
Optimizing Distributed Resource Allocation using Epistemic Game
Theory: A Model-driven Engineering Approach
Fazle Rabbi
1,2
, Lars Michael Kristensen
1
and Yngve Lamo
1
1
Bergen University College, Bergen, Norway
2
University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway
Keywords:
Metamodelling, Epistemic Game Theory, Model Transformation, Optimization, Distributed Systems.
Abstract:
Distributed systems modelling often involves a set of heterogeneous models where each model specifies a
set of local constraints capturing a specific view of the system. In real life, distributed systems are often
loosely connected and interdependencies are not defined into their software models. This limits the scope of
optimization of distributed resources. In this paper, we merge heterogeneous models of distributed systems
and articulate distributed resource constraints via inter-metamodel constraints. We apply model-driven en-
gineering and use model transformation rules to construct an epistemic game theory model for the purpose
of optimizing distributed resource allocation. Since the application of transformation rules normally do not
guarantee the satisfaction of constraints when applied on a model, it requires a conformance checking which
is an expensive operation. To overcome this problem, we introduce the concept of compliant rule for efficient
model transformation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Distributed systems are organized in a modular,
loosely coupled fashion such as in healthcare organi-
zations, where separate departments deliver different
types of healthcare. Each unit in a healthcare orga-
nization deals with a different set of operational con-
straints (Pinelle and Gutwin, 2006). Patients often re-
quire a diverse set of services which are provided by
different health facilities. However, the medical care
provided by various health facilities are not neces-
sarily optimized to reduce patients’ waiting time and
other important aspects of getting healthcare services.
While optimizing the resource allocation of a
healthcare system, game theory is more suitable
choice as there are many participants and it is required
to reason about optimality respecting patients prefer-
ences and priorities. Healthcare systems need to be
equipped with uncertainty management as many pa-
tients attending do not have an obvious diagnosis at
presentation; also there are varieties of uncertainty in
healthcare (Han et al., 2011). We propose to use epis-
temic game theory for optimizing the use of health-
care resources with the aim of improving the quality
and efficiency of healthcare services. Game theory is
the discipline of science that models strategic situa-
tions where individuals reason about others choices
for decision making. Epistemic game theory (Perea,
2012; Perea, 2014) can be viewed as rational deci-
sion making under uncertainty. It can play an im-
portant role in coordinating distributed systems or in
the design of interconnected systems. A model driven
approach for meta-modelling epistemic game theory
was introduced in (Rabbi et al., 2016a). We inves-
tigated how distributed systems may be coordinated
to optimize their resources respecting a distributed
set of local constraints (Rabbi et al., 2016a). How-
ever, there are situations where loosely coupled dis-
tributed systems have to deal with a set of global con-
straints. For instance, patients scheduled appointment
time for getting a healthcare service should not con-
flict with other scheduled appointments for getting
other healthcare services. In this paper, we enhance
the approach with inter-metamodel (i.e., global) con-
straints.
We present our approach with a running example
from the healthcare domain. Let us consider that you
and Barbara are two orthopedic patients at the same
hospital. Both you and Barbara are asked to visit the
department of orthopedic surgery on the same day at
9am. When you report to the front desk of the or-
thopedic department you are asked to take an X-ray
from the radiology department which is located on the
same floor as the orthopedic department. The ortho-
Rabbi F., Kristensen L. and Lamo Y.
Optimizing Distributed Resource Allocation using Epistemic Game Theory: A Model-driven Engineering Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0006121400410052
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development (MODELSWARD 2017), pages 41-52
ISBN: 978-989-758-210-3
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
41

pedic department sends an imaging order electroni-
cally to the radiology department which includes pa-
tients information and an instruction about the X-ray.
It took some time for you to reach to the radiology de-
partment as you have a long leg cast. Barbara reported
to the front desk right after you, but she reached the
radiology department before you. The radiology de-
partment is equipped with a queue automation and
therefore you will be served after Barbara. While you
are waiting for your turn at the radiology department
you do not know that Dr. Logan (your doctor) will be
out soon for his round at the inpatient medical wards.
Barbara also does not know that she will not be served
at the orthopedic department before 10.30am because
there are more patients waiting to see her doctor Dr.
Bryan. When you are done with the X-ray and return
to the orthopedic department, you find that Dr. Lo-
gan is out for the rounds and you will have to wait
until 12pm. It could have been an optimal decision
to have your X-ray done before Barbara as Barbara
will have to wait until 10.30am anyway. Even though
the orthopedic department and the radiology depart-
ment are located on the same floor they do not share
their appointment schedules and as a result, the over-
all wait time for patients to get health services are in-
creased. We propose to use epistemic game theory for
optimizing the use of distributed resources and add re-
source constraints to game theory. This paper presents
a formal treatment of distributed resource constraints
via inter-metamodel constraints. For the efficient con-
struction of game theory models we introduce the idea
of compliant rules.
The paper is organized as follows: In section 2, we
present a formal model for distributed resource con-
straints. Section 3 presents a model transformation
technique for resource allocation. Section 4 presents
a game theory model for optimizing resource alloca-
tion. Section 5 introduces compliant rules and co-
ordination of transformation rules, section 6 presents
some related works and section 7 concludes the paper.
2 MODELLING RESOURCE
CONSTRAINTS
Our approach is based on category theory (Barr and
Wells, 1995), model transformations (Ehrig et al.,
2006) and epistemic game theory (Perea, 2012). We
use Diagrammatic Logic (Diskin and Wolter, 2008)
and the Diagram Predicate Framework (DPF) (Rutle,
2010) for the formal development of metamodel spec-
ifications. DPF is suitable for developing domain
specific modelling languages and has support for an
unbounded number of metalevels. In DPF, a model
is represented by a diagrammatic specification S =
(S,C
S
: Σ) consisting of an underlying graph S to-
gether with a set of atomic constraints C
S
specified
by a predicate signature Σ. A predicate signature con-
sists of a collection of predicates, each having a name,
an arity (or shape graph), a visualization, and a se-
mantic interpretation (see Table 1). A predicate is
used to specify a constraint in a model by means of
graph homomorphisms. An atomic constraint (p, δ)
is added to a graph S by a predicate symbol p and
a graph homomorphism δ : α
Σ
(p) → S where α
Σ
(p)
represents the shape graph of predicate p. DPF pro-
vides a formalization of multi level meta-modelling
by defining the conformance relation between mod-
els at adjacent levels of a meta-modelling hierarchy.
There are two kinds of conformance: typed by and
satisfaction of constraints. Figure 1(i) and (ii) shows
the DPF metamodel specifications of an orthopedic
department (S
1
) and a radiology department (S
2
), re-
spectively. These specifications are constrained by
predicates from Table 1.
Constraints are added into the specifications by
graph homomorphisms from the shape graph of the
predicates to the model elements. Below is a list of
constraints specified in S
1
and S
2
:
• C1. A patient must have exactly one birthdate in
an instance of S
1
(specified by <mult(1,1)> )
• C2. A person must have exactly one birthdate in
an instance of S
2
(specified by <mult(1,1)> )
• C3. An appointment time-slot (i.e., TS@Dept)
allocated to a patient in an instance of S
1
must
belong to that patients assigned doctor (specified
by <composite>)
• C4. A person can only check-in for an exami-
nation in an instance of S
2
if the person has an
imaging order (specified by <pre-condition>)
• C5. Only registered persons are allocated with
examination time-slots (i.e., TS@Lab) in an in-
stance of S
2
(specified by <pre-condition>)
• C6. An appointment time-slot in an instance of
S
1
must not be allocated to more than one patient
(specified by <injective>)
• C7. An exam time-slot in an instance of S
2
must
not be allocated to more than one person (speci-
fied by <injective>)
2.1 Distributed Resource Constraints
Usually orthopedic doctors need to inspect the X-ray
reports of the patient during consultation. Therefore
MODELSWARD 2017 - 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
42

Ф
1
TS@Dept
assigned
Doctor
[1..1]
belongsTo
birthdate
Imaging
Exam
hasOrder
admittedTo
Doctor
Patient
Department
Date
Prescription
[comp]
1
TS@Lab
checkin
[1..1]
birthdate
Imaging
Exam
hasOrder
Registration
Person
Dept
Date
Report
[Pcond]
[Pcond]
2
ѱ
1
ѱ
2
birthdate
Imaging
Exam
hasOrder
Patient
Dept
Date
0
Ф
2
( i )
( iii )
( ii )
TS@Dept
assigned
Doctor
[1..1]
belongsTo
checkin
admittedTo
orderingDept
Doctor
Patient
Dept
Registration
Imaging
Exam
[comp]
Prescription
Date
birthdate
Report
+
[Pcond]
[Pcond]
TS@Lab
( iv )
[1..1]
Figure 1: (i) Metamodel specification of an orthopedic department, (ii) Metamodel specification of a radiology department,
(iii) overlap specification, (iv) merged metamodel specification with an inter-metamodel constraint.
Table 1: Predicates of a signature, Σ.
p Arity Visualization Semantic interpretation
f must have at least n and
at most m instances for
each instance of X
For each instance of f there
exists an instance of g with the
same source node
For each composition of
instances f;g, there exists an
instance of h
If there are instances of f and g
with the same source node,
then there exists an ordering of
values between instances of Y
and Z
Instances of f never maps
distinct elements of its domain
to the same element of its
codomain
<mult
(n,m
)>
<pre
-
condition>
<composite>
<precede>
1
1 2
1 2
3
1
2
3
f
g
h
f
g
f
h
X Y
Z
f
g
X Y
Z
f
g
[Pcond]
X
f
Y
[n..m]
[comp]
X Y
Z
f
g
[prcd]
3
f
g
2
1 2
f
X
f
Y
[inj]
<injective>
α (p)
∑
orthopedic patients’ time-slot at the radiology depart-
ment must be preceded by the time-slot at the orthope-
dic department. We will refer to this constraint as C8.
We use the concept ‘time-slot’ for an appointment or
an examination to represent the time assigned for a
scheduled job. A time-slot t2 which include informa-
tion about the start-time and end-time of a scheduled
job is preceded by a time-slot t1 if the end-time of t2
are less than the end-time of t1. To model this dis-
tributed resource constraint, we need to merge speci-
fications S
1
and S
2
.
While merging specifications, atomic constraints
specified in the component metamodel specifications
need to be preserved. We merge specifications in such
a way that for any component metamodel specifica-
tion S
i
there exists a specification morphism from S
i
to the merged metamodel specification. The defini-
tion of specification morphism is given below (Rutle,
2010):
Definition 1 (Specification Morphism). Given two
specifications S = (S,C
S
: Σ) and S
0
= (S
0
,C
S
0
: Σ),
a specification morphism φ : S → S
0
is a graph
homomorphism φ : S → S
0
such that for any atomic
constraint (p, δ) ∈ C
S
implies (p,δ; φ) ∈ C
S
0
as
illustrated in the following diagram.
α (p)
∑
S
S
’
Ф
δ
δ;Ф
=
Diskin et al. presented an approach of merging
metamodels by making metamodels explicit and by
introducing a correspondence span between compo-
nent metamodels (Diskin et al., 2010) (Diskin, 2011).
We adapt the approach with specification morphisms
in order to preserve constraints into the merged meta-
model specifications. Details of merging heteroge-
neous metamodels and specifying inter-metamodel
constraints can be found in (Diskin et al., 2010). Un-
like (Diskin et al., 2010), in our approach the head
of the span is an overlap specification given in DPF
which specifies the common concepts of both meta-
models and the legs of the span are specification
Optimizing Distributed Resource Allocation using Epistemic Game Theory: A Model-driven Engineering Approach
43

morphisms. Figure 1(iii) shows the overlap specifi-
cation S
0
= (S
0
,C
S
0
: Σ) (highlighted in grey) and
Figure 1(iv) shows the merged metamodel specifica-
tion S
+
= (S
+
,C
S
+
: Σ). S
+
is constructed by merg-
ing component metamodel specifications S
1
and S
2
modulo their overlap S
0
(i.e., common elements ap-
pear only once in the merge). Overlaps are specified
by two specification morphisms S
1
ψ
1
←−− S
0
ψ
2
−−→ S
2
where S
0
contains all common concepts, S
1
and S
2
are the underlying graphs of specifications S
1
and
S
2
. Any pair of elements x
1
∈ S
1
and x
2
∈ S
2
are
considered to be the same if there is an element
x ∈ S
0
such that ψ
1
(x) = x
1
and ψ
2
(x) = x
2
. Fol-
lowing (Diskin et al., 2010), we call this configu-
ration of metamodel specifications and mappings a
multi-metamodel specification M, and write M =
(S
1
, S
2
, S
0
, ψ
1
, ψ
2
). The multi-metamodel specifi-
cation M declares the unification of concepts Date,
birthdate, hasOrder, ImagingE xam, orderingDept
and unifies also the following concepts:
• Patient and Person since ψ
1
(Patient) = Patient
and ψ
2
(Patient) = Person
• Department and Dept since ψ
1
(Dept) =
Department and ψ
2
(Dept) = Dept
The mappings φ
1
: S
1
→ S
+
and φ
2
: S
2
→ S
+
in Figure 1 maps elements from S
1
and S
2
to the cor-
responding elements in S
+
.
Definition 2 (Merged Metamodel Specification).
Given two (component) metamodel specifications
S
1
= (S
1
,C
S
1
: Σ) and S
2
= (S
2
,C
S
2
: Σ), a merged
metamodel specification S
+
= (S
+
,C
S
+
: Σ) of S
1
and S
2
is given by two specification morphisms
φ
1
: S
1
→ S
+
, φ
2
: S
2
→ S
+
and a multi-metamodel
specification M = (S
1
, S
2
, S
0
, ψ
1
, ψ
2
) such that the
graph S
+
is obtained by the pushout of ψ
1
and ψ
2
.
This is illustrated in the following diagram:
Ф
1
ѱ
1
ѱ
2
0
S
Ф
2
1
S
2
S
+
S
PO
∑
α (p ) ....
1
δ
1
δ ;
1
Ф
1
∑
... α (q )
1
δ'
1
δ‘ ;
1
Ф
2
∑
α (d )
...
1
δ
d
δ
d2
δ
d1
δ ; = δ ;
d1
Ф
1
d2
Ф
2
The binary case can be generalized to the N-ary
case by constructing S
+
as a so-called colimit and
preserving all the atomic constraints specified in the
component metamodels. Constraints of component
metamodel specifications are preserved in a merged
metamodel specification. Additional constraints may
be added into a merged metamodel specification.
The distributed resource constraints are added into
the merged metamodel specification by means of
inter-metamodel constraints. The distributed resource
constraint C8 is added into S
+
by using the predicate
<precede>. In general, merged metamodel specifica-
tions have the following properties:
Theorem 1. Let S
+
be a merged metamodel spec-
ification obtained from component metamodel spec-
ifications S
1
, . . . S
n
. For any component metamodel
specification S
i
(1 ≤ i ≤ n), there exists a specification
morphism from S
i
to S
+
.
Proof. This follows directly from the definition of
merged metamodel specification.
A model (I,ι) of a metamodel specification S =
(S,C
S
: Σ) is a graph I together with a typing graph
homomorphism ι : I → S . In order to be a valid model
of a metamodel specification S the typing morphism
must satisfy the atomic constraints specified in C
S
.
Here we define the merged model of two component
models.
Definition 3. Given two (component) models
(I
1
, ι
1
), (I
2
, ι
2
) of metamodel specifications S
1
, S
2
and an overlap model I
1
g
1
←−− I
0
g
2
−−→ I
2
typed by the
overlap specification of S
1
and S
2
. The merged
model is a graph I
+
together with a typing graph
homomorphism ι
+
: I
+
→ S
+
where S
+
is the under-
lying graph of the merged metamodel specifications
of S
1
, S
2
such that the graph I
+
is obtained by the
pushout of g
1
and g
2
and the top face constitute a
van Kampen square in the category of Graph as
illustrated in the following diagram:
(top)
S
0
S
1
S
2
S
+
I
0
I
1
I
2
I
+
ѱ
1
ѱ
2
φ
1
φ
2
ι
1
ι
0
ι
+
ι
2
g
1
h
2
h
1
g
2
The reader interested in the property of van Kam-
pen square may wish to consult (Mantz, 2014). It is
possible that the atomic constraints when preserved in
a merged metamodel specification may conflict with
other constraints or may become redundant. There
exists some research for detecting these problems au-
tomatically such as the alloy analyzer which may be
used to detect these problems by specification anal-
ysis (Wang et al., 2015). An atomic constraint speci-
fied in a component metamodel and satisfied in a com-
MODELSWARD 2017 - 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
44

ponent model may become unsatisfiable in a merged
model or vice versa. Figure 2 shows an example of
a model merge where a component model (I
1
, ι
1
) is
typed by the underlying graph S
1
of the metamodel
specification S
1
. The predicate p is used to con-
straint S
1
by a graph homomorphism δ : α
Σ
(p) → S
1
.
The edge 1
e
1
−−→ 2 is mapped to A
f
−→ B and the edge
2
e
2
−−→ 1 is mapped to B
g
−→ A. The overlap specifi-
cation is given by (S
1
, S
2
, S
0
, ψ
1
, ψ
2
) which unifies
of the following concepts: A and AA, B and BB. To
check if (I
1
, ι
1
) satisfies the constraint (p, δ) we extract
the fragment (O
∗
) of the component model that is af-
fected by the constraint. Again, to check if the merged
model (I
+
, ι
m
) satisfies the constraint (p, δ;φ
1
) we ex-
tract the fragment (O
∗
m
) of the merged model that is af-
fected by the constraint. The object O
∗
is obtained by
the pullback of α
Σ
(p)
δ
−→ S
1
ι
1
←− I
1
and the object O
∗
m
is obtained by the pullback of α
Σ
(p)
δ;φ
1
−−−−→ S
+
ι
m
←−− I
+
.
Since we obtain two different objects by the pullback
operation, it is possible that the satisfaction of the lo-
cal constraint will vary.
Typing, l
1 2
e
α
(p)
∑
δ
PB(1)
m
l*
A
f
B
δ*
1
e
2
g
AA BB AA BB
g
a b
:f
a
:f
b
AA BB
f
g
a
:g
b
a
:g
b
:f
a
:g
b
:f
δ*
l*
1
m
m
l
1
l
2
ѱ
1
ѱ
2
Ф
1
PB(2)
Ф
2
Ф*
1
Ф*
2
O*
I
1
I
2
S
+
S
1
S
0
S
2
O*
m
I
+
δ;
Ф
1
Figure 2: Construction of pullback for a component model
I
1
and merged model I
+
.
3 RESOURCE ALLOCATION
Our example introduced earlier consists of two com-
ponent metamodels representing two distributed sys-
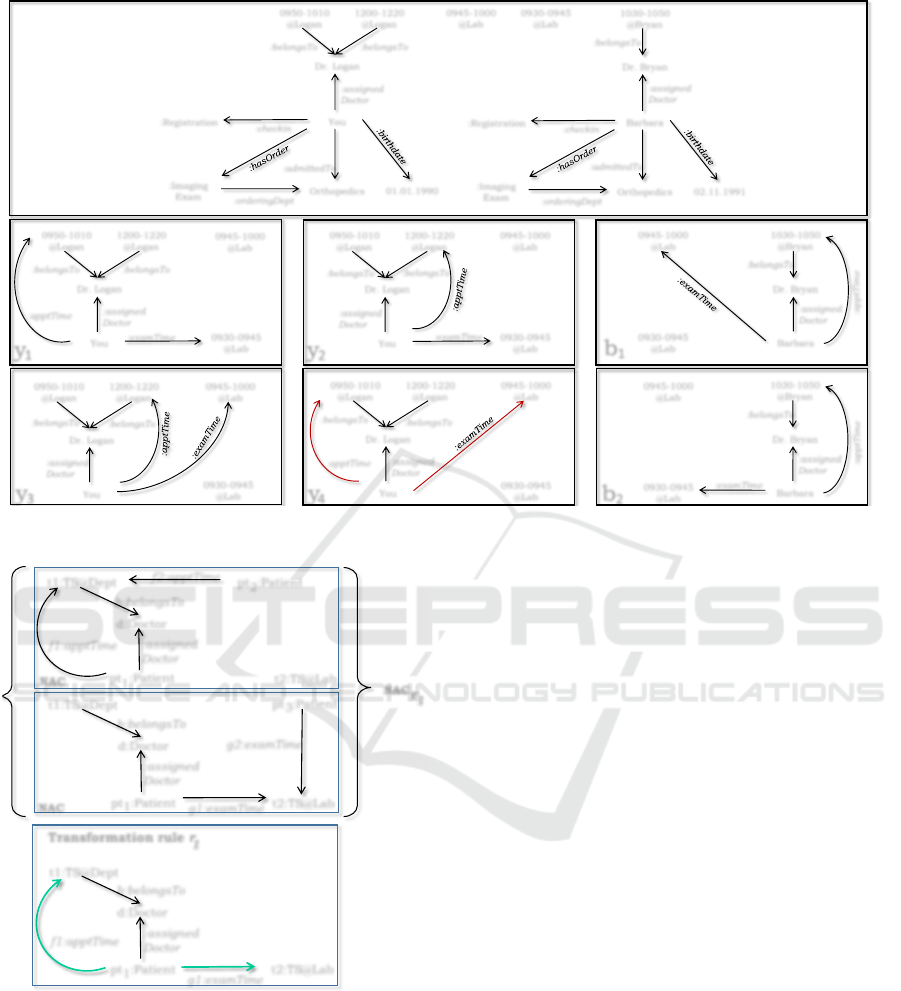
tems and an inter-metamodel constraint C8. Figure 3
shows a model (I, ι
I
) of the merged metamodel S
+
of Figure 1. The typing ι
I
of the modelling elements
are not explicitly represented in the figure. In the fig-
ure, You and Barbara are instances of Patient, your
assigned doctor is Dr.Logan and Barbara’s assigned
doctor is Dr.Bryan. Dr. Logan has two available time-
slots: 0950 − 1010@Logan and 1200 − 1220@Logan
and Dr. Bryan has one available time-slot: 1030 −
1050@Bryan. There are two available time-slots
at the radiology department: 0945 − 1000@Lab and
0930− 0945@Lab. In time-slot 0950− 1010@Logan,
09:50 is the start time and 10:10 is the end time.
Model (I,ι
I
) need to be completed with resource al-
location for you and Barbara at the radiology and or-
thopedic department. One can find that there are four
possible choices of resource allocation for you and
two possible choices of resource allocation for Bar-
bara with the available resources.
We use a transformation approach where transfor-
mation rules have a set of negative application condi-
tions proposed by Lambers et al., in (Lambers et al.,
2008) for allocating resources to the patients. Figure 4
illustrates a rule r
1
typed by the merged metamodel
S
+
. The typing information of a modelling element
in r
1
appears after a colon (:). The rule specifies that
a patient pt
1
is allocated with an appointment time-
slot t1 and an exam time-slot t2 if t1 belongs to pt
1
’s
assigned doctor d and t1, t2 are not allocated to any
other patient. The green color is used to indicate el-
ements that the rule is going to produce. Negative
application conditions (NACs) are typically used in
graph transformation to prohibit an infinite number of
rule applications.
The rule can be applied over the model (I,ι
I
) in
six different ways since there are six matches. Fig-
ure 3 shows briefly the choices of resource allocation
for you in y
1
− y
4
and for Barbara in b
1
, b
2
. y
1
shows a
resource allocation where you are assigned with exam
time-slot 0930 − 0945@Lab at the radiology depart-
ment and appointment time-slot 0950− 1010@Logan
at the orthopedics department with Dr. Logan. This
resource distribution is valid since it is not violating
any constraint. Similarly, other valid resource distri-
butions are y
2
, y
3
, b
1
and b
2
. However y
4
is not valid
as it is violating the distributed resource constraint
C8: your exam time-slot 0945 − 1000@Lab must
be preceded by your appointment time-slot 0950 −
1010@Logan.
We apply epistemic game theory for the optimiza-
tion of resources over the valid choices of resource
allocation. Epistemic game theory is a broad area of
research that formalizes the assumptions about ratio-
nality and mutual beliefs in a formal language to an-
alyze games. It introduces a Bayesian perspective on
decision-making in strategic situations. In a strate-
gic game, the outcome does not only depend on the
choice of a single player but also on the choices of
other players. The combination of all the players’
choices is called a strategy profile. From an epistemic
point of view, the strategy profile should include the
beliefs players have about each other’s possible ac-
tions (and beliefs). This model of interdependent de-
cision making can essentially represent a wide array
of social interactions. A metamodel for modelling
epistemic aspects of a system as presented in (Rabbi
et al., 2016a) is shown in Figure 5. Players in an epis-
Optimizing Distributed Resource Allocation using Epistemic Game Theory: A Model-driven Engineering Approach
45
:assigned
Doctor
:belongsTo
:checkin
:admittedTo
:orderingDept
Dr. Logan
You
Orthopedics
:Registration
:Imaging
Exam
01.01.1990
0945-1000
@Lab
:assigned
Doctor
:belongsTo
:checkin
:admittedTo
:orderingDept
Dr. Bryan
Barbara
Orthopedics
:Registration
:Imaging
Exam
02.11.1991
0930-0945
@Lab
0950-1010
@Logan
1200-1220
@Logan
:belongsTo
1030-1050
@Bryan
I
:assigned
Doctor
:belongsTo
Dr. Logan
You
0945-1000
@Lab
0930-0945
@Lab
0950-1010
@Logan
1200-1220
@Logan
:belongsTo
:examTime
:apptTime
:assigned
Doctor
:belongsTo
Dr. Logan
You
0945-1000
@Lab
0930-0945
@Lab
0950-1010
@Logan
1200-1220
@Logan
:belongsTo
:assigned
Doctor
:belongsTo
Dr. Logan
You
0945-1000
@Lab
:assigned
Doctor
:belongsTo
Dr. Bryan
Barbara
0950-1010
@Logan
1200-1220
@Logan
:belongsTo
1030-1050
@Bryan
:apptTime
:assigned
Doctor
:belongsTo
Dr. Logan
You
0945-1000
@Lab
:assigned
Doctor
:belongsTo
Dr. Bryan
Barbara
0950-1010
@Logan
1200-1220
@Logan
:belongsTo
1030-1050
@Bryan
:apptTime
:examTime
:apptTime
y
1
y
3
y
2
y
4
0930-0945
@Lab
0930-0945
@Lab
:examTime
0945-1000
@Lab
0930-0945
@Lab
0945-1000
@Lab
0930-0945
@Lab
b
1
b
2
Figure 3: A model (I,ι
I
) of S
+
(top) and individual resource allocation.
pt :Patient
t1:TS@Dept
pt :Patient
f2:apptTime
pt :Patient
t2:TS@Lab
f1:apptTime
b:belongsTo
t1:TS@Dept
g1:examTime
d:Doctor
:assigned
Doctor
f1:apptTime
g1:examTime
pt :Patient
t2:TS@Lab
pt :Patient
g2:examTime
Transformation rule r
1
NAC
NAC
NAC
r
1
b:belongsTo
d:Doctor
:assigned
Doctor
b:belongsTo
d:Doctor
:assigned
Doctor
t1:TS@Dept
t2:TS@Lab
1
1
1
2
3
Figure 4: Transformation rule r
1
for individual resource al-
location of patients.
temic game may have choices. The surjective con-
straint imposed on the hasChoice relation ensures that
instances of Choice must be associated with players.
An instance of Belie f connects the choices of a player
with other players’ choices denoting the choice com-
bination of players. In game theory, utility represents
the motivation or satisfaction of players. The higher
the utility the more the outcome is preferred. We use
the <utility(n)> predicate to assign utility to an in-
stance of a belief. A utility assigned to an instance of
a belief denotes the utility that a player derives from
the outcome induced by the choice combination. We
use the <prob(r)> predicate to annotate an instance
of a belief with probability. Of course in a healthcare
setting, patients do not have to know about each oth-
ers choices; they are not expected to make decisions
for mutual benefits. We propose to construct a strat-
egy profile for them indirectly with an aim to optimize
resource allocation respecting patients’ preferences.
Given an initial epistemic model ξ of the meta-
model in Figure 5 with two instances of Player: You
and Barbara, we use coupled model transformation
rules to automatically produce choices for you and
Barbara. For each valid choice of resource alloca-
tion of individual patients from Figure 3, we create
choices in ξ. The special kind of coupled transfor-
mation rule with coordinating edges creates choices ξ
and establishes links from choices to instances of the
merged metamodel S
+
. Coordinating edges are used
to co-ordinate between heterogeneous models and or
modelling elements (Rabbi et al., 2014) (Rabbi et al.,
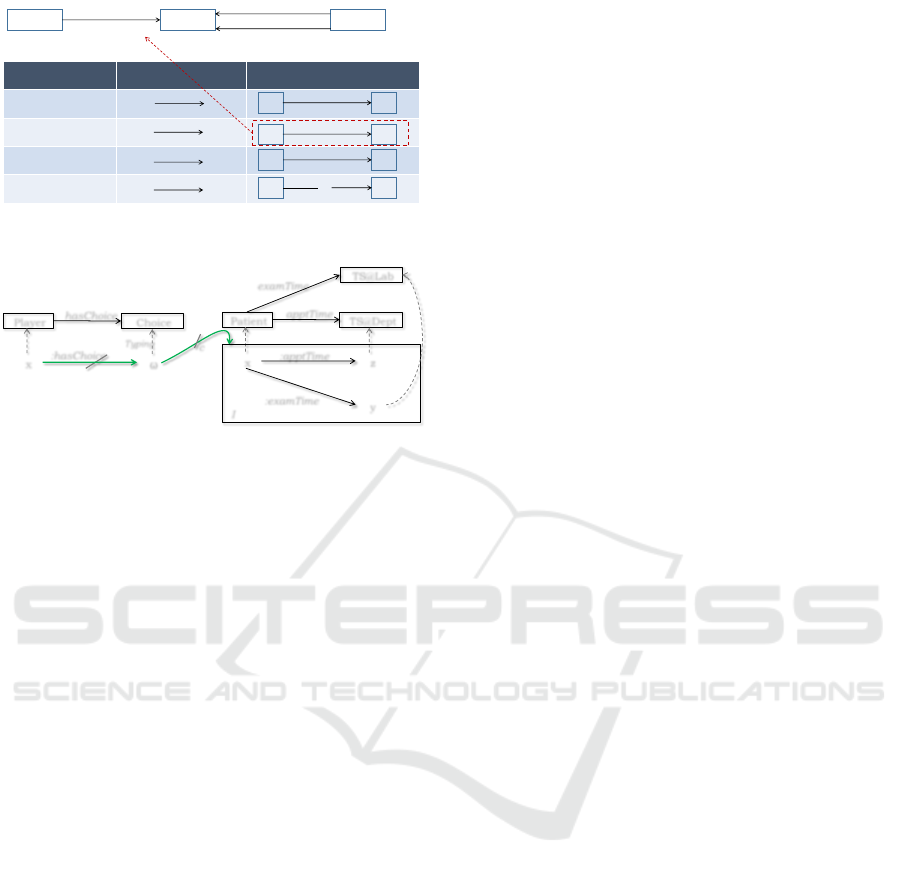
2015). Figure 6 shows a transformation rule that iden-
tifies a player and produces choices for the player.
The rule specifies that if we have an instance x of type
Player in the epistemic model and x is an instance of
Patient in a model (I, ι
I
) of S
+
, such that x is allocated
with an appointment time-slot z and an exam time-slot
y, then we create an epistemic choice ω for player x
MODELSWARD 2017 - 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
46
Player Choice Belief
source
[1..*]
hasChoice
[surj]
Predicate, p Arity Visualization
<
mult(n,m)>
<
surjective>
<
prob(r)>
<
utility(n)>
X Y
[n..m]
X Y
[surj]
1 2
1 2
target
[1..*]
1 2
X Y
(r)
constraint
1 2
X Y
n
Figure 5: Metamodel for modelling epistemic aspects.
Typing
Patient
TS@Dept
x z
:apptTime
apptTime
Player
Choice
x
ω
:hasChoice
hasChoice
c
I
y
:examTime
TS@Lab
examTime
Typing, ι
Model (I, ι )
I
I
Figure 6: Transformation rule r
2
for producing epistemic
choices.
in the epistemic model and create a coordinating edge
c linking the choice ω to the model (I,ι
I
).
Figure 7 illustrates the result of the application
of this transformation rule over the possible choices
of resource allocation from Figure 3. Figure 7(left)
shows an epistemic model ξ where You and Barbara
are instances of Player. Choices for you and Bar-
bara are produced in ξ where the choices are linked
to the models of the merged metamodel S
+
in Fig-
ure 7(right) by coordinating edges shown in blue.
Note that we only produce epistemic choices for valid
models of the entity metamodel. Since y
4
is not a
valid model, we did not produce any epistemic choice
for y
4
.
Figure 8 briefly presents the coordinating meta-
model used for coordinating heterogeneous metamod-
elling hierarchies. The coordinating metamodel spec-
ifies that we may have coordinating-edges between
nodes. The coordinating-edge may be instantiated
in an arbitrary level of a metamodelling hierarchy.
Rossini et al. presented a formal way of specify-
ing this requirement in DPF using deep metamod-
elling (Rossini et al., 2012). A reference with multi-
potency at a metalevel i can be instantiated in all
metalevels below i. Since the coordinating-edge has
multi-potency, it can be instantiated in an arbitrary
metalevel. In Figure 8, S
+
, y
1
, y
2
are placeholder
nodes representing the identity of the (meta)models.
The instance of the coordinating-edge c
1
establishes
a link between an epistemic choice instance to the in-
stance y
1
by referring to the node y
1
.
4 OPTIMIZATION OF
RESOURCE ALLOCATION
In this section we discuss how resource allocation
of distributed systems may be optimized using epis-
temic game theory. In our example, the patients were
asked to come to the hospital at 9am and the clinic
at the orthopedic department remains open until 5pm.
Therefore, the maximum time spent by the patients
to get healthcare services could be 8 hours (480 min-
utes). We calculate the utility based on the time spent
at the hospital by the patients to get healthcare ser-
vices. If a patient spends m minutes in total to get
services, then her utitity is (480 − m). Therefore, the
longer the patients are waiting, the lower utility they
get. Our target is to optimize the resource alloca-
tion for the patients so that their wait time will be
reduced. Consider the choice y
1
for you, which rep-
resents the resource allocation of 0930 − 0945@Lab
and 0950 − 1010@Logan. This gives a utility of
480 − 70 = 410 as you are spending only 70 minutes
at the hospital to get your services. Similarly, we can
calculate Barbara and your utilities and complete the
epistemic model ξ with belief instances by perform-
ing a Cartesian product of Barbara and your choices
as shown in Figure 9. Curved arrows in Figure 9 are
representing belief instances which will be referred to
as belief arrows. The belief arrow from y
1
to b
1
with
an attribute 410 is representing an instance of Belie f
with utility 410.
An essential element of epistemic game theory
analysis is the notion of belief hierarchies which are
used to characterize solution concepts. We obtain be-
lief hierarchies from an epistemic model by following
belief arrows starting from any choice of a player. In
our epistemic model we are only considering simple
belief hierarchies. The idea of a simple belief hier-
archy states that the whole belief hierarchy may be
summarized by a combination of beliefs about play-
ers’ choices. A belief hierarchy is simple if it con-
tains at most one belief of each player. The epistemic
model in Figure 9 represents six simple belief hier-
archies of which three are: (i) y
1
410
−−−→ b
1
370
−−−→ y
1
; (ii)
y
1
410
−−−→ b
2
370
−−−→ y
1
; (iii) y
2
280
−−−→ b
1
370
−−−→ y
2
. Typically a
belief hierarchy specifies a player’s belief over other
players’ beliefs but in the healthcare context we use a
belief hierarchy to specify a systems belief about pa-
tient’s choices. The belief hierarchy y
1
410
−−−→ b
1
370
−−−→ y
1
can be read as: the system believes that you will con-
sider making appointments represented in y
1
if Bar-
bara considers making appointments represented in
b
1
; and Barbara considers making appointments rep-
resented in b
1
if you consider making appointments
Optimizing Distributed Resource Allocation using Epistemic Game Theory: A Model-driven Engineering Approach
47

:assigned
Doctor
:belongsTo
Dr. Bryan
Barbara
1030-1050
@Dept
:examTime
:apptTime
0945-1000
@Lab
0930-0945
@Lab
b
2
:assigned
Doctor
:belongsTo
Dr. Bryan
Barbara
1030-1050
@Dept
:apptTime
0945-1000
@Lab
0930-0945
@Lab
b
1
:assigned
Doctor
:belongsTo
Dr. Logan
You
0945-1000
@Lab
0930-0945
@Lab
0950-1010
@Dept
1200-1220
@Dept
:belongsTo
y
3
:assigned
Doctor
:belongsTo
Dr. Logan
You
0945-1000
@Lab
0950-1010
@Dept
1200-1220
@Dept
:belongsTo
y
2
0930-0945
@Lab
:examTime
Entity models (Instances of the merged
metamodel shown in Figure 1)
Epistemic model
Barbara
:hasChoice
:hasChoice
y
1
:assigned
Doctor
:belongsTo
Dr. Logan
You
0945-1000
@Lab
0930-0945
@Lab
0950-1010
@Logan
1200-1220
@Logan
:belongsTo
:examTime
:apptTime
You
:hasChoice
:hasChoice
:hasChoice
y ( )
0930-0945@Lab
0950-1010@Logan
1
y ( )
0930-0945@Lab
1200-1220@Logan
2
y ( )
0945-1000@Lab
1200-1220@Logan
3
b ( )
0945-1000@Lab
1030-1050@Bryan
1
b ( )
0930-0945@Lab
1030-1050@Bryan
2
+
Figure 7: Epistemic choices produced by the application of model transformation rules.
+
0950-1010
@Logan
:belongsTo
y
2
:assign
Doctor
Dr. Logan
You
0950-1010
@Logan
120
@
:belongsTo
:apptTime
0950-1010
@Logan
:belongsTo
y
1
:assign
Doctor
:be
Dr. Logan
You
0950-1010
@Logan
120
@
:belongsTo
:e
:apptTime
You
:hasChoice
:hasChoice
y ( )
0930-0945@Lab
0950-1010@Logan
1
y ( )
0930-0945@Lab
1200-1220@Logan
2
Node
coordinating-edge
arrow
TS@Dept
belongsTo
checkin
Registration
[comp]
[Pcond]
TS@Lab
Player Choice
[1..*]
hasChoice
[surj]
[1..*]
c
1
c
2
Figure 8: Heterogeneous metamodelling with Coordinating
metamodel.
Barbara
You
:hasChoice
y ( )
0930-0945@Lab
0950-1010@Logan
1
y ( )
0930-0945@Lab
1200-1220@Logan
2
y ( )
0945-1000@Lab
1200-1220@Logan
3
b ( )
0945-1000@Lab
1030-1050@Bryan
1
b ( )
0930-0945@Lab
1030-1050@Bryan
2
410
370
410
370
280
370
280
370
280
370
280
370
Figure 9: Epistemic model with combination of beliefs.
represented in y
1
. In our approach, uncertainty can
be modelled by assigning probability to the belief ar-
rows.
An important concern regarding the belief hierar-
chies is their consistency. A consistent belief hier-
archy represents a solution concept that satisfies all
the constraints specified in the metamodel specifica-
tions. Following (Rabbi et al., 2016a) we determine
how inconsistent combination of beliefs can be au-
tomatically removed from an epistemic model. If a
combination of beliefs includes choices from a ho-
mogeneous metamodel, then the models are merged
into a single model. For instance if we wish to check
if the combination of beliefs represented by the be-
lief hierarchy y
1
410
−−−→ b
1
370
−−−→ y
1
is consistent, we need
to merge the models linked to y
1
and b
1
since they
are typed by the merged metamodel S
+
. The merged
model is then checked for consistency and if it vi-
olates any constraint specified in its metamodel, we
conclude that the combination of beliefs is incon-
sistent and should be discarded from the epistemic
model.
The combination of beliefs represented by the be-
lief hierarchy y
1
410
−−−→ b
2
370
−−−→ y
1
is inconsistent as the
merged instance is violating constraint C7 (see sec-
tion 2). The reason is that according to the injec-
tive constraint imposed on the reference examT ime,
patients cannot have the same time-slot. Therefore,
assigning time-slot 0930 − 0945@Lab to both of you
and Barbara is making the merged instance inconsis-
tent. To check that a constraint is satisfied in a given
model of a metamodel, we inspect the part of a model
which is affected by the constraint. This is checked
by projecting out the part of the model which is af-
fected by the constraint. This is formally defined as a
pullback operation in category theory.
MODELSWARD 2017 - 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
48

Similarly we can show that the combination of
beliefs represented by the belief hierarchies y
2
280
−−−→
b
2
370
−−−→ y
2
, y
3
280
−−−→ b
1
370
−−−→ y
3
are inconsistent. Fig-
ure 10 shows an epistemic model with only consistent
combination of beliefs.
Barbara
You
:hasChoice
y ( )
0930-0945@Lab
0950-1010@Logan
1
y ( )
0930-0945@Lab
1200-1220@Logan
2
y ( )
0945-1000@Lab
1200-1220@Logan
3
b ( )
0945-1000@Lab
1030-1050@Bryan
1
b ( )
0930-0945@Lab
1030-1050@Bryan
2
410
370
280
370
280
370
Figure 10: Epistemic model with consistent combination of
beliefs.
Barbara
You
:hasChoice
y ( )
0930-0945@Lab
0950-1010@Logan
1
y ( )
0930-0945@Lab
1200-1220@Logan
2
y ( )
0945-1000@Lab
1200-1220@Logan
3
b ( )
0945-1000@Lab
1030-1050@Bryan
1
b ( )
0930-0945@Lab
1030-1050@Bryan
2
410
370
280
370
Figure 11: Epistemic model with rational combination of
beliefs.
The epistemic choice y
2
which represents the re-
source allocation of 0930 − 0945@Lab and 1200 −
1220@Logan is not a rational choice since this is not
optimal for any of the epistemic choices for Barbara.
If you are allocated with time-slot 0930 − 0945@Lab
at the radiology department, it will be optimal for
you to see the doctor in appointment time-slot 0950 −
1010@Logan. Therefore, the epistemic choice y
2
is
dominated by y
1
. The epistemic choice y
3
is a ratio-
nal choice since this is optimal if Barbara is allocated
with time-slot 0930 − 0945@Lab at the radiology de-
partment.
Figure 11 shows belief combinations with rational
choices. The combination of beliefs is rational as the
choices consist of the belief combinations are all ra-
tional choices with respect to the choice combination
represented by the combination of beliefs.
Following (Perea, 2012) (Rabbi et al., 2016a), a
simple belief hierarchy generated by a combination
of beliefs leads to a Nash equilibrium if the combi-
nation of beliefs is rational. Therefore, we obtain two
Nash equilibria from the epistemic model represented
in Figure 11:
• Allocating time-slot 0930 − 0945@Lab and
0950 − 1010@Logan for you is rational if time-
slot 0945 − 1000@Lab and 1030 − 1050@Bryan
are allocated to Barbara gives a total utility of
(410 + 370) = 780;
• Allocating time-slot 0945 − 1000@Lab and
1200 − 1220@Logan for you is rational if time-
slot 0930 − 0945@Lab and 1030 − 1050@Bryan
are allocated to Barbara gives a total utility of
(280 + 370) = 650.
However, the first equilibrium has a higher total
utility for the system.
5 COORDINATION OF
TRANSFORMATION RULES
Scalability is an important issue regarding the appli-
cation of optimization techniques in real-life scenario.
In our approach, we proposed to use model transfor-
mation rules for allocating resources. In general, the
result of the application of a model transformation
rule may become inconsistent i.e., may violate the
constraints specified in a metamodel. Therefore, the
application of a model transformation rule requires a
consistency checking which is a time consuming op-
eration. To tackle this problem, we need techniques
to reduce the complexity of consistency checking. In
this section, we introduce the idea of a compliant rule
that preserves the validity of a model.
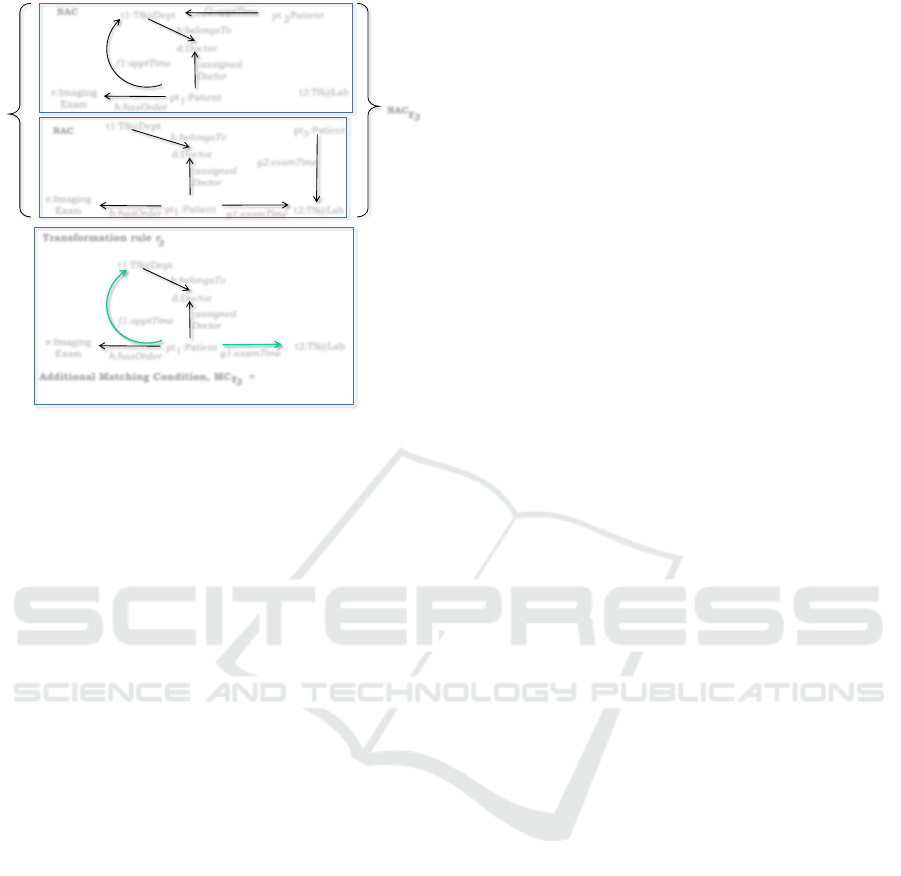
The transformation rule r
1
presented in Figure 4
is not compliant with the set of atomic constraints
specified in the merged metamodel specification S
+
of Figure 1. If the rule is applied over a valid model,
it does not guarantee that the result will be a valid
model conforming to S
+
. The rule can be enhanced
so that while matching with a model it makes sure that
the result will be a valid model.
Definition 4 (Compliant Rule). Given a metamodel
specification S = (S,C
S
: Σ). A transformation rule
r is compliant with a set of atomic constraints from
C
S
if the application of r over any valid model of S
results in a valid model of S.
Figure 12 shows a transformation rule r
3
which
is compliant with the set of atomic constraints C
S
+
specified in S
+
(Figure 1). The addition of new in-
stances of examT ime and apptT ime in a valid model
of S
+
can possibly violate atomic constraints C3, C5,
C6, C7 and C8. The transformation rule r
3
makes
sure that when applied on a valid model of S
+
, the
addition of new elements does not violate any of the
above mentioned constraints. The additional match-
ing condition endT ime(t2) < endT ime(t1) specified in
r
3
makes sure that C8 is not violated. Therefore the
application of r
3
will not require any further consis-
tency checking.
Optimizing Distributed Resource Allocation using Epistemic Game Theory: A Model-driven Engineering Approach
49
pt :Patient
t1:TS@Dept
pt :Patient
f2:apptTime
pt :Patient
t2:TS@Lab
f1:apptTime
b:belongsTo
t1:TS@Dept
g1:examTime
d:Doctor
:assigned
Doctor
f1:apptTime
g1:examTime
pt :Patient
t2:TS@Lab
pt :Patient
g2:examTime
Transformation rule r
3
NAC
NAC
NAC
r
e:Imaging
Exam
h:hasOrder
Additional Matching Condition, MC =
3
r
3
{ ‘endTime(t2) < endTime(t1)’ }
t2:TS@Lab
b:belongsTo
t1:TS@Dept
d:Doctor
:assigned
Doctor
e:Imaging
Exam
h:hasOrder
b:belongsTo
d:Doctor
:assigned
Doctor
e:Imaging
Exam
h:hasOrder
1
1
1
2
3
Figure 12: Transformation rule r
3
for individual resource
allocation of patients.
Further enhancement of the rule is performed by
amalgamation of rule r
3
(Figure 12) and r
2
(Fig-
ure 6). Rule amalgamation is a model transformation
technique commonly used for coordinating rules with
overlapping parts (Lamo et al., 2013). To apply a rule
over a source model requires to perform an injective
matching. In order to reduce the number of match-
ing we coordinate rule r
3
and r
2
. Figure 13 shows a
transformation rule r
4
that we formulate by combin-
ing r
3
and r
2
. While allocating resources for individ-
ual patients the rule r
4
produces epistemic choices at
the same time. The rule is also compliant with the
set of constraints specified in the merged metamodel
specification and therefore if the rule is applied over a
valid model, it guarantees consistency.
6 RELATED WORK
The necessity of merging different formalisms of soft-
ware specifications is intrinsic to the discipline of
software engineering. Category theory has been con-
sidered to be a viable solution to accommodate the di-
versity of formalisms (Fiadeiro and Maibaum, 1995;
Diskin et al., 2010; Rutle, 2010). Diskin et al.,
(Diskin et al., 2010) introduced the concept of inter-
metamodel constraints to specify constraints over in-
terdependent models and later on K
¨
onig et al., (K
¨
onig
and Diskin, 2016) proposed an advanced consistency
checking algorithm for inter-metamodel constraints.
A slight different but related idea was presented by
Rabbi et al., in (Rabbi et al., 2014) which formalizes
the co-ordination among metamodels, using a linguis-
tic extension of the metamodelling hierarchy. The
proposed linguistic extension is based on an added
metalevel which models the integration of two or
more different aspects of a system.
Bak et al. presented a language called Clafer that
unifies features and class modelling (Bak et al., 2016).
The language is supported by a tool that supports
model based analyses such as consistency checking,
instance completion, single and multi-objective opti-
mization. The tool utilizes existing model based an-
alyzers such as Alloy (relational logic solver) (Jack-
son, 2002), Z3 (SMT solver) (De Moura and Bjørner,
2008), Choco 3 (constraint satisfaction problems and
constraint programming solver) (Jussien et al., 2008)
by translating Clafer models into the backend solvers.
While Clafer provides a concise notation for feature
modeling it does not support modelling distributed
systems with inter-metamodel constraints. Also the
optimization technique is different in contrast to the
optimization technique of epistemic game theory.
Alanen and Porres investigated an approach for
automatic discovery of the difference and union of
models in the context of a version control system
(Alanen and Porres, 2003). They presented algo-
rithms to calculate the difference between models for
MOF-based models. This work can be adapted in or-
der to identify overlaps between component models
for merging DPF (meta)model specifications.
7 CONCLUSION
This paper is based on the metamodelling epistemic
game theory approach introduced in (Rabbi et al.,
2016a). Epistemic games are relevant for modeling
distributed systems in order to optimize the use of
shared resources. We proposed several enhancement
in this paper by incorporating model merge with inter-
metamodel constraints and compliant rules.
In this paper, we adopted merged metamodel
specifications and specified distributed resource con-
straints via inter-metamodel constraints. We applied
model transformations to produce epistemic game
theory models for the purpose of optimizing the use
of distributed resources. Currently we are investigat-
ing the Clafer (Bak et al., 2016) and WebDPF tool
(Rabbi et al., 2016b) for reasoning over DPF meta-
models. In order to apply the proposed method effi-
ciently, we presented the concept of compliant rules.
An automatic resolution of compliant rules is out of
scope of this paper and it is currently under investiga-
tion.
MODELSWARD 2017 - 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
50

pt :Patient
t1:TS@Dept
pt :Patient
f2:apptTime
pt :Patient
t2:TS@Lab
f1:apptTime
b:belongsTo
t1:TS@Dept
g1:examTime
d:Doctor
:assigned
Doctor
f1:apptTime
g1:examTime
pt :Patient
t2:TS@Lab
pt :Patient
g2:examTime
NAC
NAC
NAC
r
e:Imaging
Exam
h:hasOrder
Additional Matching Condition, MC =
4
r
4
{ ‘endTime(t2) < endTime(t1)’ }
t2:TS@Lab
b:belongsTo
t1:TS@Dept
d:Doctor
:assigned
Doctor
e:Imaging
Exam
h:hasOrder
b:belongsTo
d:Doctor
:assigned
Doctor
e:Imaging
Exam
h:hasOrder
Typing
Player
Choice
pt
ω
:hasChoice
hasChoice
c
Instance, (I, ι )
I
1
1
1
2
3
1
Figure 13: Transformation rule r
4
for resource allocation and producing epistemic choices.
REFERENCES
Alanen, M. and Porres, I. (2003). Difference and Union
of Models, pages 2–17. Springer Berlin Heidelberg,
Berlin, Heidelberg.
Bak, K., Diskin, Z., Antkiewicz, M., Czarnecki, K., and
Wasowski, A. (2016). Clafer: unifying class and
feature modeling. Software and System Modeling,
15(3):811–845.
Barr, M. and Wells, C., editors (1995). Category Theory
for Computing Science, 2nd Ed. Prentice Hall Inter-
national (UK) Ltd., Hertfordshire, UK.
De Moura, L. and Bjørner, N. (2008). Z3: An efficient smt
solver. In Proceedings of the Theory and Practice of
Software, 14th International Conference on Tools and
Algorithms for the Construction and Analysis of Sys-
tems, TACAS’08/ETAPS’08, pages 337–340, Berlin,
Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
Diskin, Z. (2011). Model Synchronization: Mappings, Tiles,
and Categories, pages 92–165. Springer Berlin Hei-
delberg, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Diskin, Z. and Wolter, U. (2008). A diagrammatic logic for
object-oriented visual modeling. Electronic Notes in
Theoretical Computer Science, 203(6):19 – 41. Pro-
ceedings of the Second Workshop on ACCAT, 2007.
Diskin, Z., Xiong, Y., and Czarnecki, K. (2010). Specify-
ing overlaps of heterogeneous models for global con-
sistency checking. In Proceedings of the First Inter-
national Workshop on Model-Driven Interoperability,
MDI ’10, pages 42–51, NY, USA. ACM.
Ehrig, H., Ehrig, K., Prange, U., and Taentzer, G.
(2006). Fundamentals of Algebraic Graph Transfor-
mation. Monographs in Theoretical Computer Sci-
ence. Springer.
Fiadeiro, J. L. and Maibaum, T. (1995). Interconnecting
formalisms: Supporting modularity, reuse and incre-
mentality. SIGSOFT Softw. Eng. Notes, 20(4):72–80.
Han, P. K., Klein, W. M., and Arora, N. K. (2011). Vari-
eties of uncertainty in health care: A conceptual tax-
onomy. Medical decision making: an international
journal of the Society for Medical Decision Making,
31(6):828–838.
Jackson, D. (2002). Alloy: A lightweight object mod-
elling notation. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol.,
11(2):256–290.
Jussien, N., Rochart, G., and Lorca, X. (2008). Choco: an
Open Source Java Constraint Programming Library.
In CPAIOR’08 Workshop on Open-Source Software
for Integer and Contraint Programming (OSSICP’08),
pages 1–10, Paris, France, France.
K
¨
onig, H. and Diskin, Z. (2016). Advanced local checking
of global consistency in heterogeneous multimodel-
ing. In Wasowski, A. and L
¨
onn, H., editors, Modelling
Foundations and Applications - 12th European Con-
ference, ECMFA’16/STAF’16, volume 9764 of LNCS,
pages 19–35. Springer.
Lambers, L., Ehrig, H., Prange, U., and Orejas, F. (2008).
Embedding and Confluence of Graph Transformations
with Negative Application Conditions, pages 162–
177. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Lamo, Y., Mantz, F., Rutle, A., and de Lara, J. (2013).
A declarative and bidirectional model transformation
approach based on graph co-spans. In Proceedings
of the 15th Symposium on Principles and Practice
of Declarative Programming, PPDP ’13, pages 1–12,
NY, USA. ACM.
Mantz, F. (2014). Coupled Transformations of Graph Struc-
tures applied to Model Migration. PhD thesis, De-
partment of Mathematics and Informatics, Philipps-
Universit
¨
at Marburg, Germany.
Perea, A. (2012). Epistemic Game Theory: Reasoning and
Choice. Cambridge University Press, 1 edition.
Optimizing Distributed Resource Allocation using Epistemic Game Theory: A Model-driven Engineering Approach
51

Perea, A. (2014). Fron classical to epistemic game theory.
International Game Theory Review, 16(01):1440001.
Pinelle, D. and Gutwin, C. (2006). Loose coupling and
healthcare organizations: Deployment strategies for
groupware. Comput. Supported Coop. Work, 15(5-
6):537–572.
Rabbi, F., Lamo, Y., and MacCaull, W. (2014). Co-
ordination of multiple metamodels, with application
to healthcare systems. In 1st International Workshop
on (Meta)modelling for Healthcare Systems (MMHS),
2014, volume 37 of Procedia Computer Science,
pages 473–480. Elsevier.
Rabbi, F., Lamo, Y., and Yu, I. C. (2016a). Towards a cate-
gorical approach for meta-modelling epistemic game
theory. In Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE 19th Interna-
tional Conference on Model Driven Engineering Lan-
guages and Systems, pages 57–64. ACM.
Rabbi, F., Lamo, Y., Yu, I. C., and Kristensen, L. M. (2015).
Towards a Multi Metamodelling Approach for Devel-
oping Distributed Healthcare Applications. . NIK:
Norsk Informatikkonferanse, ISSN: 1892-0721.
Rabbi, F., Lamo, Y., Yu, I. C., and Kristensen, L. M.
(2016b). WebDPF: A web-based metamodelling
and model transformation environment. In MOD-
ELSWARD 2016 - Proceedings of the 4rd Interna-
tional Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and
Software Development, Rome, Italy, 19-21 February,
2016., pages 87–98. SciTePress.
Rossini, A., de Lara, J., Guerra, E., Rutle, A., and Lamo, Y.
(2012). A graph transformation-based semantics for
deep metamodelling. In Proceedings of the 4th Inter-
national Conference on Applications of Graph Trans-
formations with Industrial Relevance, AGTIVE’11,
pages 19–34. Springer-Verlag.
Rutle, A. (2010). Diagram Predicate Framework: A For-
mal Approach to MDE. PhD thesis, Department of
Informatics, University of Bergen, Norway.
Wang, X., Rutle, A., and Lamo, Y. (2015). To-
wards user-friendly and efficient analysis with al-
loy. In Proceedings of the 12th Workshop on
Model-Driven Engineering, Verification and Valida-
tion, MoDeVVa@MoDELS 2015, volume 1514 of
CEUR Workshop Proceedings, pages 28–37. CEUR-
WS.org.
MODELSWARD 2017 - 5th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
52
