
A Dynamic and Collaborative Truck Appointment Management
System in Container Terminals
Ahmed Azab
1
, Ahmed Karam
2
and Amr Eltawil
1
1
Department of Industrial Engineering and Systems Management, Egypt-Japan University of Science and Technology,
POBox 179, New Borg Elrab city, 21934 Alexandria, Egypt
2
Mechanical Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering at Shoubra, Benha University, Cairo, Egypt
Keywords: Container Terminal, Integrated Simulation Optimization, Dynamic Model, Collaboration, Truck Appointment
System.
Abstract: Given the rising growth in containerized trade, Container Terminals (CTs) are facing truck congestion at the
gate and yard. Truck congestion problems not only result in long queues of trucks at the terminal gates and
yards but also leads to long turn times of trucks and environmentally harmful emissions. As a result, many
terminals are seeking to set strategies and develop new approaches to reduce the congestions in various
terminal areas. In this paper, we tackle the truck congestion problem with a new dynamic and collaborative
truck appointment system. The collaboration
provides shared decision making among the trucking companies
and the CT management, while the dynamic features of the proposed system enable both stakeholders to cope
with the dynamic nature of the truck scheduling problem. The new Dynamic Collaboration Truck
Appointment System (DCTAS) is developed using an integrated simulation-optimization approach. The
proposed approach integrates an MIP model with a discrete event simulation model. Results show that the
proposed DCTAS could reduce the terminal congestions and flatten the workload peaks in the terminal.
1 INTRODUCTION
In maritime logistics, one of the most important
performance measures is the delivery time of a
container to a customer. The containerized cargos are
transported through the global supply chain, and each
chain consumes a part of the total delivery time. Due
to that, the decision makers in each phase of the
transhipment operations are trying to reduce the total
transshipment time taking into consideration the
financial, economic, environmental, and even
political barriers.
Container terminals are essential nodes in the
global supply chain due to the tremendous growth of
the containerized cargo trade around the world (figure
1). As a result, the research interests are directed to
tackle the CTs’ problems and develop robust and
reliable solutions for the terminal operators. Figure 2
illustrates the various areas in CTs. Most of CTs can
be divided into three main areas: Seaside, yard area,
and landside. The seaside is the area where the vessels
are berthed, loaded and/or unloaded with the desired
containers using quay cranes. Containers are
transported by internal transport means like manned
trucks or automated guided vehicles to be temporarily
stored in the yard blocks. At the yard, handling
operations are performed using the yard equipment
like yard cranes and straddle carriers. The operations
in each yard block depend on vessel’s operations and
hinterland operations. On the other side of the
terminal, the landside comprises the gates, which are
provided with X-Ray scanners where an import
container is allowed to leave the terminal, and an
export container is allowed to enter the yard area.
CT problems were classified by (Bierwirth and
Meisel 2010) to operational problems and strategic
problems. The operational problems are related to the
scheduling of operations and assignment of the
resources. Operational problems are solved
simultaneously in the short term and solutions and
schedules are updated daily. Examples include berth
allocation and quay crane assignment (Karam and
Eltawil 2015; Karam and Eltawil 2016), and
container handling problems (Mohamed Gheitha et
al. 2014; Gheith et al. 2016). In this paper, more
discussion about landside problems will be
introduced mainly for managing the external trucks
arrival.
Azab A., Karam A. and Eltawil A.
A Dynamic and Collaborative Truck Appointment Management System in Container Terminals.
DOI: 10.5220/0006188100850095
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES 2017), pages 85-95
ISBN: 978-989-758-218-9
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
85

Figure 1: Global containerized trade, 1996–2015 (million
TEUs and percentage annual change). (Source: UNCTAD
secretariat).
Export/import containers are delivered/picked up
from the terminal by external trucks. These trucks are
operated by trucking companies to perform the
delivery/pick-up operations in minimal time and cost.
On the other hand, CTs set the appropriate schedules
and rules to reduce the congestion in various terminal
areas. To manage the transaction between the
terminal and the trucking companies, some CTs
adopted a Truck Appointment System (TAS) to
control the arrival of external trucks, while some
other terminals do not follow an appointment system.
The appointment systems can be used to increase the
service quality in CTs for all transshipment means;
trucks, train, barges and vessels (Zehendner and
Feillet 2014). Many terminals have developed Truck
Appointment Systems (TAS) to make balance in
truck arrivals to alleviate the terminal rush hours. The
benefits of the TAS have been reported in literature
as will be shown later. In this paper, we propose a
dynamic and collaborative appointment management
solution to support decision makers in the terminals
gain more benefits from applying the appointment
systems.
Figure 2: Operation areas of a seaport container terminal
and flow of transports (Steenken et al. 2005).
The remaining of the paper is organized as
follows. Section 2 discusses related literature. The
proposed system is explained in section 3. Section 4
presents the numerical experiment. Section 5 shows
the results, and section 6 illustrates the conclusion.
2 PREVIOUS WORK
Landside operations affect the whole terminal
performance and therefore, decision problems related
to landside operations received an increasing interest
in literature. Scheduling the arrival of external trucks
is considered one of the most important landside
problems addressed in the literature. One of the
earliest case studies is conducted by Murty et al.
(2005) at HongKong International Terminal (HIT) ,
which resulted in the reduction of terminal congestion
using the truck appointment system. Authors
developed a decision support system based on an
information system to help in making the terminal
operational decisions efficiently. A comprehensive
study by Morais and Lord (2006) is developed to
review the appointment system implemented in
terminals across North America. They adopted
various strategies to reduce the idling of truck,
congestion at gates and emissions related to CT
drayage operations. Namboothiri and Erera, (2008)
used a planning strategy for pickup and delivery
operations in CTs based on an integer programming
heuristic. The sequence of the drayage operations is
determined by minimizing the transportation cost. An
improvement in productivity and capacity utilization
is obtained with some sensitivity to poor selection of
the appointment time.
Huynh and Walton (2008) and Huynh (2009)
investigated limiting the arrivals and individual
appointments versus the block appointments. In
addition, they introduced combined mathematical
model and DES model. Guan and Liu (2009) stated
that the TAS is one of the most viable strategies to
avoid the terminal congestion and improve the system
efficiency. To achieve that, authors formulated a
nonlinear optimization model and applied a multi-
server queuing model. Chen and Yang (2010) studied
the export container’s drayage operations in Chinese
CT. They proposed an integer programming model in
order to reduce the transportation cost through time
window management. They indicated that the peak
arrivals are smoothed by solving the problem using a
genetic algorithm (GA). Zhao and Goodchild (2010)
studied the impact of using the arrival information of
external trucks on the yard operations. They
concluded that prior knowledge about the arrival time
ICORES 2017 - 6th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
86

of external trucks reduces the queue lengths at gates
and re-handling frequency at the yard. Chen et al.
(2011) introduced a stationary time-dependent
queueing model providing a supporting tool to
improve demand management at CTs.
Simulation was used in many studies for
developing and testing truck appointment systems.
Sharif et al., (2011) developed an agent-based
simulation model to achieve a steady arrival of
external trucks at container terminals. The results
showed that the congestion at CTs can be minimized
by using gate congestion information and estimating
the truck idling times. Karafa (2012) conducted a case
study using a dynamic traffic simulation model to
investigate the congestions and related emissions.
They concluded that extending the gate working
hours increases the terminal productivity and reduces
the emissions especially at peak hours. Based on a
previous work, Van Asperen et al., (2013) used a DES
model to investigate the effect of truck announcement
system on the yard operations performance, and a
significant reduction in yard crane moves is obtained
using the proposed algorithms.
Zhang et al., (2013) developed an optimization
approach for truck appointments to reduce the heavy
truck congestions in CTs. A method based on Genetic
Algorithms (GA) and Point Wise Stationary Fluid
Flow Approximation (PSFFA) was designed to solve
the problem that resulted in reducing truck turn times.
In a series of papers, Chen, Govindan, Yang, et al.
(2013), Chen, Govindan and Yang (2013) and Chen,
Govindan and Golias (2013) studied various
strategies and approaches to optimize the
appointments of external trucks in the terminal.
Various performance measures and objective are
examined such as transportation cost, fuel
consumption, shifted arrivals, and truck waiting
times. A new concept of chassis exchange introduced
by Dekker et al., (2013) to reduce the CT congestion
using simulation as a calculation tool. Zhao and
Goodchild (2013) used a hybrid approach of
simulation and queuing models to examine the impact
of the TAS on the performance of yard crane
operations. The results showed a significant
improvement in system performance and efficiency.
Zehendner and Feillet (2014) formulated a mixed
integer programming model to get the optimum
number of appointments considering the CT
workload. Results are validated using DES to ensure
the improvements of service quality for both the
trucks and also for all terminal resources.
Azab and Eltawil (2016) studied the effect various
arrival patterns of external trucks on truck turn times
in CTs through a simulation-based study. Their
results show that arrival patterns have a significant
effect on the terminal performance in such a way that
makes it important to consider the arrival pattern
effects during the design of the truck appointment
system. Li et al., (2016) proposed some response
strategies that help in solving the problem of truck
arrivals’ deviation from its appointments. Results
showed that the greenness of operations is
significantly affected by the use of truck
appointments. Chen and Jiang (2016) introduced
some strategies to manage the truck arrivals within
the time windows based on truck-vessel service
relationship to reduce the terminal congestion.
To sum up, an increasing attention is paid to the
TAS in literature. However, only two studies (Phan
and Kim (2015) and Phan and Kim (2016))
investigated the TAS with considering the
collaboration among trucking companies and the
container terminal. In these two papers, an iterative
approach is used to model the collaboration among
trucking companies and the terminal operator. The
iterative approach consists of two levels which are
interconnected by a feedback loop. The first level is a
mathematical model which includes a sub-problem
for each trucking company to minimize the total
waiting cost of trucks at the yard. On the other hand,
the second level is a procedure to estimate the
expected times at the yard of trucks based on the
solution of first level. This iterative approach enables
the collaboration process.
By careful investigation of the approaches
proposed in Phan and Kim (2015) and Phan and Kim
(2016), we notice three gaps that are needed to be
covered to improve the existing approaches. The first
gap is related to the second level where a simple
procedure is typically used to estimate the truck turn
times. This simple procedure lacks real world aspects
such as the waiting times of trucks at gate. The second
gap is that the existing approach did not consider the
randomness of the terminal operations. The third gap
is related to the number of times the trucking
companies and terminal operator send their decisions
to each other. According to Phan and Kim (2016) ,
their iterative approach needs about nine iterations on
average to terminate and produce the final solution.
In contrast, the proposed system in this paper requires
only 2 iterations between trucking companies and the
container terminal. From a practical point of view,
large number of iterations may cause some of
trucking companies not to submit their appointment
applications for some reasons such as not having time
to reschedule their truck operation or forgetting to
resubmit their applications. In this case, the quality of
the solution may be impaired.
A Dynamic and Collaborative Truck Appointment Management System in Container Terminals
87
Based on the above understandings, we propose a
new approach for dynamic and collaborative truck
appointment scheduling in container terminals. The
proposed approach considers the collaboration
among trucking companies and terminal operators by
a pre-processing integration of a mixed integer
programming model and a discrete event simulation
(DES) model. The contributions of the proposed
approach are as follows:
1) The turn times of trucks are estimated based on a
simulation model which enables capturing several
real world aspects as well as the stochastic nature
of the terminal operations.
2) By employing the pre-processing integration, the
trucking companies send their rescheduled
appointments to the terminal two times only.
Thus, this improves the applicability of the
proposed new appointment system.
3 THE PROPOSED DYNAMIC
AND COLLABORATIVE
TRUCK APPOINTMENT
SYSTEM
In this section, the proposed Dynamic Collaborative
Truck Appointment System is introduced (DCTAS)
based on the collaboration concepts. The paper
introduces an integrated simulation optimization
approach to achieve the collaboration goal
considering both the dynamic and stochastic nature of
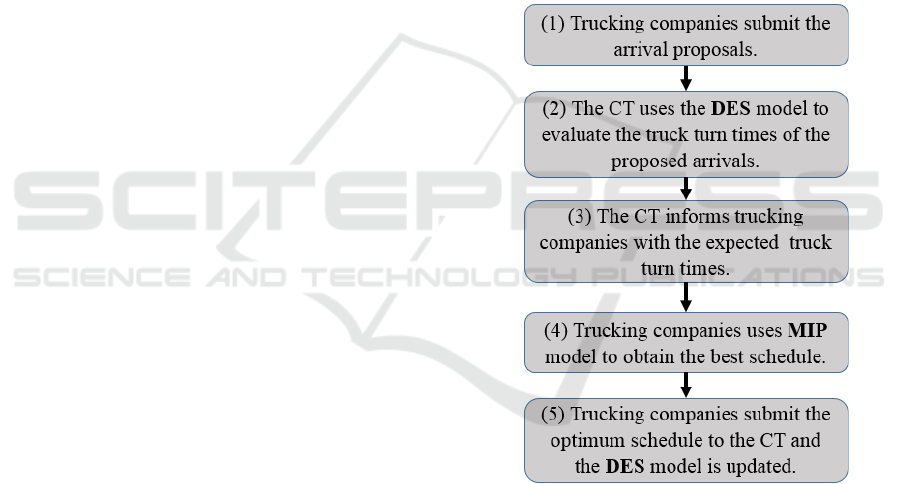
the problem. The proposed DCTAS (figure 3) can be
illustrated in five operational steps as follows:
Step (1): each trucking company submits an
arrival proposal to the terminal. This proposal
contains the preferable arrival time of their external
trucks based on some factors such as; ship arrival,
container dwell time, ship departure, available trucks,
etc.
Step (2): once the terminal operators receive the
submitted proposal, the terminal working load is
updated and the performance measures are
determined. To do this, a DES model of the terminal
is introduced to help the terminal operator to estimate
the total truck turn time for the trucking company and
evaluate the terminal congestion at each yard block
(YB) during each working hour (time window). It is
assumed that the workload of the CT contains the set
of confirmed appointments that are already reserved
before the terminal appointment application's
deadline for each time window (Tw) and the ship
tasks assigned to each yard block.
Step (3): The terminal operators publishes the
schedule information online with the expected turn
times for all submitted requests. Each trucking
company is then capable of knowing how much time
they are supposed to spend in the terminal (turn time)
to achieve their delivery/pick up tasks.
Step (4): To avoid going to the terminal in
congestion times, the trucking company will use the
mixed integer programming (MIP) model available as
a scheduling tool for their trucks. The MIP model is
solved to reduce the transportation cost in the CT
considering the previous preferable arrival time (step
1) and the terminal performance measures (step 2),
and a new arrival request will be issued.
Step (5): the new schedule will be submitted as a
confirmed appointment request and the terminal
workload will be updated waiting the new requests to
be submitted and confirmed.
Figure 3: The operational steps of the proposed DCTAS.
As illustrated, the DCTAS provides an interactive
management strategy between the stakeholders to
cope with the dynamic nature of the appointment
process in CTs. Interacting communication among
stakeholders can be implemented easily using an
online collaboration platform. In a previous work,
(Azab et al. 2016) adopted a design thinking strategy
to design and synthesize an online information system
for transportation logistics. Whenever a trucking
company is ready to submit the preferable arrival
times, the system receives the appointments and deals
with the workload updates and changes hourly.
ICORES 2017 - 6th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
88
Moreover, using the DES model is expected to
enhance the solution and to accommodate the
system’s actual variability and randomness. This
randomness results from the stochastic operations and
events such as the gate service rate, inter-terminal
traveling times, yard crane handling rates, quay crane
handling rate, and the failure of equipment. The
proposed simulation optimization approach integrates
the MIP model with the DES model in a pre-
processing way (Bierwirth and Meisel 2015) in which
the problem under particular circumstances is solved
to produce the input data for the other problem. The
DES model provide the input to the MIP model. After
solving the MIP model, the optimum truck
appointment schedule is evaluated using the
simulation model to get the turn time of trucks after
optimization.
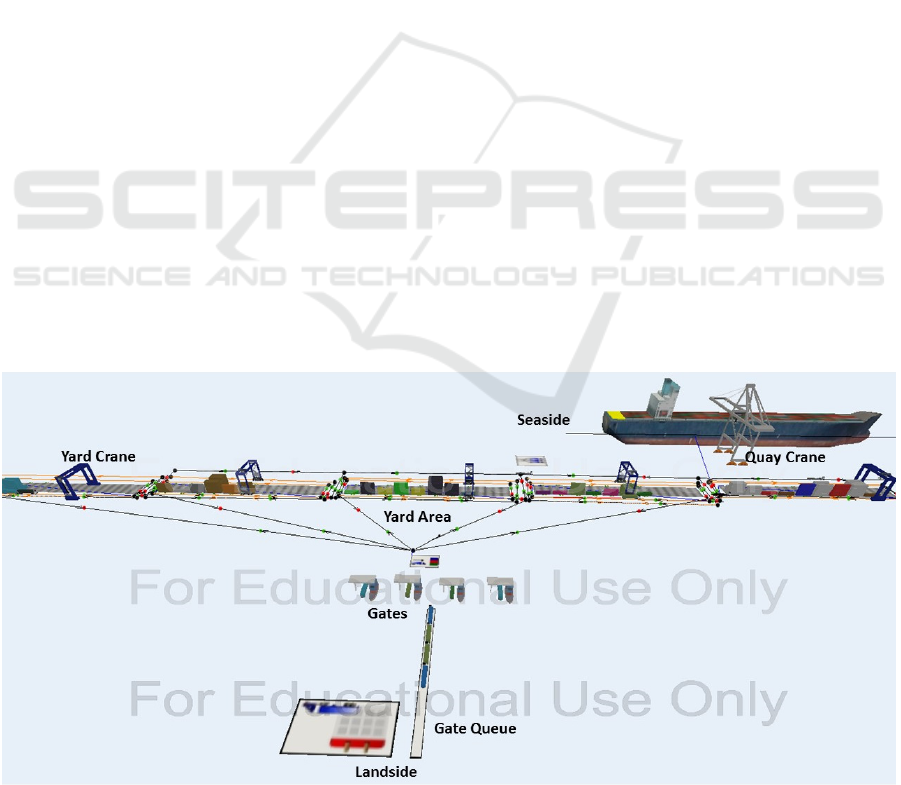
3.1 The DES Model
The DES model is built using “Flexsim CT
®
”
package, which is a special software for simulating
container terminal operations. The basic elements of
the model are shown in figure 4. The 3D DES model
includes five yard blocks, five yard cranes, four gates,
and a single shared gate queue. When the external
truck arrives at the gate according to the
predetermined schedule (Tables 2-3), the truck joins
a single queue shared among the four gates. Trucks
will leave the gate queue to the first available gate and
will be processed according to an Erlang distribution
(0.65,4) (Guan and Liu 2009). Once the truck
completes processing at the gate, the trucks are
directed to the yard block that contains a container to
be picked up or to the location of the container where
it will be dropped off. Yard cranes are the equipment
that handles the container within the blocks to/from
the external trucks. The external trucks leave the
terminal after finishing the pickup/drop off operation.
On the seaside of the terminal, the arriving vessels are
berthed, and there is a truck gang that serves each
quay crane assigned to the vessel. The internal trucks
deliver the containers between the seaside and yard
area. At the yard block, the highest priority is given
to shipside operations, next to gate side operations
and lastly to internal yard operations.
There are some assumptions that are used in this
simulation model. At the gates, it is assumed that all
arriving trucks will share the same queue before
going to the first available gate, and external trucks
travel time within the terminal is neglected. As a
result, the truck turn time will be the sum of the gate
queue waiting time, the gate service time, the yard
waiting time, and the yard service time. To obtain
more accurate results, each time window is divided
into four time intervals, and the average truck turn
time is calculated per each time interval. Moreover,
the collision of trucks traveling through the internal
transportation network of the terminal is not
considered. Because the problem is regarded as a
design problem for a new appointment system, the
input parameters are driven from literature and based
on some experience. Berth and yard cranes service
rates are represented by the average net moves/hr
calculated form the busy time and truck throughput
for each crane. Table 1 illustrates the input parameters
to the DES model.
Figure 4: 3D discrete event simulation model.
A Dynamic and Collaborative Truck Appointment Management System in Container Terminals
89

Table 1: the input parameters to DES model.
General parameters
Working hours (Tws) 8:00 am- 12 pm
Truck speed (max) 300 m/min (18 km/hour)
Container dwell time Exponential(0.3) [days]
Gate Parameters
Process time (min) Erlang (0.65, 4)
Gate capacity 1 truck/one gate
Yard parameters
Crane speed (max) 90 m/min (empty/loaded)
Block capacity (max) 24 containers
Crane net moves 27.7 move/hr (average)
Quayside parameters
crane speed (max) 120 m/min (empty/loaded)
Crane net moves 12.3 move/hr (average)
3.2 The Scheduling Problem: MIP
Model
In most container Terminals, the arrival of external
trucks from the hinterland is a random process that is
affected by the preferable arrival times of trucking
companies. These preferable arrival times are not
known by the terminal operators to be considered in
planning and scheduling operations. As a result, a
truck may arrive during a congestion time where the
waiting time is costly and the emissions are high. On
the other hand, if these trucks are forced to come at
certain times that are specified by the terminal
operators, it may be inconvenient for some trucking
companies due to the trucks availability and other
operations outside the terminal. To tackle this
problem, the following mathematical model
considers both, the convenience of trucking
companies to arrive at their preferable times and the
total time spent in the terminal which is influenced by
the terminal congestion.
Based on the mathematical models formulated by
(Phan and Kim 2015), we modified the model to
consider the truck turn time (TT
jt
) of trucks which is
derived from the DES model. The proposed DCTAS
assumes that each trucking company develops its
preferable schedule considering the available number
of trucks at each time window (s
kτ
). The trucking
company’s operator defines all tasks to be performed,
which represents a pick up or a delivery operation for
one container using one truck. Tasks that are assigned
in the same preferable arrival hour (time window) are
grouped together in one task group. For a certain task
group, Containers can be delivered or picked up from
the same yard block or from several yard blocks (table
2). The used parameters and indices in MIP model are
defined as follows:
i index for a task group
j index for a yard block
k index for a trucking company
τ index of a time window
t index of a time interval. Note that multiple
time intervals exist in a time window
b
i
l
earliest possible (lower) bound of the time
window for task group i
b
i
u
latest possible (upper) bound of the time
window for task group i
d
i
number of tasks to be done for task group i
S
kτ
number of available trucks of company k
during time window τ
p
i
most preferable time window at which
containers of task group i to be stored or
retrieved
σ number of time intervals per each time window
a
ij
maximum number of containers of task i that
can be allocated to yard block j
w
i
+
cost of late arrival by a unit time compared
with the preferable time window of task i
w
i
-
cost of early arrival by a unit time compared
with the preferable time window of task i
w
k
truck waiting cost in the terminal of truck
company k per time interval
P congestion penalty in $, a strategic parameter
determined by the terminal manager.
TT
jt
average truck turn time for a truck arriving at
yard block j at time interval t derived variables
from the DES model
Sets
I set of task groups.
K set of trucking companies.
T set of time intervals.
J set of yard blocks j
W set of time windows.
Decision variables:
X
ijτ
number of trucks for task group i which are
deployed to yard block j at time window τ
Derived variables from the MIP model:
λ
ijt
average arrival rate of trucks for task group i at
yard block j at time interval t
ICORES 2017 - 6th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
90

Minimize:
(1)
Subjected to:
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
The objective function (1) is to minimize the cost
of shifting (delaying or advancing) the appointment
and the truck turn time (TT
jt
) cost within the terminal.
The total number of scheduled trucks must satisfy the
number of containers to be delivered or picked up (2).
Constraint (3) states that the number of trucks to be
assigned to task i cannot be larger than the resource
level of the trucking company. The capacity
constraint of each yard block is described in (4) to
ensure that the number of containers for each task
group have to be smaller than or equal to the available
spaces in yard blocks. There is an earliest and latest
feasible time window for each container (5). To
calculate the arrival rate for each task group,
constraint (6) is used. Constraint (7) illustrates the
domain of each variable in the problem.
4 NUMERICAL EXPERIMENTS
In this section, a numerical example is solved to
illustrate the operational scenario and performance of
the proposed DCTAS. Table 2 shows a proposed
appointment application for 4 trucking companies.
Each trucking company is assumed to have a specific
number of containers (d
i
) in the terminal. The task
group is a set of tasks that will be submitted by the
same trucking company at the same preferred arrival
time (p
i
). It is assumed also that each trucking
company knows which yard block (j) holds its
containers. To create a workload in the terminal, the
externally confirmed applications and inter-terminal
tasks are developed in order to investigate the
response of the proposed system to the heavy-loaded
time windows. The proposed system (DCTAS) is
expected to shift the proposed arrival appointments to
the time windows where the turn time cost will be
minimized with consideration of the preferred arrival
times. Table 3 illustrates the tasks that are assumed to
be already reserved and confirmed.
To start working with the DCTAS, all tasks are
loaded to the simulation model input. Each task has a
corresponding arrival time, the number of containers,
and yard block location. By running the DES model,
the external trucks arrive to the terminal model
according to the predetermined scheduled times and
released out of the system as the task is completed.
The average truck turn times at each yard block are
recorded for each time window to be used in the MIP
model input. Other performance measures can be
derived from the simulation model such as the queue
length at gates, waiting times at gates and yard,
service rate at gates and yard, cranes’ utilization, etc.
Table 2: Proposed appointment applications for four
trucking companies.
Truck.
Company
Task
group
di Pi j
TC1
1 5 2 1
2 3 4 2
3
1
3
1
2 2
TC2
4 3 4 4
5 4 3 2
6 4 1 3
TC3
7
4
2
1
2 3
8
2
1
2
3 4
TC4
9 3 2 4
10
1
3
3
5 5
A Dynamic and Collaborative Truck Appointment Management System in Container Terminals
91
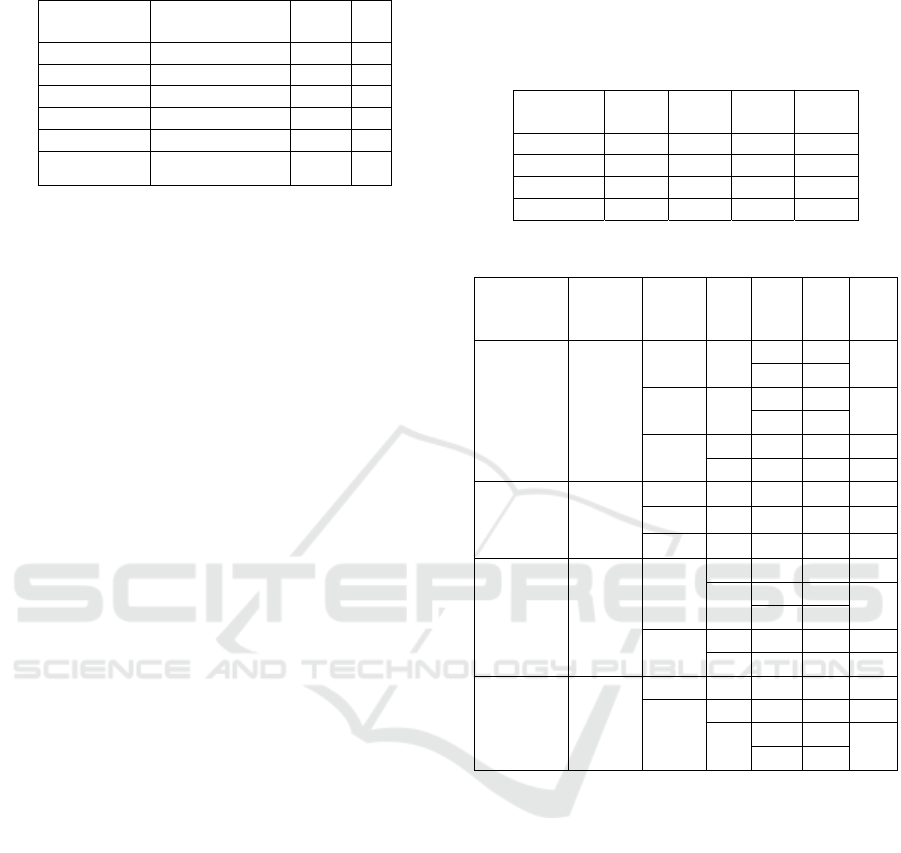
Table 3: the reserved tasks in the CT.
Confirmed
tasks
Di Tw j
11 30 2 1
12 30 3 2
13 30 2 3
14 30 2 4
15 30 3 5
16 10 (to ship) 3-4 1
To get statistically reliable results, the simulation
model is run for 35 replications which are used to
determine the 95% confidence intervals of the
targeted mean performance measures. After obtaining
the results from the simulation model, the derived
variables are sent to the MIP model. The MIP model
is solved using a personal computer with Intel
®
Core
i7 CPU and 4 GB RAM. IBM Ilog CPLEX
Optimization Studio version 12.2 is used to code the
problem and get the optimum solution. The cost
parameters in the objective function are assumed to
be $1, $4, $5, and $2 per each time for
w
i
+
, w
i
-
, w
k
, and P respectively. Table 4 shows the
available number of trucks (s
kτ
) for each trucking
company per each time window. In Constraint 3, the
number of available trucks is used to guarantee that
the new assigned tasks do not exceed the trucking
company’s available trucks per each time window.
5 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
Table 5 shows the MIP model optimum solution of
the provided instance. In Table 4, di represents the
number of containers submitted before solving the
problem. After solving the DCTAS problem, the X
ijt
describes the new scheduled tasks proposed for the
trucking company to reduce the total cost of
delivering a container to the terminal. There are three
possibilities noticed from the results to occur after the
solution to the input schedule of the DCTAS. The first
possibility, there will be no change in the schedule
such as task group 8. The second possibility, the task
group preferred time window will be advanced or
delayed resulting in an advancing and/or delaying
cost without any change in the number of containers
per task. For example, the arrival time of task group
5 is shifted from Tw3 to Tw2. This seems reasonable
because, at yard block 2, the workload in Tw3 was the
highest among the other three time windows in the
same block before the solution. The third possibility
is that the task group will be decomposed to smaller
mini-task groups. It is evident that the second and
third possibility may occur together like in task
groups 1, 2, 7, and 10.
Table 4: the available number (S
kτ
) of trucks for each
trucking company per each time widow.
Truck.
Company
Tw1 Tw2 Tw3 Tw4
TC1 3 5 6 4
TC2 7 4 1 5
TC3 6 1 2 4
TC4 3 4 3 4
Table 5: The DCTAS solution.
Truck.
Company
Obj.
value
($)
Task
group
di Xijt Tw j
TC1 137.8
1 5
2 1
1
3 4
2 3
1 1
2
2 2
3
1 1 4 1
2 2 2 2
TC2
114.7
4 3
3
4 4
5 4
4
2 2
6
4
4
1 3
TC3
101.75
7
4 4 4 1
2
1 2
3
1 3
8
2 2 1 2
3 3 1 4
TC4 130.31
9 3 3 4 4
10
1 1 4 3
5
4 2
5
1 3
To investigate the solution performance, the
simulation model is used to test the performance of
the output schedule from the MIP model and compare
it with simulation results before solving the MIP
model. In other words, we need to see how the
proposed schedule differs from the optimum schedule
after applying the DCTAS. The average truck turn
times at each block j per each time window τ (TT
jτ
)
are recorded for the proposed (preferred)
appointments and the optimum appointments. Figures
(5-9) show a comparison between the TT
jτ
values for
the proposed (preferred) appointments by the
trucking companies versus the optimum
appointments after applying the DCTAS.
ICORES 2017 - 6th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
92
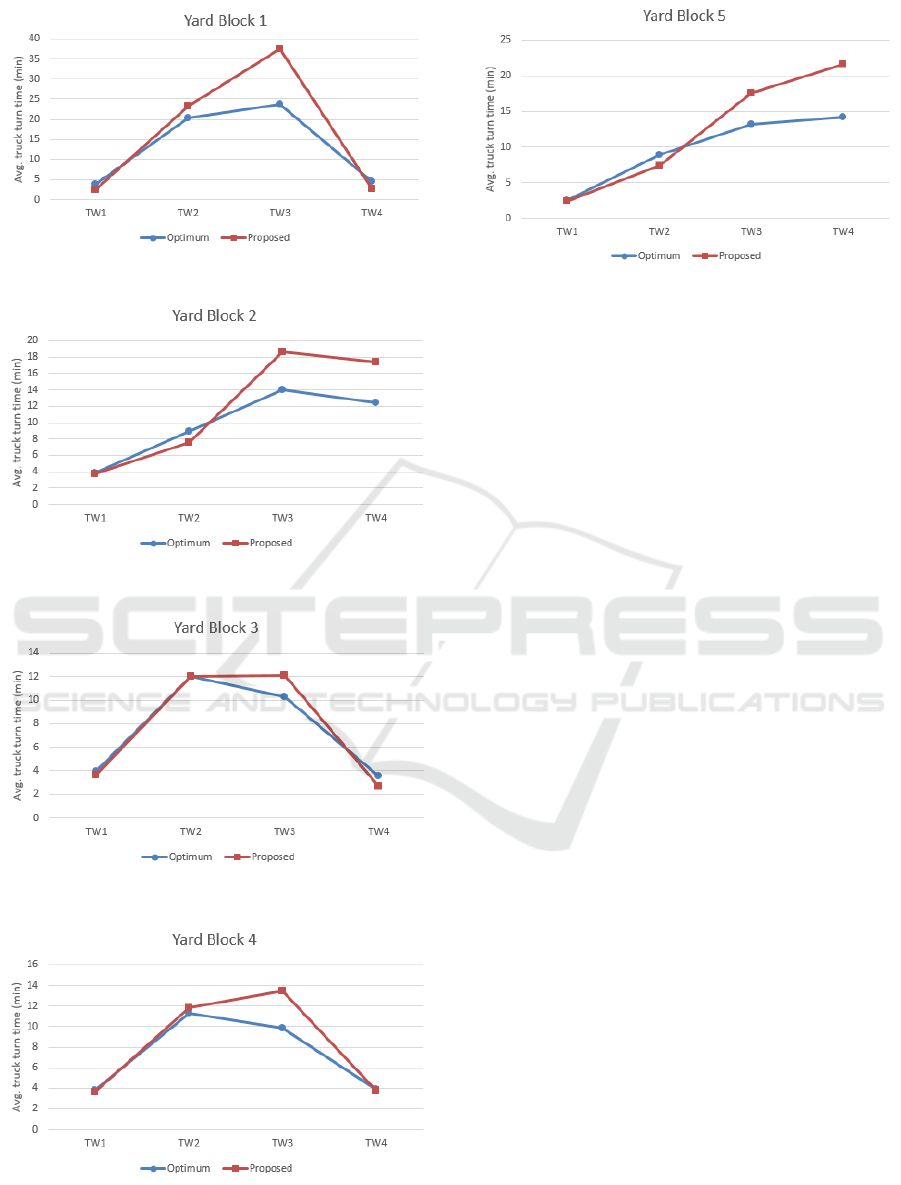
Figure 5: Average TT
1τ.
Figure 6: Average TT
2τ.
Figure 7: Average TT
3τ.
Figure 8: Average TT
4τ.
Figure 9: Average TT
5τ.
Results show that there is a difference between the
TT
jτ
values before and after applying the proposed
appointment management system. To confirm this
difference, a t-test is conducted for TT
jτ
values with a
95% confidence interval using Minitab 17 statistical
software to test the 35 samples (replications) of TT
jτ
.
The statistical results show that there is a significant
difference between the average TT
jτ
values before and
after solution for most points such as Tw3 at YB1,
Tw4 at YB2, Tw4 at YB3, Tw3 at YB4, and Tw4 at
YB. While, some points did not depict significant
differences in average TT
jτ
such as Tw1 at YB2, Tw2
at YB3, Tw2 at YB4, Tw4 at YB4. It is noticed that
the number of proposed tasks within some task
groups increased after solution because some task
groups are decomposed to two or three tasks.
However, this reduces the turn time cost for the
external trucks, some trucking companies may be
inconvenient due to shifting their preferable arrival
times. For the CT, distributing the arrival
appointments over the terminal working hours is good
to avoid congestion in certain times windows. From
another side, reducing congestion and decreasing
waiting time will result in less emissions and less fuel
cost as well increased efficiency for the trucking
companies. The results showed also that the average
queue length at gates is reduced by 21% and the
average truck turn time is reduced by 22.6% after
applying the proposed system.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper proposed an integrated appointment
system by which both the CT and trucking companies
collaborate in determining the arrival schedule of
external trucks. The proposed Dynamic Collaboration
Truck Appointment System (DCTAS) integrates a
discrete event simulation model with an MIP model
A Dynamic and Collaborative Truck Appointment Management System in Container Terminals
93

using pre-processing integration. In the proposed
DCTAS, the terminal operator firstly uses the
simulation model to evaluate the turn times of the
trucks considering their preferred arrival times. Then,
the trucking companies solve the MIP model to
reduce the total stay cost in the terminal. Finally, the
terminal operator uses the rescheduled appointments
of the trucking companies as inputs to the simulation
model to produce the final appointment times and
container schedule.
The results showed that the DCTAS could reduce
truck congestion at the time windows where the
terminal workloads are high. Moreover, the DCTAS
could smooth the terminal workload and balance the
arrival processes of external trucks. Thus, both
stakeholders can benefit from applying the proposed
appointment strategy. In addition, the rescheduling
frequency is reduced compared to the existing
literature approaches.
For future work, the proposed system will be
implemented to a real case study and the effect of
applying the proposed DCTAS on landside
operations, yard operations and seaside operations
will be investigated. Also, it is important to examine
the emissions from trucks and terminal equipment
after applying the DCTAS. One more issue that is
expected to increase the appointment system
performance is to consider truck sharing and
collaboration between the trucking companies to
reduce the empty truck trips. For instance, a trucking
company may have a truck with an empty trip during
a pickup task, which can be utilized by another
trucking company to deliver a container to the
terminal. This truck sharing process can be
considered also in the appointment process.
REFERENCES
Van Asperen, E., Borgman, B. & Dekker, R., 2013.
Evaluating Impact Of Truck Announcements On
Container Stacking Efficiency. Flexible Services And
Manufacturing Journal, 25(4), Pp.543–556.
Azab, Ahmed; Mostafa, Noha; And Park, Jaehyun,
"Ontimecargo: A Smart Transportation System
Development In Logistics Management By A Design
Thinking Approach" (2016). PACIS 2016 Proceedings.
Paper 44 Http://Aisel.Aisnet.Org/Pacis2016/44.
Azab, A.E. & Eltawil, A.B., 2016. A Simulation Based
Study Of The Effect Of Truck Arrival Patterns On
Truck Turn Time In Container Terminals, ECMS 2016
Proceedings Edited By: Thorsten Claus, Frank
Herrmann, Michael Manitz, Oliver Rose European
Council For Modeling And Simulation.
Doi:10.7148/2016-0080.
Bierwirth, C. & Meisel, F., 2010. A Follow-Up Survey Of
Berth Allocation And Quay Crane Scheduling
Problems In Container Terminals. European Journal Of
Operational Research, 244(3), Pp.675–689. Available
At: Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.1016/J.Ejor.2009.05.031.
Bierwirth, C. & Meisel, F., 2015. A Follow-Up Survey Of
Berth Allocation And Quay Crane Scheduling
Problems In Container Terminals. European Journal Of
Operational Research, 244(3), Pp.675–689. Available
At: Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.1016/J.Ejor.2009.05.031.
Chen, G., Govindan, K., Yang, Z.Z., Et Al., 2013. Terminal
Appointment System Design By Non-Stationary
M(T)/E K/C(T) Queueing Model And Genetic
Algorithm. International Journal Of Production
Economics, 146(2), Pp.694–703. Available At:
Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.1016/J.Ijpe.2013.09.001.
Chen, G., Govindan, K. & Golias, M.M., 2013. Reducing
Truck Emissions At Container Terminals In A Low
Carbon Economy: Proposal Of A Queueing-Based Bi-
Objective Model For Optimizing Truck Arrival Pattern.
Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And
Transportation Review, 55(X), Pp.3–22. Available At:
Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.1016/J.Tre.2013.03.008.
Chen, G., Govindan, K. & Yang, Z., 2013. Managing Truck
Arrivals With Time Windows To Alleviate Gate
Congestion At Container Terminals. International
Journal Of Production Economics, 141(1), Pp.179–
188. Available At:
Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.1016/J.Ijpe.2012.03.033.
Chen, G. & Jiang, L., 2016. Managing Customer Arrivals
With Time Windows: A Case Of Truck Arrivals At A
Congested Container Terminal. Annals Of Operations
Research, Pp.1–17. Available At:
"Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.1007/S10479-016-2150-3.
Chen, G. & Yang, Z., 2010. Optimizing Time Windows For
Managing Export Container Arrivals At Chinese
Container Terminals. Maritime Economics &
Logistics, 12(1), Pp.111–126.
Chen, X., Zhou, X. & List, G.F., 2011. Using Time-Varying
Tolls To Optimize Truck Arrivals At Ports.
Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And
Transportation Review, 47(6), Pp.965–982. Available
At: Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.1016/J.Tre.2011.04.001.
Dekker, R. Et Al., 2013. A Chassis Exchange Terminal To
Reduce Truck Congestion At Container Terminals.
Flexible Services And Manufacturing Journal, 25(4),
Pp.528–542.
Gheith, M., Eltawil, A.B. & Harraz, N.A., 2016. Solving
The Container Pre-Marshalling Problem Using
Variable Length Genetic Algorithms. Engineering
Optimization, 48(4), Pp.687–705. Available At:
Http://Www.Tandfonline.Com/Doi/Full/10.1080/0305
215X.2015.1031661.
Guan, C. & Liu, R. (Rachel), 2009. Container Terminal
Gate Appointment System Optimization. Maritime
Economics & Logistics, 11(4), Pp.378–398.
Available At:
Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.1057/Mel.2009.13.
Huynh, N., 2009. Reducing Truck Turn Times At Marine
Terminals With Appointment Scheduling.
ICORES 2017 - 6th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
94

Transportation Research Record: Journal Of The
Transportation Research Board, 2100, Pp.47–57.
Huynh, N. & Walton, C.M., 2008. Robust Scheduling Of
Truck Arrivals At Marine Container Terminals. Journal
Of Transportation Engineering, 134(8), Pp.347–353.
Karafa, J., 2012. Simulating Gate Strategies At Intermodal
Marine Container Terminals. , (May). Available At:
Http://Www.Memphis.Edu/Ifti/Pdfs/Student_Reserach
_Jeff_Karafa.Pdf.
Karam, A. & Eltawil, A.B., 2015. A New Method For
Allocating Berths, Quay Cranes And Internal Trucks In
Container Terminals. 2015 International Conference
On Logistics, Informatics And Service Science, LISS
2015.
Karam, A. & Eltawil, A.B., 2016. Functional Integration
Approach For The Berth Allocation, Quay Crane
Assignment And Specific Quay Crane Assignment
Problems. Computers And Industrial Engineering,
Pp.1–15.
Li, N. Et Al., 2016. Disruption Management For Truck
Appointment System At A Container Terminal: A
Green Initiative. Transportation Research Part D:
Transport And Environment.
Mohamed Gheitha, A.B.E.& N.A.H. & Mizuno, 2014. An
Integer Programming Formulation And Solution For
The Container Pre- Marshalling Problem M. In Pp.
2047–2056.
Morais, P. & Lord, E., 2006. Terminal Appointment System
Study. Transportation Research Board, 1(March),
P.123.
Murty, K.G. Et Al., 2005. Hongkong International
Terminals Gains Elastic Capacity Using A Data-
Intensive Decision-Support System. Interfaces, 35(1),
Pp.61–75.
Namboothiri, R. & Erera, A.L., 2008. Planning Local
Container Drayage Operations Given A Port Access
Appointment System. Transportation Research Part E:
Logistics And Transportation Review, 44(2), Pp.185–
202.
Phan, M.H. & Kim, K.H., 2016. Collaborative Truck
Scheduling And Appointments For Trucking
Companies And Container Terminals. Transportation
Research Part B: Methodological, 86, Pp.37–50.
Phan, M.H. & Kim, K.H., 2015. Negotiating Truck Arrival
Times Among Trucking Companies And A Container
Terminal. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics
And Transportation Review, 75, Pp.132–144. Available
At: Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.1016/J.Tre.2015.01.004.
Sharif, O., Huynh, N. & Vidal, J.M., 2011. Application Of
El Farol Model For Managing Marine Terminal Gate
Congestion. Research In Transportation Economics,
32(1), Pp.81–89. Available At:
Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.1016/J.Retrec.2011.06.004.
Steenken, D., Vob, S. & Stahlbock, R., 2005. Container
Terminal Operation And Operations Research - A
Classification And Literature Review. Container
Terminals And Automated Transport Systems: Logistics
Control Issues And Quantitative Decision Support,
Pp.3–49.
Zehendner, E. & Feillet, D., 2014. Benefits Of A Truck
Appointment System On The Service Quality Of Inland
Transport Modes At A Multimodal Container Terminal.
European Journal Of Operational Research, 235(2),
Pp.461–469. Available At:
Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.1016/J.Ejor.2013.07.005.
Zhang, X., Zeng, Q. & Chen, W., 2013. Optimization
Model For Truck Appointment In Container Terminals.
Procedia - Social And Behavioral Sciences, 96(Cictp),
Pp.1938–1947. Available At:
Http://Www.Sciencedirect.Com/Science/Article/Pii/S1
877042813023458.
Zhao, W. & Goodchild, A. V, 2013. Using The Truck
Appointment System To Improve Yard Efficiency In
Container Terminals. Maritime Economics & Logistics,
15, Pp.101–119. Available At: Http://Www.Palgrave-
Journals.Com/Mel/Journal/V15/N1/Pdf/Mel201223a.P
df?WT.Ec_Id=MEL-201303.
Zhao, W. & Goodchild, A. V., 2010. The Impact Of Truck
Arrival Information On Container Terminal
Rehandling. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics
And Transportation Review, 46(3), Pp.327–343.
Available At:
Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.1016/J.Tre.2009.11.007.
A Dynamic and Collaborative Truck Appointment Management System in Container Terminals
95
