
MP-ABT: A Minimal Perturbation Approach for Complex Local
Problems
Ghizlane El Khattabi
1
, El Mehdi El Graoui
1
, Imade Benelallam
1,2
and El Houssine Bouyakhf
1
1
LIMIARF, Faculty of Sciences, Mohammed V University, Agdal, Rabat, Morocco
2
INSEA, National Institute of Statistics and Applied Economic, Irfane, Rabat, Morocco
Keywords:
Multi Agent System, Distributed Constraint Satisfaction Problem, Complex Local Problem, Minimal
Perturbation Problem.
Abstract:
The ability of Distributed Constraints Reasoning (DCR) to solve distributed combinatorial problems brings the
DCR to have a considerable interest in multi-agent community. Hence, many DisCSP algorithms have been
proposed in order to solve such distributed problems. The major limit of these algorithms is the simplification
assumptions. The scientists assume that each agent is a simple one; it handles just one variable. But in
the complex local problem case; where each agent has more than one variable; two methods are used: The
compilation and the decomposition. These methods transform the original problem so as to make it as a simple
one. In this paper, we propose a new protocol: MP-ABT (Minimal Perturbation complex local problems in the
Asynchronous Backtracking). It is a resolution algorithm of DisCSPs with complex local problems. It is based
on the ABT algorithm and the Dynamic CSP. Each complex agent is seen as a Minimal Perturbation Problem
(MPP) and any received message is considered as a new intra-constraint perturbation event. The complex local
problem is updated and a new MPP local solution is reported. The MP-ABT is presented and compared to
three ABT families. Our experimental results show the MP-ABT effectiveness.
1 INTRODUCTION
The growing interest in Distributed Constraint Reaso-
ning (DCR)(Yokoo et al., 1992) has prompted resear-
chers to propose several distributed approaches, whit-
her the global problem is naturally distributed among
agents. These agents have to communicate in order
to revise their local solutions. The distributed Con-
straint Satisfaction Problem formalism (DisCSP) has
been, widely, used in this context.
The DisCSP can be formalized as: a set of agents,
a set of variables, a set of intra-agent constraint (con-
straints that link two variables of the same agent) and
inter-agent constraints (constraints that link two va-
riables of two different agents) and a function that
associates each variable an agent. Several resolution
algorithms have been developed. The pioneer appro-
aches are : Asynchronous Backtracking (ABT) (Yo-
koo et al., 1992), Asynchronous Forward Checking
(AFC) (Meisels and Zivan, 2007) and Nogood-Based
Asynchronous Forward Checking (AFC-ng) (Wahbi
et al., 2013). Authors often concentrate on simplifi-
cation assumptions; where each agent owns only one
variable. They assume that the existing algorithms are
easily extended to the most general case. Although,
this is not completely true, because ignoring local re-
solution strategy can lead to a global costly resolution.
However, managing the trade off between com-
plex local problems and distributed search effort can
give a way to great improvements. There are several
real complex local problems that can benefit from this
trade off strategy, as the meeting scheduling problem,
the road traffic and the multi-robot exploration.
In the literature, several techniques have been pro-
posed. They reformulate the complex local CSP pro-
blems, so that there is exactly one variable per agent.
The two most known approaches are: (i) Compilation
that defines, for each complex agent, a single new ab-
stract variable whose domain is the set of solutions to
local CSP problem. Hence, to find the whole soluti-
ons set will be impossible, once granularity of local
problems becomes larger. However, this method is
used by a few number of researchers as the ABT-cf
(Ezzahir et al., 2007; Ezzahir et al., 2008). (ii) De-
composition that creates a virtual agent, for each vari-
able, in order to manage its domain. Several methods
have used this method, as the multi-AWC (Yokoo,
1995), the Multiple local variables Distributed Bre-
268
El Khattabi G., El Graoui E., Benelallam I. and Bouyakhf E.
MP-ABT: A Minimal Perturbation Approach for Complex Local Problems.
DOI: 10.5220/0006203502680275
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2017), pages 268-275
ISBN: 978-989-758-219-6
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

akout (Multi-DB (Hirayama and Yokoo, 2002)) and
the Multi Dynamic Priorisation with Penalties algo-
rithm (Multi-DynApp) (Magaji et al., 2014). The big
issue that arises with this method is the loss of the cen-
tralization nature of the local problems, and several
additional messages, that have not to be exchanged
locally.
In (Burke and Brown, 2006), the authors propo-
sed some improvements to the compilation method
of Yokoo (compilation). It is based on the interchan-
geability principle; the external variables (i.e., varia-
bles that are constrained with other agents) in a lo-
cal problem are the only variables that have a direct
effect on the resolution process; by: (i) removing
interchangeable solutions from the new constructed
domain and (ii) identifying interchangeable solutions
by considering the inter-agent constraints, in order to
speed up the search. In (Ezzahir et al., 2007; Ezza-
hir et al., 2008), the authors present the ABT-cf algo-
rithm (ABT with compilation formulation), that con-
sists of integrating the compilation formulation and
the interchangeability in the ABT algorithm. These
methods (i.e., compilation, decomposition and com-
pilation with interchangeability) are not suitable in the
context of a realistic use. This is due to the load of
extra messages when using the decomposition formu-
lation and to the computational run time in the context
of the compilation.
Our contribution is focused on how to choose the
local solutions, after receiving a new message. Howe-
ver, a carefully chosen solution may allow neighbor
agents to avoid unnecessary messages. Whereas, if
each new solution is totally different from the previ-
ous one, then an avalanche batch of messages may be
generated. So, in this paper, we propose a new al-
gorithm, named MP-ABT, that improves the original
ABT in the context of complex local problems. MP-
ABT keeps the centralized nature of the local pro-
blems, without having neither to compile solutions,
nor to decompose variables. It is based on Minimal
Perturbation Problem formalism (MPP). When a new
solution is needed, it looks for an optimal solution to
the newly generated CSP, that it is as close as possible
to the former complex local problem solution.
Inspiring from reality, each agent is seen as an
MPP problem. It considers each received message
as a new constraint perturbation of its complex local
problem. Afterward, the agent has not to prepare any
solution beforehand. It reacts in real time. It looks
for the nearest solution to its former assignment (the
solution that satisfies all new constraints and minimi-
zes the number of changed values). In the MP-ABT
algorithm, we use the HS-MPP approach locally (as
an MPP algorithm), in order to reduce the number of
changed local variables, hence the number of distur-
bed neighbor agents.
In the following, we present the Asynchronous
Backtracking ABT (Section 2.1), The Hybrid Search
for Minimal Perturbation Problems HS-MPP (Section
2.2), then we describe the MP-ABT algorithm and
show some properties of this new algorithm (Section
3). And then, in order to better understand the MP-
ABT algorithm, we apply it on a simple example. Fi-
nally, we show experiment results that illustrate the
efficiency of our newly developed algorithm (Section
5).
2 BASIC ALGORITHMS
2.1 Asynchronous Backtracking
The Asynchronous Backtracking algorithm (ABT)
was developed by Yokoo et al. in (Bessi
`
ere et al.,
2005). Yet, in this communication protocol, the pro-
blem is solved asynchronously, by each agent. The
priority order of the agents is set alphabetically. In
general it is put alphabetically (i.e., A
i
is higher prio-
rity than A
j
if i < j). The inter-agent constraints are
directed from higher priority agents to the lower pri-
ority agents. Each agent stores the variable assign-
ments of other agents (higher priority agent assign-
ments) in the AgentView structure, and the conflicts
(nogoods) of low priority agents in the NogoodStore
structure.
When the protocol starts, each agent attributes a
value to its variable and sends it to the lower prio-
rity agents Γ
+
(sel f ) via OK? messages. After re-
ceiving a new OK? message, the receiver has to up-
date its AgentView and NogoodStore (by storing the
new assignments and removing the incoherent no-
goods), then it has to check the consistency of its
value with the AgentView. If it is inconsistent, self
should look for a new consistent value. But if self
can not find a consistent value, it generates a new no-
good (that contains the assignments of higher priority
agents Γ
−
(sel f ), saying that this assignments subset
can not be a part of a global solution) and sends a no-
good message to the low priority agent (backtrack).
A nogood ngd contains two sides. The left hand side
lhs(ngd) is a conjunction of values chosen by the hig-
hest priority agents. The right hand side rhs(ngd)
contains the assignment of the lowest priority agent.
The set of values that form the nogood constitute the
partial assignment that can not be part of the global
affection (i.e., the problem solution). When a nogood
is sent to the lowest agent (i.e., the owner of the as-
signment that exists in the rhs of the nogood), that
MP-ABT: A Minimal Perturbation Approach for Complex Local Problems
269

means that as long as the higher priority agents do not
change the values which exist in the lhs, the receiver
can not choose the value that exists in the rhs of the
nogood.
When an agent receives a nogood message, it has
to store it in its NogoodStore, and return a new value
that is unremoved by the NogoodStore and is consis-
tent with the AgentView. If the nogood contains va-
lues of agents that are not constrained with the nogood
message receiver (i.e., they do not exist in Γ
−
(sel f )),
it requests them via AddLink messages. The latter,
should add a new link with self (adl), aiming to in-
form self by their assignments, whenever they change
their values. After receipt of either an OK? mes-
sage or a nogood message. If this message requires
a change of its value, the ABT agent chooses its value
by browsing its domain sequentially. If the reviewed
value is inconsistent with its AgentView, it creates a
nogood to be stored in its NogoodStore, and spends
to the next value. A value is selected if it is consistent
with the AgentView and not removed by its Nogood-
Store. If it does not find a consistent value, it creates a
new nogood, by solving the nogoods which exist in its
NogoodStore. The algorithm is made up to solve sim-
ple problems, where each agent possesses just one va-
riable. But in the complex case, where agents handle
multiple variables, it assumes to do a simple transfor-
mation either with the compilation or the decompo-
sition. For each complex local CSP, the compilation
creates a new abstract variable whose domain is the
set of all the local solutions. The decomposition cre-
ates, for each variable, a virtual agent.
2.2 Hybrid Search for Minimal
Perturbation Problems
The Hybrid Search for Minimal Perturbation Pro-
blems (HS-MPP) (Zivan et al., 2011; EL Graoui et al.,
2016) is an approach that solves minimal perturbation
problems (MPPs).
MPP. A Minimal Perturbation Problem (MPP) is a
solved CSP problem that is altered. Where the main
task is to find a new solution in such a way that this
latter does not differ much from the solution of the
original CSP. The MPP can be formulated as a CSP
P, an initial solution S
1
of P and a distance function f
defining the distance between any two assignments. A
solution of an MPP problem is a solution S
2
, such that
the distance f (S
1
, S
2
) between S
1
and S
2
is minimal.
The HS-MPP method aims to minimize the Ham-
ming distance as a distance function.
Hamming distance. The hamming distance is a
mathematical concept that computes the number of
positions where two entities, with the same length,
differ. In our case, on two different assignments of
the same local problem (i.e., the same agent), this
measure computes the number of positions where the
variable values differ. For example, a local problem
of an agent Ai, with three local variables X
i.1
, X
i.2
,
and X
i.3
, had an initial solution S
1
= {X
i.1
= 1, X
i.2
=
1, X
i.3
= 1}. After a constraint modification, the solu-
tion becomes S
2
= {X
i.1
= 1, X
i.2
= 2, X
i.3
= 2}. So,
the Hamming distance of S
1
and S
2
is equal to 2.
The HS-MPP algorithm takes variables, domains,
constraints and the previous solution as parameters,
and returns a closest solution or an empty one, saying
that there is no solution to this MPP problem.
3 MP-ABT
3.1 Description of the Algorithm
The main contribution of MP-ABT is highlighted
when an agent receives a new Ok? or Nogood mes-
sage. In the ABT algorithm, if such message requires
a new assignment, the receiver chooses a consistent
local solution randomly. This assignment is chosen
without considering the former local solution. In this
approach, the MPP formalism is used in order to be-
nefit from the former solution, to minimize the local
perturbations and to reduce the number of disturbed
neighbor agents.
The MP-ABT merges the Asynchronous Back-
tracking algorithm ABT, and the Hybrid Search for
Minimal Perturbation Problems algorithm HS-MPP.
This algorithm extends the ABT algorithm, in order
to tackle DisCSPs with complex local problems, with
less perturbations. The idea is to consider each lo-
cal complex problem as an MPP problem and each
new received message as a new constraint perturba-
tion. The aim is to find a new solution that is as close
as possible to the former solution.
The local search of ABT can not be directly repla-
ced by the HS-MPP approach. Because in the local
search of the ABT protocol, the ABT agent stores no-
goods during the search of a local consistent solution.
So, if it can not find a consistent local solution, it has
justifications to create a new nogood. But in the case
of HS-MPP, the local consistent value is searched in
a single execution. Therefore, if the returned value is
empty (i.e., there is no consistent local solution), the
agent has no justifications to construct the nogood.
That is why, we have to make several modifications
to the original pseudo code of ABT. In the following,
ICAART 2017 - 9th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
270

Algorithm 1: MP-ABT algorithm.
1: procedure MP-ABT myvalue ← empty;
2: end ← false;
3: CheckAgentView();
4: while ¬end do
5: msg ← getMsg();
6: Switch (msg.type)
7: Ok? : ProcessInfo(msg);
8: ngd : ResolveConflict(msg);
9: stp : end ← true;
10: Adl : SetLink(msg);
11: end while
12: end procedure
13: function CHOOSEVALUE(VariableDomains, NO-
GOODSTORE)
14: if (one of VariableDomains is empty) then
return empty
15: end if
16: Create a MPP problem with the same variables of
the initial local problem;
17: Attribute VariableDomains to the variables;
18: Add the non redundant rhs(nogood) of the Nogood-
Store as a not equal constraint of the MPP problem;
return MPP.getSolution
19: end function
20: procedure UPDATE(myAgentView, newAssig)
21: add(newAssig, myAgentView);
22: for { each ng ∈ myNogoodStore} do
23: if (¬Coherent(lhs(ng), myAgentView)) then
24: remove(ng, myNogoodStore);
25: end if
26: end for
27: for {each ng ∈ Justi fications} do
28: if (¬Coherent(lhs(ng), myAgentView)) then
29: remove(ng, Justifications);
30: if (rhs(ng) is not removed by a nogood in
Justi f ications ) then
31: restore rhs(ng).value to the
currentDomains;
32: end if
33: end if
34: end for
35: for each local variable do
36: Remove inconsistent values from
currentDomain;
37: Add a nogood in justi f ications for each remo-
ved value;
38: end for
39: end procedure
we are going to describe how the MP-ABT algorithm
is running. The Algorithm 1 provides the procedu-
res and functions executed by each MP-ABT agent,
that do not exist in the ABT pseudo code, or they are
changed.
As the ABT agent, each MP-ABT agent assigns
values to its variables, sends them to the correspon-
40: procedure BACKTRACK
41: newNogood ← solve(myNogoodStore ∪
Justi f ications);
42: if newNogood = empty then
43: end ← true;
44: sendMsg: stp (system);
45: else
46: sendMsg:ngd(newNogood);
47: Update (myAgentView, rhs(newNogood) ←
unknown);
48: CheckAgentView();
49: end if
50: end procedure
ding agents, and then switches to the listening posi-
tion, in order to respond to incoming messages (ABT
pseudo-code (Bessi
`
ere et al., 2005)).
After the reception of an Ok? message, for each
local variable of its local problem, the receiver fil-
ters the variables domains. it removes all values that
are inconsistent with sender values from the variable
domain. For each filtered value, it adds a nogood to its
’Justifications’ structure (Update procedure, line 89).
This structure contains the deleted value and the vari-
able that cause this value removal. The resulting no-
good contains a shorter partial assignment that causes
the inconsistency, and not the whole assignment of
the local problem. Hence it enjoys the benefits of the
interchangeability to speed up the resolution process.
During the filtering process, the agent tests the whole
domain even if, it may contain values that are already
deleted. These redundant justifications aim to save all
suppression causes of each value. Foremost, self up-
dates the ’Justifications’ and NogoodStore structures,
by removing the nogoods that become obsolete (Up-
date procedure, lines 76 and 81). Then, it restores va-
lues to the variables domains (Update procedure, line
83). A value is restored to its domain if and only if all
the corresponding justifications are removed (Update
procedure, line 82). Finally, it chooses a new local
solution (ChooseValue procedure).
For this, it follows the succeeding steps:
- It checks if there is an empty filtered domain (line
66).
- If so, it returns an empty value, in order to send a
nogood message, without looking for a new local
solution.
- Otherwise, it declares a new MPP problem. The
latter contains its local problem variables which
are defined on their new corresponding filtered
domains, its local constraints (intra-agent con-
straints), and then it adds the valid nogoods, that
are compatible with the other agent value, which
MP-ABT: A Minimal Perturbation Approach for Complex Local Problems
271
exist in its NogoodStore as new constraints (lines
68, 69 and 70).
- Finally, it looks for a new closest solution to its
current solution, using the HS-MPP algorithm.
- If it finds a new solution, it will send this so-
lution to the corresponding agents (CheckAgent-
View procedure).
- Otherwise, it generates a new nogood, using the
stored justifications and the received nogoods
(Backtrack procedure, line 55).
After the reception of a nogood message, the agent
stores it in its NogoodStore, and chooses a new closest
solution, using the same manner described previously.
3.2 MP-ABT Properties
The MP-ABT has the same properties as the ABT:
soundness, completeness and termination.
MP-ABT is sound.
Proof: Since the local search of ABT is replaced
by the MPP approach in MP-ABT. The only risk
that may cause the unsoundness of MP-ABT is that
it will has no way to record the deletion reasons of
each local solution. But as it records justifications
during the filtering operation, therefore it remains
also sound, as the ABT algorithm.
MP-ABT is complete.
Proof: The MP-ABT uses the filtered domain, the
existing intra-agent constraints and the valid received
nogoods as inputs to the MPP algorithm. Since the
HS-MPP algorithm is sound, the returned solution
will satisfy all constraints (the original constraints,
and the received nogoods). So the local solution
of each agent, satisfy its inter-agent and intra-agent
constraints. Then the algorithm is complete.
MP-ABT can always terminate.
Proof: The filtering process speeds up the search,
and can never be trapped in an infinite loop, since the
domains are finite. In addition, since the HS-MPP
algorithm finds the solution in a limited time, so the
whole problem can be solved also in a finite time. On
the contrary, it speeds up the search, because it gives
the local decision in just one loop, without doing the
compilation nor the decomposition process.
4 EXAMPLE
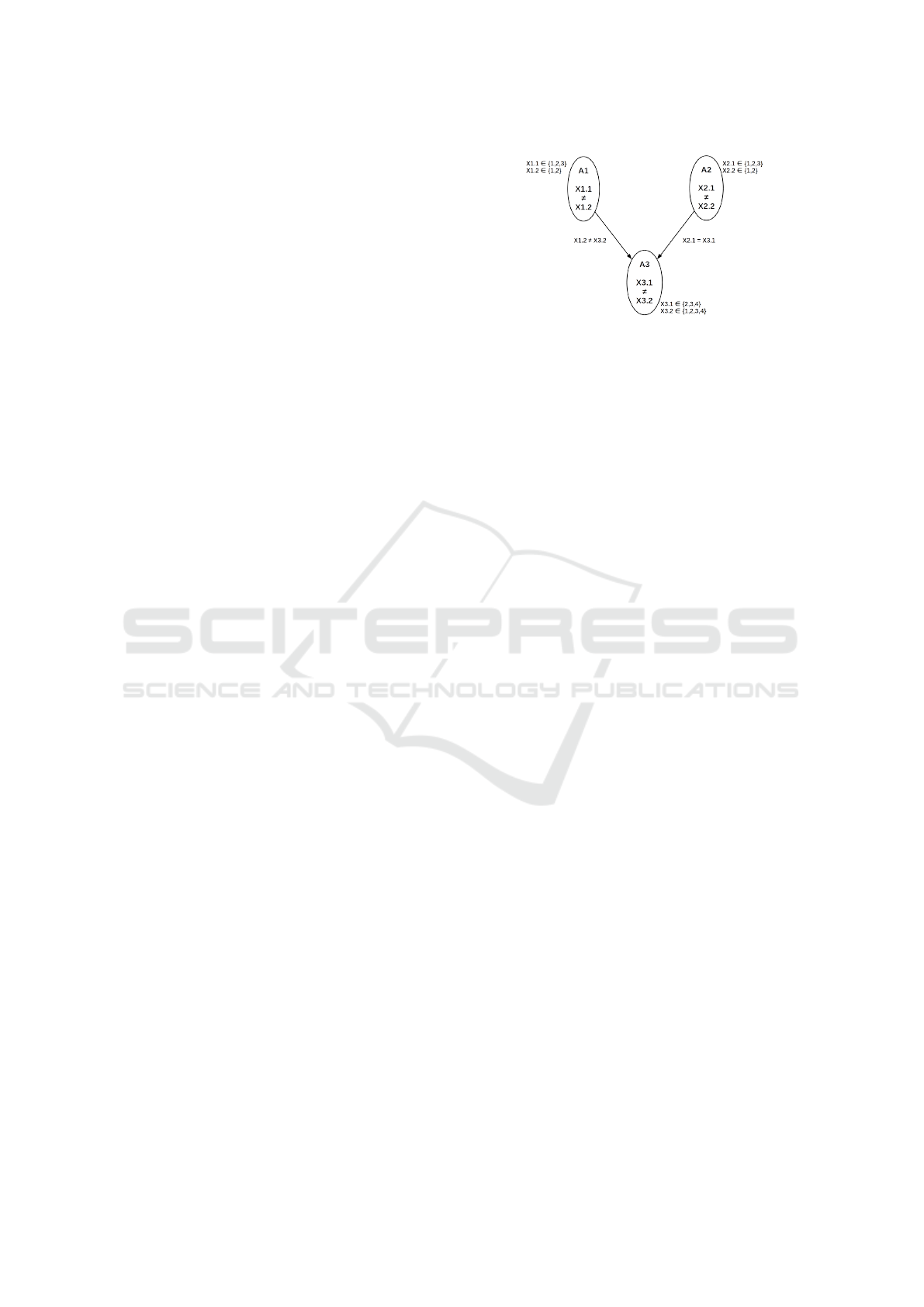
The figure 1 illustrates a complex DisCSP example
containing three agents A
1
, A
2
and A
3
, and two va-
Figure 1: Example of DisCSP with complex local problems.
riable per agent: X
1.1
, X
1.2
, X
2.1
, X
2.2
, X
3.1
and X
3.2
.
The domains of variables are D(X
1.1
) = D(X
2.1
) =
{1, 2, 3}, D(X
1.2
) = D(X
2.2
) = {1, 2}, D(X
3.1
) =
{2, 3, 4}, and D(X
3.2
) = {1, 2, 3, 4}. The intra-agent
constraint is the not equal constraint (all local vari-
ables should be not equal) and the inter-agent con-
straints are X
1.2
6= X
3.2
and X
2.1
= X
3.1
. We assume
that the priority order of agents is lexicographic (A
1
>
A
2
> A
3
).
When the MP-ABT protocol starts, each agent
chooses its first assignment and communicates it to
the lower priority agents. Agents A
1
and A
2
choose
the values (1, 2) (i.e., the first variable is equal to 1
and the second is equal to 2), and send OK? messa-
ges, carrying its affectations, to the Agent A
3
. Af-
ter receiving the OK? message from A
1
, the agent A
3
stores the received values in its AgentView, removes
inconsistent values from its domains and stores a jus-
tification for each removed value. It deletes the va-
lue 2 from the X
3.2
domain (because X
1.2
= 2 and
X
1.2
6= X
3.2
), adds the nogood X
1.2
= 2 → X
3.2
6= 2
as a deletion justification to its ’Justifications’ struc-
ture, and checks if its values remain consistent. the
assignment (1, 2) still consistent, so A
3
switches to
the listening state. When A
3
receives the second OK?
message from A
2
, it does the same treatment. It up-
dates its AgentView with the received values, deletes
the values 2, 3, and 4 from the X
3.1
domain (because
X
2.1
= 1 and X
2.1
= X
3.1
). So, the domains become:
D(X
3.1
) = {
/
0}, and D(X
3.2
) = {1, 3, 4}. In the ot-
her hand, it adds these nogoods to its ’Justifications’
structure X
2.1
= 1 → X
3.1
6= 2, X
2.1
= 1 → X
3.1
6= 3,
and X
2.1
= 1 → X
3.1
6= 4. A
3
finds that the X
3.1
dom-
ain is empty, so it sends a nogood
/
0 → X
2.1
6= 1 to
A
2
.
After receiving the nogood message, A
2
stores it
in its NogoodStore. It creates a new MPP problem
whose variables are its local variables (X
2.1
∈ {1, 2, 3}
and X
2.2
∈ {1, 2}) and constraints are X 2.1 6= X2.3
and X2.1 6= 1; the second constraint is taken from
the nogood that exists in the A
2
NogoodStore; retrie-
ves the HS-MPP local solution (3, 2), which is clo-
ICAART 2017 - 9th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
272

sest to its current solution (1, 2), and sends it to the
agent A
3
via an OK? message. A
3
removes the no-
goods from its ’Justifications’ structure, because they
become obsolete, and restores the values 2, 3, and 4 to
the D(X
3.1
). Then it filters out the values 2 and 4 from
D(X
3.1
), and stores the nogoods X2.1 = 3 → X 3.1 6= 2
and X2.1 = 3 → X 3.1 6= 4 in the ’Justifications’ struc-
ture. The current values (2, 1) of A
3
does not re-
main valid, so A
3
generates a new MPP problem with
X
3.1
∈ {3}, X
3.2
∈ {1, 3, 4}, and X
3.1
6= X
3.2
. The retur-
ned local solution by the HS-MPP approach is (3, 1).
We saw, by this example, one of the advantages
of the MP-ABT, that is the nogood content, which is
very pointed. It allows to know the real cause of a
conflict and to implicate the responsible variable. Not
just the responsible agent, as is done in the ABT al-
gorithm.
Note that, even the filtering process, helps to de-
tect the conflict without the need of looking for a new
solution.
Finally, if the variable X
2.2
of the agent A
2
was
constrained with other external variables, A
2
will not
disrupt the other agents. The same thing with the vari-
able X
3.2
of the agent A
3
. So we minimize the number
of the global perturbation, by minimizing it locally.
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
In this section, we evaluate the performance of our
new algorithm MP-ABT, by comparing it with the
algorithms: ABT-comp, the ABT-decomp, and the
ABT-cf. The checked constraints during the compi-
lation and the decomposition are also computed.
In the ABT-comp algorithm, each agent searches
all its local problem solutions, prepares its new dom-
ain, that contains the found solutions in the compila-
tion process and starts the ABT protocol, considering
each agent as a simple one (i.e., that has just one local
variable).
The ABT-decomp agent creates a virtual agent, for
each local variable. The original problem will be dis-
tributed between the created agents. So the problem
becomes simple, and ABT algorithm is applied.
The ABT-cf is an extension of ABT-comp. Af-
ter preparing the new domain (using the compilation),
The ABT-cf agent applies the interchangeability prin-
ciple in order to remove interchangeable solutions,
and speed up the search, by considering the inter-
agent constraints.
The algorithms are evaluated on Random Com-
plex DisCSPs. The assessment is made against
the number of exchanged messages (# MSGs) that
measures the number of the perturbations and the
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5 0.6
0.7 0.8 0.9
0
200
400
p
2
MSGs
ABT-comp
ABT-decomp
ABT-cf
MP-ABT
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5 0.6
0.7 0.8 0.9
0
500
1,000
1,500
p
2
CCCs
ABT-comp
ABT-decomp
ABT-cf
MP-ABT
Figure 2: Benchmarking with < 0.3, 0.7, 0.3, 5, 5, 2, p
2
>.
communication load, and the Concurrent Constraint
Checks (# CCCs), it is a metric used in distribu-
ted constraint solving, which simulates the computa-
tion time and computes the computation effort. All
random Complex DisCSP problems are characteri-
zed by (ia, ib, c, n, d, v, p
2
) where, ia is the
intra-agent density, ib the inter-agent density, c the
connection density, n the number of agents, d the
domain size, v the number of variables per agent
and p
2
is the tightness of constraints. We select
problems in four most representative areas classes
of the constraints: < 0.3, 0.7, 0.3, 5, 5, 2, p
2
>, <
0.7, 0.3, 0.7, 5, 5, 2, p
2
>, < 0.3, 0.7, 0.3, 5, 5, 4, p
2
>,
and < 0.7, 0.3, 0.7, 5, 5, 4, p
2
>. The tightness p
2
is
varied from 0.1 to 0.9 by the step 0.1. For each fixed
set (ia, ib, c, n, d, v, p
2
), we generated 10 instance,
and we took their average.
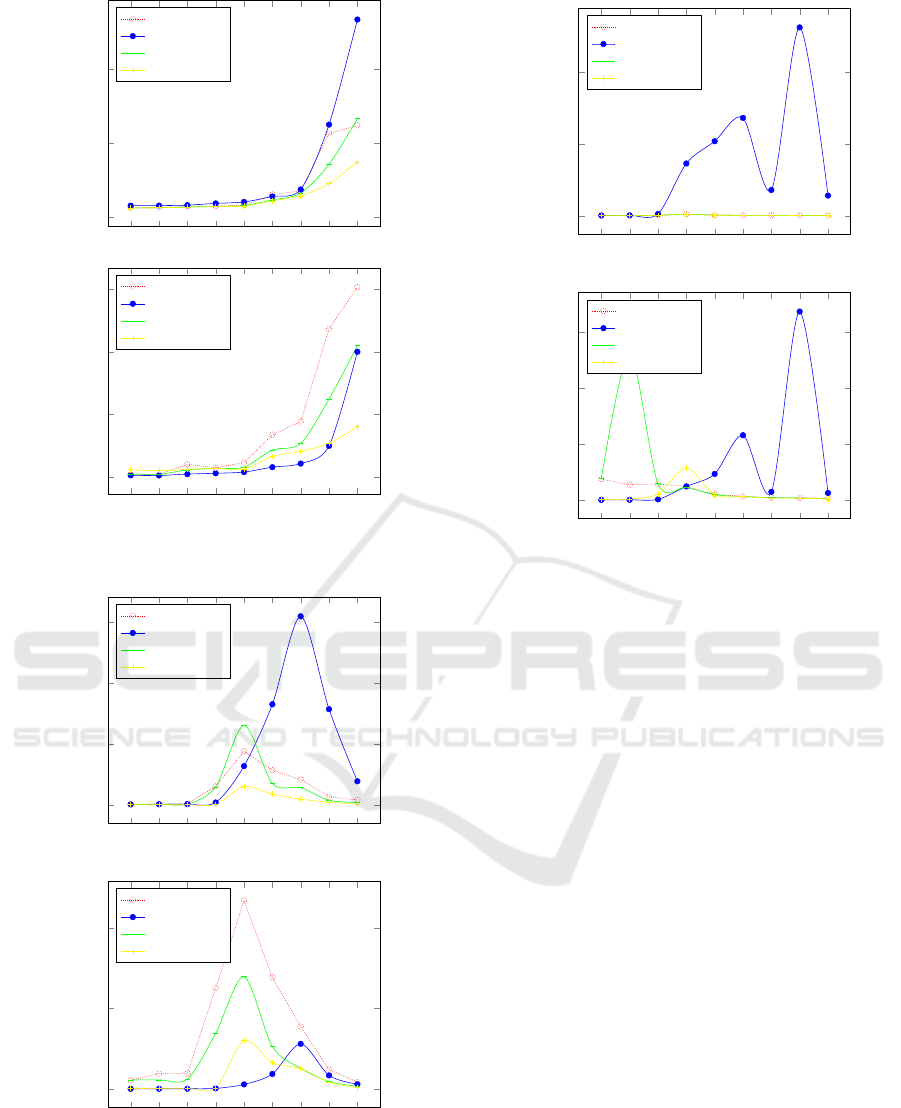
The figure 2 shows the performances of ABT-
comp, ABT-decomp, ABT-cf, and MP-ABT, functi-
oning on the first class of constraints < 0.3, 0.7, 0.3,
5, 5, 2, p
2
>. The figure 3 exhibits the behaviors of
the four algorithms, against the second class of con-
straints < 0.7, 0.3, 0.7, 5, 5, 2, p
2
>.
In the two classes where each agent handles two
variables, we observe that, in general, the ABT-comp
is the less-performance algorithm. It exchanges more
messages (more disturbance) and checks more con-
straints concurrently. It is due to the size of the new
constructed domain by the compilation. The ABT-cf
MP-ABT: A Minimal Perturbation Approach for Complex Local Problems
273
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5 0.6
0.7 0.8 0.9
0
100
200
p
2
MSGs
ABT-comp
ABT-decomp
ABT-cf
MP-ABT
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5 0.6
0.7 0.8 0.9
0
200
400
600
p
2
CCCs
ABT-comp
ABT-decomp
ABT-cf
MP-ABT
Figure 3: Benchmarking with < 0.7, 0.3, 0.7, 5, 5, 2, p
2
>.
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5 0.6
0.7 0.8 0.9
0
0.5
1
1.5
·10
4
p
2
MSGs
ABT-comp
ABT-decomp
ABT-cf
MP-ABT
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5 0.6
0.7 0.8 0.9
0
0.5
1
·10
5
p
2
CCCs
ABT-comp
ABT-decomp
ABT-cf
MP-ABT
Figure 4: Benchmarking with < 0.3, 0.7, 0.3, 5, 5, 4, p
2
>.
outperforms the ABT-comp by the deletion of the in-
terchangeable solutions, but still not exceed the MP-
ABT, because the content of nogoods, in the ABT-cf,
does not speed up the search. It involves a solution
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5 0.6
0.7 0.8 0.9
0
1
2
·10
4
p
2
MSGs
ABT-comp
ABT-decomp
ABT-cf
MP-ABT
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
0.5 0.6
0.7 0.8 0.9
0
0.5
1
1.5
·10
5
p
2
CCCs
ABT-comp
ABT-decomp
ABT-cf
MP-ABT
Figure 5: Benchmarking with < 0.7, 0.3, 0.7, 5, 5, 4, p
2
>.
of the local problem of the agent, not just the vari-
ables that cause the conflict. So, instead of deleting
the responsible variable values, the algorithm deletes
just a solution, and the next sent value of a variable
may be the same that already caused the problem. In
the ABT-decomp algorithm, even if the domain size
is still the same, it is also less efficient than MP-ABT,
because of the creation of the virtual agents, that in-
creases the size of the global problem. And so, there
is more exchanged messages without any importance,
and more checked concurrent constraints.
For 4 variables per agent, the evaluation results
are shown in figures 4 and 5. In this level, the per-
formance of the MP-ABT algorithm becomes more
important. In contrary of the first results (i.e., 2 va-
riables per agent), the out-performance began to be
important in the problems with low tightness too. In
this case, the local problems become more constrai-
ned. So, it is too hard and complex to find the whole
compiled domain, in ABT-comp and ABT-cf. So, the
domain contains several values. Therefore more con-
straints are tested. For the ABT-decomp which is ba-
sed on the decomposition, it makes a big effort. It can
loop several times in order to find one local consistent
solution.
Our aim is to minimize the number of perturbati-
ons (i.e., the number of exchanged messages). while,
such results exhibit that our principal aim is achie-
ved, in the case of two variables per agent as well as
in the case of four variables per agent. In addition
ICAART 2017 - 9th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
274

of our main goal, we have also reduced the number
of concurrent constraint checks, in most tightness va-
lues, especially when the constraint network becomes
dense.
The different evaluation results demonstrate that
the MP-ABT is a very effective way to decrease the
number of messages and therefore the number of per-
turbations. We observe that, the more variables we
have, the less disturbance MP-ABT does. And even
if problems become insolvable. The MP-ABT algo-
rithm remains better, due to the nogood content. The
nogood used by the MP-ABT contains just the so-
lution parts that cause the failure (contrary to ABT-
comp and the ABT-cf that reports all the solution with
the different variables). So, instead of deleting just
one solution after the reception of a nogood message,
we can delete a group of solutions. In addition, the
filtering process used in the MP-ABT, minimizes the
number of checked constraints.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we have proposed a new complete algo-
rithm: Minimal Perturbation complex local problems
in the Asynchronous Backtracking MP-ABT. It is an
upgrade of the ABT algorithm. It is able to solve Dis-
CSP problems with complex local problems, while
minimizing the perturbations, without any transfor-
mation of the original problem, as it is done by the
compilation and decomposition methods.
The MP-ABT algorithm considers each complex
local problem as an MPP problem, and each recei-
ved message as a perturbation of the intra-agent con-
straints. After a message reception, the MP-ABT
agent tries to find a closest local solution to its cur-
rent values, using the HS-MPP algorithm.
The experimentations show that the MP-ABT al-
gorithm outperforms the different ABT versions, in
terms of the number of exchanged messages and the-
refore the number of perturbations, while minimizing
the computational effort, especially when problems
are dense and contain more variables per agent.
We perceive to generalize the method of the mi-
nimal perturbation in the complex local problems, in
order to be integrated in the existing DisCSP algo-
rithms, as the AFC and AFC-ng algorithms.
REFERENCES
Bessi
`
ere, C., Maestre, A., Brito, I., and Meseguer, P. (2005).
Asynchronous backtracking without adding links: a
new member in the abt family. Artificial Intelligence,
161(1):7–24.
Burke, D. A. and Brown, K. N. (2006). Applying inter-
changeability to complex local problems in distribu-
ted constraint reasoning. In Workshop on Distributed
Constraint Reasoning (AAMAS 06), pages 1–15.
EL Graoui, E. M., Benelallam, I., Bouyakhf, E. H., et al.
(2016). A commentary on hybrid search for minimal
perturbation in dynamic csps. Constraints, 21(2):349–
354.
Ezzahir, R., Belaissaoui, M., Bessiere, C., and Bouyakhf,
E. H. (2007). Compilation formulation for asynchro-
nous backtracking with complex local problems. In
2007 International Symposium on Computational In-
telligence and Intelligent Informatics, pages 205–211.
IEEE.
Ezzahir, R., Bessiere, C., Bouyakhf, E., and Belaissaoui,
M. (2008). Asynchronous backtracking with compila-
tion formulation for handling complex local problems.
ICGST International Journal on Artificial Intelligence
and Machine Learning, AIML, 8:45–53.
Hirayama, K. and Yokoo, M. (2002). Local search for dis-
tributed sat with complex local problems. In Procee-
dings of the first international joint conference on Au-
tonomous agents and multiagent systems: part 3, pa-
ges 1199–1206. ACM.
Magaji, A. S., Arana, I., and Ahriz, H. (2014). Local se-
arch for discsps with complex local problems. In Web
Intelligence (WI) and Intelligent Agent Technologies
(IAT), 2014 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Joint Con-
ferences on, volume 3, pages 56–63. IEEE.
Meisels, A. and Zivan, R. (2007). Asynchronous forward-
checking for discsps. Constraints, 12(1):131–150.
Wahbi, M., Ezzahir, R., Bessiere, C., and Bouyakhf,
E. H. (2013). Nogood-based asynchronous forward
checking algorithms. Constraints, 18(3):404–433.
Yokoo, M. (1995). Asynchronous weak-commitment se-
arch for solving distributed constraint satisfaction pro-
blems. In International Conference on Principles and
Practice of Constraint Programming, pages 88–102.
Springer.
Yokoo, M., Ishida, T., Durfee, E. H., and Kuwabara, K.
(1992). Distributed constraint satisfaction for formali-
zing distributed problem solving. In Distributed Com-
puting Systems, 1992., Proceedings of the 12th Inter-
national Conference on, pages 614–621. IEEE.
Zivan, R., Grubshtein, A., and Meisels, A. (2011). Hy-
brid search for minimal perturbation in dynamic csps.
Constraints, 16(3):228–249.
MP-ABT: A Minimal Perturbation Approach for Complex Local Problems
275
