
Automatic View Finding for Drone Photography
based on Image Aesthetic Evaluation
Xiaoliang Xiong, Jie Feng and Bingfeng Zhou
Institute of Computer Science and Technology, Peking University, 100871, Beijing, China
Keywords:
Drone Control, Automatic View Finding, Drone Photography, Image Aesthetic Evaluation.
Abstract:
Consumer-level remotely controlled smart drones are usually equipped with high resolution cameras, which
make them possible to become unmanned “flying camera”. For this purpose, in this paper, we propose an
automatic view finding scheme which can autonomously navigate a drone to an proper space position where
a photo with an optimal composition can be taken. In this scheme, an automatic aesthetic evaluation for
image composition is introduced to navigate the flying drone. It is accomplished by applying commonly used
composition guidelines on the image transmitted from the drone at current view. The evaluation result is then
conversely used to control the flight and provide feedback for the drone to determine its next movement. In
flight control, we adopt a downhill simplex strategy to search for the optimal position and viewing direction
of the drone in its flying space. When the searching converges, the drone stops and take an optimal image at
current position.
1 INTRODUCTION
Consumer-level remotely controlled smart drones are
a special kind of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
that are equipped with an on-board computer for
navigation and communication. The drone usually
has 4 propellers and can be controlled conveniently
by a ground remote controller, which is usually also a
computer with a two way communication link with
the drone. In this paper, we describe a control
scheme that combines drone’s high programmable
maneuverability and the theory of image aesthetic
measurement to achieve the automatic view finding
on the drone’s autonomous flight. Particularly,
our drone control scheme for optimal view finding
comprises the following steps:
• Detect the photographic subject;
• Locate the subject at a proper position in current
view and evaluate the image aesthetics;
• Adjust the drone position based on the aesthetic
evaluation so that a photo with better composition
can be obtained.
In the first step, the photographic subject is detected
by searching predefined specific features (such as
This work is partially supported by NSFC grants
#61370112, #61602012.
human face or buildings) in the image sequence. With
the detected subject, we evaluate the image aesthetics
by considering several commonly used composition
rules to calculate its aesthetic score. According to
the evaluation, we control the flight by heuristically
adjusting the drone flying status until a maximal score
is reached, and then an image is captured as the
optimal photo.
For the image aesthetic evaluation, it is a
subjective activity and many factors (like personal
sentiment) can influence the judgement. However,
there are still some widely accepted guidelines for the
photographer when shooting a photograph, which are
suitable for the computational aesthetic evaluation.
These guidelines include: rule of thirds, diagonal
dominance, visual balance and proper region size etc.
Liu et al. first quantize these guidelines and formulate
an aesthetic score criteria (Liu et al., 2010). We
adopt similar aesthetic measurements in this paper to
automate the process of image aesthetic evaluation,
and use the aesthetic score to control the flight.
Vision-based navigation is widely used in the
autonomous control for the robot or the automobile
(Lenz et al., 2012; Bills et al., 2011). In these
applications, images provide position information for
the device to locate itself in the environment for path
planning. In this paper, our drone is navigated to a
proper position based on the aesthetic score. As the
282
Xiong X., Feng J. and Zhou B.
Automatic View Finding for Drone Photography based on Image Aesthetic Evaluation.
DOI: 10.5220/0006255402820289
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2017), pages 282-289
ISBN: 978-989-758-224-0
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

aesthetic evaluation depends on the relative position
between the photographic subject and the camera,
it can give feedback to the drone to determine its
next movement. During this adjustment, a downhill
simplex strategy (Press et al., 1992) is adopted to
navigate the drone to the position corresponding to
a higher aesthetic score.
In summary, the main contributions of this paper
include:
• Propose an aesthetic evaluation algorithm which
is oriented to the real-time optimal view finding
for drone photography;
• Develop a real-time flight control algorithm using
downhill simplex method based on the image
aesthetic evaluation;
• Implement the aesthetic evaluation and flight
control algorithms on a remotely controlled
drone platform, which enables our drone to
automatically fly to an proper position where a
photo with optimal composition can be taken by
the on-board camera.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 UAV Navigation
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are currently
widely used in applications like surveillance and
aerial photography (Joubert et al., 2015; Roberts and
Hanrahan, 2016). The researching topics focusing
on UAVs include obstacle avoidance and autonomous
navigation. And the solutions can be categorized into
two classes: active-sensor-based methods (Bachrach
et al., 2011; Benet et al., 2002) and vision-based
methods (Lenz et al., 2012; Soundararaj et al., 2009).
Active-sensor-based Methods. Active sensors such
as laser range finders (Bachrach et al., 2011), sonar,
and infrared detectors (Benet et al., 2002) are often
used for obstacle avoidance during UAV or robot
navigation in indoor environments. These devices are
cheap and have fast response for distance detection.
However, they are not suitable for unstructured
outdoor environments. Also, most of these sensors
have high power requirements and can not be
adequately supplied in consumer level aeriel vehicles.
Vision-based Methods. Vision signals including
image and depth information are commonly used
in UAV autonomous flight. They can be easily
captured using lightweight cameras which are small-
sized, require low power supply and offer long-
range sensing. Without any extra equipment, Lenz
et al. use a single monocular camera and propose a
parallel algorithm based on Markov Random Field
classification for an aerial robot to avoid obstacles
autonomously (Lenz et al., 2012). Soundararaj et
al. fly a miniature helicopter in indoor environments,
using a data-driven image classification method to
achieve real-time 3D localization and navigation
(Soundararaj et al., 2009). These works analyse the
image captured by the onboard camera to navigate
the vehicle. However, they all need prior knowledge
of the flying environment. Bills et al. utilize
the perspective cues to estimate the desired flying
direction to navigate the flight (Bills et al., 2011).
They avoid reconstructing the 3D environment for its
complexity. Harbar et al. uses a stereo camera to
capture and build 3D environment map for obstacle
detection and dynamic path updating (Hrabar, 2008).
This takes considerable computational time and
power, which is not suitable for UAVs.
2.2 Automatic Photography
Using robots to take photos is not a novel problem.
Byers et al. had developed an autonomous robot
system for taking photographs of people at social
events (Byers et al., 2003). Their robot walks
on the floor, and needs remote path planning and
motion control. Kim et al. designed their own
hardware and created a “robot photographer” to take
pictures for human by skin color detection (Kim et al.,
2010). The camera direction is controlled via human
voice recognition, but the position of the camera can
not move according to the human motion. These
robots take photos by selecting proper photographic
opportunity based on customized clues, which is not
general enough. We solve these problems by adopting
a flying vehicle that controlled by image aesthetic
evaluation.
There are also some works on semi-automatic
photograph. Fu et al. present a data-driven
pose suggestion tool, serving as a guidance for the
photographer (Fu et al., 2013). They identify a similar
pose for the current subject from a large collection of
reference poses, based on which the subject should
do some refinement to match the selected pose.
They only focus on the pose suggestion and other
photography tips are guaranteed manually.
2.3 Image Quality Assessment
In computer vision, different levels of image features
are adopted to evaluate the image quality (Ke et al.,
2006; Luo and Tang, 2008). For computational
photography, image composition is an important
Automatic View Finding for Drone Photography based on Image Aesthetic Evaluation
283

Figure 1: Photographs automatically taken by our drone. The image on the top-right corner of each column is an temporary
view, from which the drone begins to search and navigate by the aesthetic score, finally stops at the optimal view.
measurement for the photographer to create aes-
thetically pleasant photos (Yao et al., 2012). It
refers to the arrangement of visual elements during
view finding. There are no absolute rules to create
a good photograph, but heuristic principles, which
may lead to more pleasant composition, can be
concluded based on the experience of professional
photographers.
The principles include rule of thirds, shapes
and lines, visual balance, and diagonal dominance
etc.(Krages, 2005). Many efforts have been made
on image editing to improve the composition, like
image cropping (Liu et al., 2010; Ni et al., 2013),
warping (Jin et al., 2012) and resizing (Li et al.,
2015). But all these approaches are post-processing
after the images are taken, and they will more or less
lose or distort the image content during composition
optimization. Different from these works, we evaluate
the image aesthetics online and search for an optimal
composition during photographing.
3 AUTOMATIC VIEW FINDING
Human photographers take aesthetically pleasant
photos according to certain widely accepted guide-
lines. For drone photography, we propose an
automatic view finding scheme on the basis of image
aesthetic evaluation, so that a remotely controlled
drone may imitate such human behaviors. The drone
is equipped with an onboard camera which can take
live video stream during the flight. The photographic
subjects are firstly detected from the video image
sequence. Then, we evaluate the image aesthetics
by analysing its composition, to determine whether
it satisfies general composition rules. According to
the aesthetic score, the drone can be navigated to
a better viewpoint, until an optimal view with the
highest score is reached. In this way, an aesthetically
satisfactory photo can be captured by the drone. The
main work flow of our method is shown in Fig.2.
3.1 Feature Detection
Given an image, we calculate its aesthetic score based
on an analysis of its spatial structures, considering the
distributions of photographic subjects and prominent
lines in the image. Hence, the photographic subjects
should be automatically detected first. And the
constituent of the subjects depends on what type
of photo we want to take. For human portrait
photography, we can detect the human body by the
face features. For natural sceneries, the subjects can
be detected by their geometry structures.
Photographic Subject Detection
For human portraits, we first estimate whether there
are people in the image, using a face detection method
based on Haar features (Viola and Jones, 2004). A
cascade classifier is pre-trained on the Haar features
of sampling dataset. Then, it is used to determine
whether the selected region of the input image is a
face by sliding a window with different size over the
image. With the detected faces, we can estimate the
bodies of the subjects.
Line Detection
The prominent lines in an image are also important
elements for aesthetic evaluation. We first detect the
line segments existing in an image based on Hough
Transform (Duda and Hart, 1972). Then these line
segments are merged if they are on approximately the
same line.
3.2 Image Aesthetic Evaluation
There are various guidelines for shooting well-
composed photographs. Here, we consider three
most effective guidelines: rule of thirds, visual
balance and proper region size, which are well-
defined and prominent in many aesthetic images
(Fig.3). These guidelines are widely used in rule-
based image composition optimization (Liu et al.,
2010; Jin et al., 2012; Li et al., 2015), and we
GRAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
284

Figure 2: The work flow of our automatic view finding.
During the flight, the drone captures images, evaluates their
aesthetics and adjusts its flying status to searching for an
optimal view.
make some adaption on them to evaluate the image
aesthetics during automatic view finding.
For the rule of thirds, photographers are en-
couraged to place the main subject around four
third points (green dots in Fig.3a) intersected by
two equally spaced horizontal lines and two equally
spaced vertical lines (red dash lines in Fig.3a, i.e.
third lines) in the image. Also, prominent lines should
keep align with these four third lines (Fig.3b). In
visual balance, multiple subjects are suggested to be
distributed evenly in the image. And proper region
size tells the photographer what’s the proper size that
the subjects should occupy the whole image.
According to (Liu et al., 2010), the aesthetic score
of a given image is calculated as:
E =
w
1
E
RT
+ w
2
E
V B
+ w
3
E
RS
w
1
+ w
2
+ w
3
, (1)
where E
RT
, E
V B
, E
RS
are the quantization of rule
of thirds, visual balance and proper region size,
respectively. w
1
, w
2
, w
3
are weights of each guideline.
E
RT
is a combination of the point and line
constraints,
E
RT
= λ
point
E
point
+ λ
line
E
line
. (2)
It measures how close the photographic subjects lie to
the third points (E
point
) and how close the prominent
lines lie to the third lines (E
line
). In Fig.3a, the tower
is placed near the right-top power point to follow
point constraint. And Fig.3b shows the prominent line
placing near the bottom third line to follow the line
constraint.
E
V B
quantizes the harmony of an image-
composition. An arrangement of all salient regions
is considered balanced if their weighted center is
near to the image center. In Fig.3c, two subjects are
placed on two sides of the image to create a visually
balanced composition.
Figure 3: Three composition guidelines. (a,b)Rule of
Thirds, (c)Visual Balance, (d)Proper Region Size.
E
RS
is a measurement of the proper region size
of the photographic subjects in an image. Liu
et al. surveyed over 200 professional images and
obtained a distribution of salient region ratio, which
includes three dominant peaks at 0.1, 0.56 and 0.8,
corresponding to small, medium, and large sized
regions, respectively. Similarly, we encourage subject
region size that follows this distribution. Fig.3d
shows a subject occupying about 0.1 of the whole
image.
Specially, for single-subject photographing, the
subject must be placed near the third points to satisfy
the rule of thirds, or near the image center to satisfy
the visual balance. Hence, there should be a tradeoff
between the two rules, or else both rules will be
violated. Therefore, we change the weights w
1
, w
2
for each rule based on our photograph situation. If
we tend to place the subject near the third point, we
take w
2
= 0. For multiple subjects, the visual balance
is more important and we take λ
point
= 0, or else all
the subjects will be placed on one side of the image to
form a visually unbalanced composition.
In summary, we adopt similar formulations for
the guidelines as in (Liu et al., 2010) for the image
aesthetic evaluation. Some modifications are made
in our implementation: 1) Salient regions are defined
based on the photographic subjects; 2) The diagonal
dominance is not used in our aesthetic evaluation as
the UAV is always flying horizontally; 3) Different
weights are adopted for each guideline, to take
photographs with different style.
3.3 Automatic View Finding
As described in the last section, the image aesthetic
evaluation is a combination of three quantized
composition guidelines. It measures how the
photographic subjects distribute in the captured
frame, and describes the relative position of the drone
and the subjects. Based on this evaluation, an optimal
Automatic View Finding for Drone Photography based on Image Aesthetic Evaluation
285
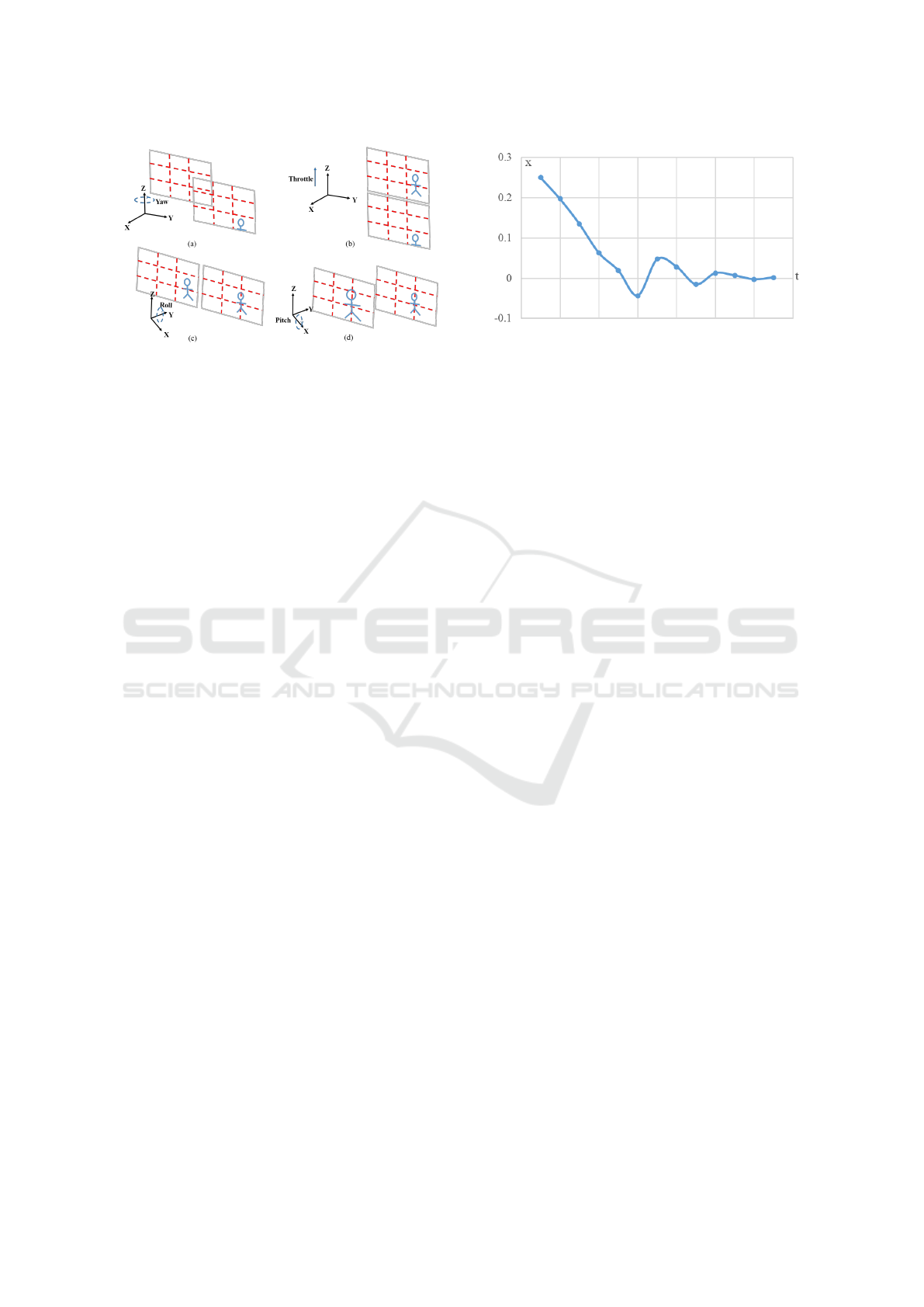
Figure 4: Flight adjustment. (a) Yaw at a fixed position to
adjust camera direction, (b) Throttle to fly up and down,
(c) Roll to move left and right, (d) Pitch to move front and
back. These movements cause the relative position of the
photographic subject changing in the image, resulting in
new aesthetic score.
view with the highest aesthetic score can be found.
If current frame does not reach the highest score, the
drone should adjust its flight to the direction where
the score increases. Thus, the drone flight control
depends on the aesthetic score, and the navigation
becomes the searching of the highest score.
3.3.1 Flight Control Model
Generally, a drone has 4 flying status: throttle (fly
up and down), roll (move left and right), yaw (rotate
along fixed point) and pitch (move front and back).
Note that, since the onboard camera has fixed focal
length, we move the drone front and back to change
the subject region size.
Fig.4 shows the four flying status. Given a
movement x
i
, i ∈ {t, r, y, p} at each status (t, r, y, p
for throttle, roll, yaw, pitch), the drone moves in
corresponding direction and consequently causes the
varying of image aesthetic score. Specially, the
movement x
i
describes both the moving direction and
step length. Thus, the score E in Eq.1 can also
be written as E = f (x
t
, x
r
, x
y
, x
p
). Here, f is an
implicit function of the four flying status, and there
is no precise model of how each variable affects the
aesthetic score.
In order to take a photo with optimal composition,
our target function for automatic view finding is
max E = f (x
t
, x
r
, x
y
, x
p
), (3)
where x
i
∈ (x
i
− ε
i
, x
i
+ ε
i
) and (x
i
− ε
i
, x
i
+ ε
i
) is a
small interval defining the searching space in each
dimension.
This function can be optimized by a downhill
simplex method (Press et al., 1992) in the 4D
space of x
t
, x
r
, x
y
, x
p
. Downhill simplex method is
efficient in multi-dimensional function optimization,
Figure 5: Variable variation during optimal view searching
using downhill simplex method.
which requires only function evaluations rather than
derivatives. In our 4-dimensional case, a simplex is
the geometrical figure consisting of 5 vertices and all
their interconnecting line segments. The method then
takes a series of steps including reflection, expansion
and contraction on the simplex, until it reaches the
maximum of the target function.
3.3.2 Optimal View Searching
Different from mathematical function optimization,
we should consider that: in the actual drone move-
ments, drastic changes are not allowed and multi-
dimensional variation is not preferred. Considering
that human photographers adjust the camera settings
step by step, we also navigate our drone in one
dimension each time.
After the photographic subject is detected during
our drone turning around the yaw-axis, it begins
to search an optimal view to increase the aesthetic
score. For each dimension, we give an initial estimate
of x
i
, i ∈ {t, r, y, p}. Then they are transformed
into drone controlling commands, and navigate the
drone to a new viewpoint. The image under this
new viewpoint is evaluated. If the aesthetic score
increases, the movement in this direction continues,
or else the drone should fly to the opposite direction
with a smaller step length. Fig.5 shows the
x
y
variation tendency in the optimal view finding
(x
r
, x
p
, x
t
variation is similar). At the beginning of the
searching, it changes with a large decrement and the
step length becomes smaller gradually as it gets closer
to the optimal view.
We use a multi-thread mechanism to perform
the flight control based on the aesthetic evaluation.
For the image aesthetic evaluation, it calculates the
aesthetic score E
1
of current frame I
1
transmitted from
the drone, and sends a signal to the flight control
thread when the evaluation is completed. The flight
control thread then begins to search a better view
where the aesthetic score increases.
GRAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
286

The detailed optimal view finding algorithm is
shown in Alg.1. When the subjects are not detected,
we give the drone a yaw movement and set χ
y
= 0.25,
where 0.25 is the speed relative to the maximum
speed that the drone can reach and the value is set
according to our experiments. When subjects occur in
the camera view, we test if the aesthetic score changes
between current frame I
1
and previous frame I
0
. If
so, a flight adjustment that affects the corresponding
composition rules is needed. For example, if E
RT
increases, it means the subject center gets closer to the
third point (with v gets smaller). And we set x
t
=
v
H
x
t
to decrease the movement vibration. With adjusted
x
t
, x
r
, x
y
, x
p
, controlling commands are sent to the
drone, which navigates the drone to a new viewpoint.
Then image aesthetic score under this view is input
into Alg.1 for further optimal view searching. In
the algorithm, W, H are the image width and height,
respectively. τ and δ are constant threshold and we
take τ = 0.95, δ = 0.1 .
Our target function converges until the drone
vibrates small enough in each dimension (|λ
i
| <
δ). Naturally, the image aesthetic score reaches its
highest value. Then we stop the drone movement and
take the image at current viewpoint as the optimal
photograph. When the subjects in the frame move, the
aesthetic score of the image will change and it is no
longer the optimal view. Therefore the view searching
will be repeated until a new optimal view is found. In
fact, that implicitly leads to object tracking.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
We implement our automatic view finding scheme
on a remotely controlled drone platform which
consists of an off-the-shelf flying vehicle “Parrot
AR. Drone” and a common laptop. The drone
contains two cameras: one facing forward for image
capture (with resolution 1280x720) and another
vertically downwards, a sonar height sensor, and
an onboard computer for command processing and
communication with the PC. Commands and images
are exchanged via a WiFi adhoc connection between
our host machine and the drone. The image aesthetic
evaluation and optimal view finding algorithm run on
a common laptop (2.10GHz Pentium dual core, 1GB
RAM), with a Linux OS of Ubuntu 14.04.
As described in section 3, our automatic
view finding is based on the image aesthetic
evaluation. The image aesthetic score reflects how
the photographic subjects distribute in the image.
For human portrait photography, we first detect the
human faces, then estimate the bodies and place them
Algorithm 1: Optimal view finding using downhill simplex
searching.
Input: the aesthetic score E
1
of current frame I
1
, and
its three components E
1
RT
, E
1
V B
, E
1
RS
;
Output: the controlling commands x
t
, x
r
, x
y
, x
p
for
each dimension;
Initialization: Set the initial aesthetic score E
0
= 0
of previous frame I
0
, and its three components E
0
RT
=
0, E
0
V B
= 0, E
0
RS
= 0; Set x
t
= 0, x
r
= 0, x
y
= 0, x
p
= 0;
Set λ
i
= MAX FLOAT, i = 1, ·· · , 5;
1: if E
1
== 0 then Subjects not detected
2: x
y
= χ
y
;
3: else Optimal view searching
4: if E
1
> τ and |λ
i
| < δ then
5: Capture the image I
1
; Optimal view found
6: else
7: x
t
= 0.25, x
r
= 0.25, x
y
= 0.25, x
p
= 0.25;
8: Calculate the vector (u, v) between the
center of mass and the nearest third point;
9: if E
1
RT
6= E
0
RT
then
10: x
t
= λ
1
x
t
; Throttle to satisfy RT, λ
1
=
v
H
11: x
r
= λ
2
x
r
; Roll to satisfy RT, λ
2
=
u
W
12: x
y
= λ
3
x
y
; Yaw to satisfy RT, λ
3
=
u
2
+v
2
W
2
+H
2
13: Calculate the vector (s, t) between the
center of mass and the image center C;
14: if E
1
V B
6= E
0
V B
then
15: x
r
= x
r
+ λ
4
x
r
; Roll to satisfy VB, λ
4
=
s
W
16: x
y
= x
y
+ λ
5
x
y
; Yaw to satisfy VB, λ
5
=
s
2
+t
2
W
2
+H
2
17: Calculate the distance d between the area
ratio of current frame and the nearest perfect area
ratio r;
18: if E
1
RS
6= E
0
RS
then
19: x
p
=
d
r
x
p
; Pitch to satisfy RS
20: Send command x
t
, x
r
, x
y
, x
p
to the drone;
21: E
0
= E
1
, E
0
RT
= E
1
RT
, E
0
V B
= E
1
V B
, E
0
RS
= E
1
RS
;
at the proper position satisfying the composition
guidelines. Face detection is the most time-
consuming step in our method, so we down-sample
the captured images by 2x to reduce the searching
space. After the subjects are detected, we turn to
subject tracking between the adjacent frames using
Camshift (Comaniciu and Meer, 2002) to improve
the detection accuracy. Subjects in the former frame
are back projected onto the latter frame and the new
subject is searched near the projected center.
Under current view, we compare the current
aesthetic score with previous score to determine the
drone movement. If the score increases, current
movement continues and the step length decreases.
Or else the drone stops and moves back to the
previously better view. The optimal view searching
Automatic View Finding for Drone Photography based on Image Aesthetic Evaluation
287

(a) (b) (c) (d)
Figure 6: The process of our automatic view finding using downhill simplex searching. (a) An initial view is found where the
subjects are first detected. (b) One temporary view. (c) The optimal view. (d) The aesthetic score variation during optimal
view searching.
continues until the aesthetic score changes slightly.
All computation can be accomplished in real-time
(with frame rate at about 20 fps).
Validation
To validate the effectiveness of our method, we sim-
plify the aesthetic evaluation by detecting concentric
circles and placing it at the center of the image (Fig.6:
first row). The optimal view search begins at the
initial view with score 0.486 and the score increases
when the center of the circles gets closer to the image
center. Even with external interference, the drone can
finally stop at the view aiming at the concentric circle
center (with aesthetic score 0.975).
Single Subject
For single subject, the rule of thirds and the visual
balance can not be guaranteed at the same time. If we
want to place the subject at the image center, we can
take λ
point
= 0 and eliminate the point constraints in
rule of thirds (Fig.6: first row). If we tend to place
the subject near the third point, we can take w
2
= 0
and do not consider the visual balance (Fig.6: second
row, the score changes from 0.739 and finally reaches
0.952 with several steps searching).
Multiple Subjects
For multiple subjects, the visual balance is more
important than the point constraints in rule of thirds.
So we take λ
point
= 0 and place the subjects evenly
in the image to avoid unbalanced composition. In
Fig.6, the third and forth row show two cases of our
drone taking photos for multiple subjects. Since these
subjects may not occur in the camera view at the
same time, our method search the optimal view only
for the detected subjects. In the forth row, the left-
most person is not detected first and the initial view
is actually optimal for the two detected subjects (with
score 0.952). When new subjects are detected, current
view is not the optimal and the search keeps going on
until a new optimal view with score 0.958 is reached.
Fig.6(d) shows the aesthetic score variation during
automatic view searching. With the evaluated score of
images where subjects are first detected, we estimate
the flight adjustment and send control commands
to the drone. After several steps of searching, it
arrives at the optimal view and then takes photos.
Fig.1 shows the photos taken by the drone using our
automatic view finding.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we propose an automatic view finding
scheme based on image aesthetic evaluation, which
makes a remotely controlled drone capable of
GRAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
288

automatically taking photographs satisfying several
basic composition guidelines. The drone is navigated
by the aesthetic score gradually to the view satisfying
these guidelines. And we adopt a downhill simplex
method to heuristically search for the optimal
view. Experiments on human portrait photography
demonstrate the efficiency of our method. In fact, our
device can also take photos for any other subjects with
a clearly defined features like the human face.
As a prerequisite, the subject detection is crucial
to guarantee that our method can work well. In human
portrait photography, the face detection will fail if the
subject turns his head away from the camera. The
aesthetic score drops to 0 and our drone will stop
current movement and go back to find a higher score.
If the face detection still fails, it will stop current
searching and start a new one.
We are exploring more rules and clues in
practical photographing, such as color, illumination,
or geometry, to make our automatic photographer
more intelligent. Meanwhile, we notice that rule-
based aesthetic evaluation is not general enough to
capture the diversity of possible photographs. Many
rules are not convenient to be quantized. We are
trying to overcome these problems with data driven
methods.
REFERENCES
Bachrach, A., Prentice, S., He, R., and Roy, N. (2011).
Range robust autonomous navigation in gps-denied
environments. Journal of Field Robotics, 28(5):644–
666.
Benet, G., Blanes, F., Sim, J. E., and Prez, P. (2002). Using
infrared sensors for distance measurement in mobile
robots. Robotics & Autonomous Systems, 40(4):255–
266.
Bills, C., Chen, J., and Saxena, A. (2011). Autonomous
mav flight in indoor environments using single image
perspective cues. In IEEE International Conference
on Robotics and Automation (ICRA),2011, pages
5776–5783.
Byers, Z., Dixon, M., Goodier, K., Grimm, C. M.,
and Smart, W. D. (2003). An autonomous robot
photographer. In IROS 2003, volume 3, pages 2636–
2641 vol.3.
Comaniciu, D. and Meer, P. (2002). Mean shift:
a robust approach toward feature space analysis.
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine
Intelligence, 24(5):603–619.
Duda, R. O. and Hart, P. E. (1972). Use of the hough
transformation to detect lines and curves in pictures.
Communications of The ACM, 15(1):11–15.
Fu, H., Han, X., and Phan, Q. H. (2013). Data-driven
suggestions for portrait posing. In SIGGRAPH Asia
2013, Technical Briefs, pages 29:1–29:4.
Hrabar, S. (2008). 3d path planning and stereo-based
obstacle avoidance for rotorcraft uavs. In IROS, pages
807–814.
Jin, Y., Wu, Q., and Liu, L. (2012). Aesthetic photo
composition by optimal crop-and-warp. Computers
& Graphics, 36(8):955–965.
Joubert, N., Roberts, M., Truong, A., Berthouzoz, F.,
and Hanrahan, P. (2015). An interactive tool for
designing quadrotor camera shots. ACM Transactions
on Graphics, 34(6):238.
Ke, Y., Tang, X., and Jing, F. (2006). The design of
high-level features for photo quality assessment. In
CVPR’06, volume 1, pages 419–426.
Kim, M.-J., Song, T. H., Jin, S. H., Jung, S. M.,
Go, G.-H., Kwon, K. H., and Jeon, J. W.
(2010). Automatically available photographer robot
for controlling composition and taking pictures. In
IROS, pages 6010–6015.
Krages (2005). Photography: The Art of Composition.
Allworth Press.
Lenz, I., Gemici, M., and Saxena, A. (2012). Low-power
parallel algorithms for single image based obstacle
avoidance in aerial robots. In IROS, pages 772–779.
Li, K., Yan, B., Li, J., and Majumder, A. (2015). Seam
carving based aesthetics enhancement for photos.
Signal Processing-image Communication, 39:509–
516.
Liu, L., Chen, R. C., Wolf, L., and Cohenor, D. (2010).
Optimizing photo composition. Computer Graphics
Forum, 29(2):469–478.
Luo, Y. and Tang, X. (2008). Photo and video quality
evaluation: Focusing on the subject. In ECCV 2008,
Marseille, France, October 12-18, pages 386–399.
Ni, B., Xu, M., Cheng, B., Wang, M., Yan, S., and Tian,
Q. (2013). Learning to photograph: A compositional
perspective. Trans. Multi., 15(5):1138–1151.
Press, W. H., Teukolsky, S. A., Vetterling, W. T., and
Flannery, B. P. (1992). Numerical Recipes in C: The
Art of Scientific Computing. Cambridge University
Press, New York, NY, USA, 2nd edition.
Roberts, M. and Hanrahan, P. (2016). Generating dynami-
cally feasible trajectories for quadrotor cameras. ACM
Transactions on Graphics, 35(4):61.
Soundararaj, S. P., Sujeeth, A. K., and Saxena, A. (2009).
Autonomous indoor helicopter flight using a single
onboard camera. In IROS, pages 5307–5314.
Viola, P. and Jones, M. J. (2004). Robust real-time face
detection. International Journal of Computer Vision,
57(2):137–154.
Yao, L., Suryanarayan, P., Qiao, M., Wang, J. Z.,
and Li, J. (2012). Oscar: On-site composition
and aesthetics feedback through exemplars for
photographers. International Journal of Computer
Vision, 96(3):353–383.
Automatic View Finding for Drone Photography based on Image Aesthetic Evaluation
289
