
fMRI and Voxel-based Morphometry in Detection of Early Stages of
Alzheimer's Disease
Andrey V. Sokolov
1,3
, Sergey V. Vorobyev
2
, Aleksandr Yu. Efimtcev
1,3
, Viacheslav S.
Dekan
1,3
,
Gennadiy E.
Trufanov
1,3
, Vladimir Yu. Lobzin
2
and Vladimir A. Fokin
1,3
1
Department of Radiology, Military Medical Academy n.a. S.M. Kirov, Klinicheskaya str., Saint-Petersburg, Russia
2
Department of Neurology, Military Medical Academy n.a. S.M. Kirov, Lesnoi pr., Saint-Petersburg, Russia
3
Department of Radiology, North-West Federal Medical Research Center n.a. V.A. Almazov, Akkuratova str.,
Saint-Petersburg, Russia
Keywords: Alzheimer’s Disease, Functional MRI, Voxel-based Morphometry.
Abstract: Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia in older adults. Loss of memory is the
usual first symptom and different brain regions are involved to this pathological process. The aim of the
study was to investigate the organization of cortical areas responsible for visual memory and determine
correlation between memory impairment and atrophy of memory specific brain regions in early stages of
AD. Voxel-based MR-morphometry was used to evaluate brain atrophy and functional MRI was used to
detect specific brain regions responsible to visual memory task in patients with Alzheimer's disease and in
control group. FMRI was performed on Siemens Magnetom Symphony (1.5 T ) with the use of Blood
Oxygenation Level Dependent technique (BOLD), based on distinctions of magnetic properties of
hemoglobin. For test stimuli we used blocks of 12 not related images for "Baseline" and 12 images with 6
presented before for "Active". Stimuli were presented 3 times with reduction of repeated images to 4 and 2.
For functional and morthometric data post-processing we used SPM8. Patients with Alzheimer's disease
showed less activation in hippocampal formation (HF) region and parahippocampal gyrus then the control
group (p<0.05). The study also showed reduced activation in posterior cingulate cortex (p<0.001). Voxel-
based morphometry showed significant atrophy of grey matter in Alzheimer’s disease patients, especially of
both temporal lobes (fusiform and parahippocampal gyri); frontal lobes (posterior cingulate and superior
frontal gyri). The study showed correlation between memory impairment and atrophy of memory specific
brain regions of frontal and medial temporal lobes. Reduced activation in hippocampal formation and
parahippocampal gyri, in posterior cingulate gyrus in patients with Alzheimer's disease correlates to
significant atrophy of these regions, detected by voxel-based morphometry. The use of functional MRI and
voxel-based morphometry provides the way to find alterations in brain function on early stages of AD
before the development of significant irreversible structural damage.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cognitive impairment is one of the most common
neurological disorders. Especially high prevalence
of neurological disease with clinical cognitive
impairment is among the senior people. 10-15% of
elderly people have severe cognitive impairment –
dementia. Dementia significantly reduces the quality
of life of patient and his family. Dementia causes
additional difficulties in the diagnosis and treatment
of opportunistic disease, and doctors have
difficulties in collecting anamnesis, assessment of
patient complaints. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the
most common form of dementia. Enormous number
of publications are devoted to cognitive disorders
research, based on the results of imaging studies.
Functional MRI (fMRI) and voxel-based
morphometry (VBM) open up new opportunities in
study of AD pathogenesis (Vasconcelos, L.G., 2011;
Odinak, M.M., 2011).
Different brain regions are involved to the
pathological process in AD irregularly. Primary
neuronal damage in the early stages of disease was
noted in the mediobasal parts of the frontal lobes of
the brain. Morphological changes are also defined in
the hippocampus, deep and posterior parts of
temporal and parietal lobes of the brain. The
Sokolov A., Vorobyev S., Efimtcev A., Dekan V., Trufanov G., Lobzin V. and Fokin V.
fMRI and Voxel-based Morphometry in Detection of Early Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease.
DOI: 10.5220/0006109600670071
In Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2017), pages 67-71
ISBN: 978-989-758-215-8
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
67

preferential involvement of mediobasal structures of
the temporal lobe in the pathological process have
been confirmed by numerous MRI studies, which
demonstrates significant hippocampus gray matter
atrophy in patients with Alzheimer's disease (Frisoni
G.B., 2008; Karas G.B., 2004; Zhang N., 2011).
More informative is to assess atrophy progression in
dynamics, and therefore morphometry of various
brain structures is used (Lobzin, V.Yu., 2013).
Alzheimer's disease is characterized by
progressive decline in memory. Functional MRI
allows to investigate alterations in brain function
before development of significant structural damage
(Bassett, S.S., 2006). Golby A. et al. (2005)
examined the functional competency of certain brain
regions and their relationship with specific
behavioural memory deficit in Alzheimer’s disease.
Results of fMRI resting state studies have so far
relatively consistently pointed to the early
involvement of posteromedial grey matter, such as
the posterior cingulum and precuneus (Pihlajamaki
M., 2008).
The purpose of this study was to evaluate brain
activation by visual memory task in patients with
Alzheimer's disease and to determine correlation
between memory impairment and atrophy of
memory specific brain regions of frontal and medial
temporal lobes.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Participants
We studied 27 patients with Alzheimer's disease
(mean age 69,6±8,9 years), 22 matched by age
(68,8±4,3 years) volunteers without evidence of
brain lesions for VBM, and 20 healthy volunteers
(35±5,1 years) for fMRI as a control group. Young
volunteers were chosen as a control group for fMRI
due to the absence of significant differences in
healthy individuals of different ages according to our
previous study (Odinak M.M. et al, 2011). Patients
with Alzheimer's disease underwent a course of
medical treatment in the neurological department of
Military Medical Academy. Their evaluation
included physical and neurological examination,
brain imaging (MRI), blood analysis, including
markers of inflammation, hormones, cholesterol and
APOE. All of them underwent neuropsychological
assessment to determine memory impairment,
attention, thinking, speech and visual-spatial
functions, using the following methods: Mini-
Mental State Examination (MMSE), Frontal
Assessment Battery (FAB), Free and Cued Selective
Reminding Test with Immediate Recall (FCSRT-
IR), Clock Drawing Test, Montreal Cognitive
Assessment (MoCA), Trail Making Test (TMT),
Digit-span task (forward and backward), Luria´s
Memory Words test (10 words), Digit Symbol
Substitution Test. The study included patients with
mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia. The
diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease was established
according to the NIA criteria (2011).
Each participant gave written informed consent
to participate in the study. The study was approved
by Ethics Committee of Military Medical Academy.
2.2 fMRI and VBM Data Acquisition
To investigate the organization of memory and
localize cortical areas activated by visual memory
task we used functional magnetic resonance imaging
and to evaluate brain atrophy of patients with
Alzheimer's disease voxel-based MRI morphometry
was performed. Conventional T1- and T2-weighted
images in three orthogonal planes were obtained
also.
fMRI was performed on 1.5 T MR-scanner
(Magnetom Symphony) with BOLD (Blood
Oxygenation Level Dependent) technique, that is
based on distinctions of magnetic properties of
haemoglobin. Functional MR images were acquired
using echo-planar imaging (EPI) with repetition time
(TR) = 3700 ms, echo time (TE) = 50 ms, flip angle
= 90º, field of view (FOV) = 230 mm and matrix
size 128*128. For test stimuli we used series of 12
not related images for "baseline" and 12 images with
for "active". 6 images in “active” period have been
already presented in “baseline”. Stimuli were
presented 3 times with reduction of repeated images
to 4 and 2. A finger switch response system was
used to collect patient responses.
To obtain high resolution images of whole brain
for Talairach coregistration and reslicing along
different planes, we used 3D MPRAGE
(Magnetization Prepared Rapid Acquisition Gradient
Echo) – T1-sequence with the following parameters:
repetition time (TR) = 2000 ms, echo time (TE) =
4,38 ms, flip angle = 10º, field of view (FOV) = 250
mm, 160 slices and matrix size 256*256.
2.3 fMRI and VBM Data
Post-processing
For functional data post-processing we used SPM8
(Welcome Department of Imaging Neuroscience,
University College, London, UK) software package
BIOIMAGING 2017 - 4th International Conference on Bioimaging
68
running under MATLAB R2010a (The Mathworks,
Sherborn, MA, USA) programming. For voxel-
based morphometry we used VBM toolbox of
SPM8. Template space was defined by standard EPI
template data in SPM (MNI coordinates - Montreal
neurologic Institute, McGill University, Montreal,
Canada).
VBM data were visualized with MRICron
(http://www.mccauslandcenter.sc.edu/mricro/mricro
n/), using Talairach atlas masks (Talairach and
Tournoux, 1988).
3 RESULTS
Examining each group separately, we found that
group of healthy volunteers showed activation of
cingulated gyrus (p<0.001). Cingulate gyrus plays
an essential role in memory formation and provide
intercommunications between brain regions.
Controls also showed statistically significant
activation in hippocampal formation (HF) and
parahippocampal gyrus and Broadman area 6 (BA6).
The function of BA6 is to organize complex motor
response while carrying out the instructions, in
particular the definition of "right" or "wrong"
stimulus. 80% of controls showed activation of
BA40, which plays the role in recognition of visual
images.
Group comparison analysis allows to identify
certain brain regions with different activation
patterns. Patients with Alzheimer's disease showed
less activation in hippocampal formation (HF) and
parahippocampal gyri comparing to healthy controls
group (p<0.05). The study also showed reduced
activation in posterior cingulate gyrus (p<0.001).
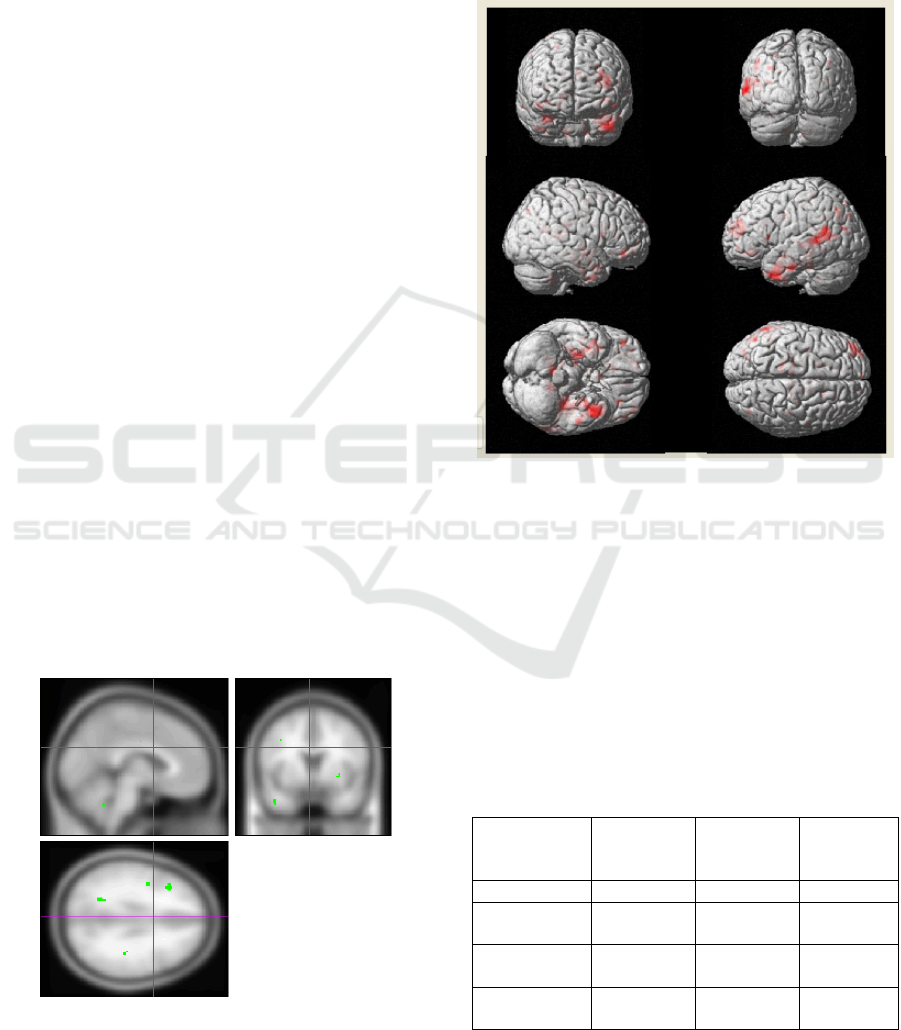
Figure 1: Reduced activation in posterior cingulated gyrus
and in hippocampal formation region in AD patients
(p<0.001).
The results demonstrate that a lot of different
brain regions participating in the differentiation of
the stimuli are involved. This corresponds to the
opinion, that the morphological substratum of higher
cortical functions is a set of combined functional
centers (Luria A., 1962), thereby confirming the
concept of dynamic functional localization.
Figure 2: Differences in activation between AD group and
healthy controls (three-dimensional volume-rendered
display).
Voxel-based morphometry showed significant
general atrophy of grey matter in AD patients,
especially of both temporal lobes (fusiform and
parahippocampal gyri), frontal lobes (and superior
frontal gyri), parietal lobes and cingulate gyrus.
However, the most significant changes were found
in mediobasal temporal lobe (up to 3.6 cm
3
at p
<0,01) and thalamuses (up to 4.5 cm
3
at p = 0,02).
Table 1: The values of volumes (cm
3
) of different brain
regions, based on MRICron analysis.
Cerebral
Region
AD
patients
group
Control
group
p-value
Frontal lobes 365,9±18,0 382,4±6,3 <0,01
Temporal
lobes
217,4±3,9 225,7±3,2 <0,01
Parietal
lobes
179,0±5,3 181,9±3,6 0,03
Hippocampal
region
3,6±0,5 3,9±0,1 <0,01
fMRI and Voxel-based Morphometry in Detection of Early Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
69
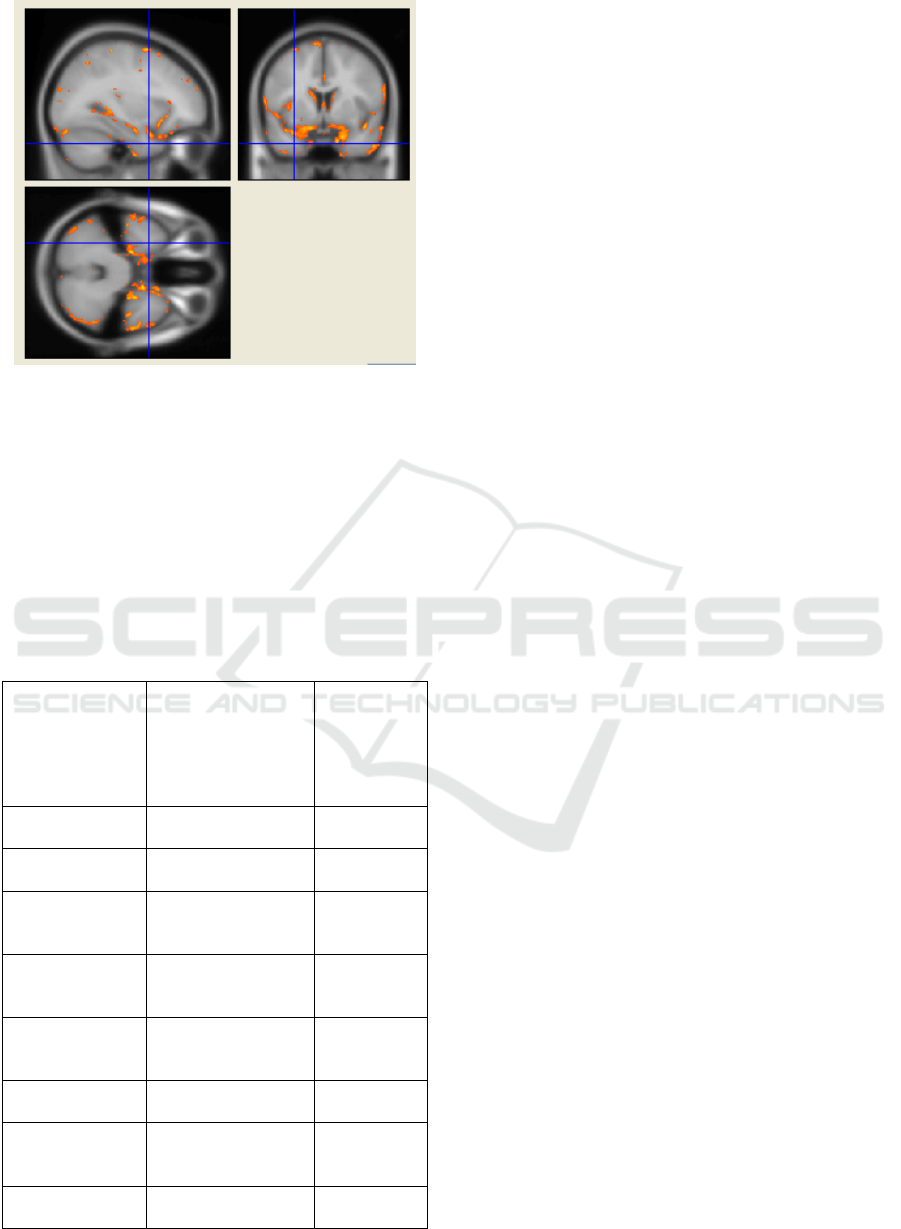
Figure 3: Brain atrophy in Alzheimer's disease patients
comparing to the control group (p<0.001).
In this study we identified patterns of cognitive
deficits of varying severity in accordance to the
volume changes of certain brain structures. For this
purpose, a correlation analysis was performed
comparing the results of neuropsychological
assessment and identified brain volumes. The most
significant correlations are shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Correlations between brain atrophy and
neuropsychological assessment.
Cerebral
Region
Neuropsychological
scale
Spearman's
rank
correlation
coefficient
(r),
p<0,05
Total gray
matter volume
MMSE orientation
subtest
0,56
Temporal lobe
MMSE total,
FCSRT-IR
0,57
0,56
Parietal lobe
MMSE
Luria´s Memory
Words test
0,44
0,53
Cingulate cortex
Luria´s Memory
Words test,
FCSRT-IR
0,85
0,86
Frontal lobe
MMSE total,
categorical verbal
fluency
0,51
0,43
Occipital lobe
TMT «А»
TMT «В»
– 0,86
– 0,78
Hippocampal
formation region
MMSE orientation
subtest,
FCSRT-IR
0,52
0,65
Thalamus
MMSE attention
subtest,
0,70
According to the correlation analysis there is a
decrease of certain brain structures volume
accompanied by deterioration of specific cognitive
functions. This was true for such intellectual-mental
functions such as memory, attention and thinking.
Atrophy of temporal and parietal lobes associated
with a reduction of scale results: MMSE (r = 0,57
and r = 0,54, respectively, at p <0,05) and 5 words
test (r = 0,53, p <0,05).
4 CONCLUSION
In summary, combined application of fMRI and
VBM allows to assess brain atrophy along with
functional component of memory impairment and
can help to detect Alzheimer's disease related
changes in early stages before they may be revealed
by means of conventional MRI study. The study
showed correlation between memory impairment
and atrophy of memory specific brain regions of
frontal and medial temporal lobes. Thus, reduced
activation in hippocampal formation and
parahippocampal gyri, in posterior cingulate gyrus in
patients with Alzheimer's disease correlates to
significant atrophy of these regions, detected by
voxel-based morphometry, and to deterioration of
specific cognitive functions. Obtained data
correspond to comprehensive conceptions of
pathogenesis and general clinical features of AD.
Combined fMRI and voxel-based morphometry
study can be used in clinical practice in patients with
AD and cognitive disorders.
REFERENCES
Bassett, S.S., 2006. Familial risk for Alzheimer’s disease
aters fMRI activation patterns. Brain 2006, 129, p.
1229-1239.
Frisoni G.B., 2008. The pilot European Alzheimer's
Disease Neuroimaging Initiative of the European
Alzheimer's Disease Consortium. Alzheimers Dement.
2008. 4(4):255-64.
Golby, A. et al, 2005. Memory encoding in Alzheimer’s
disease: an fMRI study of explicit and implicit
memory. Brain. 2005, 128, P. 773-787.
Karas G.B., 2004. Global and local gray matter loss in
mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease.
F.Neuroimage. 2004. 23(2):708-16.
Lobzin, V.Yu., 2013. Voxel-based morphometry in
Alzheimer’s disease and vascular cognitive
impairment. Vestnik Rossiiskoi Voenno-medicinskoi
Academii. 2013. № 3 (43). P. 48-54.
BIOIMAGING 2017 - 4th International Conference on Bioimaging
70

Luria A., 1962. Supreme human cortical functions.
Moscow, MGU, P 402.
Pihlajamaki, M., Sperling R.A., 2008. FMRI:use in early
Alzheimer’s disease and in clinical trials. Future
Neurology. 2008; 3(4): p. 409-421.
Odinak, M.M., Vorobyev S.V., 2011. Functional magnetic
resonance imaging as estimation method of state
cognitive functions. Vestnik Rossiiskoi Voenno-
medicinskoi Academii. 2011. № 4 (36). P. 7-13.
Talairach, J., 1988. Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the
human brain. Thieme, New York, 1988. – P. 122.
Vasconcelos, L.G., 2011. Voxel-based morphometry
findings in Alzheimer’s disease: neuropsychiatric
symptoms and disability correlations – preliminary
results. Clinics. 2011. Vol.66, № 6. P. 1045-1050.
Zhang N., 2011. An MRI brain atrophy and lesion index to
assess the progression of structural changes in
Alzheimer's disease, mild cognitive impairment, and
normal aging: a follow-up study. J Alzheimers Dis.
2011; 26 Suppl 3: 359-67.
fMRI and Voxel-based Morphometry in Detection of Early Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
71
