi-resolution grid is much smaller when com-
pared to the uniform grid, and thus, the optimization
procedure is much faster.
Afterwards, the grid deformation energy is de-
fined, based on the significance of each hyperrectan-
gle. This energy term allows significant hyperrectan-
gles to be more magnified, in order to enhance the pat-
terns that exist in them. The optimization procedure
minimizes the grid deformation energy and enhances
significant regions of the input data space. The core
idea of the optimization approach is to assign to each
hyperrectangle a size that corresponds to its underling
significance, while keeping their distortion to a mini-
mum.
3.1 Generation of the Hierarchical
Significance Map
The hierarchical significance map takes multiple grid
resolutions into account, and is able to efficiently
identify significant regions. This hierarchical proce-
dure has been used before in the literature for the gen-
eration of saliency maps on images (Itti et al., 1998)
and meshes (Jia et al., 2014). The advantage of this
hierarchical definition over the single-layer approach,
is that it captures both large and small patterns, since
low resolution grids might lose small patterns but can
capture large patterns, while the opposite stands true
for high resolution grids.
For the creation of the hierarchical significance
map, a hierarchy of layers is generated. Each layer
covers the input space with different grid resolutions.
The significance map is calculated and normalized for
each layer separately. Afterwards, the significance
maps of each individual layer are superpositioned for
the generation of the hierarchical significance map
which will be used for the deformation procedure.
For the generation of the hierarchical significance
map, the grid of each layer of the hierarchy must be
defined. Each one/two/three-dimensional grid G =
(V, E, F) is comprised of a set of vertices V , a set
of edges E and a set of hyperrectangles F, where
V =
v
T
0
, v
T
1
, ....., v
T
end
, and v
i
∈ R
N
is the vertex po-
sition in the N-dimensional space. The vertices and
edges partition the input space into a grid comprised
of hyperrectangles of the same size. The reason why
the hyperrectangles have the same size is that in each
layer, the grid is uniform, i.e. each dimension is
equally partitioned. An example of equal hyperrect-
angle size is provided in Figure 2(a).
Each hyperrectangle f
i
∈ F is comprised of a set
of edges E( f
i
) ⊂ E and vertices V ( f
i
) ⊂V . The total
number of hyperrectangles is
N
∏
i=1
n
i
, where n
i
is the
number of partitions per dimension. Each partition in
a dimension is a line segment, equal in size with all
the other partitions in the same dimension.
Let G
l
= (V
l
, E
l
, F
l
) denote the grid in layer l with
n
l
partitions per dimension. Each grid G
l
has n
l
= 2
l
partitions per dimension, e.g. the grid of layer 1, G
1
has n
1
= 2 partitions per dimension. The value of l
is within l ∈ [1, .., M], where M is the maximum level
allowed, and depends on the maximum resolution al-
lowed by the multi-resolution grid defined in Section
3.2.
The first step towards the generation of the hierar-
chical significance map is the definition of a single-
layer high resolution significance map in the input
data space. There are multiple choices for the selec-
tion of the appropriate single-layer significance map.
In the context of this work, the experimental results
were created and compared using both entropy(Cover
and Thomas, 2012) and saliency maps (Wu et al.,
2013)(Wang et al., 2008). Afterwards, the calcula-
tion of the significance value for each hyperrectangle
is defined as the average significance value of the re-
gion covered by it, while the significance map of layer
l is defined as S
l
. The significance value of each hy-
perrectangle f
l
i
is denoted as s
l
i
∈ S
l
. The second step
is the normalization of significance maps of each in-
A Hierarchical Magnification Approach for Enhancing the Insight in Data Visualizations
31

Figure 1: Method overview: The first step is the generation of hierarchical significance map. Afterwards the multi-resolution
grid is generated and the optimization is applied onto this grid based on the hierarchical significance map in order to identify
its optimal deformation. The result is a deformed visualization space which enhances cluttered areas on the display. An HR
copy of this Figure can be found in the following link http://www.iti.gr/
∼
drosou/HierarchicalMagnification/Fig1.jpg.
dividual layer, for the subsequent superposition of the
maps. The operator ℵ(.) defined in (Itti et al., 1998)
is utilized so as to normalize each significance map.
The same normalization operator ℵ(.) has also
been used in other research works (e.g. (Jia et al.,
2014) and (Lee et al., 2005)), and has as a result the
promotion of significance maps, which are comprised
of a small number of high significance values, while
efficiently suppressing significance maps with a large
number of similar values.
The final hierarchical significance map is created
for the resolution of the last layer of the grid hier-
archy G
M
. To achieve this, let us denote as Q
f
l
i
,
where l is the level of the hierarchy and f
l
i
∈ F
l
is a
specific hyperrectangle belonging to layer l, as the set
of hyperrectangles from all the layers of the hierar-
chy, so that they intersect with the N-dimensional hy-
perrectangle f
l
i
. In the specific case of this paper that
n
l
= 2
l
partitions per dimension are considered, if two
hyperrectangles intersect, it means that one contains
the other. The same stands true for every n
l
= r
l
for
r ∈ N
>1
. In the same notion Q
s
f
l
i
is the set of sig-
nificance values of all the hyperrectangles belonging
to Q
f
l
i
. The superpositioning of the different maps
is performed on layer M and the final hierarchical sig-
nificance map, denoted as S
hier
, is calculated for each
hyperrectangle in layer M. Let s
h
i
be the final hierar-
chical significance value of hyperrectangle f
M
i
∈ F
M
.
The calculation of s
h
i
is described in Eq.(1)
s
hier
i
=
∑
s
l
j
∈Q
s
(
f
M
i
)
ℵ
s
l
j
(1)
Finally, the hierarchical significance map is de-
fined as S
hier
=
S
s
hier
i
.
3.2 Multi-resolution Grid
The multi-resolution grid is a non-uniform grid on the
N-dimensional space, in which the distribution of hy-
perrectangles is not uniform, but instead distributes
more hyperrectangles in regions with high signifi-
cance. The advantage of the multi-resolution grid is
that regions with high significance are less distorted
when magnified, since they have higher resolution.
In addition the optimization space of the vertex po-
sitions of the grid is much smaller when compared to
the full resolution grid, and thus, has better speed per-
formances and also produces better results (as shown
in Section 4.1).
The algorithm for the creation of the multi-
resolution grid is similar to the one used for the cre-
ation of a quad tree. The algorithm takes as input a
specific user-defined significance threshold. In the
context of this work this threshold is set to a value that
results in the reduction of the number of optimization
variables by 20% to 50%, depending on the appli-
cation. This algorithm has as a result, that the sig-
nificance value of each hyperrectangle is the largest
possible value, which is smaller than the provided
threshold (i.e. the infimum). The multi-resolution
grid is denoted as G
mul
(V
mul
, E
mul
, F
mul
), where F
mul
are hyperrectangles of the multi-resolution grid, V
mul
the vertices and E
mul
the edges.
The significance value s
mul
i
of each hyperrectangle
f
mul
i
∈ F
mul
in the multi-resolution grid is calculated
from the hierarchical significance map S
hier
defined in
Section 3.1. For this calculation, the values of hierar-
chical significance map S
hier
have to be mapped on the
hyperrectangles in F
mul
. As explained in Section 3.1,
the hierarchical significance map S
hier
is defined for
each hyperrectangle of the grid G
M
in the maximum
layer of the grid hierarchy layer M.
Let P( f
mul
i
) denote the set of all hyperrectan-
gles from grid G
M
, which intersect with f
mul
i
∈ F
mul
.
Additionally, let P
s
( f
mul
i
) denote the set of signifi-
cance values of all the hyperrectangles belonging to
P( f
mul
i
). The procedure of calculation of the signifi-
cance value of each hyperrectangle f
mul
i
∈ F
mul
in the
multi-resolution grid G
mul
is defined in Eq.(2).
IVAPP 2017 - International Conference on Information Visualization Theory and Applications
32

s
mul
i
=
∑
∀s
hier
j
∈P
s
(
f
mul
i
)
s
hier
j
(2)
The significance map of the multi-resolution grid
G
mul
is defined as S
mul
=
S
s
mul
i
. The algorithm for
the computation of the multi-resolution grid can be
found in the following link http://www.iti.gr/
∼
drosou/
HierarchicalMagnification/multiResGrid.png.
3.3 Grid Deformation Procedure
This section follows the work presented in (Wang
et al., 2008) and (Wu et al., 2013), regarding the grid
deformation procedure. The deformation procedure
presented here has been firstly proposed by (Wang
et al., 2008) for image resizing. The same proce-
dure has afterwards been utilized by (Wu et al., 2013)
for resizing data visualizations. More details can be
found in (Wang et al., 2008) and (Wu et al., 2013).
The purpose of grid deformation is to enlarge sig-
nificant regions of the input space, and visualize any
patterns that were previously hidden due to high clut-
tering. The deformation method takes as input a grid
G = (V, E, F) and its significance map S, where V
the matrix of vertices, E matrix of edges, and F the
matrix of hyperrectangles. These matrices have spe-
cific relationships between them, i.e. F = QV and
E = HV , where Q and H are also matrices which de-
pend on the grid. The result of deformation is a new
grid G
0
=
V
0
, E
0
, F
0
, created by changing the posi-
tions of the vertices in V , according to the given sig-
nificance map.
According to (Wang et al., 2008) and (Wu et al.,
2013), the ideal deformation of each v
i
∈V into a new
position should be defined as v
0
i
= c ∗v
i
, where c is the
scale factor. This equation refers to the uniform scal-
ing case, and requires an extension of the area covered
by the data in the input space. In the case that the area
covered by the data in the input space is considered
static, then the enlargement is not possible. One of
the alternatives proposed in the literature (see Section
2) is to introduce a non-linear deformation of each hy-
perrectangle, so that more space is given to more sig-
nificant hyperrectangles (Wang et al., 2008)(Wu et al.,
2013).
The main objective of the utilized grid defor-
mation method is to minimize the total deformation
energy, defined as the distance from the uniformly
scaled position. Let f
i
∈ F be a hyperrectangle de-
fined as f
T
i
= q
i
V , where q
i
is a 2
N
×|V | matrix (N is
the dimension) and its element in the r
th
row and c
th
column is defined as:
q
i,rc
=
1 , i f v
c
∈ f
i
, and f
i,r
= v
c
0 , else
(3)
where f
i
, r is the r
th
vertex in f
i
. Given Q =
h
q
T
0
, q
T
1
, ...., q
T
|F|
i
T
, the matrix of hyperrectangles is
defined as F = QV .
The uniformly scaled hyperrectangle is defined as
f
0
i
= c
i
f
i
, where c
i
is the desired scale matrix for the
i
t
h hyperrectangle. Let F
T
= [ f
1
, f
2
, .., f
|F|
] be a ma-
trix of all the quads, and W
F
be a |F|×|F| matrix of
the significance of each quad, while its element in the
r
th
row and c
th
column is defined as:
W
F,rc
=
√
s
r
, i f r = c
0 , else
(4)
where s
r
is the significance of hyperrectangle f
r
. Fur-
thermore, let C be the desired scale matrix C with:
C
rc
=
c
r
, i f r = c
0 , else
(5)
The total hyperrectangle deformation energy is
defined in Eq.(6)
W
F
F
0
−W
F
CF
2
=
W
F
QV
0
−W
F
CQV
2
(6)
The minimization of the total hyperrectangle de-
formation energy allows for the hyperrectangles with
large significance, to have a smaller distance from
their uniformly scaled version (which refers to the
lack of distortion for all the objects), and thus, under
the constraint of static space, significant hyperrectan-
gles are enlarged more than less significant ones.
An additional energy term that is used for the de-
formation procedure is the edge bending, as proposed
in (Wu et al., 2013) and (Wang et al., 2008).
Given an edge e
k
, its uniformly scaled version is
defined as e
0
k
= l
k
e
k
, where l
k
is a 2 ×2 scale matrix.
Let E
T
= [e
1
, e
2
, .., e
|E|
] be a matrix of all the edges,
and W
E
be a |E|×|E| matrix of the significance of
each edge, while its element in the r
th
row and c
th
column is defined as:
W
E,rc
=
√
s
r
, i f r = c
0 , else
(7)
where s
r
is the average significance factor for all the
hyperrectangles in which edge e
r
belongs. Further-
more, let L be the desired scale matrix L with:
L
rc
=
l
r
, i f r = c
0 , else
(8)
The total edge bending energy is defined as
W
E
E
0
−W
E
LE
2
=
W
E
HV
0
−W
E
LHV
2
(9)
where H is a matrix such that E = HV . The edge
bending energy term scales the edge lengths and tries
A Hierarchical Magnification Approach for Enhancing the Insight in Data Visualizations
33

to retain the edge orientations, after the grid deforma-
tion.
Finally, the optimum deformed grid is defined as
a solution to the following minimization problem:
argmin
V
0
W
F
(QV
0
−CQV )
2
+
W
E
(HV
0
−LHV )
2
(10)
subject to the following constraints:
v
0
i,d
= min[d] , i f v
0
i,d
is on the lower
boundary o f dimention d
v
0
i,d
= max[d] , i f v
0
i,d
is on the upper
boundary o f dimention d
where v
0
i,d
is the coordinate of vertex v
i
∈V in the d
th
dimension, and min [d] and max[d] are the lower and
upper boundaries of the d
th
dimension as defined by
the input dataset. After the minimization of the to-
tal deformation energy D defined in Eq.(10), the new
grid G
0
=
V
0
, E, F
is found, where V
0
=
S
i
v
0
i
. The
dataset is deformed to this new grid G
0
, taking the
initial grid into account G and utilizing linear interpo-
lation in the one/two/three-dimensional space.
At this point it should be mentioned that that the
proposed method illustrates the objects (e.g. graphs,
wordclouds, etc.) to be magnified, via the processing
of their corresponding significancies at certain time-
instances. In this context, a direct comparison be-
tween different time-instances, would be rather prone
to inconsistencies. Moreover, the reader should note
that the deformation grid depicted in most of the fig-
ures, is used for demonstration purposes, while it
would be meaningful in illustration cases where a
comparison to the original shape of the magnified ob-
ject is wanted.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
This section presents the application of the Magnifica-
tion approach to the following different visualization
approaches: 1) Word clouds, 2) Scatterplots, and 3)
Choropleth maps.
4.1 Evaluation Metrics
4.1.1 Pattern Preservation
The Pattern Preservation (PP) evaluation metric cap-
tures the degree in which the local regions in the mag-
nified space preserve the patterns that existed in the
input space. This metric is based on graph match-
ing on the kNN (k-Nearest Neighbors) graphs be-
tween the input and magnified spaces (example of
this metric is presented in (Hautam
¨
aki et al., 2008)).
Graph representations of the input data, and subse-
quent graph matching, have been used in the liter-
ature for the comparison of 3D objects and point
clouds (e.g. (Hilaga et al., 2001)(Tung and Schmitt,
2005)(Mademlis et al., 2008)), as well as for speaker
identity recognition (e.g. (Hautam
¨
aki et al., 2008)).
A large change in the number of neighbors for each
data instance represents a large change of the ini-
tial pattern due to the magnification procedure. The
graph matching distance is found using the graph edit
distance(Gao et al., 2010) between the labeled kNN
graphs of the input and magnified spaces.
4.1.2 Size Perception
The Size Perception (SP) evaluation metric attempts
to quantify the humans’ visual perception of different
sizes of objects. Equivalently with most of the human
senses, the human perception of an external stimuli is
not linearly proportional to the intensity of the stim-
uli. For instance, acousticians say that doubling of the
volume (loudness) should be sensed as a level differ-
ence of +10dB.
Similarly, the SP metric captures a significant an-
alytical task, the degree in which the resizing factor
of the objects is correctly perceived in the magnified
space. In this respect, the Stevens’ Power Law (Zwis-
locki, 2009) has been utilized, according to which the
perception of the intensity of a sensory stimuli is a
power function of the actual intensity of the stimuli
(i.e. ψ(I) = kI
a
, whereby I is the intensity of the input
stimuli, ψ(I) is the subjective magnitude of the sen-
sation, a is an exponent that depends on the sensory
type of the stimulation, and k a constant). According
to Brewer et al. (Brewer, 1994) k = 0.98 and a = 0.87,
when size perception is regarded.
The proposed evaluation metric measures the ab-
solute difference of the actual input size, from the size
perceived by the visualization: SP =
∑
i
|
ψ(I
i
) −L
i
|
,
where ψ(I
i
) is the perceived size of the i
th
visual ob-
ject, and L
i
its intended size as specified from the in-
put data.
4.1.3 Jensen−Shannon divergence
The Jensen−Shannon Divergence (JSD) (Endres
and Schindelin, 2003) is used in probability the-
ory in order to measure the distance between two
one-dimensional distributions. It is based on the
Kullback−Leibler divergence(Endres and Schindelin,
IVAPP 2017 - International Conference on Information Visualization Theory and Applications
34
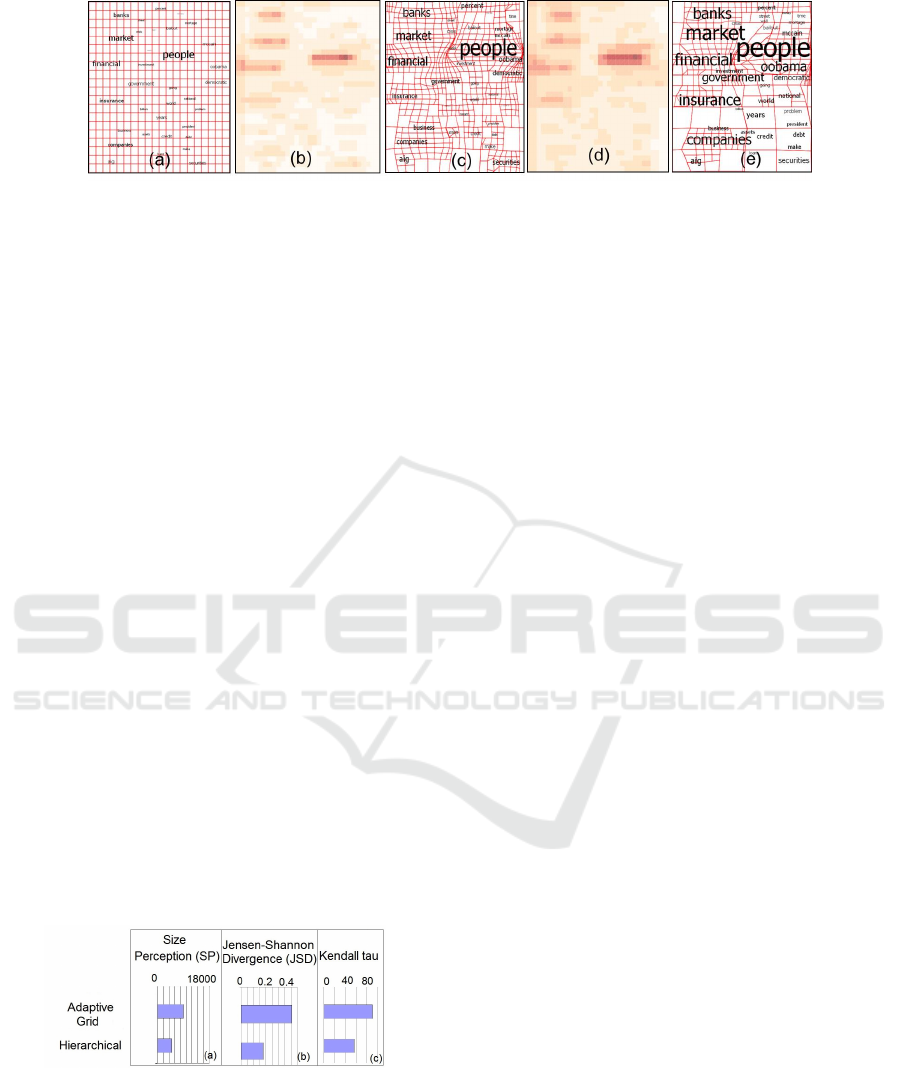
Figure 2: Results of the application of the Magnification approach on the word cloud visualization with magnification factor
equal to 4. (a) Input visualization (b) Single layer significance map proposed in (Wu et al., 2013). (c) Results obtained from
the single layer significance map (in (b)). (d) Hierarchical significance map generated from the saliency based significance
map proposed in (Wu et al., 2013). (e) Result obtained from the hierarchical significance map (in (d)). The proposed approach
in (e), takes better advantage of the empty space, and enlarges more the words of the visualization. An HR copy of this Figure
can be found in the following link http://www.iti.gr/
∼
drosou/HierarchicalMagnification/Fig2.jpg.
2003), and is a symmetric metric.
4.2 Word Clouds
In this experiment, the efficiency of the proposed
multi-resolution magnification approach is demon-
strated on the word clouds visualization.
The resizing of the word cloud in smaller screens
can cause cluttering. The most common reason for
this type of cluttering is that some words can be-
come very small to read/understand, which unavoid-
ably leads to information loss. High cluttering is
also caused by not preserving the relative sizes of the
words in the deformed space. In order to solve this is-
sue, we utilize non-linear deformation that increases
the size of the words, while also preserving the rela-
tive sizes of the words. The increase in the size of the
words is performed in such a way (through the use of
the significance map and the deformation procedure),
so as to preserve the relative sizes of the words as
much as possible, and thus, have a minimum change
in the relationship between different words. Hence,
the size of the words in the magnified space is (al-
most) proportional to the size of the words in the input
space.
Figure 3: The evaluation results using the SP (a) and JSD
(b) and Kendall tau (c) metrics applied on Figure 2(c), and
Figure 2(e) respectively. Smaller values represent better re-
sults. The hierarchical approach provides the best results in
all the metrics.
In this context, each word is considered as a vi-
sual item, which is attached on all the grid cells that
contain it. After the grid deformation, the position
of the words is adjusted by means of interpolation,
while the final word resizing is found from the as-
sociated cell deformations. In addition, in order to
avoid word overlapping, a collision avoidance algo-
rithm which can change the positions of the words in
case of collision was implemented.
In this experiment, a context-preserving word
cloud by a force-directed algorithm (Cui et al., 2010)
was used on a real dataset with 13,828 news arti-
cles spanning one year (from 2008 to 2009) that were
related to American International Group (AIG). The
context-preserving word cloud results in positioning
semantically-similar words close to each other.
Figure 2 presents the results of applying the pro-
posed Magnification approach on the aforementioned
word cloud visualization. Figure 2(a) shows the input
data. Figure 2(b) and Figure 2(d) illustrate the single
layer and hierarchical significance maps respectively,
generated using the significance map proposed in (Wu
et al., 2013) as a base. As shown in these figures, the
hierarchical significance map is smoother around sig-
nificant regions. The corresponding results of each of
these maps are shown in Figure 2(c) and Figure 2(e),
in which the first utilizes the single layer significance
map, while the latter utilizes the hierarchical signifi-
cance map. Figure 2(e) utilizes better the empty space
for the magnification of the words, and produces bet-
ter results.
Figure 3 presents the evaluation results applied
on Figure 2, using the SP and JSD evaluation met-
rics presented in Section 4.1, as well as the Kendal
tau distance metric presented in the next paragraphs.
The SP metric shows that the multi-resolution grid has
the smallest distance between the perception of the
sizes of the words, and their intented size, and thus,
it is more perceptually consistent. The JSD metric
is used to compare the normalized distribution of the
sizes of the words in the input word cloud with re-
spect to the word sizes in the deformed spaces. The
proposed approach provides the better results. A fig-
A Hierarchical Magnification Approach for Enhancing the Insight in Data Visualizations
35
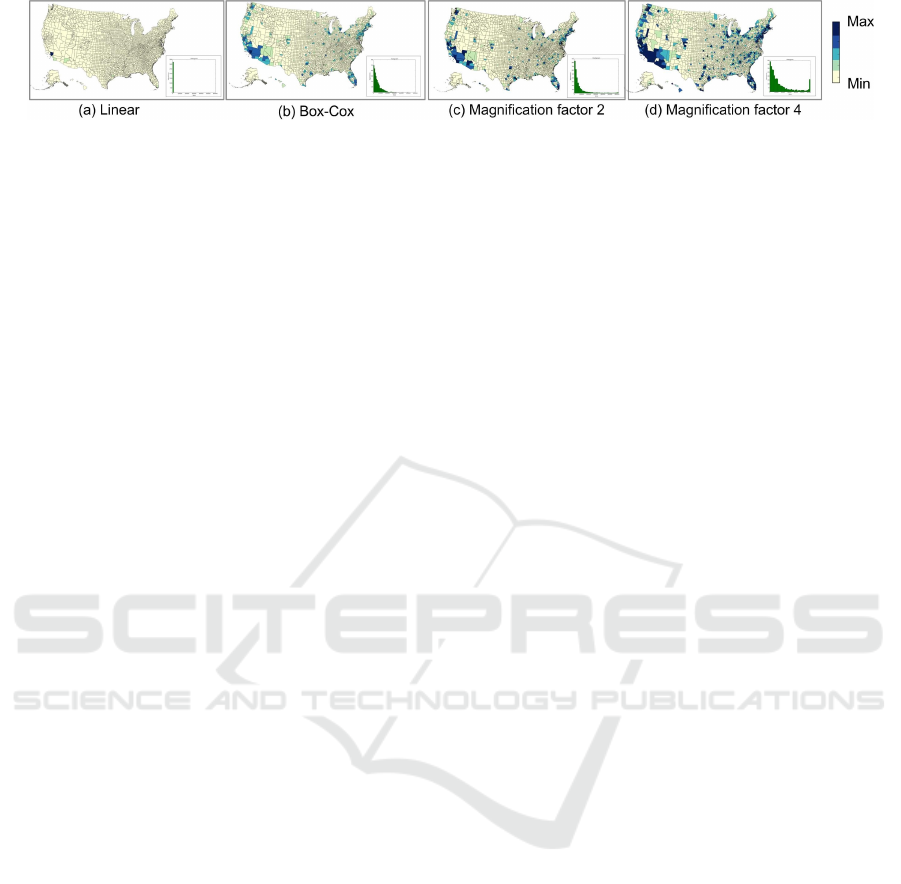
Figure 4: Results of the application of the Magnification approach on a choropleth map, visualizing the unemployment
data for each US area in 2011. The lower right part of each subfigure shows the corresponding distribution. (a) Lineal
mapping. (b) Box-Cox mapping(Maciejewski et al., 2013). (c) Magnification factor equal to 2. (d) Magnification factor
equal to 4. Although subfigure (d) loses some information regarding the high values of the dataset, it provides more color
resolution to the lower ranges of the data (where the majority of the data values lies), and thus, small differences between
the different states are better visualized and perceived. An HR copy of this Figure can be found in the following link http:
//www.iti.gr/
∼
drosou/HierarchicalMagnification/Fig4.jpg.
ure that shows the normalized distributions can be
found in the following link http://www.iti.gr/
∼
drosou/
HierarchicalMagnification/normDistr.png.
In order to measure how the relative sizes of the
words change, after the application of each defor-
mation method, we utilize the Kendall tau distance
(Fagin et al., 2003). This is a distance metric be-
tween two ordered lists. In this case the first or-
dered list is the list of sizes of the input words, and
the second is the list of words in the magnified re-
sult. Figure 3(c) shows the results of this metric.
Smaller values represent a greater preservation of
the relative ordering of the sizes in the words. The
smallest Kendall tau distance is obtained by the pro-
posed hierarchical approach. A figure that shows
how the ordered lists change for each method can be
found in the following link http://www.iti.gr/
∼
drosou/
HierarchicalMagnification/wordsOrder.png.
4.3 Scatterplots
This section presents the application of the Magnifi-
cation approach on scatterplot visualizations. Each
point in the scatterplot is attached to a specific hy-
perrectangle of the grid. After the magnification pro-
cedure, the new point positions are found by means
of interpolation on the new hyperrectangle positions.
The size of the points does not change.
For the generation of the scatterplots, the data
from INSPIRE (Wong and Thomas, 2009) is used.
These data reveal the topic distribution of IEEE Vis,
IEEE InfoVis and, IEEE VAST proceeding papers
published from 2006 to 2008.
Figure 5 presents the results of the application of
the magnification approach on the scatterplot visual-
ization of the aforementioned INSPIRE dataset. Two
types of significance maps were utilized, the entropy
and saliency(Wu et al., 2013) maps, using both one
layer and hierarchical significance definition. The hi-
erarchical significance map takes better advantage of
the empty space, and enlarges the significant areas
more, with minimum deformation of the local pattern
distribution.
The values of the PP evaluation metric applied on
Figure 5 are shown in Figure 6. Since the size of the
points in the scatterplot remains the same after the
magnification procedure, only the PP metric is used.
This figure reveals that the best results are obtained
from the hierarchical grid approach proposed in this
work, using the saliency-based significance map pro-
posed in (Wu et al., 2013).
Figure 7 presents an example of application of
the Magnification approach on a 3D scatterplot vi-
sualization using the forest fires dataset(Cortez and
Morais, 2007), which contains meteorological data
from burned forests in the northeast region of Por-
tugal. Specifically, the Fine Fuel Moisture Code
(FFMC), Drought Code (DC), and the Initial Spread
Index (ISI), are used for the generation of the scatter-
plot. The hierarchical grids for the initial and magni-
fied scatterplots are shown in Figure 7(a) and Figure
7(b), using entropy significance map, while the cor-
responding magnification results are shown in Figure
7(c) and Figure 7(d). The correlations between the
visualized variables, which are hidden in the initial
view due to high cluttering, are visualized better in
the magnified result.
4.4 Choropleth Maps
This section presents the application of the Mag-
nification approach on choropleth maps, in which
color is utilized to encode quantitative information.
In this visualization, each area of the map has a
specific attribute value which is mapped on to its
color. The magnification approach is applied on the
1-dimensional input dataset, and afterwards, the mag-
nified space is mapped onto the color values. For this
visualization the unemployment of 2011 from the US
Census (Census, 2014) dataset is used.
Figure 4 presents the results of the Magnifica-
tion approach on the choropleth map. Figure 4(a)
presents the case of linear mapping, Figure 4(b) the
Box-Cox transformation proposed by (Maciejewski
IVAPP 2017 - International Conference on Information Visualization Theory and Applications
36

Figure 5: Results of the application of the Magnification approach on a scatterplot visualization with magnification factor
equal to 3. (a) Input visualization. (b),(e) Single layer and hierarchical significance maps generated using the entropy of each
hyperrectangle. (c),(d),(f),(g) Results of the significance maps shown in (b) and (e) using the method proposed in (Wu et al.,
2013) and in this paper respectively. (h),(k) Single layer and hierarchical significance maps generated from the saliency based
significance map proposed in (Wu et al., 2013). (i),(j),(l),(m) Results of the significance maps shown in (h) and (k) using the
method proposed in (Wu et al., 2013) and in this paper respectively. An HR copy of this Figure can be found in the following
link http://www.iti.gr/
∼
drosou/HierarchicalMagnification/Fig5.jpg.
Figure 6: PP metric for Figure 5. The smaller the value
the better the results. The best results are obtained from
proposed approach using a saliency significance map.
Figure 7: Application of the Magnification approach
on a 3D scatterplot visualization using the forest fires
dataset(Cortez and Morais, 2007). An HR copy of this
Figure can be found in the following link http://www.iti.gr/
∼
drosou/HierarchicalMagnification/Fig7.jpg.
et al., 2013), while Figure 4(c) and Figure 4(d) present
the results with a magnification factor manually se-
lected to be equal to 2 and 4 respectively. The right
lower part of the figures shows the histogram of the
distribution of the data in each case.
In the case of linear mapping shown in Figure
4(a), due to the fact that the distribution is very
skewed towards zero, most of the information is clut-
tered and is not visualized. On the other hand, the
visualization on Figure 4(c) and Figure 4(d) is more
uniformly distributed, and the choropleth map shows
more information regarding the status of the civilian
labor force to the different areas of the US. It should
be noted that the results and distribution of the data
for the (Maciejewski et al., 2013) mapping resemble
the results of the magnification approach for a magni-
fication factor equal to 4. The visualization in Figure
4(d) provides more information regarding the distri-
bution of the data in the lower ranges of its values,
and the small differences between the different states
are more evident.
Figure 8: The JSD metric measures the distance of the color
distribution created from the deformation methods in Fig-
ure 4, from the optimum uniform distribution (according to
(Brewer and Pickle, 2002)). Using a magnification factor
equal to 4, the results are better than Box-Cox mapping.
For the evaluation of the deformation results in
Figure 4, the work presented by Brewer and Pickle
(Brewer and Pickle, 2002) is used. Specifically,
Brewer and Pickle contacted multiple user studies
in order to evaluate the effectiveness of the different
color mapping techniques in choropleth maps, and in-
vestigate how they affected user performance in vari-
ous tasks. They found that the best mapping method is
the quantile mapping, which assigns the same number
of data objects to each of the available colors. This is
in fact a uniform distribution in the color plane. Tak-
ing this fact into account, the use of the JSD metric is
used to measure the distance of the distribution of the
colors created by the deformation procedure, from the
optimum uniform distribution.
The results of the JSD metric are presented in Fig-
ure 8, which show that increasing of the magnification
factor results in more uniform distributions, and thus,
better results. Using magnification factor equal to 4,
the results are better than Box-Cox mapping.
A Hierarchical Magnification Approach for Enhancing the Insight in Data Visualizations
37

4.5 User Evaluation Results
This section presents the results of the user evalua-
tion studies. The participants were presented with
a variety of visualization methods that were magni-
fied utilizing either the proposed magnification ap-
proach, or other state-of-the-art methods. The appli-
cations considered resizing/magnification of: scatter-
plot, word cloud and color (in choropleth maps). In
the case of scatterplot and word cloud magnification,
the approach proposed by Wu et al. (Wu et al., 2013)
was used for comparison. In the case of the choro-
pleth map, the Box-Cox mapping (Maciejewski et al.,
2013) has been used for comparison with the pro-
posed approach. For the evaluation studies, the same
datasets presented in this paper were utilized.
Three visualizations were given for each applica-
tion, the input visualization, and the two result vi-
sualizations (produced by applying the proposed ap-
proach and the other state-of-the-art method respec-
tively). The participants were asked to select one of
the result visualization. The following questions were
asked to the participants depending on the applica-
tion:
• In the scatterplot and word cloud applica-
tion: Which result provides better understand-
ing/insight about the input visualization?
• In the choropleth map application: Which result
represents more information about the input data?
Table 1: The results of the user evaluation studies on 22
individuals. The participants had to select between the pro-
posed hierarchical approach and other state-of-the-art meth-
ods.
Hierarchical Other p-val
Scatter-
plot
63.64% 36.36% 0.2008
Choro-
pleth
95.45% 4.55% 0.00002
Word-
cloud
81.82% 18.18% 0.0028
Overall 80.03% 19.69% 1.522e-
06
The results of the user evaluation studies are illus-
trated in Table 1. As shown in this figure, the par-
ticipants selected the results of hierarchical approach
more often than the competing method. The differ-
ence is larger in the choropleth map and word cloud
visualizations. Smaller difference can be found in the
scatterplot application. General discussion with the
users after the evaluation revealed two distinct groups.
The first group preferred displays with dense clusters,
that had a large distance between them, and this is
the reason they selected the less magnified result (i.e.
the competing method in (Wu et al., 2013), since the
magnification using the hierarchical method was gen-
erally larger). On the other hand, the second group
found that the more magnified view provided better
insight regarding the fine details within a cluster. Ta-
ble 1 also presents the results of hypothesis testing,
i.e. chi-square goodness of fit, in order to identify
the difference of the observed distributions with re-
spect to random guess. In all the cases except for the
scatterplot visualization, the results are indeed statis-
tically significant. Overall, 80.03% of the participants
selected the hierarchical approach with p-value below
0.005.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This work introduces a hierarchical magnification ap-
proach that enables the interactive reduction of vi-
sual clutter, and the magnification of significant re-
gions of the data in multiple dimensions. Significant
regions are uniformly magnified with minimum dis-
tortion, while the distortion is distributed to the less
significant areas of the display. This is particularly
useful for visualization resizing to fit small screens.
The proposed hierarchical significance map com-
bines the information of the significance maps over
multiple grid scales, based on each hyperrectangle’s
intersections with other hyperrectangles, and the sig-
nificance of each grid using a normalization operator.
The proposed approach identifies both small and large
objects/patterns, and scales them with minimum dis-
tortion in the magnified space. In addition, the intro-
duction of the multi-resolution grid reduces the num-
ber of variables in the optimization space, and thus,
decreases the running time of the algorithm.
The efficiency of the proposed approach was
demonstrated on multiple visualization approaches,
and the results were found to be superior to previous
methods using multiple evaluation metrics and user
studies.
The main advantage of the proposed approach is
that it does not address specific application areas. The
proposed approach can be used in order to enhance
any type of significance map, but the exact choice of
the significance map depends on the application.
Future work includes the research of additional
irregular grid formations (e.g. non-rectangular grids
based on edge detection algorithms), and their effect
on the distortion after the optimization procedure. Al-
ternative significance maps will also be considered,
IVAPP 2017 - International Conference on Information Visualization Theory and Applications
38

since an important aspect of the future work includes
the automatic selection of the most appropriate signif-
icance map based on the input dataset.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work has been partially supported by the Euro-
pean Commission through project Scan4Reco funded
by the European Union H2020 programme under
Grant Agreement n
o
665091. The opinions expressed
in this paper are those of the authors and do not neces-
sarily reflect the views of the European Commission.
REFERENCES
Bertini, E. and Santucci, G. (2006). Give chance a
chance: Modeling density to enhance scatter plot
quality through random data sampling. Information
Visualization, 5(2):95–110.
Brewer, C. A. (1994). Cartography: thematic map design.
Cartographic Perspectives, (17):26–27.
Brewer, C. A. and Pickle, L. (2002). Evaluation of meth-
ods for classifying epidemiological data on choropleth
maps in series. Annals of the Association of American
Geographers, 92(4):662–681.
Census (2014). US Census Bureau (available at
http://www.census.gov/).
Cortez, P. and Morais, A. d. J. R. (2007). A data mining
approach to predict forest fires using meteorological
data.
Cover, T. M. and Thomas, J. A. (2012). Elements of infor-
mation theory. John Wiley & Sons.
Cui, W., Wu, Y., Liu, S., Wei, F., Zhou, M. X., and Qu, H.
(2010). Context preserving dynamic word cloud vi-
sualization. In Pacific Visualization Symposium (Paci-
ficVis), 2010 IEEE, pages 121–128. IEEE.
Eisemann, M., Albuquerque, G., and Magnor, M. (2011).
Data driven color mapping. Proceedings EuroVA.
Ellis, G. and Dix, A. (2007). A taxonomy of clutter
reduction for information visualisation. Visualiza-
tion and Computer Graphics, IEEE Transactions on,
13(6):1216–1223.
Endres, D. M. and Schindelin, J. E. (2003). A new met-
ric for probability distributions. Information Theory,
IEEE Transactions on, 49(7):1858–1860.
Fagin, R., Kumar, R., and Sivakumar, D. (2003). Compar-
ing top k lists. SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathemat-
ics, 17(1):134–160.
Gao, X., Xiao, B., Tao, D., and Li, X. (2010). A survey of
graph edit distance. Pattern Analysis and applications,
13(1):113–129.
Hautam
¨
aki, V., Kinnunen, T., and Fr
¨
anti, P. (2008). Text-
independent speaker recognition using graph match-
ing. Pattern Recognition Letters, 29(9):1427–1432.
Hilaga, M., Shinagawa, Y., Kohmura, T., and Kunii, T. L.
(2001). Topology matching for fully automatic simi-
larity estimation of 3D shapes. In Proceedings of the
28th annual conference on Computer graphics and in-
teractive techniques, pages 203–212. ACM.
Itti, L., Koch, C., and Niebur, E. (1998). A model of
saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene anal-
ysis. IEEE Transactions on pattern analysis and ma-
chine intelligence, 20(11):1254–1259.
Jia, S., Zhang, C., Li, X., and Zhou, Y. (2014). Mesh resiz-
ing based on hierarchical saliency detection. Graphi-
cal Models.
Keim, D. A., Hao, M. C., Dayal, U., Janetzko, H., and Bak,
P. (2010). Generalized scatter plots. Information Vi-
sualization, 9(4):301–311.
Lee, C. H., Varshney, A., and Jacobs, D. W. (2005). Mesh
saliency. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG),
volume 24, pages 659–666. ACM.
Maciejewski, R., Pattath, A., Ko, S., Hafen, R., Cleveland,
W. S., and Ebert, D. S. (2013). Automated box-cox
transformations for improved visual encoding. Visu-
alization and Computer Graphics, IEEE Transactions
on, 19(1):130–140.
Mademlis, A., Daras, P., Axenopoulos, A., Tzovaras, D.,
and Strintzis, M. G. (2008). Combining topological
and geometrical features for global and partial 3-D
shape retrieval. Multimedia, IEEE Transactions on,
10(5):819–831.
Rosenholtz, R., Li, Y., Mansfield, J., and Jin, Z. (2005).
Feature congestion: a measure of display clutter. In
Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human fac-
tors in computing systems, pages 761–770. ACM.
Tao, J., Wang, C., Shene, C.-K., and Kim, S. H. (2014).
A Deformation Framework for Focus+Context Flow
Visualization. Visualization and Computer Graphics,
IEEE Transactions on, 20(1):42–55.
Thompson, D., Bennett, J., Seshadhri, C., and Pinar, A.
(2013). A provably-robust sampling method for gen-
erating colormaps of large data. In Large-Scale Data
Analysis and Visualization (LDAV), 2013 IEEE Sym-
posium on, pages 77–84. IEEE.
Tung, T. and Schmitt, F. (2005). The Augmented Multires-
olution Reeb Graph Approach for Content-based Re-
trieval of 3d Shapes. International Journal of Shape
Modeling, 11(1):91–120.
Wang, Y.-S., Tai, C.-L., Sorkine, O., and Lee, T.-Y. (2008).
Optimized scale-and-stretch for image resizing. In
ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), volume 27,
page 118. ACM.
Wang, Y.-S., Wang, C., Lee, T.-Y., and Ma, K.-L. (2011).
Feature-preserving volume data reduction and focus+
context visualization. Visualization and Computer
Graphics, IEEE Transactions on, 17(2):171–181.
Wong, P. C. and Thomas, J. (2009). Visual analytics: build-
ing a vibrant and resilient national science. Informa-
tion Visualization, 8(4):302–308.
Wu, Y., Liu, X., Liu, S., and Ma, K.-L. (2013). Vi-
Sizer: a visualization resizing framework. Visualiza-
tion and Computer Graphics, IEEE Transactions on,
19(2):278–290.
Zwislocki, J. J. (2009). Stevens’ Power Law. Sensory Neu-
roscience: Four Laws of Psychophysics, pages 1–80.
A Hierarchical Magnification Approach for Enhancing the Insight in Data Visualizations
39
