
Towards Developing Dialogue Systems with Entertaining Conversations
Hai-Long Trieu, Hiroyuki Iida, Nhien Pham Hoang Bao and Le-Minh Nguyen
Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Nomi City, Ishikawa, Japan
Keywords:
Dialogue Systems, Game Refinement, Goal-driven Dialogue Systems, Entertaining Conversation.
Abstract:
This paper explores a novel approach to developing a dialogue system that is able to make entertaining conver-
sations with users. It proposes a method to improve the current goal-driven dialogue systems which support
users for specific tasks while satisfying users’ goals with entertaining conversations. It then develops a dia-
logue system in which a set of features are considered to generate entertaining conversations, while reasonably
prolonging the original too short dialogue. The game refinement measure is employed for the assessment of
attractiveness since the conversations in dialogue systems can be seen as the process by which a player creates
shoots or moves to win a game. The dialogues generated by the proposed method are evaluated by human
subjects. The results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed method. The present idea can be a promising
way to realize dialogue systems with entertaining conversations although further investigations are needed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Dialogue systems have become applicable in various
tasks including technical support services, language
learning tools, and entertainment (Young et al., 2013;
Shawar and Atwell, 2007). Recently, the systems
have been popular in different domains (Banchs and
Li, 2012) and commercially exploitable (Pieraccini
et al., 2009; Griol et al., 2010). In dialogue systems, a
system (or robot) communicates with a human using
natural languages in spoken-based or text-based con-
versations. Dialogue systems can be divided into two
branches: task-oriented (or goal-driven), and chat-
oriented (or non-goal-driven). Goal-driven systems
focus on supporting users to complete a specific task
like accommodation services, booking transportation
or requesting specific information (Busemann et al.,
1997; Seneff and Polifroni, 2000; Stallard, 2000).
Meanwhile, the objective of non-goal-driven systems
is for entertainment or to provide a means for partic-
ipating in a game (Weizenbaum, 1966; Ogura et al.,
2003; Wallis, 2010).
The most successful approach for goal-driven sys-
tems is based on the partially observable Markov
decision process (POMDP) (Young et al., 2013;
Pietquin and Hastie, 2013) and learning features using
neural network models (Henderson et al., 2014). For
non-goal-driven systems (Ritter et al., 2011; Banchs
and Li, 2012; Ameixa et al., 2014), there are ap-
proaches like using neural networks in natural lan-
guage modeling and machine translation (Sordoni
et al., 2015; Shang et al., 2015).
For the goal-driven applications, one of the main
tasks of current dialogue systems is to satisfy users’
goals. This is an important task to make the systems
applicable. Nevertheless, this may result in the prob-
lem that the systems tend to directly respond to satisfy
users’ goals immediately; in other words, the dialogue
speed is too fast. The systems will be successful and
effective when they not only satisfy users’ goals but
also generate interesting and intelligent conversations
during the dialogues’ progress to attract the users.
In this work, we improve goal-driven dialogue
systems to generate interesting and intelligent conver-
sations while benefiting from game refinement theory
(Iida et al., 2004). The idea originates from the corre-
spondences between dialogues and games including
goals and progress to obtain the goals. In order to
win a game, players try to create successful shoots
(e.g. in soccer) or moves (e.g. in chess). Meanwhile,
for dialogues, users ask questions to a dialogue sys-
tem in order to reach specific goals, and the conver-
sations between the user and the system to obtain the
user’s goals correspond to shoots or moves in games.
Therefore, the progress to satisfy the user’s goals in
dialogues can be seen as the progress when players
enjoy the game. In order to generate interesting dia-
logues, we apply game refinement theory (Iida et al.,
2004; Sutiono et al., 2015), which has been proposed
as a measure of game sophistication. The dialogues
are generated and their length is reasonably controlled
with a focus on a set of important features of conver-
Trieu H., Iida H., Pham Hoang Bao N. and Nguyen L.
Towards Developing Dialogue Systems with Entertaining Conversations.
DOI: 10.5220/0006192105110518
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2017), pages 511-518
ISBN: 978-989-758-220-2
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
511

sations. Experiments are conducted using a data set
of dialogues about restaurant information. The game
refinement measure is used to assess the of attractive-
ness of dialogues. In addition, we conduct a web-
based human evaluation to score the generated dia-
logues.
The structure of the paper is as follows. In Sec-
tion 2 we introduce our proposed method to improve
dialogue systems. Specifically, the correspondences
between dialogues and games are analyzed before we
discuss the game refinement measure, the means that
we use to improve dialogue systems. Then, we de-
scribe proposed features to generate dialogues. Ex-
periments, results and the discussion are presented in
Section 3. Finally, concluding remarks are drawn in
Section 4.
2 DEVELOPING DIALOGUE
SYSTEMS
In this section, we analyze the correspondences be-
tween dialogues and games. Then, we discuss game
refinement theory, by which we improve dialogue sys-
tems that generate attractive dialogues. The dialogues
are generated using some features that are described
thereafter.
2.1 Dialogues and Games
Dialogues contain some characteristics that are also
included in games. In order to win a game like chess
or soccer, players should have successful moves or
shoots. In dialogue systems, the user also has some
specific goals, and each informative answer generated
by the system that satisfies the user’s goal can be seen
as successful moves or shoots in games. The progress
of conversations between the system and the user cor-
responds to the progress in games, in which the user
asks questions to reach the goals. When the user ob-
tains all of the goals from information generated by
the system, the dialogue can be complete, or in other
words, the game finishes. In this way, when the user
has a specific number of goals in advance, the dia-
logues can be seen as pre-set score games like volley-
ball or tennis.
Game players usually feel excited with games not
only because they win the game but because the game
progress is also interesting. The question is how to
improve dialogue systems so that they not only gener-
ate informative answers to satisfy users’ goals but also
help users feel interested in the dialogues’ progress?
2.2 Game Refinement Measure
The game refinement measure was derived from a
mathematical model of game outcome uncertainty
within the framework of game refinement theory (Iida
et al., 2004). In this work, dialogues can be seen as
a kind of game, and the game refinement measure is
used to evaluate and improve dialogue systems.
2.2.1 Model
In the game refinement theory, there are two impor-
tant factors: the game speed and the game information
progress (Sutiono et al., 2015). Game speed relates to
the scoring rate, while game information progress fo-
cuses on game outcome. In well-known games like
soccer and basketball, the scoring rate is calculated
based on two factors: the total score (goals) and the
time or steps to achieve the goal(s). The total score is
the average number of successful shoots (say G) while
the steps needed to achieve the goal are based on the
average number of attempted shoots (say T ). There-
fore, the scoring rate or game speed of the games can
be calculated by the ratio of G to T . Meanwhile,
other sport games in which the goal is set in advance,
like volleyball and tennis, the average number of to-
tal points per game corresponds to the time or steps
to achieve the goal. For boardgames such as Go and
chess, the steps are based on the average depth of
game tree (game length), and the goal is estimated by
the average branching factor.
When one already knows the game outcome, for
instance when the game finishes, the game progress
x(t) will be given as a linear function of time t with
0 ≤t ≤T and 0 ≤x(t) ≤G, as shown in Equation (1).
x(t) =
G
T
t (1)
Nevertheless, it is difficult to know the game infor-
mation progress x(t) during the game until it finishes.
In other words, the game outcome is uncertain by the
endgame in many games, called balanced games or
seesaw games. We show in Figure 1 an illustration
of game progress in terms of outcome certainty. Fig-
ure 1 shows that the game outcome is uncertain until
the very end of the game in balanced games or seesaw
games. This leads to an exponential function as a re-
alistic model of game information progress, which is
given by Equation (2).
x(t) = G(
t
T
)
n
(2)
Here n stands for a constant parameter which is given
based on the perspective of an observer in the game
considered. If one knows the game outcome, for ex-
ample after the game, or if one can exactly predict
ICAART 2017 - 9th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
512

in advance the game outcome and its progress, then
we have n = 1, where x(t) is a linear function of time
t. During the in-game period, various values of the
parameter n for different observers, including players
and supporters, are determined. For example, some
observers might be optimistic with 0 ≤ t < 1. How-
ever, when one feels any difficulty to win or achieve
the goal, the parameter would be n > 1. Meanwhile,
we reasonable assume that the parameter would be
n ≥ 2 in many cases, like balanced or seesaw games.
Thus, the acceleration of game information progress
¯x(t) is obtained by deriving Equation (2) twice. Solv-
ing it at t = T , we have Equation (3).
¯x(T ) =
G
T
2
n(n −1) (3)
It is assumed in the current model that the game
information progress in any type of games is happen-
ing in our minds. Hence, it is reasonably expected that
the larger the value
G
T
2
is, the more the game becomes
exciting due to the uncertainty of the game outcome.
Thus, its root square
√
G
T
is used as a game refinement
measure (say R) for the game under consideration, as
defined in Equation (4).
R =
√
G
T
(4)
Figure 1: A game progress model of outcome certainty.
2.2.2 Refinement Values of Sophisticated Games
We show, in Table 1, several sophisticated games in-
cluding soccer, basketball and table tennis from sports
games, chess and Go from board games (Sutiono
et al., 2015). Note that G and T of board games cor-
responds to the branching factor and the game length,
respectively. We see that sophisticated games have a
similar R value which we call a zone value between
0.07 and 0.08. This indicates the same or similar de-
gree of game sophistication where players may feel
the same degree of engagement or excitement regard-
less of different type of games.
Table 1: Refinement values of some well-known games.
Games G T R
Soccer 2.64 22 0.073
Basketball 36.38 82.01 0.073
Table Tennis 54.863 96.465 0.077
Chess 35 80 0.074
Go 250 208 0.076
Figure 2: An example of the greeting feature.
2.3 Generating Dialogues
The current dialogue systems focus on how to maxi-
mize the users’ goals. This is an important task that
benefits for users in many applications. Nevertheless,
the further objective of dialogue systems is not only to
satisfy user’s goals but also to help the users enjoyable
with the dialogue progress. Focusing solely on users’
goals as in the current dialogue systems may result
in obtaining the goals (the dialogue’s speed) fast. In
other words, the systems tend to provide informative
answers to satisfy the user’s goals immediately. This
is useful and reasonable; nonetheless, from the view-
point of game refinement theory or entertaining con-
versations, the dialogues should contain uncertainty
with a longer progress to satisfy the user’s goals grad-
ually, which enables to create intelligent dialogues.
For this purpose, we focus on some important features
such as greeting, user’s topics, dialogue prolongment,
feedback, surprising and grammar.
Greeting. The system can start conversations with
users by some random topics like weather, sports, or
foods, etc. We name this feature as greeting. Instead
of starting the progress to obtain the user’s goal im-
mediately, using random topics would help to reduce
the dialogue speed, and this is also a natural method
to start conversations of human. We present an exam-
Towards Developing Dialogue Systems with Entertaining Conversations
513
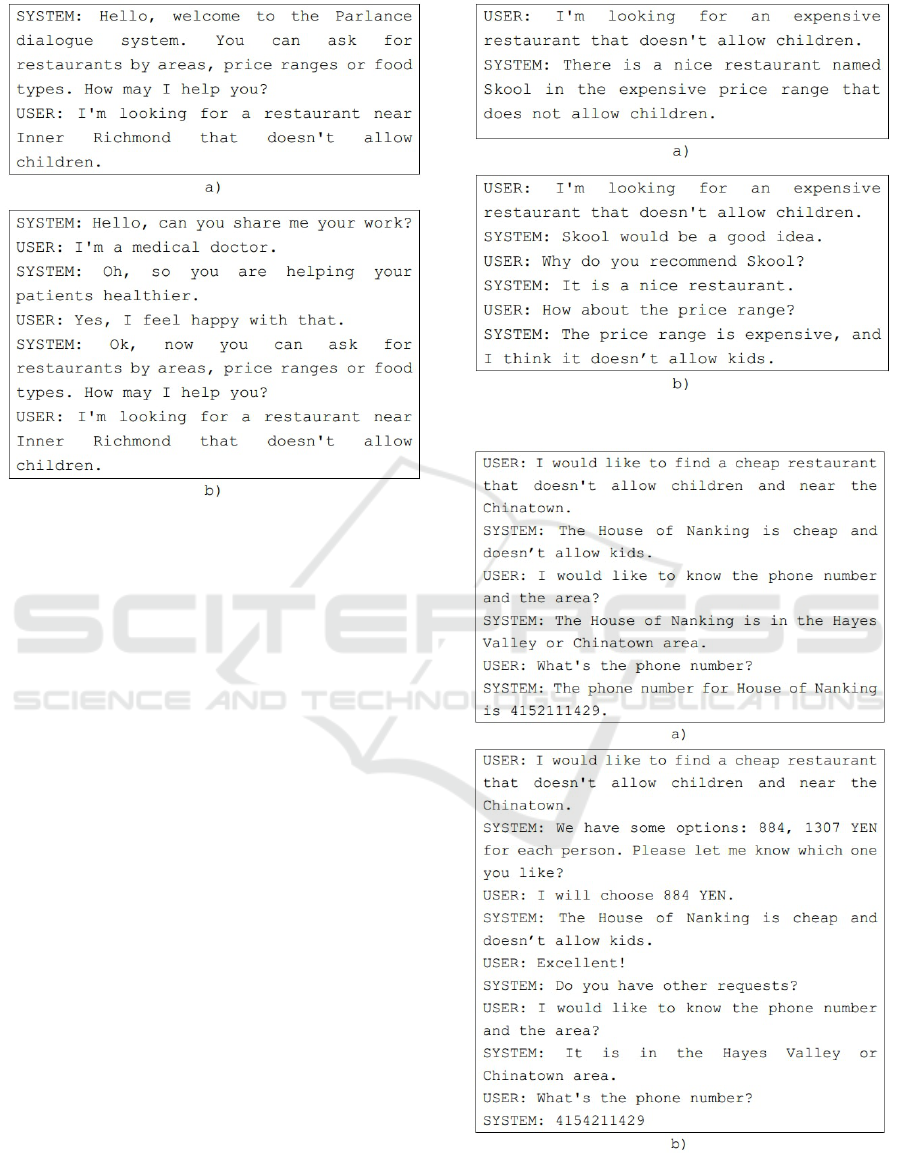
Figure 3: An example of the user’ topics feature.
ple of this feature in Figure 2, in which Figure 2(a) is
a baseline dialogue while Figure 2(b) is the dialogue
generated by using the proposed feature.
Users’ Topics. Conversations can be also started by
some topics related to the users like jobs or hobbies.
In order to do that, the system should contain a corpus
covering vocabulary and context of various domains
including jobs and hobbies. This feature can help to
reduce the dialogue speed and attract users because
this indicates that the system seems to understand spe-
cific fields or domains like human. Figure 3 presents
an example of this feature.
Dialogue Prolongment. The system sometimes
provides several information together for the user at
the same time to answer a specific question of the
user. Nevertheless, such multiple information can be
divided into smaller parts in order that the necessary
information will be provided for the user step by step.
This may attract the user raising more questions to
obtain the goals when the system partly provides in-
formation for the user gradually. By this way, the di-
alogue speed is also reduced. Nevertheless, it should
be further considered when asking so many questions
to obtain a goal may lead to negative effects for the
user. We show, in Figure 4, an example of this fea-
ture.
Figure 4: An example of the dialogue prolongment feature.
Figure 5: An example of the feedback feature.
Feedback. When the user asks a question, the sys-
tem does not need to respond directly to the question;
ICAART 2017 - 9th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
514

Figure 6: An example of the surprising feature.
instead the system may provide some specific options
related to the answer. This helps to reduce the dia-
logue speed while the user still obtains necessary in-
formation. Figure 5 shows an example of this case.
Surprising. In the game’s progress model as shown
in Figure 1, the amount of game outcome informa-
tion in the game’s opening is small; however, this be-
comes much more as the game approaches the end.
The acceleration of game information progress fol-
lows an exponential function. We propose using a
feature namely ”surprising” in which the system tries
to ask questions related to a specific goal. In this case,
it is unusual when the system actively asks questions
as suggestions for the user even when the user has not
yet provided the request. This would enable to create
interesting conversations especially when the sugges-
tion can match with the goal in the user’s mind, which
may lead to a surprising emotion for the user. It may
be exciting when the system actively can satisfy the
user rather than the process of asking by the user and
answering by the system. This feature is reasonable
in the game refinement model when suggesting op-
tions by the system may lead to a small amount of
necessary information at the beginning of the conver-
sation; however, by the end the user may obtain a goal
surprisingly when one of the options matched with a
specific goal of the user. We present an example in
Figure 6.
Figure 7: An example of the grammar feature.
Grammar. We describe here a feature which may
help to generate natural dialogues. The human-
human dialogues usually contain less formal gram-
mar. Therefore, we try to apply this feature in gener-
ating dialogues when we remove the complete gram-
mar in some cases. Figure 7 illustrates an example
of this feature. In the example, some information like
phone number or address may not need to be provided
grammatically.
3 ASSESSMENT
Our work is to improve dialogue systems which
can ensure providing informative responses to satisfy
users’ goals and create an interesting progress in di-
alogues. For this purpose, it is assumed that the first
task of satisfying the goals is already obtained in or-
der that we can focus mainly on the second task which
produces interesting progress of dialogues. Thus, we
use an existed set of dialogues as the baseline, and
our objective is to improve the baseline dialogues that
become interesting and intelligent while retaining the
user’s goals in the dialogues.
3.1 Data
We use a data set of real dialogues which provide in-
formation about certain venues in San Francisco on
the restaurants domain (Wen et al., 2015).
1
Dia-
logues include turns in which each turn is usually a
1
https://www.repository.cam.ac.uk/handle/1810/251304
Towards Developing Dialogue Systems with Entertaining Conversations
515

pair of utterances between the system and the user.
In reality of human-human conversations, one may
sometimes be silent or in other words ignore the turn.
In this baseline dialogues data set, almost turns are
symmetrical in which each turn usually contains two
utterances of both the system and the user. The base-
line dialogues contain 1066 dialogues with 6198 turns
in which 6 turns on average for each conversation to
obtain about three or four goals including the name,
address, foods, or areas of a restaurant. This means
that the dialogue speed is so fast when almost of the
system’s response can satisfy one of the user’s goals
immediately.
In order to generating interesting and intelligent
dialogues, we design a set of rules using the features
described in Section 2. The proposed ideas are imple-
mented using Java, wehreas the rules and implemen-
tation detail are available at the site.
2
3.2 Assessment using Game Refinement
Measure
By using the features, the baseline dialogues can be
enhanced to prolong with more turns, and we call the
generated dialogues as enhanced dialogues. Enhanc-
ing more turns leads to a slower speed of dialogues,
where users need to wait more turns to obtain the
goals. Table 2 describes the number of goals and turns
in the baseline and the enhanced dialogues. The aver-
Table 2: Statistics on the number of dialogues, goals and
turns: baseline dialogues and enhanced dialogues com-
pared.
Systems Dialogues Goals Turns
Baseline 1,006 4,249 6,198
Enhanced 1,006 4,249 12,534
age number of goals and the average number of turns
are shown in Table 3. The game refinement value is
calculated based on these two parameters using Equa-
tion (4), where G and T stands for the average num-
bers of users’ goals and turns in dialogues, respec-
tively. Thus we figure out the game progress model
of dialogues x(t) as shown in Equation (1) to derive
the game refinement measure.
Table 3: Game refinement values: baseline dialogues and
enhanced dialogues compared.
Systems Goals Turns R
Baseline 4.224 6.161 0.334
Enhanced 4.224 12.459 0.165
2
https://github.com/nguyenlab/DialogueGame
The refinement ratio of the baseline dialogues is
0.334 which is much higher than the balanced ratio of
sophisticated games as shown in Table 1 which is in
the range of 0.076 to 0.078. Meanwhile, our method
obtains a lower ratio than the baseline: 0.165. The
high ratio of the baseline dialogues indicates that the
speed of the dialogues is so fast; in other words, the
outcome of the dialogue can be obtained in few turns
and easy to predict. This is different from interesting
games in which the game’s progress should contain
some uncertainty, and the game’s outcome cannot be
predicted until the endgame. In the proposed method,
users have to wait for more turns to obtain the goal,
which indicates that the progress of the dialogue con-
tains some uncertainty rather than straightforward re-
sponses from the system. This can help the users feel
more interesting in the dialogue’s progress. Nonethe-
less, this should be further improved to obtain the bal-
anced ratio. In addition, the refinement ratio of dia-
logues also needs to be further investigated to find a
comfortable ratio for this domain.
3.3 Assessment with Human Subjects
We admitted that the change of feelings and emo-
tion does happen in our minds when playing games
or being in conversations. Nevertheless, it is quite
challenge to measure the exciting or intelligence of
dialogues, which is related to biology and emotion
in our minds. In order to perform this task, human
evaluation experiments were conducted while invit-
ing volunteers to evaluate the dialogues. There were
11 participants (postgraduate students) from various
fields including natural language processing (NLP),
games, robotics, and general (participants work in
other fields).
The evaluation contains 20 pairs of dialogues, in
which each pair of dialogues includes a baseline di-
alogue randomly selected from the baseline data set
and output dialogue generated by using the proposed
method (enhanced dialogue). We created a web-based
evaluation page available at
3
so that it can be easy to
extend and evaluate this task in popularity.
Table 4: Human assessment results. Equal, Better, Worse:
the enhanced dialogue achieves equally, better or worse
score than the baseline dialogue, respectively.
Factors Equal Better Worse
Satisfaction 64.25% 32.40% 3.35%
Interesting 38.55% 57.54% 3.91%
Table 4 presents the human assessment results.
3
http://150.65.242.105:8080/dialoguesystem/
ICAART 2017 - 9th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
516

We considered two factors to compare the baseline
and enhanced dialogues including satisfaction and in-
teresting. The satisfaction indicates the degree that
users satisfy with the responses from the system while
the interesting shows how interesting the dialogue’s
progress. The results show that the enhanced dia-
logues are recognized more interesting than the base-
line dialogues with up to 57.54% of the dialogues.
Meanwhile, the enhanced dialogues still satisfy the
users’ goals, or even the users can obtain more sat-
isfaction with the enhanced dialogues. Specifically,
64.25% of the enhanced dialogues satisfy the users’
goals equally with the baseline dialogues. Surpris-
ingly, 32.40% of the enhanced dialogues are rec-
ognized more satisfaction with the users’ goals. It
should be noted that the enhanced dialogues do not
always satisfy users or make the dialogue’s progress
more interesting, in which 3.35% of the enhanced di-
alogues do not satisfy the users’ goals as the base-
line dialogues, and 3.91% is less interesting. This can
be explained that users sometimes want to obtain the
goals as fast as possible and only consider the knowl-
edge aspect rather than entertaining; in that case, the
longer dialogues may lead to less satisfaction and less
interesting.
Table 5: Scoring by human subjetcs working in different
fields.
Area Factors Equal Better Worse
(%) (%) (%)
Robotics Satisfaction 82.50 12.50 5
Interesting 32.50 62.50 5
NLP Satisfaction 61.67 31.67 6.67
Interesting 43.33 53.33 3.33
Games Satisfaction 50 50 0
Interesting 0 95 5
General Satisfaction 59.32 40.68 0
Interesting 50.85 45.76 3.39
The evaluation results are presented in Table 5 to
compare between the study areas. The highest ratios
that the enhanced dialogues are more interesting than
the baseline dialogues are 95% and 62.50%, evaluated
by the participants from games and robotics areas, re-
spectively. Meanwhile, the participants from the gen-
eral field evaluated the high ratio that the enhanced
dialogues are better in both satisfaction and interest-
ing factors with 40.68% and 45.76%, respectively.
Table 6 presents the ratios of enhanced dialogues
that obtain the higher scores than the baseline dia-
logues in both factors: satisfaction and interesting.
Participants from the games area evaluated this ratio
up to 50% while the ratios are 33.90% in the general
area and 10% in the robotics area.
Table 6: Ratio of enhanced dialogues that are better than
the baseline dialogues in both factors: satisfaction and in-
teresting.
Area Ratio
All 27.37%
Robotics 10%
NLP 25%
Games 50%
General 33.90%
3.4 Discussion
This research is the first effort in applying the game
refinement theory to evaluate dialogues. It is neces-
sary to find comfortable values of game refinement
for the dialogue domain as other games shown in Ta-
ble 1. The comfortable values can be seen as the
value’s range of r in Equation (5).
r =
√
G
T
(5)
Where G and T stands for the average numbers
of users’ goals and turns in dialogues, respectively.
Finding the comfortable refinement values for dia-
logues is important when we apply the game refine-
ment measure to evaluate attractiveness of dialogues.
In order to explore the balanced or comfortable game
refinement values in the dialogue domain, we need
further investigations using general data of dialogues
in which a large data set of human-human dialogues
should be analyzed for the game refinement’s param-
eters. This should be conducted in future researches.
4 CONCLUDING REMARKS
To our best knowledge, this is the first result in the di-
rection to develop dialogue systems with entertaining
conversations while benefiting from the game refine-
ment theory. We proposed a method to improve the
current goal-driven dialogue systems which support
users for specific tasks while satisfying users’ goals
with entertaining conversations. We then developed
a dialogue system in which a set of features are con-
sidered to generate entertaining conversations while
reasonably prolonging the original too short dialogue.
Game refinement measure was employed for the as-
sessment of attractiveness since the conversations in
dialogue systems can be seen as the process when a
player creates shoots or moves to win a game. The en-
hanced dialogues generated by the proposed method
are evaluated by human subjects as well as game re-
finement measure. The assessment results confirmed
Towards Developing Dialogue Systems with Entertaining Conversations
517

the effectiveness of the proposed method. The present
idea can be a promising way to realize dialogue sys-
tems with entertaining conversations although further
investigations are needed.
REFERENCES
Ameixa, D., Coheur, L., Fialho, P., and Quaresma, P.
(2014). Luke, i am your father: dealing with out-of-
domain requests by using movies subtitles. In Interna-
tional Conference on Intelligent Virtual Agents, pages
13–21. Springer.
Banchs, R. E. and Li, H. (2012). Iris: a chat-oriented di-
alogue system based on the vector space model. In
Proceedings of the ACL 2012 System Demonstrations,
pages 37–42. Association for Computational Linguis-
tics.
Busemann, S., Declerck, T., Diagne, A. K., Dini, L., Klein,
J., and Schmeier, S. (1997). Natural language dia-
logue service for appointment scheduling agents. In
Proceedings of the fifth conference on Applied natu-
ral language processing, pages 25–32. Association for
Computational Linguistics.
Griol, D., Callejas, Z., and L
´
opez-C
´
ozar, R. (2010). Sta-
tistical dialog management methodologies for real ap-
plications. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual Meeting
of the Special Interest Group on Discourse and Dia-
logue, pages 269–272. Association for Computational
Linguistics.
Henderson, M., Thomson, B., and Young, S. (2014). Word-
based dialog state tracking with recurrent neural net-
works. In Proceedings of the 15th Annual Meeting of
the Special Interest Group on Discourse and Dialogue
(SIGDIAL), pages 292–299.
Iida, H., Takahara, K., Nagashima, J., Kajihara, Y., and
Hashimoto, T. (2004). An application of game-
refinement theory to mah jong. In Entertainment
Computing–ICEC 2004, pages 333–338. Springer.
Ogura, K., Masuda, T., and Ishizaki, M. (2003). Building a
new internet chat system for sharing timing informa-
tion. In Proc. of the 4th SIGDIAL, pages 97–104.
Pieraccini, R., Suendermann, D., Dayanidhi, K., and Lis-
combe, J. (2009). Are we there yet? research in com-
mercial spoken dialog systems. In International Con-
ference on Text, Speech and Dialogue, pages 3–13.
Springer.
Pietquin, O. and Hastie, H. (2013). A survey on metrics
for the evaluation of user simulations. The knowledge
engineering review, 28(01):59–73.
Ritter, A., Cherry, C., and Dolan, W. B. (2011). Data-
driven response generation in social media. In Pro-
ceedings of the conference on empirical methods in
natural language processing, pages 583–593. Associ-
ation for Computational Linguistics.
Seneff, S. and Polifroni, J. (2000). Dialogue management
in the mercury flight reservation system. In Proceed-
ings of the 2000 ANLP/NAACL Workshop on Conver-
sational systems-Volume 3, pages 11–16. Association
for Computational Linguistics.
Shang, L., Lu, Z., and Li, H. (2015). Neural responding
machine for short-text conversation. In Association
for Computational Linguistics, pages 196–205.
Shawar, B. A. and Atwell, E. (2007). Chatbots: are they
really useful? LDV Forum, 22(1):29–49.
Sordoni, A., Galley, M., Auli, M., Brockett, C., Ji, Y.,
Mitchell, M., Nie, J.-Y., Gao, J., and Dolan, B. (2015).
A neural network approach to context-sensitive gen-
eration of conversational responses. In Conference
of the North American Chapter of the Association for
Computational Linguistics, pages 196–205.
Stallard, D. (2000). Talk’n’travel: a conversational system
for air travel planning. In Proceedings of the sixth
conference on Applied natural language processing,
pages 68–75. Association for Computational Linguis-
tics.
Sutiono, A. P., Ramadan, R., Jarukasetporn, P., Takeuchi,
J., Purwarianti, A., and Iida, H. (2015). A mathemat-
ical model of game refinement and its applications to
sports games. EAI Endorsed Trans. Creative Tech-
nologies, 2(5):1–7.
Wallis, P. (2010). A robot in the kitchen. In Proceed-
ings of the 2010 workshop on companionable dia-
logue systems, pages 25–30. Association for Compu-
tational Linguistics.
Weizenbaum, J. (1966). Elizaa computer program for the
study of natural language communication between
man and machine. Communications of the ACM,
9(1):36–45.
Wen, T.-H., Gasic, M., Mrk
ˇ
si
´
c, N., Su, P.-H., Vandyke, D.,
and Young, S. (2015). Semantically conditioned lstm-
based natural language generation for spoken dialogue
systems. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on
Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing,
pages 1711–1721, Lisbon, Portugal. Association for
Computational Linguistics.
Young, S., Gasic, M., Thomson, B., and Williams, J. D.
(2013). Pomdp-based statistical spoken dialog sys-
tems: A review. In IEEE, volume 101, pages 1160–
1179.
ICAART 2017 - 9th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
518
