
Discrete Strategy Game-theoretic Topology Control in Wireless Sensor
Networks
Evangelos D. Spyrou
1
, Shusen Yang
2
and Dimitrios K. Mitrakos
1
1
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece
2
Institute of Information and System Science, School of Mathematics and Statistics,
Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xian City, China
Keywords:
Transmission Power, Transmission Reliability, Potential Game, Pareto Optimality, Packet Reception Ratio.
Abstract:
One of the most significant problems in Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) deployment is the generation of
topologies that maximize transmission reliability and guarantee network connectivity while also maximising
the network’s lifetime. Transmission power settings have a large impact on the aforementioned factors. In-
creasing transmission power to provide coverage is the intuitive solution yet with it may come with lower
packet reception and shorter network lifetime. However, decreasing the transmission power may result in
the network being disconnected. To balance these trade-offs we propose a discrete strategy game-theoretic
solution, which we call TopGame that aims to maximize the reliability between nodes while using the most
appropriate level of transmission power that guarantees connectivity. In this paper, we provide the conditions
for the convergence of our algorithm to a pure Nash equilibrium as well as experimental results. Here we
show, using the Indriya WSN testbed, that TopGame is more energy-efficient and approaches a similar packet
reception ratio with the current closest state of the art protocol ART.
1 INTRODUCTION
A significant problem in Wireless Sensor Network
(WSN) topology management is to guarantee con-
nected network topologies that have a high transmis-
sion reliability. The simple approach would be to in-
crease the radio transmission power levels of uncon-
nected nodes. However, this is too simple and does
not account for the complexities of the wireless chan-
nel. An increase in transmission power might cause
an increase in interference, decreasing the number of
packets received (i.e. lowering Packet Reception Ra-
tio, or PRR). On the other hand, as we see in (Spy-
rou and Mitrakos, 2015b), if the distance between
the transmitter-receiver and interferer-receiver is dif-
ference by approximately a factor of 2, interference
does not cause packet loss. This indicates that a node
may select a high transmission power level, in order
to strengthen its signal, without suffering from packet
loss. There is a sweet spot in PRR related to trans-
mission power levels that can keep PRR to a high
level while not using a larger transmission power level
than necessary. The transmission power also affects
the energy consumption of the node, directly influ-
encing the lifetime of the WSN (Antonopoulos et al.,
2009). In order to handle this trade-off we present a
discrete strategy distributed game-theoretic approach
that maximizes each node’s PRR while using the op-
timal transmission power from an optimisation prob-
lem; guaranteeing connectivity. We call our approach
TopGame.
Specifically, we focus on the trade-offs between
energy consumption, and PRR. We use game theory,
since it can appropriately describe the behavior of
selfish nodes and find an optimal solution in a dis-
tributed manner. Modeling systems with selfish algo-
rithms have been shown to provide efficient solutions
that improve network performance (Yeung and Kwok,
2006). We consider nodes to be individual players
that play selfishly in order to find a best response for
their objectives. In this paper we present our model
and prove that this game is a potential game (Mon-
derer and Shapley, 1996). Potential games are games
where the incentive of players to change their strat-
egy can be expressed in a single global function, the
potential function. Potential games have been used
in wireless networks in a plethora of problems, in-
cluding power control (Heikkinen, 2006) (Spyrou and
Mitrakos, 2015a), cognitive radio (Neel et al., 2004),
gateway selection (Song et al., 2011) and channel al-
location (Chen et al., 2011). In our game-theoretic
formulation we prove that there is an equilibrium
Spyrou E., Yang S. and Mitrakos D.
Discrete Strategy Game-theoretic Topology Control inWireless Sensor Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0006128700270038
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Sensor Networks (SENSORNETS 2017), pages 27-38
ISBN: 421065/17
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved
27

point. Next, we provide testbed results to show the
convergence of our proposed algorithm and we com-
pare it to the closest state of the art algorithm, Adap-
tive Robust Topology (ART)
1
, with respect to connec-
tivity, energy-efficiency and PRR. To our knowledge
this is the first practical topology control game that
has been evaluated on a real testbed system, and show
the following:
• TopGame exhibits slightly lower network PRR
than ART, since it exploits a Transmission Relia-
bility metric to determine each node’s final trans-
mission power.
• Using TopGame, the network’s relative energy
consumption is less by 5% than ART’s, due to
the fact that TopGame can use a per node trans-
mission power setting, which remains so after the
optimisation process. Also, connectivity is pre-
served.
• TopGame’s operation increases contention for ac-
cessing the wireless medium, since it keeps a
steady transmission power level and it includes
the bootstrapping period. This explains the
slightly less PRR of our approach.
• TopGame includes mathematical proofs to sup-
port the convergence of each node’s transmission
power in the form of the Nash equilibrium of a
potential game.
• We prove that the Price of Stability and Price
of Anarchy of TopGame is 1. This shows that
TopGame can find the optimal equilibrium of the
game.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 pro-
vides the related work, Section 3 introduces topology
control in WSN, Section 4 describes game theory ba-
sics and potential games, Section 5 formally describes
TopGame, Section 6 shows the experimental results
obtained and Section 7 presents the conclusions.
2 RELATED WORK
The characteristics and behaviors of wireless links are
now more understood. There has been work measur-
ing the effects of varying power levels and showing
the irregularity of radio ranges and the lack of link
symmetry (Son et al., 2005) (Zhao and Govindan,
2003). The relationship between PRR and RSSI for
the Chipcon CC2420 radio was established in (Lin
et al., 2006). Subsequent work then looked at the
differences in behavior between indoor and outdoor
1
Note that by ART we mean the optimised ART.
networks, and fluctuations in link quality over longer
durations of time (Hackmann et al., 2008).
Regarding of Topology Control (TC) specifically,
(Hackmann et al., 2008) contributes a comprehensive
review of this field which we summarise. Given the
diversity of link behaviors influenced by their envi-
ronment, experimentation for much of the early TC
work was carried out using graph theory and simula-
tion studies for tractability reasons. Yet, this work
did not consider aspects like realistic radio ranges,
node distributions or node capability/capacities into
account, limiting their usefulness for real sensor net-
works (Li et al., 2005a; Li et al., 2005b) (Burkhart
et al., 2004) (Blough et al., 2007) (Gao et al., 2008).
For example, some have assumed that link costs are
proportional to link length, but in reality a more com-
plex relationship is evident (Son et al., 2005) (Gane-
san et al., 2002) (Zhao and Govindan, 2003). The
main competitors in the practical Topology control
area are PCBL (Son et al., 2005) and ART (Hack-
mann et al., 2008), which we introduce next.
PCBL was derived from link quality observations
showing that links with a very high PRR remain quite
stable. They then categorise links as blacklisted, mid-
dling or highly reliable. The power in the latter is
minimised to their lowest stable power setting while
the blacklisted are not used at all. The middling links
are those that lie between the two and are set to full
power. Given the expense of probing the network
to establish the link categories, this protocol cannot
work with dynamic routing protocols such as CTP
(Gnawali et al., 2009). CTP aims to find the least
expensive routes through the network. To overcome
such link probing, link quality metrics have been
used to approximate PRR in ATPC (Lin et al., 2006).
Specifically there is a link between RSSI and PRR,
and LQI and PRR over a monotonically-increasing
curve. Further, linear correlations between transmis-
sion power levels and RSSI/LQI are observed at the
receiver but are different for each environment moni-
tored. Therefore, ATPC estimates the slope and uses
closed feedback to adjust the model to the current sit-
uation to achieve lower bound RSSI (PRR).
Hackmann et al., showed that RSSI and LQI can-
not always realistically estimate PRR in indoor envi-
ronments (Hackmann et al., 2008), nor can instanta-
neous probing represent the behaviors of a link over
time. They propose ART, which does not rely on es-
timates of link quality nor does it involve long boot-
strapping phases. Being more dynamic, ART adapts
link power to changes in the environment as well as
contention using a gradient. Also, where applications
expect acknowledgment messages, ART can piggy-
back these to reduce communication overhead. ART
SENSORNETS 2017 - 6th International Conference on Sensor Networks
28

selects the appropriate transmission power based on
the failures observed when the target PRR is 95% and
a contention gradient.
In (Hao et al., 2015), the authors proposed a
distributed topology control and channel allocation
game-theoretic algorithm. The main objective of
the work is the relief of interference and the energy
consumption balancing. They examined the connec-
tion between topology control and channel allocation.
They designed a game-theoretic model that takes into
account transmission power, energy consumption and
interference suffered by a node. They have proven the
existence of Nash Equilibrium and they developed an
algorithm that preserves connectivity by jointly set-
ting the transmission power and channel. Lastly, their
algorithm converges to Pareto optimality.
Tan et al. (Tan et al., 2015), suggested a topology
control scheme where every node tunes its transmis-
sion power adaptively, in order to use its harvested en-
ergy in an efficient manner. The authors, proposed an
ordinal potential game model where high harvesting
nodes cooperate with the low harvesting nodes to en-
sure network connectivity. They proved the existence
of a Nash Equilibrium and they designed an algorithm
that achieves it.
Abbasi at al. (Abbasi and Fisal, 2015), investi-
gated the issue of topology control in wireless sen-
sor networks, in order to perform energy consumption
minimisation and energy balancing. Their approach
accomplished their objectives by adjusting transmis-
sion power on the nodes and preserving connectivity.
The authors utilised a game-theoretic scheme to ad-
dress energy welfare topology control. They showed
that their proposed game-theoretic solution is a poten-
tial game and it achieves a unique Nash equilibrium,
which is Pareto optimal as well.
Nahir et al. (Nahir et al., 2008), provided a game-
theoretical solution to the topology control problem,
by addressing three major issues: the price of estab-
lishing a link, path delay and path congestion prone-
ness. They established that bad performance due to
selfish play in the considered games is significant,
while all but one are guaranteed to have a Nash equi-
librium point. Furthermore, they showed that the
price of stability is typically 1; hence, often optimal
network performance can be accomplished by being
able to impose an initial configuration on the nodes.
Furthermore, the authors express their concern re-
garding the computational tractability of their solu-
tion.
Komali et al. (Komali et al., 2008), analysed the
creation of energy efficient topologies with two pro-
posed algorithms. Specifically, their game-theoretic
model specified that nodes have the incentive to pre-
serve connectivity with a sufficient number of neigh-
bours and that the network will not partition. They
proved that their game is an exact potential game and
that a subset of the resulting topologies is energy ef-
ficient. They addressed the major issue of fair power
allocation by providing the argument of efficient allo-
cation vs fair allocation.
3 WSN AND TOPOLOGY
CONTROL
Wireless sensor networks are networks of small com-
putational devices fitted with radio transceivers for
communication and sensors to capture data. Topol-
ogy control can be defined by the construction of
a graph that represents the nodes and links in the
network that does not consist of any disjoint parts.
Good topology control mechanisms can be character-
ized by providing an energy efficient network, offer-
ing high throughput and doing so with a low over-
head. Energy-efficiency equates to the use of the
minimum transmission power that guarantees con-
nectivity, where throughput can be maximised by re-
ducing interference and contention on the wireless
medium. However, minimum transmission power
does not guarantee a high reliability of transmission
resulting in high throughput. This is due to a weak
signal that may be significantly influenced by a small
portion of interference.
For the most part, hitherto link asymmetry has
been ignored, and the use of different transmission
power levels when a node transmits to different neigh-
bours may cause undesired packet loss. In addition,
in a dense network, a node having a large number of
neighbours may not be able to cope with transmission
power changes when unicasting to different recipi-
ents in that neighbourhood while expecting to achieve
a high PRR as well. As observed by Ahmed et al.
(Ahmed et al., 2009), environmental effects and dif-
ferent node transmission powers are the major cause
of link asymmetry in WSNs.
4 GAME THEORY AND
POTENTIAL GAMES
Game theory studies mathematical models of conflict
and cooperation (Von Neumann et al., 2007), between
nodes in our work. Therefore, our meaning of the
term game corresponds to any form of social inter-
action between two or more nodes. The rationality
of a node is satisfied if it pursuits the satisfaction of
Discrete Strategy Game-theoretic Topology Control inWireless Sensor Networks
29

its preferences through the selection of appropriate
strategies. The preferences of a node need to satisfy
general rationality axioms, then its behavior can be
described by a utility function. Utility functions pro-
vide a quantitative description of the node’s prefer-
ences and the main objective is therefore the maxi-
mization of its utility function.
In this work, we focus on strategic non-
cooperative games, since we consider nodes to act
as selfish players that want to preserve their interests.
The intuition behind this is that the nodes will reach
an optimal state, without having to pay a price to
maximize their payoffs. The Nash equilibrium is the
most important equilibrium in non-cooperative strate-
gic form games. It is defined as the point where no
node will increase its utility by unilaterally changing
its strategy. It got its name from John F. Nash who
proposed it (Nash Jr, 1950).
In 2008, (Daskalakis et al., 2008) Daskalakis
proved that finding a Nash equilibrium is PPAD-
complete . Polynomial Parity Arguments on Directed
graphs (PPAD) is a class of total search problems
(Papadimitriou, 1994) for which solutions have been
proven to exist, however, finding a specific solution
is difficult if not intractable. This development lead
researchers to concentrate a specific class of games
called ’Potential Games’, due to the important prop-
erties that pure Nash equilibria will always exist and
best response dynamics are guaranteed to converge.
This class of games consists of the exact and or-
dinal potential games. In this paper we utilise exact
potential games and refer the reader to (Monderer and
Shapley, 1996) for details on potential games. In or-
der to use exact potential games, it is essential to have
a potential function that has the same behavior as the
individual utility function, when a player unilaterally
deviates.
More formally:
A game GhN, A,ui, with N players, A strategy
profiles and u the payofffunction, is an exact potential
game if there exists a potential function
V : A → R (1)
subject to
∀i ∈ N,∀σ
−i
∈ A
−i
,∀σ
i
,σ
′
i
∈ A
i
(2)
where σ
i
is the strategy of player i, σ
′
i
is the deviation
of player i, σ
−i
is the set of strategies followed by
all the players except player i and A
−i
is the set of
strategy profiles of all players except i such as
V(σ
i
,σ
−i
) −V(σ
′
i
,σ
−i
) = u
i
(σ
i
,σ
−i
) − u
i
(σ
′
i
,σ
−i
)
(3)
5 TopGame
We developed the TopGame algorithm that aims to
guarantee connectivity, by locating the best response
of PRR and transmission power. The intuition behind
this research is that TopGame will force nodes to con-
verge to the best transmission power.
A WSN consists of a set of nodes N and each
node i ∈ N can switch its transmission power p
k
i
∈ P,
where k ∈ 3,7, 11,15,19,23,27, 31 and P is the set
of the available transmission power levels of our ex-
ample CC2420 transceiver. In this paper, we employ
4 transmission power levels, namely 11,15, 19,23, in
order to identify the PRR when transmission powers
that operate mostly on the gray area (Son et al., 2004)
are used. Let a vector P = (p
1
,p
2
,...,p
|N|
) be an allo-
cation of the transmission power level of each sensor
node. The total number of possible power allocations
is 4
|N|
. The aim of this paper is to determine a power
allocation in a distributed way, which can achieve a
best response rade-off between network connectivity,
energy-efficiency and transmission reliability, using
game theory.
5.1 Connectivity Definition and
Measurement
In this paper we consider the small-world Model A
from (Ganesh and Xue, 2007), where there are N
nodes in the network and each one arbitrarily selects
m nearest neighbours to connect to. Essentially, we
utilise the variant of this small-world model, where
node locations are being modeled by a stochastic
point process. The number of neighbours consists
of nearest neighbours and shortcuts. A shortcut is an
edge between two nodes if either of the two nodes ex-
ist in the nearest neighbour set of the other. If a node
is connected by a nearest neighbour and a shortcut,
multiple edges are replaced by a single one. The pres-
ence of the shortcuts reduces the network diameter.
Furthermore, we have to note that m is the number of
neighbours a node has in terms of a spatial graph, and
(N − 1)p is the number of neighbours it has via short-
cuts. In order to ensure connectivity the quantities
m = (1 + δ)
p
2log(N) and Np = (1+ δ)
p
2log(N),
where δ > 0, are sufficient. Hence connectivity is pre-
served with a smaller degree of (nearest neighbours
plus shortcuts). We select a degree of 6 for each each
node. It is well known that the node degree can be
reached by adjusting the transmission power; hence,
the transmission power level that satisfies connectiv-
ity satisfies the condition that more than 6 nodes exist
in the neighbourhood of each node.
SENSORNETS 2017 - 6th International Conference on Sensor Networks
30

5.2 Transmission Reliability (TR)
For a wireless link (i, j), the Packet Reception Ratio
PRR
i, j
is defined as the ratio of the number of packets
received by node j over the number of packets sent by
node i. It can be expressed by approximation as
PRR
i, j
= (1− ξ
i, j
)
l
(4)
where l is the packet length in bits.
The Bit Error Rate (BER), which we denote as
ξ
i, j
, is given by the following formula (Fu et al., 2012)
ξ
i, j
=
1
2
1−
r
γ
i, j
1+ γ
i, j
!
(5)
where γ
i, j
is the Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise
Ratio (SINR) of the transmission from node i to node
j. γ
i, j
is given by
γ
i, j
=
H
i, j
p
i
∑
t6=i,t6= j
p
t
H
t, j
+ N
0
(6)
where N
0
is the white noise and H
i, j
is the channel
gain of the wireless link (i, j) and H
t, j
is the channel
gain between the receiver and an interferer. Due to
the path loss, the larger the distance between nodes t
and j the smaller the H
t, j
. We focus on static WSNs,
hence, we assume that the channel is slow fading in
nature and the channel gain of every link remains con-
stant before the convergence of the TopGame algo-
rithm.
To measure the reliability of links around node i,
we define a new metric called Transmission Reliabil-
ity (TR
i
) as
TR
i
(p
i
, p
−i
) =
∑
j∈N
i
(p
i
,p
−i
),k∈N
j
(p
i
,p
−i
),k6=i
PRR
k, j
S
j∈N
i
(p
i
,p
−i
)
(N
j
(p
i
, p
−i
) − {i})
(7)
where p
i
is the power level of node i, p
−i
means the
power levels of all nodes except i, N
i
(p
i
, p
−i
) is the
set of nodes such that ∀ j ∈ N
i
(p
i
, p
−i
), PRR
i, j
> 0.
For instance, Figure 1 shows a sub-graph of
a WSN for a given transmission power allocation.
For each link (i, j) PRR
i, j
> 0. In this sub-graph
N
6
= 2, 15,7,11 and βTR
6
= (PRR
1,2
+ PRR
15,2
+
PRR
12,2
+ PRR
2,15
+ PRR
9,15
+ PRR
7,15
+ PRR
15,7
+
PRR
10,7
+ PRR
11,7
+ PRR
7,11
+ PRR
14,11
)/11.
In practice, everynode i can obtain TR
i
at run time
by every node j in N
i
calculating the
PRR
k, j
as the
average PRR
k, j
, k ∈ N
j
− {i} and periodically broad-
casting PRR
k, j
. Thereafter node i calculates TR
i
.
Figure 1: An example to explain Transmission Reliability
metric.
5.3 Utility and Potential Function
We define the utility function of each node i as,
u
i
(p
i
) = TR
i
− c
i
p
i
(8)
where c
m
is the price assigned to each strategy played
by a node/player.
Our strategy domain consists of 4 strategies,
which are 11,15,19, 23, which correspond to the val-
ues in table 1. Notably, the 2 smallest and 2 largest
transmission power levels of the CC2420 radio have
been excluded. The main reason is to see TopGame
operate under medium to large SINR regime. The sec-
ond reason is to simplify TopGame.
Table 1: Transmission Power Levels and Values.
PA LEVEL dB mA
11 -10 11.2
15 -7 12.5
19 -5 13.9
23 -3 15.2
It is straightforward to see that the above utility
function has a minimum under the following condi-
tion of medium to high SINR values. We do the price
assignment in a similar way with (Candogan et al.,
2010). The prices assigned at every node has the value
1 except when it reaches its maximizer. Each node
then assigns the price given below:
c
i
= dif f(TR
i
) (9)
Hence, if we take the first derivative to obtain the min-
imum, it follows that there is a local minimum. Since
we wish to maximize the function we simply take the
negative of (8).
u
i
(p
i
) = c
i
p
i
− TR
i
(10)
Discrete Strategy Game-theoretic Topology Control inWireless Sensor Networks
31

Thereafter we wish to define the potential function
and prove that the game G is a potential game.
Proposition 1. The game G is a potential game. The
potential function is given by
V(p) =
∑
i
c
i
p
i
−
∑
i
TR
i
, p
i
∈ A (11)
Proof. This comes as a result by taking the character-
isation of the potential games in (Monderer and Shap-
ley, 1996) where
∂V (p)
∂p
i
=
∂u
i
(p)
∂p
i
,i ∈ N.
V(p
i
, p
−i
)−V(p
′
i
, p
−i
) = u
i
(p
i
, p
−i
)−u
i
(p
′
i
, p
−i
)+
N
∑
m∈N,m6=i
(u
m
(p
m
, p
−m
) − u
m
(p
′
m
, p
−m
))
Since only one node can deviate
N
∑
m∈N,m6=i
(u
m
(p
m
, p
−m
)− u
m
(p
′
m
, p
−m
)) = 0. Hence we
conclude that Γ is an exact potential game. This proof
comes as a result of the fact that given a strategy of
a node/player m, p
m
∈ N and an alternative strategy
p
′
m
∈ N and taking the assumption that the strategies
of all the other nodes remain the same, we have
u
i
(p
i
, p
−i
) − u
i
(p
i
, p
′
−i
) =
V
i
(p
i
, p
−i
) −V
i
(p
i
, p
′
−i
) (12)
where p
−i
is the transmission power strategy of all the
nodes excluding that of the node i. Hence, the game
is a potential game.
Remark 3.1: The potential function is signifi-
cant since its maximisation, when a specific policy
is played, results in this policy being an equilibrium
of the designed game. In this work, the strategy set
is discrete; hence, in the case that the potential func-
tion satisfies particular types of concavity, such as the
Larger Midpoint Property (LMP) (Ui, 2008), the con-
verse is true as well. If a policy is an equilibrium,
it maximises the potential function. Thus, we may
consider the TopGame as the following optimisation
problem.
ˆp
i
= argmaxV
i
(i) (13)
As presented in (Altman et al., 2009), we consider
two n-dimensional vectors δ(1), δ(2). Definition 1:
(Marshall et al., 2010) A vector δ(2) majorises δ(1),
which we denote as δ(1) ≺ δ(2), if δ(2) is more ”un-
regular” in the following fashion:
k
∑
i=1
δ
[i]
(1) ≤
k
∑
i=1
δ
[i]
(2),k = 1,2,...,n − 1
k
∑
i=1
δ
[i]
(1) =
k
∑
i=1
δ
[i]
(2)
(14)
where δ
[i]
(m) is a permutation of δ
i
(m) satisfying the
condition δ
[1]
(m) ≥ δ
[2]
(m) ≥ ... ≥ δ
[n]
(m),m = 1,2
Equation (8) suggests that the largest element of
δ(2) is larger than the largest element of δ(1). Conse-
quently, the smallest element of δ(2) is smaller than
the smallest element of δ(1). Thereafter we proceed
in Schur convexity properties of majorisation.
Definition 2:: A function f : R
n
→ R is Schur con-
cave if δ(1) ≺ δ(2) suggests f(δ(1)) ≥ f(δ(2)). f is
Schur convexif the inequality suggests that f(δ(1)) ≤
f(δ(2)).
Definition 1 dictates that there is strong majori-
sation; however, at least one of the inequalities of
(8) is strict. Furthermore, Proposition C.2 of (Mar-
shall et al., 2010) dictates that a function f : R
n
→ R
that is symmetric and convex(concave), is also Schur-
convex (concave). Hence, we need to show that our
potential function is Schur-concave, in order to pro-
ceed with the majorisation properties.
Lemma 1. Function V is concave in N
Proof. It is obvious that the function is concave, since
if we take the second derivative test the first term
will be set to 0 and the second term is a concave
term (raised to power) for medium to large SINR val-
ues. Note that for very high SINR values the second
derivative of (10) become positive and the function
becomes convex as we can deduct from (Meshkati
et al., 2006).
Proposition 2. If the function u(p) is concave then
the function V(p) is Schur concave.
Proof. The proof is given by using the following
corollary from (Marshall et al., 2010).
Corollary 5.0.1. Let φ(x) =
n
∑
i=1
g(x) where g is con-
cave (convex). Then φ is Schur-concave (convex)
Theorem 5.1. The Game G reaches the global opti-
mum via the potential function V(p) maximisation.
Proof. Recall that the potential V(p) Schur concave
and it satisfies the LMP. It follows that if p
∗
is a Nash
equilibrium strategy, then it maximises the potential
and is the global maximum. Assume that there is an-
other strategy profile p
′∗
that maximises the poten-
tial and is the global maximum. This means by p
∗
majorises p
′∗
. Since V(p) is Schur concave it fol-
lows by definition that V(p
′∗
) ≥ V(p
∗
). Since, p∗
maximises the potential, this is only possible when
V(p
′∗
) = V(p
∗
). Hence, p
∗
is the global optimum.
This also comes as a result of the fact that we
have shown that there is a critical point in the function
SENSORNETS 2017 - 6th International Conference on Sensor Networks
32

V(p). It follows from (Jorswieck and Boche, 2006) -
Theorem 2.22 - that the critical point p
∗
is the global
optimum.
Notably, Schur concavity of V not only allows us
to capture the optimal policies, but it allows the com-
parison of the performance of two non-optimal strate-
gies, whenever one of the policies majorises the other.
Theorem 5.2. The price of stability of the game is 1
Proof. It follows from the previous theorem that
shows that the game reaches the global optimum.
Thereafter, we will proceed with the derivation
of the Price of Anarchy (PoA) (Nisan et al., 2007),
in order to further check the optimality of the game.
Firstly, though, we start with the following result.
Definition 5.1. (Pareto efficient) (Myerson, 1991)
A strategy profile (p
OPT
i
, p
OPT
−i
), is considered to
be strongly Pareto efficient if and only if there
exists no other strategy profile (p
i
, p
−i
) such that
u
i
(p
i
, p
−i
) ≥ u
i
(p
OPT
i
, p
OPT
−i
),∀i ∈ N and u
i
(p
i
, p
−i
) >
u
i
(p
OPT
i
, p
OPT
−i
) for at least one node m. On the other
hand, a strategy profile (p
OPT
i
, p
OPT
−i
) is weakly Pareto
efficient if and only if there exists no strategy profile
(p
i
, p
−i
) such that u
i
(p
i
, p
−i
) > u
i
(p
OPT
i
, p
OPT
−i
),∀i ∈
N. We use the term Pareto efficient for both weak and
strong cases.
Definition 5.2. A pure strategy NE is a Pareto effi-
cient pure strategy NE if it is Pareto efficient.
Theorem 5.3. A maximizer of V, which coincides
with the optimal solution of (11), is a Pareto efficient
pure strategy NE.
Proof. We have shown previously that the game G
reaches the maximum which is a pure strategy NE.
Hence (p
OPT
i
, p
OPT
−i
) constitutes an optimal solution
of (11). There is no other strategy that maximises
the potential. That is that there is no strategy profile
(p
1
,...p
i
) ∈ P
i
i∈N
, such that
u
i
(p
1
,...p
i
) = V(p
1
,...p
i
) > u
i
(p
OPT
m
, p
OPT
−i
)
= V(p
OPT
i
, p
OPT
−i
),∀i ∈ N (15)
Thus, considering Definition 5.2, (p
OPT
i
, p
OPT
−i
) is
Pareto efficient. Moreover, let us assume the ∀i ∈ N,
p
i
is an alternative strategy of node/player i, where
p
i
6= p
OPT
i
. Then, we obtain
u
i
(p
i
, p
OPT
−i
) ≥ u
i
(p
OPT
i
, p
OPT
−i
) (16)
We see that there is no node that can unilaterally
change its transmission power/ strategy, in order to
increase its utility. Furthermore, the strategy pro-
file (p
OPT
1
,..., p
OPT
i
) is also a pure strategy NE. To
summarise, (p
OPT
1
,..., p
OPT
i
) is a Pareto efficient pure
strategy NE.
Since, the game G may have more than one pure
strategy NEs, we will check the optimality of the NE
to show the relationship between the local optimal
NE and the Pareto efficient NE. Even though we have
shown that the Game G goes to the global optimum,
we will strengthen this proof even further, by evaluat-
ing the ratio between the highest utility and the worst-
case NE, namely the PoA.
Theorem 5.4. PoA = 1, i.e. a pure strategy profile of
G is Pareto efficient.
Proof. We assume that p
OPT
i
is a Pareto efficient NE.
Also, assume that p
∗
i
is an arbitrary pure strategy NE
p
∗
i
= (p
∗
i
, p
∗
−i
). Then for any arbitrary node/player i,
we have
u
i
(p
∗
) = V(p
∗
) = c
i
p
∗
i
− TR
∗
i
(17)
Note that u
i
(p
∗
) ≥ u
i
(p
OPT
i
, p
∗
−i
) according to the
definition of a game. Therefore, we have
u
i
(p
∗
) = V(p
∗
) = c
i
p
∗
i
− TR
∗
i
≥ u
i
(p
∗
) = V(p
OPT
) = c
i
p
OPT
i
− TR
OPT
i
(18)
Furthermore , since we have assumed that p
OPT
is
a Pareto-optimal pure strategy NE, ∀i ∈ N
V(p
OPT
) ≥ V(p
∗
) (19)
Combining (18) and (19) we have V(p
OPT
) ≥
V(p
∗
),∀i ∈ N. Hence, PoA = 1.
5.4 Algorithm Design
The TopGame algorithm is a cross-layer approach
that encapsulates information taken from the routing,
MAC and physical layers. In particular, the PRR and
neighbour information are obtained from the routing
layer, the transmission power used is acquired from
the radio and the MAC is responsible for triggering
the game to determine the topology in the case of
nodes failing or newly added to the network.
Initially, all nodes start communicating at their
maximum transmission power p
max
= 23. Node i col-
lects the neighbour information, such as current trans-
mission power levels used by its neighbours and their
respective PRR. This occurs simultaneously, since the
number of neighbours is determined via periodic bea-
cons being broadcast and the PRR obtained by unicas-
ting to random neighbours using a gossip-based pro-
tocol (Dammer and Hinrichsen, 2003). The nodes are
also synchronised using beacons with a firefly-based
(Breza and McCann, 2008) algorithm.
Node i iterates through its 4 available transmission
power levels, it computes TR for each power level and
Discrete Strategy Game-theoretic Topology Control inWireless Sensor Networks
33
it finally maximises its utility function u
i
. Note that
for practical reasons the pricing of each node’s utility
function is set to 1. The global optimum is accom-
plished as we can see in Theorem 5.1. Pseudocode of
TopGame is presented in Algorithm 1.
Algorithm 1: TopGame at node i.
Require: A
i
= {p
i
1
, p
i
2
,..., p
i
max
}
Require: degree = 6, p
i
= p
max
1: for i = 1 to N
i,p
do
2: get p
−i
,PRR
i,k
∈ N
i
3: N
i
← N
p
i
i
4: compute TR
i
5: u
i
(p
i
, p
−i
) = c
i
∗ p
i
− TR
i
6: end for
7: ˆp
i
= argmaxu
i
(m)
In the case of the addition or a failure of node,
nodes that detect a change in their neighbourtable ini-
tiate TopGame from the start, since their TR will be
affected by the topological change. This is due to the
fact that TopGame is a repeated game only on topo-
logical alterations.
5.4.1 Message Overhead
The message overhead per transmission power con-
sists of the sum of the broadcast messages for syn-
chronisation and the unicast messages transmitted to
each of the neighbours of every node. That is,
O
TopGame
= f
sync
∗ N + N ∗ f
link
∗ m∗ M (20)
where N is the number of nodes, m is the window
of the unicast transmission to obtain PRR and M is
the number of neighbours of every node for a given
transmission power.
Since f
sync
= Θ(1), f
link
= Θ(N) and M = Θ(1),
provided some constants c
1
,c
2
,c
3
we have: f
sync
≤
c
1
, f
link
≤ c
2
∗ N,M ≤ c
3
. Therefore, 20 can be ex-
pressed as follows:
O
TopGame
≤ f
sync
∗ N + N ∗ f
link
∗ m∗ M
⇒ O
TopGame
≤ c
1
∗ N + c
2
∗ N ∗ m∗ c
3
⇒ O
TopGame
≤ N ∗ (c
1
+ m∗ c
2
∗ c
3
)
⇒ O
TopGame
= O(N)
6 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
AND RESULTS
In order to evaluate TopGame, in comparison to ART,
we performed 120 minute experiments using 50 nodes
selected at random on Indriya. The data rate of the
nodes was 250 kbps and each node transmits 4 pack-
ets per second. In addition each node calculates its
PRR over a window of 8 packets. Each node finishes
iterating through all the transmission power levels and
the utility function of each power level has been ob-
tained in order to proceed with the maximisation.
Our aim is to show that converging to lower trans-
mission powers, may provide similar reception per-
formance. In this section we will provide results
that show that TopGame approachesART (Hackmann
et al., 2008) in terms of PRR and is slightly better in
energy-efficiency while ensuring that the network is
connected.
6.1 Performance and Energy
Consumption
Initially, we obtained the average PRR and relative
energy consumption, in order to evaluate both algo-
rithms globally. The network average PRR is pro-
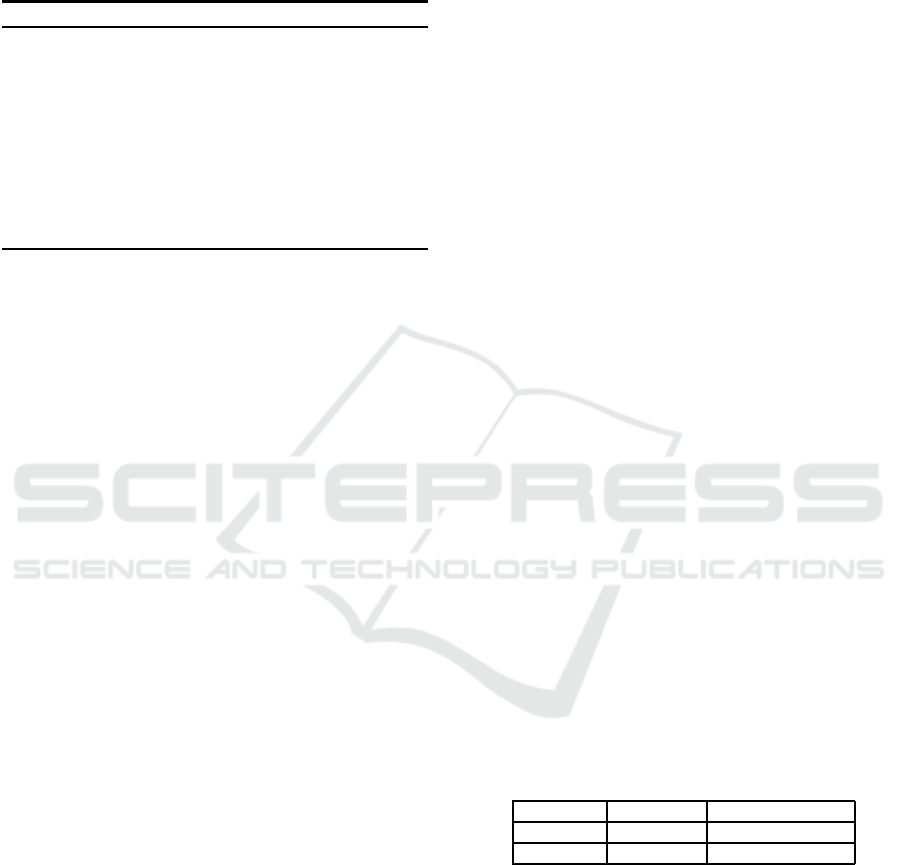
vided in Figure 2 (a). Specifically, we observe that
TopGame exhibits an average network PRR of 44.7%,
while ART 48.1%. Moreover, the standard deviation
of ART is higher than TopGame’s by 3%.
The difference in the PRR between the two
schemes is not quite significant; However, we have
shown that a game theoretic algorithm, with a more
systematic approach, exhibits similar performance
with a state-of-the-art practical algorithm such as
ART. Further, the formation of less links does indi-
cate that TopGame uses its utility function that finds
the sweet spot per node. On the other hand, ART fluc-
tuates between its two packet failure thresholds; thus,
forming more links. As we have seen in a previous
section, contention is related to the number of neigh-
bours (K) of each node. Table 2 presents the average
degree of the network and the number of links that are
formed with TopGame and ART.
Table 2: Average K and formed links.
Average K Number of Links
ART 7 360
TopGame 7 338
In order to examine whether the difference in the
PRR average of TopGame and ART is a result of
channel collision we performed 2 hour experiments
measuring the Clear Channel Assessment (CCA) fail-
ures. Figure 2 (c) presents the CCA failures ratio of
TopGame and ART. Briefly, a CCA operation occurs
when the MAC layer receives a packet to transmit,
then it instructs the physical layer to check channel
availability (CCA) in two consecutive slots. If the
channel is found to be available in both slots, the node
proceeds with its transmission. Otherwise, the node
SENSORNETS 2017 - 6th International Conference on Sensor Networks
34
(a) Average PRR
(b) Average Relative Energy
Consumption
(c) Average CCA Failures Ratio
Figure 2: TopGame and ART average Relative Energy, Mean PRR and CCA failures Mean of 50 nodes.
attempts CCA again after a random back-off, which it
repeats a certain number of times and it calls a failure
of access to the upper layer. Hence, with TopGame
exhibiting nearly 10% more CCA failures than ART,
it is natural to assume that the difference in average
PRR comes from a higher interference and collisions
of TopGame of the bootstrapping period, since it ini-
tially forms a larger number of links that are included
in the graph. Specifically, TopGame exhibits 43%
failures, while ART’s percentage is 33.6%.
In our experiments we were unable to directly
monitor the energy consumed by the listening and
transmitting periods of each node. Thus, we decided
to use unicast communications as an indicator to cal-
culate the relative average energy. Making the as-
sumption that all nodes spend the same amount of en-
ergy in listening, to get a rough idea of relative energy
consumption, we added the number of unicast mes-
sages transmitted by ART and TopGame with their
respective transmission powers and multiplied them
with the corresponding mA radio energy consump-
tion. The relative energy consumption of the two al-
gorithms can be seen in Figure 2 (b). TopGame con-
sumes 5% less energy than ART, including the boot-
strapping period.
This is due to the fact that the nodes do not fluc-
tuate on a per packet basis and they are not targeting
a very high PRR value as dictated in the ART thresh-
olds; hence, TopGame is slightly more energy effi-
cient. We present an example of two links from both
TopGame and ART, in order to show the difference in
the switching between transmission powers and the
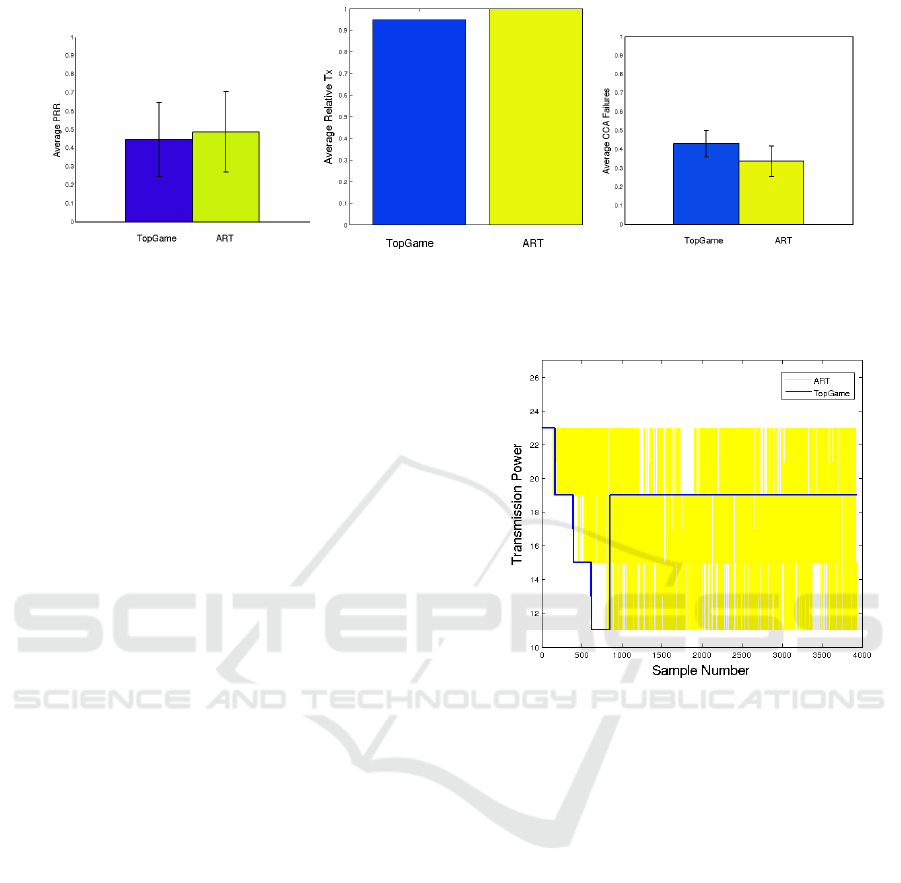
convergence of TopGame. From the figures 3 and 4,
it is clear that ART switches its transmission power
according to packet drops; hence, the Tx fluctuation
in the figure. On the other hand, TopGame collects
TR for each available transmission power and con-
verges to the transmission power maximizing the util-
ity function. Also, we are not aware of the energy cost
Figure 3: ART and TopGame Node 13 Tx levels.
of the continuous Tx switch. We assume it is negli-
gible. Note that TopGame is repeated only when a
neighbourhood change is detected.
Recall that ART’s intention is to reach the target
PRR of 95%, yet we observe that its reception qual-
ity is significantly lower. TopGame also does not at-
tain this lofty figure. We believe that is the case for
our scheme because of the bimodal distribution of
802.15.4 link qualities (Srinivasan et al., 2007).
By looking at the Cumulative Density Functions
(CDF) of the two algorithms in figure 5, we observe
that TopGame has a slightly higher probability of
forming poorer quality links of PRR lower than 20%.
ART has a lower probability of forming medium to
high quality links. Furthermore, TopGame exhibits a
sightly higher probability of establishing links with
PRR over 80%. It would be strong to claim that
TopGame is better than ART; however, approaching
the numbers of ART is significant, since it relies in
concrete theoretical basis.
Finally, we compared the RAM and ROM over-
head of TopGame with ART. Table 3 shows that
Discrete Strategy Game-theoretic Topology Control inWireless Sensor Networks
35
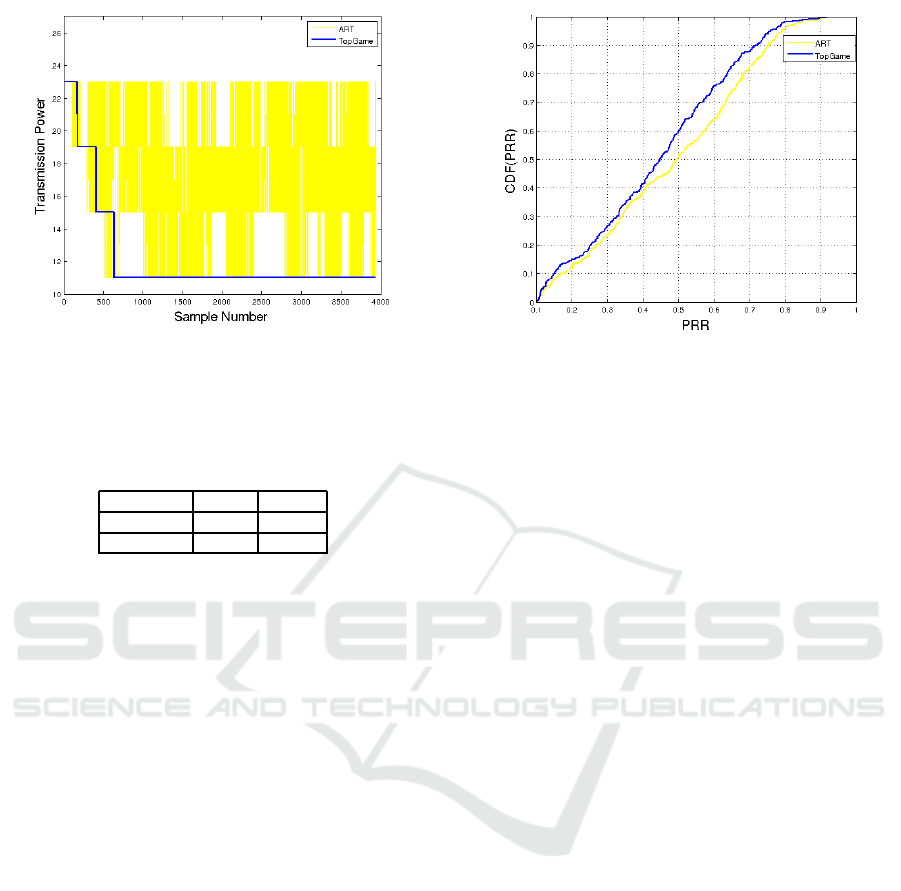
Figure 4: ART and TopGame Node 41 Tx levels.
TopGame consumes 2348 more ROM bytes than
ART, while it produces an overhead in RAM of 342
bytes.
Table 3: RAM and ROM (bytes).
RAM ROM
TopGame 3426 25228
ART 3084 22880
6.2 Connectivity
After we obtained the results we evaluated connectiv-
ity offline using method that determines whether the
resulting graph is connected. This was to evaluate the
connectivity model we discussed in a previous sec-
tion. We have shown that the average degree of each
node is greater than 6 nodes. We derived the avail-
able links from TopGame and ART’s data sets and we
created their respective adjacency matrices. There-
after, we used the matrices to find a zero eigenvalue.
In the case that the corresponding eigenvector has 0s,
then a sum of non-zero number of rows/columns of
the adjacency is 0 (Horn and Johnson, 2005). Hence,
the degrees of these nodes are 0 and the graph is dis-
connected. Both TopGame and ART resulted in fully
connected graphs.
7 CONCLUSIONS
Compared with the state of the art protocol ART, we
showed that TopGame is a general solution provid-
ing efficient robust Topology Control minimising the
costs of communications while ensuring connectivity.
First, we evaluated ART and TopGame on Indriya us-
ing 50 nodes to determine the average PRR and the
average relative TX power. We evaluated connectiv-
ity based on a method that checks the eigenvector of
Figure 5: CDF for ART and TopGame.
each algorithms adjacency matrix (links) and deter-
mined that the resulting graph is connected. The ex-
periments on Indriya showed that TopGame reduces
power consumption compared with ART without sig-
nificantly degrading link quality. Macro-benchmarks
comparing TopGame to ART protocol indicated that
TopGame provides guaranteed connectivity and ex-
hibited slightly lower PRR than its competitor and
5% improvement on energy consumption. The corre-
sponding Probability Density Functions showed that
TopGame has a slightly higher probability of hav-
ing links of low quality (< 20%) than ART. More-
over, ART has a lower probability of creating links
of > 20 − 80% PRR. Finally, TopGame has a better
probability of creating high PRR links (> 80%) This
is a promising factor of the comparison between the
two algorithms in terms of performance, since the av-
erage network PRRs were not significantly different.
In terms of energy consumption, we presented results
that show that TopGame converges to lower transmis-
sion power levels than ART making it more energy-
efficient.
The main differences between ART and TopGame
are that ART establishes per-link power levels while
TopGame establishes power settings for a given
neighbourhood of nodes, and thus can be seen as non
link-based. A node running ART will have to switch
between transmission powers to transmit packet to
its neighbours. This has an impact on the transmis-
sion power selection in larger networks, since the
target PRR (95%) is not reached and nodes select
high transmission powers. TopGame’s power is set
to cover the neighbourhood and therefore has no such
switching overhead. ART obtains data and makes de-
cisions by indirectly considering link asymmetry in
that; hence ART selected higher transmission power
levels. In fact, their unoptimised version not using
the contention gradient verify these phenomena and
SENSORNETS 2017 - 6th International Conference on Sensor Networks
36

even the improved version also shows a decrease in
PRR. However, link asymmetry is taken into account
in TopGame; where bi-directional information helps
to ensure both the connectivity of all nodes and that
we will converge at a Nash Equilibrium. Finally, in
terms of implementation, ART is closely coupled to
CTP whereas, though TopGame is slightly more ex-
pensive in terms of speed and footprint, it is agnostic
to WSN Operating System or stack implementations
and is therefore more generally applicable. We aim to
interface our approach with CTP or other state of the
art routing protocol such as the Backpressure Collec-
tion Protocol (BCP) (Moeller et al., 2010).
REFERENCES
Abbasi, M. and Fisal, N. (2015). Noncooperative game-
based energy welfare topology control for wireless
sensor networks. Sensors Journal, IEEE, 15(4):2344–
2355.
Ahmed, N., Misra, P., Jha, S., and Ostry, D. (2009). Char-
acterization of link asymmetry in wireless sensor net-
works. In ACM SenSys, pages 373–374.
Altman, E., Kumar, A., and Hayel, Y. (2009). A po-
tential game approach for uplink resource allocation
in a multichannel wireless access network. In Pro-
ceedings of the Fourth International ICST Confer-
ence on Performance Evaluation Methodologies and
Tools, page 72. ICST (Institute for Computer Sci-
ences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications
Engineering).
Antonopoulos, C., Prayati, A., Stoyanova, T., Koulamas, C.,
and Papadopoulos, G. (2009). Experimental evalua-
tion of a WSN platform power consumption. In IEEE
IPDPS, pages 1–8. IEEE.
Blough, D., Leoncini, M., Resta, G., and Santi, P. (2007).
Topology control with better radio models: Implica-
tions for energy and multi-hop interference. Perfor-
mance Evaluation, 64(5):379–398.
Breza, M. and McCann, J. (2008). Lessons in implementing
bio-inspired algorithms on wireless sensor networks.
In Adaptive Hardware and Systems, 2008. AHS’08.
NASA/ESA Conference on, pages 271–276. IEEE.
Burkhart, M., Von Rickenbach, P., Wattenhofer, R., and
Zollinger, A. (2004). Does topology control reduce
interference? In ACM MOBIHOC, pages 9–19.
Candogan, U. O., Menache, I., Ozdaglar, A., Parrilo, P.,
et al. (2010). Near-optimal power control in wireless
networks: A potential game approach. In INFOCOM,
2010 Proceedings IEEE, pages 1–9. IEEE.
Chen, J., Yu, Q., Cheng, P., Sun, Y., Fan, Y., and Shen, X.
(2011). Game theoretical approach for channel allo-
cation in wireless sensor and actuator networks. IEEE
transactions on automatic control, 56(10):2332–2344.
Dammer, S. and Hinrichsen, H. (2003). Epidemic spreading
with immunization and mutations. Physical Review E,
68(1):016114.
Fu, Y., Sha, M., Hackmann, G., and Lu, C. (2012). Practical
control of transmission power for wireless sensor net-
works. In Network Protocols (ICNP), 2012 20th IEEE
International Conference on, pages 1–10. IEEE.
Ganesan, D., Krishnamachari, B., Woo, A., Culler, D., Es-
trin, D., and Wicker, S. (2002). Complex behavior at
scale: An experimental study of low-power wireless
sensor networks. Technical report, Citeseer.
Ganesh, A. and Xue, F. (2007). On the connectivity and di-
ameter of small-world networks. Advances in Applied
Probability, 39(4):853–863.
Gao, Y., Hou, J., and Nguyen, H. (2008). Topology control
for maintaining network connectivity and maximizing
network capacity under the physical model. In IEEE
INFOCOM, pages 1013–1021.
Gnawali, O., Fonseca, R., Jamieson, K., Moss, D., and
Levis, P. (2009). Collection tree protocol. In ACM
SenSys, pages 1–14.
Hackmann, G., Chipara, O., and Lu, C. (2008). Robust
topology control for indoor wireless sensor networks.
In ACM SenSys, pages 57–70. ACM.
Hao, X.-C., Wang, M.-Q., Hou, S., Gong, Q.-Q., and Liu,
B. (2015). Distributed topology control and channel
allocation algorithm for energy efficiency in wireless
sensor network: From a game perspective. Wireless
Personal Communications, 80(4):1557–1577.
Heikkinen, T. (2006). A potential game approach to dis-
tributed power control and scheduling. Computer Net-
works, 50(13):2295–2311.
Horn, R. and Johnson, C. (2005). Matrix analysis. Cam-
bridge university press.
Jorswieck, E. and Boche, H. (2006). Majorization and
matrix-monotone functions in wireless communica-
tions. Foundations and Trends in Communications
and Information Theory, 3(6):553–701.
Komali, R., MacKenzie, A., and Gilles, R. (2008). Effect
of selfish node behavior on efficient topology design.
IEEE Tran. Mobi. Comput., pages 1057–1070.
Li, L., Halpern, J., Bahl, P., Wang, Y., and Watten-
hofer, R. (2005a). A cone-based distributed topology-
control algorithm for wireless multi-hop networks.
IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw., 13(1):147–159.
Li, N., Hou, J., and Sha, L. (2005b). Design and analysis
of an MST-based topology control algorithm. IEEE
Trans. Wireless Commun., 4(3):1195–1206.
Lin, S., Zhang, J., Zhou, G., Gu, L., Stankovic, J., and He,
T. (2006). ATPC: adaptive transmission power control
for wireless sensor networks. In ACM SenSys, pages
223–236.
Marshall, A. W., Olkin, I., and Arnold, B. (2010). In-
equalities: theory of majorization and its applica-
tions. Springer Science & Business Media.
Meshkati, F., Poor, H. V., Schwartz, S. C., and Balan,
R. V. (2006). Energy-efficient power and rate con-
trol with qos constraints: a game-theoretic approach.
In Proceedings of the 2006 international conference
on Wireless communications and mobile computing,
pages 1435–1440. ACM.
Moeller, S., Sridharan, A., Krishnamachari, B., and
Gnawali, O. (2010). Routing without routes: The
Discrete Strategy Game-theoretic Topology Control inWireless Sensor Networks
37

backpressure collection protocol. In Proceedings of
the 9th ACM/IEEE International Conference on In-
formation Processing in Sensor Networks, pages 279–
290. ACM.
Monderer, D. and Shapley, L. (1996). Potential games.
Games and economic behavior, 14:124–143.
Myerson, R. B. (1991). Game theory: analysis of conflict.
Harvard University.
Nahir, A., Orda, A., and Freund, A. (2008). Topology de-
sign and control: A game-theoretic perspective. In
IEEE INFOCOM, pages 1620–1628.
Nash Jr, J. (1950). The bargaining problem. Econometrica:
Journal of the Econometric Society, pages 155–162.
Neel, J. O., Reed, J. H., Gilles, R. P., et al. (2004). Con-
vergence of cognitive radio networks. In WCNC, vol-
ume 4, pages 2250–2255.
Nisan, N., Roughgarden, T., Tardos, E., and Vazirani, V. V.
(2007). Algorithmic game theory, volume 1. Cam-
bridge University Press Cambridge.
Papadimitriou, C. H. (1994). On the complexity of the par-
ity argument and other inefficient proofs of existence.
Journal of Computer and system Sciences, 48(3):498–
532.
Son, D., Krishnamachari, B., and Heidemann, J. (2004).
Experimental study of the effects of transmission
power control and blacklisting in wireless sensor net-
works. In Sensor and Ad Hoc Communications and
Networks, 2004. IEEE SECON 2004. 2004 First An-
nual IEEE Communications Society Conference on,
pages 289–298. IEEE.
Son, D., Krishnamachari, B., and Heidemann, J. (2005).
Experimental study of the effects of transmission
power control and blacklisting in wireless sensor net-
works. In IEEE SECON, pages 289–298. IEEE.
Song, Y., Wong, S. H., and Lee, K.-W. (2011). A game
theoretical approach to gateway selections in multi-
domain wireless networks. Gateways, 1:S1.
Spyrou, E. D. and Mitrakos, D. K. (2015a). Approximat-
ing nash equilibrium uniqueness of power control in
practical wsns. arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.05141.
Spyrou, E. D. and Mitrakos, D. K. (2015b). On the homo-
geneous transmission power under the sinr model. In
4th International Conference on Telecommunications
and Remote Sensing, ICTRS 2015.
Srinivasan, K., Kazandjieva, M., Agarwal, S., and Levis, P.
(2007). The beta-factor: Improving bimodal wireless
networks. In ACM SenSys.
Tan, Q., An, W., Han, Y., Liu, Y., Ci, S., Shao, F.-M., and
Tang, H. (2015). Energy harvesting aware topology
control with power adaptation in wireless sensor net-
works. Ad Hoc Networks, 27:44–56.
Ui, T. (2008). Discrete concavity for potential games. In-
ternational Game Theory Review, 10(01):137–143.
Von Neumann, J., Morgenstern, O., Rubinstein, A., and
Kuhn, H. (2007). Theory of games and economic be-
havior. Princeton Univ Pr.
Yeung, M. and Kwok, Y. (2006). A game theoretic approach
to power aware wireless data access. IEEE transac-
tions on mobile computing, pages 1057–1073.
Zhao, J. and Govindan, R. (2003). Understanding packet
delivery performance in dense wireless sensor net-
works. In ACM SenSys, pages 1–13.
SENSORNETS 2017 - 6th International Conference on Sensor Networks
38
