
Cuff-less Calibration-free Blood Pressure Estimation under
Ambulatory Environment using Pulse Wave Velocity and
Photoplethysmogram Signals
Haruyuki Sanuki
1
, Rui Fukui
1
, Tsukasa Inajima
2
and Shin'ichi Warisawa
1
1
Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 5-1-5 Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa-shi, Chiba 277-8563, Japan
2
The University of Tokyo Hospital, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8655, Japan
Keywords: Blood Pressure Monitoring, Pulse Wave Velocity, Photoplethysmogram, Electrocardiogram.
Abstract: This paper presents a blood pressure estimation method based on pulse wave velocity (PWV). Although
there are a variety of methods based on PWV to estimate blood pressure, most of them require calibration
per patient, and the patient has to remain still. The goal of our research is to develop a calibration-free blood
pressure estimation method that is applicable not only during rest but also during exercise. To accomplish
our goal, we extracted properties of blood vessels from photoplethysmogram (PPG) signals, and compared
several regression models, such as the deductive model based on blood vessel physics equation, and the
inductive model based on machine learning. Twenty-four participants performed exercise, measuring blood
pressure, electrocardiogram (ECG) and PPG. The best result showed that the mean error for the estimated
systolic blood pressure (SBP) against cuff-based blood pressure was 0.18 ± 8.68 mmHg. Although there
was not a big difference between the regression models, PWV and Augmentation Index are effective
features to estimate SBP. In addition to this, Heart Rate was effective only for the young men, and height
ratio of c-wave to a-wave of acceleration pulse wave might be effective for elderly men. These results
suggest that our proposed method has the potential for cuff-less calibration-free blood pressure estimation
which include measurements during rest and exercise.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the number of hypertension patients
has increased, and around 40% of adults aged 25 and
over were estimated to have hypertension (World
Health Organization, 2014). Hypertension can lead
to various diseases such as a life-threatening heart
disease, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), and renal
insufficiency. Since most people are not aware of
their hypertension, they are not treated in time.
Monitoring one's blood pressure is required for the
prevention, early detection, and early recovery of
hypertension.
However, single blood pressure measurement is
the mainstream in hospitals or at home. It is difficult
to monitor the changes of blood pressure, especially
indicators like short-term changes and changes
during the day, which are important to diagnose a
patient’s body. Moreover, white-coat hypertension,
which leads to high blood pressure when measured
in the medical environment, could cause
misdiagnosis. To diagnose and treat such patients
properly, continuous blood pressure monitoring is
required.
Nowadays, Ambulatory Blood Pressure
Monitoring (ABPM) is used for continuous blood
pressure measurement. Figure 1 shows ABPM
equipment. ABPM measures blood pressure by a
cuff every 15 minutes or so. It is rather
uncomfortable and the patient has to remain still.
Figure 1: ABPM equipment.
The method based on pulse wave velocity (PWV)
has been intensively studied because of its potential
42
Sanuki H., Fukui R., Inajima T. and Warisawa S.
Cuff-less Calibration-free Blood Pressure Estimation under Ambulatory Environment using Pulse Wave Velocity and Photoplethysmogram Signals.
DOI: 10.5220/0006112500420048
In Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2017), pages 42-48
ISBN: 978-989-758-212-7
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

for tracking blood pressure change continuously
without a cuff (Mukkamala et al., 2015). PWV is the
velocity of an arterial pulse propagating through the
arterial wall and can easily be calculated from Pulse
Transit Time (PTT). PTT is the time interval
between an R-wave peak of electrocardiogram
(ECG) and a particular point of
photoplethysmogram (PPG). PWV is obtained by
dividing distance from the heart to a particular
peripheral site by PTT.
Based on previous researches, a formula which
takes continuity equation and Navier-Stokes
equation estimates systolic blood pressure (SBP).
The formula is as follows (Lopez, 2010, Inajima,
2012).
(1)
is the pulse wave velocity, and coefficients b
1
and b
2
are parameters related to individual blood
vessel properties. Traditionally, the coefficients are
calibrated by measuring blood pressure and PWV
beforehand.
Gesche et al. established a model with PWV to
estimate systolic blood pressure (SBP) during
exercise with initial calibration, and the standard
deviation of estimation error (SD) was 10.1 mmHg
(Gesche, 2012). Ding et al. established a model with
PWV and photoplethysmogram intensity ratio to
estimate blood pressure during rest with initial
calibration, and SD was 5.21 mmHg for SBP and
4.06 mmHg for diastolic blood pressure (DBP) (Ding,
2015). Kauchuee et al. investigated the relationship
between PTT and blood pressure and found that non-
linear models are better than linear models.
Kachuee’s model without calibration during rest
achieved 16.17 mmHg for SBP and 8.45 mmHg for
DBP (Kachuee, 2015).
Although there are a variety of methods based on
PWV to estimate blood pressure, the application of
the PWV-based method has several problems. First,
individual blood vessel properties differ from person
to person. Most of the methods, therefore, require
calibration per person. Secondly, current methods
still lack application during exercise. Thirdly, there
is not enough accuracy of blood pressure
measurement based on PWV for medical use.
The objective of our study is to establish a
calibration-free blood pressure estimation method
based on PWV during rest and exercise. To achieve
the objective, we extracted properties of blood
vessels from photoplethysmogram (PPG) signals and
compared several regression models, such as the
deductive model based on blood vessel physics
equation and the inductive model based on machine
learning.
In this research, we focused on SBP that is
superior to Diastolic blood pressure as a predictor of
CVDs (Mourad, 2008).
This paper is organized as follows. Chapter 2
shows an overview of our methodology including
peak detection method, feature extraction, regression
models and evaluation method. Chapter 3 explains
the experiment, and Chapter 4 describes the result.
Lastly, Chapter 5 is the conclusion of this research
and future perspectives.
2 METHOD
Our method estimates SBP by using ECG and PPG.
The method is demonstrated in Figure 2. While
extracting features from ECG and PPG signals, we
use peak detection to extract features automatically.
Therefore, we first explain the peak detection
method before feature extraction.
Figure 2: Overview of the method to estimate SBP.
2.1 Peak Detection
In order to extract features from ECG and PPG
signals automatically, we need to build a robust
pattern-matching model. Therefore, we applied
Continuous Wavelet Transform (CWT), which is
widely used for R spike detection (Legarreta, 2005)
and PPG waveform analysis (Fan, 2011). The
Mexican Hat wavelet was selected as the mother
wavelet, because of its similarity with the ECG and
PPG signals (Daubechies, 1992). We found optimal
scales for each signal using annotations provided on
small data. Figure 3 shows an R spike detection of
ECG signal, and Figure 4 shows a foot point
detection of PPG signal.
Cuff-less Calibration-free Blood Pressure Estimation under Ambulatory Environment using Pulse Wave Velocity and Photoplethysmogram
Signals
43

Figure 3: R spike detection of ECG signal.
Figure 4: Foot point detection of PPG signal.
2.2 Feature Extraction
We extract Heart Rate (HR) from ECG signal, PPG
features from PPG signal, and PWV from ECG and
PPG signals.
2.2.1 PWV and HR
PWV was calculated by dividing the participant's
height by time interval between R-wave peak of
ECG and three points of PPG, which are the steepest
slope of the corresponding upstroke (PWV
m
), the
maximum point (PWV
p
), and the minimum point
(PWV
b
), as shown in Figure 5. HR is calculated by
the time interval between the nearest R spikes.
Figure 5: Definition of each PWV.
2.2.2 PPG Features
The PPG signal reflects the blood volume of the
vessel, measured by red, green or infrared light,
which is irradiated into the tissue and is absorbed or
reflected. The features extracted from PPG signal
have relationships with blood vessel conditions
(Elgendi, 2012). Most researches extract features
from velocity pulse waves (first derivative) and
acceleration pulse waves (second derivative) of the
PPG signal to interpret the original PPG signal
(Takazawa, 1998). In this research, features are
extracted from volume pulse waves and acceleration
pulse waves.
In volume pulse waves, Inflection Point Area
Ratio (IPA), Augmentation Index (AI), Crest Time
(CT), and Large Artery Stiffness Index (LASI) are
extracted.
Inflection Point Area Ratio (IPA): IPA is the
ratio of the four pulse areas between the
selected points, S1, S2, S3 and S4, which are
shown in Figure 6. IPA is used as an indicator
of the total peripheral resistance (Wang, 2009).
In this research, it is proposed to use the ratio
of S2, S3, and S4 to S1.
Figure 6: Definition of S1, S2, S3 and S4.
Augmentation Index (AI): AI is the ratio of the
height of the diastolic peak to height of the
systolic peak (Figure 7). AI is a measure of the
wave reflection and arterial stiffness
(Takazawa, 1998).
Crest Time (CT): CT is the time interval
between the foot point and the systolic peak
(Figure 7). CT is an important feature for
classifying cardiovascular diseases (Alty,
2007).
Large Artery Stiffness Index (LASI): LASI is
the time interval between the systolic peak and
the diastolic peak (Figure 7). LASI is related
to large artery stiffness (Elgendi, 2012).
Figure 7: Definition of AI, CT, and LASI.
BIOSIGNALS 2017 - 10th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
44
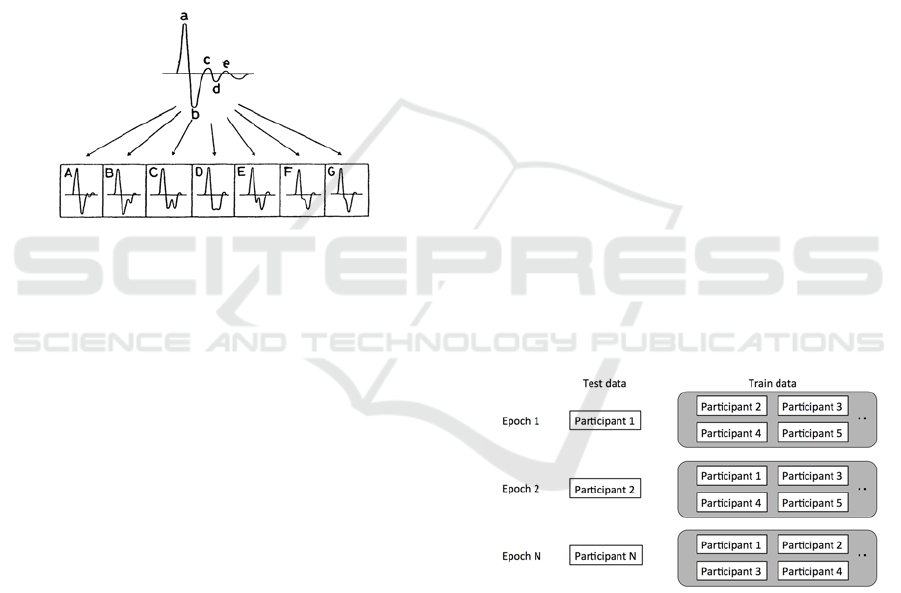
As Figure 8 shows, an acceleration pulse wave
includes five component waves, namely a-wave, b-
wave, c-wave, d-wave and e-wave. The type of
acceleration pulse waveform varies depending on the
blood vessel conditions. The height ratios and the
time intervals of each wave are extracted.
Height ratio b/a, c/a, d/a, e/a; each height ratio
reflects arterial stiffness. If arterial stiffness
increased, b/a would increase and c/a, d/a, e/a
would decrease (Takazawa, 1998).
Time interval between a-wave and b-wave
(a_b), a-wave and c-wave (a_c), a-wave and d-
wave (a_d), a-wave and e-wave (a_e). Time
interval of each wave describes acceleration
pulse waveform.
Figure 8: Acceleration pulse wave waveform. Waveform
differs depending on the vascular status (Homma, 1992).
In this research, features are selected in each
regression model by greedy forward selection
(Caruana, 1994).
2.3 Regression Model
In this research, two main approaches are taken to
choose a better regression model. One is the
deductive model based on blood vessel physics
equation, which is represented as Eq. (1), while the
other is the inductive model based on machine
learning.
2.3.1 Model based on Physics Equation
As shown in Eq. (2), the extracted features determine
individual blood vessel condition parameters b
1
and
b
2
. We use PWV
m
as pulse wave velocity in Eq. (2).
⋯
⋯)
(2)
is the partial regression coefficient and
is the
extracted feature. We named this model as LR.
2.3.2 Model based on Machine Learning
We use the inductive model based on machine
learning, not using a hypothesis but learning only
from the data.
Three regression models are selected, K-Nearest
Neighbours (KNN), Random Forest (RF) and Linear
Support Vector Machine (SVM).
K-Nearest Neighbours (KNN): KNN is the
simplest nonparametric decision procedure,
and predicts a sample data by using its K-
nearest neighbors (Cover, 1967).
Random Forest (RF): RF is a combination of
tree predictors, such that each tree depends on
the values of random features sampled
independently and with the same distribution
for all trees in the forest (Breiman, 2001).
Linear Support Vector Machine (SVM): SVM
is the algorithm that maximizes the margin
between the training patterns and the decision
boundary, and is widely used for classification
and regression problems (B. E. Boser, 1992).
Each hyper-parameter is optimized by cross
validation.
2.4 Evaluation
As shown in Figure 9, in order to evaluate the
accuracy without any individual dependency, each
participant's data is taken out as test data in turn, and
is evaluated with the data of remaining train data.
Figure 9: Cross-validation for independent validation.
Though it is better to split data into three sets, which
are training data, validation data and test data, we
will split data into two sets, train data and test data,
because of the small sample size.
3 EXPERIMENTS
We conducted experiments on 18 young men
(22.9±1.2 years) and six elderly men (43.3±9.3
Cuff-less Calibration-free Blood Pressure Estimation under Ambulatory Environment using Pulse Wave Velocity and Photoplethysmogram
Signals
45

years). All participants underwent an exercise test for
28 minutes on a bicycle ergometer, and four
minutes of rest before and after the test, acquiring
ECG, PPG and SBP by sphygmomanometer. The
timing of load increase and decrease is shown in
Figure 10. The load was adjusted corresponding to
their exercise capacity.
Participants wear the ECG sensor surrounding
the heart, PPG sensor at the right index finger, and a
sphygmomanometer with a cuff (Tango M2 from
SunTech Medical) on the left arm. SBP was
measured every two minutes by a cuff and the
sampling rate of ECG and PPG measurements were
both at 1 kHz. ECG and PPG signals are sampled at
the same time with same microcomputer that would
guarantee the synchronization. As a reference,
participants wear PPG sensor at the right earlobe and
finger cuff (ClearSight from Edwards Lifesciences)
on the right middle finger. Figure 11 shows a
schematic of the experimental set-up. All the
participants gave their informed consent prior to the
experiment.
Figure 10: Exercise weight transition.
Figure 11: Schematic of the experimental set-up.
4 RESULTS
The SBP distribution histogram is shown in Figure
12, including 341 SBP measurements. The mean
SBP measured by the sphygmomanometer was
128.05±16.90 mmHg.
Figure 12: Histogram of SBP measurements.
We defined two groups, Group A only contains
young men and Group B contains both, young and
elderly men. The reason for not grouping elderly
men is that the sample size was not large enough.
The results from various regression models are
shown in Table 1. Although KNN showed the best
regression model for estimating SBP, there was not a
big difference between the deductive model based on
blood vessel physics equation and the inductive
model based on machine learning.
Table 1: Standard Deviation of estimation error for each
regression model.
LR KNN SVM RF
Group A [mmHg] 8.68 8.65 8.74 9.28
Group B [mmHg] 8.79 8.68 8.75 9.20
Table 2 shows the feature subset that is selected by
each regression model and Eq. (3) shows the
deductive model based on the blood vessel physics
equation. While PWV is an important feature in each
group, as expected, AI also appeared to be an
important feature. HR is only effective for young
men, and the height ratio of c-wave to a-wave of
acceleration pulse wave might be effective for
elderly men.
Group A
13.0 1.83/1
3.3+125.9
Group B
0.3/ 11.2
4.8+128.0
(3)
Hereinafter, KNN is selected as the most accurate in
the regression model evaluation, according to Table
2. Figure 13 shows the plot of cuff-based SBP and
estimated SBP of Group B, and the correlation
coefficient was r=0.86 (p-value<0.01). Figure 14
gives the Bland-Altman plot, comparing for the
BIOSIGNALS 2017 - 10th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
46

Table 2: The feature subset that is selected by greedy forward selection in each regression model. Group A is the young
men group and Group B is the young and elderly men group. ○ is the selected feature.
PWV
b
PWV
m
PWV
p
HR
IPA
(S2/S1, S3/S1, S4/S1)
AI CT LASI
Height ratio
(b/a, c/a, d/a, e/a)
Time interval
(a_b, a_c, a_d, a_e)
A
LR
-
-
-
HR × PWV
m
2
S3/S1 × PWV
m
2
○
-
-
-
-
KNN
○
○
-
○
-
○
-
-
-
a_b
SVM
-
○
-
○
-
○
-
○
-
a_c, a_e
RF
-
○
-
○
-
○
-
-
-
-
B
LR
-
○
-
-
-
○
-
-
c/a × PWV
m
2
-
KNN
○
○
-
-
-
○
-
-
e/a
-
SVM
○
○
-
-
-
○
-
-
c/a a_e
RF
-
○
-
-
-
○
-
-
c/a
-
performance of the proposed method with the cuff-
based measurements of Group B. A total of 94.73%
of the measurements lies in the limits of agreement
(1.96×SD).
Figure 13: Correlation plot of SBP.
Figure 14: Bland-Altman plot of SBP.
Our proposed model for Group B, which contains
young and elderly men, showed that the mean error
was 0.18±8.68 mmHg, and the mean absolute
difference (MAD) was 6.93 mmHg, achieving grade
C as IEEE standard requirement (IEEE Standards
Association, 2014).
5 DISCUSSIONS
Previous researches show an effective model with
initial calibration during rest or exercise. The present
study proposed the calibration-free blood pressure
estimation method based on PWV during rest and
exercise and the method achieved grade C as IEEE
standard requirement. Moreover, we showed that
PPG features, especially AI, are effective to estimate
SBP. Although we tried to find the cause of large
error lying out of the limits of the agreement in
particular subjects, we were not able to find it out
because of the small sample size.
Some limitations remain in this research. One is
that our proposed model are validated by cuff-based
blood pressure but should be validated by invasive
arterial blood pressure. Furthermore, the proposed
model applied to 18 young men (22.9±1.2 years) and
6 elderly men (43.3±9.3 years), which is not enough
to pass the standard requirement. Finally, the
situation is limited to rest and specific exercise
compared to ambulatory environment.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this research, we presented a calibration-free
blood pressure estimation method under ambulatory
environment. Using PPG features, especially AI,
enhances the accuracy of blood pressure estimation.
HR is only effective to estimate SBP for young men,
and height ratio of c-wave to a-wave of acceleration
pulse wave might be effective in elderly men.
According to the IEEE standard, the proposed
method achieved grade C in the SBP estimation.
In order to apply our method to daily use, we
have to address some issues.
Validation should be conducted with a larger
sample size, including female participants,
elderly participants and hypertensive patients,
Cuff-less Calibration-free Blood Pressure Estimation under Ambulatory Environment using Pulse Wave Velocity and Photoplethysmogram
Signals
47

to pass the standard requirement and to
investigate the difference between the
hypertensive participants and non-
hypertensive participants as well as the elderly
participants and the young participants.
Although we considered the situation of rest
and exercise, other situations that could cause
blood pressure changes, such as stressful
situations, should be taken into account.
Motion artifact can obscure the waveform of
PPG signals obtained from the hand for daily
use. Therefore, obtaining PPG signal from
different specific portions of a body that are
less affected by motion artifact should be
considered.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was supported by Pacific Medico Co.
for providing ECG and PPG measurement devices.
REFERENCES
Alty, S., Angarita, J. N., Millasseau, S., Chowienczyk P.,
2007. Predicting arterial stiffness from the digital
volume pulse waveform. IEEE Transactions on
Biomedical Engineering, 54(12), pp.2268–2275.
Boser, B. E., Guyon, I. M., Vapnik, V.N., 1992. A training
algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. Proceedings
of the fifth annual workshop on Computational
learning theory - COLT '92, pp.144-152.
Breiman, L., 2001. Random forests. Machine Learning,
45(1), pp. 5-32.
Caruana, R. Freitag, D., 1994. Greedy attribute selection.
Machine Learning Proceedings 1994, pp.28–36.
Cover, T. M., Hart, P. E., 1967. Nearest neighbor pattern
classification. IEEE Transactions on Information
Theory, 13(1), pp.21-27.
Daubechies, I., 1992. Ten lectures on wavelets. Society for
Industrial and Applied Mathematics Philadelphia, PA.
Ding, X. R., Zhang, Y. T., Liu, J., Dai, W. X., Tsang, H.
K., 2016. Continuous cuffless blood pressure
estimation using pulse transit time and
photoplethysmogram intensity ratio. IEEE
Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 63(5),
pp.964–972.
Elgendi, M., 2012. On the analysis of fingertip
photoplethysmogram Signals. Current Cardiology
Reviews, 8(1), pp.14–25.
Fan, Z., Zhang, G., Liao, S., 2011.Pulse wave analysis.
Advanced Biomedical Engineering, pp.21-40.
Gesche, H., Grosskurth, D., Kuchler, G., Patzak, A., 2012.
Continuous blood pressure measurement by using the
pulse transit time: comparison to a cuff-based method.
European Journal of Applied Physiology, 112(1),
pp.309–315.
Homma, S., Ito, S., Koto, T., Ikegami, H., 1992.
Relationship between accelerated plethysmogram,
blood pressure and arteriolar elasticity. Japanese
Journal of Physical Fitness and Sports Medicine,
41(1), pp.98–107.
Inajima, T., Imai, Y., Shuzo, M., Lopez, G., Yanagimoto,
S., Iijima, Katsuya, Morita, H., Nagai, R., Yahagi, N.,
Yamada, I., 2012. Relation between blood pressure
estimated by pulse wave velocity and directly
measured arterial pressure. Journal of Robotics and
Mechatronics, 24(5), pp.811-819.
IEEE Standards Association, 2014. IEEE standard for
wearable, cuffless blood pressure measuring devices.
Kachuee, M., Kiani, M. M., Mohammadzade H., Shabany
M., 2015. Cuff-less high-accuracy calibration-free
blood pressure estimation using pulse transit time.
2015 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and
Systems (ISCAS).
Legarreta, I.R., Addison, P. S., Reed, M. J., Grubb, N.,
Clegg, G. R., Robertson, C. E., Watson, J. N., 2005.
Continuous wavelet Transform modulus maxima
analysis of the electrocardiogram: beat characterisation
and beat-to-beat measurement. International Journal
of Wavelets, Multiresolution and Information
Processing, 03(01), pp.19–42.
Lopez, G., Shuzo, M., Ushida, H., Hidaka, K.,
Yanagimoto, S., Imai, Y., Kosaka, A., Delaunay, J. J.,
Yamada, I., 2010. Continuous blood pressure
monitoring in daily life. Journal of Advanced
Mechanical Design, Systems, and Manufacturing, 4(1),
pp.179–186.
Mourad, J.J., 2008. The evolution of systolic blood
pressure as a strong predictor of cardiovascular risk
and the effectiveness of fixed-dose ARB/CCB
combinations in lowering levels of this preferential
target. Vasc Health Risk Manag, 4(6), pp.1315–1325.
Mukkamala, R., Hahn, J., Inan, O. T., Mestha, L. K., Kim,
C., Toreyin, H., Kyal, S., 2015. Toward ubiquitous
blood pressure monitoring via pulse transit time:
theory and practice. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical
Engineering, 62(8), pp.1879–1901.
Takazawa, K., Tanaka, N., Fujita, M., Matsuoka, O., Saiki,
T., Aikawa, M., Tamura, S., Ibukiyama, C., 1998.
Assessment of vasoactive agents and vascular aging by
the second derivative of photoplethysmogram
waveform. Hypertension, 32(2), pp.365–370.
Wang, L., Pickwell, M. E., Liang, Y. P., Zhang, Y. T.,
2009. Noninvasive cardiac output estimation using a
novel photoplethysmogram index. 2009 Annual
International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in
Medicine and Biology Society, pp.1746-1749.
World Health Organization, 2014. Global Health Statistics
2014.
BIOSIGNALS 2017 - 10th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
48
