
3D Human Shapes Correspondence using the Principal Curvature Fields
on a Local Surface Parametrization
Ilhem Sboui, Majdi Jribi and Faouzi Ghorbel
CRISTAL Laboratory, GRIFT Research Group, National School of Computer Sciences, La Manouba University,
La Mannouba, Tunisia
ilhem.sboui@gmail.com, majdi.jribi@ensi.rnu.tn, faouzi.ghorbel@ensi.rnu.tn
Keywords:
3D Human Shapes, Correspondence, Darcyan Coordinates System, Principal Curvatures, Symmetry.
Abstract:
In this paper, we address the problem of the correspondence between 3D non-rigid human shapes. We propose
a local surface description around the 3D human body extremities. It is based on the mean of principal
curvature fields values on the intrinsic Darcyan parametrization constructed around these points. The similarity
between the resulting descriptors is, then, measured in the sense of the L
2
distance. Experiments on a several
human objects from the TOSCA dataset confirm the accuracy of the proposed approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
Non-rigid three-dimensional shapes matching has
been an active research topic in computer vision over
the last years. It is a key task in many applications
such as space-time reconstruction, motion tracking
and recognition, shape retrieval and videos indexing.
The goal of non rigid shape matching is to find a map
f : S → T between points on one surface S to their
equivalent points on a second surface T.
The problem of establishing a correspondence be-
tween non-rigid shapes remains challenging and par-
ticularly tough since the correspondence involves sur-
faces representing differentposes of an articulated ob-
jects and generally highly deformed surfaces.
In this context, several methods have been proposed
for finding a correspondence between non-rigid 3D
shapes in the state-of-the-art. A detailed survey on
3D shapes matching methods was proposed by (Van
Kaick et al., 2010). Two categories of 3D non-rigid
correspondence can be distinguished according to the
resolution of the matched points: sparse and dense.
Various approaches have addressed the sparse corre-
spondence which aims to map a small set of points on
a given surface. The most common ones consist on
extracting local shape descriptors at a set of feature
points. (Zhang et al., 2008) proposed a method which
is robust to the symmetry problem and consists on
deforming a given shape to have alignment between
feature points and then minimizing resulting distor-
tion. Later, (Zheng et al., 2013) proposed a shape de-
scriptor based on iso-lines of harmonic fields between
shape extremal points to establish a correspondence.
Then, they, demonstrated the effectivenessof their de-
scriptor to intrinsic reflectional symmetry. (Yaron and
Thomas, 2009) proposed a method for only nearly-
isometric surfaces using the Mobius transform. A de-
scriptor based on fuzzy geodesics to find correspon-
dences between sparse sets of points on shapes differ-
ing by extreme deformations was presented by (Sun
et al., 2010). On the other hand, (Ovsjanikov et al.,
2010) proposed an approach which relies on match-
ing feature points in a space of a heat kernel for a
given point on a surface and then the correspondence
is obtained by searching the most similar heat kernel
maps . Moreover, (Yusuf Sahillio˘glu, 2014) proposed
an algorithm relying on the dynamic programming to
match shape extremities which was unable to com-
pletely alleviate the symmetrical flip problem.
One of the alternatives centered around the notion of
minimum distortion correspondence is the method of
(Bronstein et al., 2006). They introduced the gener-
alized multidimensional scaling (GMDS) which al-
lows finding the minimum distortion embedding of
one surface onto another using an approximation to
the Gromov-Hausdorff distance.
Various prominent methods in the literature seek
to find dense correspondence between 3D non-rigid
shapes. One of the notable approaches is proposed by
(Kim et al., 2011) consisting on combining multiple
low-dimensional intrinsic maps to produce a blended
map. They, then, associated confidence and consis-
tency weights to each map and find the best blending
to establish a final correspondence. An other alterna-
tive, introduced also by (Bronstein et al., 2009) was
Sboui I., Jribi M. and Ghorbel F.
3D Human Shapes Correspondence using the Principal Curvature Fields on a Local Surface Parametrization.
DOI: 10.5220/0006266606310636
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2017), pages 631-636
ISBN: 978-989-758-225-7
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
631

based on the diffusion distance instead of the geodesic
one in the GromovHausdorff framework. Some at-
tempts to find dense correspondence based on embed-
ding the shapes onto a spectral domain like the ap-
proach of (Jiang et al., 2013) using a non-rigid vari-
ant of the ICP (Iterative Closest Point) algorithm and
(Aalo et al., 2013) who proposed a spectral formu-
lation for the generalized multidimensional scaling
method denoted as spectral GMDS.
Within this context, (Taylor et al., 2012) focused on
matching human shapes in various poses using an ef-
ficient learned regression function for the articulated
shapes correspondences.
Very recently, (Wei et al., 2015) developeda newdeep
learning approach using a convolutional neural net-
work architecture for finding dense correspondences
between human bodies.
In this paper, we propose a novel approach to find a
sparse correspondence between deformed shapes of
type 3D human body. Our proposal consists on an
intrinsic local description of the human surfaces ex-
tremities. It is based on the construction of a lo-
cal discrete representation known by Darcyan Coor-
dinates System. Then, principal curvatures field are
computed for each discrete representation around the
extracted extremities. Matched points are obtained by
measuring the similarity between their correspondent
local representations in the sense of the L
2
distance.
Thus, this paper will be structured as follows: In the
second section, we describe the proposed descriptor
construction process. For the next section, we repre-
sent our 3D human bodies correspondence approach.
The fourth section is devoted to the experimental re-
sults on 3D human objects from the TOSCA dataset
and our proposed solution to handle the problem of
the symmetry.
2 HUMAN SHAPES
CORRESPONDENCE
We intend to establish a sparse correspondence be-
tween 3D human body objects with different non rigid
deformations. We propose to make a correspondence
between these shapes extremities since they give a
good description of human body structure. The pro-
posed approach is based on an intrinsic description
of the extreme points neighborhood using the darcyan
representation and the principal curvature field. We
present, in this section, all the steps of the construc-
tion of the novel local description around the extrem-
ities points.
2.1 Extremities Extraction
In this section, we intend to extract extremities over
the human body shapes applying the robust approach
proposed by (Julien et al., 2006) which results a set
of interest points invariant to the human pose. This
approach is described below:
Let x
1
and x
2
be the farthest vertices on a surface mesh
M in the sense of the geodesic distance. We denote by
g
dist
(x, y) the geodesic distance between x and y two
vertices on M.
We consider g
1
and g
2
two scalar functions associated
to each vertex x of M. g
1
and g
2
are defined as follow:
g
1
= g
dist
(x, x
1
) and g
2
= g
dist
(x, x
2
)
We denote by E
1
and E
2
the sets of the local extrema
of, respectively, g
1
and g
2
. The set of extremities,
denoted by E, is defined by the intersection of E
1
and
E
2
:
E = E
1
T
E
1
Figure 1 illustrates the resulting extreme points on 3D
human surfaces.
Figure 1: 3D human shapes extremeties.
2.2 Darcyan Coordinates System
Representation
After the extraction of the extreme points, local de-
scription around these points must be performed in
order to ensure the good correspondence between dif-
ferent shapes. But, for the same 3D object, different
meshes may exist. In fact, each mesh depends on its
initial parametrization. For this reason, we propose
to use the well known Darcyan Coordinates System,
introduced by D’Arcy Thompson (Thompson, 1917).
Such parametrization is well adapted to our context
since it is constructed around a reference point.
Here, we, briefly, recall the construction process of
the Darcyan representation.
This parametric representation materialized by coor-
dinates system relatively to a given point on a sur-
face is, in fact, obtained by the superposition of the
geodesic level curves around the reference point and
the radial lines coming from the same point.
Thus, let S be a two dimensional differential mani-
fold, and let consider U
r
the geodesic potential field
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
632

coming from a reference point r on S.
This function U
r
: S → R
+
computes for any point p
on S the length of the geodesic curve joining it to the
reference point r. This function is well defined, since
a geodesic curve between two points of a 2D differ-
ential manifold exists (Cohen and Kimmel, 1997).
A geodesic level curve of value equal to λ around a
reference point r on the surface S can be formulated
as follows:
L
λ
r
= {p ∈ S;U
r
(p) = λ} (1)
L
λ
r
is materialized by the set of all points on S having
the same geodesic distance λ from r. Therefore, the
surface S can be approximately reconstructed by all
these geodesic level curves, so that, S ≈ ∪
λ
L
λ
r
.
We remind as well as the process of radial lines curves
construction from a reference point r of the surface S.
Like mentioned in (Gadacha and Ghorbel, 2013), the
radial curves represent a solution of the followingsys-
tem :
dP(t)
dt
= −∇U
r
(P)
P(0) = r
dP(t)
dt
|
t=0
= α
(2)
Where P(t) is the geodesic path emanating from r and
following the opposite gradient ∇ direction onU
r
. Ra-
dial lines curves, denoted by C
α
, are therefore gener-
ated according to the angular direction α which can
be arbitrary taken. Similar to geodesic level curves, a
reconstruction of the surface S can be approximated
by ∪
α
C
α
.
Here we define Darcyan representation D as the su-
perposition of both n geodesic level curves and m ra-
dials lines curves relatively to a given point r.
D
k,l
(r) =
L
λk
r
S
C
αl
r
, 1 ≤ k ≤ n, 1 ≤ l ≤ m
Figure 2 shows the steps of the Darcyan coordinate
system construction.
Figure 2: Darcyan system reconstruction: (a)-geodesic level
curves, (b)-Radial curves. (c) The superposition of both sys-
tem of curves.
Consequently, the Darcyan coordinates system is
obtained by the superposition of both these sets of
curves emanating from a reference point. We pro-
pose to extract the intersection points between these
two kinds of curves. The resulting discrete paramet-
ric points are ordered since each point is indexed by
the level of geodesic curve and the radial line it be-
longs to.
2.3 Principal Curvature Computation
Let S be a given surface. X : (u, v) ∈ D ⊂ R
2
→
(x(u, v), y(u, v), z(u, v)) ∈ S ⊂ R
3
is a parametric rep-
resentation of S.
At a point p = X(x
u
, x
v
) on S, let consider the tangent
plane according to the basis (u, v).
The normal vector to S at p is denoted by N(p) =
x
u
∧x
v
kx
u
∧x
v
k
respecting a chosen orientation.
Thus, the curvature formulation is given using the fol-
lowing coefficients:
E = x
u
.x
u
, F = x
u
.x
v
, G= x
v
.x
v
, L = x
uu
.
→
N
, M = x
uv
.
→
N
and N = x
vv
→
N
K
G
=
LN−M
2
EG−F
2
K
M
=
EN−2FM+GL
2(EG−F
2
)
E, F and G denote the first fundamental coefficients,
while L, M, N are the second ones.
K
G
and K
M
represent, respectively, the Gaussian cur-
vature and the Mean curvature p = X(x
u
, x
v
).
Therefore, the principal curvatures are deducted
from these formulations K
G
= k
max
.K
min
and K
M
=
(k
max
+k
min
)
2
.
k
max
and k
min
define the principal maximal and mini-
mal curvatures respectively.
2.4 Darcyan Principal Curvature Fields
Descriptor
Relying on the Darcyan representation and the prin-
cipal curvature fields computation on this local
parametrization recalled above, we define a novel 3D
shape descriptor, based on intrinsic geometric prop-
erty, which is invariant under Euclidean motions.
We propose to compute the mean of both
principal maximal and minimal curvatures on the
intersection points of each geodesic level curve.
We denote
k
i
max
and k
i
min
the mean of, respec-
tively, k
max
and k
min
for the i
th
geodesic level
curve. Hence the novel descriptor is defined by
n
k
1
max
, k
1
min
, .., k
i
max
, k
i
min
, ..., k
m
max
, k
m
min
o
1≤i≤m
. Here,
m indicates the number of geodesic level curves. The
proposed descriptor is illustrated in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Illustration of the proposed descriptor: (a) the
Darcyan representation construction around a reference
point, (b) the vector of curvature fiels computation and the
obtained intersection points(in red color).
3D Human Shapes Correspondence using the Principal Curvature Fields on a Local Surface Parametrization
633

Figure 4: 3D human shapes matching approach.
2.5 3D Human Shapes Extremities
Matching
In order to establish non-rigid correspondence be-
tween human surface objects, we compute the pro-
posed descriptor around each extreme point. The gen-
erated vectors consist on the mean of principal curva-
ture field values over the parametric discrete points.
Thereafter, We search for the minimal distance L
2
be-
tween all the pairs of the resulting vectors to find the
most similar ones.
The targeted matching is then acquired by finding the
similarity between the resulting descriptors. This pro-
cess is also illustrated in Figure 4.
3 EXPERIMENTATION
In this section, we present the experimental results in
order to test the effectiveness of our approach. We
have conducted the experiments on several 3D human
objects in different poses from the TOSCA database
(Bronstein and Bronstein, 2008) which contains 3D
objects undergoing non-rigid deformations.
We first of all present the approximation of the pro-
posed description steps on the 3D meshes.
3.1 Approximation on 3D Meshes
A 3D object is assumed to be a 2D differential mani-
fold. In practice, it is materialized by a 3D mesh. It
is, therefore, necessary to approximate the proposed
approach on the 3D meshes. The computation of the
geodesic paths and distances on the triangle meshes
is achieved by the use of the Fast Marching algorithm
(Kimmel and Sethian, 1998). While for the principal
curvature computation, we rely on the algorithm of
(Meyer et al., 2002). Figure 5 illustrates the Darcyan
intrinsic parametric representation around the extrem-
ities of a 3D human body mesh.
Figure 5: Darcyan representation around a human body ex-
tremities from the TOSCA dataset.
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
634
3.2 The Correspondence Results
We evaluate our matching approach on different hu-
man objects of the TOSCA database (David, Victoria
and Michael). We have chosen for each object the
same number of poses. After the normalization of
these shapes, we have extracted the extremities for
all these body shapes. We have, then, constructed
our proposed descriptor around these selected points.
Figure 6 shows some results of our correspondence
method.
Figure 6: Correspondence results for various human mod-
els from the TOSCA dataset, green lines indicate correct
matches.
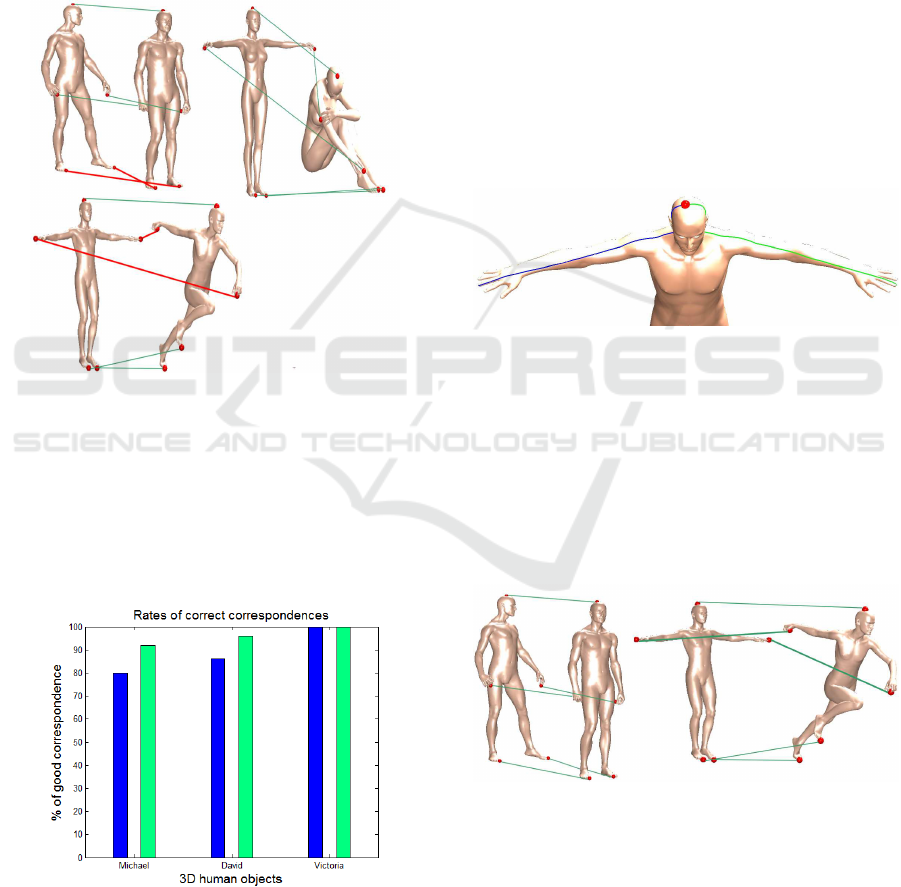
The obtained correct correspondence percentages
range from 80% to 100% for the three human models
in the chosen poses. The bars colored in blue, in Fig-
ure 7, show the correct matching rates. We deem that
our approach seems to be able of handling 3D human
shapes with various poses.
Figure 7: The Correspondence rates for human models from
the TOSCA dataset, the blue and green colors indicate, re-
spectevely, the percentage of the correct matches and the
obtained ones allevating the problem of the symmetry.
The resulting correspondences show, in some
cases, a confusion in the human sides. Hence, a left
hand or a left foot may be matched to a right one of
another object. This confusion is due to the symmet-
ric structure of the human shape.
To alleviate the problem of the symmetry, we propose
to add another geometrical property that could distin-
guish the right part from the left one of the human
body. For this type of shapes, the top of the head is
the unique extreme point that has not a symmetrical
equivalent.
Thus, we propose to compute the sign of the angle
between the two vectors V
1
and V
2
: the vector V
1
is
a reference one. It corresponds to the tangent to the
geodesic curve at the top of the head and joining this
point to the tip of the noise. For the vector V
2
, it cor-
responds to the tangent at the top of the head to the
geodesic curve joining this last point and the other se-
lected extremities (Figure 8).
Figure 8: Geodesic curves joining the top of the head and
the hand extremities.
The computed angle for the right part of the hu-
man body has an opposite sign comparing with the
one of the left part. This process allows to raise
up the correspondence results as shown in Figure 9.
For the object David the percentage of correct corre-
spondence increases from 86% to 96% for the object
David and from 80% to 92% for the object Michael.
The green bars in Figure 7 show the new percentages.
Figure 9: Correspondence after the symmetry correction.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have proposed a novel approach to
establish the correspondencebetween 3D human bod-
ies undergoing non-rigid deformations. We have pre-
sented a novel intrinsic description based on a princi-
3D Human Shapes Correspondence using the Principal Curvature Fields on a Local Surface Parametrization
635

pal curvatures computation on a local parametrization
using the Darcyan coordinates system. We have also
proposed a solution for the problem of the symmetri-
cal extremities. The obtained results show the perfor-
mance of our proposed method for studying the 3D
human body matching.
In future works, we intend to achieve the optimal res-
olution of the local Darcyan representation by find-
ing the suitable number of the geodesic levels and the
radial lines curves. We propose also to perform the
experimentation on others 3D human databases with
different properties and to test the robustness of the
intrinsic descriptor to the noise.
REFERENCES
Aalo, Y., Dubrovina, A., and Kimmel, R. (2013). Spectral
generalized multi-dimensional scaling. pages 380–
392.
Bronstein, A. and Bronstein, M. (2008). Regularized partial
matching of rigid shapes. In European Conference on
Computer Vision, pages 143–154. Springer.
Bronstein, A. M., Bronstein, M. M., and Kimmel,
R. (2006). Generalized multidimensional scal-
ing: a framework for isometry-invariant partial
surface matching. Proceedings of the National
Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,
103(5):1168–1172.
Bronstein, A. M., Bronstein, M. M., Kimmel, R., Se-
ries, I. M. a. P., Hall, L., and E, C. S. S. (2009).
A Gromov-Hausdorff Framework with Diffusion Ge-
ometry for Topologically-Robust Non-rigid Shape
Matching. pages 612–626.
Cohen, L. and Kimmel, R.(1997). Global Minimum for Ac-
tive Contour Models. International Journal on Com-
puter Vision, 24(1):57–78.
Gadacha, W. and Ghorbel, F. (2013). A stable and accurate
multi-reference representation for surfaces of R3: Ap-
plication to 3D faces description. IEEE International
Conference on Automatic face and Gesture Recogni-
tion (FG2013), Shanghai- China.
Jiang, L., Zhang, X., and Zhang, G. (2013). Partial
shape matching of 3D models based on the Laplace-
Beltrami operator eigenfunction. Journal of Multime-
dia, 8(6):655–661.
Julien, T., Mohamed, D., and Jean-Philippe, V. (2006).
Invariant highlevel reeb graphs of 3d polygonal
meshes. International Symposium on 3D Data Pro-
cessing, Visualization, and Transmission (3DPVT),
page 105?112.
Kim, V. G., Lipman, Y., and Funkhouser, T. (2011).
Blended intrinsic maps. ACM Transactions on Graph-
ics, 30(4):1.
Kimmel, R. and Sethian, J. a. (1998). Computing geodesic
paths on manifolds. Proceedings of the National
Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,
95(15):8431–8435.
Meyer, M., Desbrun, M., Schr¨oder, P., and Barr, A. H.
(2002). Discrete Differential-Geometry Operators for
Triangulated 2-Manifolds. International Workshop on
Visualization and Mathematics.
Ovsjanikov, M., M´erigot, Q., M´emoli, F., and Guibas, L.
(2010). One point isometric matching with the heat
kernel. Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Pro-
cessing, 29(5):1555–1564.
Sun, J., Chen, X., and Funkhouser, T. A. (2010). Fuzzy
geodesics and consistent sparse correspondences for:
eformable shapes. 29(5):1535–1544.
Taylor, J., Shotton, J., Sharp, T., and Fitzgibbon, A. (2012).
The vitruvian manifold: Inferring dense correspon-
dences for one-shot human pose estimation. pages
103–110.
Thompson, D. (1917). On growth and form. University
press in Cambridge, Cambridge, MA.
Van Kaick, O., Zhang, H., Hamarneh, G., and Cohen-Or, D.
(2010). A Survey on Shape Correspondence. Com-
puter Graphics Forum, xx:1–23.
Wei, L., Huang, Q., Ceylan, D., Vouga, E., and
Li, H. (2015). Dense human body correspon-
dences using convolutional networks. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1511.05904.
Yaron, L. and Thomas, F. (2009). M¨obius voting for surface
correspondence. 28(3):72.
Yusuf Sahillio˘glu, Y. Y. (2014). Multiple shape correspon-
dence by dynamic programming. 33(7):121–130.
Zhang, H., Sheffer, A., Cohen-Or, D., Zhou, Q., Van Kaick,
O., and Tagliasacchi, A. (2008). Deformation-driven
shape correspondence. Eurographics Symposium on
Geometry Processing, 27(5):1431–1439.
Zheng, Y., Tai, C.-L., Zhang, E., and Xu, P. (2013). Pair-
wise harmonics for shape analysis. IEEE transactions
on visualization and computer graphics, 19(7):1172–
1184.
VISAPP 2017 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
636
