
A Novel Dictionary Learning based Multiple Instance Learning
Approach to Action Recognition from Videos
Abhinaba Roy
1
, Biplab Banerjee
2
and Vittorio Murino
1
1
Pattern Analysis and Computer Vision, Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Genova, Italy
2
Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, India
{abhinaba.roy, vittorio.murino}@iit.it, bbanfcs@iitr.ac.in
Keywords:
Action Recognition, Multiple Instance Learning, Dictionary Learning, Support Vector Machines.
Abstract:
In this paper we deal with the problem of action recognition from unconstrained videos under the notion of
multiple instance learning (MIL). The traditional MIL paradigm considers the data items as bags of instances
with the constraint that the positive bags contain some class-specific instances whereas the negative bags
consist of instances only from negative classes. A classifier is then further constructed using the bag level
annotations and a distance metric between the bags. However, such an approach is not robust to outliers and
is time consuming for a moderately large dataset. In contrast, we propose a dictionary learning based strategy
to MIL which first identifies class-specific discriminative codewords, and then projects the bag-level instances
into a probabilistic embedding space with respect to the selected codewords. This essentially generates a fixed-
length vector representation of the bags which is specifically dominated by the properties of the class-specific
instances. We introduce a novel exhaustive search strategy using a support vector machine classifier in order to
highlight the class-specific codewords. The standard multiclass classification pipeline is followed henceforth
in the new embedded feature space for the sake of action recognition. We validate the proposed framework
on the challenging KTH and Weizmann datasets, and the results obtained are promising and comparable to
representative techniques from the literature.
1 INTRODUCTION
Action recognition is an active field of research, given
the huge amount of video data captured from diverse
sources and the wide range of applications in domains
such as surveillance, health-care monitoring, robot
navigation, etc. (Poppe, 2010). However, the recog-
nition of human action and activity is a challenging
task given the intra-action variability, problems due to
occlusion and scene clutter, and background effects.
The aforementioned issues necessitate the design of
intelligent machine learning techniques to efficiently
extract informative concepts from the videos in order
to recognize the human actions and activities depicted
in the videos.
The traditional action recognition pipeline is
based on three major stages: 1) extraction of lo-
cal features; 2) dictionary learning followed by fea-
ture encoding, and 3) action classification (Laptev,
2005). Local features including space-time interest
points (Laptev, 2005), dense and improved trajecto-
ries (Wang et al., 2011), optical flow based features
(Brox and Malik, 2011) are very popular since they
highlight local changes in the spatio-temporal do-
main. Alternatively, local feature descriptors are also
pooled to obtain video-level representations (Wang
et al., 2012). In addition to local interest point fea-
ture descriptors, mid-level features in terms of body
parts (Zhou et al., 2015) or deep features (Tran et al.,
2015) are used frequently to discover abstract repre-
sentations from videos. A detailed discussion on dif-
ferent video-based feature extraction techniques (both
shallow and deep features) can be obtained in (Wein-
land et al., 2011) and (Negin and Bremond, 2016).
One inherent problem to the aforementioned ap-
proaches is that it is implicitly very hard to high-
light the discriminative class-specific local descrip-
tors since many of them contain little information re-
garding the underlying semantic classes. Some rank-
ing strategies are generally adopted to highlight such
potentially discriminative local descriptors in order
to build a robust dictionary (Kreutz-Delgado et al.,
2003). However, instead of detecting discriminative
local interest points, another line of research proceeds
with extracting all local descriptors while filtering
out the effects of the un-representative ones during
Roy, A., Banerjee, B. and Murino, V.
A Novel Dictionary Learning based Multiple Instance Learning Approach to Action Recognition from Videos.
DOI: 10.5220/0006200205190526
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2017), pages 519-526
ISBN: 978-989-758-222-6
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
519

learning process. In particular, the Multiple Instance
Learning (MIL) paradigm (Zhou, 2004) assumes the
videos as bags of instances (local descriptors) with-
out being concerned about their discriminative capa-
bilities. However, in the MIL formulation it is re-
quired that a given bag contains at least one class-
specific descriptor. Several MIL paradigms are pro-
posed in the literature including Citation-KNN (Wang
and Zucker, 2000), MISVM (Andrews et al., 2002),
MILBoost (Zhang et al., 2005), which have been ap-
plied in diverse domains like image and video recog-
nition and retrieval (Ali and Shah, 2010). However,
since it is known beforehand that the extracted local
interest point based descriptors from videos may re-
fer to both the positive as well as negative classes, it
is possible to convert the MIL problem into the equiv-
alent discriminative dictionary learning based classi-
fication problem. To this end, first step is performing
a pre-processing stage to highlight the discriminative
codewords, and to further project the bags in an em-
bedding space in such a way that the effects of the
uninteresting bag level instances are reduced to a pos-
sible extent.
Following the above intuition, in this paper we
propose a discriminative dictionary learning based
formulation to the MIL problem for action recog-
nition. Considering videos as bags of local spatio-
temporal feature points, we initially introduce a dis-
criminative codeword learning strategy by exhaus-
tively and randomly exploring the feature space.
Specifically, we employ the multiclass SVM classifier
at the instance (local descriptor) level and mark the in-
stances with high classification scores to be discrimi-
native. We divide the local descriptors of the training
videos into several non-overlapping train-test pairs
and construct the multiclass SVM. Since we know
the class labels of such instances (which are similar
to those of the corresponding videos), it is possible
to validate the results of SVM stage for each train-
test pair. For all such pairs, we select the descrip-
tors in the test sets which lie far from the correspond-
ing SVM hyperplanes and further consider them to
be class-specific. All such potentially effective class-
specific local descriptors are accumulated and further
clustered separately to define the codewords for the
classes. Once we obtain them, the videos (bags) are
subsequently projected in a probabilistic embedding
space with respect to the selected codewords. This
essentially represents each bag as a fixed size feature
vector. We use the Gaussian Radial Basis Function
(RBF) distance measure to find the distance between
the bag level instances and the selected codewords.
As a consequence, the bag level instances which are
closer to the corresponding class level codewords are
assigned higher weight than the ones with little corre-
spondence to that semantic class.
Finally, the multiclass SVM classifier is employed
for the task of action recognition in the new embed-
ding feature space. In contrast to the traditional MIL
based methods which account for the distance be-
tween the bags in a Gram matrix as a distance be-
tween all pairs of the instances, the proposed method
is devoid of such extensive calculations. We can sum-
marize the main contributions of the work as follows:
• We propose a dictionary learning based formula-
tion of the MIL problem and use it for the task of
action recognition from videos.
• We validate the results on the challenging KTH
and Weizmann datasets and observe that the pro-
posed framework sharply outperforms the stan-
dard bag of words based action recognition
pipeline, MISVM and MILBoost based MIL ap-
proaches.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In
section 2 we report a number of related works from
the literature. Section 3 details the proposed action
recognition framework which is followed by the ex-
perimental evaluations in section 4. We conclude the
paper in Section 5 with references to future endeav-
ours that can further be carried out.
2 RELATED WORK
We primarily focus on two complementary aspects of
MIL strategy here and discuss relevant papers from
the literature: the dictionary learning paradigm and
the application of dictionary learning to MIL.
2.1 Dictionary Learning
Dictionary learning strategies can be supervised or
unsupervised in nature. Traditional dictionary learn-
ing techniques are primarily based on vector quantiz-
ing the local features using a sophisticated clustering
technique like k-means. There are several inherent
issues to the dictionary learning problem: the size
of the codebook, the discriminability of the selected
codewords and the clustering technique adopted for
vector quantization. Several publications speak about
methods for handling the aforementioned issues for
tasks including image and video recognition (Jurie
and Triggs, 2005). Apart from the vector quantiza-
tion based approaches, sparse dictionary learning is
also very popular in the computer vision literature.
A class of unsupervised dictionary learning strate-
gies compute over-complete sparse bases consider-
ICPRAM 2017 - 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
520

Figure 1: Work flow of current work done in 4 major steps: 1) Input video is read 2) STIP feature extracted as in (Laptev, 2005)
3) Discriminative dictionary learning 4) Probabilistic feature space embedding (better visible in Fig. 3) 5) Classification.
ing the idea of alternate optimization (Olshausen and
Field, 1997). Such techniques iteratively update the
dictionary components and sparse coefficients for the
input samples using k-SVD and matching pursuit
based methods. (Wang et al., 2010) proposes the LLC
where a locality constraint was added to the loss func-
tion of sparse coding. (Lee et al., 2006) introduces an
l
1
-norm based sparse coding algorithm where feature-
sign search algorithm is applied for encoding and La-
grange dual method for dictionary learning. Effective
sampling strategies for the BoW model is the focus
of discussion in (Nowak et al., 2006) where several
aspects including the codebook size, clustering tech-
niques adopted etc. are exhaustively studied.
On the contrary, the supervised approaches in-
clude the class support in building the dictionary. La-
bel consistent SVD (Jiang et al., 2011), logistic re-
gression based sparse coding (Mairal et al., 2009) ex-
plicitly consider the class discrimination in designing
the sparse bases for dictionary learning. Two different
clustering based approaches for keypoints selection
are introduced in (Lin et al., 2016) for the purpose of
dictionary learning based generic scene recognition.
Distance measures among the keypoints are modelled
in an online fashion to filter out keypoints with low
capability.
2.2 Dictionary Learning based MIL
Approaches
The MIL approaches consider the feature set in a
video as a feature bag and the video label as the bag
label. In order to properly classify the bags, several
distance measures including bag to bag, class to bag
or bag to class (Verma and Jawahar, 2016) are intro-
duced.
The straightforward way to employ MIL for dic-
tionary learning is first to learn a classifier for each
semantic class and further use the classifier to select
positive instances. This is followed by the dictionary
learning stage for encoding the bags. (Sapienza et al.,
2014) proposes an MIL framework which trains one
discriminative classifier for every action category by
mi-SVM algorithm for action detection. In contrast,
M
3
IC formulates a robust maximum margin multiple
instance clustering problem for the MIL task (Zhang
et al., 2009). This paradigm is further extended to
M
4
IC (Zhu et al., 2013) in terms of a two-layer
structure for action recognition to automatically ex-
ploit a mid-level acton representation. These weakly-
supervised actons are learned via a max-margin multi-
channel MIL framework, which can capture multiple
mid-level action concepts simultaneously.
Our framework is closely related to that of (Wang
et al., 2013) and (Li et al., 2016) in the sense
that it employs a cross-validation stage in tagging
the bag level instances as discriminative or non-
discriminative. We, instead, propose a novel random-
ized search strategy to explore the feature space and
highlight potentially discriminative instances in terms
of a multiclass classification. Further, a probabilistic
embedding space is introduced to project the videos
in a new space which is largely dominated by class-
specific instances.
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
As aforementioned, the main objective of this work
is to learn a discriminative dictionary for an MIL
based approach to action recognition from videos. A
key observation in action recognition based on ad-hoc
spatial-temporal interest points is that, not all the ex-
tracted local keypoints possess inherent discrimina-
tive capabilities. Keeping this in mind, our frame-
work is broadly consisted of three stages: Discrimi-
native dictionary learning by concatenating discrimi-
native local descriptors of all the classes; a probabilis-
tic embedding to project the video bags in a new fea-
ture space; multiclass SVM based classification of the
A Novel Dictionary Learning based Multiple Instance Learning Approach to Action Recognition from Videos
521
videos in the new space. A flowchart of the proposed
framework is presented in Fig. 1.
For notional convenience, let us consider that we
are provided with a training set {X
i
, Y
i
}
N
i=1
, where X
i
represents a video (bag) consisting of multiple lo-
cal keypoints and Y
i
= {1, 2, . . . L} denotes the corre-
sponding class label of X
i
. Each X
i
is a bag of N
i
lo-
cal spatio-temporal keypoints X
i
= {x
1
i
, x
2
i
, x
3
i
, . . . , x
N
i
i
}
which are represented by the concatenation of the his-
togram oriented gradients (HOG) and histogram of
optical flow (HOF) histograms (x
j
i
∈ R
162
).
We elaborate the stages in the following.
3.1 Dictionary Learning based
Formulation of MIL
In a normal MIL binary classification setting, each
training sample is a bag containing a number of in-
stances. A bag is positive (label +1) if there is at
least one positive instance otherwise the bag is tagged
as negative one. In the current setup, the STIP key-
points which effectively demarcate a given action
class from the rests are termed positive instances for
a the class. One such positive instances are identified
for all the classes, we initiate a dictionary learning
stage by vector quantizing the instances separately for
all the classes and further model an embedding space
to project the instances of all the videos into a fixed
size vector.
In order to precisely identify them for all the ac-
tion categories, we employ a two-stage framework
as follows. In the first step, we formulate a multi-
class SVM based discriminative codeword selection
framework by randomly exploring the instance space
and further build a class-specific dictionary. Further-
more, we create an embedding of each video based
on the similarity between instances constituting the
video bags and the codewords in the constructed dic-
tionary.
Both the stages are detailed in the following.
3.2 Discriminative Class-specific
Codeword Learning
The discriminative dictionary learning stage is solely
based on randomly exploring the instance space. In
contrast to the previous ranking based approaches for
discriminative codewords selection, we randomly se-
lect a subset of instances from all the classes and train
a multiclass SVM subsequently. Another random dis-
joint subset of instances is selected in order to evalu-
ate the trained SVM. Since , the labels of the instances
is identical to the video label, it is directly possible to
assess the performance of the SVM model.
From the test set of the instances, we separate the
ones residing far from the hyperplane and mark them
to be discriminative. It is reasonable to assume this
since the instances placed closer to the hyperplane are
most likely to be shared by multiple classes and are
thus ambiguous. In addition, as we select the train-
ing and test sets of instances randomly, we can fo-
cus at disjoint areas in the feature space at each run.
This process is iterated a large number of times with
training-test pairs of different sizes and all such po-
tentially discriminative codewords (instances residing
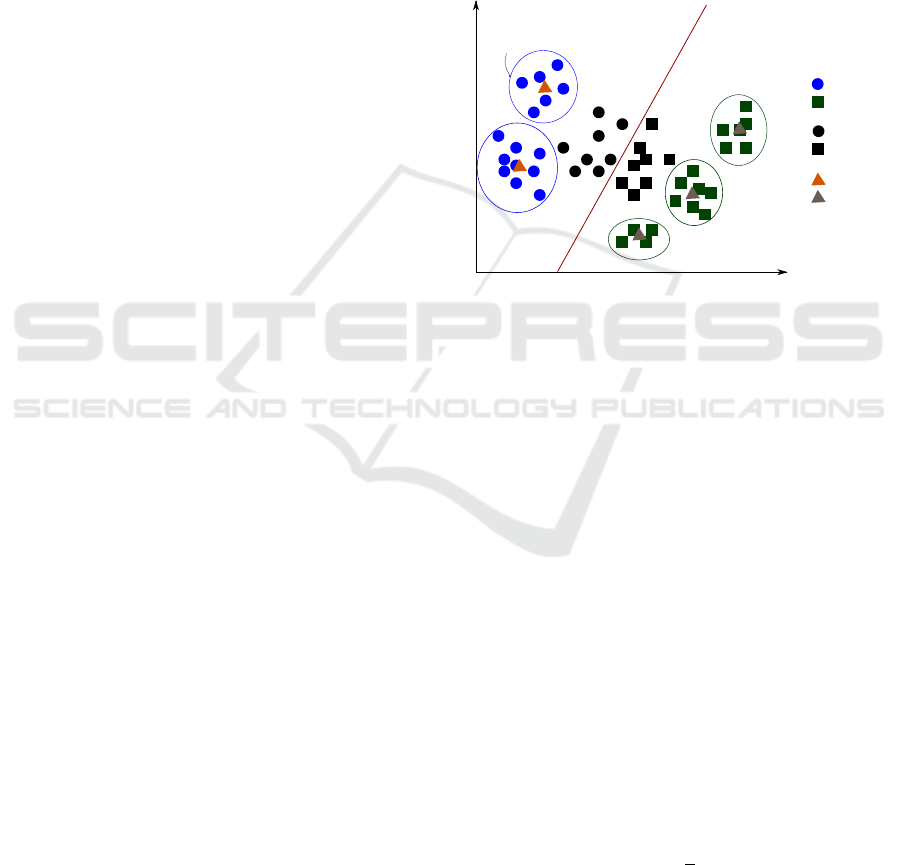
far from the hyperplane) are accumulated (Fig. 2).
Class A
Class B
Cluster of
interest points
Non support
vectors
Support
vectors
Generated
codewords
Figure 2: Example of Discriminative interest point selec-
tion. Non-support vectors, blue points in this case; are more
reliable representatives of their respective classes and their
corresponding regions dominant in that particular class.
Moreover, since instances from a given area in the
feature space are likely to occur multiple times across
videos of same action, it is rhetorical to use all the se-
lected instances from all the videos for building the
dictionary. For practical convenience, we apply a k-
means clustering with a sufficiently large cluster num-
ber on the selected set of potentially discriminative
instances of all the classes identified previously and
the set of cluster centroids are accumulated to formu-
late the final dictionary. let the set of codewords be
denoted as C = {µ
l
}
M
l=1
.
3.3 Probabilistic Embedding from
Constructed Dictionary
The distance (p) between a given instance x
j
i
of the
video bag X
i
to the l
th
is computed in terms of the
Gaussian RBF distance as:
p
jl
i
= exp(−
γ
2
||x
j
i
− µ
l
||
2
2
) (1)
where γ is the hyper-parameter associated with the
RBF kernel. p
jl
i
varies between 0 to 1 and is inversely
proportional to the distance between x
j
i
and µ
l
.
ICPRAM 2017 - 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
522

We calculate the similarities of Equation 1 be-
tween all the instances of the video bag X
i
and the
selected set of codewords. Further, we retrieve an em-
bedding φ
l
i
of X
i
for the l
th
(1 ≤ l ≤ M) dimension by
max-pooling the distance measures between all the in-
stances of X
i
and the l
th
codeword as follows:
φ
l
i
= max
r
(p
jl
i
) (2)
and furthermore φ
i
∈ R
L
represents an embedding
of the video bag X
i
which signifies a vector of all
similarity scores between the instances and the L dis-
criminative codewords. As it can be inferred from
the aforementioned technique for feature embedding,
it is understood that we highlight the best bag level
instance candidates given M codewords in terms of
the similarity measures. Additionally, this guarantees
a fixed size representation of a video irrespective of
number of interest points initially extracted.
Finally, the multiclass dual SVM formulation is
adopted in constructing the classifier in the new em-
bedding space for the sake of action recognition.
(Chang and Lin, 2011).
Ɛ
Ɛ
Ɛ
Ɛ Ɖ Ɖ Ɖ
Ɛ Ɖ Ɖ Ɖ
Ɛ Ɖ Ɖ Ɖ
߶ с
Figure 3: Example of video embedding into concept space:
C
1
, C
2
and C
3
are codewords (concepts). s
1
,s
2
and s
3
are
interest points from a video. Similarities are calculated ac-
cording to equation 1. Column-wise max-pooling operation
gives the embedding φ of the corresponding video.
4 EXPERIMENTS
To establish the empirical validation of out proposed
method, we compare out results on two different chal-
lenging action recognition datasets and compare our
results with other standard MIL techniques.
4.1 Datasets
KTH Dataset. The KTH dataset (Schuldt et al.,
2004) contains 6 types of actions (boxing, hand clap-
ping, hand waving, jogging, running and walking)
performed by 25 subjects in 4 different scenarios in-
cluding indoor, outdoor, changes in clothing and vari-
ations in scale. Each video clip contains one subject
performing a single action. Each subject is captured
in a total of 23 or 24 clips, giving a total of 599 video
clips. Each clip is sampled at 25Hz and lasts between
10 to 15 seconds. Some Example frames are shown
in Fig. 4
1
.
WEIZMANN Dataset. The Weizmann (Blank et al.,
2005) contains 90 video clips from 9 different sub-
jects. Each video clip contains one subject perform-
ing a single action. There are 10 different action cat-
egories: walking, running, jumping, gallop sideways,
bending, one-hand-waving, two-hands-waving, jump-
ing in place, jumping jack, and skipping. Each clip
lasts about 2 seconds at 25 Hz (Fig. 5).
4.2 Experimental Setup
For dictionary learning as well as final action classi-
fication, we use multi class SVM. Matlab toolbox of
standard libSVM (Chang and Lin, 2011) is used. For
all experiments, linear kernel is used with a high value
of parameter C (in the range of 10
2
to 10
5
).
For class-specific codebook generation, we chose
value of fraction of data to selected for validation (α)
in the range of 10
−2
to 10
−4
. This ensures disjoint
selection of training and testing instances as well as
make the process fast. We ran 500 fold cross valida-
tion for KTH and 300 fold cross validation for Weiz-
mann dataset. Number of local codewords are exper-
imentally determined. In this work, 400 class wise
codewords are used for KTH, giving a dictionary of
size 400*6 = 2400 whereas 200 class wise codewords
are used for Weizmann, resulting in a 200*10 = 2000
worded dictionary. It should be noted that
Final multi class SVM classification is carried out
using Leave-One-Out Cross-Validation (LOOCV).
Clips from a single subject in a dataset is used as
the testing data, and the remaining clips as the train-
ing data. This was repeated so that each group of
clips in the dataset is used once as the testing data.
More specifically, for the KTH dataset the clips of
24 subjects were used for training and the clips of
the remaining subject were used for validation. For
the Weizmann dataset, the training set contains 8 sub-
jects. Final results are shown in the next subsection.
4.3 Results
Results are encouraging for both KTH and Weiz-
mann datasets. In particular, we obtain recognition
of 92.1% with KTH and 84.33% with Weizmann.
As pointed out before, codebook sizes are 2400 (400
class-specific codewords from each of the class) for
1
The examples are taken from http://www.nada.kth.se/
cvap/actions/actions.gif
A Novel Dictionary Learning based Multiple Instance Learning Approach to Action Recognition from Videos
523

Figure 4: Example frames from KTH dataset.
Figure 5: Example frames from weizmann dataset.
KTH and 2000 (200 class-specific codewords from
each class) is for Weizmann respectively. These val-
ues were established after empirical cross validation.
In order to validate the worth of our method, we
compare our results with two different types of ap-
proaches. First, We compare with Bag of Word (Bow)
based models with several spatio temporal features,
namely, Dense STIP, HOG, HOF, 3D gradient spa-
tio temporal descriptor ad local spatio temporal vol-
umetric features. We also compare our results with
two standard multi class multi instance learning tech-
niques namely MISVM and MILBoost. Our approach
outperforms all the mentioned works. It is observed
that results with spatio temporal features with BoW
are somewhat comparable with our approach while
the MIL approaches provide are much worse, espe-
cially in case Weizmann data where recognition is
below 50% with both MIL approaches. This is a
strong indication of failure of conventional MIL tech-
niques, with this multitude of interest points and in-
tricate class structure. In a multi class complicated
setting such as this, classes tend to share common
instance subspace amongst themselves and discrim-
inative power of such shared subspaces are naturally
less. A classifier built on direct distance metric be-
tween the bags treats all instances equally in terms
of their discriminative ability and is severely prone to
error due to noise and outliers. Whereas in our ap-
proach we build an initial dictionary based discrim-
inating instances thus minimising the effect of in-
stances in the shared subspace as well as noise and
outliers. Also,distance calculation between bags with
high number of instances is time consuming and ren-
ders these MIL approaches slow. Using a codebook
and the subsequent probabilistic embedding not only
reduces the size of data to be processed immensely
but also makes the process faster. Comparison with
other results are shown in Table 1. Values in each box
indicate the recognition accuracy in percentage (%).
ICPRAM 2017 - 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
524

Table 1: Experimental results.
Method KTH Weizmann
Spatio-temporal
Volume (Liu et al.,
2008)
- 68.4
Dense STIP
(HOG+HOF)
(Wang et al., 2009)
86.1 -
HOG (Laptev et al.,
2008)
81.6 -
HOF (Laptev et al.,
2008)
89.7 -
3D gradient spatio
temporal descriptor
+ BoW (Klaser
et al., 2008)
91.8 84.3
MISVM (Andrews
et al., 2002)
72 41.2
MILBoost (Zhang
et al., 2005)
64.7 35.3
Our method 92.1 84.33
5 CONCLUSIONS
We propose a dictionary learning based MIL
paradigm for the purpose of action recognition from
videos in this paper. In contrast to the traditional MIL
framework which consider the presence of some pos-
itive instances in the positive bag and the absence
of the same in the negative ones, we propose a two
stage algorithm which first identifies discriminative
class-specific local features using a randomized ex-
haustive search strategy. Based on the selected set of
effective codewords, we project the videos (bags) in
a probabilistic embedding space. The standard clas-
sification paradigm is followed henceafter using for
action recognition. We introduce a novel SVM based
cross-validation technique to identify the discrimina-
tive keypoints which reduces the bias substantially.
Our class-specific discriminative local feature selec-
tion uses a randomized SVM approach, which, in
contrast to the usual vector quantization method, can
handle both convex and non-convex classes. Further,
the use of an embedding space highlights the effects
of class-specific instances and attenuates the non-
interesting keypoints from further processing. We
obtain enhanced classification performance with the
proposed paradigm in comparison to the standard dic-
tionary learning based action recognition strategy and
two standard MIL strategies for the KTH and Weiz-
mann datasets. We further plan to extend the proposed
framework by introducing efficient bag level distance
measures in building the kernel matrix for bag classi-
fication.
REFERENCES
Ali, S. and Shah, M. (2010). Human action recognition in
videos using kinematic features and multiple instance
learning. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and
machine intelligence, 32(2):288–303.
Andrews, S., Tsochantaridis, I., and Hofmann, T. (2002).
Support vector machines for multiple-instance learn-
ing. In Advances in neural information processing
systems, pages 561–568.
Blank, M., Gorelick, L., Shechtman, E., Irani, M., and
Basri, R. (2005). Actions as space-time shapes. In
Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer
Vision (ICCV’05) Volume 1, volume 2, pages 1395–
1402. IEEE.
Brox, T. and Malik, J. (2011). Large displacement optical
flow: descriptor matching in variational motion esti-
mation. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and
machine intelligence, 33(3):500–513.
Chang, C.-C. and Lin, C.-J. (2011). Libsvm: a library for
support vector machines. ACM Transactions on Intel-
ligent Systems and Technology (TIST), 2(3):27.
Jiang, Z., Lin, Z., and Davis, L. S. (2011). Learning
a discriminative dictionary for sparse coding via la-
bel consistent k-svd. In Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition (CVPR), 2011 IEEE Conference on,
pages 1697–1704. IEEE.
Jurie, F. and Triggs, B. (2005). Creating efficient codebooks
for visual recognition. In Tenth IEEE International
Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’05) Volume 1,
volume 1, pages 604–610. IEEE.
Klaser, A., Marszałek, M., and Schmid, C. (2008). A spatio-
temporal descriptor based on 3d-gradients. In BMVC
2008-19th British Machine Vision Conference, pages
275–1. British Machine Vision Association.
Kreutz-Delgado, K., Murray, J. F., Rao, B. D., Engan, K.,
Lee, T.-W., and Sejnowski, T. J. (2003). Dictionary
learning algorithms for sparse representation. Neural
computation, 15(2):349–396.
Laptev, I. (2005). On space-time interest points. Interna-
tional Journal of Computer Vision, 64(2-3):107–123.
Laptev, I., Marszalek, M., Schmid, C., and Rozenfeld,
B. (2008). Learning realistic human actions from
movies. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
2008. CVPR 2008. IEEE Conference on, pages 1–8.
IEEE.
Lee, H., Battle, A., Raina, R., and Ng, A. Y. (2006). Effi-
cient sparse coding algorithms. In Advances in neural
information processing systems, pages 801–808.
Li, H., Chen, J., Xu, Z., Chen, H., and Hu, R. (2016). Multi-
ple instance discriminative dictionary learning for ac-
tion recognition. In 2016 IEEE International Con-
ference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing
(ICASSP), pages 2014–2018. IEEE.
A Novel Dictionary Learning based Multiple Instance Learning Approach to Action Recognition from Videos
525

Lin, W.-C., Tsai, C.-F., Chen, Z.-Y., and Ke, S.-W. (2016).
Keypoint selection for efficient bag-of-words feature
generation and effective image classification. Infor-
mation Sciences, 329:33–51.
Liu, J., Ali, S., and Shah, M. (2008). Recognizing human
actions using multiple features. In Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition, 2008. CVPR 2008. IEEE
Conference on, pages 1–8. IEEE.
Mairal, J., Ponce, J., Sapiro, G., Zisserman, A., and Bach,
F. R. (2009). Supervised dictionary learning. In
Advances in neural information processing systems,
pages 1033–1040.
Negin, F. and Bremond, F. (2016). Human action recogni-
tion in videos: A survey.
Nowak, E., Jurie, F., and Triggs, B. (2006). Sampling strate-
gies for bag-of-features image classification. In Euro-
pean conference on computer vision, pages 490–503.
Springer.
Olshausen, B. A. and Field, D. J. (1997). Sparse coding
with an overcomplete basis set: A strategy employed
by v1? Vision research, 37(23):3311–3325.
Poppe, R. (2010). A survey on vision-based human action
recognition. Image and vision computing, 28(6):976–
990.
Sapienza, M., Cuzzolin, F., and Torr, P. H. (2014). Learning
discriminative space–time action parts from weakly
labelled videos. International Journal of Computer
Vision, 110(1):30–47.
Schuldt, C., Laptev, I., and Caputo, B. (2004). Recogniz-
ing human actions: a local svm approach. In Pat-
tern Recognition, 2004. ICPR 2004. Proceedings of
the 17th International Conference on, volume 3, pages
32–36. IEEE.
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., and Paluri,
M. (2015). Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d
convolutional networks. In 2015 IEEE International
Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pages 4489–
4497. IEEE.
Verma, Y. and Jawahar, C. (2016). A robust distance with
correlated metric learning for multi-instance multi-
label data. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM on Multi-
media Conference, pages 441–445. ACM.
Wang, H., Kl
¨
aser, A., Schmid, C., and Liu, C.-L. (2011).
Action recognition by dense trajectories. In Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2011 IEEE
Conference on, pages 3169–3176. IEEE.
Wang, H., Ullah, M. M., Klaser, A., Laptev, I., and Schmid,
C. (2009). Evaluation of local spatio-temporal fea-
tures for action recognition. In BMVC 2009-British
Machine Vision Conference, pages 124–1. BMVA
Press.
Wang, J., Yang, J., Yu, K., Lv, F., Huang, T., and Gong,
Y. (2010). Locality-constrained linear coding for
image classification. In Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition (CVPR), 2010 IEEE Conference on,
pages 3360–3367. IEEE.
Wang, J. and Zucker, J.-D. (2000). Solving multiple-
instance problem: A lazy learning approach.
Wang, X., Wang, B., Bai, X., Liu, W., and Tu, Z. (2013).
Max-margin multiple-instance dictionary learning. In
ICML (3), pages 846–854.
Wang, X., Wang, L., and Qiao, Y. (2012). A comparative
study of encoding, pooling and normalization meth-
ods for action recognition. In Asian Conference on
Computer Vision, pages 572–585. Springer.
Weinland, D., Ronfard, R., and Boyer, E. (2011). A sur-
vey of vision-based methods for action representation,
segmentation and recognition. Computer vision and
image understanding, 115(2):224–241.
Zhang, C., Platt, J. C., and Viola, P. A. (2005). Multiple
instance boosting for object detection. In Advances in
neural information processing systems, pages 1417–
1424.
Zhang, D., Wang, F., Si, L., and Li, T. (2009). M3ic: Max-
imum margin multiple instance clustering. In IJCAI,
volume 9, pages 1339–1344.
Zhou, Y., Ni, B., Hong, R., Wang, M., and Tian, Q. (2015).
Interaction part mining: A mid-level approach for
fine-grained action recognition. In Proceedings of
the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, pages 3323–3331.
Zhou, Z.-H. (2004). Multi-instance learning: A survey. De-
partment of Computer Science & Technology, Nanjing
University, Tech. Rep.
Zhu, J., Wang, B., Yang, X., Zhang, W., and Tu, Z. (2013).
Action recognition with actons. In Proceedings of the
IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision,
pages 3559–3566.
ICPRAM 2017 - 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
526
