Towards a Diminished Reality System that Preserves Structures and
Works in Real-time
Hugo
´
Alvarez
1
, Jon Arrieta
2
and David Oyarzun
3
1
Department of Interactive Computer Graphics, Vicomtech-IK4, San Sebastian, Spain
2
On Board Area - Technology Department, CAF Signalling, San Sebastian, Spain
3
Co-founder & CEO, Nuavis, San Sebastian, Spain
Keywords:
Diminished Reality, Augmented Reality, Real-time.
Abstract:
This paper presents a Diminished Reality system that is able to propagate textures as well as structures with
a low computational cost, almost in real-time. An existing inpainting algorithm is optimized in order to
reduce the high computational cost by implementing some Computer Vision techniques. Although some of
the presented optimizations can be applied to a single static image directly, the global system is mainly oriented
to video sequences, where temporal coherence ideas can be applied. Given that, a novel pipeline is proposed
to maintain the visual quality of the reconstructed image area without the need of calculating everything again
despite slow camera motions. To the best of our knowledge, the prototype presented in this paper is the
only Diminished Reality system focused on structure propagation that works near real-time. Apart from the
technical description, this paper presents an extensive experimental study of the system, which evaluates the
optimizations in terms of time and quality.
1 INTRODUCTION
Augmented Reality (AR) is a major field of research
that is getting more and more support in the last few
years. As a result of this popularity, new research
branches have emerged. Diminished Reality (DR) can
be considered as one of the branches of AR that has
awaken the interest of researchers in the last decade.
AR is a mechanism that enriches the real world by
adding virtual elements to it. A typical example could
be the Google Glass (Google Inc., 2013), where the
user is able to see everything normally (real world),
but it is also able to see augmented content (messages,
videos or images) at the same time. On the contrary,
Diminished Reality (DR) basically does the opposite
effect of AR. The objective of DR is to remove un-
desired objects from the image, video or user view.
A combination of these two technologies can be used
to create an interactive virtual environment where the
user can add/remove virtual/real objects in real-time.
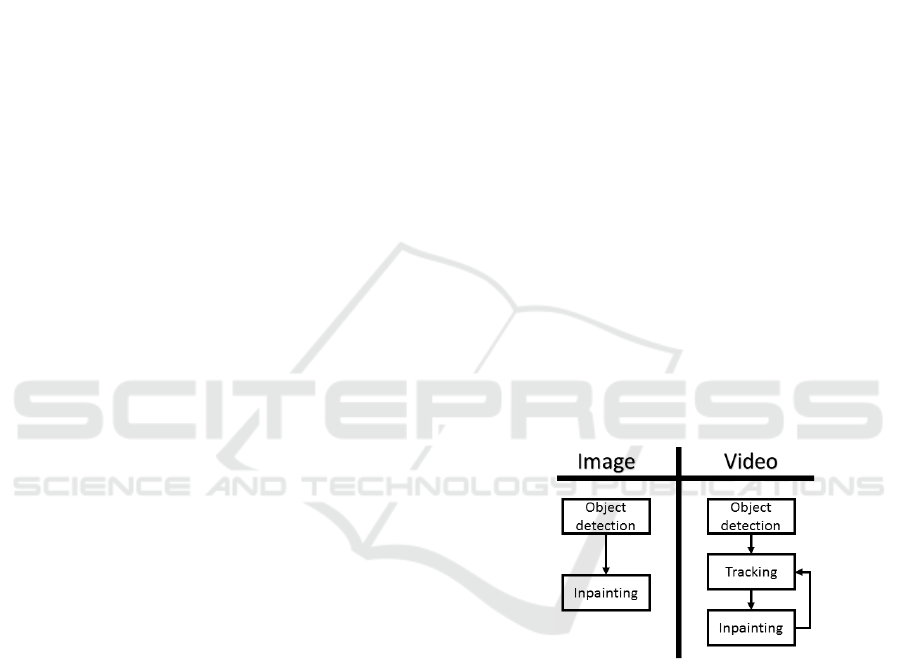
A DR technique is divided in three main modules:
object detection, tracking and inpainting. The object
detection module consists in recognizing the object
that needs to be occluded, the tracking system aims
to follow the object in the subsequent frames, and the
inpainting module consists in reconstructing the area
Figure 1: General DR system diagram.
where the object is located. Figure 1 compares the
process of DR in image and video applications. As it
can be seen in the diagram, for a single image appli-
cation the tracking step is not required (it is enough
with the initial detection), while the video processing
includes a loop to extrapolate and exploit the informa-
tion of the previous frames to the subsequent ones.
The problem of actual inpainting techniques is
that they require a high computational cost for the in-
painting step. Existing techniques, such as (Criminisi
et al., 2004), (Komodakis and Tziritas, 2007), (Liu
and Caselles, 2013) have made efforts to improve the
visual quality of the results without taking care of the
processing time. Consequently, it is uncomfortable
334
à ˛Alvarez H., Arrieta J. and Oyarzun D.
Towards a Diminished Reality System that Preserves Structures and Works in Real-time.
DOI: 10.5220/0006097803340343
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2017), pages 334-343
ISBN: 978-989-758-225-7
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

to implement these techniques directly to process a
live video because they would take too much time to
process each of the frames. One of the biggest opti-
mizations in computing time was presented in (Barnes
et al., 2009). The proposed randomized patch search
reduced considerably the processing time of the exist-
ing techniques. This technique can propagate textures
easily but it presents some limitations when structures
need to be propagated. On the other hand, a robust
technique for image inpainting was presented by (Cri-
minisi et al., 2004). This technique defines the prior-
ities of the filling order to maintain structural infor-
mation. Nonetheless, it is too slow for video appli-
cations, as it lasts minutes to recover a high quality
video frame.
To the best of our knowledge, the only existing
DR systems that are able to work near real-time are
(Herling and Broll, 2010) and (Herling and Broll,
2012). In both cases the inpainting method proposed
by (Barnes et al., 2009) is optimized. As mentioned
before, this algorithm is fast and efficient when prop-
agating textures, but it is not so accurate when struc-
tures need to be processed.
The solution presented in this paper spreads out
the real-time DR solutions by implementing an opti-
mized version of (Criminisi et al., 2004), which is a
robust algorithm that preserves structures. Moreover,
two different tracking techniques have been integrated
in order to create a robust system.
The rest of the paper is organized in 5 sections
as follows. In Section 2 we provide an overview of
some works related to DR and similarities with our
contribution. Then, in Section 3 we present all op-
timizations that have been introduced to get a near
real-time DR system that preserves texture and struc-
ture patterns. Section 4 shows extensive experiments
that validate the proposed system. Finally, Section 5
presents the main conclusions drawn from this work.
2 RELATED WORK
According to the number of cameras or views, DR
techniques can be classified in two groups:
• Multiview-based methods: (Lepetit et al., 2001)
and (Zokai et al., 2003) use cameras ore frames
from different points of view in order to seg-
ment the object that needs to be removed. The
result is almost perfect because these techniques
generate a 3D representation of the scene, going
from a 2D problem to a 3D problem, which fa-
cilitates the distinction between object and back-
ground. The weakness of these methods is that in
most real problems there is no control or ability to
place multiple cameras to get frames from differ-
ent points of view and do the 3D reconstruction.
• Frame-based methods: Most of the existing
methods like (Wexler et al., 2007), (Simakov
et al., 2008), (Herling and Broll, 2010), (Her-
ling and Broll, 2012), (Kawai et al., 2013a) and
(Kawai et al., 2013b) are based on the information
of a single camera. They do the image inpainting
based on the previous, actual and sometimes next
frames too (they do a backward process). In this
case, when multiple frames are used it is to ap-
ply temporal coherence rules. Even if these tech-
niques are not as accurate as the previous ones,
they are applicable in much more scenarios.
This article focuses on the frame-based methods,
because they are the trend in the last few years due to
their versatility for most scenarios.
(Wexler et al., 2007) present a novel algorithm
able to reconstruct damaged or missing frames from
videos. They introduce a coherence term, which
means that the reconstructed area should maintain the
same value in all the video. All video frames are used
in the inpainting step in a process called space-time
video completion. Even if this algorithm obtains re-
ally good results, there is no possibility to implement
it in real-time. Apart from that, this algorithm is de-
signed to work with static cameras.
(Simakov et al., 2008) design an innovative
method called bidirectional similarity. This method is
presented in their article in order to summarize data.
This summarization can be applied in images as well
as videos, and it can be used for several applications,
such as automatic cropping, photo reshuffling, im-
age collage, object removal and more. Simakov et
al. define the bidirectional similarity in two terms
called completeness and coherence. Completeness
means that all the patches contained in the input im-
age should be in some part of the output image. Co-
herence means that all the patches contained in the
output image should come from the input image. This
algorithm is also not applicable in real-time applica-
tions because of its high computational time.
(Herling and Broll, 2010) describe the first self-
contained real-time capable DR system for video ap-
plications. The main challenge for this technique is
making (Barnes et al., 2009) close to real-time with-
out loosing quality in the image. The same authors
present an evolution of the initial solution in (Her-
ling and Broll, 2012). In the new version, they add
a fingerprint selection to select the area and use a seg-
mentation technique to select the object inside the re-
gion of interest. They also change the object tracking
mechanism from an active snake (Kass et al., 1988)
approach to a two phase contour tracking approach.
Towards a Diminished Reality System that Preserves Structures and Works in Real-time
335

They use a homography based contour tracking in the
first phase, while in the second phase, the new con-
tour is refined and adjusted regarding to the undesired
object area. This improvement leads to better con-
tour point correspondences between successive video
frames.
(Kawai et al., 2013a) propose a DR system con-
sidering background structures. They focus on the in-
painting more than on the detection or tracking pro-
cesses. The aim of this work is to overcome the prob-
lem of perspective distortion of regular patterns that
appears in exemplar-based inpainting. This is done
by rectifying the input image and applying changes
based on similar patterns from the image. Their
scheme, presented in (Kawai et al., 2013b) as well
as in (Herling and Broll, 2012), uses a homography to
ensure temporal consistency and to determine search-
ing areas in the next frame. The problem is that the
homography assumption works well when the back-
ground is almost planar, but the results in non-planar
backgrounds are not accurate. In their method, the
scene around the target object is divided into multiple
planes, whose number is automatically determined.
Inpainted textures are successfully overlaid on the tar-
get object under comparatively unrestricted camera
motion using the estimated planes and the camera
pose calculated by a complementary Visual-SLAM
system.
According to our prototype, the idea of the patch
search optimization explained in (Barnes et al., 2009)
has been taken into account to improve (Criminisi
et al., 2004). Apart from that, the coherence term ex-
plained by Wexler et al. has been also applied for
video applications in order to obtain a better visual
effect and reduce even more the computational time.
Thus, our DR system has similarities with the work
described in (Herling and Broll, 2012). The main dif-
ference is that we optimize an inpainting method that
offer us more robustness to propagate structures, and
consequently, it is more complicated. As a result, the
DR system proposed in this article is the only DR
solution designed for structure propagation that can
work near in real-time.
3 PROPOSED DIMINISHED
REALITY
The DR solution that is presented in this article works
near real-time and is capable of propagating struc-
tures. Like any other DR system, it is composed
by three main modules (Figure 1): object detection,
tracking and inpainting.
According to our prototype, it is important to note
Figure 2: Manual object detection. The white circle is se-
lected by the user using the mouse.
that the object detection is done manually, as the user
needs to select the area of the object that needs to be
removed (i.e. the region of interest, ROI). The user
is responsible for drawing the outline of the object in
the image with the mouse (Figure 2). Although this
step can be done automatically by an advanced object
recognition, this article focuses on the optimization
of the inpainting phase, so this improvement has not
been addressed.
Two different tracking methods (Camshift (Brad-
ski, 1998) and Lucas-Kanade optical flow (Bouguet,
2001)) have been implemented to deal with objects
of different appearances and to develop a more ro-
bust prototype. In the case of the Camshift track-
ing algorithm, it recalculates the position of the ROI
based on colour information, so it supports objects
that are homogeneous, without texture. The optical
flow tracking, meanwhile, searches keypoints inside
the ROI that will be tracked in subsequent frames, so
it is oriented to objects with texture. As the optical
flow tracking provides greater accuracy in estimating
the motion of the ROI over time, its use is preferable.
For further details of these techniques, please refer to
the corresponding sources.
Two modes of execution are allowed for the in-
painting step. The first one performs the inpainting
process in each new frame, following the procedure
shown in Figure 1. The second one, however, ap-
plies a motion model (represented by a homography)
to update the pixels and it only calls the inpainting
function when a strong movement is detected (when
the motion model is not a good estimation). Fig-
ure 3 shows the flow diagram of the second execu-
tion mode. It is noteworthy that this second execution
mode is oriented to video applications, when several
sequential frames are available and where the motion
model makes sense.
Additionally, the proposed DR system has been
designed to be modular in order to facilitate the cre-
ation of different setups during the validation pro-
cess (see Section 4). Thus, it is simple to integrate
a new object detection, tracking or inpainting algo-
rithm. Similarly, it is also possible to change the
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
336
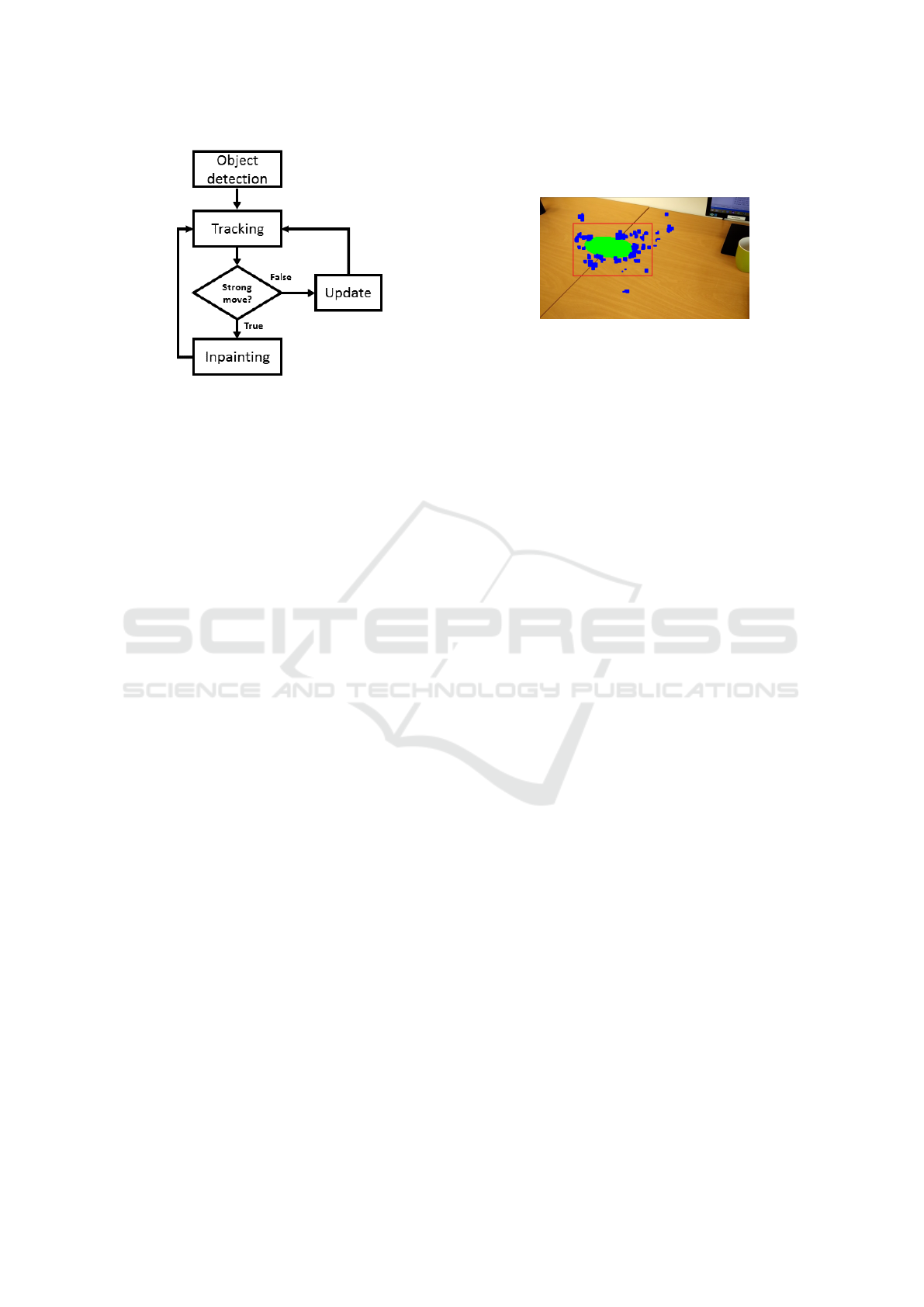
Figure 3: Proposed DR system diagram.
parameterization (patch searching area, image down-
sampling size, etc.) to adapt to different environ-
ments.
3.1 Real-time Optimizations
As it is mentioned in the introduction, the inpainting
technique that uses the prototype presented in this ar-
ticle is based on (Criminisi et al., 2004). Furthermore,
we have implemented all the optimizations using the
publicly available code (Rahul Verma, 2013) as a ba-
sis. This section includes the optimizations that have
been introduced to speedup the process of inpainting
and reach the real-time goal.
3.1.1 Patch Search Reduction
One of the most important changes from the origi-
nal algorithm is the change of the patch searching
area. In its original version, the area that has to be
reconstructed is divided into small patches (called
target patches) and each one is filled by copying
patches from the rest of the image (called source
patches). However, the proposed algorithm searches
source patches only in the surroundings of each target
patch. Even though there is a loss of information, in
most of the cases this information is useless for the in-
painting, and therefore, a pointless processing. It has
been observed that in many cases, the closest patches
were the best matches for the target patch. Figure 4
is an example of the tests that were performed. As
it is shown in the image, the target region is marked
in green, and the source patches are marked in blue.
Most of the source patches come from the surround-
ings of the masked region (red rectangle). Therefore,
a reduction of the search area would improve the pro-
cessing time with a small impact on the result. We
have implemented the scheme proposed by Goyal et
al. for determining the patch search area, which has
been set proportional to the patch size and is config-
urable for each execution.
Figure 4: Patch correspondences. Green area (target
patches) is reconstructed with the information of the blue
patches (source patches). The red rectangle represents the
bounded search area that could be used almost without lat-
ering the result.
SSD (Sum of Squared Differences) is the most
common technique used in exemplar-based inpaint-
ing algorithms to meassure the difference between the
source and target patches. (Criminisi et al., 2004)
does not define any rule to choose one patch or an-
other when there are two or more patches with the
same SSD value. Thus, we have introduced a new
condition for the patch selection. In (Goyal et al.,
2010), they define a variance term to decide between
patches with the same SSD. In our approach, the eu-
clidean distance between the target and source patch
locations is calculated and compared, and the nearest
source patch between the candidates with the same
SSD value is chosen as the best exemplar patch for the
target patch. This is coherent due to the fact that the
lighting conditions are more stable in surrounding ar-
eas, reducing the possibility of introducing undesired
artefacts.
Figure 5 shows the differences between searching
in the whole image and our optimized local search. As
it can be seen in the images, there is not much differ-
ence between the original algorithm and the result of
the optimized search in terms of quality. In some parts
of the image the original algorithm performs slightly
better than the optimized one (compare the building
in Figure 5 c and d), but in other parts even the opti-
mized version works better (note the bush over the sea
in Figure 5 c and d). Summarizing, it can be said that
the optimized search reduces the computational time
while keeping similar quality results.
3.1.2 Image Cropping and Downsampling
The original image is cropped by a proportional size
to the ROI. Thus, there is a reduction in the area that
need to be processed during the inpainting process.
Moreover, the cropped image is downsampled sev-
eral scale factors to decrease the number of pixels that
are processed (Figure 6), reducing the processing time
substantially. These modifications reduce the time of
Towards a Diminished Reality System that Preserves Structures and Works in Real-time
337

(a) (b) (c) (d)
(e) (f) (g) (h)
Figure 5: Comparison between the optimized search area
and the existing approaches, (Criminisi et al., 2004) (a-
d) and (Goyal et al., 2010) (e-h). Images taken from
(Bertalmio et al., 2000) and (Goyal et al., 2010). From (a) to
(d) and from (e) to (h): Input image; Mask that defines the
ROI; Result from (Criminisi et al., 2004) or (Goyal et al.,
2010); Result using the proposed optimized patch search.
both, the computation of the patch priority as well as
the search of patch correspondences. After calculat-
ing patch correspondeces in the low scale, matches
are mapped directly to the original image based on
the cropping offset and the scaling factor. Although
we have observed that using the correspondences cal-
culated in the low scale slightly reduces the resulting
visual quality, it is a necessary modification to achieve
real-time (see Section 4).
Figure 6: Cropping and downsampling steps.
3.1.3 Patch Propagation
The patch propagation optimization is an essential
module for implementing a real-time system. In our
approach, a motion model between two consecutive
frames is calculated using the tracking information.
Given the location of some features (at least 4) in
the previous and current frames, we are able to cal-
culate a perspective transformation (represented by a
homography) that relates the movement between the
two frames. Thus, the new locations of the patches
can be obtained by a simple matrix multiplication,
which simplifies calculating patch correspondences
and avoid having to search them in each frame.
The efficiency of this method relies on having an
accurate tracking system. Given that, two different
tracking systems have been implemented to explore
their response and achieve a robust solution: (Brad-
ski, 1998) and (Lucas et al., 1981). (Bradski, 1998) is
a tracking system based on colour histograms. There-
fore, it is very suitable for working with textureless
objects. Nevertheless, it is not especially robust to
rotations, as it only provides four points around the
object (four corners that define the oriented bounding
box of the object) to feed the homography calculation.
On the other hand, (Lucas et al., 1981) tracks feature
points that are detected on the object (ROI). In the ini-
tial frame, some feature points are detected with the
FAST detector (Rosten and Drummond, 2005), and in
subsequent frames the new locations of these points
are updated using the optical flow estimation. In this
case, as there are multiple points to feed the homogra-
phy calulation, an hypothesis-verification methodol-
ogy (known as RANSAC (Fischler and Bolles, 1981))
is applied, which offers higher accuracy and more ro-
bustnes against the movements of the camera. The
main drawback of this tracking system is that it does
not work well with textureless objects, i.e., it requires
objects that provide feature points on their surface.
The ability to employ the motion estimation gave
us the chance of working in real-time. However, we
have observed that the inpainting quality degrades
considerably after a large movement, i.e., when there
is a viewpoint change between the current state and
the starting point where the complete patch corre-
spondence algorithm was performed. To solve this
degradation, the prototype presented in this article in-
cludes a control module (Figure 3) that keeps track of
the cumulative movement applied to the camera. It is
calculated by detecting the center of the object from
the tracking points and comparing it to the initial po-
sition. When this distance exceeds a threshold, the
original inpainting algorithm is executed to calculate
new patch correspondences, more appropriate to the
current viewpoint. It is note worthy that he threshold
can be configured to adapt the margin of movement
for each scenario.
Another difficulty when working with the mo-
tion estimation approach is handling scale transfor-
mations. In this case, gaps between patches appear
when all the patches are updated with the homogra-
phy estimation. This happens because the shape of
the object differs between the initial and subsequent
frames. This effect is especially noticeable when the
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
338

size of the object in the current frame is bigger than in
the initial moment. Figure 7 (b) is an example where
the mentioned undesired gaps are shown. In order to
overcome this problem, a pixel level correction has
been implemented. It is a two iteration process. In
the first iteration all the target patches are updated as
usual. The change is that a mask that contains the
status of all the pixels that form the ROI is main-
tained. Thus, the status of each pixel is initialized
as not update, and after the first iteration, the status
of those pixels that have been updated is changed. In
the second iteration, the same procedure is applied,
but in this case, each source pixel is copied to those
pixels that are inside a predefined radius of the tar-
get pixel. Before copying each pixel, it checks in the
mask wether the pixel has been already updated (in
the first iteration) or not. With this procedure the vi-
sual quality is maintained (Figure 7 (c)) and calling
the original inpainting algorithm is avoided. Never-
theless, it is not convenient to apply a big radius be-
cause the result would degrade in strong scalings. In
our approach, we assure a good quality combining the
sensitivity of the control module (to raise the original
inpainting algorithm when a strong scale transforma-
tion is applied) and the pixel correction radius.
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 7: Scaling example of patch propagation. From left
to right: Original frame; Patch propagation with motion es-
timation; Patch propagation with motion estimation and gap
filling.
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
This section provides a performance and quality eva-
lution of the prototype. It is divided in three subsec-
tions: implementation details, results and discussion.
4.1 Implementation Details
The main module that has been paid attention in our
DR system is the inpainting process. The proposed
solution should maintain a balance between quality
and speed. Speed is a parameter that can easily be
measured objectively, and therefore, the results that
are obtained from this kind of measurement can di-
rectly be interpreted. However, the quality is a sub-
jective indicator that needs an extra step to proof its
validity. In order to quantify the quality, a web form
with videos that were processed with different con-
figurations (see below) was prepared and presented to
different users.
The different configurations that have been con-
sidered are:
The modular design of the proposed solution al-
lows us to change from one configuration to another
easily in the process of testing. Hence, a progressive
testing process is presented, starting from the original
algorithm and introducing each optimization up to the
final prototype.
• Original (vO): Consists in executing frame by
frame the original algorithm proposed by (Crim-
inisi et al., 2004).
• Original+Patch search (vOP): Consists in exe-
cuting the original algorithm plus the patch search
optimization (Section 3.1.1), which consists in re-
ducing the patch search area.
• Original+Patch search+Downsampling(vOPD):
Consists in executing the algorithm with the op-
timized search and using image downsampling
(Section 3.1.2) to accelerate the process.
• Final (vF): Consists in executing the algorithm
with all the optimizations mentioned in this arti-
cle. Patches are calculated just when there is a
big movement, and the rest of the video process-
ing consists in finding the correspondence using
the motion model estimation (Section 3.1.3). Ad-
ditionally, this configuration has been executed in
turn with the two tracking systems described in
Section 3.1.3, Camshift (vFC) and Optical Flow
(vFOF).
Similarly, several scenarios with different com-
plexity have been considered, starting from the most
simple one up to the most complex one:
• Simple scenario: Consists in removing an object
in a non-structural background. For example, a
piece of paper on the top of a table (Figure 8 (a)).
• Medium scenario: Consists in removing an ob-
ject in a simple structural background. For ex-
ample, a mobile phone that partially occludes the
junction of two tables (Figure 8 (b)).
• Complex scenario: Consists in removing an ob-
ject in a complex structural background. For ex-
ample, a card that is in front of a building with
homogeneous color and several structural compo-
nents (Figure 8 (c)).
Moreover, three different videos were recorded for
each scenario to represent different motions: rota-
tion, translation and scaling. All these videos were
recorded in 720p.
Towards a Diminished Reality System that Preserves Structures and Works in Real-time
339
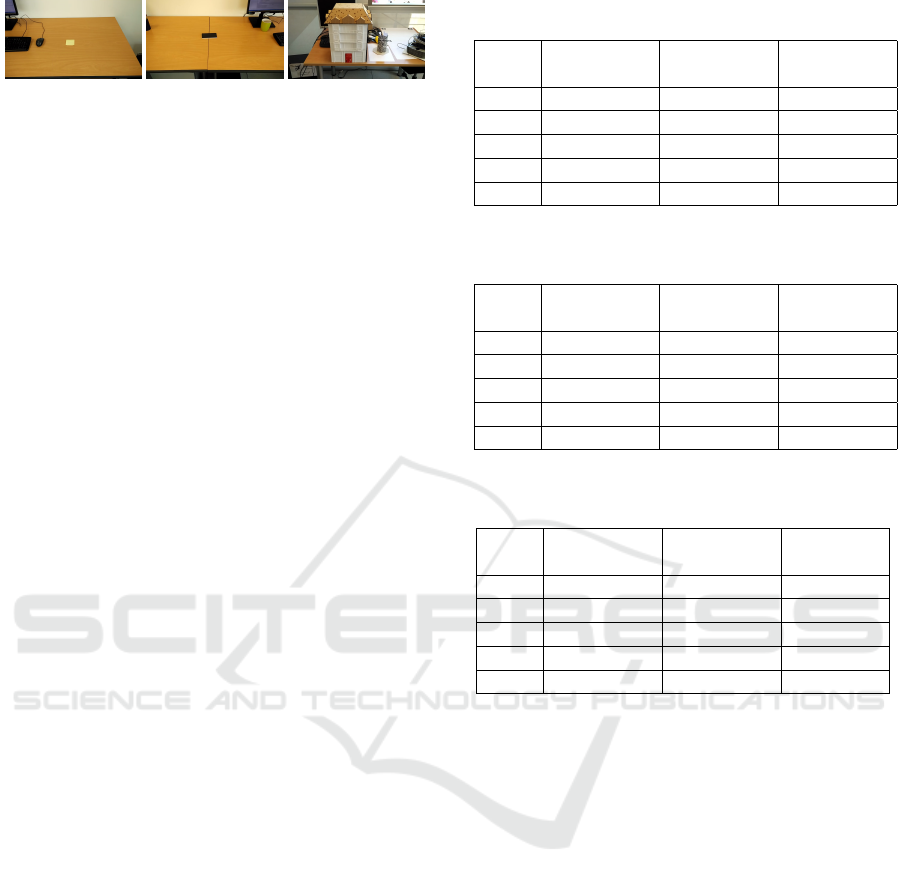
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 8: Simple (a), medium (b) and complex (c) scenarios
used in the experiments.
For each of these cases the timing information as
well as the output video were recorded to obtain some
comparisons and conclusions. The hardware setup
consists of an Intel i5-3470 at 3.20GHz and 8 GB of
RAM running under windows 8.1. The code was writ-
ten in C++ using the OpenCV library (Itseez, 2016).
4.2 Experimental Results
4.2.1 Time
Figure 9 shows the execution time of each configu-
ration for each scenario according to the motion ap-
plied. As expected, the procesing time decreases
when more optimizations are introduced. In the case
of the scaling, there is an increase of the process-
ing time in the latter frames. This happens because
the object that needs to be inpainted becomes bigger
over time, and as a result, more patches are needed
to cover the area. With respect to the final versions
with Camshift and Optical Flow tracking systems, it
can be seen that they have a really low processing
time in most of the frames (between 50-60 millisec-
onds when there are no peaks, i.e., when the origi-
nal inpainting method is not called and the motion es-
timation is used). In the case of the Optical Flow,
there is a peak at the beginning because patches are
initialized using the original inpainting function. In
the rest of the video the tracking algorithm is robust
against movements and avoids calculating the patches
again (Section 3.1.3). On the other hand, the Camshift
shows peaks all over the video because it needs to re-
calculate the patches to maintain a good visual qual-
ity.
Furthemore, Tables 1, 2 and 3 present the total
procesing times for simple, medium and complex sce-
narios respectively. It can be observed that the pro-
posed DR system has reduced computational cost sev-
eral orders of magnitude compared to the original so-
lution.
4.2.2 Quality
15 users with skills in computer graphics (but with-
out extensive knowledge in DR) took part in the ex-
periment. To each user the videos reconstructed with
the different configurations were presented (see some
Table 1: Simple scenario, total processing time (in seconds)
for each configuration and motion.
Config.
Rotation
(199 frames)
Translation
(152 frames)
Scaling
(177 frames)
vO 52862,84 53526,35 105292,73
vOP 3097,53 3226,45 5098,17
vOPD 259,69 266,97 425,49
vFC 17,04 23,12 12,85
vFOF 10,77 8,62 9,08
Table 2: Medium scenario, total processing time (in sec-
onds) for each configuration and motion.
Config.
Rotation
(199 frames)
Translation
(152 frames)
Scaling
(102 frames)
vO 92435,89 53548,90 57551,18
vOP 5209,06 3478,99 3712,20
vOPD 409,29 283,65 309,46
vFC 31,00 37,49 15,47
vFOF 14,80 22,33 6,18
Table 3: Complex scenario, total processing time (in sec-
onds) for each configuration and motion.
Config.
Rotation
(175 frames)
Translation
(135 frames)
Scaling
(75 frames)
vO 61440,18 43449,94 22814,54
vOP 2467,36 2119,33 1574,21
vOPD 278,24 232,88 117,40
vFC 16,69 23,61 4,91
vFOF 11,83 9,40 5,46
frame examples in Figures 11, 12 and 13). Thus,
the users evaluated each video from 1 to 5, being
1 the worse quality and 5 the best one. Figure 10
shows the answers that were recorded, which exhibit
a tendency. All the users increased the score when
more optimizations where incorporated. This is be-
cause the original algorithm and the first optimiza-
tions (vOP and vOPD) recalculate all the patches ev-
ery frame, so correspondences can change in consec-
utive frames even when there are almost no changes
in the scene (for example, due to small light varia-
tions). This generates a different image reconstruc-
tion in each frame, which is perceived negatively by
the user. vOP scores better than vO because it uses
a bounded patch search, which favors the stability of
the correspondences over time. vOPD, by contrast,
has worse results because correspondences are calcu-
lated in a low scale, which can introduce some inac-
curacies. vFC and vFOF introduce temporal coher-
ence and maintain stable the correspondences along
the video sequence, which improves the visual per-
ception considerably and explains their high score.
As vFOF is able to maintain the motion estimation for
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
340
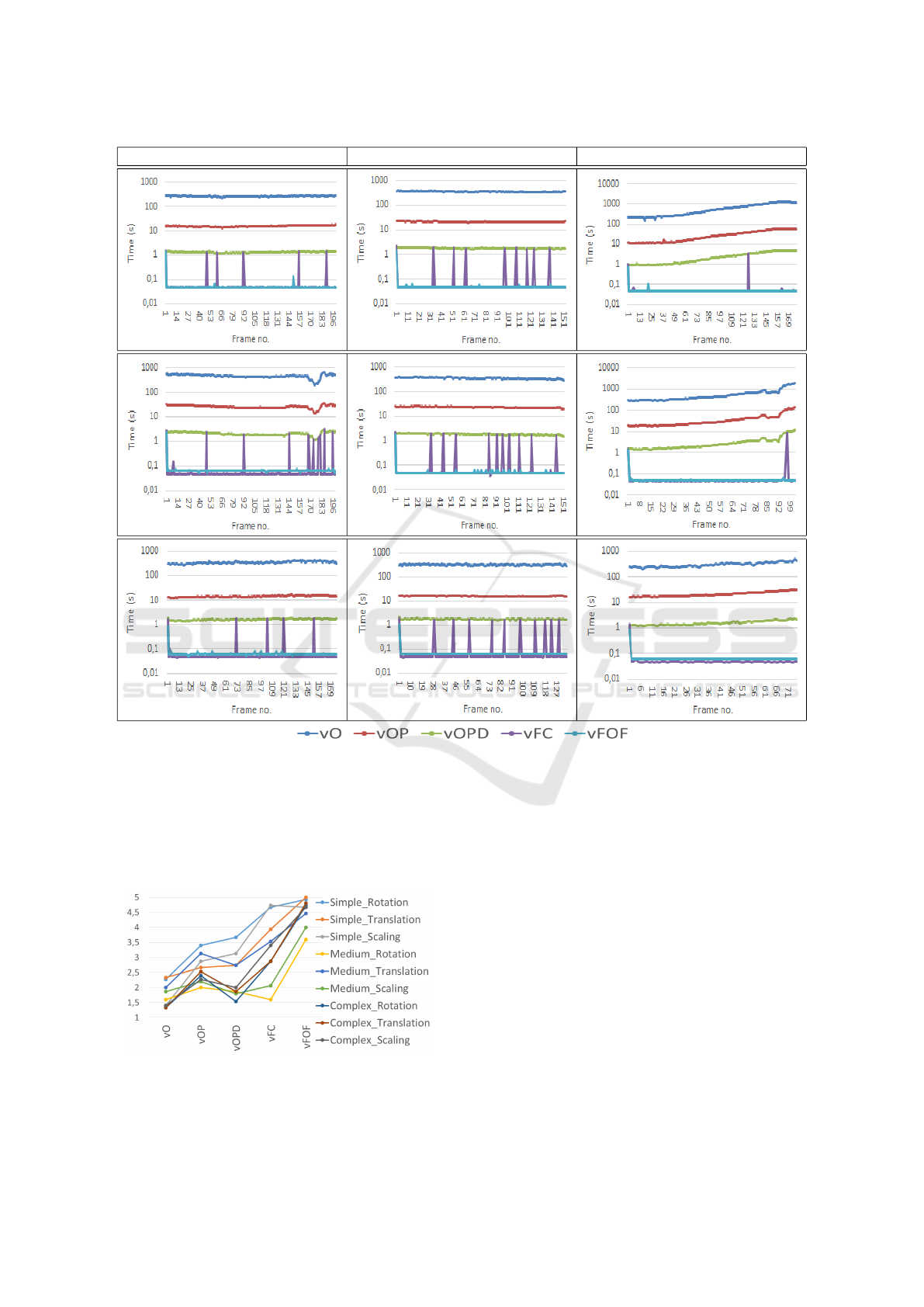
Rotation Translation Scaling
Figure 9: Execution times for simple (top row) medium (middle row) and complex (bottom row) scenarios.
longer time than vFC (i.e. without calling to the origi-
nal algorithm and recalculating the correspondences),
especially in the rotation case (Figure 11), vFOF has
the highest score.
Figure 10: Responses of the users assessing the visual qual-
ity of each reconstructed video using different configura-
tions.
4.3 Discussion
The time evaluation that has been conducted shows
that each proposed optimization decreases the com-
putational time. vOP and vOPD optimizations can
be applied to a single image directly, while vFC and
vFOF exploit temporal coherence ideas and are ori-
ented to video applications.
Given the results of the quality experiment, the
proposed optimizations do not harm the quality of the
visual perception. Even vFC and vFOF obtain bet-
ter visual perception for a complete video sequence.
Nonetheless, this quality evaluation has been per-
formed for a video sequence. For a single static im-
age, the visual results with or without optimizations
are similar (see Figures 5, 11, 12 and 13). In this
case, what we do get is a noticeable reduction in the
computational cost.
Towards a Diminished Reality System that Preserves Structures and Works in Real-time
341

Source vO vOP vOPD vFC vFOF
Figure 11: Frame samples for the rotation sequence in simple (top), medium (middle) and complex (bottom) scenarios.
Source vO vOP vOPD vFC vFOF
Figure 12: Frame samples for the translation sequence in simple (top), medium (middle) and complex (bottom) scenarios.
Source vO vOP vOPD vFC vFOF
Figure 13: Frame samples for the scaling sequence in simple (top), medium (middle) and complex (bottom) scenarios.
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
342

5 CONCLUSIONS
In this article, some optimizations have been pro-
posed to get a DR system that preserves structures
and works near real-time. Patch search reduction
and downsampling optimizations are valid for a sin-
gle static image, while the global system is mainly
oriented to video applications, where the temporal
coherence let us using tracking techniques to main-
tain the reconstrunction of the image stable along the
video sequence. Two different tracking methods have
been considered to study their influence in the final
image reconstruction and to obtain a robust DR sys-
tem. A battery of experiments has demosntrated a
substantial saving in the computational cost (several
orders of magnitude), while maintaining the visual
perception quality at acceptable levels. The use of
parallel computing techniques is an issue that will be
addressed in the future.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partially funded with a Torres
Quevedo grant from the Ministry of Economy and
Competitiveness of the government of Spain.
REFERENCES
Barnes, C., Shechtman, E., Finkelstein, A., and Goldman,
D. (2009). Patchmatch: A randomized correspon-
dence algorithm for structural image editing. ACM
Transactions on Graphics-TOG, 28(3):24.
Bertalmio, M., Sapiro, G., Caselles, V., and Ballester, C.
(2000). Image inpainting. In Proceedings of the 27th
annual conference on Computer graphics and interac-
tive techniques, pages 417–424. ACM Press/Addison-
Wesley Publishing Co.
Bouguet, J.-Y. (2001). Pyramidal implementation of the
affine lucas kanade feature tracker description of the
algorithm. Intel Corporation, 5(1-10):4.
Bradski, G. R. (1998). Real time face and object tracking
as a component of a perceptual user interface. In Ap-
plications of Computer Vision, 1998. WACV’98. Pro-
ceedings., Fourth IEEE Workshop on, pages 214–219.
IEEE.
Criminisi, A., P
´
erez, P., and Toyama, K. (2004). Region
filling and object removal by exemplar-based image
inpainting. Image Processing, IEEE Transactions on,
13(9):1200–1212.
Fischler, M. A. and Bolles, R. C. (1981). Random sample
consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with appli-
cations to image analysis and automated cartography.
Commun. ACM, 24(6):381–395.
Google Inc. (2013). Google AR Glasses. http://
www.google.es/glass/start/.
Goyal, P., Diwakar, S., et al. (2010). Fast and enhanced
algorithm for exemplar based image inpainting. In
Image and Video Technology (PSIVT), 2010 Fourth
Pacific-Rim Symposium on, pages 325–330. IEEE.
Herling, J. and Broll, W. (2010). Advanced self-contained
object removal for realizing real-time diminished real-
ity in unconstrained environments. In Mixed and Aug-
mented Reality (ISMAR), 2010 9th IEEE International
Symposium on, pages 207–212. IEEE.
Herling, J. and Broll, W. (2012). Pixmix: A real-time ap-
proach to high-quality diminished reality. In Mixed
and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), 2012 IEEE Interna-
tional Symposium on, pages 141–150. IEEE.
Itseez (2016). Open source computer vision library.
https://github.com/itseez/opencv.
Kass, M., Witkin, A., and Terzopoulos, D. (1988). Snakes:
Active contour models. International journal of com-
puter vision, 1(4):321–331.
Kawai, N., Sato, T., and Yokoya, N. (2013a). Diminished
reality considering background structures. In Mixed
and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), 2013 IEEE Interna-
tional Symposium on, pages 259–260. IEEE.
Kawai, N., Yamasaki, M., Sato, T., and Yokoya, N. (2013b).
[paper] diminished reality for ar marker hiding based
on image inpainting with reflection of luminance
changes. ITE Transactions on Media Technology and
Applications, 1(4):343–353.
Komodakis, N. and Tziritas, G. (2007). Image completion
using efficient belief propagation via priority schedul-
ing and dynamic pruning. Image Processing, IEEE
Transactions on, 16(11):2649–2661.
Lepetit, V., Berger, M.-O., and Lorraine, L.-I. (2001). An
intuitive tool for outlining objects in video sequences:
Applications to augmented and diminished reality. tC,
2:t3.
Liu, Y. and Caselles, V. (2013). Exemplar-based image in-
painting using multiscale graph cuts. Image Process-
ing, IEEE Transactions on, 22(5):1699–1711.
Lucas, B. D., Kanade, T., et al. (1981). An iterative image
registration technique with an application to stereo vi-
sion. In IJCAI, volume 81, pages 674–679.
Rahul Verma (2013). Inpainting algorithm source. https://
github.com/surahul/Inpaint.
Rosten, E. and Drummond, T. (2005). Fusing points and
lines for high performance tracking. In In Tenth IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision, pages
1508–1515.
Simakov, D., Caspi, Y., Shechtman, E., and Irani, M.
(2008). Summarizing visual data using bidirectional
similarity. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion, 2008. CVPR 2008. IEEE Conference on, pages
1–8. IEEE.
Wexler, Y., Shechtman, E., and Irani, M. (2007). Space-time
completion of video. Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on, 29(3):463–476.
Zokai, S., Esteve, J., Genc, Y., and Navab, N. (2003). Multi-
view paraperspective projection model for diminished
reality. In Mixed and Augmented Reality, 2003. Pro-
ceedings. The Second IEEE and ACM International
Symposium on, pages 217–226. IEEE.
Towards a Diminished Reality System that Preserves Structures and Works in Real-time
343
