
Towards Process Mining of EMR Data
Case Study for Sepsis Management
Gert-Jan de Vries
1
, Ricardo Alfredo Quintano Neira
2,1
, Gijs Geleijnse
1
, Prabhakar Dixit
1,3
and Bruno Franco Mazza
4
1
Philips Research - Healthcare, High Tech Campus 34, Eindhoven, The Netherlands
2
Industrial Engineering Department, Pontif
´
ıcia Universidade Cat
´
olica do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
3
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherlands
4
Intensive Care Unit, Hospital Samaritano, S
˜
ao Paulo, Brazil
Keywords:
Process Analysis, Sepsis.
Abstract:
Imagine you have cold shivers and a racing heartbeat and high fever. Clear thinking is impossible! Ceiling
lights flash by as you are rushed to the emergency department (ED). You feel your body is getting even sicker.
Doctors are doing their utmost to treat this acute and threatening condition, while they work piece together
all small parts of evidence to set the diagnosis and start targeted treatment. In this situation, the clinical staff
depends on a clinical pathway protocol to streamline communication and deliver care according to the latest
medical evidence. Today, such clinical pathways are mainly executed and tracked using paper. Hence, there
is ample opportunity for technology in a supportive role. Automated process analysis can help improve these
processes of delivering standardized care beyond their current level. In this paper, we provide insight into
the steps required to perform process mining to EMR data in the challenging domain of sepsis treatment and
provide learnings from our preliminary analysis of these data using process mining techniques.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening complication of
an infection, where inflammatory responses through-
out the body are triggered, which can lead to damage
of multiple organ systems, causing them to fail. Sep-
sis is a condition with a very big impact on patient
condition, and has high mortality rates. It is also char-
acterized by high annual incidence rates, e.g., in the
US 3-10 in 1000 people are hospitalized with sepsis
(Kempker and Martin, 2016). The associated health-
care costs are also high; in 2011 it accounted for
$20.3 billion, which is 5.2% of total US hospital costs,
therewith the most expensive condition treated (Torio
and Andrews, 2013).
The management of sepsis is complicated by the
difficulties of detecting the condition. Recently, the
community adopted a new definition of sepsis and
a strategy for screening was proposed (Singer et al.,
2016). As we evaluate our methods on data collected
before 2016, this paper focuses on the method com-
monly accepted until that date, where screening for
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS)
symptoms is used to evaluate starting the treatment
for sepsis. Hence, we adopt the 1992 definition from
the American College of Chest Physicians / Society
of Critical Care Medicine (Bone et al., 1992): “Sep-
sis is the Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome
(SIRS) to the presence of infection”. A patient is
screened positive for SIRS if two or more of the fol-
lowing criteria are met:
• Temperature > 38°C or < 36°C
• Heart rate > 90/min
• Respiratory rate > 20/min or PaCO
2
< 32 mmHg
(4.3 kPa)
• White blood cell count > 12000/mm
3
or
< 4000/mm
3
or > 10% immature bands
Patients are considered to be septic when the SIRS
criteria are satisfied in combination with a suspected
or established infection. As the SIRS criteria are
not specific, many patients meeting the SIRS crite-
ria will, however, not have or develop sepsis (Lord
et al., 2014). When sepsis is complicated by organ
dysfunction, it is called severe sepsis, which can turn
into septic shock when hypotension persists despite
fluid resuscitation. Mortality rates vary strongly per
de Vries G., Quintano Neira R., Geleijnse G., Dixit P. and Mazza B.
Towards Process Mining of EMR Data - Case Study for Sepsis Management.
DOI: 10.5220/0006274405850593
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

geography, but are known to increase with the three
levels of sepsis: up to 30% for sepsis, 50% for severe
sepsis and 80% for septic shock over the timespan of
1 year (Jawad et al., 2012). A multi-center study in
Brazilian Intensive Care Units (ICUs) showed rates
of 34.7%, 47.3% and 52.2% at 28 days, respectively
(Silva et al., 2004).
In 2002 the Surviving Sepsis Campaign (SSC)
was launched as a global campaign to reduce mortal-
ity due to sepsis. The guidelines they published, along
with the updates made over the last years, are now
widely adopted in clinical practice (Dellinger et al.,
2004; Dellinger et al., 2008; Dellinger et al., 2013).
The SSC provided a care bundle that comprises the
following steps:
To be completed within 3 hours of presentation:
• Measure lactate level
• Obtain blood cultures prior to administration
of antibiotics
• Administer broad spectrum antibiotics
• Administer 30mL/kg crystalloid for hypoten-
sion or lactate ≥ 4 mmol/L
To be completed within 6 hours of presentation:
• Apply vasopressors (for hypotension that does
not respond to initial fluid resuscitation) to main-
tain a mean arterial pressure (MAP) ≥ 65 mmHg
• In the event of persistent hypotension after ini-
tial fluid administration (MAP < 65 mmHg) or if
initial lactate was ≥ 4 mmol/L, reassess volume
status and tissue perfusion and document findings
• Remeasure lactate if initial lactate elevated.
As these guidelines provide a recommendation,
hospitals implement these guidelines adapted to their
standards of care. These guidelines are translated
into clinical pathways (CPs), which are “complex in-
tervention[s] for the mutual decision making and or-
ganisation of care processes for a well-defined group
of patients during a well-defined period” (European
Pathway Association, 2016). In this field, Key Perfor-
mance Indicators (KPIs) are often described in terms
of adherence to such guidelines.
During the interpretation and translation process,
the guidelines are made actionable for the clinical
staff: tasks and responsibilities are defined and a
communication structure around the pathway is put
in place. CPs are implemented in different areas of
health care, such as acute care (e.g., for chest pain
in the emergency room (ER), stroke diagnosis), in-
tegrated oncology care and chronic disease manage-
ment (e.g., coordination of care for heart failure pa-
tients). Often, the clinical pathway of a patient is
managed using a paper sheet. However, this leads to
double data entry as the status needs to be recorded
in the Health IT system as well as on paper. More-
over, the current phase on the pathway, when repre-
sented on paper, is only available to those accessing
the sheet, typically at the bed side.
In this research, we are interested in solutions to
monitor the status of the patient in a clinical pathway
by analyzing data from the Electronic Medical Record
(EMR). To this end, we model the clinical pathway in
a computer interpretable format. The events in this
model are associated with data from the EMR. How-
ever, there might not always be in one-to-one corre-
spondence. For example, events such as patient trans-
ferred to ICU or Vital Signs measured may be associ-
ated with only single time-stamped entries in the pa-
tient record, but as we will see in the following, events
such as Blood Volume Expansion performed might be
more complicated to retrieve.
Process mining is the technique to extract infor-
mation from event logs (van der Aalst, 2011). In gen-
eral, the scientific field is concerned with two research
areas: process discovery and conformance checking.
Process discovery deals with identifying a model that
describes the behavior as observed in a set of event
logs. In process discovery, the challenge is to identify
a model that is not too general but is also not over-
fitting the behavior as encountered in the set of event
logs. In conformance checking, on the other hand, a
collection of event logs is compared with a reference
model with the aim to research whether the observed
behavior is matching the expected behavior. In par-
ticular, common deviations or delays in processes can
be analyzed. As many KPIs are based on times-to-
event or performing actions in a certain order, results
from conformance checking can be used as input to
KPI analysis.
Applying process mining to event logs obtained
from EMRs is known to be a challenging topic,
as was concluded in several studies in the appli-
cation of process mining techniques domains such
as oncology, surgery, cardiology, diabetes and clin-
ical images (Rojas et al., 2016). Already in 2008,
Mans et al. describe explorations to discover pro-
cess models from hospital data on stroke care (Mans
et al., 2008). Nonetheless, these past attempts were
performed on relatively straightforward clinical pro-
cesses with homogenous patient populations, or in-
corporated prospective data collection. To the best
of our knowledge, two other studies looked into ap-
plying process mining for sepsis, however results are
limitedly published (Mannhardt et al., 2016; Mcgre-
gor et al., 2011).
In general, process mining techniques can only be
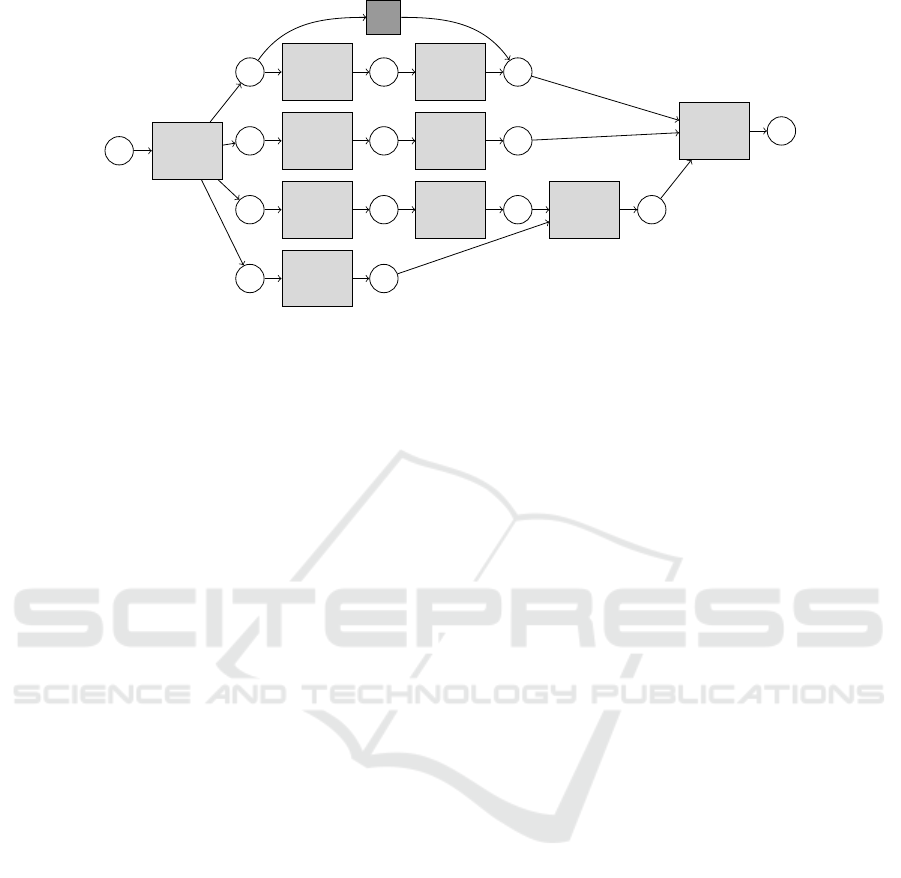
Admission
Volume
expansion
prescr
Lactate
prescr
Blood
culture
prescr
Volume
expansion
admin
Lactate
collect
Blood
culture
collect
Antibiotics
prescr
Antibiotics
admin
Discharge
Figure 1: Petri net of the simplified model representing the clinical pathway for sepsis management, used for conformance
checking.
applied if the event log describes a recognizable pro-
cess. The event log for a patient from an EMR will
contain events related to various processes and ac-
tions. The vast majority of these raw events will not
be directly related to the care according to the refer-
ence pathway, but rather reflect routine sub-processes
that the staff follows in usual care. Hence when ana-
lyzing the event log, a projection needs to be created
of events that describe actions and data related to the
pathway. In this paper, we are interested in exploring
the potential of applying process mining techniques
on a complete patient record from an EMR. We draw
learnings from the modeling, data extraction and pro-
cess mining steps.
2 METHODS
The data used in our study have been obtained from
Hospital Samaritano, a private, Brazilian hospital
having over 300 beds. For extracting the data from
the Health IT system we identified the database tables
and attributes that could represent the sepsis treat-
ment activities from the ICU and emergency depart-
ment (ED) processes. For the selection of sepsis hos-
pitalizations, we considered hospitalization registries
that had at least one diagnosis or death related to
sepsis using an ICD, 10th edition (ICD-10) code list
for sepsis (Canadian Institute for Health Information,
2009). Also, we included patients that were assigned
a prescription template related to sepsis. The ICD-
10 codings we selected, were validated by 3 Brazilian
specialists and the sepsis selection method was val-
idated by the physician responsible for the deploy-
ment of the sepsis protocol in the hospital. We ex-
tracted 4516 sepsis hospital encounters for a period
of two years. To protect the identity of patients and
caregivers, we pseudonymized the patient data. Im-
portant aspect with respect to the process analysis is
that dates were shifted with a fixed amount of days
per patient-encounter. Hence, the relative times be-
tween events per hospital admission were not altered.
The data analysis was conducted with approval of the
institution’s ethics committee.
As indicated in the introduction, the raw data
from the EMR requires interpretation or abstraction to
bring it to the level of event analysis suitable to derive
meaningful insights. The ultimate aim would be the
analysis in terms of KPIs, however that would require
more validation and comparison to the formal quality
assessment procedure, which is beyond the scope of
this paper. To this end, we focussed on the important
elements in the first three hours of care as described in
the SSC care bundle: Lactate measurement, obtaining
blood cultures, antibiotics administration and volume
expansion. The first two are relatively easily obtained
from the data as they refer to procedures that are di-
rectly ordered as such and registered in the EMR. The
antibiotics are retrieved in a similar method, using a
long list of antibiotics names and active components.
Volume expansion is, however, not directly registered
as such in the EMR, but required interpretation of se-
quences of low-level events of administrating fluid.
To this end, we collected all administrations of vol-
ume expanders and implemented a windowed thresh-
olding that searches for sufficient fluid administration
(≥ 90%∗ 30mL/kg in 4 hours) such that it can be con-
sidered fluid administration with the purpose of vol-
ume expansion. For each of these four elements of
care we collect the times of request and times of ad-
ministration or collection, which gives 8 event types.
To mark the start and end of event traces, we also in-
clude the moment of admission and discharge, yield-
ing a total of 10 different event types.
In order to avoid that incomplete timestamps,

that only contain the date of the event, would nega-
tively influence the results, we corrected timestamps
of ’00:00:00’ in appropriate cases as we found that
these timestamps referred to the midnight before the
actual event must have happened. To allow for a more
complete conformance checking, we chose to correct
these timestamps as follows: if the event related to
collection or administration and if the corresponding
prescription event was present, we corrected the time-
stamp to one second after the corresponding prescrip-
tion event. By doing so, we corrected the order of
events, however it should be noted that these times-
tamps should still be considered imprecise and were
thus excluded from any time-to-event analysis.
Our explorative analysis started with retrieving the
times to event for each of the care elements as a step
towards measuring KPIs. Note that we used the time
of presentation (admission) as time zero to be able
to measure all other timestamps relative to this time
of admission. After that, we used the ProM soft-
ware (van der Aalst et al., 2007) to perform confor-
mance analysis of the model outlined by the SSC care
bundle. To this end, we constructed the model as a
Petri net, displayed in Figure 1, that represents the
different steps that can happen concurrently, and the
(time-wise) dependency between obtaining the blood
cultures and administration of antibiotics. While this
model might seem an oversimplification of clinical re-
ality, it does contain all the critical steps outlined in
the SSC care bundle (see Introduction) and provides a
first step towards more elaborate pathway models. In
the process of conformance checking, the event traces
in the event log are aligned with the model and a dis-
tance is calculated for the alignment. We used the
’standard distance function’ that assigns a cost of 0 in
case log and model agree and 1 in case of disagree-
ment (move on log or move on model) (van der Aalst
et al., 2012).
3 RESULTS
The cohort extracted for the present analysis, using
the inclusion criteria outlined in the previous section,
consisted of 4516 patients. 4442 patients entered the
hospital via the ED and were selected for the subse-
quent analysis. These patients have a median age of
37.7 years, 51.5% were male, median length of stay
(LOS) was 5 hours, and 2.5% died in hospital. Further
descriptive statistics can be found in Table 1.
3.1 Events
In total there were 37635 events extracted for the
4442 patient admissions. 4204 events had a time-
stamp of 00:00:00. The vast majority (4162) of these
events were the collection of lactate. For 3700 events
we could correct the timestamps using the aforemen-
tioned procedure, another 504 could not be corrected
(no corresponding request event could be found) and
were removed. Note that for the time-to-event anal-
ysis, we excluded all the 4204 events with imprecise
timestamps.
Table 2 shows the number of events retrieved from
the EMR. We observe that all event types are highly
represented in the database, with at least 85% (lactate
collection) and more than 95% of cases for the other
obligatory event types. Volume expansion is less of-
ten represented, however this is also considered an
optional (conditional) event, as specified in the model
(Figure 1).
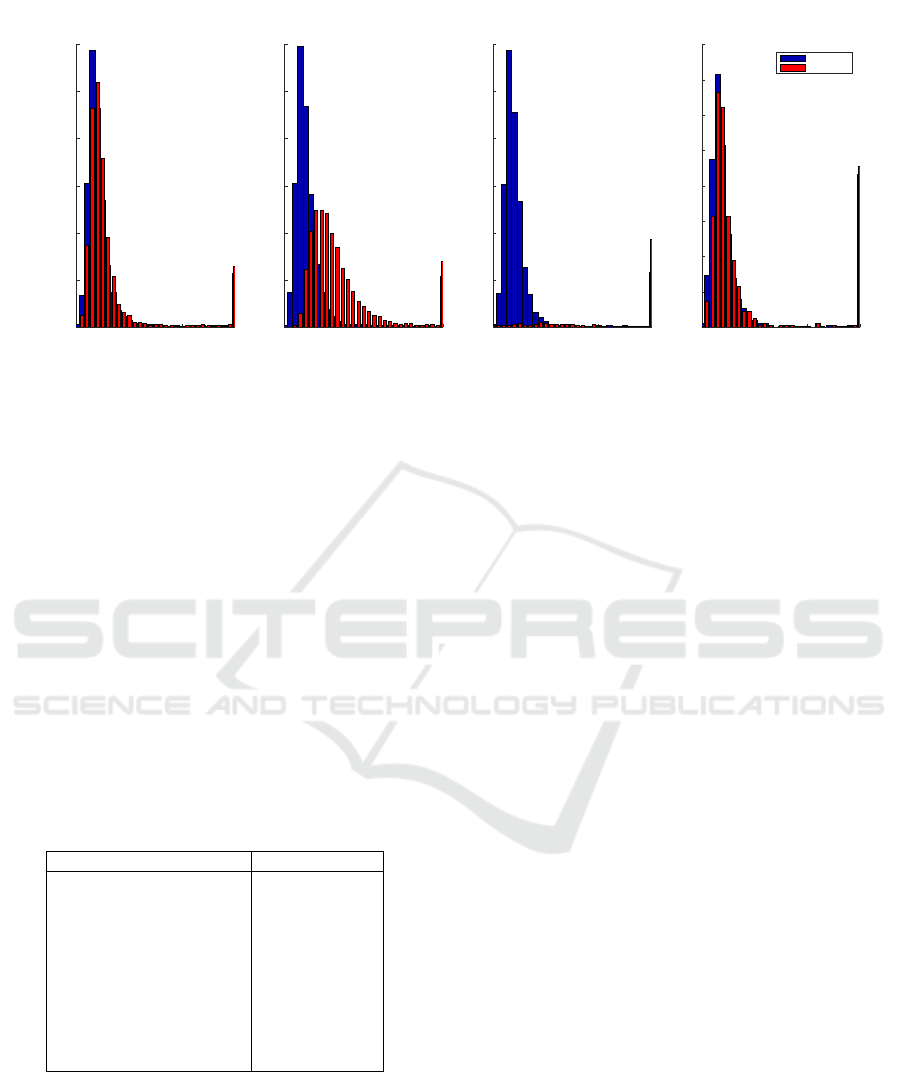
Figure 2 shows the histograms of time-to-event
(from the moment of presentation) for each of the pre-
scription and administration/collection events. Note
that that the rightmost bars in the histograms (at 3
hours from presentation) contain all samples with
times ≥ 3 hours. We observe that the vast major-
ity of events happen within the first hour after pre-
sentation, with modes being 16 minutes for prescrip-
tion of antibiotics and volume expansion, and 17 min-
utes for lactate and blood cultures. For administra-
tion/collection, the mode are 15 minutes for lactate,
19 for volume expansion, 21 minutes for antibiotics
and 38 for blood cultures. The following fractions of
prescription events happen outside of the window of 3
hours: Lactate (5.4%), Antibiotics (5.2%), Blood cul-
tures (4.9%), Volume expansion (14.7%). Note that
for lactate collection, the number of events found is
much smaller than for the others due to the inaccurate
timestamping mentioned earlier.
Conformance analysis using ProM yielded the re-
sults presented in Figure 3. The number of prescrip-
Table 1: Descriptive statistics of the patient population.
Name Valid N N (%)
Median [25th-75th]
Age (year) 4442 37.5 [26.0-56.3]
Male 4442 2295 (51.7%)
LOS (hour) 4439 5.0 [3.4-75.2]
Died in hospital 4442 113 (2.5%)
Initial diagnosis 4442
Missing 77 (1.7%)
Infections / Parasites 1041 (23.4%)
Respiratory 1631 (36.7%)
Abnormalities 953 (21.5%)
Other 740 (16.7%)
0:00 1:00 2:00 3:00
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
Antibiotics
0:00 1:00 2:00 3:00
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
Blood culture
0:00 1:00 2:00 3:00
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
Lactate
Time to event (hours)
0:00 1:00 2:00 3:00
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
Volume expansion
prescribed
admin/collect
Figure 2: Distributions of time-to-event (from the moment of presentation) for the four care elements. The blue histograms
represent the time to prescription, the red histograms represent the time to administration or collection. The horizontal axes
represent time (hh:mm), the vertical axes represent counts.
tion events conforming to the model are the same
as the number of (valid) events found in the time-
to-event analysis. For the administration/collection
events, we see different numbers of conforming
events as compared to the numbers of events found
in the time-to-event analysis. This is because the con-
formance checking does not only take into account
presence of the events in the log, but also whether the
order is according to the model. Here we see, for ex-
ample, that there are 4352 blood culture prescriptions
found in correspondence to the model versus 90 not;
similarly, 1229 volume expansions that are in corre-
spondence with the model. Note that volume expan-
sion is, following the guidelines, an optional step if
certain conditions are not met.
Table 2: Numbers of events found.
Event name N (%)
Admission 4442 (100.0%)
Discharge 4431 (99.8%)
Blood culture prescr 4355 (98.0%)
Blood culture collect 4339 (97.7%)
Antibiotics prescr 4324 (97.3%)
Antibiotics admin 4309 (97.0%)
Lactate prescr 4231 (95.2%)
Lactate collect 3772 (84.9%)
Volume expansion prescr 1465 (33.0%)
Volume expansion admin 1463 (32.9%)
Volume expansion is only managed when clinically indicated (see also
Figure 1).
If we now connect these numbers to the earlier
found number of events logged (Table 2), we can de-
rive, e.g., that for 3772 − 3751 = 21 lactate collec-
tions there was a log-entry, however not in the order
prescribed by the model. Similarly, we can see that
for volume expansion there are 1465 − 1461 = 4 pre-
scriptions that are logged, however not in the way an-
ticipated by the model. For antibiotics administration
we observe many (4309 − 252 = 4057) not conform-
ing events, which turned out to be caused by an order
mismatch with the blood culture collection (i.e., an-
tibiotics administered before blood cultures were col-
lected). Potential reasons for these mismatches will
be discussed in the next section.
4 DISCUSSION
In our analysis, we have first looked into time-to-
event analysis, which looks at the number of events
logged and can derive various statistics from the
timestamps of these events. Although this can give
a good insight into how processes are executed on
average, and identify outliers with respect to time-
to-event, it does not take into account correct order
of events. Using process mining, and conformance
checking in particular, we can also study the order
in which events occur and study deviations in more
detail. One particular challenge that we tried to ad-
dress here, is that EMRs are general tools to support
overall clinical processes and that fields in the EMR
can be used for multiple conditions and are pathway
aspecific by design. Often patients are concurrently
evaluated and treated for a variety of conditions, and
there is often little or no evidence of which data en-
tries relate to which diagnosis; this relation has to be
inferred. Also, it is important to stress that not all pa-
tient care activities are documented in the EMR.
Before reflecting on the results obtained, we
would like to emphasize that this experiment of gath-

Admission
4442/0
Volume
expansion
prescr
1461/0
Lactate
prescr
4231/211
Blood
culture
prescr
4355/87
Volume
expansion
admin
1461/0
Lactate
collect
3751/691
Blood
culture
collect
4333/109
Antibiotics
prescr
4323/119
Antibiotics
admin
252/4190
Discharge
4422/20
Figure 3: Output of conformance analysis in ProM, showing per event type the number cases that conform to that step in the
model versus that do not.
ering KPI information directly from EMR data with-
out a thorough, manual, quality analysis is likely to
provide an underestimation of guideline adherence
compared to reality. This is due to the following list
of potential causes for our analysis not picking up ad-
herent behavior:
• Not logged: Action has been performed but not
logged
• Incorrect timestamping: Action has been per-
formed but with incorrect or imprecise timestamp
• Incomplete querying: The query used for inter-
preting the EMR data can miss certain cases
Hence, we should not interpret the outcomes of our
current analysis as quality measure for the care per-
formed before carrying out a more thorough quality
analysis. We are also reporting intermediate results,
and therefore cannot draw conclusions on the KPIs
themselves, but our focus is to share the challenges
relating to process mining on ”real-life” EMR data.
Although the blood volume expansion does only
happen when clinically indicated, the relatively low
number of blood volume expansion events, might
suggest that our interpretation of the EMR data is not
completely covering the different ways these events
are reflected in the EMR, rather than they are often not
prescribed, or that they are prescribed, but not logged.
Further analysis is required to analyze the volume ex-
pansion management of these sepsis patients. In any
case, the quality of the logging influences the results.
Bose et al. distinguish 27 classes of quality issues
with event logs (Bose et al., 2013). In our data, we
observe presence of the following classes of issues:
missing events, missing timestamps, incorrect times-
tamps and imprecise timestamps. The first category
has been reflected upon already, the missing, incorrect
and imprecise timestamps typically reflect clinical re-
ality as it is simply not possible to 100% accurately
timestamp all events. Imprecise timestamping can be
observed in the lactate collections where often only
date information was information. Incorrect times-
tamping might be observed in, e.g., many antibiotics
administration events that are found not conforming
to the model (4195 out of 4304). This is further sub-
stantiated by the notion that the clinical staff at the
hospital, at which the study was performed, is all well
aware of the fact that antibiotics influence the results
of the laboratory measurements from the blood sam-
ples. It might well be that there are differences in the
actual time of performing the event versus the mo-
ment of logging in the EMR, or alternatively that we
made incorrect assumptions in the interpretation of
raw data. Further verification with the hospital’s qual-
ity assurance process is required to find the reason of
this mismatch.
The treatment of sepsis in the ED is a particu-
larly challenging environment as the condition is life
threatening and quick responses are required, which
we anticipated to potentially lead to problems in pro-
cess mining with respect to the aforementioned qual-
ity issues. Despite that, we observed high levels of
presence of events in the eventlog: at least 85% for
all obligatory events. The inherently diverse group of
patients with sepsis poses a challenge to process anal-
ysis techniques. We have shown that for a relatively
simple model, we can successfully apply process min-
ing techniques, with the ultimate aim of measuring
KPIs. This provides a good outlook in the possibili-
ties to also analyze the sepsis pathway at a finer grain.
It remains, however, topic of research what the opti-
mal level of detail in the process modelling is for a
given purpose. The heterogeneity of sepsis patients
might become more prominent in more detailed anal-
ysis and require some form of clustering before per-
forming process analyses on the subgroups. Patients
can be clustered on patient or on process characteris-

tics (see, e.g., (de Medeiros et al., 2007)).
One particular issue that we faced when interpret-
ing the EMR data was that we observed the need to
interpret the purpose of actions performed from the
event logs rather than purely the actions themselves.
As an example, the administration of fluid in itself
can happen for a multitude of reasons, however in or-
der to interpret whether volume expansion was per-
formed, we had to monitor whether a certain amount
of fluid was prescribed in a certain amount of time.
Similarly, for antibiotics we would like to know that
they were prescribed and administered for the purpose
of managing sepsis, however this intended purpose is
not stored with the medication prescriptions. One way
of obtaining more information on the purpose of cer-
tain actions performed is through careful analysis of
clinical notes, where typically the intend of the med-
ical staff is reflected. This will, however require the
use of natural language processing (NLP) techniques
to be able to extract structured information from these
unstructured text data. Important to note in this re-
spect is the lack of ground truth in such analysis of
EMR data; the only evidence of what happened with
the patient is the data in the EMR. Hence, the inter-
pretation of raw EMR data should be given sufficient
attention.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
We have shown that we can successfully use pro-
cess mining to follow selected events derived from the
main KPIs for the sepsis pathway purely from EMR
data. However, no conclusion should be drawn about
the actual quality of care or adherence to these guide-
lines before verification with the clinical quality as-
surance process. It should be noted that it required a
great effort in data preparation to create the event log
and time-consuming manual quality checks to inter-
pret the EMR data in terms of the concepts required
for the pathway analysis. Using process mining tech-
niques, we can analyze beyond the pure presence or
absence of events and also address correct versus in-
correct order with respect to a model that represents
best practice. Applying these techniques on a dataset
gathered at a large Brazilian hospital, we could an-
alyze the data in terms adherence to the guidelines
provided by the SSC. The reason for deviation in or-
der of administering antibiotics and collecting blood
cultures, however requires further research. In gen-
eral, further follow up with the quality department
would be required to quantify the accuracy of our as-
sessment in comparison to the formal quality process
that is in place in the hospital at hand. This actually
highlights a big limitation of the data driven analysis
of processes in general: it is impossible from event
data alone to distinguish whether event logs are miss-
ing due to actions not being performed, performed
actions not being logged or logged actions not being
picked up by the data extraction and interpretation.
For that reason, results should always be interpreted
with care and at least a randomized sample should be
analyzed through a formal quality assessment process
in order to quantify the accuracy of the overall data-
driven analysis results.
Although our analysis shows high levels of avail-
ability of time stamps (at least 85% per obligatory
event type), there is room for improvement. The qual-
ity of the event log generated from the EMR data
could be further improved by better support from the
data entry module to allow for more accurate and
timely data entry and the use of structured reporting
over free-text notes. It should be noted, though, that
this will remain difficult in busy environments such
as the ER, where top priority is to provide acute care
to the patient. It might require a change in the work-
flow to improve the precision of timestamps of time
critical events such as lactate collection.
Our present analysis is limited to a relatively small
and simple model to reflect sepsis care. Nevertheless,
this model allows already for analysis in terms of vari-
ous clinical KPIs. Future work includes the extension
of the model used for conformance analysis in order
to assess the clinical pathway in further detail. In our
future aim of extending the model to cover more de-
tailed steps in the sepsis care pathway, we expect that
more elaborate data interpretation might be required.
While many steps have already been taken to digi-
tize hospital data in structured fields, rich information
can also be found in non-structured text fields such as
clinical notes. The analysis of such data will require
NLP approaches to reliably retrieve structured infor-
mation from text. Being able to analyze adherence
to such a more detailed model would open up further
analysis of conformance to and deviations from the
best practice. The application of process discovery
techniques can also provide a bottom-up view of the
process as it is performed by the clinical practition-
ers. A root cause analysis into the reasons for devia-
tion could help to further improve the guidelines and
standard of care for sepsis.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank the clinical and technical staff
at Hospital Samaritano for their help in collecting the

event data, as well as our colleagues from Philips Re-
search for making this work possible.
REFERENCES
Bone, R. C., Balk, R. A., Cerra, F. B., Dellinger, R. P., Fein,
A. M., Knaus, W. A., Schein, R. M. H., and Sibbald,
W. J. (1992). Definitions for Sepsis and Organ Failure
and Guidelines for the Use of Innovative Therapies in
Sepsis. Chest, 101(6):1644–1655.
Bose, R. P. J. C., Mans, R. S., and van der Aalst, W. M. P.
(2013). Wanna improve process mining results? In
2013 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence
and Data Mining (CIDM), pages 127–134.
Canadian Institute for Health Information (2009). In Focus.
A National Look at Sepsis. Ottawa, Ont: CIHI.
de Medeiros, A. K. A., Guzzo, A., Greco, G., van der
Aalst, W. M. P., Weijters, A. J. M. M., van Dongen,
B. F., and Sacc
`
a, D. (2007). Process Mining Based
on Clustering: A Quest for Precision. In Hofstede,
A. t., Benatallah, B., and Paik, H.-Y., editors, Busi-
ness Process Management Workshops, number 4928
in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 17–29.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Dellinger, R. P., Carlet, J. M., Masur, H., Gerlach, H., Ca-
landra, T., Cohen, J., Gea-Banacloche, J., Keh, D.,
Marshall, J. C., Parker, M. M., Ramsay, G., Zimmer-
man, J. L., Vincent, J.-L., and Levy, M. M. (2004).
Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for manage-
ment of severe sepsis and septic shock. Intensive Care
Medicine, 30(4):536–555.
Dellinger, R. P., Levy, M. M., Carlet, J. M., Bion, J., Parker,
M. M., Jaeschke, R., Reinhart, K., Angus, D. C.,
Brun-Buisson, C., Beale, R., Calandra, T., Dhainaut,
J.-F., Gerlach, H., Harvey, M., Marini, J. J., Marshall,
J., Ranieri, M., Ramsay, G., Sevransky, J., Thompson,
B. T., Townsend, S., Vender, J. S., Zimmerman, J. L.,
and Vincent, J.-L. (2008). Surviving Sepsis Cam-
paign: International guidelines for management of se-
vere sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Intensive Care
Medicine, 34(1):17–60.
Dellinger, R. P., Levy, M. M., Rhodes, A., Annane, D., Ger-
lach, H., Opal, S. M., Sevransky, J. E., Sprung, C. L.,
Douglas, I. S., Jaeschke, R., Osborn, T. M., Nun-
nally, M. E., Townsend, S. R., Reinhart, K., Kleinpell,
R. M., Angus, D. C., Deutschman, C. S., Machado,
F. R., Rubenfeld, G. D., Webb, S. A., Beale, R. J., Vin-
cent, J.-L., Moreno, R., and Surviving Sepsis Cam-
paign Guidelines Committee including the Pediatric
Subgroup (2013). Surviving sepsis campaign: in-
ternational guidelines for management of severe sep-
sis and septic shock: 2012. Critical Care Medicine,
41(2):580–637.
European Pathway Association (2016). E-p-a definition of
care pathway. http://http://e-p-a.org/.
Jawad, I., Luk
ˇ
si
´
c, I., and Rafnsson, S. B. (2012). As-
sessing available information on the burden of sepsis:
global estimates of incidence, prevalence and mortal-
ity. Journal of Global Health, 2(1):010404.
Kempker, J. A. and Martin, G. S. (2016). The Changing
Epidemiology and Definitions of Sepsis. Clinics in
Chest Medicine, 37(2):165–179.
Lord, J. M., Midwinter, M. J., Chen, Y.-F., Belli, A., Brohi,
K., Kovacs, E. J., Koenderman, L., Kubes, P., and Lil-
ford, R. J. (2014). The systemic immune response
to trauma: an overview of pathophysiology and treat-
ment. Lancet (London, England), 384(9952):1455–
1465.
Mannhardt, F., de Leoni, M., Reijers, H. A., and van der
Aalst, W. M. P. (2016). Decision mining revisited -
discovering overlapping rules. In Nurcan, S., Soffer,
P., Bajec, M., and Eder, J., editors, Advanced Informa-
tion Systems Engineering: 28th International Confer-
ence, CAiSE 2016, Ljubljana, Slovenia, June 13-17,
2016. Proceedings, pages 377–392. Springer Interna-
tional Publishing, Cham.
Mans, R., Schonenberg, H., Leonardi, G., Panzarasa, S.,
Cavallini, A., Quaglini, S., and van der Aalst, W.
(2008). Process mining techniques: an application to
stroke care. Studies in health technology and infor-
matics, 136:573.
Mcgregor, C., Catley, C., and James, A. (2011). A pro-
cess mining driven framework for clinical guideline
improvement in critical care. In In LEMEDS Work-
shop.
Rojas, E., Munoz-Gama, J., Sep
´
ulveda, M., and Capurro,
D. (2016). Process mining in healthcare: A literature
review. Journal of biomedical informatics, 61:224–
236.
Silva, E., Pedro, M. d. A., Sogayar, A. C. B., Mohovic,
T., Silva, C. L. d. O., Janiszewski, M., Cal, R. G. R.,
de Sousa, E. F., Abe, T. P., de Andrade, J., de Matos,
J. D., Rezende, E., Assuno, M., Avezum, A., Rocha,
P. C. S., de Matos, G. F. J., Bento, A. M., Corrła,
A. D., Vieira, P. C. B., Knobel, E., and Brazilian Sep-
sis Epidemiological Study (2004). Brazilian Sepsis
Epidemiological Study (BASES study). Critical Care
(London, England), 8(4):R251–260.
Singer, M., Deutschman, C. S., Seymour, C. W., Shankar-
Hari, M., Annane, D., Bauer, M., Bellomo, R.,
Bernard, G. R., Chiche, J.-D., Coopersmith, C. M.,
Hotchkiss, R. S., Levy, M. M., Marshall, J. C., Martin,
G. S., Opal, S. M., Rubenfeld, G. D., van der Poll, T.,
Vincent, J.-L., and Angus, D. C. (2016). The Third In-
ternational Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Sep-
tic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA, 315(8):801–810.
Torio, C. M. and Andrews, R. M. (2013). National Inpa-
tient Hospital Costs: The Most Expensive Conditions
by Payer, 2011: Statistical Brief #160. In Health-
care Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical
Briefs. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
(US), Rockville (MD).
van der Aalst, W., Adriansyah, A., and van Dongen, B.
(2012). Replaying History on Process Models for
Conformance Checking and Performance Analysis.
Wiley Int. Rev. Data Min. and Knowl. Disc., 2(2):182–
192.
van der Aalst, W. M. P. (2011). Process Mining: Discov-
ery, Conformance and Enhancement of Business Pro-
cesses. Springer, Place of publication not identified,
2011 edition edition.

van der Aalst, W. M. P., van Dongen, B. F., G
¨
unther, C. W.,
Mans, R. S., de Medeiros, A. K. A., Rozinat, A., Ru-
bin, V., Song, M., Verbeek, H. M. W., and Weijters, A.
J. M. M. (2007). ProM 4.0: Comprehensive Support
for Real Process Analysis. In Kleijn, J. and Yakovlev,
A., editors, Petri Nets and Other Models of Concur-
rency ICATPN 2007, number 4546 in Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, pages 484–494. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
