
Towards View-point Invariant Person Re-identification via Fusion of
Anthropometric and Gait Features from Kinect Measurements
Athira Nambiar
1
, Alexandre Bernardino
1
, Jacinto C. Nascimento
1
and Ana Fred
2
1
Institute for Systems and Robotics, Instituto Superior T
´
ecnico, Av. Rovisco Pais, 1, 1049-001, Lisbon, Portugal
2
Telecommunications Institute, Instituto Superior T
´
ecnico, Av. Rovisco Pais, 1, 1049-001, Lisbon, Portugal
{anambiar, alex, jan}@isr.tecnico.ulisboa.pt, afred@lx.it.pt
Keywords:
Person Re-identification, Biometrics, Anthropometrics, Gait, Kinect, Data Fusion.
Abstract:
In this work, we present view-point invariant person re-identification (Re-ID) by multi-modal feature fusion of
3D soft biometric cues. We exploit the MS Kinect
TM
sensor v.2, to collect the skeleton points from the walking
subjects and leverage both the anthropometric features and the gait features associated with the person. The
key proposals of the paper are two fold: First, we conduct an extensive study of the influence of various
features both individually and jointly (by fusion technique), on the person Re-ID. Second, we present an
actual demonstration of the view-point invariant Re-ID paradigm, by analysing the subject data collected in
different walking directions. Focusing the latter, we further analyse three different categories which we term as
pseudo, quasi and full view-point invariant scenarios, and evaluate our system performance under these various
scenarios. Initial pilot studies were conducted on a new set of 20 people, collected at the host laboratory. We
illustrate, for the first time, gait-based person re-identification with truly view-point invariant behaviour, i.e.
the walking direction of the probe sample being not represented in the gallery samples.
1 INTRODUCTION
As the technology revolution brought greater access
to sophisticated multimedia systems, as well as ad-
vances in computer vision and machine learning tech-
niques, an exponential growth of smart surveillance
systems is underway. The automatic analysis of data
collected in surveillance camera networks serves a
significant role in the analysis of people and crowd
behaviours in public spaces.
Person re-identification (Re-ID) is one of the most
interesting, yet challenging, tasks in video surveil-
lance. It consists in recognizing an individual in dif-
ferent locations over a set of non-overlapping camera
views (Barbosa et al., 2012). The classical approaches
in Re-ID consist in exploiting the appearance cues,
such as colour or texture of apparel, thus assuming
that subjects will not change their clothing within the
observation period. However, they restrain the sys-
tem from long term applications, since those features
undergo drastic variations over long periods.
Hence, a new trend in Re-ID is to leverage longer
term biometric traits, called soft-biometrics. Soft bio-
metrics are physical, behavioral or adhered human
characteristics, classifiable in predefined human com-
pliant categories which are established by humans
with the aim of differentiating individuals (Dantcheva
et al., 2010). Soft biometric features leverage char-
acteristic human traits such as anthropometric mea-
surements, height, body size and gait, which are co-
herent for a long term analysis (Nixon et al., 2015).
Soft-biometric features are more stable over long pe-
riods than appearance cues and, hence, could be em-
ployed towards long term Re-ID applications. Differ-
ent from hard biometrics (e.g. fingerprint, iris, etc.),
they lack the distinctiveness and time invariance to
identify a person with high reliability. However, they
have certain advantages over hard biometrics, mak-
ing them best suited to deploy in surveillance appli-
cations e.g. non obtrusiveness, acquisition from dis-
tance, non-requirement for the cooperation of the sub-
ject, computational and time efficiency, and human
interpretability.
In this work, we propose a biometric enabled per-
son re-identification system, using two kinds of soft
biometric features i.e. anthropometric features and
gait features, extracted from the human body skeleton
computed by a Microsoft Kinect
TM
sensor v.2. An-
thropometry involves the systematic measurement of
the physical properties of the human body, primarily
dimensional descriptors of body size and shape. Hu-
man gait includes both the body posture and dynam-
108
Nambiar A., Bernardino A., Nascimento J. and Fred A.
Towards View-point Invariant Person Re-identification via Fusion of Anthropometric and Gait Features from Kinect Measurements.
DOI: 10.5220/0006165301080119
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2017), pages 108-119
ISBN: 978-989-758-226-4
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

ics while walking (Lee and Grimson, 2002). The cues
are extracted from range data which are computed us-
ing an RGBD camera. Hence, the great constraint
of appearance constancy hypothesis can be relaxed
and facilitated towards long-term person Re-ID. To
the best of our knowledge only a very limited number
of works have been employed in this regard, further-
more, they employ view-point dependent approaches
i.e. data is collected and algorithms are tested with
a single walking direction with respect to the cam-
era.(Barbosa et al., 2012), (Gianaria et al., 2014) and
(Andersson and Araujo, 2015). In this paper, we pro-
pose a view-point invariant person re-identification
method tested with subjects walking in different di-
rections, by using multi-modal feature fusion of an-
thropometric and gait features.
The major contributions of the paper are two fold:
• First, to validate the effect of various anthropo-
metric and gait features in distinguishing a person
among the population and facilitate towards per-
son Re-ID from those soft-biometric cues. In or-
der to better understand this, we conduct a thor-
ough study by exploiting individual features or
combination of features (via fusion).
• Second, is the actual demonstration of the real
impact of view-point on the Re-ID paradigm.
Since skeleton coordinates provided by kinect
data are, in principle, view-point invariant (can
be normalized to a canonical view-point by a
roto-translation transformation), many works as-
sume view point invariance from the start and do
not validate experimentally this assumption. De-
spite skeleton coordinates are naturally view point
invariant, their computation is not (the skeleton
reconstruction process depends on view points
and self-occlusions). Most work in the litera-
ture do single-view probe and single (same)-view
gallery (which is basically the view-point depen-
dent approach), which does not allow assessing
the view-point invariant characteristics of the al-
gorithm. In order to perform a benchmark assess-
ment, we experiment in this work explicitly dif-
ferent view-points in the probe and gallery sam-
ples. In addition, we conduct several tests of view-
point invariance: (i) single-view-point probe with
multi-view-point gallery (pseudo view-point in-
variance); (ii) novel-view-point probe with multi-
view-point gallery (quasi view-point invariance)
and (iii) novel-view-point probe with single-view-
point gallery (full view-point invariance). The for-
mer two require a large effort in the gallery cre-
ation. The latter, is the easiest and most flexible
form since only a single camera is required and
the person enrollment stage is very simple (one
pass only).
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. We
review the related works in Section 2. In Section 3,
we explain the proposed methodology. In particular,
we present the data acquisition set up, feature extrac-
tion, signature matching and evaluation methodology.
In Section 4, we detail the various experiments con-
ducted and the results achieved. We summarize our
work and enumerate some future work plans in Sec-
tion 5.
2 RELATED WORK
Many of the classical Re-ID systems found in the
literature were built on appearance based features
(Doretto et al., 2011), (Riccio et al., 2014), exploit-
ing the colour/ texture of the clothing. However, this
prevents the Re-ID application when the apparel is
changed. In recent years, a new trend employing bio-
metric information has blossomed, owing to the pre-
cise and advanced data capturing machines (e.g. HD
cameras, motion capture, kinect sensor), especially in
analysing the 3D body information that enables view-
point invariance.
Many works have been proposed towards view-
point invariant Re-ID. In (Zhao et al., 2006), (Iwashita
et al., 2010) multiple 2D cameras were used to recon-
struct the 3D volumes and thus achieve view-point in-
variance. Other works use multiple 2D cameras to
fit 3D models in the volumetric data e.g. 3D ellip-
soids (Sivapalan et al., 2011), articulated cylinders
(Ariyanto and Nixon, 2011) and 3D volume shape by
the intersection of projected silhouettes (Seely et al.,
2008). Current state-of-the-art view-point invariant
techniques are presented in (Iwashita et al., 2014),
(Fernandez et al., 2016). In (Iwashita et al., 2014),
a method using a 4D gait database was proposed. At
each frame of a gait sequence, the observation angle
is estimated from the walking direction by fitting a
2D polynomial curve to the foot points. Then, a vir-
tual image corresponding to the estimated direction is
synthesized from the 4D gait database. (Fernandez
et al., 2016) presents a multi-view-point gait recogni-
tion technique based on a rotation invariant gait de-
scriptor derived from the 3D angular analysis of the
movement of the subject.
Some works exploiting view-point invariant
RGBD sensors (e.g. kinect) have also been pro-
posed in the literature. In the work by (Barbosa
et al., 2012), they leveraged the soft-biometric cues
of a body for person Re-ID. However they used only
the static body information i.e. skeleton based fea-
tures and surface based features, in the frontal view.
Towards View-point Invariant Person Re-identification via Fusion of Anthropometric and Gait Features from Kinect Measurements
109
Later, some works employed the gait features as well,
e.g. stride and arm kinematics (Gabel et al., 2012),
knee angles (Aarai and Andrie, 2013), anthropomet-
ric and dynamic statistics (Gianaria et al., 2014), an-
thropometric and angles of lower joints (Andersson
and Araujo, 2015).
In this work, we build on the aforementioned
state-of-the-art works by proposing some novel ways
of improving the Re-ID algorithm, in terms of feature
extraction, feature fusion and impact of view angles.
In particular, we examine the Re-ID accuracy of vari-
ous anthropometric and gait features via both individ-
ual as well as joint schemes. In addition, we explicitly
conduct a view-point invariant Re-ID scenario by col-
lecting video sequences of people walking in differ-
ent directions, whereas previous related works collect
data in a much controlled predefined single direction
say, frontal or lateral.
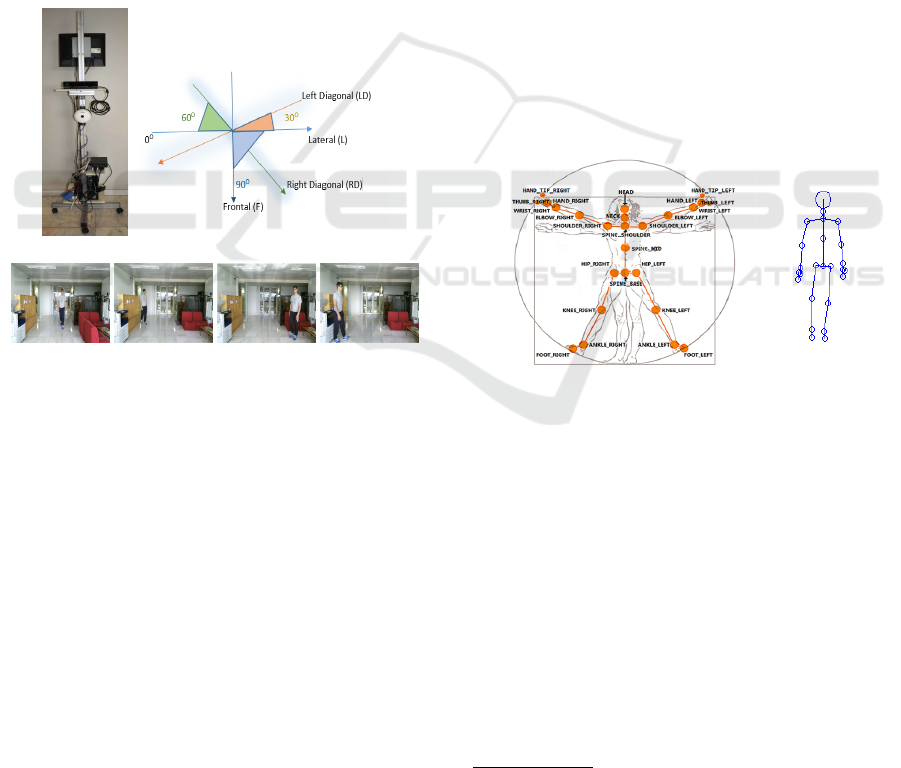
(a) (b)
(c) (d) (e) (f)
Figure 1: Data acquisition: (a) System set up (b) Sub-
ject walking directions in front of the acquisition system
(c) Sample frames from our data acquisition, in four dif-
ferent directions- frontal(∼90
◦
), right diagonal(∼60
◦
), left
diagonal(∼30
◦
) and lateral(∼0
◦
) respectively.
3 PROPOSED METHOD
In this section, we explain the data acquisition and
proposed methodology. More specifically, we detail
the set up and the data collection procedure conducted
in the host laboratory. Then, we describe various
stages of data analysis including pre-processing, fea-
ture extraction, signature matching and experimental
evaluation strategies.
3.1 Data Acquisition Set Up
For the data acquisition, we used a mobile platform,
in which the kinect sensor was fixed at a height of an
average human (See Fig. 1(a) for the data acquisition
system). This mimics normal surveillance scenarios
as well as changes in the position of camera over time,
as in a long term person Re-ID scenario. The kinect
device is composed of a set of sensors, which is ac-
companied with a Software Development Kit (SDK),
that is able to track movements from users by using
a skeleton mapping algorithm, and is able to provide
the 3D information related to the movements of body
joints. We acquired all the three available data i.e.
skeleton, colour and depth. Since the proposed gait
algorithm employs the skeleton information, it neces-
sitates to be of multiple frames with high frame rate,
and hence captured at the full frame rate of the sen-
sor @ 30fps. In this second version of the device, it is
able to track 25 joints at 30 frames per second. Colour
and depth information are employed for appearance
based features, which generally require single frame,
and hence was captured at 1fps. However, these were
not used in the current work.
(a) (b)
Figure 2: (a) Skeleton positions relative to the human body
1
(b) A sample skeleton body visualization from our collec-
tion.
In order to ensure view-point invariance in our ac-
quisition set up, we collected multiple views of 20
subjects in four different directions, along both ways,
as shown in Fig. 1(b). We define the direction angle
with respect to the image plane. Lateral walk (L) is
at ∼0
◦
and frontal walk (F) is at ∼90
◦
. And there are
two diagonal walks at different view angles. Right di-
agonal (RD) begins at one of the corners of the hall,
which has ∼60
◦
, whereas Left diagonal (LD) begins
somewhere in the half way, thus defining ∼30
◦
. In
each of these four directions, a minimum of three
1
For body joint types and enumeration, refer to the
link: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/microsoft.
kinect.jointtype.aspx
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
110
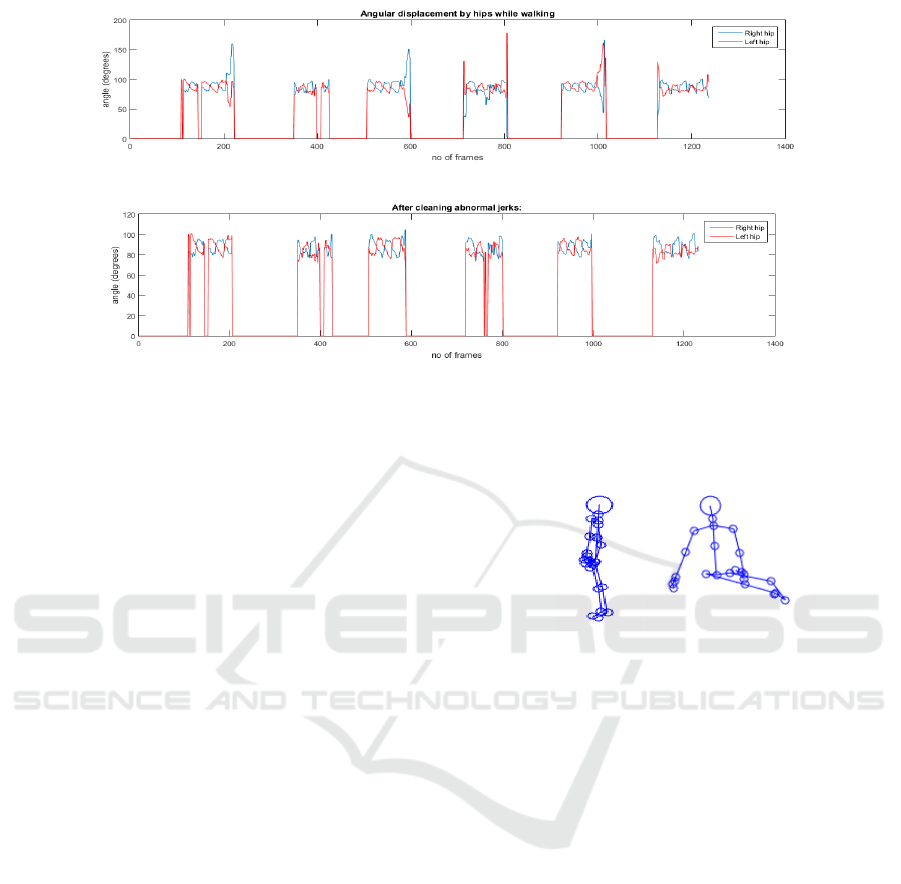
(a)
(b)
Figure 3: (a) The abnormal shifts towards the ending of each sequence are due to the jerks of skeleton occurring at its
respective frames. (b) Abnormal frames are filtered out. Now we have the cleaned frames selected.
walking sequences were collected both in the front
and rear views (refer Fig. 1(c)-(f)). During the walk-
ing, the people are assumed to walk with their natural
gait. Altogether we have 240 video sequences com-
prising 20 subjects (12 video sequences per person) in
the aforementioned directions. Since kinect gets the
joint information of the skeleton data, it is in princi-
ple, view-point and scale invariant. In addition to that,
we hypothesize that the subject makes straight walks
during a single gait acquisitions, as kinect depth range
is limited (80cm to 4 meters) .
Kinect can track in real-time a skeleton model,
composed of 25 body joints, as shown in Fig. 2(a).
The skeleton joints can be used to describe the body
measurements (anthropometrics) as well as the body
movements (gait) in real time and in 3D space (Shot-
ton et al., 2013).
3.2 Pre Processing
Prior to the feature extraction, we applied some pre-
processing for noise removal. The primary effect of
noise are jerks/ abnormalities in the skeleton data,
during the sequences (see examples in Fig. 4). In
addition, in some frames, the skeleton is not detected.
We could observe that, when the person approaches
the boundary of the kinect range, these issues occur
very often. In order to handle such situations, we
propose a semi- automatic approach to select the best
frames to retain and further analyse out of a video se-
quence.
Humans walk in a periodic fashion. It is neces-
sary to estimate the gait feature over each of these
periods of walking, known as gait cycle, which acts
(a) (b)
Figure 4: (a) Some views confuse the joint positions mak-
ing the skeleton based approach quite difficult (b) Abnormal
jerks occuring at certain frames, during the video sequence.
as the functional unit of gait. A gait cycle comprises
of sequence of events/ movements during locomotion
since one foot contacts the ground until the same foot
again contacts the ground. Prior to getting the gait
period, we intend to filter out the unwanted jerks by
means of exploiting the evolution of hip angles over
time. We noticed that the jerks made these angles
to grow abnormally, which also created drastic vari-
ations in the corresponding signals. An example of
such a situation is depicted in Fig. 3(a). In order
to clean/ remove such unwanted frames, we put a
threshold on the angular values (usually, the normal
expected values of hip angles are in between 70
◦
<hip
angle<105
◦
). Only the frames containing the an-
gles in between the upper and lower threshold are se-
lected. This step automatically cleans our noisy data.
A cleaned version of the previous signal is depicted in
Fig. 3(b).
The next step is gait cycle estimation. In order to
have a better overview of how the lower limbs move
along the video sequences, we compute the distance
between the feet during a gait sequence. The three
Towards View-point Invariant Person Re-identification via Fusion of Anthropometric and Gait Features from Kinect Measurements
111

Table 1: List of anthropometric and gait features used in our experiments. (L& R correspond to ‘left and right’ and x& y
correspond to ‘along x and y axes’).
Anthropometric
features
Gait features
Height Hip angle(L&R) Hip position(L&R)(x& y)
Arm length Knee angle(L& R) Knee position(L&R)(x& y)
Upper torso Foot distance Ankle position(L&R)(x& y)
Lower torso Knee distance Hand position(L&R)(x& y)
Upper-lower ratio Hand distance Shoulder position(L&R)(x& y)
Chestsize Elbow distance Stride
Hipsize Head position(x& y) Stride length
Spine position(x& y) Speed
consecutive peaks in such a signal provides a gait cy-
cle. Referring to Fig. 5, we can see that in each
video sequence, the frames between adjacent mark-
ers (stars in same colour) make a gait cycle
2
. At this
point, we make this step manually. Albeit we pro-
vide the method to automatically select the adjacent
peaks defining a gait cycle, we carry out a manual
verification by checking the real video sequence and
the signal peaks to verify that they are aligned. Also,
the phase is verified at this point by checking which
leg is in movement. From the peak signal alone, this
information is not easy to extract.
After selecting the frames defining gait cycle, we
extract the features.
3.3 Feature Extraction
After data acquisition and filtering, attributes were
extracted for each walk, both static physical features
defining the anthropometric measurements and
dynamic gait features defining the kinematics in
walking. To each subject, an identifier was provided
for re-identification. The extracted feature attributes
are explained in detail, next.
Anthropometric features: Under the anthropomet-
ric feature set, we collected many body measurements
defining the holistic body proportions of the subject.
This includes height, arm length, upper torso length,
lower torso length, upper to lower ratio, chest size,
hip size. These seven features constitute the body fea-
tures.
The length of a body part is defined as the sum of
the lengths of the links between the delimiting joints.
For example, the arm length is the sum of Euclidean
2
Note that, we collect three sequences of walking per
person in each direction. Since the person makes a walk
in a direction, and then a return walk to the initial point,
apparently we have 6 sequences, as we can see in Fig. 5.
However, we do not consider the return walks in this work,
and hence, we have altogether 3 video sequences under con-
sideration, as marked.
distances from shoulder to elbow (joint 4-joint 5),
elbow to wrist (joint 5- joint 6) and wrist to hand
(joint 6- joint 7). We calculate these static features
across each frame, and then compute the mean value
of each feature over a gait cycle. The mean value of
the anthropometrics over gait periods, are used as the
static feature descriptors in our experiments.
Gait features: Under the gait features, we collect be-
havioural features, deriving from the continuous mon-
itoring of joints during the gait. The key advantage of
using the kinect is to collect a rich set of view-point
invariant
3
dynamic spatio-temporal features derived
from the body movements.
First we computed three scalar features related to
walking, viz., stride length, stride time and the speed
of walking. The stride length is the distance between
two stationary positions of the same foot while walk-
ing (Equation (1)). It comprises the left step length
and right step length
4
. The duration to complete a
stride is called stride time (Equation (2)). It is ob-
tained by calculating the number of video frames in
a gait cycle divided by the frame rate of acquisition
(30 fps). From these two, we can obtain the speed of
walking as the ratio between stride length and stride
time ( Equation (3)).
Stride length = Left Step length + Right Step length
(1)
Stride time =
Number of frames in gaitcycle
30
(2)
Speed =
Stride length
Stride time
(3)
3
As mentioned before, despite the joint coordinates can
be easily transformed to a canonical reference frame, the
process to estimate the joints positions suffers from self-
occlusions due to view-point.
4
Step length is the distance between the heel contact
point of one foot and that of the other foot.
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
112
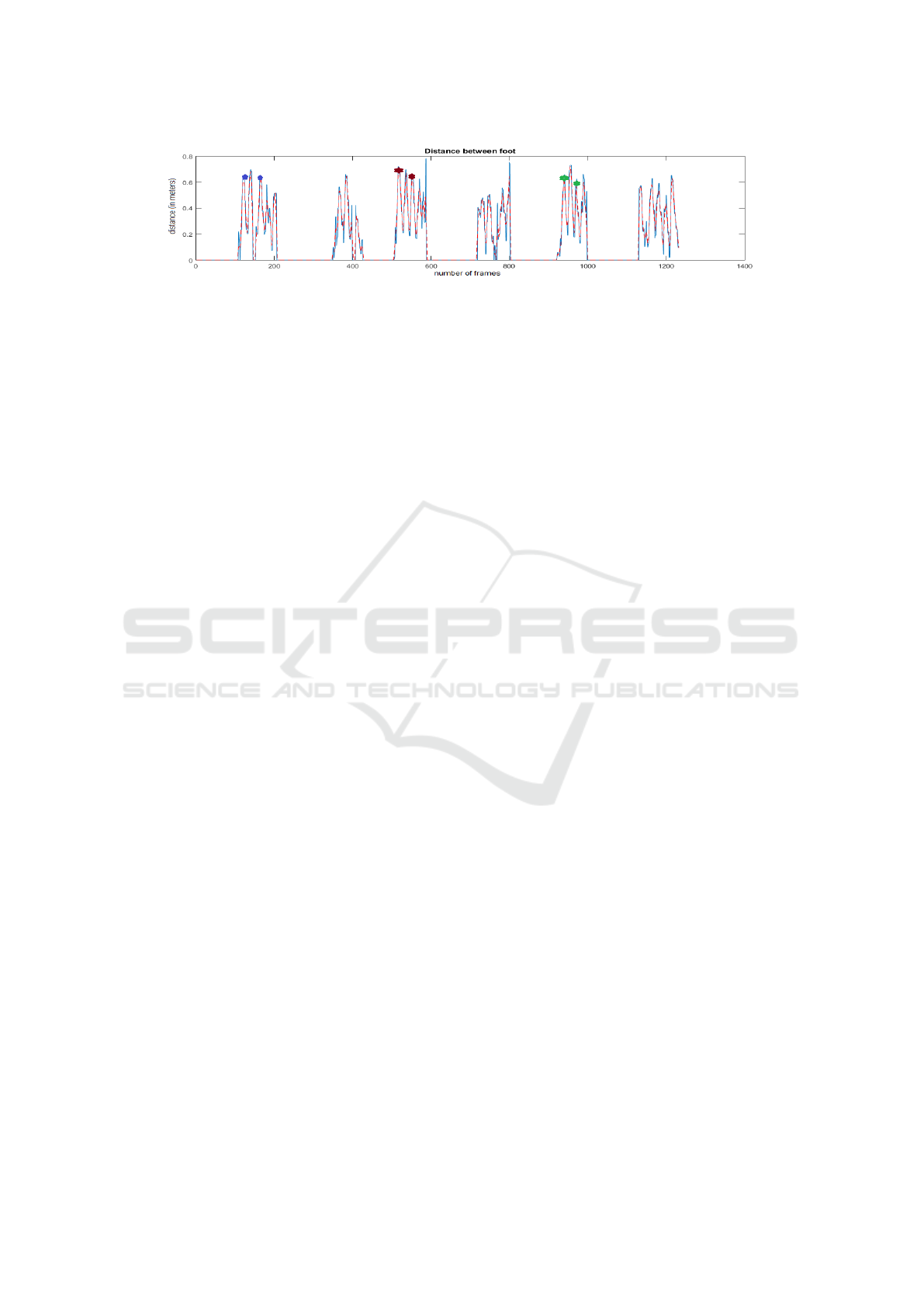
Figure 5: Gait cycle estimation. The two adjacent markers (3 consecutive peak) within a sequence, represent a gait cycle.
In addition, we also computed a set of 32 features,
related to the temporal evolution of the angles (at var-
ious body joints), distance (between various right-left
limbs during the gait) as well as the position (evolu-
tion of body joint along the gait). From these spatio-
temporal gait signals, we extract the mean and vari-
ance of the signal. Altogether, we have a feature set
containing 35 gait features (3 scalar and 32 dynamic)
and 7 anthropometric features. Table 1 presents a de-
tailed list of the feature set.
3.4 Signature Matching
This section explains how the features can be em-
ployed either individually or jointly towards the Re-
ID problem. A classical Re-ID problem is usually
evaluated by considering two sets of signatures (fea-
ture descriptors) collected from people: a gallery set
and a probe set. Then, the Re-ID evaluation is car-
ried out via associating each of the signature of the
probe set to a corresponding signature in the gallery
set. To evaluate the performance of Re-ID algorithms
in closed-set scenarios, the cumulative matching char-
acteristic (CMC) curve (Grother and Phillips, 2004)
is the most acclaimed and popular method of choice.
The CMC curve shows how often, on average, the
correct person ID is included in the best K matches
against the training set, for each test image. In other
words, it represents the expectation of finding the cor-
rect match in the top K matches.
Nearest Neighbor (NN) is among the most pop-
ular as well as most performing classifier, which is
commonly used in similar full body biometrics realm
(Andersson and Araujo, 2015), (Barbosa et al., 2012).
Hence, in this work, we exploit NN approach for the
classification, using the Euclidean distance as met-
ric. Suppose, we have signatures representing each
individual feature vectors, the Euclidean distance be-
tween the signature in the probe is compared against
the rest in the gallery. Then, the most similar sig-
nature in the gallery is selected as the correct Re-ID
class.
Concerning anthropometric features in our work,
the feature vector is composed of multiple body fea-
tures, where each of the features has a numerical value
associated with an individual trait e.g. height, arm
length. In the case of gait features, these individual
features are vectors representing mean and variance.
Hence, while computing the Euclidean distance, we
calculate the distance for each individual feature in
the probe, against their corresponding feature peers in
the gallery. Thus, we get the Euclidean distance of
each probe feature against the gallery, as a distance
matrix.
Let us define a probe descriptor P, which is a con-
catenation of n individual features.
P = [p
1
, p
2
, ··· , p
i
, ··· p
n
] ∈ IR
1×n
(4)
The gallery contains a set of similar feature de-
scriptors, which we represent as a matrix G. Each row
of G represents an n-dimensional feature vector cor-
responding to an individual. Likewise, k feature de-
scriptors from multiple subjects are arranged to make
a gallery matrix of dimension k ×n , as follows.
G =
g
1,1
g
1,2
. .. g
1,i
. . . g
1,n
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
g
j,1
g
j,2
. . . g
j,i
. . . g
j,n
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
g
k,1
g
k,2
. . . g
k,i
. . . g
k,n
∈ IR
k×n
(5)
Then, for the Euclidean distance computation, we
calculate the distance of each individual probe feature
element, say, p
i
, (i = 1, ..., n) against its counterpart
feature samples in gallery i.e. g
j,i
, ( j = 1, ..., k), as a
distance vector viz., D(p
i
, g
j,i
).
D(p
i
, g
j,i
) = |p
i
− g
j,i
| ,
∀ i = 1, .., n & j = 1, .., k.
(6)
This results in a distance matrix D∈ IR
k×n
, as
follows in Equation 7. Each element in the matrix D
is given by d
j,i
= D(p
i
, g
j,i
).
Towards View-point Invariant Person Re-identification via Fusion of Anthropometric and Gait Features from Kinect Measurements
113

D =
d
1,1
d
1,2
. . . d
1,i
. . . d
1,n
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
d
j,1
d
j,2
. . . d
j,i
. . . d
j,n
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
d
k,1
d
k,2
. . . d
k,i
. . . d
k,n
∈ IR
k×n
=
h
d
1
d
2
. . . d
i
. . . d
n
i
∈ IR
k×n
(7)
Our idea is to get a single distance score, corre-
sponding to the overall feature set. We accomplish
this via a score level fusion strategy. Since differ-
ent features have different magnitude ranges, the dis-
tance scores also will have its impact. Hence, while
doing the fusion, the score will be biased towards
the higher measured distance, leading to the prob-
lem of heterogeneity of measures. In order to avoid
this, we carry out a min-max normalization strategy,
which normalize each of the feature distance score
within the [0,1] range. More specifically, we nor-
malise each column corresponding to a particular fea-
ture, separately, i.e. considering the distance vector
corresponding to a particular feature as in Equation 7,
d
i
= [d
1,i
, ··· , d
j,i
, ··· , d
k,i
]
T
, the normalized distance
vector z
i
= [z
1,i
, ··· , z
j,i
, ··· , z
k,i
]
T
is computed as fol-
lows:
z
i
=
d
i
− min(d
i
)
max(d
i
) − min(d
i
)
(8)
Afterwards, we generate the fused feature score Z,
by summing the individual normalised distance vec-
tors, z
i
with i = 1, ..., n.
Z =
z
1
+ z
2
+ ·· · + z
i
+ ·· · + z
n
∈ IR
k×1
(9)
Then, we sort the fused score Z in the ascending
order and calculate the final CMC curve based on the
ranked list of matches.
3.5 Evaluation Methodology
In order to evaluate our proposal, we conduct multiple
extensive experiments to verify the impact of each
feature individually and jointly, as well as the influ-
ence of various view-points on the Re-ID paradigm.
Basically, we conduct two major experiments in this
regard. 1) view-point dependent and 2) view-point
independent.
In the view-point dependent Re-ID experiment,
the walking direction is pre-defined. Hence, the
gallery and probe contains the samples from the sub-
jects with the same walking direction. Apparently,
this is a much simpler problem of person recog-
nition
5
. In this view-point dependent experiment,
further detailed analysis is carried out in order to
understand the impact of various features (individual
vs fusion) on the overall Re-ID.
In the view-point independent Re-ID experiment,
the key idea is to corroborate the effect of differ-
ent walking directions in the Re-ID scenario. We
categorize three major view-point invariant scenarios
in this regard -a) Pseudo view-point invariance, b)
Quasi view-point invariance and c) Full view-point
invariance- based on the samples available in the
gallery and probe sets (See Table 2). The Re-ID be-
comes more challenging while moving from pseudo
towards full view-point invariant, due to the limited
availability of samples in the training set as well as
the challenging view angles in the probe set.
Table 2: Chart showing the Re-ID accuracy rates for Exper-
iment 4.2.2.
Index View-point
invariance
Gallery Probe
a Pseudo Multi views Single view
b Quasi Multi views Novel view
c Full Single view Novel view
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
Since a standard gait dataset with different views ac-
quired with kinect sensor was unavailable, we created
a new one consisting of 20 people walking in four dif-
ferent directions i.e. frontal (F), left diagonal (LD),
right diagonal (RD) and lateral (L). We have asked
each person to walk naturally along a hall in four di-
rections, and three times in each direction. Thus, al-
together we have 12 sequences per person in different
directions i.e. a total of 240 sequences in the dataset.
In this work, we conduct multiple experiments,
as explained in Section 3.5. In the first experiment,
we conduct Re-ID in individual directions, and in the
second experiment, we employ view-point invariant
Re-ID. In each of these experiments, we evaluate the
performance of our system via CMC curve analysis.
More specifically, each sequence in the probe is tested
against the training set and the ranked list of Re-ID is
obtained via signature matching. (The rank is com-
puted by person i.e. best of the three sequences.) The
process is repeated for all probe sequences. Then the
5
Recognition is a special case of Re-ID, in which the
operator has much control on the conditions (same camera,
no change in view-point/ illumination/ background etc.)
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
114
average over all probe sequences Re-ID is computed
and represented as CMC result.
4.1 Experiment 1: View-point
Dependent Re-ID
In this experiment, we test Re-ID in individual di-
rections. This is done to verify the performance of
the proposed method along specific directions. Or
in other words, we test how well the system can act
when both the probe and gallery contain the features
extracted in a particular direction. We carry out a
leave-one-out evaluation strategy, in which any of the
gait sequences will be selected as a probe and tested
against the remaining 59 sequences. This is then re-
peated 60 times, with each of the gait sequence used
exactly once as the test data, and the average Re-ID
result is computed.
We exploit both the anthropometric and gait fea-
tures. Regarding the anthropometric features, we se-
lect seven body measurements: height, arm length,
upper torso, lower torso, upper-lower ratio, chest and
hip (see Table 1 for the list of features). An example
for the estimation of ‘height’ feature is shown in Fig.
6, by calculating the mean information within a gait
period.
No of frames
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35
Height of person
1.7
1.71
1.72
1.73
1.74
1.75
1.76
1.77
1.78
1.79
Height estimate
Mean -- 1.74e+00
Std Deviation -- 2.45e-02
Figure 6: Height estimation from the sequence of frames
within a gait cycle.
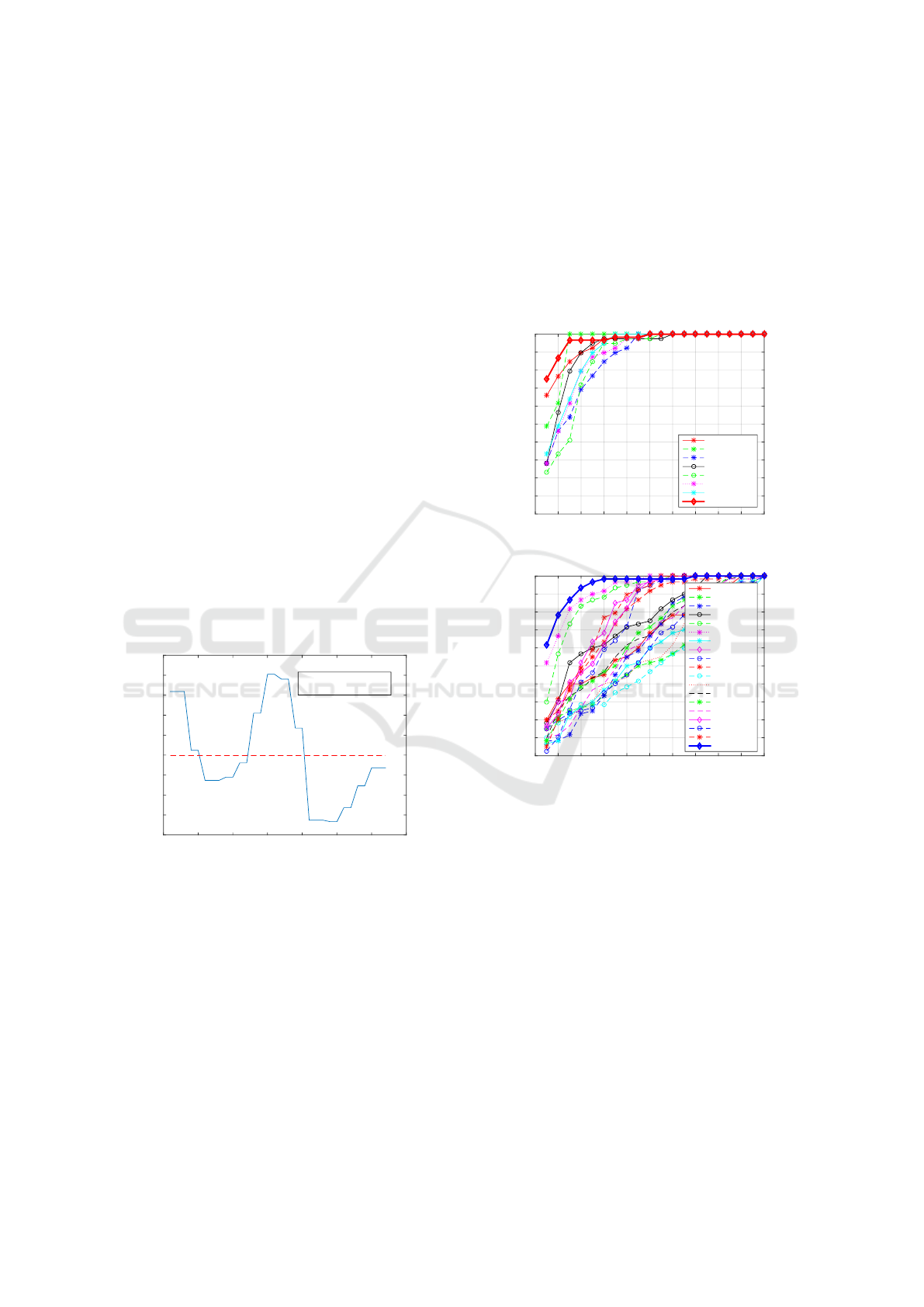
First, we analysed the Re-ID ability of our frame-
work exploiting individual features. An example of
CMC curve produced from each anthropometric fea-
tures in frontal view is shown in Fig. 7(a). Among
them, the most informative features are the height and
arm length information with Rank-1 CMC accuracy
of 65.9% and 48.7% respectively.
Similarly, we also analysed the impact of other in-
dividual gait features separately. Please refer to Fig.
7(b). It includes various body angles, distances and
evolution of certain joints, along the time. The mean
and variance information are extracted to generate
the feature vector. We noticed that, all of those gait
features are less informative and distinguishable in
comparison with the anthropometric features. Refer-
ing to Fig. 7(b), the important gait features are the
elbow distance and hand distance achieving Rank-1
CMC rates 51.67% and 30%, respectively whereas
the least informative features were speed and stride
length which achieved 5.12% and 2.5% accuracy re-
spectively.
Cumulative Rank score
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Re-identification Rate (%)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
height
arm
upper torso
lower torso
Upper-lower ratio
chest
hip
fusion static
(a)
Cumulative Rank score
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Re-identification Rate (%)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
hipAngle
kneeAngle
footDist
kneeDist
handDist
elbowDist
headXPosi
headYPosi
spineXPosi
spineYPosi
hipPosi
kneePosi
anklePosi
handPosi
shouldPosi
stride length
stride duration
speed
fusion dynamic
(b)
Figure 7: Individual feature performance towards Re-ID:
(a) Static anthropometric features and scalar gait features
(stride length, stride time and speed). The bold red curve
with diamond markers corresponds to the fusion CMC re-
sult obtained by exploiting all the anthropometric features.
(b) Dynamic gait features. The result by fusing all the gait
features is shown in bold blue curve with diamond markers.
Next, we conducted fusion of the multiple features
aka multi-modal fusion. Initially, various anthropo-
metric features were fused together which resulted in
the bold red CMC curve in Fig. 7(a), which achieved
75% Re-ID rate at Rank-1. Similarly, the fusion of
gait features were also conducted. The result is shown
with the bold blue CMC curve in Fig. 7 (b), which
achieved 61.67% Rank-1 Re-ID rate. We could ob-
serve that, fusion of body related measurements pro-
duced higher Re-ID performance in comparison with
the fusion of the gait features. It was quite noteworthy
Towards View-point Invariant Person Re-identification via Fusion of Anthropometric and Gait Features from Kinect Measurements
115
Cumulative Rank score
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Re-identification Rate (%)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
anthropometric features
gait features
anthropomeric+ gait features
(a) Frontal
Cumulative Rank score
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Re-identification Rate (%)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
anthropometric features
gait features
anthropomeric+ gait features
(b) Left diagonal
Cumulative Rank score
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Re-identification Rate (%)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
anthropometric features
gait features
anthropomeric+ gait features
(c) Right diagonal
Cumulative Rank score
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Re-identification Rate (%)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
anthropometric features
gait features
anthropomeric+ gait features
(d) Lateral
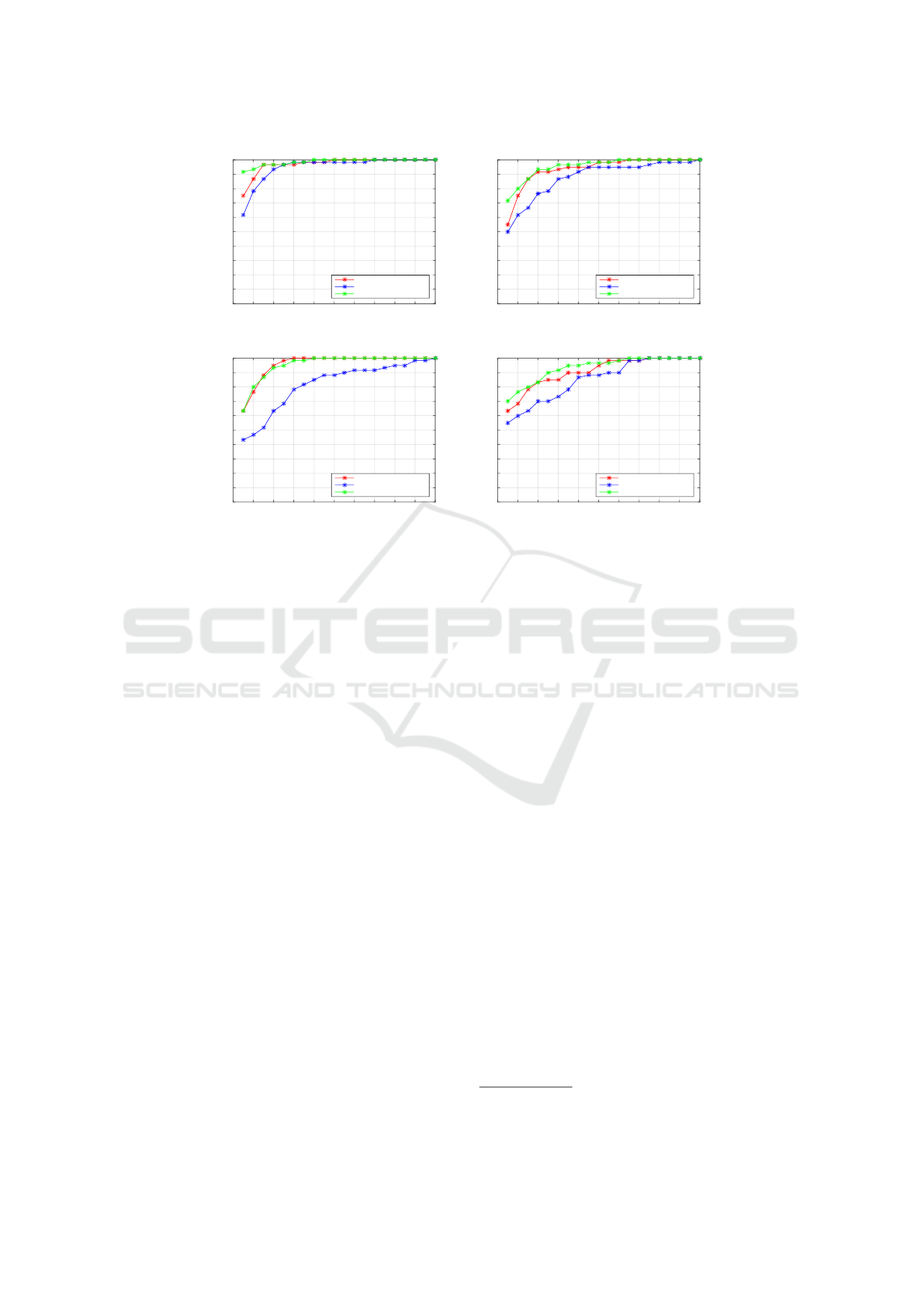
Figure 8: Multimodal fusion of anthropometric features, gait features (using mean-variance) and the fusion of both, in various
directions. (a) Frontal (b) Left diagonal (c) Right diagonal (d) Lateral.
that even by combining 35 gait features, it couldn’t
achieve similar Re-ID accuracy as obtained by the an-
thropometric fusion by seven features. This gives the
intuition that in frontal view, anthropometrics features
are more significant than the gait features in discrim-
inating the population.
After conducting the fusion among the anthropo-
metric features and gait features separately, we further
conducted the multimodal fusion of all the biometric
features (i.e. both anthropometric and gait features),
altogether. The results obtained in these multi-modal
fusion technique in frontal sequence is presented to-
gether in Fig. 8(a). Red and blue curves denote an-
thropometric fusion (75% Rank-1 score) and gait fu-
sion (61.67% Rank-1 score) result respectively. The
combined anthropometric+ gait fusion result is repre-
sented via green curve with a Rank-1 Re-ID accuracy
of 91.67%. We could observe that the na
¨
ıve integra-
tion could improve the overall performance while fus-
ing both anthropometrics and gait features together.
Similar experiments are also conducted in the
other three views as well, i.e. left diagonal, right di-
agonal and lateral. We show the fusion results of all
the three experiments in Fig. 8(b), (c) and (d) with an
overall Rank-1 scores of 71.67%, 63.33% and 70%,
respectively. In all these scenarios also, we could ob-
serve that the anthropometric features outperform the
gait features. Also, while fusing both the anthropo-
metric and gait features together, the overall perfor-
mance improved.
A similar human classification strategy based on
gait features has been reported in (Gianaria et al.,
2014), by employing 20 people. In contrast to our
methodology, they have conducted the experiments
only in a single view (i.e. frontal) as well as an ex-
haustive selection of the set of different features along
with a SVM classification scheme. However, our ex-
periments were explicitly made in different views,
and via naive score-level fusion of multi-modalities.
Hence, an approximate comparative analysis is made
at this point, particularly Fig. 8(a) referring to the
frontal Re-ID experiment. The highest classifica-
tion accuracy observed in their case is 96.25% (19.25
times the chance level
6
) under fine tuned parame-
ter set (elbow distance, knee distance, mean of head,
mean of knee). Nevertheless, our direct approach of
naive fusion also could achieve quite similar result
91.67% (18.34 times the chance level) without the ex-
haustive feature search or the fine tuning of the param-
eter set.
6
Chance level is Re-ID of 1 subject out of 20 subjects,
i.e. 0.05.
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
116

4.2 Experiment 2: View-point
Independent Re-ID
In Section 4.1, we have conducted experiments along
various view angles at ∼0
◦
, ∼30
◦
, ∼60
◦
and ∼90
◦
,
separately. Albeit we could analyse the impact of
various features in each of these directions, we did
not so far experiment how feasible and robust is our
system in order to perform in view-point invariant
scenario i.e. irrespective of any particular direction.
Hence, we conduct a thorough analysis of various
view-point independent Re-ID schemes i.e. pseudo
view-point invariant, quasi view-point invariant and
full view-point invariant.
Cumulative Rank score
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Re-identification Rate (%)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
anthropometric features
gait features
anthropomeric+ gait features
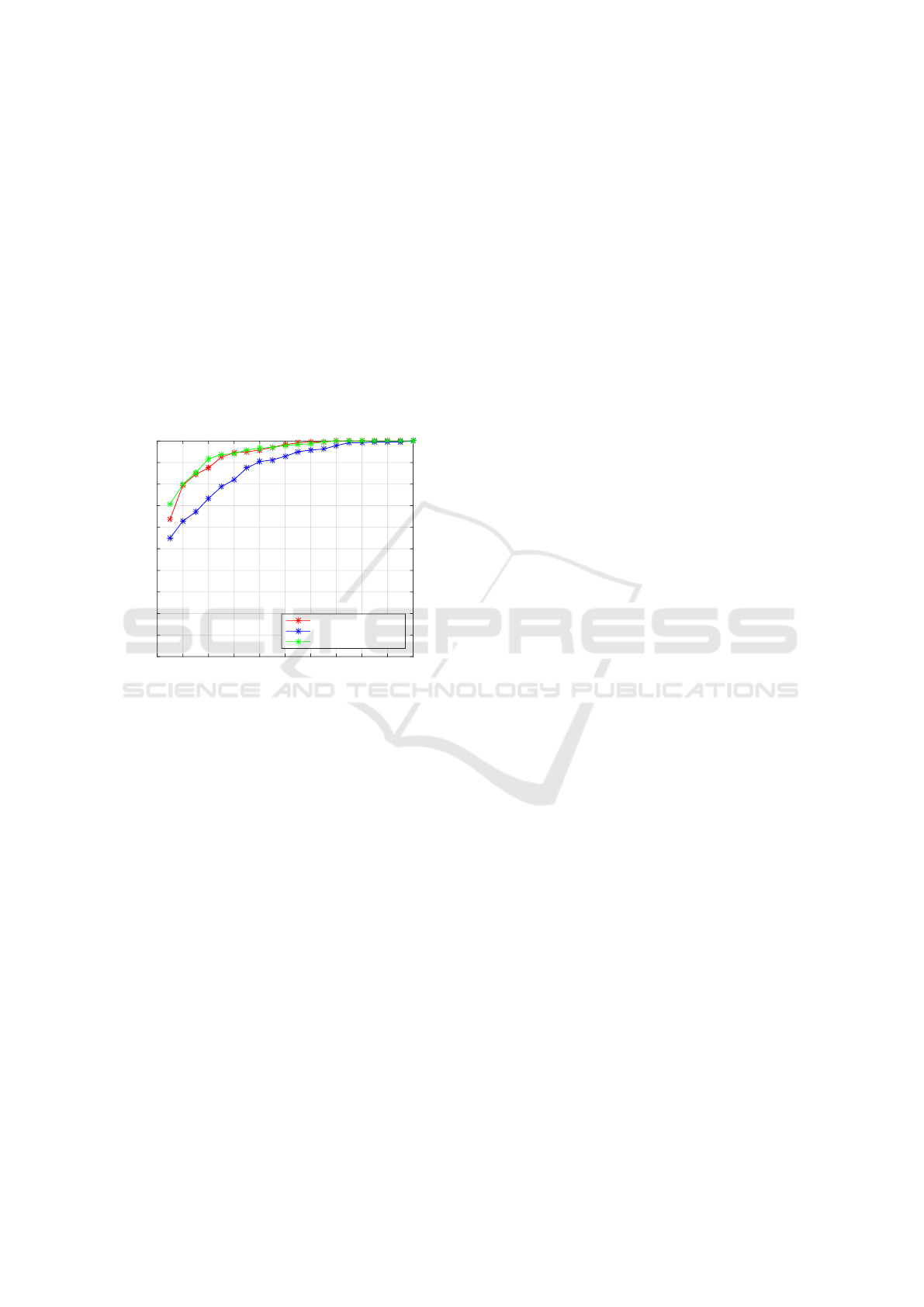
Figure 9: Pseudo view-point invariant Re-ID results using
anthropometrics+ gait.
4.2.1 Pseudo View-point Invariant Re-ID
Experiment
In pseudo view-point invariant case, we consider that
the gallery contains samples from multiple views.
And, the probe will be a new sample taken from any
of these views. This kind of set up requires either a
large number of cameras with different camera views
(in the case of normal surveillance case), or the per-
sons different views acquired in the enrollment phase
(authentication phase). The nomenclature ‘pseudo’ is
attributed to the fact that the probe view is already
encountered among the gallery views and hence its a
pseudo view-point invariant Re-ID.
Since we have used 20 people’s gait in four
different directions, each with three sequences,
altogether we have 240 gait sequences. We conduct
a leave-one-out evaluation strategy, in which any of
these sequences will be selected as a probe and tested
against the remaining 239 sequences in different
views. Altogether 240 runs were conducted and
the averaged result was computed. The achieved
performance of the system is depicted in Fig. 9.
We could observe that, the fusion of anthropomet-
ric features achieved 63.75% (red curve in Fig. 9) and
the fusion of gait features achieved 55% with (blue
curve in Fig. 9) respectively. While combining both
of them, we could obtain improvements in their per-
formance i.e. ∼71% Rank-1 Re-ID rate. This is a
promising result highlighting the performance and ro-
bustness of our system towards handling various di-
rection of gait, which is a big challenge in the Re-
ID task. Our intuition is that the increased number
of samples per person (12 sequences) compared to a
single direction (three sequences) could enhance the
Re-ID rate.
4.2.2 Quasi View-point Invariant Re-ID
Experiment
Here, in the quasi-view-point invariant scenario, the
gallery contains multiview samples of the subjects.
However, the probe sample is taken from a new view
angle which has not been introduced in the training
phase. This is a realistic scenario, where a new cam-
era view is encountered in which the person has to be
re-identified, provided that many other training sam-
ples in different views are available in the gallery.
This is a more challenging case than the pseudo view-
point invariant case, since the probe direction is en-
countered in the system for the first time.
In order to test this case, we keep all the samples
in a particular direction in the test set, whereas all the
other three directions are made available in the train-
ing phase. In particular, we have 180 gait sequences
of 20 people corresponding to three directions be-
ing kept in the training set. The 60 gait sequences
from the fourth walking direction (which was not in-
troduced in the training phase) are used for testing.
Hence, 60 runs per view are carried out and the aver-
age result is estimated. We conduct the experiment for
all the frontal, left diagonal, right diagonal and lateral
views as the test direction.
The Re-ID rates at Rank-1, Rank-5 and Rank-
10 are presented in Table 3. It is observed that the
highest Rank-1 CMC rate for the anthropometric fu-
sion is reported in the frontal view case (41.33%)
and the counterpart for the gait fusion was reported
in lateral view (31.67%). Coherent results were also
observed in the fusion of anthropometric+ gait case
as well, where frontal samples got re-identified with
the highest recognition rate (65%) followed by lat-
eral samples (41.67%) among all the directions, in
the Rank-1 scenario. With Rank-5 and Rank-10 rates
in CMC curves, the Re-ID accuracy improved drasti-
Towards View-point Invariant Person Re-identification via Fusion of Anthropometric and Gait Features from Kinect Measurements
117
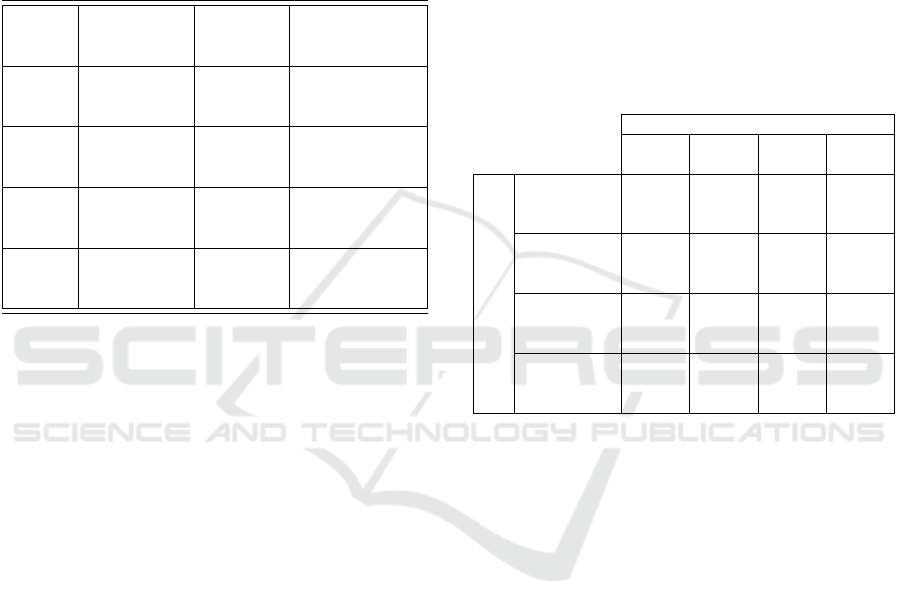
cally >73.33% and >90% respectively, in all the di-
rections. Once again the highest Re-ID rates were re-
ported in frontal case (Rank 5- 86.67% and Rank 10-
98.33%). This means that, given other multiple views
in the gallery set, frontal view probes are the best in
re-identifying people.
Table 3: Chart showing the Re-ID accuracy rates for Exper-
iment 4.2.2. The accuracy rates shown in each cell repre-
sents Rank-1, Rank-5 and Rank-10 CMC rates respectively.
The highest Re-ID rate observed is highlighted in bold let-
ters.
Probe
direction
Anthropometric
based Re-ID
Gait
based
Re-ID
Anthropometric +
gait based Re-ID
Frontal 41.33%
90.00%
98.33%
26.67%
68.33%
96.67%
65.00%
86.67%
98.33%
Left
Diagonal
33.33%
73.33%
91.67%
21.67%
53.33%
88.33%
28.33%
73.33%
90.00%
Right
Diagonal
28.33%
80.00%
93.33%
10.00%
56.67%
90.00%
31.67%
83.33%
93.33%
Lateral 40.00%
68.33%
93.33%
31.67%
70.00%
81.67%
41.67%
75.00%
96.67%
4.2.3 Full View-point Invariant Re-ID
Experiment
Full view-point invariance is the case which has only
one walking direction in the gallery and any new ar-
bitrary walking direction for the probe. In terms of
creating a training set, this is the easiest way because
it requires only one camera and one view of the per-
son to create a gallery. At the same time, it is the
most challenging scenario in terms of Re-ID, since it
requires to get recordings from merely one view and
able to Re-ID in any other arbitrary view.
We conducted 12 various combinations of probe-
gallery set based on the walking direction, in order to
guarantee a truly view-point invariant Re-ID. The ex-
periments and the results achieved are reported in Ta-
ble. 4. In each of the test case (e.g. frontal), we keep
any of the other three view-point data sequences as the
gallery (e.g. left diagonal or right diagonal or lateral).
And the same procedure is repeated for all the four
directions. In all of these experiments, each of the
probe and gallery contains 60 gait sequences from 20
people. Per each combination, 60 runs were carried
out and the average Re-ID resut is estimated. In the
tabular results (see Table. 4), we report only the over-
all anthropometric+ gait multimodal fusion results at
various ranks (Rank-1, 5 and 10) of CMC curves.
It is observed that the highest Re-ID rates (48.33%)
are achieved when frontal sequences are kept in the
gallery. With the diagonal samples the second best
Re-ID results are achieved (∼35%).
Despite most works assume that kinect data is
pose invariant, this is not really the case as demon-
strated in all the experiments of our work. Re-ID rates
are always better in the frontal view that in the other,
due to the quality of the data acquired. We show that
with an adequate use of pre-processing and soft bio-
metrics we can achieve some level of view-point in-
variance, but still not perfect.
Table 4: Chart showing the Re-ID accuracy rates for Exper-
iment 4.2.3. The accuracy rates shown in each cell repre-
sents Rank-1, Rank-5 and Rank-10 CMC rates respectively.
The highest Re-ID rate observed is highlighted in bold let-
ters.
PROBE
Frontal Left
Diagonal
Right
Diagonal
Lateral
Frontal -
-
-
26.67%
78.33%
91.67%
48.33%
88.33%
93.33%
48.33%
73.33%
93.33%
GALLERY
Left Diagonal 33.33%
75.00%
90.00%
-
-
-
30.00%
70.00%
85.00%
35.00%
78.33%
96.67%
RightDiagonal 35.00%
85.00%
95.00%
25.00%
68.33%
83.33%
-
-
-
18.33%
58.33%
85.00%
Lateral 18.33%
78.33%
90.00%
28.33%
78.33%
93.33%
15.00%
68.33%
86.67%
-
-
-
5 CONCLUSIONS & FUTURE
WORK
A view-point invariant Re-ID system exploiting the
skeleton information provided by the kinect sensor
has been proposed. We have used both the static and
dynamic features related to the human posture and
walking, in order to extract features to classify the
people in the population. Extensive study on the im-
pact of various features both individually and jointly,
as well as various view angles have been conducted.
We have acquired the kinect data in-house from 20
people walking in four different directions, and anal-
ysed our proposed methodology.
We could observe that the static anthropometric
features are more informative than gait features, when
employed individually. However, while fusing many
static anthropometric features and dynamic gait fea-
tures, we noticed that the overall recognition accu-
racy increases in both cases. Also, by combining
the whole set of static and dynamic features, the fi-
nal overall Re-ID rate improved further. In addition
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
118

to evaluations in individual directions, we also con-
ducted view-point invariant Re-ID experiments in re-
alistic conditions where people walk in different di-
rections. Three cases studies were conducted in this
regard viz. pseudo, quasi and full view-point in-
variant. It is found that our system is quite robust
and promising with a Rank-1 Re-ID rate of ∼92%
in view-point dependent scenarios and ∼71%, ∼65%
and ∼48% in pseudo, quasi and full view-point in-
dependent scenarios, respectively. Since the direct
comparison with other works are not possible due to
the novelty of the approach, we carry out compara-
tive analysis against the most similar view-point de-
pendent approach (Gianaria et al., 2014) in the front
view, and very similar Re-ID results (19 times and 18
times the chance level, respectively) were reported.
In the future, we envisage to extrapolate this study
by collecting more data in more random directions of
walk. Also, in terms of the feature fusion, we would
like to employ context based fusion or feature selec-
tion strategies (eg: quasi-exhaustive learning strategy
(Barbosa et al., 2012), correlation-based feature sub-
set selection (Andersson and Araujo, 2015)), in order
to fine tune the selection of most informative features
and thus improve the Re-ID accuracy.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the FCT projects
[UID/EEA/50009/2013], AHA CMUP-
ERI/HCI/0046/2013 and FCT doctoral grant
[SFRH/BD/97258/2013].
REFERENCES
Aarai, K. and Andrie, R. (2013). 3d skeleton model de-
rived from kinect depth sensor camera and its appli-
cation to walking style quality evaluations. In Inter-
national Journal of Advanced Research in Artificial
Intelligence 2.
Andersson, V. O. and Araujo, R. M. (2015). Person identifi-
cation using anthropometric and gait data from kinect
sensor. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Con-
ference on Artificial Intelligence.
Ariyanto, G. and Nixon, M. S. (2011). Model-based 3d gait
biometrics. In In International Joint Conference on
Biometrics (IJCB).
Barbosa, I. B., Cristani, M., Alessio, D. B., Bazzani, L.,
and Murino, V. (2012). Re-identification with rgb-d
sensors. In Computer VisionECCV 2012. Workshops
and Demonstrations.
Dantcheva, A., Velardo, C., D’angelo, A., and Dugelay, J.
(2010). Bag of soft biometrics for person identifica-
tion : New trends and challenges. In Mutimedia Tools
and Applications, Springer.
Doretto, G., Sebastian, T., Tu, P., and Rittscher, J. (2011).
Appearance-based person reidentification in camera
networks: Problem overview and current approaches.
In Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized
Computing, 2.
Fernandez, D., Madrid-Cuevas, F., Carmona-Poyato, A.,
Muoz-Salinas, R., and Medina-Carnicer, R. (2016). A
new approach for multi-view gait recognition on un-
constrained paths. In Journal of Visual Communica-
tion and Image Representation 38.
Gabel, M., Gilad-Bachrach, R., Renshaw, E., and Schuste,
A. (2012). Full body gait analysis with kinect. In An-
nual International Conference of the IEEE Engineer-
ing in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC).
Gianaria, E., Grangetto, M., Lucenteforte, M., and
Balossino, N. (2014). Human classification using gait
features. In Biometric Authentication 8897.
Grother, P. and Phillips, P. J. (2004). Models of large pop-
ulation recognition performance. In Proceedings of
the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition.
Iwashita, Y., Baba, R., Ogawara, K., and Kurazume, R.
(2010). Person identification from spatio-temporal 3d
gait. In Proceedings of the International Conference
on Emerging Security Technologies.
Iwashita, Y., Ogawarab, K., and Kurazume, R. (2014). Iden-
tification of people walking along curved trajectories.
In Pattern Recognition Letters 48.
Lee, L. and Grimson, W. (2002). Gait analysis for recog-
nition and classification. In Proc. IEEE International
Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recogni-
tion.
Nixon, M. S., Correia, P. L., Nasrollahi, K., Moeslund,
T. B., Hadidd, A., and Tistarelli, M. (2015). On soft
biometrics. In Pattern Recognition Letters 68.
Riccio, D., Marsico, M., Distasi, R., and Ricciardi, S.
(2014). A comparison of approaches for person re-
identification. In International Conference on Pattern
Recognition Applications and Methods.
Seely, R. D., Samangooei, S., Middleton, L., Carter, J. N.,
and Nixon, M. S. (2008). The university of southamp-
ton multi-biometric tunnel and introducing a novel 3d
gait dataset. In 2nd IEEE International Conference on
Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems BTAS.
Shotton, J., Sharp, T., Kipman, A., Fitzgibbon, A., Finoc-
chio, M., Blake, A., Cook, M., and Moore, R. (2013).
Real-time human pose recognition in parts from sin-
gle depth images. In Communications of the ACM
(CACM), 56(1).
Sivapalan, S., Chen, D., Denman, S., Sridharan, S., and
Fookes, C. (2011). 3d ellipsoid fitting for multiview
gait recognition. In In Proceedings of 8th IEEE Inter-
national Conference on Advanced Video and Signal-
Based Surveillance (AVSS).
Zhao, G., Liu, G., Li, H., and Pietikinen, M. (2006). 3d
gait recognition using multiple cameras. In 7th Inter-
national Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture
Recognition.
Towards View-point Invariant Person Re-identification via Fusion of Anthropometric and Gait Features from Kinect Measurements
119
