
A Comparison of Statistical Linkage Keys with Bloom Filter-based
Encryptions for Privacy-preserving Record Linkage using Real-world
Mammography Data
Rainer Schnell
1
, Anke Richter
2
and Christian Borgs
3
1
City, University of London, Northampton Square, London EC1V 0HB, U.K.
2
Institute for Cancer Epidemiology, Ratzeburger Allee 160, 23538 L
¨
ubeck, Germany
3
University of Duisburg-Essen, German Record Linkage Center, Lotharstr. 65, 47057 Duisburg, Germany
Keywords:
Medical Record Linkage, Patient Identification Codes, Pseudonyms.
Abstract:
New EU regulations on the need to encrypt personal identifiers for linking data will increase the importance of
Privacy-Preserving Record Linkage (PPRL) techniques over the course of the next years. Currently, the use of
Anonymous Linkage Codes (ALCs) is the standard procedure for PPRL of medical databases. Recently, Bloom
filter-based encodings of pseudo-identifiers such as names have received increasing attention for PPRL tasks. In
contrast to most previous research in PPRL, which is based on simulated data, we compare the performance
of ALCs and Bloom filter-based linkage keys using real data from a large regional breast cancer screening
program. This large regional mammography data base contains nearly 200.000 records. We compare precision
and recall for linking the data set existing at point
t
0
with new incident cases occuring after
t
0
using different
encoding and matching strategies for the personal identifiers. Enhancing ALCs with an additional identifier
(place of birth) yields better recall than standard ALCs. Using the same information for Bloom filters with
recommended parameter settings exceeds ALCs in recall, while preserving precision.
1 INTRODUCTION
Many medical studies link different databases contain-
ing information on the same patient (Jutte et al., 2010).
If unique common identifiers are available, linking is
trivial. However, in many situations in practice such
unique identification numbers are not available. If pri-
vacy is not an issue, probabilistic record linkage based
on pseudo-identifiers such as surname, first name, date
of birth and address information can be used (Herzog
et al., 2010). Under legal constraints demanding pri-
vacy for pseudo-identifiers, privacy-preserving record
linkage (PPRL, for an overview see (Vatsalan et al.,
2013)) is required.
In general, jurisdictions for linking patient data dif-
fer widely. Therefore, the technical details to comply
with national legal requirements vary between coun-
tries. In the US, the HIPAA rules require the removal
of nearly all information used for record linkage. The
current legal situation in Europe has made pseudomy-
sation of record linkage identifiers factually mandatory:
Due to increasing privacy concerns of the population,
the European Council, Parliament and Commission
agreed on a new “General Data Protection Regula-
tion” (Council of European Union, 2016), which will
be part of the national jurisdictions in all 28 member
states of the European Union by May 2018. The regu-
lation clearly demands pseudonymisation techniques
able to withstand re-identification attacks, but does
not require absolute anonymization.Given this recent
development, the demand for PPRL solutions will in-
crease sharply.
Currently, due to the regional and organisational
fragmentation of medical health care, the standard set-
ting for medical record linkage is based on a one-time-
exchange between otherwise computationally sepa-
rated organizational units. This constraint restricts the
number of potential PPRL solutions to a small sub-
set of the many different PPRL approaches which
have been suggested (for a review, see (Vatsalan et al.,
2013)). Nearly all applied PPRL protocols use three
types of actors: Two or more data holders, one linkage
unit and a research group. In general, in such settings,
all units interact only once. Most protocols assume
that all partners act according to the protocol (but may
keep track of all local computations). This assumption
is called ‘honest, but curious’ or ‘semi-honest’ model
(Goldreich, 2004).
276
Schnell R., Richter A. and Borgs C.
A Comparison of Statistical Linkage Keys with Bloom Filter-based Encryptions for Privacy-preserving Record Linkage using Real-world Mammography Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0006140302760283
In Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2017), pages 276-283
ISBN: 978-989-758-213-4
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

For such scenarios, only three approaches for link-
ing medical data have been used repeatedly for real-
word applications of large medical databases (Schnell,
2015): Using a third-party trustee, using encrypted
identifiers
1
and using Bloom-filters.
If a third-party data trustee (Kelman et al., 2002) is
used, unencrypted patient pseudo-identifiers are trans-
ferred to a trusted third party, which links the pseudo-
identifiers and assigns a new identification number to
the linked records. These newly constructed IDs are
then used for linkage by a research group.
By far the most common approach in practical set-
tings is the use of encrypted pseudo-identifiers. Here,
the identifiers are concatenated into a single string
which is then encrypted. The resulting encrypted string
is called an anonymous linking code (ALC, (Herzog
et al., 2007)).
Many of the more recent PPRL approaches (see
(Vatsalan et al., 2013; Karapiperis et al., 2016) for
reviews) have limited scalability, so they can not be
used with large datasets. For example, although techni-
cally interesting, all homomorphic encryption methods
are computationally expensive and do not scale well
(Karakasidis et al., 2015). An exception are Bloom fil-
ter approaches. (Schnell et al., 2009) first suggested the
use of Bloom filters for privacy-preserving record link-
age. The approach is based on splitting each identifier
into a set of substrings of length 2 (bigrams), which
are mapped into a binary vector for each identifier with
a linear combination of different cryptographic hash
functions such as SHA-1 and MD-5. The similarity
of these binary vectors (Bloom filters) approximates
the similarity of the pseudo-identifiers, which makes
Bloom filters attractive for error-tolerant PPRL.
Although using separate Bloom filters for each
pseudo-identifier is the most common approach, the
use of one common binary vector is harder to attack.
The use of a single Bloom filter for all identifiers
has been first proposed in (Schnell et al., 2011) and
has been explored further by (Durham, 2012). The
resulting composite Bloom filter is called a Crypto-
graphic Long-term Key (CLK) in the original publica-
tion or ‘record based Bloom filter’ (RBF) by (Durham,
2012). CLKs have been used on real world data exten-
sively (Randall et al., 2014; Schnell and Borgs, 2015;
Schmidlin et al., 2015).
1
Although data sets without direct personal identifiers,
but containing indirect identifying information such as date
of hospital admission and discharge are occasionally sug-
gested (Karmel and Gibson, 2007) for record linkage, they
rarely contain enough discriminating information for unique
linkage pairs.
Our Contribution.
No previous publication com-
pared the performance of CLKs with the performance
of the more traditional ALCs using real-world data.
Therefore, we report on a new study assessing the per-
formance of different variations of CLKs and ALC
variants using real-world data from a large regional
breast cancer screening program (Katalinic et al.,
2007). Furthermore, for the first time, we compare
the effect of including additional identifiers to linkage
keys and Bloom filter encodings.
2 PREVIOUS WORK
Currently, only two different versions of encoding iden-
tifiers seem to be in practical use for PPRL: Anony-
mous Linkage Codes (ALCs) and Bloom filters. Both
will be described shortly.
2.1 ALC Variants
ALCs are an encrypted single string formed by con-
catenating substrings or functions of different pseudo-
identifiers. These pseudo-identifiers should be stable
over time and free of errors. Most often, first name,
surname, date of birth and sex are used for construct-
ing ALCs. The resulting combination of identifiers
is encrypted using cryptographic hash functions. The
resulting hashed string is used as the linkage key. If
two ALCs match exactly, the corresponding records
are classified as representations of the same real-world
entity. Due to the cryptographic hash function, it is
nearly impossible to decrypt the identifiers directly.
The most simple and widely-used ALC is con-
structed in three steps (Herzog et al., 2007): all identi-
fiers are preprocessed using a set of rules (for example,
removal of non-alphabetical characters from names,
removal of non-digits from dates, and capitalization
of all characters). The resulting preprocessed identi-
fiers are then concatenated to form one single string,
which is finally encrypted with a cryptographic hash
function. Examples of applications of Basic ALCs are
described by (Kijsanayotin et al., 2007; Sch
¨
ulter et al.,
2007; Johnson et al., 2010; Tessmer et al., 2011).
The design of the Basic ALC is not error-tolerant,
since even the replacement of a single letter will result
in an entirely different hash code. As spelling and ty-
pographical errors in patient identifiers are common,
many true record pairs will not be classified as matches.
Hence patients with variations in their respective iden-
tifiers might have different characteristics than patients
with agreeing identifiers. Ignoring this problem can
result in biased estimates (Ridder and Moffitt, 2007).
A Comparison of Statistical Linkage Keys with Bloom Filter-based Encryptions for Privacy-preserving Record Linkage using Real-world
Mammography Data
277

Different approaches to constructing ALCs allow
for some errors in identifiers. The Swiss Federal Of-
fice for Statistics asked the Cryptological Unit of the
Swiss Military to develop a privacy-preserving link-
age method for medical patient data (Office f
´
ed
´
eral de
la statistique, 1997).To construct this ALC variation,
the Soundex code of surname and first name are cre-
ated after some preprocessing. The Soundex codes are
concatenated with the date of birth and sex. The re-
sulting string is encrypted using a cryptographic hash
function (Office f
´
ed
´
eral de la statistique, 1997). Appli-
cations and reviews of the Swiss ALC are discussed
in (Borst et al., 2001; Holly et al., 2005; Eggli et al.,
2006; El Kalam et al., 2011).
Another approach to construct more error-tolerant
ALCs was invented by the Australian Institute of
Health and Welfare (AIHW). Their solution uses sub-
strings of first and last names instead of the full string.
(Ryan et al., 1999) tested several variations and con-
cluded that the second, third, and fifth character of the
surname combined with the characters at the second
and third position of the first name concatenated with
sex and date of birth performed best. The resulting
string forms the Statistical Linkage Key (SLK) which is
often included in data published by the AIHW (Karmel
et al., 2010). After applying a cryptographic hash func-
tion to the SLK, the Encrypted SLK, sometimes also
denoted as 581-Key is the ALC variant that is widely
used in Australian data linkage (Taylor et al., 2014).
(Karmel et al., 2010) tested the effect of adding dif-
ferent versions of state and postcode to the 581-Keys.
In general, 581-Keys don’t seem to be considered as
state-of-the-art any longer (Randall et al., 2016).
2.2 Simple Bloom Filters
Bloom filters have been used for calculating string
similarities in privacy-preserving probabilistic record
linkage (Schnell et al., 2009). A Bloom filter is an
array of data proposed by Howard (Bloom, 1970) for
checking the set membership of records efficiently
(Broder and Mitzenmacher, 2003). It is represented
by a bit array with a length of
l
bits initially set to
zero. For the mapping,
k
independent hash functions
h ∈ {h
1
, . . . , h
k
}
are used.To store the set of entities
S =
{
x
1
, x
2
, . . . , x
n
}
in the Bloom filter, each element
x
i
∈ S
is hashed using the
k
independent hash functions.
The bit positions given by the hash functions are set to
1. If a bit was already set to 1, nothing is changed.
To store all elements of a set in Bloom filters, we
apply the double hashing scheme proposed by (Kirsch
and Mitzenmacher, 2006). They show that using two
independent hash functions is sufficient to implement a
Bloom filter with
k
hash functions without an increase
in the asymptotic false positive probability (Kirsch and
Mitzenmacher, 2006). Therefore, the positional values
of the
k
hash functions are computed with the function
g
i
(x) = (h
1
(x) + i · h
2
(x)) mod l (1)
where
i ∈ {0, . . . , k − 1}
and
l
is the length of the bit
array. We use two different keyed hash message au-
thentication codes (HMACs), namely, HMAC-SHA1
(
h
1
) and HMAC-MD5 (
h
2
) (Krawczyk et al., 1997) to
create the Bloom filters.
2.3 Composite Bloom Filters
For some applications, a single linkage key has to be
used. If separate Bloom filters are used, for these ap-
plications, the set of Bloom filters has to be combined
in a composite Bloom filter. Storing all of the identi-
fiers used in a single Bloom filter was first proposed by
(Schnell et al., 2011). This is called a Cryptographic
Long-term Key (CLK), since they were intended for
use in a longitudinal study of offenders.
For the construction of a CLK, each identifier is
split into a set of
n
-grams. Each set is stored using
k
hash functions using the same Bloom filter of the
length
l
for all
n
-gram sets of all identifiers used. This
additive Bloom filter represents the CLK.
After preprocessing, first name and surname are
split into bigrams, birth year into unigrams. In the
second step, the first
n
-gram set (e.g. first name) is
stored in the Bloom filter. Each bigram is hashed
k
times. Bits having indices corresponding to the hash
values are set to one. In the third step, the second
n
-
gram set (e.g. surname) is mapped to the same Bloom
filter. Finally, unigrams are mapped to the same bit
array.
2.4 Cryptographic Attacks on ALCs
Frequency attacks on standard ALCs have not been
reported in the literature so far. Discussions about the
security of ALCs and 581-Keys up to now are hypo-
thetical, not empirical (Randall et al., 2016).
However, since the same password is used for all
records, within a combination of sex and date of birth,
the most frequent name/surname combination will
also yield the most frequent ALC. Therefore, given a
large random sample, the most frequent name/surname
combinations have a high risk of re-identification.
Under the (unrealistic) assumption of uniformly dis-
tributed dates of birth, age and sexes, there are about
365 ∗ 100 ∗ 2 = 73.000
combinations possible. This
way, in a database of
10.000.000
records, about 137
records per combination are expected. If the frequency
HEALTHINF 2017 - 10th International Conference on Health Informatics
278

distribution of names is skewed, aligning the most fre-
quent name subsets could identify a large proportion
of the records using this simple frequency alignment.
2.5 Cryptographic Attacks on Bloom
Filters
Bloom filter-based PPRL has been attacked by two
different techniques: by applying a Constrained Satis-
faction Solver (CSS) on frequencies of entire Bloom
filters (Kuzu et al., 2011; Kuzu et al., 2013) and by a in-
terpreting the Bloom filter bit patterns as a substitution
cipher (Niedermeyer et al., 2014).
The first attack is a variant of a simple rank swap-
ping attack (Domingo-Ferrer and Muralidhar, 2016)
which used the estimated length of the encrypted
strings as additional information. (Kuzu et al., 2011)
consider their attack on separate Bloom filters as suc-
cessful, but not their attack on composite Bloom filters
(Kuzu et al., 2013). It should be noted that this CSS
attack is based on the entire data set of Bloom filters,
therefore it is no decoding, but an alignment. This
way of attack is impossible if many groups of similar
cases generates a new bit pattern, for example by us-
ing salted encodings (Niedermeyer et al., 2014). In a
salted encoding, a stable identifier such as date of birth,
year of birth or place of birth is added to the password
determining the hash functions.
The second attack attempted the actual revealing
of all identifiers as clear text by a cryptanalysis of
individual bit patterns within the Bloom filters (Nie-
dermeyer et al., 2014). This attack is based on the
limited number of bit patterns generated by the lin-
ear combination of two hash functions in the double-
hashing scheme (Kirsch and Mitzenmacher, 2006)
of the initial proposal. Exploiting this specific con-
struction of the hash functions, (Niedermeyer et al.,
2014) were successful with basic Bloom filters and
(Kroll and Steinmetzer, 2015) with CLKs/composite
Bloom filters. Therefore, replacing the double-hashing
scheme by random hashing should prevent the suc-
cess of this attack on Bloom filters (Niedermeyer et al.,
2014). Random hashing is based on the idea of using
bigrams as seeds for random number streams. This
could be implemented by a linear-congruential pseudo-
random number generator (LCG, (Stallings, 2014)),
to generate a sequence
X
with the length
k
for each
n
-gram.Random hashing increases the number of pos-
sible bit patterns (
l = 1000, k = 15
) for a given
n
-
gram from less than
10
6
to more than
6.8 · 10
32
. There-
fore, the Niedermeyer-attack should fail for randomly
hashed Bloom filters. This theoretical expectation has
been empirically verified by (Schnell and Borgs, 2016).
In conclusion, for salted Bloom filter encodings
using random hashing, no successful attack method
is known. Of course, the number of records using the
same salt should not exceed the minimum required
for a frequency attack either on the whole pattern or
the individual attributes mapped to the Bloom filter.
Based on experiments reported by (Schnell and Borgs,
2016), this minimum number seems to be about 300
records. In most medical applications, this number is
only exceeded in national databases. For this, an ad-
ditional salt has to be used. Given this condition, we
consider Bloom filter-based encodings as meeting the
requirements of the EU Protection Regulation (Coun-
cil of European Union, 2016) for a pseudonymisation
method.
3 METHODS
Using real data from a German state-wide breast can-
cer screening program (Katalinic et al., 2007), we com-
pared the CLK encryption with the Basic and Swiss
ALCs and the encrypted SLK (581-Key).
The test data consists of mammography records of
patients in a German state, covering about 3.4% of the
total German population. File A consists of cases until
the end of 2011 (with one record for each case) with
n = 138.131
records, file B encompasses cases after
2011 (more than one record per case was possible)
with n = 73.004 cases in 198.475 records.
The standard CLK is set up with a length of
l = 1000
. First name and Surname were padded with
spaces before being split into bigrams (Robertson
and Willett, 1998). The other identifiers were split
into unigrams. Each set of
n
-grams is hashed using
k = 10
HMACs (Hash functions) and a different cryp-
tographic key. Since CLKs allow for matching strate-
gies other than exact matching (Schnell et al., 2011),
following (Schnell, 2014), Multibit Trees with various
Tanimoto-thresholds were used. The statistical linkage
keys were evaluated using exact matching.
The set of identifiers used consisted of first name,
surname, date of birth and sex. According to recent
studies, including more stable identifiers is desirable
(Schnell and Borgs, 2015). Address information is very
volatile, since places of residence may change during
the course of a lifetime. Therefore, (Schnell and Borgs,
2015) suggested using places of birth as an additional
identifier for Bloom filter-based PPRL. In the second
experiment, we did this by adding place of birth to the
set of identifiers for the CLKs and 581-Keys.
Since the real-world data sets used here contained
only current places of residence, we simulated the
place of birth according to German administrative pop-
ulation counts. We introduced artificial 10% address
A Comparison of Statistical Linkage Keys with Bloom Filter-based Encryptions for Privacy-preserving Record Linkage using Real-world
Mammography Data
279
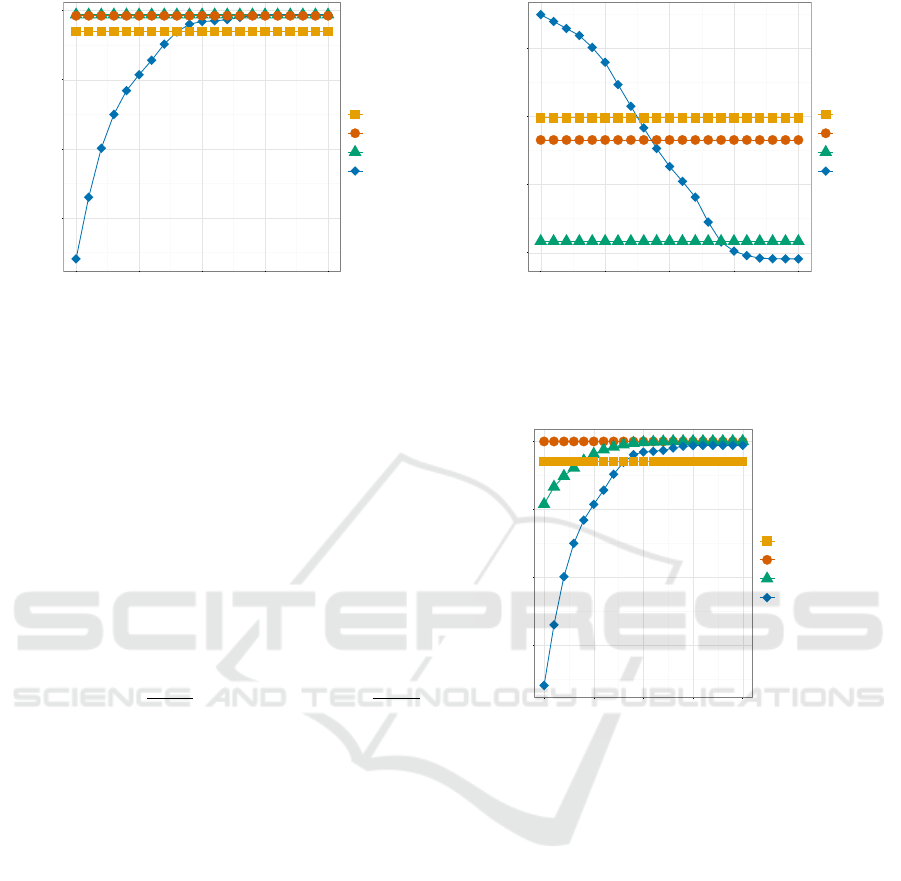
0.925
0.950
0.975
1.000
0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00
Tanimoto-Threshold
Precision
Encryption
581-Key
Swiss ALC
Basic ALC
CLK k=10
Figure 1: Precision of the CLK and encrypted statistical
linkage key variants. Since the ALCs were matched exactly,
their values are shown as constants, while several similarity
thresholds were used for CLKs.
changes to the simulated data. As the two linked files
refer to different years, this percentage should reflect a
worst-case scenario for the amount of regional mobility
in the population.
The current gold standard in use at the cancer
screening program is considered as reflecting the true
matching status. Based on this classification, the com-
pared methods will yield true positive (TP), false posi-
tive (FP), true negative (TN) and false negative (FN)
classifications of record pairs.
This way, we can compare the methods using preci-
sion (
Precision =
TP
TP+FP
) and recall (
Recall =
TP
TP+FN
)
(Baeza-Yates and Ribeiro-Neto, 1999).
According to legal requirements, unencrypted iden-
tifiers were processed only at the office of the data
holder. ALCs, 581-Key and CLKs were generated with
Python 3, while R (R Core Team, 2016) was used for
the matching and statistical computation.
4 RESULTS
Figures 1 and 2 show the results of the standard CLK
(
k = 10
hash functions) against the encrypted linkage
keys in terms of precision and recall. Lowering the
threshold improves the recall. Precision is stable until
the threshold approaches 0.88. Above this threshold,
precision drops considerably. Given this set of iden-
tifiers, CLK does not exceed the performance of the
Swiss ALC and the 581-Key.
All in all, ALCs offer higher precision (less false
positives) compared to the CLK. However, the CLK
outperforms the ALCs in terms of recall as the simi-
larity threshold is lowered below 0.88. At the recom-
mended Tanimoto-threshold of 0.85 (Schnell, 2015),
0.95
0.96
0.97
0.98
0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00
Tanimoto-Threshold
Recall
Encryption
581-Key
Swiss ALC
Basic ALC
CLK k=10
Figure 2: Recall of the CLK and encrypted statistical link-
age key variants. Since the ALCs were matched exactly,
their values are shown as constants, while several similarity
thresholds were used for CLKs.
0.925
0.950
0.975
1.000
0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00
Tanimoto-Threshold
Precision
Encryption
581-Key
581-Key + Birthplace
CLK k=10 + Birthplace
CLK k=10
Figure 3: Precision of the 581-Key and CLK with and with-
out inclusion of places of birth.
CLKs show more (0.7% – 2.8%) true positives than
both standard ALC variants (see table 1), even out-
performing the 581-Key. However, given this set of
identifiers, the amount of false positives is consider-
ably higher. Since CLKs should perform better if more
(stable) identifiers are included. Therefore, for the sec-
ond set of experiments, we included place of birth and
hashed it into the original CLKs. We did the same with
the 581-Key, concatenating place of birth to the 581-
Key before hashing it again. Figures
??
and 4 show
that the performance now exceeds the standard ALCs
in terms of recall while showing improved precision
values.
Table 1 lists the detailed classifications in terms of
true (TP) and false positive (FP) record pairs, as well
as missed record pairs (false negatives (FN)) along
with recall and precision at a Tanimoto-threshold of
0.85 for all ALCs, the 581-Key and the CLKs. Details
on the results for adding the simulated place of birth
HEALTHINF 2017 - 10th International Conference on Health Informatics
280
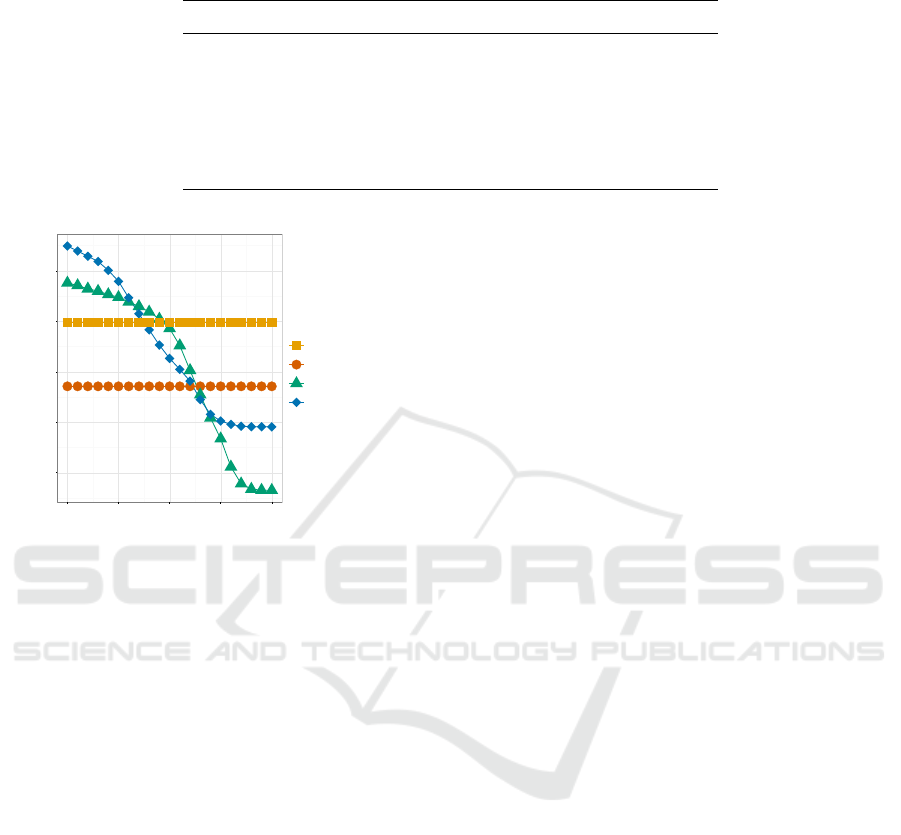
Table 1: Classification results for all methods presented. CLK results are based on a Tanimoto-threshold of 0.85 using Multibit
Trees.
Variant TP FP FN Prec. Rec.
Basic ALC 51.587 79 2.620 0.998 0.952
Swiss ALC 52.454 101 1.816 0.998 0.967
581-Key 52.633 400 1.640 0.992 0.970
CLK
k10
53.012 1.260 1.196 0.977 0.978
581-Key
+place of birth
51.945 5 2.328 0.999 0.957
CLK
k10+place of birth
52.840 251 1.368 0.995 0.975
0.94
0.95
0.96
0.97
0.98
0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00
Tanimoto-Threshold
Recall
Encryption
581-Key
581-Key + Birthplace
CLK k=10 + Birthplace
CLK k=10
Figure 4: Recall of the 581-Key and CLK with and without
inclusion of places of birth.
are shown as well. The CLKs consistently show more
true positive classifications, while the ALCs and 581-
Key perform better in terms of precision (fewer false
positives).
It has to be noted that adding the place of birth to
the set of identifiers improves the precision for both
the 581-Key and the CLKs, while only decreasing re-
call marginally (likely due to the 10% errors simulated
for the birth places). A CLK with birthplace informa-
tion stored in it outperforms all standard ALC variants
and the 581-Key without additional identifiers in both
recall and precision.
Since the simulated birth places assumed a worst-
case setting of 10% errors in the data, real-world ap-
plications using CLKs will benefit from including ad-
ditional stable identifiers. These results show the po-
tential of using Bloom filters for real-world privacy-
preserving record linkage applications, especially if
additional stable information is available.
5 DISCUSSION
In this paper, we showed a real-world application of
the Cryptographic Long-term Key. Previously, ALCs
were built by encrypting hashed or sampled identifiers.
The CLK, representing an array of bits allows for simi-
larity comparisons using Multibit Trees. The presented
simulation results show better recall, but lower preci-
sion than best-performing ALCs. Since CLKs can be
easily fine-tuned by selecting different thresholds, the
impact of linkage errors on substantial results can be
easily studied. Therefore, we consider the impact of
increased false positives as not limiting the application
of CLKs.
Precision and recall of CLKs will exceed ALCs
and 581-Keys if more stable identifiers can be used.
Recently, (Brown et al., 2016) showed that the optimal
choice of identifiers and parameters is critical for the
performance of Bloom filter-based PPRL. Their results
vary, depending on the set of identifiers used. They also
showed the need for stable identifiers, as errors and
missing values (for example, in recent addresses) will
reduce recall.
After fine-tuning parameters and identifier sets,
PPRL linkage quality comparable to clear text link-
age can be achieved with CLKs. Furthermore, using
Multibit Trees as suggested by (Schnell, 2014), PPRL
using CLKs can be done (without additional blocking)
on standard hardware with two files containing 5 mil-
lion records each in a little over 4 days (Brown et al.,
2016). If additional blocks such as date of birth are
used, linkage can be done in less than an hour (Schnell,
2015).
Bloom filters can be used to represent other data
than strings: (Vatsalan and Christen, 2016) demon-
strated the use of numerical and date information, (Far-
row and Schnell, 2017) tested the inclusion of distance-
preserving locational data. Both techniques will extend
the number of possible applications for PPRL.
Currently, there is no known way of attacking
CLKs and state-of-the-art variants of single Bloom fil-
ters (Schnell and Borgs, 2016). Therefore, they might
be used to link files using personal identifiers accord-
ing to the de-facto anonymity standard required by the
new EU regulation on data protection.
A Comparison of Statistical Linkage Keys with Bloom Filter-based Encryptions for Privacy-preserving Record Linkage using Real-world
Mammography Data
281

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The study was supported by German Research Founda-
tion (DFG) research grant SCHN 586/17-2 awarded to
the first author. The first author would like to thank the
Isaac Newton Institute for Mathematical Sciences for
support and hospitality during the programme ‘Data
Linkage and Anonymisation’ (which was supported by
the EPSRC grant Number EP/K032208/1) when work
on this paper was undertaken.
REFERENCES
Baeza-Yates, R. and Ribeiro-Neto, B. d. A. (1999). Modern
Information Retrieval. Addison-Wesley, Harlow.
Bloom, B. H. (1970). Space/time trade-offs in hash coding
with allowable errors. Communications of the ACM,
13(7):422–426.
Borst, F., Allaert, F.-A., and Quantin, C. (2001). The Swiss
solution for anonymous chaining patient files. In Patel,
V., Rogers, R., and Haux, R., editors, Proceedings of
the 10th World Congress on Medical Informatics: 2–5
September 2001; London, pages 1239–1241, Amster-
dam. IOS Press.
Broder, A. and Mitzenmacher, M. (2003). Network applica-
tions of Bloom filters: a survey. Internet Mathematics,
1(4):485–509.
Brown, A., Borgs, C., Randall, S., and Schnell, R. (2016).
High quality linkage using multibit trees for privacy-
preserving blocking. International Population Data
Linkage Conference (IPDLN2016): 24.08-26.08.2016;
Swansea.
Council of European Union (2016). Council regulation (EU)
no 679/2016.
Domingo-Ferrer, J. and Muralidhar, K. (2016). New direc-
tions in anonymization: Permutation paradigm, verifia-
bility by subjects and intruders, transparency to users.
Information Sciences, 337–338:11–24.
Durham, E. A. (2012). A framework for accurate, efficient
private record linkage. Dissertation. Vanderbilt Univer-
sity.
Eggli, Y., Halfon, P., Chikhi, M., and Bandi, T. (2006). Am-
bulatory healthcare information system: A conceptual
framework. Health Policy, 78:26–38.
El Kalam, A., Melchor, C., Berthold, S., Camenisch, J.,
Clauss, S., Deswarte, Y., Kohlweiss, M., Panchenko,
A., Pimenidis, L., and Roy, M. (2011). Further pri-
vacy mechanisms. In Camenisch, J., Leenes, R., and
Sommer, D., editors, Digital Privacy, pages 485–555.
Springer, Berlin.
Farrow, J. and Schnell, R. (2017). Locational privacy pre-
serving distance computations with intersecting sets of
randomly labelled grid points. Journal of the Royal
Statistical Society, Series A, Under review.
Goldreich, O. (2004). Foundations of Cryptography. Volume
2, Basic Applications. Cambridge University Press,
Cambridge.
Herzog, T. N., Scheuren, F. J., and Winkler, W. E.
(2007). Data Quality and Record Linkage Techniques.
Springer, New York.
Herzog, T. N., Scheuren, F. J., and Winkler, W. E. (2010).
Record linkage. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Com-
putational Statistics, 2(5):535–543.
Holly, A., Gardiol, L., Eggli, Y., Yalcin, T., and Ribeiro, T.
(2005). Ein neues gesundheitsbasiertes Risikoaus-
gleichssystem f
¨
ur die Schweiz. G+G Wissenschaft,
5(2):16–31.
Johnson, S. B., Whitney, G., McAuliffe, M., Wang, H., Mc-
Creedy, E., Rozenblit, L., and Evans, C. C. (2010). Us-
ing global unique identifiers to link autism collections.
Journal of the American Medical Informatics Associa-
tion, 17(6):689–695.
Jutte, D. P., Roos, L. L., and Brownell, M. D. (2010). Ad-
ministrative record linkage as a tool for public health.
Annual Review of Public Health, 31:91–108.
Karakasidis, A., Koloniari, G., and Verykios, V. S. (2015).
Scalable blocking for privacy preserving record linkage.
In Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International
Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining,
KDD ’15, pages 527–536, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Karapiperis, D., Verykios, V. S., Katsiri, E., and Delis, A.
(2016). A tutorial on blocking methods for privacy-
preserving record linkage. In Karydis, I., Sioutas,
S., Triantafillou, P., and Tsoumakos, D., editors, Algo-
rithmic Aspects of Cloud Computing: First Interna-
tional Workshop, ALGOCLOUD 2015, Patras, Greece,
September 14-15, 2015. Revised Selected Papers, pages
3–15. Springer International Publishing, Cham.
Karmel, R., Anderson, P., Gibson, D., Peut, A., Duckett, S.,
and Wells, Y. (2010). Empirical aspects of record link-
age across multiple data sets using statistical linkage
keys: the experience of the PIAC cohort study. BMC
Health Services Research, 10(41).
Karmel, R. and Gibson, D. (2007). Event-based record link-
age in health and aged care services data: a method-
ological innovation. BMC Health Services Research,
7:154.
Katalinic, A., Bartel, C., Raspe, H., and Schreer, I. (2007).
Beyond mammography screening: quality assurance in
breast cancer diagnosis (the quamadi project). British
Journal of Cancer, 96(1):157–161.
Kelman, C. W., Bass, A. J., and Holman, C. D. J. (2002).
Research use of linked health data: a best practice pro-
tocol. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public
Health, 26(3):251–255.
Kijsanayotin, B., Speedie, S. M., and Connelly, D. P. (2007).
Linking patients’ records across organizations while
maintaining anonymity. Proceedings of the 2007 Amer-
ican Medical Informatics Association Annual Sympo-
sium, page 1008.
Kirsch, A. and Mitzenmacher, M. (2006). Less hashing same
performance: building a better Bloom filter. In Azar, Y.
and Erlebach, T., editors, Algorithms-ESA 2006. Pro-
ceedings of the 14th Annual European Symposium: 11-
13 September 2006; Z
¨
urich, Switzerland, pages 456–
467, Berlin. Springer.
Krawczyk, H., Bellare, M., and Canetti, R. (1997). HMAC:
keyed-hashing for message authentication. Internet
RFC 2104.
HEALTHINF 2017 - 10th International Conference on Health Informatics
282

Kroll, M. and Steinmetzer, S. (2015). Who Is
1011011111...1110110010? Automated Cryptanalysis
of Bloom Filter Encryptions of Databases with Several
Personal Identifiers. In Biomedical Engineering Sys-
tems and Technologies 2015, pages 341–356. Springer.
Kuzu, M., Kantarcioglu, M., Durham, E., and Malin, B.
(2011). A constraint satisfaction cryptanalysis of
Bloom filters in private record linkage. In The 11th
Privacy Enhancing Technologies Symposium: 27–29
July 2011; Waterloo, Canada.
Kuzu, M., Kantarcioglu, M., Durham, E. A., Toth, C., and
Malin, B. (2013). A practical approach to achieve pri-
vate medical record linkage in light of public resources.
Journal of the American Medical Informatics Associa-
tion, 20(2):285–292.
Niedermeyer, F., Steinmetzer, S., Kroll, M., and Schnell, R.
(2014). Cryptanalysis of basic bloom filters used for
privacy preserving record linkage. Journal of Privacy
and Confidentiality, 6(2):59–69.
Office f
´
ed
´
eral de la statistique (1997). La protection des
donn
´
ees dans la statistique m
´
edicale. Technical report,
Neuchatel.
R Core Team (2016). R: A Language and Environment for
Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical
Computing, Vienna, Austria.
Randall, S., Ferrante, A., Boyd, J., Brown, A., and Semmens,
J. (2016). Limited privacy protection and poor sensi-
tivity: Is it time to move on from the statistical linkage
key-581? Health Information Management Journal,
45(2):71–79.
Randall, S. M., Ferrante, A. M., Boyd, J. H., Bauer, J. K., and
Semmens, J. B. (2014). Privacy-preserving record link-
age on large real world datasets. Journal of Biomedical
Informatics, 50:205–212.
Ridder, G. and Moffitt, R. (2007). The econometrics of data
combination. In Heckman, J. J. and Leamer, E. E.,
editors, Handbook of Econometrics, volume 6B, pages
5469–5547. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Robertson, A. M. and Willett, P. (1998). Applications of
n-grams in textual information systems. Journal of
Documentation, 54(1):48–67.
Ryan, T., Holmes, B., and Gibson, D. (1999). A national min-
imum data set for home and community care. Canberra,
AIHW.
Schmidlin, K., Clough-Gorr, K. M., Spoerri, A., and SNC
study group (2015). Privacy preserving probabilistic
record linkage (P3rl): a novel method for linking ex-
isting health-related data and maintaining participant
confidentiality. BMC medical research methodology,
15:46.
Schnell, R. (2014). An efficient privacy-preserving record
linkage technique for administrative data and censuses.
Journal of the International Association for Official
Statistics, 30(3):263–270.
Schnell, R. (2015). Privacy preserving record linkage. In Har-
ron, K., Goldstein, H., and Dibben, C., editors, Method-
ological Developments in Data Linkage, pages 201–
225. Wiley, Chichester.
Schnell, R., Bachteler, T., and Reiher, J. (2009). Privacy-
preserving record linkage using Bloom filters. BMC
Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 9(41).
Schnell, R., Bachteler, T., and Reiher, J. (2011). A novel
error-tolerant anonymous linking code. Working Paper
WP-GRLC-2011-02, German Record Linkage Center,
Duisburg.
Schnell, R. and Borgs, C. (2015). Building a national peri-
natal database without the use of unique personal iden-
tifiers. In 2015 IEEE 15th International Conference
on Data Mining Workshops (ICDM 2015), pages 232–
239., Atlantic City, NJ, USA. IEEE Publishing.
Schnell, R. and Borgs, C. (2016). Randomized response and
balanced bloom filters for privacy preserving record
linkage. In 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference
on Data Mining Workshops (ICDM 2016), Barcelona,
Dec 12, 2016 - Dec 15, 2016. IEEE Publishing.
Sch
¨
ulter, E., Kaiser, R., Oette, M., M
¨
uller, C., Schmeisser,
N., Selbig, J., Beerenwinkel, N., Lengauer, T., D
¨
aumer,
M., and Hoffmann, D. (2007). Arevir: A database to
support the analysis of resistance mutations of human
immunodeficiency. European Journal of Medical Re-
search, 12(Supplememt III):10–11.
Stallings, W. (2014). Cryptography and Network Security:
Principles and Practice. Pearson, New Jersey, 6 edi-
tion.
Taylor, L. K., Irvine, K., Iannotti, R., Harchak, T., and Lim,
K. (2014). Optimal strategy for linkage of datasets
containing a statistical linkage key and datasets with
full personal identifiers. BMC Medical Informatics and
Decision Making, 14:85.
Tessmer, A., Welte, T., Schmidt-Ott, R., Eberle, S., Barten, G.,
Suttorp, N., and Schaberg, T. (2011). Influenza vaccina-
tion is associated with reduced severity of community-
acquired pneumonia. European Respiratory Journal,
38(1):147–153.
Vatsalan, D. and Christen, P. (2016). Privacy-preserving
matching of similar patients. Journal of Biomedical
Informatics, 59:285–298.
Vatsalan, D., Christen, P., and Verykios, V. S. (2013). A tax-
onomy of privacy-preserving record linkage techniques.
Information Systems, 38(6):946–969.
A Comparison of Statistical Linkage Keys with Bloom Filter-based Encryptions for Privacy-preserving Record Linkage using Real-world
Mammography Data
283
