
Development of Instant Measuring Model for Oxygen Permeability
and Water Content of Hydrogel Contact Lens
Chih-Wei Hung
1
, Kuo-Cheng Huang
1
, Hsin-Yi Tsai
1
, Yu-Hsuan Lin
1
and Patrick Joi-Tsang Shum
2
1
Instrument Technology Research Center, National Applied Research Laboratories, 20,
R&D Rd. VI. Hsinchu Science Park, 30076, Hsinchu City, Taiwan
2
Department of Ophthalmology, Cathay General Hospital, No. 2, Ln. 59,
Jiancheng Rd., Xizhi Dist, 22174, New Taipei City, Taiwan
Keywords: Hydrogel Contact Lens, Oxygen Permeability, Water Content, Dehydration Rate.
Abstract: The diffusion coefficient D, gas solubility k of material and the thickness of lens t were used to evaluate the
oxygen permeability Dk/t of contact lenses (CLs). However, the nominal value Dk/t is usually not consistent
with the actual oxygen permeability of wearing CL. As the oxygen travel through the hydrogel, it need to be
carried by water molecules in the lens material; thus, the higher the water content (WC) of the material, the
higher the Dk/t value. In order to obtain the WC and Dk/t of wearing CL, we create a testing platform to
simulate the wearing status of CL. When the light traveled through the lens, we found that the attenuation in
green light is smoother than other wavelengths. Moreover, the WC is higher, its dewatering rate at room
temperature is lower, and the light attenuation is relatively smaller. Comparing with the other CL of similar
WC, the Dk/t of CL is higher if it has higher dehydration. In the study, we evaluated the WC and Dk/t of
hydrogel CL based on the light attenuation in eight minutes. The attenuation degree of light after traveling
through the CL can be used to estimate the Dk/t of hydrogel CL.
1 INTRODUCTION
The contact lens (CL) can be divided into soft CL and
hard CL based on their material hardness, wherein the
main material of soft CLs are hydrated polymer and
hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA), and the
traditional hard CL material are polymethyl metha-
crylate (PMMA). However, the PMMA was replaced
by the hydrophobic gas permeable material in recent
year. Because the soft CL is relatively soft, it is easily
attached to cornea; therefore, the patient will feel
more comfortable while wearing. However, the eyes
is prone to irritation or dryness if extended-wear CL,
because the eye covered by the CL is not easy to
contact with air. In addition, the high water content of
CL is readily to cause the microbial and bacterial
attachment, and a substantial increase of infection
rate in eyes, or even result in the proliferation of
capillaries around the eyes. On the contrary, the hard
CL will cause a foreign body sensation (FBS) in his
eyes when the patient begins to wear it, but has a
better correction effect for patients with high myopia
or astigmatism due to the smaller coverage area of
eye. Moreover, the hard CL which has a lower water
content is less susceptible to microbial and bacterial
attachment, so the infection rates of eyes dropped
significantly.
In accordance with (ISO-11539, 1999) standards
for the classification of soft CL, The CL material can
be classified by a six-part code. The category
classification is based on material composition,
oxygen permeability, etc., wherein the composition
can be distinguished depending on the compound of
silicon (Si) and fluorine (F) and the water content and
ionic monomers are also included. Hard CL can be
made from hexafocon, enflufocon or polymethyl
methacrylate (PMMA). Soft CL materials are mostly
2-hydroxy-ethyl methacrylate (HEMA), methacrylic
acid (MAA), methyl methacrylate (MMA), vinyl
pyrrolidone (VP), etc. (Tranoudis and Efron, 2004),
or can be stamper manufactured in different
proportions of these materials.
An important indicator to evaluate the quality of
CL is so-called oxygen permeability. In general, the
oxygen permeability of CL is denoted by Dk, where
D is the diffusion coefficient which represents the
ability of the gas diffusion through the CL material;
that is, the moving speed of the gas molecules in CL.
k is the solubility coefficient which indicates the
degree of dissolved oxygen in CL, and Dk is the
Hung C., Huang K., Tsai H., Lin Y. and Shum P.
Development of Instant Measuring Model for Oxygen Permeability and Water Content of Hydrogel Contact Lens.
DOI: 10.5220/0006107301750182
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology (PHOTOPTICS 2017), pages 175-182
ISBN: 978-989-758-223-3
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
175

product of the diffusion coefficient and solubility
coefficient. The units of Dk value are 10-11 (cm3 O2
cm)/ (cm3 sec mmHg) or "barrier". The higher is the
value of Dk, the better is the oxygen permeability of
CL. In addition, the Oxygen transmissibility (Dk/t) of
the local region of CL is expressed as oxygen
permeability (Dk) of the material of CL is divided by
the thickness (t) of CL.
There are two commonly methods to measure the
Dk or Dk/t of CL, the polarographic and coulometric
technologies (Fatt and Chaston, 1982, Refojo, et al.,
1977, Refojo and Leong, 1979, Brennan, et al., 1986,
Compañ, et al., 1996, Paterson and Doran, 1986 and
González-Méijome, et al., 2008). The polarographic
technique has often been used to determinate the Dk
coefficient of hydrogel CL, which placed directly on
the Clark-type electrode, based on the oxygen flux
through the CL. Practically, this technique has its
limitations during measuring Dk, such as the so-
called boundary-layer effect and edge effect in the
polarographic method. The boundary-layer effect
leads to the underestimation the Dk/t of sample due
to the difference of oxygen partial pressure on the two
side of sample. In addition, the edge effect means that
the lateral diffusion of oxygen occurs if the test area
is not the same on both sides of sample and results in
the Dk value of sample under test is slightly higher
than the real value. Despite these shortcomings in the
measurement of polarographic method, but it can use
some experimental procedure to amend its measured
value to close the actual value. For example, the
measuring values could be corrected by measuring
the samples of different thickness for the boundary-
layer effect (Compañ, 2002), or be multiplied by a
proper correction factor for the edge effect. In the
coulometric method, a nitrogen carrier gas flows
around the lens and transports the permeated oxygen
to the oxygen detector which produces an electrical
current, wherein the magnitude of oxygen through the
film is proportional to the amount of oxygen. The
oxygen gas transmits from upper chamber through
CL film into lower chamber during the permeability
process. However, the sample has a dehydration
effect during test when it exposed to air; therefore, the
coulometric method is not applied to the Dk
measurement of hydrogel CL because the water
content can cause changes in oxygen permeability.
The above mentioned two methods are both well
defined in the ISO standards (ISO 9913-1, 1996 and
ISO 9913-2, 2000), which also referred to the
restrictions on the use of two methods. The
polarographic method can only measure the CLs of
less than 100 Barrier, and the coulometric method
cannot be applied to the hydrogel CLs. However, the
polarographic (Fatt) and coulometric method in ISO
can be adopted to determinate the oxygen permeation
through all types of contact lenses, except the high Dk
silicone based CLs. Therefore, these standards 9913-
1&2 have now been withdrawn and replaced by (ISO
18369-3, 2006). The ISO 18369-3 specifies the
methods of testing the physicochemical properties of
CLs, which are extraction, rigid lens flexure and
breakage, oxygen permeability, refractive index and
water content. Therein, the soft CLs can also be made
of non-hydrogel materials, such as the silicone
elastomers. Based on the high performance liquid
chromatography (HPLC-EC), (Oberndorf and
Wilhelm, 2003) uses the reductive electrochemical
detection to determine oxygen at nanomolar levels,
the method had not only lens dehydration, but can
minimize the edge and boundary layer effects, the Dk
values of rigid and soft CL can be determined in the
same manner with good reproducibility. The above
mentioned measuring methods for oxygen
permeability of CLs are based on the electrochemical
or vacuum infiltration model, so the measuring results
are often not consistent due to the different measuring
method or instruments.
Therefore, this study presents a non-contact
method that can reduce the measurement error came
from the environment or instrument layout, and to
evaluate the WC and Dk/t of CL in different manner
from the absorption spectrum of CL. Therein, the full
wavelength of light was provided from the halogen
lamp, and the variation of light spectrum was
measured from the spectrometer that facing to the
light source. In addition, five types of CL with
different WC and Dk/t were employed to observe the
variation of intensity of transmission light in 8 minute
after wearing to the experimental setup.
2 FUNDEMENTAL THEORY AND
EXPERIMENT SYSTEM
2.1 Relationship between Water
Content and Oxygen Permeability
of Contact Lens
In general, the Dk/t of CLs is positive correlation to
the WC of CLs, (Hadassah and Sehgal, 2006)
presented a measurement that allowing the oxygen to
pass through the lens material and investigate the
oxygen permeability and transmissibility of contact
lenses of different thickness and curvature. Therein,
the expelled oxygen gas was collected by the
dissolution in ethanol and measured by the titration of
PHOTOPTICS 2017 - 5th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
176
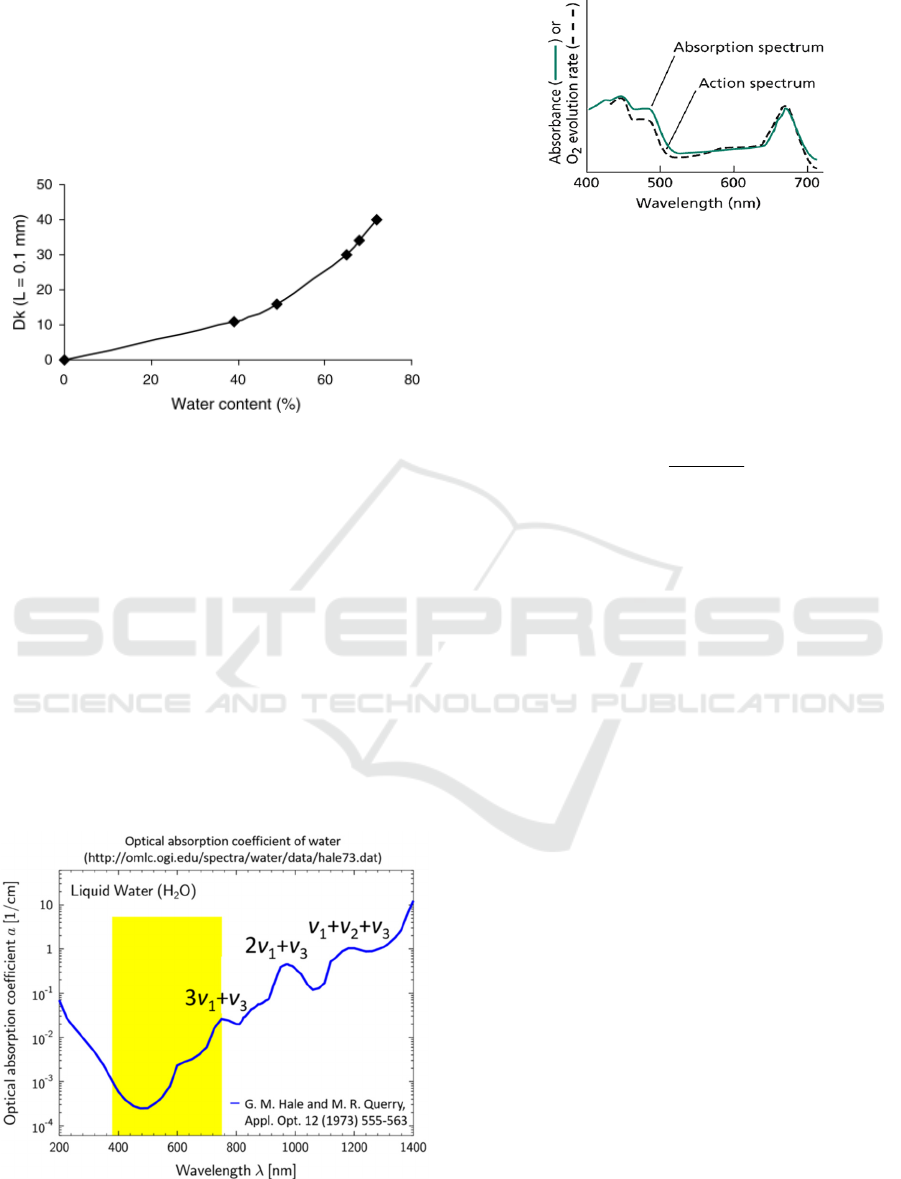
solvent, and this method could be employed in both
dry and wet conditions of lenses. The results showed
that the Dk value was directly proportional to the WC
of lens and inversely proportional to the thickness of
lens, shown as Fig. 1. Therefore, the WC of CLs while
wearing could be used to evaluate the oxygen
permeability of CLs.
Figure 1: Dk values of lens related to the water content.
(Hadassah and Sehgal, 2006).
2.2 The Spectrum of Oxygen and
Water Absorption
The substances have different light absorption,
reflectively and transmission while irradiated by the
light. (Hale and Querry, 1973) developed that the
relatively lower and stable absorption of light at
wavelength of 400-600 nm, shown as Fig. 2. In
addition, the oxygen also has lower absorbance and
O
2
evolution rate at wavelength of 500 – 650 nm,
shown as Fig. 3. Therefore, the intensity at
wavelength of 500 – 600 nm was analyzed to
investigate the variation of WC and Dk value while
wearing different CLs.
Figure 2: Absorption spectra of water. (Prahl, 2009).
Figure 3: Absorption and action spectrum of oxygen. (Taiz
and Zieger, 2015).
2.3 Development of Mathematical
Model
The attenuation (κ) of light intensity was determined
by intensity variation between without CLs (I
Ini
) and
wearing CLs (I
CL
), and which was expressed as (1).
Ini
CLIni
I
II −
=(%)κ
(1)
The κ increase with the increase of WC due to the
CLs with high WC need more water to maintain its
properties. Therefore, the WC of wearing CLs could
be calculated when
κ
ave
of each CLs in a period was
obtained, and the relationship could be expressed as
(2).
2
111
κκ(%) WC
aveave
×+×+=
γβα
(2)
where α
1
, β
1
, and γ
1
was the coefficient. In addition,
the variation (V
κ
) between the maximum and
minimum κ in a period also could be evaluated by
WC, and written as (3),
3
2
2
222κ
WC δWCWC(%) V ×+×+×+=
γβα
(3)
where α
2
, β
2
, γ
2
and δ
2
was the coefficient. Moreover,
the oxygen permeability (Dk/t) of wearing CLs could
be evaluated simultaneously from the variation
attenuation of each CLs by Eqn. (4),
2
κ3κ33
/D VVtk ×+×+=
γβα
(4)
where α
3
, β
3
, and γ
3
was the coefficient.
2.4 Layout of Measuring System
In order to measure the actually Dk value while
wearing CL, the optical measuring module was build
in this study, and several different CLs were put on
the measuring module to investigate the variation of
light intensity in a period of time. Thus, the measuring
results and the properties such as WC and Dk/t while
wearing CLs were discussed.
Development of Instant Measuring Model for Oxygen Permeability and Water Content of Hydrogel Contact Lens
177
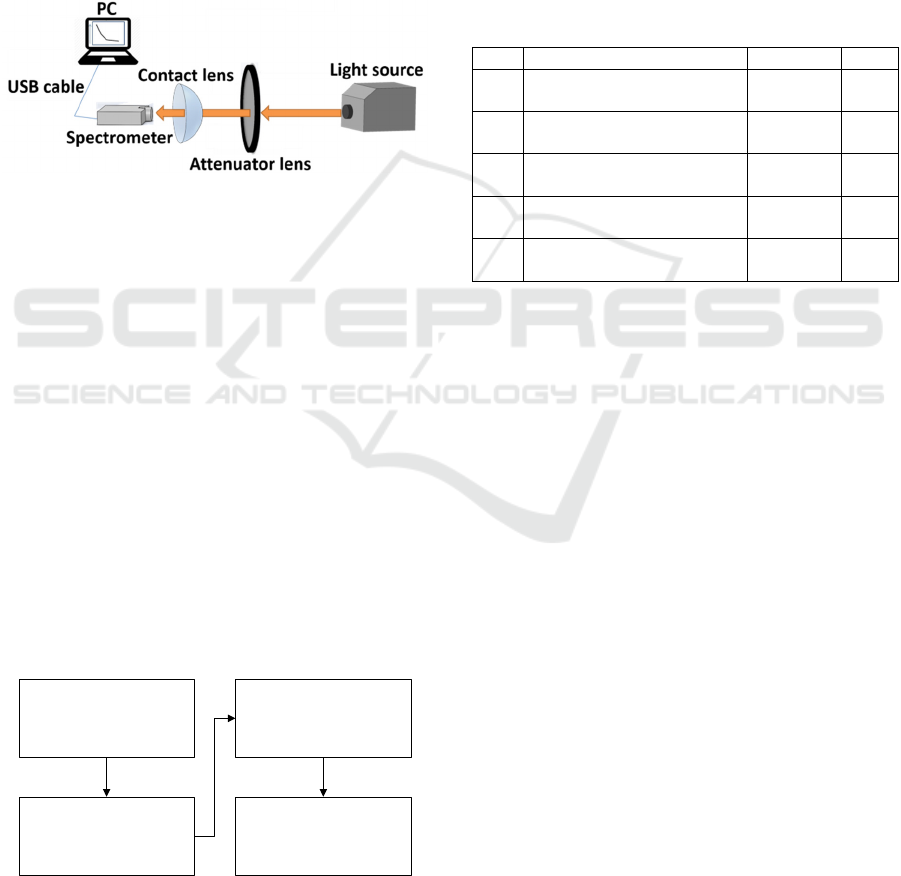
2.4.1 Setup of Experiment
In the experiment, the light source was the halogen
lamp with power of 150 watts, and the wavelength of
light ranged UV to NIR spectrum, especially 380 to
900 nm. A holder was fabricated by 3D printer to
place the CLs, and the SD1220-025-UVN spectro-
meter was placed at back of CLs and faced to the light
source to detect the transmission intensity of the light
beam. Therein, a 0.5D attenuator lens was used and
placed between the CLs and light source to decay the
light intensity that detected by spectrometer, shown
as Fig. 4.
Figure 4: Layout of the instant measuring setup for wearing
contact lens.
2.4.2 Process of Experiment
The experimental process was divided into four main
parts, shown as Fig. 5.
(1) Turned on the light source and fixed the light
intensity output from the light source by
controlling the current. In addition, connect the
spectrometer to the computer, and initialized the
spectrometer.
(2) Measure the transmission intensity directly from
the light source and 0.5D attenuator lens, and
determine the value as the reference; especially
without CLs on the holder.
(3) Put the tested CLs on the holder, and start to
count the time that exposed on the air.
(4) Measure the transmission intensity that through
the CLs, and save the date every 1 minute to
observe the variation of light intensity.
Measure transmission
intensity without CLs
Wearing CLs on
measuring setup
Measure transmission
intensity with CLs
(interval of 1 min)
Turn on light
source/spectrometer
Figure 5: Experimental process for measuring the Dk/t of
wearing CLs.
2.4.3 Preparation of Samples
In this study, five different types of CL from four
brands including NOIST, HYDRON, TICON and
BAUSCH+LOMB, and each of them has different
WC and Dk/t values, which were summarized in
Table 1. Therein, the samples of No. 1, 2, and 5 were
used to investigate the relationship of WC and decay
rate of spectrum, and the samples of No. 1, 3, and 4
with similar WC value were used to investigate the
relationship of the Dk/t and difference between
maximum and minimum of spectrum value in the
period of 8 minutes.
Table 1: Summarized of tested samples.
No. Brand/Model WC (%) Dk/t
1
MOIST/ACUVUE
1-day
58 33.3
2
HYDRON/Eye Secret
1-Day
38 26*
3
HYDRON/ UV Blocking
1-Day
55 30*
4
TICON/Hyaluronic Acid
1-Day
58 29
5
BAUSCH+LOMB/Bio true
1-Day
78 42
*: The maximum value in the interval.
3 EXPERIMENT RESULTS AND
DISCUSSIONS
The purpose of our research was to develop an
alternative to the conventional electrochemical or
vacuum infiltration method for measuring Dk/t values
of CL. To achieve our objective, we proposed an
optical technology, which offers the benefit of non-
contact skills and avoids measurement error with
different instrument that can lead the way to higher
reproducibility of measuring results. Four steps had
been taken in the experiment, so that we can evaluate
the WC and Dk/t by using the absorption spectrum of
CL.
3.1 Spectrum Intensity after Wearing
Contact Lenses
The first step of our research, three CLs with different
WC were measured using the non-contact optical
method as described in the formerly mentioned
section. The No. 1 CL had a WC of 38%, the No. 2
CL had a WC of 58% and the No.3 CL had a WC of
78%. Take the 38% WC of CL for example, the light
intensity of un-wearing CL and wearing CL can be
PHOTOPTICS 2017 - 5th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
178

shown in Fig. 6. The difference between the two
curves can also illustrated in Fig. 6. Because the
original data can’t offer enough information, the
attenuation of light was used to analyse in this study.
3.2 Light Attenuation after Wearing
Contact Lenses
The light attenuation of CL No. 2 can be shown in
Fig. 7. During the experiment, we found that the
curve of light absorption rate in UV light provide a
highly unstable status. This phenomenon may be
caused by the measuring precision of spectrometer in
300-400 wavelength range and the basic ability of
anti-ultraviolet of CL. The IR wave range in 890 to
900 nm had been chosen as standard originally,
because the study by Prahl (Prahl, n.d.) indicates that
there is a high absorption rate of water in IR light. The
relationship between light attenuation and water
content can be built up by this wave band of light.
Figure 6: The light intensity with and without wearing
contact lens.
Figure 7: The light attenuation after wearing contact lens
one minute and eight minutes. (the upper right corner is the
enlarged view of 500-600 nm).
Unfortunately, Fig. 6 shows that there is a trend to
descent in IR wavelength, so that we can’t use the
results as basic. On the other hand, in fig. 7, we also
found that the attenuation of light in green
wavelength (500-600 nm) was smoother than others.
This results are entirely consistent with Hale’s results
(Hale and Querry, 1973). So that we chose the light
ranged from 500-600 nm as the reference, the partial
enlarged view is illustrated in Fig. 7.
3.3 Calculation of Water Content
When the contact lens is wearing on the human eyes,
it needs to keep humid from tears by blinking eyes;
otherwise, the contact lens will dry off in a period of
time. In second step of our research, we found that
contact lens was tendency to dry out after 8 minutes
in our simulation model; then it provided error
information caused by the surface cracks. Therefore,
we averaged spectral attenuation from 1 to 8 minutes,
the formula of attenuation was determined in Eqn.
(1). Our results in Fig. 8 indicate that with increasing
water content of contact lens, there is an increase in
light attenuation. The average attenuation of CL with
78% WC was about 17.1% in 8 minutes; the average
attenuation of CL with 58% WC was about 8.3%, and
the average attenuation of CL with 38% WC was
about 5.2%. From this results, we concluded that the
higher water content, the more water in contact lens.
Water is like a blocked layer which can resists the
light to get through the CL. Therefore, we can use
light attenuation to estimate the WC of an unknown
contact lens by Eqn. (2) which is derived from Fig.1.
The correlation coefficient α
1,
β
1
, and γ
1
can be
calculated using Eqn. (2). Where
α
1
= -12.5025, β
1
=
11.64322 and γ
1
= -0.37138.
Figure 8: The fitting curve of the average attenuation and
water content.
Development of Instant Measuring Model for Oxygen Permeability and Water Content of Hydrogel Contact Lens
179

3.4 Calculation of Variation of Light
Attenuation
According to the knowledge in previous section, the
higher the WC of CL, the higher the Dk/t. However,
this linear relationship needs to be under ideal
conditions. When contact lens is worn on human eyes,
it will dry out along with the wearing time. Although
we blink several times to keep our eyes moist, it will
still discomfort when the CL becomes dry and the
WC isn’t maintaining the maximum value. From the
above reasons, we concluded that simple WC values
would not allow us to obtain the Dk/t values. In third
step of our research, we thus shift our attention to the
difference between maximum and minimum
attenuation of light in 8 minutes, the variation of light
attenuation can also be demonstrated in Fig. 8. In Fig.
9, the images show that the brand with 38% WC has
the highest difference value between max and min
attenuation rate. For each of the CLs, we found that
the WC increased with decreasing difference
attenuation. The difference was about 7 at 38% WC
of CL; the difference was about 4.5 at 58% of WC;
The difference was 3.8 at 78% of WC. The results
concept is intuitively and clear that the more water in
the CLs, the slower the moisture out of the CLs. The
equation of the difference of max and min attenuation
is express as Eqn. (3). Therefore, we can apply the
average of the attenuation in Eqn. (2), use the obtain
attenuation to calculate the water content. Then,
substituting WC in Eqn. (3) with Eqn. (2) yields the
relationship between WC and the difference of
maximum and minimum light attenuation. The value
of the difference attenuation was defined as a
correction factor in this research, which we can use
this factor to calculate Dk/t value in next section. The
correlation coefficient α
2
, β
2
, γ
2
and δ
2
can be
calculated using Eqn. (3). Where α
2
= 23.1557, β
2
= -
0.70445 and γ
2
= 0.00887 and δ
2
=-3.75×10
-5
.
Figure 9: The fitting curve between the variation of light
attenuation and water content.
3.5 Calculation of Oxygen Permeability
of Contact Lens
On the basic of the abstract discussed, when the
oxygen attempts to go through the material of
hydrogel, it needs to follow with water molecules in
the contact lenses; therefore, the higher the WC, the
higher the Dk/t. However, this research took two
kinds of popular CLs with both 58% WC to make a
comparison. It was found that, although the two kinds
of CLs shared the same WC, the Dk/t value of them
were totally different. So that, this research took a
correction factor that was derived by Eqn. (3) in
section 3.3 to solve the problem. During the
experiment, three brands of CLs with similar WC
were used to comparison in the fourth step of this
study. Sample No. 1, 3 and 4 in Table. 1 were used to
make comparison. Since the water content of the three
samples are not identical, the sample No. 3 with 55%
WC needs to be fixed. When Dk/t of CL is under 40,
there is a linear relationship between water content
and oxygen permeability that has been well described
by Hadassah (Hadassah and Sehgal, 2006). Due to the
relationship, Dk/t of sample No.3 can be corrected to
31.6, the revised values is illustrated in Table 2. Then,
the correction factor of section 3.3 were used as the
standard to establish the curve with Dk/t value.
Fig. 10 shows that the larger variation of light
attenuation, the larger the Dk/t value. The value of
light attenuation represents its hydrophobic ability.
When the hydrophobic ability is better, the oxygen
permeability is also higher. Use the results from
section 3.4, we can easily compute the Dk/t value by
the Eqn. (4).
In summary, from the above experiment results,
the model to collocate WC and Dk/t value has been
constructed. Eqn. (2) - (4) were used to calculated
WC and Dk/t by using light attenuation. The
correlation coefficient α
3
, β
3
, and γ
3
can be calculated
using Eqn. (4). Where α
3
= 3.9875, β
3
= 7.97879 and
γ
3
= -0.53788. Since the new contact lens is soaking in
the water and is not at wearing status, the results
Table 2: Similar to the water content of tested samples.
No. Brand/Model WC (%) Dk/t
1
MOIST/ACUVUE
1-day
58 33.3
3
HYDRON/ UV Blocking
1-Day
55 30
3*
HYDRON/ UV Blocking
1-Day (adjusted)
58* 31.6*
4
TICON/Hyaluronic Acid
1-Day
58 29
*: The value has been corrected.
PHOTOPTICS 2017 - 5th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
180

obtained from the equation are slightly different from
the data on contact lens box. The accuracy of WC and
Dk/t values that calculated by this research are up to
95% to the value that contact lenses are practically
worn on human eyes, as long as the contact lens WC
is ranged from 38% to 78% and make from hydrogel.
Figure 10: The fitting curve of light attenuation and oxygen
transmissibility.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The CLs has gradually become more popular among
patients due to the benefits of beauty and comfort.
However, the human cornea does not have blood
vessels and it obtains oxygen directly through the air,
so it causes corneal angiogenesis when the cornea
was in a hypoxic state for a long period of time, and
even would lead to aging and permanent damage of
the cornea if seriously hypoxia. Therefore, the CLs
manufacturers continue to develop the gas permeable
hydrogel CLs for patents without corneal irritation
effects after a periods of wearing. Nowadays, the
presented measuring methods for the Dk/t and WC of
CLs are almost based on the electrochemical reaction
or permeabilization within two chamber methods, and
the measuring results cannot state any instant datum
for user; therefore, this study presents an optical
method that can evaluate instantly the WC and Dk/t
of CL depended on the absorption spectrum of CL.
In the instant method, when the light travelled
through the lens, we measure the light attenuation of
500- 600nm wavelength within eight minutes to
comparison of five kinds of well-known product in
market. The hydrogel CL is placed in a specific
holder, and the both sides will be dehydrated at the
same time, so that the light attenuation through CL in
eight minutes is gradually stability. In the experiment,
we found that the WC is an important factor of light
attenuation; the average light attenuation is higher,
the WC of CL is higher and the variation of light
attenuation is also the larger in eight minutes. In
addition, the variation of light attenuation is larger,
the oxygen permeability is also greater while
compared with the CL of similar WC. Furthermore,
computed from the light attenuation and its variation
through CL, we can build a real-time measurement
model for CL’s performance. In future, we can add
thickness t as a correction factor to calculate the real
Dk/t of contact lens with different dioptres and the
instant WC and Dk/t of CL can be estimated from the
light reflection when the eyes wearing the CL.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported in part by the Ministry
of Science and Technology, Taiwan, under Grants
MOST 105-2221-E-492-016-
REFERENCES
ISO 11539: 1999. Ophthalmic Optics- Contact Lenses-
Classification of Contact Lenses and Contact Lens
Material.
Tranoudis, I., Efron, N., 2004. “Water properties of soft
contact lens materials”, Contact Lens Anterior Eye, 27,
193-208.
Fatt, I., Chaston, J., 1982. “Measurement of Oxygen
Transmissibility and Permeability of Hydrogel Lenses
and Materials”, Int. Contact Lens Clin, 9, 76-88.
Refojo, M. F., Holly, F. J., Leong, F. L., 1977.
“Permeability of Dissolved Oxygen through Contact
Lenses I. Cellulose Acetate Butyrate”, Contact
Intraocular Lens Medical J., 3, 27-33.
Refojo, M. F., Leong, F. L., 1979. “Water-Dissolved-
Oxygen Permeability Coefficients of Hydrogel
Contact-Lenses and Boundary-Layer Effects”, J.
Membr. Sci., 4, 415-426.
Brennan, N., Efron, N., Holden, B. A., 1986. “Oxygen
Permeability of Hard Gas Permeable Contact Lens
Materials”, Clin. Exp. Optom., 69, 82-89.
Compañ, V., Villar, M. A., Vallés, E. M., Riande, E., 1996.
“Permeability and Diffusional Studies on Silicone
Polymer Networks with Controlled Dangling Chains”.
Polymer, 37, 101-107.
Paterson, R., Doran, P. A., 1986. “Spray Technique for the
Determination of Membrane Diffusion and Distribution
Coefficients by the Time-Lag Method: Evaluated for
Electrolyte Transport through Charged and Uncharged
Membranes”, J. Membr. Sci., 26, 289-301.
González-Méijome, J. M., Compañ-Moreno,V., Riande, E.,
2008. “Determination of oxygen permeability in soft
contact lenses using a polarographic method:
estimation of relevant physiological parameters”,
Development of Instant Measuring Model for Oxygen Permeability and Water Content of Hydrogel Contact Lens
181

Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 47, 10,
3619-3629.
Compañ, V., Andrio, A., López-Alemany, A., Riande, E.,
Refojo, M. F., 2002. “Oxygen Permeability of
Hydrogel Contact Lenses with Organosilicon Moieties”,
Biomaterials, 23, 2767-2772.
ISO International Standard 9913-1: 1996. Optics and
optical instruments, Determination of Oxygen
Permeability and Transmissibility by the Fatt Method.
Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for
Standardization.
ISO International Standard 9913-2: 2000. Optics and
optical instruments, Determination of Oxygen
Permeability and Transmissibility by the Coulometric
Method. Geneva, Switzerland: International
Organization for Standardization.
ISO International Standard 18369-3: 2006. Ophthalmic
optics-Contact lenses. Part 3: Measurement methods.
Geneva: International Organization for Standardization.
Oberndorf, D., Wilhelm, M., 2003. “Determination of
oxygen permeability/transmissibility and storage of
contact lenses using HPLC with reductive
electrochemical detection in combination with
specifically designed sampling unit”, Anal. Chem. 75,
1374–1381.
Hadassah, J., Sehgal, P. K., 2006. “A novel method to
measure oxygen permeability and transmissibility of
contact lenses”, Clin. Exp. Optom., 89, 6, 374-380.
Hale, G. M., Querry, M. R., 1973, “Optical constants of
water in the 200nm to 200µm wavelength region”, Appl.
Opt., 12, 555-563.
Prahl, S., 2009, “Optical Absorption of Water”, Optical
Spectra, http://omlc.org/index.html.
Taiz, L., Zieger, E., 2015. Plant Physiology and
Development, Sinauer Associates, Inc.6th edition.
PHOTOPTICS 2017 - 5th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
182
