
Attribute based Encryption: Traitor Tracing, Revocation and Fully
Security on Prime Order Groups
Xiaoyi Li
1
, Kaitai Liang
2
, Zhen Liu
1
and Duncan Wong
1
1
Security and Data Sciences, Hong Kong Applied Science and Technology Research Institute, Hong Kong SAR, China
2
School of Computing, Mathematics and Digital Technology, Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, U.K.
Keywords:
Traitor Tracing, Revocation, Ciphertext-policy Attribute based Encryption, Prime Order Groups.
Abstract:
A Ciphertext-Policy Attribute-Based Encryption (CP-ABE) allows users to specify the access policies without
having to know the identities of users. In this paper, we contribute by proposing an ABE scheme which
enables revoking corrupted users. Given a key-like blackbox, our system can identify at least one of the users
whose key must have been used to construct the blackbox and can revoke the key from the system. This paper
extends the work of Liu and Wong to achieve traitor revocability. We construct an Augmented Revocable CP-
ABE (AugR-CP-ABE) scheme, and describe its security by message-hiding and index-hiding games. Then we
prove that an AugR-CP-ABE scheme with message-hiding and index-hiding properties can be transferred to a
secure Revocable CP-ABE with fully collusion-resistant blackbox traceability. In the proof for index-hiding,
we divide the adversary’s behaviors in two ways and build direct reductions that use adversary to solve the
D3DH problem. Our scheme achieves the sub-linear overhead of O(
√
N), where N is the number of users
in the system. This scheme is highly expressive and can take any monotonic access structures as ciphertext
policies.
1 INTRODUCTION
Attribute-Based Encryption (ABE) system is first in-
troduced by Sahai and Waters (Sahai and Waters,
2005), which is based on users’ roles and does not
have to know their identities in the system. In
an Attribute-Based Encryption (CP-ABE) system,
each user possesses a set of attributes and a pri-
vate key generated based on his/her attributes. The
encrypting party will define an access policy over
role-based/descriptiveattributes to encrypt a message
without having to know the identities of the targeted
receivers. As a result, only the user who owns the
appropriate attributes which satisfy the access pol-
icy are able to decrypt the ciphertext. Among the
CP-ABE schemes recently proposed, (Bethencourt
et al., 2007; Cheung and Newport, 2007; Goyal et al.,
2008; Waters, 2011; Lewko et al., 2010; Okamoto
and Takashima, 2010; Herranz et al., 2010; Lewko
and Waters, 2012a; Rouselakis and Waters, 2013),
progress has been made with regard to the schemes’
security, access policy expressivity, and efficiency.
While the schemes with practical security and ex-
pressivity (i.e. full security against adaptive adver-
saries in the standard model and high expressivity
of supporting any monotone access structures) have
been proposed in (Lewko et al., 2010; Okamoto
and Takashima, 2010; Lewko and Waters, 2012a),
the traceability of traitors which intentionally expose
their decryption keys has become an important con-
cern related to the applicability of CP-ABE. Assume
in a communication system, the sender wants to as-
sure that only those users who have paid for the ser-
vice can access the content. This concern can be
solved by encrypting the content and only receivers
who own the legitimate keys can decrypt the con-
tent correctly. If we build such a system with ABE,
however, due to the nature of CP-ABE, the attributes
(and the corresponding decryption privilege) are gen-
erally shared by multiple users. As a result, a ma-
licious user, with his attributes shared with multiple
other users, might have an intention to leak the cor-
responding decryption key or some decryption priv-
ilege in the form of a decryption blackbox/device in
which the decryption key is embedded, for example,
for financial gain or for some other incentives, as he
only has little risk of getting caught. Recently a hand-
ful of traceable CP-ABE schemes have been proposed
in (Liu et al., 2013b; Liu et al., 2013a; Deng et al.,
2014). In the whitebox traceable CP-ABE schemes,
Li, X., Liang, K., Liu, Z. and Wong, D.
Attribute based Encryption: Traitor Tracing, Revocation and Fully Security on Prime Order Groups.
DOI: 10.5220/0006220203090320
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER 2017), pages 281-292
ISBN: 978-989-758-243-1
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
281
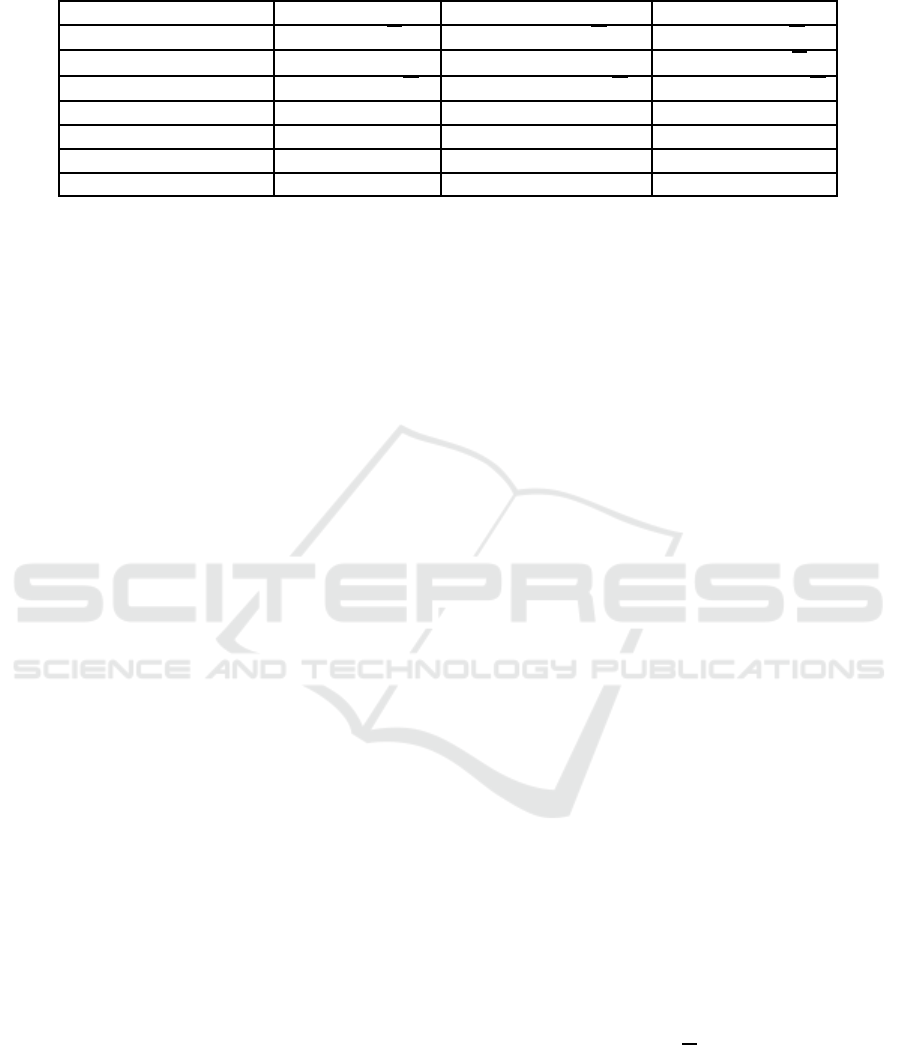
Table 1: Features and Efficiency Comparison.
(Liu et al., 2013a) (Liu and Wong, 2015b) This Paper
Ciphertext Size 2l + 17
√
N 6l + 3 + 46
√
N 6l + 3 + 46
√
N
Private Key Size |S|+ 4 6|S|+ 12 6|S|+ 9 + 3
√
N
Public Key Size |U|+ 3+ 4
√
N 24|U|+ 22+ 14
√
N 24|U|+ 22+ 23
√
N
Paring in Decryption 2|I|+ 10 6|I|+ 30 6|I|+ 30
On prime Order Groups ×
√ √
Revocation × ×
√
Order of the Groups p
1
p
2
p
3
p p
1
Let l be the size of an access policy, |S| the size of the attribute set of a private key, |U| the
size of the attribute universe, and |I| the number of attributes in a decryption key that satisfies
a ciphertext’s access policy.
given a well-formed decryption key as input, a trac-
ing algorithm can find out the malicious user who
leaked or sold well-formed decryption keys. Liu et al.
(Liu et al., 2013b) proposed such a whitebox traceable
CP-ABE scheme that can deter users from these mali-
cious behaviors. As malicious users invent a decryp-
tion blackbox/device which keeps the embedded de-
crypt keys and algorithms hidden, Liu et al.(Liu et al.,
2013a) proved that the blackbox traceable CP-ABE
scheme supports fully collusion-resistant blackbox
traceable in the standard model, where fully collusion-
resistant blackbox traceability means that the num-
ber of colluding users in constructing a decryption
blackbox/device is not limited and can be arbitrary.
This scheme is fully secure in the standard model and
highly expressive (i.e. supporting any monotonic ac-
cess structures).
It should be observed that a tracing system is not
designed to protect the encrypted content. It is used
to distinguish the compromised users from other le-
gitimate users, which means the corrupted user/key is
still remained in the system and an effective black-
box is likely to be produced with these corrupted keys
in the wild market. The exposed compromised users
need to leave or be removed from the system to avoid
incurring more losses. When any of these happens,
the corresponding user keys should be revoked. We
added the revocability in the scheme so that we can
remove the compromised keys as needed. We focus
on achieving direct revocation in traceable CP-ABE
system. In a direct revocation mechanism, it does not
need any periodic key updates and it does not affect
any non-revoked users either. A system-wide revoca-
tion list could be made public and revocation could
be taken into effect promptly as the revocation list
could be updated immediately once a key is revoked.
Specifically, we generate Q
′
i
, which is a part of cipher-
text, with a non-revoked index list
¯
R. When decrypt-
ing, we first recover
~
¯
K
i, j
which has a common item
h
∏
j
′
∈
¯
R
i
h
j
′
with Q
′
i
if they share a consistent revoca-
tion list R. Then
~
¯
K
i, j
is used in the following decryp-
tion process. To avoid a further loss, the revocation
list should be updated timely once corrupted users are
found. For the security proof for message-hiding, we
re-construct the Semi-functional Keys by replacing h
with hh
j
, which can realize revocability, and adding
the random item
~
¯
K
i, j, j
′
accordingly. As a contrast, the
random items for Semi-functional Ciphertexts remain
the same, which is irrelevant to the revocability. For
the security proof for index-hiding, we have two ways
for adversary to take and add more sub-cases in Case
II which make the security proof a non-trivial work.
In this paper, We continue our work on prime order
groups as an extension for (Liu and Wong, 2015b).
1.1 Our Results
It has been shown (e.g. in (Garg et al., 2010;
Lewko,2012)) that the constructions on composite or-
der groups will result in significant loss of efficiency
and the security will rely on some non-standard as-
sumptions (e.g. the Subgroup Decision Assumptions)
and an additional assumption that the group order is
hard to factor. The previous work in (Liu and Wong,
2015b) achieves better security than the scheme in
(Liu et al., 2013a), which is constructed on compos-
ite order groups. In this paper, we add the revoca-
bility in (Liu and Wong, 2015b) and prove it highly
expressive and fully secure in the standard model. On
the efficiency aspect, this new scheme achieves the
same efficient level as in (Liu and Wong, 2015b), i.e.
the overhead for the fully collusion-resistant black-
box traceability is in O(
√
N), where N is the number
of users in a system.
Table 1 compares this new scheme with the pre-
vious work on blackbox traceable CP-ABE (Liu
et al., 2013a) and the traceable CP-ABE on prime
order group but without revocability (Liu and Wong,
2015b). We only change the size of keypair as we
need add revocation items in the key. Both the cipher-
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
282

text and the pairing computation in decryption are
kept unchanged. This implies both this new scheme
and (Liu and Wong, 2015b) have better security than
the scheme in (Liu et al., 2013a), although all of them
are fully secure in the standard model and have over-
head in O(
√
N).
Related Work. In the literature, several revocation
mechanisms have been proposed in the context of
CP-ABE. In (Sahai et al., 2012), Sahai et al. pro-
posed an indirect revocation mechanism, which re-
quires an authority to periodically broadcast a key up-
date information so that only the non-revoked users
can update their keys. In (Attrapadung and Imai,
2009), Attrapadung and Imai proposed a direct revo-
cation mechanism, which allows a revocation list to
be specified directly during encryption so that the re-
sulting ciphertext cannot be decrypted by any decryp-
tion key which is in the revocation list even though
the associated attribute set of the key satisfies the
ciphertext policy. For ABE scheme, in (Liu et al.,
2013a) Liu et al. defined a ‘functional’ CP-ABE that
has the same functionality as the conventional CP-
ABE (i.e. having all the appealing properties of the
conventional CP-ABE), except that each user is as-
signed and identified by a unique index, which will
enable the traceability of traitors. Furthermore, Liu
et al. defined a new primitive called Augmented CP-
ABE (AugCP-ABE) and formalized its security us-
ing message-hiding and index-hiding games. Then
Liu et al. proved that an AugCP-ABE scheme with
message-hiding and index-hiding properties can be
directly transferred to a secure CP-ABE with fully
collusion-resistant blackbox traceability. With such
a framework, Liu et al. obtained a fully secure and
fully collusion-resistant blackbox traceable CP-ABE
scheme by constructing an AugCP-ABE scheme with
message-hiding and index-hiding properties. In (Liu
and Wong, 2015b), Liu et al. obtain a prime or-
der construction and it will be tempting to bring the
revocation into (Liu and Wong, 2015b) as a practi-
cal enhancement and implementation. In this paper,
we leverage the revocation idea from (Liu and Wong,
2015a).
Outline. In this paper, we follow the same framework
in (Liu and Wong, 2015b). In particular, in Section 2,
we propose a definition for CP-ABE supporting key-
like blackbox traceability and direct revocation. In
our direct revocation definition, the Encrypt algorithm
takes a revocation list R ⊆{1, ..., N} as an additional
input so that a message encrypted under the (revoca-
tion list, access policy) pair (R,A) would only allow
users whose (index, attribute set) pair (k, S) satisfies
(k ∈ [N] \R) AND (S satisfies A) to decrypt. In Sec-
tion 3, we revisit the definitions and security models
of Augmented Revocable CP-ABE (AugR-CP-ABE
for short) from (Liu and Wong, 2015a). We refer
to the ‘functional’ CP-ABE in Section 2 as Revoca-
ble CP-ABE (R-CP-ABE for short), then extend the
R-CP-ABE to AugR-CP-ABE, which will lastly be
transformed to a key-like blackbox traceable R-CP-
ABE. In Section 4 we propose our AugR-CP-ABE
construction on prime order groups and prove that
our AugR-CP-ABE construction is message-hiding
and index-hiding in the standard model. As a result,
we obtain a fully secure and fully collusion-resistant
blackbox traceable R-CP-ABE scheme on prime or-
der groups.
To construct the AugR-CP-ABE, we continue our
work in (Liu and Wong, 2015b) and leverage the re-
vocation idea from (Liu and Wong, 2015a). In par-
ticular, besides achieving the important features for
practicality, such as revocation, high expressivity and
efficiency, the construction is proved secure and trace-
able in the standard model.
2 REVOCABILITY AND
BLACKBOX TRACEABILITY
We follow the definition in (Liu and Wong, 2015a).
Given a positive integer n, our Revocable Ciphertext-
Policy Attribute-Based Encryption (R-CP-ABE) sys-
tem consists of four algorithms:
Setup(λ,U, N) → (PP,MSK). The algorithm takes
as input a security parameter λ, the attribute uni-
verse U, and the number of users N in the sys-
tem, then runs in polynomial time in λ, and out-
puts the public parameter PP and a master secret
key MSK.
KeyGen(PP,MSK,S) → SK
k,S
. The algorithm takes
as input the public parameter PP, the master se-
cret key MSK, and an attribute set S, and outputs
a private decryption key SK
k,S
, which is assigned
and identified by a unique index k ∈ [N].
Encrypt(PP,M,R, A) →CT
R,A
. The algorithm takes
as input the public parameter PP, a message M, a
revocation list R ⊆ [N], and an access policy A
over U, and outputs a ciphertext CT
R,A
such that
only users whose indices are not revoked by R and
attributes satisfy A can recover M. R and A are
implicitly included in CT
R,A
.
Decrypt(PP,CT
R,A
,SK
k,S
) → M or ⊥. The algo-
rithm takes as input the public parameter PP, a
ciphertext CT
R,A
, and a private key SK
k,S
. If
(k ∈ [N] \R) AND (S satisfies A), the algorithm
outputs a message M, otherwise it outputs ⊥ indi-
cating the failure of decryption.
Attribute based Encryption: Traitor Tracing, Revocation and Fully Security on Prime Order Groups
283

Correctness. For any attribute set S ⊆ U, index
k ∈ [N], revocation list R ⊆ [N], access policy A
over U, and message M, suppose (PP,MSK) ←
Setup(λ,U, N), SK
k,S
← KeyGen(PP,MSK, S),
CT
R,A
← Encrypt(PP,M, R,A). If (k ∈ [N] \R) ∧(S
satisfies A), then Decrypt(PP,CT
R,A
,SK
k,S
) = M.
Security. Now we define the security of a R-CP-ABE
system using a message-hiding game.
Game
MH
. The Message-hiding game is defined be-
tween a challenger and an adversary A as follows:
Setup. The challenger runs Setup(λ, U,N) and
gives the public parameter PP to A.
Phase 1. For i = 1 to Q
1
, A adaptively submits (in-
dex, attribute set) pair (k
i
,S
k
i
), and the challenger
responds with SK
k
i
,S
k
i
.
Challenge. A submits two equal-length mes-
sages M
0
,M
1
and a (revocation list, access pol-
icy) pair (R
∗
,A
∗
). The challenger flips a ran-
dom coin b ∈ {0,1}, and sends CT
R
∗
,A
∗
←
Encrypt(PP,M
b
,R
∗
,A
∗
) to A.
Phase 2. For i = Q
1
+1 to Q, A adaptively submits
(k
i
,S
k
i
), and the challenger responds with SK
k
i
,S
k
i
.
Guess. A outputs a guess b
′
∈ {0,1} for b.
A wins the game if b
′
= b under the restriction that
none of the queried {(k
t
,S
k
t
)}
Q
i=1
can satisfy (k
t
∈
[N] \R
∗
) AND (S
k
t
satisfies A
∗
). The advantage of
A is defined as MH
A
Adv
A
= |Pr[b
′
= b] −
1
2
|.
Definition 1. An N-user R-CP-ABE system is secure
if for all polynomial-time adversaries A the advan-
tage MHAdv
A
is negligible in λ.
The message-hiding game is a typical semantic
security game and is based on that for conventional
CP-ABE (Lewko et al., 2010; Lewko and Waters,
2012a), where the revocation list R is always empty.
It is clear that such a CP-ABE system (Lewko et al.,
2010; Lewko and Waters, 2012a) has the following
properties: fully collusion-resistant security, meaning
that several users should not be able to decrypt a mes-
sage that none of them are individually granted to ac-
cess, fine-grained access control on encrypted data,
and efficient one-to-many encryption.
It is worth noticing that, as pointed in (Liu et al.,
2013a), in the definition of the game: (1) the adver-
sary is allowed to specify the index of the private key
when it makes key queries for the attribute sets of
its choice, i.e., for t = 1 to Q, the adversary submits
(index, attribute set) pair (k
t
,S
k
t
) to query a private
key for attribute set S
k
t
, where Q ≤ N, k
t
∈ [N], and
k
t
6= k
t
′
∀1 ≤t 6= t
′
≤ Q (this is to guarantee that each
user/key can be uniquely identified by an index); and
(2) for k
t
6= k
t
′
we do not require S
k
t
6= S
k
t
′
, i.e., dif-
ferent users/keys may have the same attribute set. We
remark that these two points apply to the rest of the
paper.
2.1 Blackbox Traceability
Now we define the traceability against key-like de-
cryption blackbox. A key-like decryption blackbox
D can be viewed as a probabilistic circuit that takes
as input a ciphertext CT
R,A
and outputs a message
M or ⊥, and such a decryption blackbox does not
need to be perfect, namely, we only require it to be
able to decrypt with non-negligible success probabil-
ity. In particular, a key-like decryption blackbox D
is described by a (revocation list, attribute set) pair
(R
D
,S
D
) and a non-negligible probability value ε (i.e.
0 ≤ ε ≤ 1 is polynomially related to λ), and adver-
tised that for any ciphertext generated under the (re-
vocation list, access policy) pair (R,A), if ((S
D
satis-
fies A) AND ([N] \R) ∩([N] \R
D
) 6=
/
0) can be satis-
fied by S
D
and R
D
, this blackbox D can decrypt the
corresponding ciphertext with probability at least ε.
Specifically, once a blackbox is found being able to
decrypt ciphertext, we can regard it as a key-like de-
cryption blackbox with the corresponding (revocation
list, attribute set) pair (R
D
,S
D
), and the ciphertext is
related to the pair (R, A) which satisfies ((S
D
satisfies
A) AND ([N] \R) ∩([N] \R
D
) 6=
/
0). If we set the re-
vocation list R and R
D
as empty, we can get the same
definition for key-like decryption blackbox as shown
in (Liu et al., 2013a).
Trace
D
(PP,R
D
,S
D
,ε) → K
T
⊆ [N]. This is an ora-
cle algorithm that interacts with a key-like decryption
blackbox D. Given the public parameter PP, a re-
vocation list R
D
, a non-empty attribute set S
D
, and a
probability value (lower-bound) ε, the algorithm runs
in time polynomial in λ and 1/ε, and outputs an in-
dex set K
T
⊆ [N] which identifies the set of malicious
users. Note that ε has to be polynomially related to λ.
In the following Tracing Game game, the adver-
sary targets to build a decryption blackbox D that
functions as a private decryption key with the pair
(R
D
,S
D
) (as the name of key-like decryption black-
box implies) which can decrypt ciphertexts under
some (revocation list, access policy) pairs (R,A). It
captures the notion of fully collusion-resistant trace-
ability. The tracing algorithm in the game is designed
to extract the index of at least one of the malicious
users whose decryption keys have been used for con-
structing D.
Game
TR
. The Tracing Game is defined between a
challenger and an adversary A as follows:
Setup. The challenger runs Setup(λ,U, N) and
gives the public parameter PP to A.
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
284

Key Query. For i = 1 to Q, A adaptively submits
(k
i
,S
k
i
), and the challenger responds with SK
k
i
,S
k
i
.
(Key-like) Decryption Blackbox Generation. A
outputs a decryption blackbox D associated with
a (revocation list, attribute set) pair (R
D
,S
D
),
S
D
⊆U,R
D
⊆ [N] and a non-negligible probabil-
ity (lower-bound) value ε.
Tracing. The challenger runs Trace
D
(PP,R
D
,
S
D
,ε) to obtain an index set K
T
⊆ [N].
Let K
D
= {k
i
|1 ≤i ≤Q} be the index set of keys
corrupted by the adversary. We say that the adversary
A wins the game if the following conditions hold:
1. For any (revocation list, access policy) pair (R, A)
which satisfied ((S
D
satisfies A) AND ([N] \R) ∩
([N] \R
D
) 6=
/
0), we have
Pr[D(Encrypt(PP, M,R,A)) = M] ≥ ε,
where the probability is taken over the random
choices of message M and the random coins of D.
A decryption blackbox satisfying this condition is
said to be a useful key-like decryption blackbox.
2. K
T
=
/
0, or K
T
6⊆ K
D
, or
(k
t
∈ R
D
) OR (S
D
6⊆
S
k
t
) ∀k
t
∈ K
T
.
We denote by TRAdv
A
the probability that adversary
A wins this game.
Definition 2. An N-user Blackbox Traceable CP-
ABE system is traceable if for all polynomial-time ad-
versaries A the advantage TRAdv
A
is negligible in λ.
3 DEFINITION
3.1 Definitions and Security Models
An Augmented R-CP-ABE (AugR-CP-ABE) system
consists of the following four algorithms:
Setup
A
(λ,U, N) → (PP,MSK). The algorithm
takes as input a security parameter λ, the attribute
universe U, and the number of users N in the sys-
tem, then runs in polynomial time in λ, and out-
puts the public parameter PP and a master secret
key MSK.
KeyGen
A
(PP,MSK,S) → SK
k,S
. The algorithm
takes as input PP, MSK, and an attribute set S,
and outputs a private key SK
k,S
, which is assigned
and identified by a unique index k ∈[N].
Encrypt
A
(PP,M,R, A,
¯
k) → CT
R,A
. The algorithm
takes as input PP, a message M, a revocation list
R ⊆ [N], an access policy A over U, and an index
¯
k ∈ [N + 1], and outputs a ciphertext CT
R,A
. A is
included in CT
R,A
, but the value of
¯
k is not.
Decrypt
A
(PP,CT
R,A
,SK
k,S
) → M or ⊥. The algo-
rithm takes as input PP, a ciphertext CT
R,A
, and a
private key SK
k,S
. If (k ∈[N] \R) AND (S satisfies
A), the algorithm outputs a message M, otherwise
it outputs ⊥ indicating the failure of decryption.
Correctness. For any attribute set S ⊆ U, index
k ∈ [N], revocation list R ⊆ [N], access policy A
over U, encryption index
¯
k ∈ [N + 1], and mes-
sage M, suppose (PP,MSK) ← Setup
A
(λ,U, N),
SK
k,S
← KeyGen
A
(PP,MSK,S), CT
R,A
←
Encrypt
A
(PP,M,R, A,
¯
k). If (k ∈[N]\R)∧(S satisfies
A) ∧(k ≥
¯
k) then Decrypt
A
(PP,CT
R,A
,SK
k,S
) = M.
Security. The security of AugR-CP-ABE is defined
by the following three games, where the first two are
for message-hiding, and the third one is for the index-
hiding property.
In the first two message-hiding games between
a challenger and an adversary A,
¯
k = 1 (the first
game, Game
A
MH
1
) or
¯
k = N + 1 (the second game,
Game
A
MH
N+1
).
Setup. The challenger runs Setup
A
(λ,U, N) and
gives the public parameter PP to A.
Phase 1. For t = 1 to Q
1
, A adaptively submits (in-
dex, attribute set) pair (k
t
,S
k
t
), and the challenger
responds with SK
k
t
,S
k
t
, which corresponds to at-
tribute set S
k
t
and is assigned index k
t
.
Challenge. A submits two equal-length mes-
sages M
0
,M
1
and a (revocation list, access pol-
icy) pair (R
∗
,A
∗
). The challenger flips a ran-
dom coin b ∈ {0,1}, and sends CT
R
∗
,A
∗
←
Encrypt
A
(PP,M
b
,R
∗
,A
∗
,
¯
k) to A.
Phase 2. For t = Q
1
+ 1 to Q, A adaptively submits
(index, attribute set) pair (k
t
,S
k
t
), and the chal-
lenger responds with SK
k
t
,S
k
t
, which corresponds
to attribute set S
k
t
and is assigned index k
t
.
Guess. A outputs a guess b
′
∈ {0,1} for b.
Game
A
MH
1
. In the Challenge phase the challenger
sends CT
R
∗
,A
∗
← Encrypt
A
(PP,M
b
,R
∗
,A
∗
,1) to A.
A wins the game if b
′
= b under the restriction that
none of the queried {(k
t
,S
k
t
)}
Q
i=1
can satisfy (k ∈
[N] \R
∗
) AND (S
k
t
satisfies A
∗
). The advantage of
A is defined as MH
A
1
Adv
A
= |Pr[b
′
= b] −
1
2
|.
Game
A
MH
N+1
. In the Challenge phase the challenger
sends CT
R
∗
,A
∗
← Encrypt
A
(PP,M
b
,R
∗
,A
∗
,N + 1) to
A. A wins the game if b
′
= b. The advantage of A is
defined as MH
A
N+1
Adv
A
= |Pr[b
′
= b] −
1
2
|.
Definition 3. A N-user Augmented R-CP-ABE system
is message-hiding if for all probabilistic polynomial
time (PPT) adversaries A the advantages MH
A
1
Adv
A
and MH
A
N+1
Adv
A
are negligible in λ.
Attribute based Encryption: Traitor Tracing, Revocation and Fully Security on Prime Order Groups
285

Game
A
IH
. In the third game, index-hiding game, for
any non-empty attribute set S
∗
⊆ U, we define the
strictest access policy as A
S
∗
=
V
x∈S
∗
x, and require
that an adversary cannot distinguish between an en-
cryption using (A
S
∗
,R
∗
,
¯
k) and (A
S
∗
,R
∗
,
¯
k + 1) with-
out a private decryption key SK
¯
k,S
¯
k
such that (
¯
k ∈
[N] \R
∗
) ∧(S
¯
k
⊇ S
∗
). The game takes as input a pa-
rameter
¯
k ∈ [N] which is given to both the challenger
and the adversary A. The game proceeds as follows:
Setup. The challenger runs Se tup
A
(λ,U, N) and
gives the public parameter PP to A.
Key Query. For t = 1 to Q, A adaptively submits
(index, attribute set) pair (k
t
,S
k
t
), and the chal-
lenger responds with SK
k
t
,S
k
t
, which corresponds
to attribute set S
k
t
and is assigned index k
t
.
Challenge. A submits a message M and a (revoca-
tion list, access policy) pair (R
∗
,A
∗
). The chal-
lenger flips a random coin b ∈ {0,1}, and sends
CT
R
∗
,A
∗
← Encrypt
A
(PP,M,R
∗
,A
∗
,
¯
k+ b) to A.
Guess. A outputs a guess b
′
∈ {0,1} for b.
A wins the game if b
′
= b under the restriction
that none of the queried pairs {(k
t
,S
k
t
)}
Q
i=1
can sat-
isfy (k
t
=
¯
k) ∧(k
t
∈ [N] \R
∗
) ∧(S
k
t
satisfies A
S
∗
), i.e.
(k
t
=
¯
k) ∧(k
t
∈ [N] \R
∗
) ∧(S
k
t
⊇ S
∗
). The advantage
of A is defined as IH
A
Adv
A
[
¯
k] = |Pr[b
′
= b] −
1
2
|.
Definition 4. A N-user Augmented R-CP-ABE system
is index-hiding if for all PPT adversaries A the ad-
vantages IH
A
Adv
A
[
¯
k] for
¯
k = 1,. .. ,N are negligible
in λ.
3.2 The Reduction of Traceable
R-CP-ABE to AugR-CP-ABE
We now show that an AugR-CP-ABE with message-
hiding and index-hiding implies a secure and trace-
able R-CP-ABE.
Let Σ
A
= (Setup
A
,KeyGen
A
,Encrypt
A
,Dec rypt
A
)
be an AugR-CP-ABE with message-hiding
and index-hiding, define Encrypt(PP,M, A) =
Encrypt
A
(PP,M, A,1), then Σ = (Setup
A
,KeyGen
A
,
Encrypt,Decrypt
A
) is a R-CP-ABE derived from Σ
A
.
In the following, we show that if Σ
A
is message-hiding
and index-hiding, then Σ is secure. Furthermore, we
propose a tracing algorithm Trace for Σ and show
that if Σ
A
is message-hiding and index-hiding, then Σ
(equipped with Trace) is traceable.
3.2.1 R-CP-ABE Security
Theorem 1. If Σ
A
is an AugR-CP-ABE with message-
hiding and index-hiding properties, then Σ is a secure
and traceable R-CP-ABE.
Proof. Note that Σ is a special case of Σ
A
where
the encryption algorithm always sets
¯
k = 1. Hence,
Game
MH
for Σ is identical to Game
A
MH
1
for Σ
A
, which
implies that MHAdv
A
for Σ in Game
MH
is equal to
MH
A
1
Adv
A
for Σ
A
in Game
A
MH
1
, i.e., if Σ
A
is message-
hiding (in Game
A
MH
1
), then Σ is secure.
3.2.2 R-CP-ABE Traceability
Now we show that if Σ
A
is message-hiding (in
Game
A
MH
N+1
) and index-hiding, Σ is traceable. As
shown in (Liu et al., 2013a), with the following
Trace algorithm (Liu et al., 2013a), Σ achieves fully
collusion-resistant blackbox traceability against key-
like decryption blackbox.
Trace
D
(PP,R
D
,S
D
,ε) →K
T
⊆[N]: Given a key-like
decryption blackbox D associated with a non-empty
attribute set S
D
and probability ε > 0, the tracing al-
gorithm works as follows:
1. For
¯
k = 1 to N + 1, do the following:
(a) The algorithm repeats the following 8λ(N/ε)
2
times:
i. Sample M from the message space at random.
ii. Let CT
R,A
S
D
← Encrypt
A
(PP,M, R,A
S
D
,
¯
k),
where A
S
D
is the strictest access policy of S
D
.
iii. Query oracle D on input CT
R,A
S
D
, and com-
pare the output of D with M.
(b) Let ˆp
¯
k
be the fraction of times that D decrypted
the ciphertexts correctly.
2. Let K
T
be the set of all
¯
k ∈ [N] for which ˆp
¯
k
−
ˆp
¯
k
+1
≥ ε/(4N). Then output K
T
as the index set
of the private keys of malicious users.
Theorem 2. If Σ
A
is message-hiding and index-
hiding, then Σ is traceable using the Trace algorithm
against key-like decryption blackbox.
Proof. In the proof sketch below, we show that if
the key-like decryption blackbox output by the ad-
versary is a useful one then the traced K
T
will sat-
isfy (K
T
6=
/
0) ∧(K
T
⊆ K
D
) ∧
∃k
t
∈ K
T
s.t.( k
k
t
∈
[N] \ R
D
) ∧(S
D
⊆ S
k
t
)
with overwhelming proba-
bility, which implies that the adversary can win the
game Game
TR
only with negligible probability, i.e.,
TRAdv
A
is negligible.
Let D be the key-like decryption blackbox output
by the adversary, and (R
D
,S
D
) be the (revocation list,
attribute set) pair which can be used to describe D.
Define
p
¯
k
= Pr[D(Encrypt
A
(PP,M,R, A
S
D
,
¯
k)) = M],
where the probability is taken over the random choice
of message M and the random coins of D. We have
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
286

that p
1
≥ ε and p
N+1
is negligible. The former fol-
lows the fact that D is a useful key-like decryption
blackbox, and the later follows that Σ
A
is message-
hiding (in Game
A
MH
N+1
). Then there must exist some
¯
k ∈ [N] such that p
¯
k
− p
¯
k
+1
≥ ε/(2N). By the Cher-
noff bound it follows that with overwhelming proba-
bility, ˆp
¯
k
− ˆp
¯
k
+1
≥ε/(4N). Hence, we have K
T
6=
/
0.
For any k
t
∈ K
T
(i.e., ˆp
k
t
− ˆp
k
t
+1
≥
ε
4N
), we
know, by Chernoff, that with overwhelming probabil-
ity p
k
t
− p
k
t
+1
≥ ε/(8N). Clearly (k
t
∈ K
D
) ∧(k
t
∈
[N] \R
D
) ∧ (S
D
⊆ S
k
t
) since otherwise, D can be
directly used to win the index-hiding game for Σ
A
.
Hence, we have (K
T
⊆ K
D
) ∧
(k
t
∈ [N] \ R
D
) ∧
(S
D
⊆ S
k
t
) ∀k
t
∈K
T
.
4 CONSTRUCTION
Now we construct an AugR-CP-ABE scheme on
prime order groups, and prove that this AugR-CP-
ABE scheme is message-hiding and index-hiding in
the standard model. Combined with the results in Sec-
tion 3.2, we obtain a R-CP-ABE scheme that is fully
collusion-resistant blackbox traceable in the standard
model, fully secure in the standard model, and on
prime order groups.
4.1 Preliminaries
Before proposing our AugR-CP-ABE construction ,
we first review some preliminaries.
Bilinear Groups. Let G be a group generator, which
takes a security parameter λ and outputs (p,G,G
T
,e)
where p is a prime, G and G
T
are cyclic groups of or-
der p, and e : G ×G → G
T
is a map such that: (1) (Bi-
linear) ∀g,h ∈ G,a,b ∈ Z
p
,e(g
a
,h
b
) = e(g,h)
ab
, (2)
(Non-Degenerate) ∃g ∈ G such that e(g,g) has order
p in G
T
. We refer to G as the source group and G
T
as the target group. We assume that group operations
in G and G
T
as well as the bilinear map e are effi-
ciently computable, and the description of G and G
T
includes a generator of G and G
T
respectively.
Complexity Assumptions. We will base the
message-hiding property of our AugR-CP-ABE
scheme on the Decisional Linear Assumption
(DLIN), the Decisional 3-Party Diffie-Hellman As-
sumption (D3DH) and the Source Group q-Parallel
BDHE Assumption, and will base the index-hiding
property of our AugR-CP-ABE scheme on the DLIN
assumption and the D3DH assumption. Please refer
to the full version (Li et al., 2016, Appendix A) for
the details of the three assumptions.
Dual Pairing Vector Spaces. Our construction will
use dual pairing vector spaces, a tool introduced by
Okamoto and Takashima (Okamoto and Takashima,
2008; Okamoto and Takashima, 2009; Okamoto and
Takashima, 2010) and developed by Lewko (Lewko,
2012) and Lewko and Waters (Lewko and Waters,
2012b). Please refer to the full version (Li et al., 2016,
Appendix A) for the details of the dual pairing vector
spaces. As our AugR-CP-ABE construction will use
dual pairing vector spaces, the security proof will use
a lemma and a Subspace Assumption, which are in-
troduced and proved by Lewko and Waters (Lewko
and Waters, 2012b), in the setting of dual pairing vec-
tor spaces. Please refer to the full version (Li et al.,
2016, Appendix A.1 ) for the details of this lemma
and the Subspace Assumption. Here we would like
to stress that the Subspace Assumption is implied by
DLIN assumption.
To construct our AugR-CP-ABE scheme, we fur-
ther define a new notation. In particular, for any
~v = (v
1
,. .. ,v
n
) ∈ Z
n
p
,
~
v
′
= (v
′
1
,. .. ,v
′
n
′
) ∈ Z
n
′
p
, we de-
fine
(g
~v
)
~
v
′
: = ((g
~v
)
v
′
1
,. .. ,(g
~v
)
v
′
n
′
)
= (g
v
′
1
v
1
,. .. ,g
v
′
1
v
n
,. .. ,g
v
′
n
′
v
1
,. .. ,g
v
′
n
′
v
n
) ∈ G
nn
′
.
Note that for any~v,~w ∈ Z
n
p
,
~
v
′
,
~
w
′
∈ Z
n
′
p
, we have
e
nn
′
((g
~v
)
~
v
′
,(g
~w
)
~
w
′
) =
n
′
∏
j=1
n
∏
i=1
e(g
v
′
j
v
i
,g
w
′
j
w
i
)
=
n
′
∏
j=1
(
n
∏
i=1
e(g
v
i
,g
w
i
))
v
′
j
w
′
j
=
e
n
(g
~v
,g
~w
)
(
~
v
′
·
~
w
′
)
=
e(g,g)
(~v·~w)
(
~
v
′
·
~
w
′
)
= e(g,g)
(~v·~w)(
~
v
′
·
~
w
′
)
= e
nn
′
((g
~
v
′
)
~v
,(g
~
w
′
)
~w
).
Linear Secret-Sharing Schemes (LSSS). As in pre-
vious work, we use linear secret-sharing schemes
(LSSS) to express the access policies. The formal def-
initions of access structures and LSSS can be found in
the full version (Li et al., 2016, Appendix D).
Notations. Suppose the number of users N in the sys-
tem equals n
2
for some n
1
, so we use [n, n] instead
of [N] in the following content. We arrange the users
in a n ×n matrix and uniquely assign a tuple (i, j)
where 1 ≤ i, j ≤ n, to each user. A user at position
1
If the number of users is not a square, we add some
“dummy” users to pad to the next square.
Attribute based Encryption: Traitor Tracing, Revocation and Fully Security on Prime Order Groups
287

(i, j) of the matrix has index k = (i −1) ∗n + j. For
simplicity, we directly use (i, j) as the index where
(i, j) ≥ (
¯
i,
¯
j) means that ((i >
¯
i)∨(i =
¯
i∧ j ≥
¯
j)). The
use of pairwise notation (i, j) is purely a notational
convenience, as k = (i−1) ∗n+ j defines a bijection
between {(i, j)|1 ≤i, j ≤ n} and {1,...,N}. We con-
flate the notation and consider the attribute universe
to be [U] = {1, 2. ..,U}, so U serves both as a de-
scription of the attribute universe and as a count of
the total number of attributes. Given a bilinear group
order p, one can randomly choose r
x
,r
y
,r
z
∈ Z
p
, and
set
~
χ
1
= (r
x
,0,r
z
),
~
χ
2
= (0,r
y
,r
z
),
~
χ
3
=
~
χ
1
×
~
χ
2
=
(−r
y
r
z
,−r
x
r
z
,r
x
r
y
). Let span{
~
χ
1
,
~
χ
2
} be the sub-
space spanned by
~
χ
1
and
~
χ
2
, i.e. span{
~
χ
1
,
~
χ
2
} =
{ν
1
~
χ
1
+ ν
2
~
χ
2
|ν
1
,ν
2
∈ Z
p
}. We can see that
~
χ
3
is or-
thogonal to the subspace span{
~
χ
1
,
~
χ
2
} and that Z
3
p
=
span{
~
χ
1
,
~
χ
2
,
~
χ
3
} = {ν
1
~
χ
1
+ ν
2
~
χ
2
+ ν
3
~
χ
3
|ν
1
,ν
2
,ν
3
∈
Z
p
}. For any~v ∈ span{
~
χ
1
,
~
χ
2
}, we have (
~
χ
3
·~v) = 0,
and for random~v ∈Z
3
p
, (
~
χ
3
·~v) 6= 0 happens with over-
whelming probability.
4.2 AugR-CP-ABE Construction
Setup
A
(λ,U, N = n
2
) → (PP,MSK). The algo-
rithm chooses a bilinear group G of order p and
two generators g, h ∈ G. It randomly chooses
{h
j
∈ Z
p
}
j∈[n]
,(B,B
∗
),(B
0
,B
∗
0
) ∈ Dual(Z
3
p
,ψ)
and (B
1
,B
∗
1
),. .. ,(B
U
,B
∗
U
) ∈ Dual(Z
6
p
,ψ). We
let
~
b
j
,
~
b
∗
j
(1 ≤ j ≤ 3) denote the basis vectors
belonging to (B,B
∗
),
~
b
0, j
,
~
b
∗
0, j
(1 ≤ j ≤ 3) de-
note the basis vectors belonging to (B
0
,B
∗
0
), and
~
b
x, j
,
~
b
∗
x, j
(1 ≤ j ≤ 6) denote the basis vectors be-
longing to (B
x
,B
∗
x
) for each x ∈ [U]. The algo-
rithm also chooses random exponents
α
1
,α
2
∈ Z
p
, {r
i
,z
i
, α
i,1
,α
i,2
∈ Z
p
}
i∈[n]
,
{c
j,1
,c
j,2
, y
j
,h
j
∈ Z
p
}
j∈[n]
.
The public parameter PP and the master secret
key MSK are set to
PP =
(p,G,G
T
,e), g,h,g
~
b
1
,g
~
b
2
,
{h
j
}
j∈[n]
,h
~
b
1
,h
~
b
2
, {h
~
b
1
j
,h
~
b
2
j
}
j∈[n]
,
h
~
b
0,1
,h
~
b
0,2
, {h
~
b
x,1
,h
~
b
x,2
,h
~
b
x,3
,h
~
b
x,4
}
x∈[U]
,
F
1
= e(g,h)
ψα
1
, F
2
= e(g,h)
ψα
2
,
{F
1, j
= e(g,h
j
)
ψα
1
,F
2, j
= e(g,h
j
)
ψα
2
}
j∈[n]
,
{E
i,1
= e(g,g)
ψα
i,1
, E
i,2
= e(g,g)
ψα
i,2
}
i∈[n]
,
{
~
G
i
= g
r
i
(
~
b
1
+
~
b
2
)
,
~
Z
i
= g
z
i
(
~
b
1
+
~
b
2
)
}
i∈[n]
,
{
~
H
j
= g
c
j,1
~
b
∗
1
+c
j,2
~
b
∗
2
,
~
Y
j
=
~
H
y
j
j
}
j∈[n]
.
MSK =
~
b
∗
1
,
~
b
∗
2
,
~
b
∗
0,1
,
~
b
∗
0,2
, {
~
b
∗
x,1
,
~
b
∗
x,2
,
~
b
∗
x,3
,
~
b
∗
x,4
}
x∈[U]
,
α
1
,α
2
, {r
i
,z
i
, α
i,1
,α
i,2
}
i∈[n]
,{c
j,1
,c
j,2
}
j∈[n]
.
In addition, a counter ctr = 0 is implicitly in-
cluded in MSK.
KeyGen
A
(PP,MSK,S) → SK
(i, j),S
. The algorithm
first sets ctr = ctr + 1 and computes the corre-
sponding index in the form of (i, j) where 1 ≤
i, j ≤n and (i−1)∗n+ j = ctr. Then it randomly
chooses σ
i, j,1
,σ
i, j,2
,δ
i, j,1
,δ
i, j,2
∈ Z
p
, and outputs
a private key
SK
(i, j),S
= h (i, j),S,
~
K
i, j
= g
(α
i,1
+r
i
c
j,1
)
~
b
∗
1
+(α
i,2
+r
i
c
j,2
)
~
b
∗
2
·(hh
j
)
(σ
i, j,1
+δ
i, j,1
)
~
b
∗
1
+(σ
i, j,2
+δ
i, j,2
)
~
b
∗
2
,
~
K
′
i, j
= g
(α
1
+σ
i, j,1
+δ
i, j,1
)
~
b
∗
1
+(α
2
+σ
i, j,2
+δ
i, j,2
)
~
b
∗
2
,
~
K
′′
i, j
= (
~
K
′
i, j
)
z
i
,
{
~
¯
K
i, j, j
′
= h
(σ
i, j,1
+δ
i, j,1
)
~
b
∗
1
+(σ
i, j,2
+δ
i, j,2
)
~
b
∗
2
j
′
}
j
′
∈[n]\{j}
,
~
K
i, j,0
= g
δ
i, j,1
~
b
∗
0,1
+δ
i, j,2
~
b
∗
0,2
,
{
~
K
i, j,x
= g
σ
i, j,1
(
~
b
∗
x,1
+
~
b
∗
x,2
)+σ
i, j,2
(
~
b
∗
x,3
+
~
b
∗
x,4
)
}
x∈S
i.
Encrypt
A
(PP,M,R, A = (A,ρ), (
¯
i,
¯
j)) → CT
R,(A,ρ)
.
R ⊆ [n,n] is a revocation list. A is an l ×m LSSS
matrix and ρ maps each row A
k
of A to an attribute
ρ(k) ∈ [U]. The encryption is for recipients
whose (index, attributes set) pair
(i, j),S
(i, j)
sat-
isfy
(i, j) ∈[n,n] \R
∧
S
(i, j)
satisfies (A,ρ)
∧
(i, j) ≥ (
¯
i,
¯
j)
. Let
¯
R = [n,n] \ R and for i ∈
[n],
¯
R
i
= {j
′
|(i, j
′
) ∈
¯
R}, that is,
¯
R is the non-
revoked index list, and
¯
R
i
is the set of non-revoked
column index on the i-th row. The algorithm first
chooses random
κ, τ, s
1
,. .. ,s
n
, t
1
,. .. ,t
n
∈ Z
p
, ~v
c
, ~w
1
,. .. ,~w
n
∈ Z
3
p
,
ξ
1,1
,ξ
1,2
,. .. ,ξ
l,1
,ξ
l,2
∈ Z
p
, ~u
1
,~u
2
∈ Z
m
p
.
It also chooses random r
x
,r
y
,r
z
∈ Z
p
, and sets
~
χ
1
= (r
x
,0,r
z
),
~
χ
2
= (0,r
y
,r
z
),
~
χ
3
=
~
χ
1
×
~
χ
2
=
(−r
y
r
z
,−r
x
r
z
,r
x
r
y
). Then it randomly chooses
~v
i
∈ Z
3
p
for i = 1, .. .,
¯
i,
~v
i
∈ span{
~
χ
1
,
~
χ
2
} for i =
¯
i+ 1,. .. ,n.
Let π
1
and π
2
be the first entries of ~u
1
and ~u
2
respectively. The algorithm creates a ciphertext
hR,(A, ρ), (
~
R
i
,
~
R
′
i
,
~
Q
i
,
~
Q
′
i
,
~
Q
′′
i
,T
i
)
n
i=1
, (
~
C
j
,
~
C
′
j
)
n
j=1
,
(
~
P
k
)
l
k=0
i as follows:
1. For each row i ∈[n]:
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
288

• if i <
¯
i: choose random ˆs
i
∈Z
p
, then set
~
R
i
= (g
~
b
1
+
~
b
2
)
~v
i
,
~
R
′
i
=
~
R
κ
i
,
~
Q
i
= g
s
i
(
~
b
1
+
~
b
2
)
,
~
Q
′
i
= (h
∏
j
′
∈
¯
R
i
h
j
′
)
s
i
(
~
b
1
+
~
b
2
)
~
Z
t
i
i
h
π
1
~
b
1
+π
2
~
b
2
,
~
Q
′′
i
= g
t
i
(
~
b
1
+
~
b
2
)
,T
i
= e(g,g)
ˆs
i
.
• if i ≥
¯
i: set
~
R
i
= (
~
G
i
)
s
i
~v
i
,
~
R
′
i
=
~
R
κ
i
,
~
Q
i
= g
τs
i
(~v
i
·~v
c
)(
~
b
1
+
~
b
2
)
,
~
Q
′
i
= (h
∏
j
′
∈
¯
R
i
h
j
′
)
τs
i
(~v
i
·~v
c
)(
~
b
1
+
~
b
2
)
~
Z
t
i
i
h
π
1
~
b
1
+π
2
~
b
2
,
~
Q
′′
i
= g
t
i
(
~
b
1
+
~
b
2
)
, T
i
= M
(E
i,1
E
i,2
)
τs
i
(~v
i
·~v
c
)
(F
1
′
F
2
′
)
τs
i
(~v
i
·~v
c
)
F
π
1
1
F
π
2
2
,
where F
1
′
= F
1
∏
j
′
∈
¯
R
i
F
1, j
′
and F
2
′
= F
2
∏
j
′
∈
¯
R
i
F
2, j
′
respectively.
2. For each column j ∈ [n]:
• if j <
¯
j: choose random µ
j
∈Z
p
, then set
~
C
j
= (
~
H
j
)
τ(~v
c
+µ
j
~
χ
3
)
(
~
Y
j
)
κ~w
j
,
~
C
′
j
= (
~
Y
j
)
~w
j
.
• if j ≥
¯
j: set
~
C
j
= (
~
H
j
)
τ~v
c
(
~
Y
j
)
κ~w
j
,
~
C
′
j
= (
~
Y
j
)
~w
j
.
3.
~
P
0
= h
π
1
~
b
0,1
+π
2
~
b
0,2
,
{
~
P
k
= h
(A
k
·~u
1
+ξ
k,1
)
~
b
ρ(k),1
−ξ
k,1
~
b
ρ(k),2
·h
(A
k
·~u
2
+ξ
k,2
)
~
b
ρ(k),3
−ξ
k,2
~
b
ρ(k),4
}
k∈[l]
.
Decrypt
A
(PP,CT
R,(A,ρ)
,SK
(i, j),S
) → M or ⊥.
The algorithm parses CT
R,(A,ρ)
and SK
(i, j),S
to hR,
(A,ρ),(
~
R
i
,
~
R
′
i
,
~
Q
i
,
~
Q
′
i
,
~
Q
′′
i
,T
i
)
n
i=1
, (
~
C
j
,
~
C
′
j
)
n
j=1
,
(
~
P
k
)
l
k=0
i and h (i, j),S,
~
K
i, j
,
~
K
′
i, j
,
~
K
′′
i, j
,
{
~
¯
K
i, j, j
′
}
j
′
∈[n]\{j}
,
~
K
i, j,0
, {
~
K
i, j,x
}
x∈S
i respectively.
If (i, j) ∈ R or S does not satisfy (A, ρ), the algo-
rithm outputs ⊥, otherwise it
1. Computes constants {ω
k
∈ Z
p
|ρ(k) ∈ S} such
that
∑
ρ(k)∈S
ω
k
A
k
= (1, 0,...,0), then computes
D
P
=e
3
(
~
K
i, j,0
,
~
P
0
)
∏
ρ(k)∈S
e
6
(
~
K
i, j,ρ(k)
,
~
P
k
)
ω
k
.
2. Since (i, j) ∈
¯
R(= [n,n] \R) implies j ∈
¯
R
i
, the
algorithm can compute
~
¯
K
i, j
=
~
K
i, j
·(
∏
j
′
∈
¯
R
i
\{j}
¯
~
K
i, j, j
′
)
= g
(α
i,1
+r
i
c
j,1
)
~
b
∗
1
+(α
i,2
+r
i
c
j,2
)
~
b
∗
2
·(h
∏
j
′
∈
¯
R
i
h
j
′
)
(σ
i, j,1
+δ
i, j,1
)
~
b
∗
1
+(σ
i, j,2
+δ
i, j,2
)
~
b
∗
2
.
Note that if (i, j) ∈ R (implying j /∈
¯
R
i
), the al-
gorithm cannot produce such a
¯
~
K
i, j
. The algo-
rithm then computes
D
I
=
e
3
(
~
¯
K
i, j
,
~
Q
i
) ·e
3
(
~
K
′′
i, j
,
~
Q
′′
i
) ·e
9
(
~
R
′
i
,
~
C
′
j
)
e
3
(
~
K
′
i, j
,
~
Q
′
i
) ·e
9
(
~
R
i
,
~
C
j
)
.
3. Computes M = T
i
/(D
P
·D
I
) as the output mes-
sage. Assume the ciphertext is generated from
message M
′
and index (
¯
i,
¯
j), it can be veri-
fied that only when (i >
¯
i) or (i =
¯
i ∧ j ≥
¯
j),
M = M
′
will hold. This follows from the facts
that for i >
¯
i, we have (~v
i
·
~
χ
3
) = 0 (since
~v
i
∈ span{
~
χ
1
,
~
χ
2
}), and for i =
¯
i, we have that
(~v
i
·
~
χ
3
) 6= 0 happens with overwhelming prob-
ability (since ~v
i
is randomly chosen from Z
3
p
).
The correctness can be found in the full version
(Li et al., 2016, Augmented CP-ABE Defini-
tions).
4.3 Security of The AugR-CP-ABE
Construction
The following Theorem 3 and Theorem 4 show that
our AugR-CP-ABE construction is message-hiding,
and Theorem 5 shows that our AugR-CP-ABE con-
struction is index-hiding.
Theorem 3. Suppose the DLIN assumption, the
D3DH assumption, and the source group q-parallel
BDHE assumption hold. Then no PPT adversary can
win Game
A
MH
1
with non-negligible advantage.
Proof. We begin by defining our various types of
semi-functional keys and ciphertexts. The semi-
functional space in the exponent will correspond to
the span of
~
b
3
,
~
b
∗
3
, the span of
~
b
0,3
,
~
b
∗
0,3
and the span
of each
~
b
x,5
,
~
b
x,6
,
~
b
∗
x,5
,
~
b
∗
x,6
.
Semi-functional Keys. To produce a semi-functional
key for an attribute set S, one first calls the nor-
mal key generation algorithm to produce a nor-
mal key consisting of
~
K
i, j
,
~
K
′
i, j
,
~
K
′′
i, j
,{
~
¯
K
i, j, j
′
}
j
′
∈[n]\{j}
,
~
K
i, j,0
,{
~
K
i, j,x
}
x∈S
with index (i, j). One then chooses
random value γ. The semi-functional key is
~
K
i, j
(hh
j
)
γ
~
b
∗
3
,
~
K
′
i, j
g
γ
~
b
∗
3
,
~
K
′′
i, j
g
z
i
γ
~
b
∗
3
,
{
~
¯
K
i, j, j
′
h
γ
~
b
∗
3
j
′
}
j
′
∈[n]\{j}
,
~
K
i, j,0
, {
~
K
i, j,x
}
x∈S
.
Semi-functional Ciphertexts. To produce a semi-
functional ciphertext for an LSSS matrix (A,ρ) of
size l ×m, one first calls the normal encryption al-
gorithm to produce a normal ciphertext consisting of
Attribute based Encryption: Traitor Tracing, Revocation and Fully Security on Prime Order Groups
289
Lemma 4
DLIN
…… ……
Lemma 5
DLIN
Lemma 8
DLIN
Lemma 9
DLIN
Phase 1: Lemma 6 D3DH
Phase 2: Lemma 7 q-pBDHE
Figure 1: Lemmas 4, 5, 8, and 9 rely on the subspace assumption, which is implied by DLIN assumption, Lemma 6 relies on
the D3DH assumption, and Lemma 7 relies on the source group q-parallel BDHE assumption.
hR,(A, ρ), (
~
R
i
,
~
R
′
i
,
~
Q
i
,
~
Q
′
i
,
~
Q
′′
i
,T
i
)
n
i=1
,(
~
C
j
,
~
C
′
j
)
n
j=1
,
(
~
P
k
)
l
k=0
i. One then chooses random values
π
3
,ξ
k,3
(1 ≤ k ≤l) ∈ Z
p
and a random vector~u
3
∈Z
m
p
with first entry equal to π
3
. The semi-functional ci-
phertext is:
hR,(A, ρ), (
~
R
i
,
~
R
′
i
,
~
Q
i
,
~
Q
′
i
h
π
3
~
b
3
,
~
Q
′′
i
,T
i
)
n
i=1
,(
~
C
j
,
~
C
′
j
)
n
j=1
,
~
P
0
h
π
3
~
b
0,3
,(
~
P
k
h
(A
k
·~u
3
+ξ
k,3
)
~
b
ρ(k),5
−ξ
k,3
~
b
ρ(k),6
)
l
k=1
i.
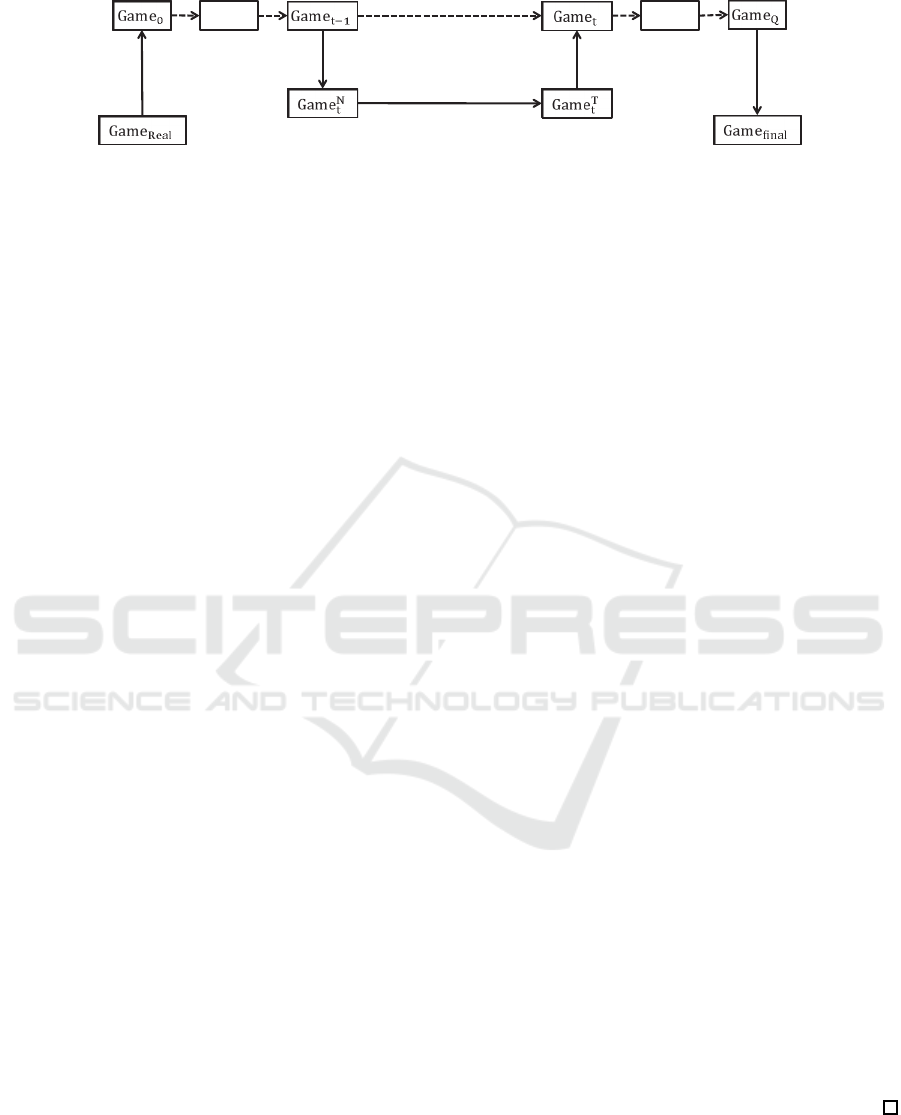
Our proof is obtained via a hybrid argument over a
sequence of games: Game
real
, Game
t
and Game
final
.
The outer structure of our hybrid argument will
progress as shown in Figure 1. First, we transition
from Game
real
to Game
0
, then to Game
1
, next to
Game
2
, and so on. We ultimately arrive at Game
Q
,
where the ciphertext and all of the keys given to the
attacker are semi-functional. We then transition to
Game
final
, which is defined to be like Game
Q
, ex-
cept that the ciphertext given to the attacker is a semi-
functional encryption of a random message. This will
complete our proof, since any attacker has a zero ad-
vantage in this final game.
The transitions from Game
real
to Game
0
and from
Game
Q
to Game
final
are relativelyeasy and can be ac-
complished directly via computational assumptions.
The transitions from Game
t−1
to Game
t
require more
intricate arguments. For these steps, we will need to
treat Phase 1 key requests (before the challenge ci-
phertext) and Phase 2 key requests (after the chal-
lenge ciphertext) differently. We will also need to de-
fine two additional types of semi-functional keys:
Nominal Semi-functional Keys. To produce a
nominal semi-functional key for an attribute
set S, one first calls the normal key generation
algorithm to produce a normal key consisting of
~
K
i, j
,
~
K
′
i, j
,
~
K
′′
i, j
,{
~
¯
K
i, j, j
′
}
j
′
∈[n]\{j}
,
~
K
i, j,0
,{
~
K
i, j,x
}
x∈S
with index (i, j). One then chooses random values
σ
i, j,3
,δ
i, j,3
∈ Z
p
. The nominal semi-functional
key is:
~
K
i, j
(hh
j
)
(σ
i, j,3
+δ
i, j,3
)
~
b
∗
3
,
~
K
′
i, j
g
(σ
i, j,3
+δ
i, j,3
)
~
b
∗
3
,
~
K
′′
i, j
g
z
i
(σ
i, j,3
+δ
i, j,3
)
~
b
∗
3
, {
~
¯
K
i, j, j
′
h
j
′
(σ
i, j,3
+δ
i, j,3
)
~
b
∗
3
}
j
′
∈[n]\{j}
,
~
K
i, j,0
g
δ
i, j,3
~
b
∗
0,3
, {
~
K
i, j,x
g
σ
i, j,3
(
~
b
∗
x,5
+
~
b
∗
x,6
)
}
x∈S
.
We note that a nominal semi-functional key still
correctly decrypts a semi-functional ciphertext.
Temporary Semi-functional Keys. A tempo-
rary semi-functional key is similar to a nomi-
nal semi-functional key, except that the semi-
functional component attached to
~
K
′
i, j
will now
be randomized (this will prevent correct de-
cryption of a semi-functional ciphertext) and
~
K
i, j
,
~
K
′′
i, j
and {
~
¯
K
i, j, j
′
}
j
′
∈[n]\{j}
change accord-
ingly. More formally, to produce a tempo-
rary semi-functional key for an attribute set S,
one first calls the normal key generation algo-
rithm to produce a normal key consisting of
~
K
i, j
,
~
K
′
i, j
,
~
K
′′
i, j
,{
~
¯
K
i, j, j
′
}
j
′
∈[n]\{j}
,
~
K
i, j,0
, {
~
K
i, j,x
}
x∈S
with index (i, j). One then chooses random val-
ues σ
i, j,3
,δ
i, j,3
,γ ∈ Z
p
. The temporary semi-
functional key is formed as:
~
K
i, j
(hh
j
)
γ
~
b
∗
3
,
~
K
′
i, j
g
γ
~
b
∗
3
,
~
K
′′
i, j
g
z
i
γ
~
b
∗
3
, {
~
¯
K
i, j, j
′
h
γ
~
b
∗
3
j
′
}
j
′
∈[n]\{j}
,
~
K
i, j,0
g
δ
i, j,3
~
b
∗
0,3
, {
~
K
i, j,x
g
σ
i, j,3
(
~
b
∗
x,5
+
~
b
∗
x,6
)
}
x∈S
.
For each t from 1 to Q, we define the additional
games: Game
N
t
and Game
T
t
.
In order to transition from Game
t−1
to Game
t
in
our hybrid argument, we will transition first from
Game
t−1
to Game
N
t
, then to Game
T
t
, and finally to
Game
t
. The transition from Game
N
t
to Game
T
t
will re-
quire different computational assumptions for Phase
1 and Phase 2 queries (As shown in Figure 1, we use
two lemmas based on different assumptions to obtain
the transition).
As shown in Figure 1, we use a series of lemmas,
i.e. Lemmas 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9, to prove the tran-
sitions. The details of these games, lemmas and their
proofs can be found in the full version (Li et al., 2016,
Appendix C.1).
Theorem 4. No PPT adversary can win Game
A
MH
N+1
with non-negligible advantage.
Proof. The argument for security of Game
A
MH
N+1
is
very straightforward since an encryption to index N +
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
290
H
1
Lemma 10
D3DH
H
2
Lemma 11
D3DH
H
3
Lemma 12
D3DH
H
4
Lemma 13
DLIN
H
5
Figure 2: Lemmas 10, 11, and 12 rely on the D3DH assumption, and Lemma 13 relies on the DLIN assumption.
1 = (n+ 1,1) contains no information about the mes-
sage. The simulator simply runs actual Setup
A
and
KeyGen
A
algorithms and encrypts the message M
b
by
the challenge access policy A and index (n + 1, 1).
Since for all i = 1 to n, the values of T
i
contain no
information about the message, the bit b is perfectly
hidden and MH
A
N+1
Adv
A
= 0.
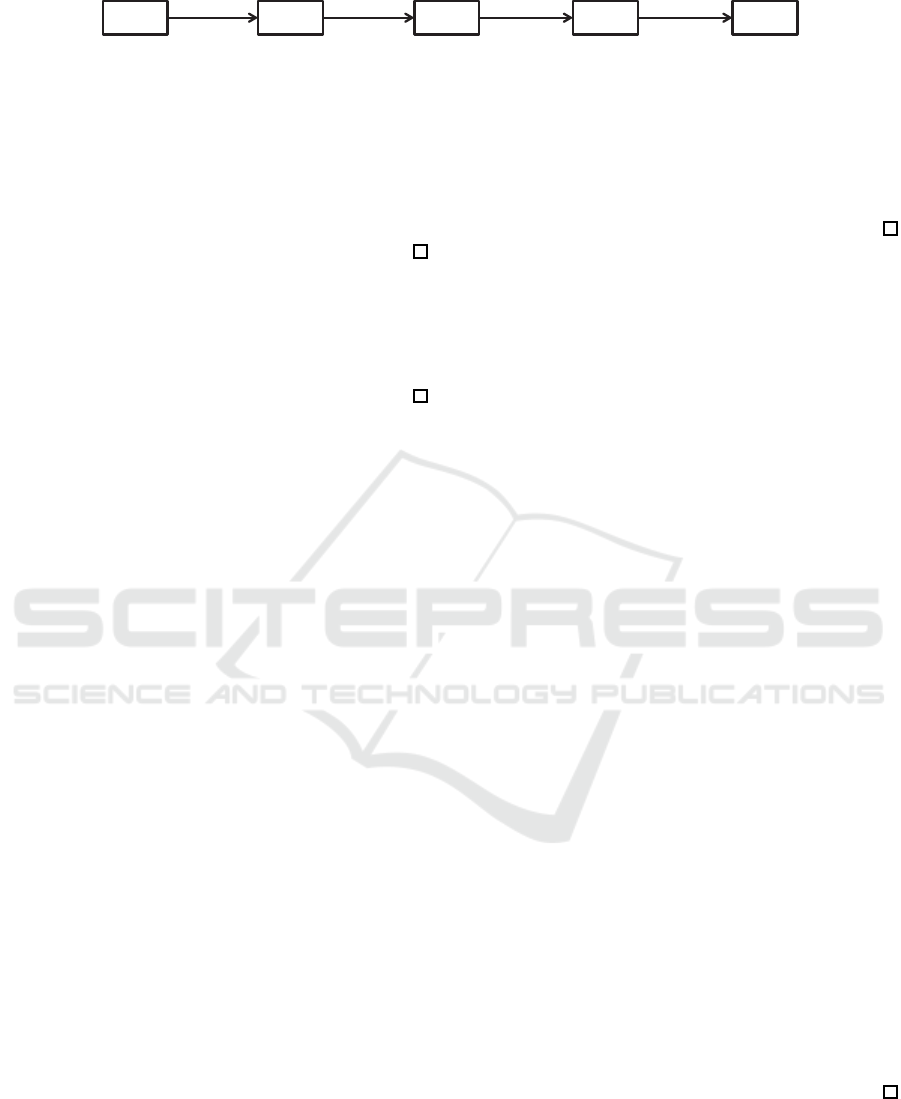
Theorem 5. Suppose that the D3DH assumption and
the DLIN assumption hold. Then no PPT adversary
can win Game
A
IH
with non-negligible advantage.
Proof. Theorem 5 follows Lemma 1 and Lemma 2
below.
Lemma 1. Suppose that the D3DH assumption holds.
Then for
¯
j < n no PPT adversary can distinguish be-
tween an encryption to (
¯
i,
¯
j) and (
¯
i,
¯
j + 1) in Game
A
IH
with non-negligible advantage.
Proof. In Game
A
IH
, the adversary A will eventually
behave in one of two different ways:
Case I: In Key Query phase, A will not sub-
mit ((
¯
i,
¯
j),S
(
¯
i,
¯
j)
) for some attribute set S
(
¯
i,
¯
j)
to
query the corresponding private key. In Challenge
phase, A submits a message M and a non-empty
attribute set S
∗
. There is not any restriction on S
∗
.
Case II: In Key Query phase, A will submit
((
¯
i,
¯
j),S
(
¯
i,
¯
j)
) for some attribute set S
(
¯
i,
¯
j)
to query
the corresponding private key. In Challenge
phase, A submits a message M and a non-empty
attribute set S
∗
with the restriction that the corre-
sponding strictest access policy A
S
∗
is not satis-
fied by S
(
¯
i,
¯
j)
. Case II has the following sub-cases:
1. (
¯
i,
¯
j) /∈ [n, n] \R
∗
, S
(
¯
i,
¯
j)
satisfies A
∗
.
2. (
¯
i,
¯
j) /∈ [n, n] \R
∗
, S
(
¯
i,
¯
j)
does not satisfy A
∗
.
3. (
¯
i,
¯
j) ∈ [n,n] \R
∗
, S
(
¯
i,
¯
j)
does not satisfy A
∗
.
We flip a random coin c ∈ {0,1} as our guess on
which case that A is in. In particular, if c = 0, we
guess that A is in Case I, Case II.1 or Case II.2.
In this case, it follows the restriction in the index-
hiding game for Augmented Broadcast Encryption
(AugBE) in (Garg et al., 2010), where the adversay
does not query the key with index (
¯
i,
¯
j) or (
¯
i,
¯
j) is not
in the receiver list [n,n] \R
∗
. If c = 1, we guess that
A is in Case I, Case II.2 or Case II.3. As of the
fully secure CP-ABE schemes in (Lewko et al., 2010;
Okamoto and Takashima, 2010; Lewko and Waters,
2012a; Lewko and Waters, 2012b; Liu et al., 2013a),
we assume that the size of attribute universe (i.e. |U|)
is polynomial in the security parameter λ, so that a
degradation of O(1/|U|) in the security reduction is
acceptable. The proof details of Lemma 1 can be
found in the full version (Li et al., 2016, Appendix
C.2).
Lemma 2. Suppose the D3DH assumption and the
DLIN assumption hold. Then for any 1 ≤
¯
i ≤ n no
PPT adversary can distinguish between an encryption
to (
¯
i,n) and (
¯
i+ 1, 1) in Game
A
IH
with non-negligible
advantage.
Proof. The proof of this lemma follows from a series
of lemmas that establish the indistinguishability of the
following games, where “less-than row” implies the
corresponding~v
i
is randomly chosen from Z
3
p
and T
i
is a random element (i.e. T
i
= e(g,g)
ˆs
i
), “target row”
implies the corresponding~v
i
is randomly chosen from
Z
3
p
and T
i
is well-formed, and “greater-than row” im-
plies the corresponding ~v
i
is randomly chosen from
span{
~
χ
1
,
~
χ
2
} and T
i
is well-formed.
• H
1
: Encrypt to column n, row
¯
i is the target row,
row
¯
i+ 1 is the greater-than row.
• H
2
: Encrypt to column n + 1, row
¯
i is the target
row, row
¯
i+ 1 is the greater-than row.
• H
3
: Encrypt to column n+1, row
¯
i is the less-than
row, row
¯
i + 1 is the greater-than row (no target
row).
• H
4
: Encrypt to column 1, row
¯
i is the less-than
row, row
¯
i + 1 is the greater-than row (no target
row).
• H
5
: Encrypt to column 1, row
¯
i is the less-than
row, row
¯
i+ 1 is the target row.
It can be observed that game H
1
corresponds to the
encryption being done to (
¯
i,n) and game H
5
corre-
sponds to encryption to (
¯
i + 1,1). As shown in Fig-
ure 2, we use a series of lemmas, i.e. Lemmas 10,
11, 12, and 13, to prove the indistinguishability of the
games H
1
and H
5
. The details of these lemmas and
their proofs can be found in the full version (Li et al.,
2016, Appendix C.3).
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we proposed a new Augmented R-
CP-ABE construction on prime order groups, and
Attribute based Encryption: Traitor Tracing, Revocation and Fully Security on Prime Order Groups
291

proved its message-hiding and index-hiding proper-
ties in the standard model. This CP-ABE achieves
full security in the standard model on prime order
groups. Our contributions are (1) adding the revoca-
tion list, and (2) proving its full security with revoca-
bility. We follow the proof method in (Liu and Wong,
2015b) for message-hiding, and build two direct re-
ductions for the proof for index-hiding. The scheme
is a fully collusion-resistantblackbox traceable R-CP-
ABE scheme. It achieves the most efficient level to
date, with overhead in O(
√
N) only.
REFERENCES
Attrapadung, N. and Imai, H. (2009). Conjunctive broadcast
and attribute-based encryption. In Pairing, pages 248–
265.
Bethencourt, J., Sahai, A., and Waters, B. (2007).
Ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption. In IEEE
Symposium on Security and Privacy, pages 321–334.
Cheung, L. and Newport, C. C. (2007). Provably secure
ciphertext policy ABE. In ACM Conference on Com-
puter and Communications Security, pages 456–465.
Deng, H., Wu, Q., Qin, B., Mao, J., Liu, X., Zhang, L.,
and Shi, W. (2014). Who is touching my cloud. In
ESORICS, Part I, pages 362–379.
Garg, S., Kumarasubramanian, A., Sahai, A., and Waters,
B. (2010). Building efficient fully collusion-resilient
traitor tracing and revocation schemes. In ACM Con-
ference on Computer and Communications Security,
pages 121–130.
Goyal, V., Jain, A., Pandey, O., and Sahai, A. (2008).
Bounded ciphertext policy attribute based encryption.
In ICALP (2), pages 579–591.
Herranz, J., Laguillaumie, F., and R`afols, C. (2010). Con-
stant size ciphertexts in threshold attribute-based en-
cryption. In Public Key Cryptography, pages 19–34.
Lewko, A. B. (2012). Tools for simulating features of com-
posite order bilinear groups in the prime order setting.
In EUROCRYPT, pages 318–335.
Lewko, A. B., Okamoto, T., Sahai, A., Takashima, K., and
Waters, B. (2010). Fully secure functional encryp-
tion: Attribute-based encryption and (hierarchical) in-
ner product encryption. In EUROCRYPT, pages 62–
91.
Lewko, A. B. and Waters, B. (2012a). New proof methods
for attribute-based encryption: Achieving full security
through selective techniques. In CRYPTO, pages 180–
198.
Lewko, A. B. and Waters, B. (2012b). New proof methods
for attribute-based encryption: Achieving full security
through selective techniques. IACR Cryptology ePrint
Archive, 2012:326.
Li, X., Liang, K., Liu, Z., and Wong, D. S. (2016). At-
tribute based encryption: Traitor tracing, revocation
and fully security on prime order groups. IACR Cryp-
tology ePrint Archive, 2016:1140.
Liu, Z., Cao, Z., and Wong, D. S. (2013a). Blackbox trace-
able CP-ABE: how to catch people leaking their keys
by selling decryption devices on ebay. In ACM Con-
ference on Computer and Communications Security,
pages 475–486.
Liu, Z., Cao, Z., and Wong, D. S. (2013b). White-box
traceable ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption
supporting any monotone access structures. IEEE
Transactions on Information Forensics and Security,
8(1):76–88.
Liu, Z. and Wong, D. S. (2015a). Practical ciphertext-policy
attribute-based encryption: Traitor tracing, revoca-
tion, and large universe. In Malkin, T., Kolesnikov,
V., Lewko, A. B., and Polychronakis, M., editors, Ap-
plied Cryptography and Network Security - 13th Inter-
national Conference, ACNS 2015, New York, NY, USA,
June 2-5, 2015, Revised Selected Papers, volume 9092
of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 127–
146. Springer.
Liu, Z. and Wong, D. S. (2015b). Traceable CP-ABE on
prime order groups: Fully secure and fully collusion-
resistant blackbox traceable. In Qing, S., Okamoto,
E., Kim, K., and Liu, D., editors, Information and
Communications Security - 17th International Con-
ference, ICICS 2015, Beijing, China, December 9-
11, 2015, Revised Selected Papers, volume 9543 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 109–124.
Springer.
Okamoto, T. and Takashima, K. (2008). Homomorphic en-
cryption and signatures from vector decomposition. In
Pairing, pages 57–74.
Okamoto, T. and Takashima, K. (2009). Hierarchical pred-
icate encryption for inner-products. In ASIACRYPT,
pages 214–231.
Okamoto, T. and Takashima, K. (2010). Fully secure func-
tional encryption with general relations from the deci-
sional linear assumption. In CRYPTO, pages 191–208.
Rouselakis, Y. and Waters, B. (2013). Practical con-
structions and new proof methods for large universe
attribute-based encryption. In ACM Conference on
Computer and Communications Security, pages 463–
474.
Sahai, A., Seyalioglu, H., and Waters, B. (2012). Dynamic
credentials and ciphertext delegation for attribute-
based encryption. In CRYPTO, pages 199–217.
Sahai, A. and Waters, B. (2005). Fuzzy identity-based en-
cryption. In EUROCRYPT, pages 457–473.
Waters, B. (2011). Ciphertext-policy attribute-based en-
cryption: An expressive, efficient, and provably se-
cure realization. In Public Key Cryptography, pages
53–70.
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
292
