
Poke-R
Using Analytics to Reduce Patient Harm
James P. McGlothlin
1
, Evan Crawford
1
, Jesse Wyatt
2
, Carlos Samayoa
2
, Yana Vaks
2
,
Brenda Bruneau
2
, Merrick Lopez
2
, Anthony Moretti
2
, Michele Wilson
2
and James Pappas
2
1
Fusion Consulting Inc, Irving, TX, U.S.A.
2
Loma Linda University Health System, Loma Linda, CA, U.S.A.
Keywords: Data Warehousing, Healthcare Analytics, Quality, Pediatric Intensive Care, Business Intelligence.
Abstract: Major events and surgeries are not the only sources of trauma during a hospital encounter. Many small, less
invasive events such as shots, line placements, blood draws, and imaging studies happen throughout a
patient’s hospital stay. Many of these less traumatic events have the potential to negatively impact patient
outcomes by increasing the risk of hospital-acquired infections through skin invasions and exposure to
organisms, reducing the patient experience by causing pain and frustration, increasing cost and causing other
complications. The goal of this project is to reduce such events when they are not clinically required. This
is an analytics project so this goal is facilitated by making accurate and meaningful information available to
the appropriate personnel. This includes timely information to clinicians so they can alter treatment, and
retrospective trend analysis to enable and track performance improvement and identify opportunities for
additional process improvement.
1 BACKGROUND
This project is based on the Prevent Pain and
Organisms from sKin and catheter Entry (POKE)
project initiated at Dixie Regional Medical Center.
Dixie Regional implemented the POKE initiative
within their Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU)
(Ridout, 2014). The results at Intermountain Health
System show that the POKE project has resulted in
reduced POKEs for NICU patients and significant
financial savings estimated at $3.5 million over 5
years for a single hospital. Reduction in length of stay
was also identified. Figure 1 and Figure 2 quantify
cost reduction associated with the original Dixie
Regional Medical Center project.
We are calling our project POKE-R because we
are including Radiology events. Radiology images
can cause serious complications later in life for
pediatric patients due to the much higher sensitivity
children have to radiation, and also reduce
patient/parent experience (Medscape, 2014) (Slovis,
2002) (Brenner, 2002). We are leveraging this prior
research and enhancing it. We are considering
anything a POKE which invades the skin or opens a
line or drain into the patient. This includes
medication administrations, blood draws, placement
of lines, drains and airways (LDAs), surgeries, and
other invasive procedures.
The goal of our project is to reduce POKE-R
events by providing detailed information to the
clinicians. Often lab draws or procedures are not
medically necessary and may cause more harm than
good (Salisbury et al, 2011). Also, many times lab
tests can be combined to use a single specimen
collection. A patient sees many providers throughout
a hospital stay and there may be redundant orders or
orders which are no longer medically warranted.
Figure 1: Hospital savings experienced by Dixie Regional
Medical Center POKE initiative.
362
McGlothlin J., Crawford E., Wyatt J., Samayoa C., Vaks Y., Bruneau B., Lopez M., Moretti A., Wilson M. and Pappas J.
Poke-R - Using Analytics to Reduce Patient.
DOI: 10.5220/0006174603620369
In Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2017), pages 362-369
ISBN: 978-989-758-213-4
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
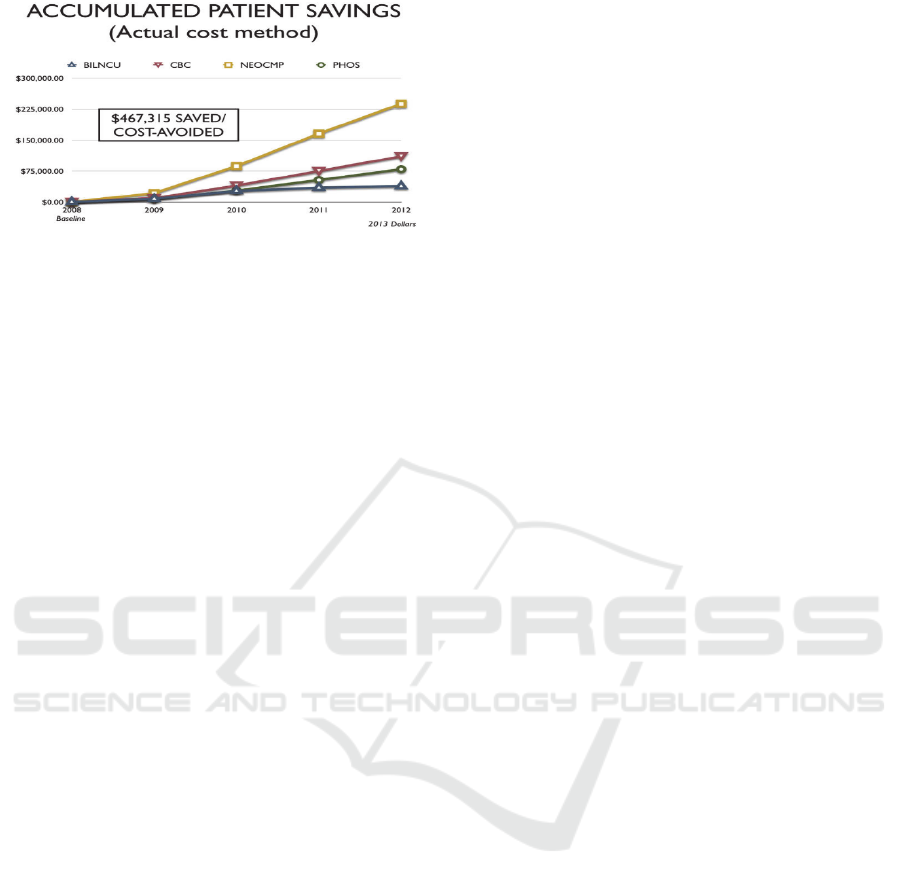
Figure 2: Patient savings experienced by Dixie Regional
Medical Center POKE initiative.
By reducing POKEs we hope to achieve each of
the following potential improvements:
Reducing hospital-acquired infections
Every time a patient’s skin is punctured, line is
opened, or catheter is placed, there is an increased risk
of a hospital-acquired infection. For example, there
is significant evidence that risk of Central Line
Associated Blood Stream Infections (CLABSI) is
increased by repeated blood lab draws (Foster and
Sabella, 2011) (Grissinger, 2011) (Sengupta et al,
2010).
Improving the patient experience and the
satisfaction of the patient and his/her family
The pain caused by invasive procedures, shots,
and placement of lines, drains and airways has a clear
effect on the patient experience and satisfactions.
Reducing anemia, blood loss and blood
transfusions
Each time blood is removed from a patient to
perform a lab test, there is an increased risk of side
effect or even the need for a blood transfusion. This
is particularly prevalent with neo-natal patients and
young pediatric patients and also with acute
myocardial infarction (AMI) patients (Bateman et al,
2008) (Salisbury et al, 2011) (McVoy and Shandler,
2013)
Reducing complications from radiology
Radiology imaging have been connected to
complications for pediatric patients including cancer.
Children have a greater sensitivity (10 times more
than a middle aged adult) to radiation dose and
computed radiography. Furthermore, the necessary
movement required for a radiological exam can
increase risks of further injury or disrupt lines, drains
and airways (Foster and Sabella, 2011) (Brenner,
2002). Finally, the physical methodology of many
imaging procedures, such as MRIs, can cause
psychological trauma and reduce the quality of the
patient experience.
Reducing length of stay
Reducing POKEs has been shown to reduce the
median length of stay for neonatal patients.
Furthermore, POKEs increase the risk of infection,
and hospital-acquired infections dramatically
increase average length of stay for patients (Alharfi et
al., 2014) (Foster and Sabella, 2011).
Reducing cost
All procedures performed incur costs so the
simple act of reducing the number of procedures
directly reduces costs. Costs are also indirectly
reduced through reduction in hospital-acquired
infections and reduced length of stay.
The principle behind our approach is value-based
medicine. The concept is to focus practice on patient
and financial value of the medical interventions. The
goal is to incorporate the highest level of evidence
based interventions while ensuring adequate patient
care and minimizing healthcare costs (Bae, 2015).
2 TECHNICAL
IMPLEMENTATION
At Loma Linda, we have an enterprise data
warehouse sourced from the clinical data in the Epic
Electronic Medical Record (EMR) System. We
implemented the POKE-R process by using the
information in this data warehouse to build a new
POKE-R fact table using standard industry
dimensional modelling data warehouse practices.
The foundation for the data warehouse is provided
by the EMR vendor, but we have extended it to
include more detailed information useful for this
project including
a) Lines, drains and airways
Needed to determine when a LDA was placed and
when it was removed.
b) Procedure performance details
Needed to know if a procedure or image was
actually performed, by who and when
c) Medication Administration Route
Needed to know how a medication was
administered
Additionally, we had to add two extensions
specifically for this project. We added an extension
and modified EMR workflow specifically for LDAs
to know how many attempts the LDA placement took.
Furthermore, physician-performed LDAs such as
central lines were documented in a different manner
so we created a special extract to get the placement
times and attempts. Finally, it was not enough to
know when a specimen was taken. We needed to
know which procedure orders shared blood draws and
Poke-R - Using Analytics to Reduce Patient
363

which required separate blood draws. If 5 lab draws
show the same collection time, it is important to know
whether they were separately drawn, or all of the tests
used the same blood collection.
With these extensions, all of the data needed to
mine the POKE-R information was available in the
data warehouse. However, before we could search
for the POKE-R events, we had to configure which
events were defined as POKEs. We did not want to
hard-code this information and we did not want the
information determined or maintained by IT
personnel as it is clinical in nature. Therefore, we
established an interface to configure POKE-R.
We needed to define every event which was a
POKE-R event and whether it was painful. This
needs to be configured using attributes of the data
elements. The following attributes were identified by
the clinician as identifying POKEs:
1. Medication Administration: Route and
Administration Event
2. Lab Test: Specimen Type and Specimen
Source
3. Procedure Order: Type and Code
Additionally, the presence of a line or drain prior
to the event can impact whether the event is a POKE
and whether it is painful. For example, blood tests
and medication administrations are considered non-
painful if they use an existing line. A urine sample is
not a POKE at all unless there is a catheter used to
obtain the specimen.
Finally, if the patient is under anesthesia at the
time of the event, it is considered non-painful.
We created a simple secure interface for the
Patient Safety and Reliability leadership to provide
and administer this clinical information. This
interface contains the data points listed above
prepopulated from the actual clinical data warehouse.
The user can then choose which values for each data
point indicate a POKE and can combine data points.
We developed software code using Microsoft
SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) to read the
POKE-R configuration file and then extract POKE-R
events from the data warehouse into a new table
within the data warehouse called PokeFact. This fact
table contains the following information:
1. Encounter ID: The encounter the POKE
happened during
2. POKE type: LDA Placement, LDA
Placement Extra Attempts, Medication
Administration, Image, Specimen Collection, Point
of Care Test (POCT), Invasive Procedure, Surgery
3. Whether the POKE has already happened
or is scheduled to happen in the future
4. When the POKE was ordered
5. The provider who ordered the POKE
6. When the POKE was scheduled to occur
7. When the POKE occurred
8. Whether the POKE is painful
9. Who performed the POKE
One thing that was very important was to
determine the scheduled POKE-R events. Our goal
was to show the clinician the upcoming POKE-R
schedule so that treatment could be altered to reduce
the POKEs. To do this we brought in every scheduled
medication administration, procedure, surgery, image
or lab test.
3 INFORMATION
PRESENTATION
At this point, we had aggregated all of the information
necessary to analyze POKE-R. The next step was to
make this information useful to a clinician.
We developed three reports. The first report was
a detailed report of patients currently in the hospital.
This report lists for each patient the total number of
pokes and painful pokes, the number of pokes and
painful pokes in the last 7 days and the number of
scheduled pokes for the next 3 days in graphical
format. This poke counts are then shown grouped by
the type of poke. Finally, every POKE performed in
the last 7 days and every POKE scheduled for the next
3 days was individually listed with details. This
reported was filtered by department so that an
individual department could see each patient in the
department. Scheduled POKEs are not always ever
performed or cancelled. They can be left in pending
status. So we dropped any scheduled POKE in the
past which was never performed. The second report
was the abridged version of the first report, showing
only the number of POKEs over the past 7 days and
what POKEs were scheduled for today. This made it
more simpler for clinicians to digest the POKE-R
information and make actionable decisions. Figure 3
shows an example of this report.
The third report was a trend of POKEs per Patient
per Day over time so we could see if performance
improvement was being achieved. This report was
able to be filtered by location, unit, or attending
provider. Figure 4 shows an example of this
retrospective report.
Together, these reports enable process
improvement and improved treatment. The provider
and treatment team are supported by the detailed
report, while the analysts in Patient Safety and
Reliability have the aggregate and retrospective
information to identify improvement opportunities.
HEALTHINF 2017 - 10th International Conference on Health Informatics
364

Figure 3: Example of abridged Patient POKE-R report.
Figure 4: Example of POKE-R trend report.
Poke-R - Using Analytics to Reduce Patient
365

4 PROCESS IMPLEMENTATION
To pilot the program, we chose a single department,
the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU). We chose
this department specifically because of the increased
risk of complications in critical care pediatric patients
including anemia and infection (Bateman et al, 2008)
(Ridout, 2014) (Sengupta et al, 2010). The abridged
report was scheduled to be automatically printed in
the PICU at 5 am every morning so clinicians could
(r to most POKEs being performed for the day. A
resident fellow and a clinical nurse specialist were
assigned specifically to manage the implementation
of the program and received the daily detailed report.
This allowed them to examine the most critical
patients and suggest opportunities for POKE-R
reduction.
At Loma Linda, the PICU uses structured
interdisciplinary bedside rounds (SIBR). Under the
SIBR methodology, all members of a patient’s care
team visit and communicate with the patient as a unit.
Figure 5 shows the SIBR methodology. Because the
SIBR methodology includes careful review of lab
work, it provides a perfect opportunity to address
potential POKEs. We have adjusted the SIBR
methodology to include POKE-R.
The methodology includes:
1. Discuss and justify each care intervention.
2. Choose interventions that are:
Supported by evidence (consider pre-test
probability)
Lead to change in treatment plan
Lowest cost
3. Considers cost in terms of financial burden and
patient experience
Deliver best possible care, at the lowest
cost to the healthcare system and the
patient.
Reduction in patient harm, exposure,
and pain are all considered.
4. Minimize ordering labs, instead perform a risk
vs. benefit analysis for each test
Please see Figure 6 for an illustration of the SIBR
POKE-R approach.
Additionally, three sets of patients were targeted
as providing significant opportunity and actively
managed using the daily report. These were patients
with traumatic brain injury (TBI), patients with
asthma and patients with external ventricular drain
(EVD) placements. These patients are especially
susceptible to infections and complications (
Alharfi et
al, 2008)
. Furthermore, asthma patients often
experience an excessive number of lab tests in order
to monitor the effects of medication on patient
potassium levels (Schuh et al, 1989). Traumatic brain
injury patients often experience sodium instability
which requires monitoring (Atchinson et al, 1993).
Therefore, these patients are likely to have a
substantial number of POKE-R events and are
particularly vulnerable to harm from these events.
Figure 5: Structured interdisciplinary bedside rounds roles and process.
HEALTHINF 2017 - 10th International Conference on Health Informatics
366

Figure 6: Order menu customized for POKE-R awareness.
5 RESULTS
Our project is in production in the PICU at Loma
Linda University Children’s Hospital. To analyze the
success of the project, we compared patients prior to
the introduction of both POKE-R and SIBR to
patients after these programs were instituted. In all,
we analysed 3,338 pediatric ICU patients.
We have seen a reduction in POKE-R events by
8.7%. Specifically, this was a decrease of 1.8 POKE-
R events per patient per week. We compared this
patient cohort with a historical control set using
standard t-test methodology. This result was
statistically significant with p <0.012. Statistical
significance for our purpose is defined as p<0.05.
Furthermore, we saw significant reductions based
on event type. Medication administrations were
reduced by 1.2 administrations per patient per week.
Specimen collections were reduced by 0.3 pokes.
Radiology procedures and point of care tests were
also reduced. We saw an increase in line pokes, but
this was expected because inserting a line actually
reduces the pokes for medication administrations and
lab draws and therefore is not discouraged by the
program. Finally, we saw a reduction in surgeries but
we do not think this change was influenced by our
POKE-R program.
To determine the statistical significance of the
data we utilized t-tests and chi-square goodness of fit
All of our results met the criteria for statistical
significance except for painful poke counts and point-
of-care testing. Table 1 shows the means, deltas and
statistical significance from our analysis. The two
rows marked in red are not considered statistically
tests and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
Poke-R - Using Analytics to Reduce Patient
367
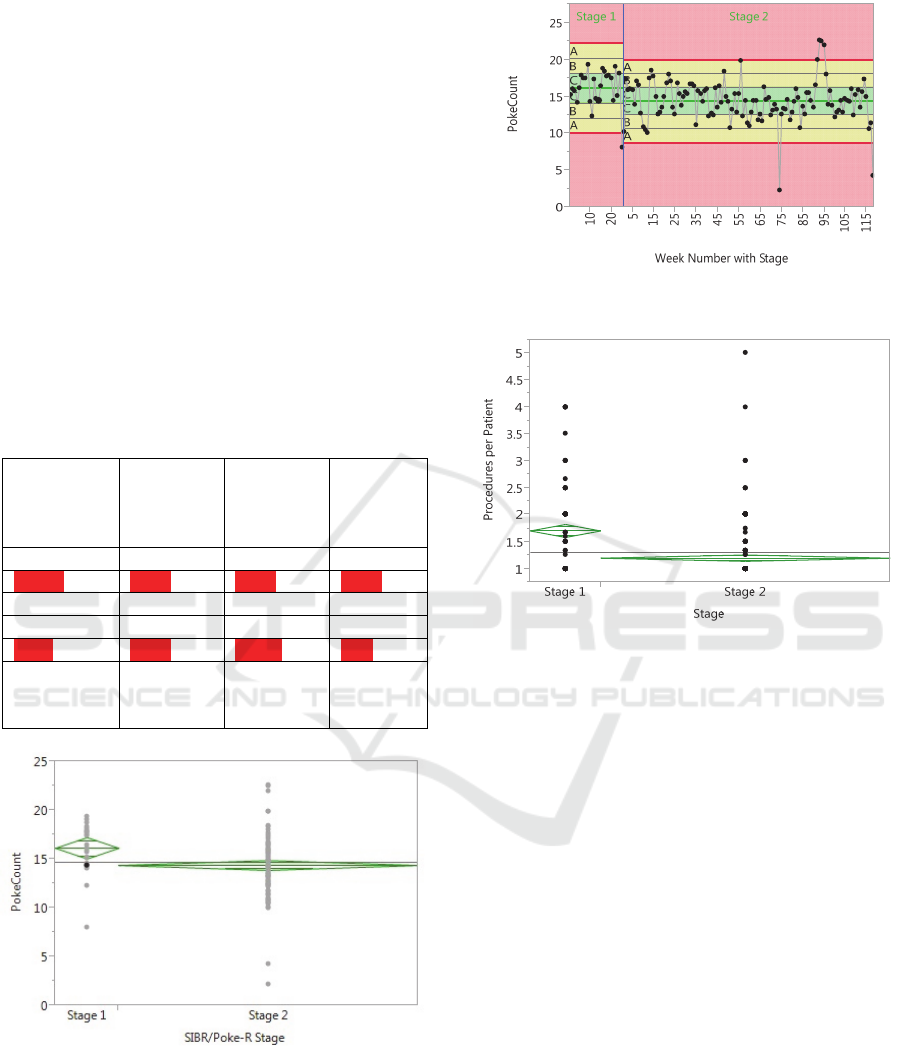
significant due to p>0.05. Figure 7 shows the the one-
way analysis of variance (ANOVA) graph for all
pokes, where stage 1 is prior to implementing our
program and stage 2 is after program implantation.
The graph has green diamonds on it which describe
the 95% confidence intervals of the mean within the
upper and lower peaks of the diamond. The line
across the middle is the mean, and the width of the
diamond is proportional to the sample size. Figure 8
shows the control chart for all pokes.
We also analyzed specifically the asthma patients
and found a decrease in metabolic panels by 30% with
p<0.0001. For patients with hypo/hypernatremia, the
metabolic panel reduction was 16%. These results
demonstrate drops in Basic Metabolic Panels
performed during the post-implementation period.
Figure 9 shows the ANOVA graph for asthma and
cerebral salt wasting patients.
Table 1: Statistics for poke analysis.
Statistical
Variable
Mean
Pokes
/patient
week
ΔControl
Set
p(Prob>
|t|)
Allpokes 14.372‐1.76 0.003
Painful 2.638 +0.10 0.472
MAR 10.57‐1.19 0.007
Specimen 2.220‐0.306 .003
POCT 0.811 ‐0.190 .157
BMP
(Asthmaand
CSW)
1.741‐0.357 .000
Figure 7: ANOVA graph for all pokes.
Figure 8: Control chart for all pokes.
Figure 9: ANOVA graph for BMP for asthma and cerebral
salt wasting patients.
6 FUTURE WORK
We would like to do more data analysis and research
to quantify the benefits of the program including:
Reduction in hospital-acquired infections
such as Central Line-associated
Bloodstream Infection (CLABSI)
Reduction in cost
Improved patient satisfaction
Additionally, patient satisfaction and cost
information are not currently in our data warehouse.
So, additional future work is to bring in these data
points. This will not only allow us to more accurately
monitor performance improvement, it will also enable
greater cost transparency to the provider, patient and
guarantor. We plan to integrate patient (and parent)
experience survey data to quantify improved
customer satisfaction and the cost benefits of our
results to the hospital, the guarantor and the payor.
Currently, the POKE-R evaluation process is
facilitated through printed and emailed reports even
though the data is in the Enterprise Data Warehouse.
HEALTHINF 2017 - 10th International Conference on Health Informatics
368

This is to eliminate the provider from having to access
multiple systems. We plan to have the POKE-R
details for a patient be directly linked to the patient’s
electronic health record. This way they can simply
view the needed POKE-R information when they are
already reviewing the patient’s chart.
Currently, we have the number of laboratory tests
but not the volume of specimen taken for the tests.
Another enhancement we want to make is to interface
with our laboratory system to get the precise volume
of blood collected. This will give us more accuracy
in measuring POKEs and associated risk for anemia.
We are also planning to roll out our POKE-R
analytics and process to more departments throughout
the hospital in the coming year.
7 CONCLUSION
We have implemented a comprehensive and
configurable analytics solution to give providers the
information they need to address excessive POKE-R
events in patients. While our project has only gone
into production in one hospital unit, we are already
seeing considerable evidence of improvement. This
project has the opportunity to reduce cost, improve
patient outcomes and increase customer satisfaction.
REFERENCES
Alharfi, I., Stewart T., Helali, I., Daoud, H., Fraser, D,
2014. Infection rates, fevers and associated factors in
pediatric severe traumatic brain injury. In Journal of
Neurotrauma.
Bateman, J., Lacroix, Boven, K., Forbes, P., Barton, et al,
2008. Anemia, Blood Loss, and Blood Transfusions in
North American Children in the Intensive Care Unit".
In American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care
Medicine.
Salisbury, A.C., Reid, K.J., Alexander, K.P., Masoudi,
F.A., Lai, S.M., Chan, P.S., Bach, R.G., Wang, T.Y.,
Spertus, J.A. and Kosiborod, M., 2011. Diagnostic
blood loss from phlebotomy and hospital-acquired
anemia during acute myocardial infarction. Archives of
internal medicine, 171(18), pp.1646-1653.
Foster, C.B. and Sabella, C., 2011. Health care–associated
infections in children. JAMA, 305(14), pp.1480-1481.
CT Radiation in Kids: How Much of a Risk,
Really? Medscape. 2014.
Grissinger, M., 2011. Capping intravenous tubing and
disinfecting intravenous ports reduce risks of infection.
In Pharmacy and Therapeutics.
McVoy, M., Shandler, A, 2013. Anemia, Bleeding, and
Blood Transfusion in the Intensive Care Unit: Causes,
Risks, Costs, and New Strategies. In Am J Crit Care.
Ridout R., 2014. Prevent Pain and Organisms from sKin
and catheter Entry (POKE): Getting to the Why of Care
[Internet]. Harvard Business School Open Forum:
Dixie Regional Medical Center. Available from:
https://openforum.hbs.org/challenge/hbs-hms-health-
acceleration-challenge/innovations/prevent-pain-and-
organisms-from-skin-and-catheter-entry-poke-getting-
to-the-why-of-care.
Slovis, T., 2002. CT and Computed Radiography: The
Pictures Are Great, But Is the Radiation Dose Greater
Than Required?. In American Journal of
Roentgenology.
Brenner D., 2002. Estimating cancer risks from pediatric
CT: going from the qualitative to the quantitative. In
Pediatric Radiology.
Axt-Adam, P., van der Wouden, P., van der Does, E.,
1993. Influencing Behavior of Physicians Ordering
Laboratory Tests: A Literature Study. In Medical Care.
Sengupta, A., Lehmann, C., Diener-West, M., Perl, T.,
Milstone, A., 2010. Catheter Duration and Risk of
CLA-BSI in Neonates With PICCs. In Pediatrics.
Kelly, M., Conway, M., Wirth, K., Potter-Bynoe, G.,
Billett, A.L. and Sandora, T.J., 2011. Moving CLABSI
prevention beyond the intensive care unit: risk factors
in pediatric oncology patients. In Infection Control &
Hospital Epidemiology, 32(11), pp.1079-1085.
Sherwood, G., Adams-McNeill,
,
J., Starck, P., Nieto, B.,
Thompson, C.. 2000. Qualitative assessment of
hospitalized patients' satisfaction with pain
management. Research in Nursing Health.
Stein, J., Murphy, D., Payne, C., Clark, D., Bronstein, W.,
Tong, D., Castle, B., Shapiro, S, 2013. A Remedy for
Fragmented Hospital Care. In Harvard Business
Review.
Atchison, J., Wachendorfb, J., Haddockb, D., Mysiwb, S.,
Gribbleb, M., & Corriganb, J. 1993. Hyponatremia-
associated cognitive impairment in traumatic brain
injury. Brain Injury.
Algaze, C. et al., 2016. Use of a Checklist and Clinical
Decision Support Tool Reduces Laboratory Use and
Improves Cost. In Pediatrics.
Bae, J.. 2015. Value-based medicine: concepts and
application. In Epidemiology and Health..
Cooke, M., 2010, Cost Consciousness in Patient Care -
What Is Medical Education's Responsibility?. In New
England Journal of Medicine.
Porter, M., 2010. What Is Value in Health Care?. In New
England Journal of Medicine.
Weinberger, S., 2011. Providing High-Value, Cost-
Conscious Care: A Critical Seventh General
Competency for Physicians. In Annals of Internal
Medicine.
Schuh, S., Parkin, P., et al., 1989, High-Versus Low-Dose,
Frequently Administered, Nebulized Albuterol in
Children With Severe, Acute Asthma. In Pediatrics.
Brenner, D.J., 2010. Should we be concerned about the
rapid increase in CT usage?. Reviews on environmental
health, 25(1), pp.63-68.
Poke-R - Using Analytics to Reduce Patient
369
