
Cost Optimization on Public Cloud Provider for Big Geospatial Data:
A Case Study using Open Street Map
Joao Bachiega Junior, Marco Antonio Sousa Reis, Aleteia P. F. de Araujo and Maristela Holanda
Department of Computer Science, University of Brasilia, Brasília/DF, Brazil
Keywords: Big Geospatial Data, SpatialHadoop, Geospatial Cloud.
Abstract: Big geospatial data is the emerging paradigm for the enormous amount of information
made available by the development and widespread use of Geographical Information System
(GIS) software. However, this new paradigm presents challenges in data management, which
requires tools for large-scale processing, due to the great volumes of data. Spatial Cloud Computing offers
facilities to overcome the challenges of a big data environment, providing significant computer power and
storage. SpatialHadoop, a fully-fledged MapReduce framework with native support for spatial data, serves as
one such tool for large-scale processing. However, in cloud environments, the high cost of processing and
system storage in the providers is a central challenge. To address this challenge, this paper presents a cost-
efficient method for processing geospatial data in public cloud providers. The data validation software used
was Open Street Map (OSM). Test results show that it can optimize the use of computational resources by up
to 263% for available SpatialHadoop datasets.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cloud computation is a model that
facilitates transparent, and on-demand, access to a set
of computational resources (for example, networks,
servers, warehousing, applications and services),
which can be acquired quickly, and released
with very little managing effort, or interaction with
the service provider. Kramer and Senner (2015)
affirm that the cloud offers virtually unlimited
resources in terms of processing power and
memory. Subsequently, the amount of computational
resources required by this vast volume of
information, aka big data, grows in an asymptotic
way. Therefore, each computational resource
wasted potentially represents wasted financial
resources – making processing in cloud environments
costly –, since public cloud providers, like Amazon
AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud and others,
charge users on a pay-per-use basis.
Big data has some specific characteristics that
distinguish it from other datasets (Sagiroglu and
Sinanc, 2013). These characteristics, known as the
7Vs, are (Pramila, 2015): i) Variety – referring to the
different types of data, with more than 80% of them
in an unstructured form; ii) Volume – the tremendous
amount of data generated each second; iii) Velocity –
the speed at which new data is being produced; iv)
Veracity – how trustworthy the data is; v) Value –the
importance of the data to the business; vi) Variability
- data with constantly changing meaning and vii)
Visualization – data presented to users in readable and
accessible way.
Consequently, some methods were developed to
process big data (Sagiroglu and Sinanc, 2013).
Among them, Apache Hadoop stands out. It is a
programming framework for distributed computing
using the divide and conquer (or Map and Reduce)
method to break down complex big data problems
into small units of work and process them in parallel.
The rise of big geospatial data creates the need for
an environment with ample computational resources
in order to process this amount of geographical
information. Some applications were developed
specifically for this big geospatial data using Hadoop
concepts (Eldawy and Mokbel, 2015): i) “GIS Tools
on Hadoop”, which works with the ArcGIS product;
ii) Parallel-Secondo as a parallel spatial DBMS that
uses Hadoop as a distributed task scheduler; iii) MD-
HBase extends HBase, a non-relational database for
Hadoop, to support multidimensional indexes; iv)
Hadoop-GIS extends Hive, a data warehouse
infrastructure built on top of Hadoop with a uniform
54
Junior, J., Reis, M., Araujo, A. and Holanda, M.
Cost Optimization on Public Cloud Provider for Big Geospatial Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0006237800820090
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER 2017), pages 54-62
ISBN: 978-989-758-243-1
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

grid index for range queries and self-join. Finally,
Eldawy and Mokbel (2015) presented SpatialHadoop,
a fully-fledged MapReduce framework, with native
support for spatial data with better performance than
all the other applications listed.
One challenge in a cloud environment is to know
the cost of processing big data in public cloud
providers. According to Zhang et al (2010),
cloud computing has impact where large companies,
such as Google, Amazon and Microsoft, strive to
provide cost-efficient cloud platforms. In this way,
the cost to execute the applications using these public
providers is fundamental information for executing
applications in a cloud. In this context, this article
presents a method for cost-efficient processing in
public cloud providers for big geospatial data using
SpatialHadoop. For this, an Open Street Map (OSM)
dataset is used with the goal of optimizing the use of
computational resources to reduce costs.
The remainder of the article is divided into 5
sections. Section 2 covers concepts of Spatial Cloud
Computing, SpatialHadoop and some related works.
Section 3 presents the method to determine the
number of data nodes in a cluster, based on dataset
size. The case study is presented in Section 4, with
information about architecture, datasets, tests and
results. Finally, Section 5 contains the conclusion and
some suggestions for future work.
2 THEORICAL REFERENCE
In this section, concepts about cloud computing will
be presented, highlighting the characteristics for an
environment to process big geospatial data and, also,
about SpatialHadoop, and related works.
2.1 Spatial Cloud Computing
Although computing hardware technologies,
including a central processing unit (CPU), network,
storage, RAM, and graphics processing unit (GPU),
have advanced greatly in past decades, many
computing requirements for addressing scientific and
application challenges, such as those for big
geospatial data processing, exceed existing
computing capabilities (Yang et al., 2011).
These challenges require a computing
infrastructure that can: i) support data discovery,
access, use and processing well, relieving scientists
and engineers of IT tasks so they can focus on
scientific discoveries; ii) provide real-time IT
resources to enable real-time applications, such as
emergency response; iii) deal with access spikes; and
iv) provide extremely reliable and scalable service for
massive numbers of concurrent users to advance
public knowledge (Eldawy et al., 2015).
Cloud computing offers facilities to overcome the
challenges of a big data environment, providing
substantial computer power and vast storage. In the
most common definition of cloud computing, NIST
(2011) indicates five essential characteristics,
namely, on demand self-service, broad network
access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and
measured service.
However, other characteristics are relevant to
defining spatial cloud computing environments.
Akdogan et al. (2014) proposed a cost-efficient
partitioning of spatial data in clouds. This partitioning
method considers location-based services and
optimizes the storage of spatial-temporal data to be
able to turn-off idle servers and reduce costs.
Yang et al. (2011) defines Spatial Cloud
Computing as the cloud computing paradigm that is
driven by geospatial sciences, and optimized by
spatiotemporal principles for enabling geospatial
science discoveries and cloud computing within a
distributed computing environment. This is expected
to supply the computational needs for geospatial data
intensity, computing intensity, concurrent access
intensity and spatiotemporal intensity.
According to NIST (2011), there are four
deployment models for clouds, namely private,
community, public and hybrid. Specifically, to public
clouds, the authors define how the cloud
infrastructure is provisioned for open use by the
general public. In this model of cloud deployment,
services are charged for using a pay-per-use method
at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of
service (e.g. storage, processing or bandwidth). When
working with big geospatial data, the volume of data
and the power of processing are always high and,
subsequently, expensive.
According to the “Gartner Magic Quadrant for
Cloud Infrastructure as a Service”, Amazon AWS is
the leading public cloud provider (Leong et al., 2016).
It offers “Elastic Map Reduce” (EMR) that uses
Hadoop fundamentals and is integrated with others
services available from providers, such as storage,
data mining, log file analysis, machine learning,
scientific simulation, and data warehousing. The case
study related in this paper were done in an Amazon
AWS environment.
2.2 SpatialHadoop
In past years, many applications have been producing
an immense volume of data, but most of these data
Cost Optimization on Public Cloud Provider for Big Geospatial Data
55

are in an unstructured format. Hadoop emerged in this
scenario. It is an open-source project from Apache
community, which processes big data. It is comprised
of a file system called Hadoop Distributed File
System (HDFS) that provides an infrastructure to
analyse and process high volume data through the
MapReduce paradigm, using the benefits of
distributed processing.
However, Hadoop does have some limitations in
processing big geospatial data related to the indexing
of HDFS files (Eldawy and Mokbel, 2015). To bypass
these limitations, SpatialHadoop was developed as a
fully-fledged MapReduce framework with native
support for spatial data. It was built on Hadoop base
code, adding spatial constructs and the awareness of
spatial data inside the core functionality of traditional
Hadoop.
SpatialHadoop comprises four main layers
(Figure 1), namely, language, operations,
MapReduce and storage. All of them execute in a
cluster environment with one master node that breaks
a MapReduce job into smaller tasks, carried out by
slave nodes.
Figure 1: SpatialHadoop high-level architecture.
The Application layer is out from the
SpatialHadoop core, but is fundamental to interact
with users. Among these applications, are:
CG_Hadoop, proposed by Eldawy et al. (2013), is a
suite of scalable and efficient MapReduce algorithms
for various fundamental computational geometry
operations, such as, polygon union, skyline, convex
hull, farthest pair, and closest pair; MNTG, a web-
based road network traffic generator, created by
Mokbel et al. (2014); TAREEG, a MapReduce-based
web service, that uses SpatialHadoop fundamentals
for extracting spatial data from Open Street Map,
proposed by Alarabi et al. (2014); SHAHED, that
uses SpatialHadoop to query and visualize spatio-
temporal satellite data, proposed by Eldawy et al.
(2015).
The language used by SpatialHadoop is Pigeon, a
simple high-level SQL-like language, extended from
Pig Latin. It is compliant with the Open Geospatial
Consortium’s (OGC) simple feature access standard,
which is supported in both open source and
commercial spatial Data Base Management System
(DBMS). Pigeon supports OGC standard data types
including point, linestring and polygon, as well as
OGC standard functions for spatial data.
The operations layer encapsulates the
implementation of various spatial operations with
spatial indexes and the new components in the
MapReduce layer. According to Aji et al. (2013), the
operations layer comprises: basic operations, range
query, k-nearest neighbor (knn) and spatial join;
CG_Hadoop, a suite of scalable and efficient
MapReduce algorithms for various fundamental
computational geometry problems, namely, polygon
union, skyline, convex hull, farthest pair, and closest
pair (Eldawy et al., 2013); and spatial data mining,
operations developed using spatial data mining
techniques.
Similar to Hadoop, the MapReduce layer in
SpatialHadoop (Figure 2) is the query processing
layer that runs MapReduce programs (Eldawy and
Mokbel, 2015). However, contrary to Hadoop where
the input files are non-indexed heap files,
SpatialHadoop supports spatially-indexed input files.
SpatialHadoop enriches traditional Hadoop systems
with two main components: SpatialFileSplitter, an
extended splitter that exploits the global index in
input files to perform early pruning of file blocks not
contributing to answer, and SpatialRecordReader,
which reads a split originating from spatially indexed
input files and exploits the local indexes to efficiently
process it.
Figure 2a: MapReduce in traditional Hadoop (Eldawy and
Mokbel, 2015).
Figure 2b: MapReduce in SpatialHadoop (Eldawy and
Mokbel, 2015).
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
56
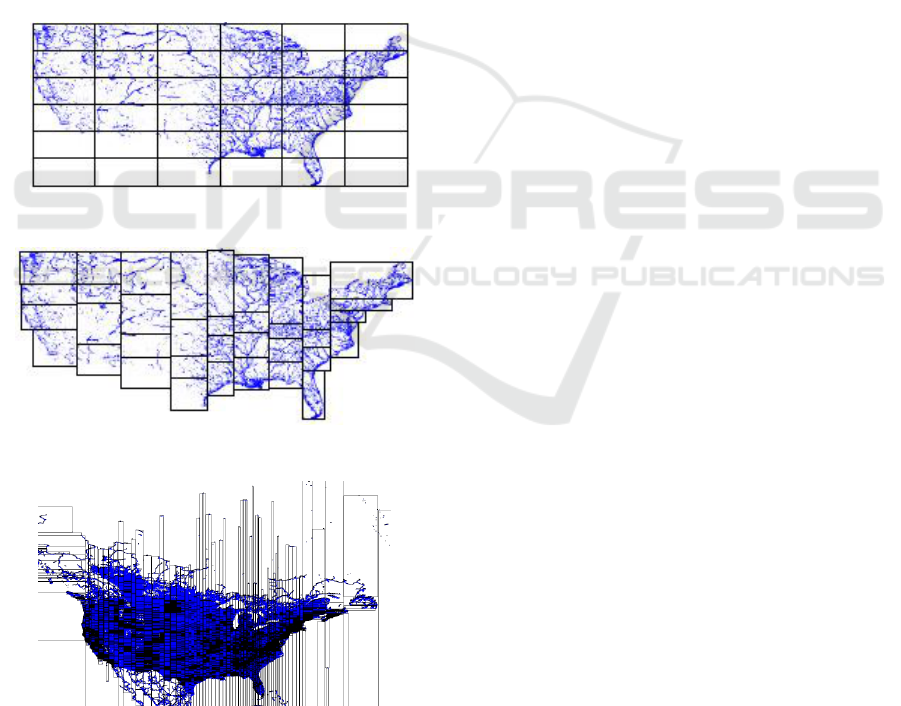
The Storage Layer creates two index layers,
global and local. The global index is applicable on a
cluster’s master node, while local indexes organize
data in each slave node. The SpatialHadoop supports
the main spatial index structures (Eldawy and
Mokbel, 2015): grid file (Figure 3a), a simple flat
index that partitions the data according to a grid, such
that, records overlapping each grid cell are stored in
one file block as a single partition; R-tree (Figure 3b),
in this indexing technique records are not replicated
which causes partitions to overlap; R+-tree (Figure
3c), a variation of the R-tree where nodes at each level
are kept disjoint, while records overlapping multiple
nodes are replicated to each node to ensure efficient
query answering.
Eldawy et al. (2013) developed four more
indexing techniques for SpatialHadoop, namely, Z-
curve, Hilbert curve, Quad tree, and K-d tree, but
these techniques are not as widely used as the others.
Figure 3a: Grid file indexing (Eldawy and Mokbel, 2015).
Figure 3b: R-tree indexing (Eldawy and Mokbel, 2015).
Figure 3c: R+-tree indexing (best viewed in color) (Eldawy
and Mokbel, 2015).
2.3 Related Work
SpatialHadoop was presented in 2013 by Eldawy and
Mokbel (2013) as the first fully-fledged MapReduce
framework with native support for spatial data. In this
article, the authors used a demonstration scenario
created on an Amazon AWS, with 20 node cluster to
compare SpatialHadoop and traditional Hadoop in
three operations, namely, range query, knn and spatial
join. In this paper, as in others, such as, Mokbel et al.
(2014), Alarabi et al. (2014), Eldawy et al. (2015) and
Eldawy et al. (2016), a static computational
environment was used to validate tests. The increase
of data nodes was done in a controlled way, without
automation.
A modular software architecture for processing
big geospatial data in the cloud was presented by
Kramer and Senner (2015). Since the proposed
framework does not distinguish whether the cloud
environment is private or public, a third-party tool –
Ansible – was used to execute provisioning scripts
Finally, in 2016, Das et al. (2016) proposed a
geospatial query resolution framework using an
orchestration engine for clouds. However, the cloud
environment used was private, and no dynamic
allocation of computational resources was performed.
None of these works presents a method to
optimize the use of computational resources, and
reduce financial costs on public cloud providers when
using SpatialHadoop to process big geospatial data.
This paper presents a case study about a cost-
efficient method to process geospatial data on public
cloud providers, optimizing the number of data nodes
in a SpatialHadoop cluster according to dataset size.
3 CLUSTER SIZING
A common uncertainty for Hadoop environment
administrators is how to define the cluster size
infrastructure. In a static environment, like a private
cloud, most of the time the computational resources
are limited and big geospatial data grows faster,
requiring ever more resources. On the other hand, in
public cloud providers, the computational resources
are unlimited, but they come with fees, so it is very
important to define a cost-effective environment.
A twenty-node cluster can be necessary to process
SpatialHadoop queries and operations on a 100Gb
dataset, but is overprovisioned to work on a dataset of
only 5Gb. To solve this problem, a formula to
calculate the quantity of data nodes based on dataset
size is fundamental. Adapting the proposal by
Hadoop Online Tutorial (2016), the following
Cost Optimization on Public Cloud Provider for Big Geospatial Data
57

formula can be used to determine the ideal number of
data nodes in a SpatialHadoop environment on public
cloud providers:
(1)
DN represents the total data nodes needed; T is the
total amount of data and d is the disk size in each
node.
It is necessary to calculate T because the total
amount of data used in a SpatialHadoop application
is not only the volume of the dataset. To calculate T,
the following formula can be used:
(2)
C represents the compression rate of the dataset,
required, because SpatialHadoop can work with
compressed files. When no compression is used, the
value must be 1. R is the number of replicas of data in
HDFS and S represents the size of the dataset. The
notation i refers to the intermediate working space
dedicated to temporarily storing results of Map Tasks.
Finally, w represents the percentage of space left
(wasted) to HDFS file system.
To demonstrate the use of these formulas, let us
consider a real Open Street Map dataset of 96Gb of
total size (2.7 billion records) available to download
at http://spatialhadoop.cs.umn.edu/datasets. Without
compression (C = 1), without replication (R = 1),
considering i = 25% and w = 20%, the value obtained
for T is 106.67. Considering that each data node has a
disk with 32Gb (d = 32) it is possible to conclude that
the ideal number of data nodes (DN) is 4.
4 CASE STUDY
To support the method proposed in this paper, a study
case using Open Street Map datasets was executed, in
a cloud environment, built in Amazon AWS provider.
The following sections detail the system architecture,
the datasets used, the tests and the results.
4.1 System Architecture
An architecture composed of three layers, namely
Web Interface, Storage and SpatialHadoop (Figure
4), was created to support the tests environment and
the proposed method.
Figure 4: System Architecture Overview.
The Web Interface Layer is a user-friendly
interface to receive inputs and to show results. In this
layer, the user selects an available dataset (or uploads
one if it is new) using the “Dataset Catalogue”. The
workflow to be executed is loaded or created through
the “Workflow Catalogue”. A workflow contains
information about queries and operations to be
executed and file index type (Grid, R-Tree or R+-
Tree). Results are available in “Results Catalogue”.
The Storage Layer stores all datasets available, the
workflows used, and the results saved after
application execution.
The SpatialHadoop Layer is the core layer. It is
responsible for provisioning the SpatialHadoop
cluster with one master node and n data nodes. The
quantity of data nodes is defined based on dataset
size, as shown in Section 3. After provisioning the
cluster, this layer indexes the dataset (based on user
choice in the Web Interface layer), processes queries
and operations, and saves the results file back in the
Storage Layer.
4.2 Open Street Maps Datasets
The OpenStreetMap (OSM) is a project for
geographic information that has a world map built by
volunteers. The project is open data and can be used
for any purpose.
The OSM files are available on Planet.osm web
site (http://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Planet.osm)
and the files used in this research are accessible on
SpatialHadoop Datasets website
(http://spatialhadoop.cs.umn.edu/datasets). The file
format is XML and can be downloaded in a
compacted way for convenience.
The datasets considered in our case study are
presented in Table 1. The Lakes’ dataset contains
boundaries of lakes in the world in a 2.7 GB
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
58
compacted file with about 8.4M records. A larger
dataset contains the boundaries of all buildings
around the world – 6 GB in compacted size, and
comprising 115M records. These files were
previously uploaded to Amazon S3, and are available
publicly on the URIs https://s3.amazonaws.com
/spatial-hadoop/input/lakes.bz2 and https://s3
.amazonaws.com/spatial-hadoop/input/buildings.
bz2, respectively.
Table 1: Datasets and their features.
Dataset
Size
Compacted
Records
Lakes
9.0 GB
2.7 GB
8.4
million
Buildings
26.0 GB
6 GB
115
million
4.3 Tests and Results
A SpatialHadoop environment was built using
Amazon AWS EMR to test the proposed method.
Although all three layers of the system architecture –
Web Interface, Storage and SpatialHadoop – were
allocated on a cloud provider, the focus of this test
scenario – performance and cost – was specifically
carried out on the SpatialHadoop layer.
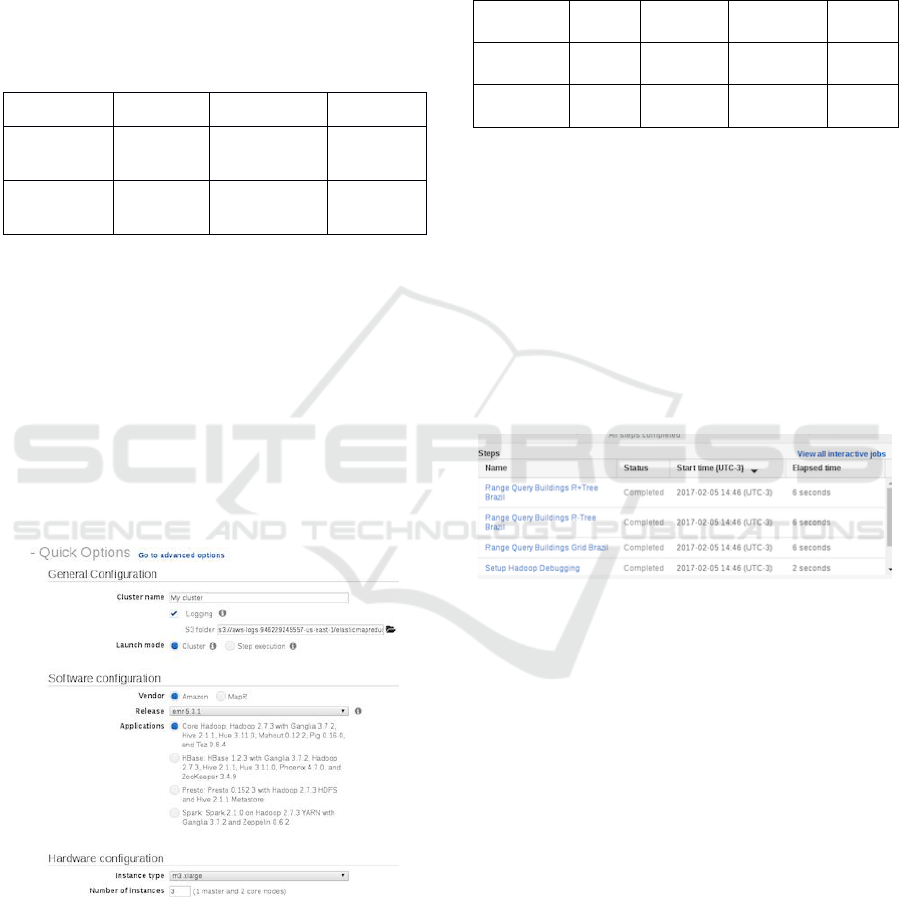
Figure 5 shows the Amazon Web Interface. For
our tests we used the Amazon interface to configure
parameters and execute the scripts.
Figure 5: Amazon Configuration Interface.
Table 2 presents the instances configurations used
to run the tests on Amazon AWS. The master node is
responsible for the cluster management and requires
more memory than datanodes. For the case study, the
master node has 15 GiB memory and 2 SSDs with 80
GiB each. The price per hour for this configuration is
US$ 0.42. The data nodes are responsible for the
spatial data processing. They have 7.5 GiB memory
and 2 SSDs with 40 GiB each. The price per hour for
each node is US$ 0.21.
Table 2: Instances Configurations on Amazon AWS.
Function
vCPU
Memory
Disk
(SSD)
Price
(US$)
Master
8
15
2x 80 Gb
0.42 /
hour
Data
Node
4
7.5
2x 40 Gb
0.21 /
hour
The clusters created for tests comprise one master
node and the quantity of data nodes based on the
formula shown in Section 3. With C = 1, R = 3, i =
25% and w = 20%, 1 data node was required for the
small dataset and 2 data nodes for the big one.
Once parameters were defined in the Web
Interface Layer and the dataset was stored in the
Storage Layer, the SpatialHadoop Layer was
configured to execute the steps (scripts). Each step
was configured with the Amazon Web Interface
(Figure 6). We defined the script and received the
results.
Figure 6: Steps on Amazon Web Interface.
The steps executed were:
• Provisioning Cluster: a defined request is sent to
the cloud provider with the number and type of master
node and data nodes. The command used in Amazon
AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) is:
aws emr create-cluster \
--applications Name=Hadoop \
--bootstrap-actions
'[{"Path":"s3://scripts-nuvem/install-
shadoop-uber.sh","Name":"Instalar
SpatialHadoop"}]' \ --ec2-attributes
'{"KeyName":"acesso-aws",
"InstanceProfile":"EMR_EC2_DefaultRole"
,"SubnetId":"subnet-55f01169",
"EmrManagedSlaveSecurityGroup":"sg-xx",
"EmrManagedMasterSecurityGroup":"sg-
xx"}' --service-role EMR_DefaultRole \
--enable-debugging \ --release- label
emr-5.1.0 --log-uri 's3n://aws-logs-2-
us-east- 1/elasticmapreduce/' \--name
Cost Optimization on Public Cloud Provider for Big Geospatial Data
59

'geo-cluster' \--instance-groups
'[{"InstanceCount":1,"InstanceGroupType
":"CORE","InstanceType":"c4.xlarge","Na
me":"Core instance group -
2"},{"InstanceCount":1,"InstanceGroupTy
pe":"MASTER","InstanceType":"c4.2xlarge
","Name":"Master instance group -
1"}]' \ --region us-east-1
• Transfer Dataset: copies an existing dataset
from Storage Layer to Data nodes.
• Index Dataset: applies the user-defined index
type to dataset. The AWS CLI command to index a
dataset using Grid is:
aws emr add-steps --cluster-id j-xx \
--steps '[{"Args":["index","s3://dados-
spatial/sports.bz2", "s3://dados-
spatial/sports.index","shape:osm","sind
ex:grid", "-overwrite"],
"Type":"CUSTOM_JAR", "ActionOnFailure":
"CONTINUE","Jar":"/usr/lib/hadoop/spati
alhadoop-2.4-uber.jar",
"Properties":"","Name":"Index"}]'
• Queries and Operations: executes the user-
defined queries and operations. The following AWS
CLI command was used to execute a KNN query:
aws emr add-steps --cluster-id j-xx \
--steps '[{"Args":["knn","s3://dados-
spatial/sports.index", "s3://dados-
spatial/sports-knn.txt", "point:-
15.763372,-47.8700677", "k:1000",
"shape:osm", "-overwrite"],
"Type":"CUSTOM_JAR","ActionOnFailure":"
CONTINUE", "Jar":"/usr/lib/hadoop/
spatialhadoop-2.4-uber.jar",
"Properties":"","Name":"KNN"}]'
• Save Results: saves the result file – usually a text
file – on Storage Layer to be accessed by user.
• Turn-off Cluster: to avoid waste of
computational resources and financial costs, all the
cluster (master node and data nodes) are turned off
unless some stickiness parameter was defined by the
user.
Table 3 presents the runtime of each task in a test
environment. The values represent an average of 3
executions for each dataset. The queries – KNN and
Range Query – and the indexing type Grid were
chosen randomly, and could be changed by any query
or operation and indexing type.
The indexing task is very important to ensure the
SpatialHadoop high performance. Note that the index
process takes up most of the time, but subsequently
the queries are done very quickly.
Table 3: Time measured in each task.
Task
Small Dataset
(seconds)
Large Dataset
(seconds)
Provisioning Cluster
300
420
Transfer Dataset
60
120
Index Dataset
600
3540
KNN
10
8
Range Query
8
6
Save Results
2
2
Turn-off Cluster
100
164
TOTAL Time
1080
4260
Given the cost of the cluster to support the Small
Dataset (1 master node and 1 data node) as US$
0.63/hour, the total cost to process these two queries
was US$ 0.19. For the cluster to support the large
dataset (comprising 1 master node and 2 data nodes),
the cost per hour is US$ 0.84, and the cost of
processing these queries is US$ 0,99.
If this cluster was created without considering the
dataset’s size – and other parameters defined in the
formula – it would be necessary to consider the
largest dataset available to ensure that any query or
operation could be executed in this cluster.
Considering all datasets available to download on the
SpatialHadoop webpage, the largest dataset – an
OSM file with 137Gb of size and 717M records about
road networks represented as individual road
segments – would require a cluster comprising 1
master node and 6 data nodes. The total cost of this
cluster would be US$ 1.68 per hour and running the
small dataset (18 minutes) would cost US$ 0.50,
costing 263% more than was really needed.
Analysing all datasets available in SpatialHadoop
webpage, and considering the scenario and
parameters defined in our test environment (C = 1, R
= 3, i = 25% and w = 20%), only 7 out of a total of 33
datasets need more than 1 data node to be executed.
On the other extreme, only 1 dataset needs a 6-node
cluster. Processing any other datasets will waste
computational resources if the proposed formula is
not applied.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORKS
The enormous volume of geographic data, produced
daily, through voluntary geographic information
systems, satellite imaging, and other systems, is
classified as Bigdata, or more specifically,
GeoBigdata. To process this geo big data, spatial
cloud computing, comprising several frameworks,
has been presented as a viable tool. In the framework
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
60

that concerns our work, SpatialHadoop has the
infrastructure to process geographic databases, and
many tools have been developed for operations, joins,
and indexing in geodatabases.
Cloud computing provides infrastructure to
process big geospatial data that needs high
performance but requires a computational
infrastructure that can be expensive, when working
on public cloud providers. With this, it is necessary to
use a cost-efficient method to avoid wasting
computational resources and increases in financial
costs.
The method proposed in this paper and
demonstrated by the case study presented, achieves
the goal of supporting a SpatialHadoop environment
on public cloud providers, while avoiding the waste
of computational resources. The formula to define the
number of data nodes was validated in the case study
and about 263% of the cost was econimized.
As future works we suggest optimizations on
performance that can be obtained using task nodes –
for job processing only - and data nodes together. In
this way, it is possible to apply scalability in
SpatialHadoop applications based on user-defined
threads, mainly in indexing task, that demands
powerful computing. Others applications can also be
tested, like SpatialSpark and ISP-MC.
REFERENCES
Ahmed, Elmustafa Sayed Ali, and Rashid A. Saeed. "A
Survey of Big Data Cloud Computing Security."
International Journal of Computer Science and
Software Engineering (IJCSSE) 3.1 (2014): 78-85.
Akdogan, Afsin. Cost-efficient partitioning of spatial data
on cloud. Big Data (Big Data), 2015 IEEE International
Conference on. IEEE, 2015.
Alarabi, L., Eldawy, A., Alghamdi, R., & Mokbel, M. F.
(2014, June). TAREEG: a MapReduce-based web
service for extracting spatial data from OpenStreetMap.
ACM SIGMOD international conference on
Management of data. ACM.
Das, J., Dasgupta, A., Ghosh, S. K., & Buyya, R. A
Geospatial Orchestration Framework on Cloud for
Processing User Queries. In IEEE International
Conference on Cloud Computing for Emerging
Markets, 2016.
Distributed System Archicteture. Hadoop cluster size.
[Online]. Available from: https://0x0fff.com/hadoop-
cluster-sizing/ 2016.10.26.
Eldawy, A., Li, Y., Mokbel, M. F., & Janardan, R. (2013,
November). CG_Hadoop: computational geometry in
MapReduce. The 21st ACM SIGSPATIAL
International Conference on Advances in Geographic
Information Systems.
Eldawy, A., Mokbel, M. F., Alharthi, S., Alzaidy, A.,
Tarek, K., & Ghani, S. (2015, April). Shahed: A
mapreduce-based system for querying and visualizing
spatio-temporal satellite data. In 2015 IEEE 31st
International Conference on Data Engineering (pp.
1585-1596). IEEE.
Eldawy, Ahmed, and Mohamed F. Mokbel. "A
demonstration of SpatialHadoop: an efficient
mapreduce framework for spatial data." Proceedings of
the VLDB Endowment 6.12 (2013): 1230-1233.
Eldawy, Ahmed, and Mohamed F. Mokbel. "Pigeon: A
spatial mapreduce language." 2014 IEEE 30th
International Conference on Data Engineering.
Eldawy, Ahmed, and Mohamed F. Mokbel.
"Spatialhadoop: A mapreduce framework for spatial
data." 2015 IEEE 31st International Conference on
Data Engineering. IEEE, 2015.
Eldawy, Ahmed, Louai Alarabi, and Mohamed F. Mokbel.
"Spatial partitioning techniques in SpatialHadoop."
Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment 8.12 (2015).
Eldawy, Ahmed, M. Mokbel, and Christopher Jonathan.
"HadoopViz: A MapReduce framework for extensible
visualization of big spatial data." IEEE Intl. Conf. on
Data Engineering (ICDE). 2016.
Eldawy, Ahmed. "SpatialHadoop: towards flexible and
scalable spatial processing using mapreduce."
Proceedings of the 2014 SIGMOD PhD symposium.
ACM, 2014.
Hadoop Online Tutorial. Formula to calculate NDFS nodes
storage. [Online]. Avilable from:
http://hadooptutorial.info/ formula-to-calculate-hdfs-
nodes-storage/ 2016.11.03.
Joshi, Pramila. "Cloud Architecture for Big Data."
International Journal of Engineering and Computer
Science. 2015.
Krämer, Michel, and Ivo Senner. "A modular software
architecture for processing of big geospatial data in the
cloud." Computers & Graphics 49 (2015): 69-81.
Leong, L., Petri, G., Gill, B., Dorosh, M. The Gartner Magic
Quadrant for Cloud Infrastructure as a Service,
Worldwide. [Online]. Available from:
https://www.gartner.com/doc/reprints?id=1-2G2O5FC
&ct=150519. 2016.11.02.
Mell, Peter, and Tim Grance. "The NIST definition of cloud
computing." (2011).
Mokbel, M. F., Alarabi, L., Bao, J., Eldawy, A., Magdy, A.,
Sarwat, M., ... & Yackel, S. (2014, March). A
demonstration of MNTG-A web-based road network
traffic generator. In 2014 IEEE 30th International
Conference on Data Engineering (pp. 1246-1249).
IEEE.
Qu, Chenhao, Rodrigo N. Calheiros, and Rajkumar Buyya.
"Auto-scaling Web Applications in Clouds: A
Taxonomy and Survey." arXiv preprint
arXiv:1609.09224 (2016).
Sagiroglu, Seref, and Duygu Sinanc. "Big data: A review."
Collaboration Technologies and Systems (CTS), 2013
International Conference on. IEEE, 2013.
Cost Optimization on Public Cloud Provider for Big Geospatial Data
61

Ward, Jonathan Stuart, and Adam Barker. "Undefined by
data: a survey of big data definitions." arXiv preprint
arXiv:1309.5821 (2013).
Yang, C., Goodchild, M., Huang, Q., Nebert, D., Raskin,
R., Xu, Y., and Fay, D. (2011). Spatial cloud
computing: how can the geospatial sciences use and
help shape cloud computing?. International Journal of
Digital Earth, 4(4), 305-329.
Yang, C., Goodchild, M., Huang, Q., Nebert, D., Raskin,
R., Xu, Y., & Fay, D. (2011). Spatial cloud computing:
how can the geospatial sciences use and help shape
cloud computing?. International Journal of Digital
Earth, 4(4), 305-329.
Zhang, Q., Cheng, L., Boutaba, R. (2010). Cloud
computing: state-of-the-art and research challenges.
Journal Internet Service Application, 1, 7-8.
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
62
