
Volume-based Human Re-identification with RGB-D Cameras
Serhan Cos¸ar, Claudio Coppola and Nicola Bellotto
Lincoln Centre for Autonomous Systems (L-CAS), School of Computer Science, University of Lincoln, LN6 7TS Lincoln,
U.K.
{scosar, ccoppola, nbellotto}@lincoln.ac.uk
Keywords:
Re-identification, Volume-based Features, Occlusion, Body Motion, Service Robots.
Abstract:
This paper presents an RGB-D based human re-identification approach using novel biometrics features from
the body’s volume. Existing work based on RGB images or skeleton features have some limitations for real-
world robotic applications, most notably in dealing with occlusions and orientation of the user. Here, we
propose novel features that allow performing re-identification when the person is facing side/backward or the
person is partially occluded. The proposed approach has been tested for various scenarios including different
views, occlusion and the public BIWI RGBD-ID dataset.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human re-identification is an important field in com-
puter vision and robotics. It has plenty of practical
applications such as video surveillance, activity
recognition and human-robot interaction. Particular
attention has been given to recognizing people across
a network of RGB cameras in surveillance systems
(Vezzani et al., 2013; Bedagkar-Gala and Shah, 2014)
and identifying people interacting with service robots
(Munaro et al., 2014c; Bellotto and Hu, 2010).
Although the task of re-identification is the same,
there are many aspects of the problem that are
application-specific. In most of the surveillance
applications, re-identification is performed by using
RGB images and extracting features based on appear-
ance such as color(Chen et al., 2015; Kviatkovsky
et al., 2013; Farenzena et al., 2010) and texture
(Chen et al., 2015; Farenzena et al., 2010). On
the other hand, with the availability of RGB-D
cameras, anthropometric features (e.g., limb lengths)
extracted from skeleton data (Munaro et al., 2014b;
Barbosa et al., 2012) and point cloud information
(Munaro et al., 2014a) are used for re-identification
in many service robot applications. There are also
some approaches that relies on face recognition for
identifying people (Ferland et al., 2015).
However, for long-term applications such as do-
mestic service robots, many existing approaches have
strong limitations. For instance, appearance and color
based approaches are not applicable as people change
often their clothes. Face recognition requires a clear
frontal image of the face, which may not be possible
all the time (e.g. person facing opposite the camera,
see Figure 1-a). Skeletal data is not always available
because of self-occluding body motion (e.g., turning
around) or objects occluding parts of the body (e.g.,
passing behind a table, see Figure 1-b and (Munaro
et al., 2014c)).
(a) (b)
Figure 1: In a real-world scenario, re-identification should
cope with (a) different views and (b) occlusions.
In order to deal with the above limitations, in this
paper we propose the use of novel biometric features,
including body part volumes and limb lengths.
In particular, we extract height, shoulder width,
length of face, head volume, upper-torso volume and
lower-torso volume. As these features are neither
view dependent nor based on skeletal data, they do
not require any special pose. In real-world scenarios,
most of the time, lower body parts of people are
occluded by some object in the environment (e.g.
chair). As our features are extracted from upper body
parts, they are robust to occlusions by chairs, tables
Cosar S., Coppola C. and Bellotto N.
Volume-based Human Re-identification with RGB-D Cameras.
DOI: 10.5220/0006155403890397
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2017), pages 389-397
ISBN: 978-989-758-225-7
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
389

and similar types of furniture, which makes our
approach very suitable for applications in domestic
environments.
The main contributions of this paper are there-
fore twofold:
• Novel human re-identification method using bio-
metric features, including body volume, extracted
with an RGB-D camera;
• New approach to extract these features without the
need of skeletal data, robust to partial occlusions,
different human orientations and poses.
The reminder of this paper is structured as follows.
Related work on RGB and depth based approaches is
described in Section 2. Section 3 explains the details
of our approach and how feature extraction is per-
formed. Experimental results with a public dataset
and new data from various scenarios are presented in
Section 4. Finally, we conclude this paper in Section
5 discussing achievements and current limitations, as
well as future work in this area.
2 RELATED WORK
Person re-identification is a problem of main impor-
tance, which has become an area of intense research
in the past years. The main goal of re-identification
is to establish a consistent labeling of the observed
people across multiple cameras or in a single camera
in non-contiguous time intervals (Bedagkar-Gala and
Shah, 2014). The approach of (Farenzena et al., 2010)
on RGB cameras, focuses on an appearance-based
method, which extracts the overall chromatic content,
spatial arrangement of colors and the presence of
recurrent patterns from the different body parts of the
person. In (Li et al., 2014), authors propose a deep
architecture which automatically learns features for
the optimal re-identification. The latter automatically
deals with transforms, misalignment and occlusions.
However, the problem of these methods is the use
of color, which is not discriminative for long-term
applications.
In (Barbosa et al., 2012), re-identification is
performed on soft biometric traits extracted from
skeleton data and geodesic distances extracted from
the depth data. These features are weighted and used
to extract a signature of the person, which is then
matched with training data. The methods in (Munaro
et al., 2014a; Munaro et al., 2014b) approach to
the problem applying feature based on the extracted
skeleton of the person. This is used not only to
calculate distances between the joints and their ratios,
but also to map the point clouds of the person to a
standard pose of the person. This allows to use a
point cloud matching technique, typical of object
recognition in which the objects are usually rigid.
However, as skeleton data is not robust for body
motion and occlusion, these approaches have strong
limitations. In addition, point cloud matching has a
high computational cost. In (Nanni et al., 2016), an
ensemble of state-of-the-art approaches is applied,
exploiting colors and, when available, depth and
skeleton data. Those approaches are weighted and
combined using the sum rule. Again, in (Pala et al.,
2016), a multi-modal dissimilarity representation
is obtained by combining appearance and skeleton
data. Similarly in (Paisitkriangkrai et al., 2015),
an ensemble of distance functions, in which each
distance function is learned using a single feature,
is built in order to exploit multiple appearance
features. While in other works the weights of such
functions are pre-defined, in the latter they are learnt
by optimizing the evaluation measures. Although the
ensemble of state-of-the-art approaches improves the
accuracy, it may suffer in long-term applications as
color and/or skeletal data are used.
Wengefeld et al. (Wengefeld et al., 2016) present a
combined tracking and re-id system to be used on
a mobile robot. Applying both laser and 3d-camera
for detection for detection and tracking and visual
appearance based re-identification. Similarly (Koide
and Miura, 2016) presents a method for person
identification and tracking with a mobile robot. The
person is recognised using height, gait, and appear-
ance features. The tracking information is also used
in (Weinrich et al., 2013), where the identification
is performed based on an appearance model, using
particle swarm optimization to combine a precise
upper bodys pose estimation and appearance. In such
approaches re-identification is used as an extra obser-
vation to keep the track of people. Thus, appearance
based features are enough to identify people in short
time intervals. However, these approaches may fail
to identify people in longer terms.
3 RGB-D HUMAN
RE-IDENTIFICATION
The proposed re-identification approach uses an up-
per body detector to find humans in the scene, seg-
ments the whole body of a person and extracts bio-
metric features. Classification is performed by a sup-
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
390

port vector machine (SVM). The flow diagram of
the respective sub-modules is presented in Figure 2.
In particular, the depth of the body is firstly esti-
mated from the bounding box detected via an up-
per body detector (Figure 3-a). Body segmentation
is performed by thresholding the whole image using
the estimated depth level (Figure 3-b). Then, impor-
tant landmark points, including head point, shoulder
points and neck points, are detected. Using these
landmark points, height of the person, distance be-
tween shoulder points, face’s length, head’s volume,
upper-torso’s volume, and lower-torso’s volume are
extracted as biometric features (Figure 3-c). The fol-
lowing subsections explain each part in detail.
3.1 Person Detection and Body
Segmentation
Person detection is performed by an RGB-D-based
upper body detector (Mitzel and Leibe, 2012). This
detector applies template matching on depth images.
To reduce the computational load, the detector first
runs a ground plane estimation to determine a region
of interest, which is the most suitable to detect the
upper bodies of a standing or walking person. Then,
the depth image is scaled to various sizes and the
template is slid over the image trying to find matches.
As a result, it detects bounding boxes of people in the
scene (Figure 3-a).
After the bounding boxes are detected on the
depth images, we segment the whole body of the
respective persons. First, the depth level of a person
is calculated by taking the average of the depth pixels
inside the upper body region (µ
d
). Then, the whole
depth image is thresholded within the depth interval,
[µ
d
− 0.5, µ
d
+ 0.5], assuming a person occupies a 1m
x 1m horizontal space. Finally, connected component
analysis is performed on the binary depth image
in order to segment the whole body of the person
(Figure 3-b).
3.2 Biometric Feature Extraction
The human body contains many biometric properties
that allow us to distinguish a person from others. Al-
though recognizing faces is one of the most intuitive
ways to identify a person, there are also other features
of the human body that can be useful. Height,
length of face, width of shoulders are among these
features. 2D body shape is also another feature that
can be used to identify people, but since it depends
on the view, it is hard to use it as a discriminative
feature. Alternatively, the features extracted from
a 3D body shape can provide view-independent
features. However, registering and matching 3D
point clouds have a high computational cost (Munaro
et al., 2014a). Thus, we propose novel volume-based
features in order to exploit the 3D information of the
human body.
In particular, we extract the following biometric
features: height of the person, distance between
shoulder points, length of face, volume of head,
volume of upper-torso, and volume of lower-torso
(Figure 3-c). In order to extract these features,
we start from the whole person’s body obtained in
the previous section, and then perform body-parts
segmentation by locating some landmark points on
it. Landmark points detection, body-parts segmen-
tation, and skeleton tracking are all well-known
research topics in computer vision. There are many
approaches to obtain state-of-the-art results (Shotton
et al., 2011; Yang and Ramanan, 2013). However, as
only a few body parts (e.g., head, torso) are required
for our approach, we simply locate segments relative
to head, neck, shoulder, and hip points.
3.2.1 Landmark Points
The highest point among those inside the 2D binary
body region is considered as the human head point
(P
head
). As the upper body detector provides the re-
gion between the shoulders and the head, it can also
be used to detect shoulder points. We detect the left
and right shoulder points (P
le f t
and P
right
) by finding
the extremes of the segment where the bottom line
of the bounding box intersects the 2D body region
(note that these are not exactly shoulder points, but
an approximation based on the visible left and right
extremes of the upper body). We also assume that the
neck is the narrowest region of the upper body. There-
fore, we project the points inside the upper body re-
gion on the y-axis of the upper body. The smallest
value corresponds to the coordinate of the neck point
(P
neck
). Next, by assuming the average torso length
of a person is around 55cm (Gordon et al., 1989), we
determine an approximate position of the hip point by
descending of the same length along the y-axis, i.e.
P
hip
= P
neck
− (0, 0.55, 0)
T
. As the point cloud is ob-
tained from the depth image, the 3D coordinates of all
the points can be computed.
After all the above points have been determined,
we extract the height of the person (feature f
1
), the
width of the shoulders ( f
2
), and the length of the face
( f
3
) as in Eq. 1.
Volume-based Human Re-identification with RGB-D Cameras
391

Figure 2: The flow diagram of the proposed approach.
Figure 3: The result of (a) the upper body detector, (b) the
body segmentation and landmark point detection: a-e) head,
neck, left, right, and hip points, c) , and (c) the extracted
biometric features: 1) height of the person, 2) distance be-
tween shoulder joints, 3) length of face, 4) head volume, 5)
upper-torso volume, and 6) lower-torso volume.
f
1
= |P
head
− pro j
GP
(P
head
)| (1)
f
2
= |P
le f t
− P
right
|
f
3
= |P
head
− P
neck
|
where pro j
GP
is the projection on the ground plane
estimated in Section 3.1.
3.2.2 Body Volume
The full volume of body parts requires to have a full
3D body model of the person. As this is computation-
ally expensive, we approximate the volume by con-
sidering only the visible part of a body part, which
roughly corresponds to half of its volume. We assume
that there is a virtual plane passing through the shoul-
der points and cutting the human body into two parts:
back and front (Fig. 4-a). Then, the body part’s vol-
ume is estimated by summing the volumes v
i
of each
3D discrete unit (Fig. 4-b). The latter is calculated as
v
i
= ∆x
i
· ∆y
i
· ∆z
i
, where ∆z
i
is the distance of point
i from the shoulders plane, while ∆x
i
and ∆y
i
are the
distances of point i to its neighboring points on the x-
and y-axes, respectively. Hence, the volume of a body
part k is estimated by the following equation:
Vol
k
=
∑
i∈Ω
k
∆x
i
· ∆y
i
· ∆z
i
(2)
where Ω
k
represents the region of body part k.
Following Eq. 2, the volume of the head (fea-
ture f
4
), upper-torso ( f
5
), and lower-torso ( f
6
) are
calculated. The final feature vector, extracted from a
single image, is therefore FV = [ f
1
, f
2
, f
3
, f
4
, f
5
, f
6
].
Figure 4: (a) Body part volumes are approximated by calcu-
lating the volume of the 3D region in front of the shoulder
plane, (b) which is done by taking the sum of the volume of
each 3D discrete unit.
3.3 Classification
For recognizing people based on the features pre-
sented in the previous subsection, we have used a
Support Vector Machine (SVM) (Cortes and Vapnik,
1995). We have trained an SVM for every subject of
the training dataset using a radial basis function.
4 EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Experimental Setup
The proposed approach has been tested in a variety of
conditions, especially when there were challenging
pose, motion and occlusions. In particular, we have
run experiments on sequences containing i) multiple
people, ii) different poses and body motions, iii)
occlusions, and iv) a large number of people from the
BIWI RGBD-ID dataset (Munaro et al., 2014a).
The first three sequences were recorded in home and
laboratory environments using a Kinect 1 mounted
on a Kompa
¨
ı robot (Figure 5-a). These sequences
were used to test the accuracy of our approach under
various view angles, person distances to the robot,
body motions, and occlusions. The first sequence
contains an elderly person wandering in the living
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
392

(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Figure 5: (a) The sequences in a laboratory environment
were recorded using a Kinect 1 mounted on a Kompa
¨
ı robot.
In these experiments, training is performed with three peo-
ple turning around themselves at increasing distance from
the camera: (b) 1m, (c) 2m, and (d) 3m.
room of a small apartment, while several other
people were standing or walking in the scene. In the
second sequence, a person was performing different
body motions such as crossing arms, scratching
head, clasping hands behind head, and bending
aside/forward/backward. Finally, the third sequence
includes a person occluded by a chair at 1m, 2.5m,
and 5m away from the robot, both while the chair
was fixed at 1m or moved together with the person.
RGB and depth images were recorded with 640x480
resolution at 30 fps.
The BIWI RGBD-ID dataset consists of video
sequences of 50 different subjects, performing a
certain motion routine in front of a Kinect 1, such
as a turning, moving the head and walking towards
the camera. The dataset includes RGB images,
depth images, and skeletal data. The images were
acquired at about 10 fps and up to one minute for
every subject. Moreover, 56 testing sequences with
28 subjects, already present in the dataset, were
collected in different locations on a different day,
with most of the subjects wearing different clothes.
A ”Still” sequence and a ”Walking” sequence are
available for each person in the testing set. In the
Walking sequence, every person walks twice towards
and twice diagonally with respect to the Kinect.
Figure 6: Re-identification results in case of multiple
people. RGB and Depth images, in which the detected
body parts are marked, are presented on the left and right
columns, respectively. The green bounding box represents
the identified person.
4.2 Multiple People
This section presents some preliminary results apply-
ing the proposed approach to recordings obtained in
a real elderly house in Lincoln, UK, as part of EN-
RICHME project
1
. The dataset contains an elderly
person wandering in the living room of a small apart-
ment. A sequence, in which the elderly turns on the
spot, is used for training. Another sequence, contain-
ing the same elderly facing backwards and walking
among other people in the scene, is applied for test-
ing. The correct re-identification of our approach dur-
ing this experiment is illustrated in Figure 6. The lat-
ter shows that our approach can segment people and
perform user re-identification in a relatively crowded
scene, despite several people very close to each other.
1
http://www.enrichme.eu/
Volume-based Human Re-identification with RGB-D Cameras
393

Table 1: Re-identification results for various body mo-
tions/poses.
Sequence Accuracy(%)
Standing-Arms Crossed 50.10
Moving Hands 74.71
Bending Aside 100.00
Bending Forward 52.29
Bending Backward 68.00
4.3 Body Pose and Motion
In this experiment, we trained an SVM classifier
with three people turning around themselves at in-
creasing distance from the camera (1m, 2m and
3m; see also Figure 5-b-d). We then recorded, on
a different day and in different environment, one
of the above people performing the following body
motions: crossing arms, scratching head, clasping
hands behind head, arms wide open, and bending
aside/forward/backward. Table 1 shows the accuracy
for each situation, where the recognition rate is calcu-
lated by single-shot results.
These preliminary results show that our approach per-
forms correct re-identification in most of the body
motion sequences. Since the shoulder points could
not be detected correctly when the arms were crossed,
the volume features could not be calculated accu-
rately. In addition, the upper body detector failed
when the person clasped his hands behind the head.
For bending aside, we can see that the proposed ap-
proach achieves 100% correct recognition. It can also
handle a certain level of bending forward or back-
ward. However, if the person bends too much, the vir-
tual shoulder plane moves in front of the body points,
so the volumes cannot be calculated and our recogni-
tion approach fails.
4.4 Occlusions
In this experiment, we have tested our approach when
the body of the person is occluded. Again, we used
the same data of Section 4.3 with three people for
training. Then, on a different day and in a different
environment, we recorded one of the three people fac-
ing the robot at 1m (close), 2.5m (middle), and 5m
(far) away, while a chair was occluding the lower part
of the body. In order to have various levels of occlu-
sion, we considered two cases: i) the chair moves as
the person moves away from the robot, ii) the chair is
fixed at 1m distance from the robot. The classification
if performed by an SVM and the single-shot recogni-
tion rate is shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Re-identification results while the body of the per-
son is occluded by a chair at various distances. In the first
three sequences, the chair moves together with the user. In
the last three sequences, the chair is fixed at a close distance.
Sequence Accuracy(%)
Chair:Close - User:Close 100
Chair:Middle - User:Middle 100
Chair:Far - User:Far 71.23
Chair:Close - User:Close 100
Chair:Close - User:Middle 100
Chair:Close - User:Far 89.41
We can see that our re-identification performs very
well even under significant occlusions, achieving
100% correct re-identification when user and chair are
up to 2.5m away from the robot. The method starts to
fail at about 5m, when the upper body detector is not
able to work properly.
4.5 BIWI RGBD-ID Dataset
In this section, we present the results on the public
BIWI RGBD-ID dataset (Munaro et al., 2014a).
The sequence with 50 subjects is used for training
and the two sequences (”Still” and ”Walking”) with
28 subjects are used for testing. The training set
contains 350 samples per person on average. For
evaluation, we compute the Cumulative Matching
Characteristic (CMC) Curve, which is commonly
used for evaluating re-identification methods (Wang
et al., 2007). For every k = {1 ···N
train
}, where
N
train
is the number of training subjects, the CMC
expresses the average person recognition rate com-
puted when the correct person appears among the k
best classification scores (rank-k). A popular way to
evaluate CMC is to calculate the rank-1 recognition
rate and the normalized Area Under Curve (nAUC),
which is the integral of the CMC. The recognition
rate is computed for every subject individually av-
eraging the single-shot results from all the test frames.
Figure 7 shows the CMC obtained by our ap-
proach using volume-based (VB) features for ”Still”
and ”Walking” test sequences. We compared our
approach to the SVM- and NN-based BIWI methods
(Munaro et al., 2014b) using both our landmark
points (denoted as ”VB”) and those provided by the
skeletal data in the BIWI RGBD-ID dataset (denoted
as ”VB-Skel”). The figure shows that the proposed
system, when using the same skeletal data of BIWI,
achieves similar and sometime better results than the
latter, in particular for the “Still” sequences. If our
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
394

(a)
(b)
Figure 7: Cumulative Matching Characteristic Curves ob-
tained by the BIWI methods in (Munaro et al., 2014b)
and our volume-based (VB) approach on BIWI RGBD-ID
dataset: (a) Still and (b) Walking sequences.
non-skeletal-based landmarks are used instead, the
performance decreases as expected, but still within
an acceptable level.
Since the test sequences contain also many frames of
the same person, it is possible to compute video-wise
results by associating each test sequence to the
subject voted by the highest number of frames. Table
3 presents the rank-1 recognition rates for single-
and multi-shots cases, and the respective nAUCs.
Again, we can see that, using skeletal data, our
approach outperforms BIWI in the “Still” sequences
and achieves comparable results in the “Walking”
sequences. Even in this case, the performance of our
non-skeletal-based version is satisfactory, consider-
ing the fact that only few landmark points are used.
This experiment unveils one of the problems of our
approach, which is the failure of landmark point
detection in particular situations, especially for the
“Walking” sequence, when there is significant body
motion, so the extracted features are not always good
enough to distinguish people robustly. However, the
experiment shows also that, when the same features
are extracted using skeletal data, our re-identification
achieves state-of-the-art results. This is an important
aspect of our approach, based on novel biometric fea-
tures which can work in both cases, with and without
skeletal data, obtaining reasonable results even with
challenging body poses and strong occlusions.
5 CONCLUSION
This paper presents a re-identification system for
RGB-D cameras based on novel biometric features.
To overcome the limitations of existing approaches
in real-world environments and domestic robot appli-
cations, we extracted both volumetric and distance
features of the human body. The proposed approach
was tested under various conditions, including oc-
clusion, challenging body movements, and different
views. The experimental results showed that our
re-identification system performed very well under
all those conditions.
Future work will consider subjects wearing dif-
ferent types of clothes (e.g. vests, jackets, etc.)
affecting the volume-based features, and will inves-
tigate possible weighted combinations of the latter
to deal more challenging outfits. To decrease the
false positives, we will investigate imposing temporal
consistency by exploiting tracking information.
Furthermore, relative features (e.g., ratio of volumes)
will be considered to overcome the affects of noisy
depth image on volume calculation, especially
when people are far from the camera. Additional
experiments will also be conducted on new, extended
datasets containing a larger variety of body poses,
occlusions, and clothes combinations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the EU H2020 project
“ENRICHME” (grant agreement nr. 643691).
Volume-based Human Re-identification with RGB-D Cameras
395
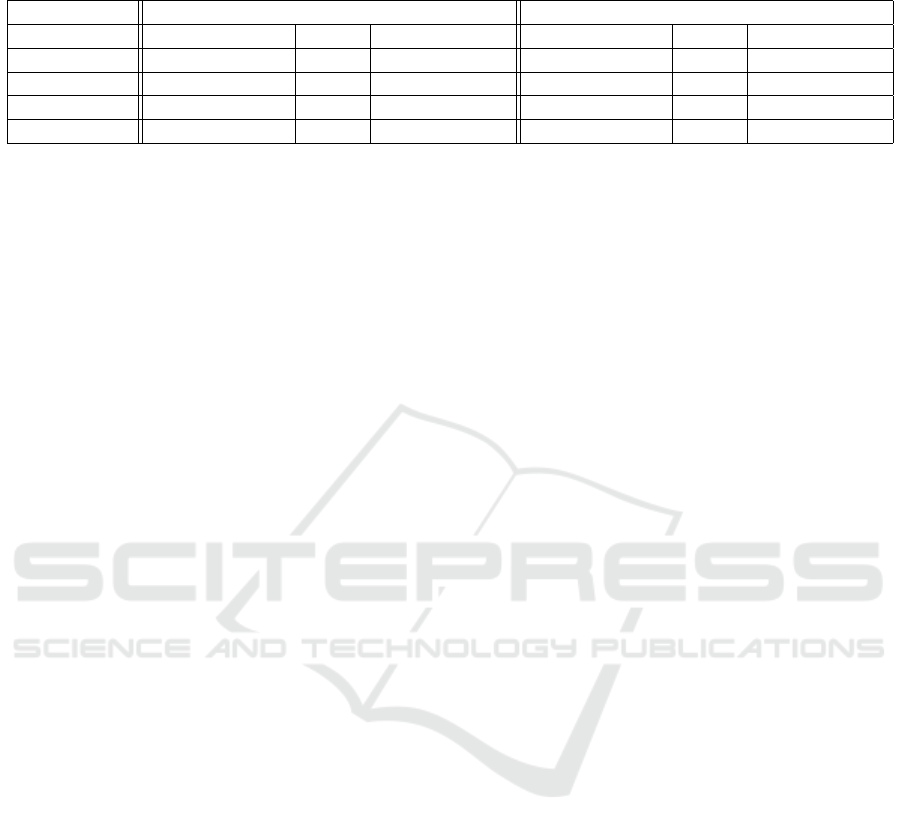
Table 3: Re-identification results of the BIWI methods in (Munaro et al., 2014b) and our volume-based (VB) approach on the
BIWI RGBD-ID dataset.
Still Walking
Single (Rank-1) nAUC Multi (Rank-1) Single (Rank-1) nAUC Multi (Rank-1)
BIWI (SVM) 11.60 84.50 10.70 13.80 81.70 17.90
BIWI (NN) 26.60 89.70 32.10 21.10 86.60 39.30
VB 12.74 73.91 17.86 6.88 71.24 17.86
VB-Skel. 32.12 91.79 42.86 18.93 82.66 42.86
REFERENCES
Barbosa, I. B., Cristani, M., Del Bue, A., Bazzani, L., and
Murino, V. (2012). Re-identification with rgb-d sen-
sors. In European Conference on Computer Vision,
pages 433–442. Springer.
Bedagkar-Gala, A. and Shah, S. K. (2014). A survey of ap-
proaches and trends in person re-identification. Image
and Vision Computing, 32(4):270 – 286.
Bellotto, N. and Hu, H. (2010). A bank of unscented
kalman filters for multimodal human perception with
mobile service robots. International Journal of Social
Robotics, 2(2):121–136.
Chen, D., Yuan, Z., Hua, G., Zheng, N., and Wang, J.
(2015). Similarity learning on an explicit polyno-
mial kernel feature map for person re-identification. In
2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition (CVPR), pages 1565–1573.
Cortes, C. and Vapnik, V. (1995). Support-vector networks.
Machine Learning, 20(3):273–297.
Farenzena, M., Bazzani, L., Perina, A., Murino, V., and
Cristani, M. (2010). Person re-identification by
symmetry-driven accumulation of local features. In
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR),
2010 IEEE Conference on, pages 2360–2367.
Ferland, F., Cruz-Maya, A., and Tapus, A. (2015). Adapting
an hybrid behavior-based architecture with episodic
memory to different humanoid robots. In Robot and
Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), 2015
24th IEEE International Symposium on, pages 797–
802.
Gordon, C. C., Churchill, T., Clauser, C. E., Bradtmiller, B.,
and McConville, J. T. (1989). Anthropometric survey
of US Army personnel: Summary statistics, interim
report for 1988. Technical report, DTIC Document.
Koide, K. and Miura, J. (2016). Identification of a spe-
cific person using color, height, and gait features for
a person following robot. Robotics and Autonomous
Systems, 84:76 – 87.
Kviatkovsky, I., Adam, A., and Rivlin, E. (2013). Color in-
variants for person reidentification. IEEE Trans. Pat-
tern Anal. Mach. Intell., 35(7):1622–1634.
Li, W., Zhao, R., Xiao, T., and Wang, X. (2014). Deep-
reid: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-
identification. In The IEEE Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
Mitzel, D. and Leibe, B. (2012). Close-range human detec-
tion and tracking for head-mounted cameras. In Pro-
ceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference,
pages 8.1–8.11. BMVA Press.
Munaro, M., Basso, A., Fossati, A., Gool, L. V., and
Menegatti, E. (2014a). 3d reconstruction of freely
moving persons for re-identification with a depth
sensor. In 2014 IEEE International Conference on
Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pages 4512–4519.
Munaro, M., Fossati, A., Basso, A., Menegatti, E.,
and Van Gool, L. (2014b). One-shot person re-
identification with a consumer depth camera. In Gong,
S., Cristani, M., Yan, S., and Loy, C. C., editors, Per-
son Re-Identification, pages 161–181. Springer Lon-
don, London.
Munaro, M., Ghidoni, S., Dizmen, D. T., and Menegatti,
E. (2014c). A feature-based approach to people re-
identification using skeleton keypoints. In 2014 IEEE
International Conference on Robotics and Automation
(ICRA), pages 5644–5651.
Nanni, L., Munaro, M., Ghidoni, S., Menegatti, E., and
Brahnam, S. (2016). Ensemble of different ap-
proaches for a reliable person re-identification system.
Applied Computing and Informatics, 12(2):142 – 153.
Paisitkriangkrai, S., Shen, C., and van den Hengel, A.
(2015). Learning to rank in person re-identification
with metric ensembles. In The IEEE Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
Pala, F., Satta, R., Fumera, G., and Roli, F. (2016). Mul-
timodal person reidentification using rgb-d cameras.
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video
Technology, 26(4):788–799.
Shotton, J., Fitzgibbon, A., Cook, M., Sharp, T., Finocchio,
M., Moore, R., Kipman, A., and Blake, A. (2011).
Real-time human pose recognition in parts from sin-
gle depth images. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion, CVPR ’11, pages 1297–1304, Washington, DC,
USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Vezzani, R., Baltieri, D., and Cucchiara, R. (2013). People
reidentification in surveillance and forensics: A sur-
vey. ACM Comput. Surv., 46(2):29:1–29:37.
Wang, X., Doretto, G., Sebastian, T., Rittscher, J., and Tu,
P. (2007). Shape and appearance context modeling. In
IN: PROC. ICCV (2007.
Weinrich, C., Volkhardt, M., and Gross, H. M. (2013).
Appearance-based 3d upper-body pose estimation and
person re-identification on mobile robots. In 2013
IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and
Cybernetics, pages 4384–4390.
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
396

Wengefeld, T., Eisenbach, M., Trinh, T. Q., and Gross, H.-
M. (2016). May i be your personal coach? bringing to-
gether person tracking and visual re-identification on
a mobile robot. ISR 2016.
Yang, Y. and Ramanan, D. (2013). Articulated human de-
tection with flexible mixtures of parts. IEEE Trans.
Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 35(12):2878–2890.
Volume-based Human Re-identification with RGB-D Cameras
397
