
Habituating Students to IPR Questions During Creative Project Work
Ville Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen and Tommi K
¨
arkk
¨
ainen
Faculty of Information Technology, University of Jyv
¨
askyl
¨
a, Finland
Keywords:
Intellectual Property Rights, Project-Based, Creativity.
Abstract:
Intellectual property rights (IPR) constitute a topic that is unavoidably encountered in digitalizing learning
environments but that has received little attention as a separate educational research topic. In a project course
context where students ideate and implement open data-themed projects, and hence IPR questions are highly
relevant, we have learned that students readily perceive this matter as a side topic and tackle it without much
deliberation. To improve students’ awareness of IPR questions, we modified our course arrangements. This
article analyzes and discusses students’ responses to IPR in this setting. We found that students consider
IPR a challenge, and we argue that they must be “habituated” to think over this matter. The temporariness,
incompleteness, and potential humor of educational projects constrain students’ interest in IPR, while the
perceived relevance of a project topic increases their interest. Students altogether appreciate that IPR questions
are raised and need to be agreed on within teams.
1 INTRODUCTION
The computing profession comprises several aspects
that are referred to as professional skills. We fo-
cus on intellectual property (IP), which has received
fairly little attention as a separate educational research
topic. This topic is, in fact, inherently challenging.
As noted by Bach et al. (2010), in the classical cre-
ative industry intellectual property rights (IPR) have a
strategic but controversial role: both individuals and
companies prefer strong IPR, whereas creative com-
munities call for weak IPR to allow for flexible recre-
ation (e.g., new music or video games).
The context of our work is project-based learn-
ing, which has a century-old documented history (Kil-
patrick, 1918). In our field of computer science and
software engineering, various project course mod-
els were already suggested decades ago (Shaw and
Tomayko, 1991). Capstone projects or senior de-
sign courses constitute an essential part of many com-
puter science and engineering programs, which is il-
lustrated in taxonomic works (Fincher et al., 2001;
Hoffman, 2014). We focus on a bachelor-level project
course where students innovate a software product us-
ing open resources, open data and open APIs (Ap-
plication Programming Interfaces). This emphasis on
creation based on available resources links with the
concept of open innovation proposed by Chesbrough
(2003). In a systematic literature review on this con-
cept, IP was mentioned both as one of the main trends
and as a popular keyword within the open innovation
literature, while student innovation did not receive at-
tention (Hossain et al., 2016). Hence, within the open
innovation research paradigm, the student setting with
regard to IPR is a novel domain.
In our experience, project-based learning in which
students collaborate with industry can make IPR
questions a relatively easy topic for students, as of-
ten such courses operate using university-made agree-
ment templates requiring not much more than signa-
tures from the students. That is, the topic of intel-
lectual property is raised to ensure the protection of
customer rights. When we devised a project-based
course based fully on students’ own ideation (no cus-
tomers involved), we noticed that IPR questions con-
stituted a “necessary evil” and that efforts had to be
taken to raise students’ attention (Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen and
K
¨
arkk
¨
ainnen, 2016).
In an open, student group innovation context, one
needs to manage IPR to prevent any concerns about
students not submitting their part of the project work
(Abdelkafi, 2011) and in order not to suppress cre-
ative work (Kiili et al., 2012). As noted by Fuller
et al. (2010), students as software developers may be
willing to rashly use software regardless of licensing
violations but be much more strict when considering
ownership of their own programming contributions.
Hence, the use of open resources in conjunction with
Isomöttönen, V. and Kärkkäinen, T.
Habituating Students to IPR Questions During Creative Project Work.
DOI: 10.5220/0006284800950102
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2017) - Volume 2, pages 95-102
ISBN: 978-989-758-240-0
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
95

self-made deliverables can create a tension that leads
to an overemphasis on one’s own achievements. In
this article, we study students’ responses to IPR in
the context of creative group-based project work.
2 IP IN STUDENTS’
COURSEWORK
The recommendations and lessons learned relating to
IPR issues in capstone projects have been strongly
based on protecting the rights of industrial partners
(e.g. Gorka et al., 2007). The importance of IPR is-
sues is thus well recognized in project courses with
explicit external customers. Under such conditions,
intellectual property is negotiated and agreed between
the university, individual students, and the customer
organization (Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen and K
¨
arkk
¨
ainen, 2008; Pil-
skalns, 2009; Vanhanen et al., 2012).
Many organizations implement several kinds of
customer projects in such a way that students can
make a selection and be allocated to the projects based
on their opinions about IPR (Goldberg, 2004; Vallino,
2014; Alexander et al., 2014). As exemplified in the
study by Vallino (2014), customer collaboration may
take a form of an open source project, a project where
IP is fully granted to the customer, a project where
only particular rights to use the project outcome are
granted to the customer (students keeping their IPR),
and a project where no rights are granted to external
parties. Sometimes IP transfer is organized in such a
way that students grant IPR to the university, which
then signs them off to the customer (Goldberg, 2004).
IP transfer is often seen as the key factor in be-
ing able to recruit companies as project sponsors and
customers (Todd and Magleby, 2005; Henson, 2010;
Warnick and Todd, 2011). Accordingly, IPR are often
straightforwardly transferred to the companies, with
other options mentioned in a sense of a backup-plan
(Alexander et al., 2014). In a study by Stearns et al.
(2003), there was no procedure for managing students
who declined to transfer IP; such students simply con-
tinued working in the capstone sequence. Generally,
IPR questions in customer collaboration are noted to
be potentially difficult to manage (Gorka et al., 2007).
A different approach is found in studies drawing
on student creativity. In the context of entrepreneurial
capstone, Shartrand and Weilerstein (2011) posit that
the entrepreneurial element transfers the usual em-
phasis on customer and university polices to the stu-
dent team as to IPR. They stress the importance of
educational possibilities to understand and learn fun-
damentals of IP in a real context and related to self-
generated artifacts, as students are then motivated
and encouraged to pursue projects beyond the pro-
vided courses—their program offers students oppor-
tunities to advance the work initiated during the cap-
stone projects.
Similarly, in the study by Silva et al. (2009), which
focused on an entrepreneurial practical course, a ma-
jor argument to ask students to reflect explicitly on
intellectual property was its motivational influence
on their creative work. They asked students to re-
view patent registers to help them see how novel their
ideas were, and they even encouraged students to file
patents. The authors argue that such procedures are
educationally valuable, preparing students for their
professional future.
Yet another entrepreneurial project course for un-
dergraduate students is presented by Pilskalns (2009).
As with our own course arrangements, important con-
tent was provided to students in the form of small
lectures, with one of the topics dealing with owner-
ship and intellectual property related to project deliv-
erables. The operational model in this case report,
however, was based on establishing a student com-
pany around a lecture-defined novel software product
whose IPR agreements were related to ensuring prof-
itability for an external investor.
Empirical findings on students’ perceptions are
found in a small survey by Kilamo et al. (2012) who
explored students’ perceptions of IPR during projects
implemented in a hatchery (Demola). In this setting,
students and companies can collaborate on student-
ideated projects. The authors noticed that students
paid little attention to IPR during their projects, which
corresponds with our prior experiences. The study by
Silvernagel et al. (2009) also highlights challenges,
reporting that it is not clear that students or faculty
members are willing to openly disclose their project
ideas, in particular if they consider their ideas to be
of value. On the other hand, the study by Silva et al.
(2009) reveals that students consider the topic of IPR
to be important. In a post-survey of 42 former stu-
dents from their course, over 90% of the respondents
considered understanding of IPR issues to be crucial
or important to solving business problems and taking
advantage of entrepreneurial opportunities.
In summary, the role of an external customer, who
typically pulls IPR from a student group, could be
replaced by the requirement of the group to deeply
consider IPR with respect to their own deliverables
potentially having business value and/or societal im-
pact. On the other hand, the literature indicates that
students regard the topic of IPR as important but may
pay little attention to it. Further, individuals collab-
orating on a shared project may demonstrate reserve
when it comes to disclosing their own project ideas.
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
96

3 THE PRESENT CONTEXT
We devised a project course where students utilize
open resources. The course is a 12-week (5 ECTS
credits) challenge where small groups ideate and im-
plement a software product using self-selected tech-
nologies. Each student group is coached on a weekly
basis by a teacher focusing on group processes and
software processes and a senior student providing
technical advise. The course begins with a lecture
on group and software processes and a briefing on
web development with open data examples. Students
present their project ideas after three weeks and then
continue with the product design and implementation.
During the last third of the project, an expert lecture
on “immaterial rights in programmers’ work” is pro-
vided to facilitate students’ within-team agreements
on IPR and their work with existing resources. The
projects are finally presented in an open-day event
where students demonstrate and let the audience test
their products. The audience consists of staff mem-
bers and other students in the department.
The course is very intensive and utilizes dialog as
its main pedagogic tool. The main learning goal is
conceptual learning about group work and software
processes in realistic conditions enabled by creative
open data projects. The course naturally introduces
students to a topical theme, use of open resources, as
well as reinforcing their technical skills. The course
is for third-year students but is also occasionally
taken by second-year and fourth-year students. The
course arrangements and completed projects are de-
scribed more thoroughly elsewhere (Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen and
K
¨
arkk
¨
ainen, 2015; Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen and K
¨
arkk
¨
ainnen,
2016).
When we previously merely guided students to
consider IPR within their groups, we noticed that
students gave little attention to the topic, cursorily
attaching licenses they might know to their project
outcomes at the very last minute. In our view, the
course lacked professionalism, and students needed
to be made more aware of IPR when undertaking cre-
ative work in a collaborative setting. To raise stu-
dents’ awareness, we designed an agreement template
to be used by each student group (Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen and
K
¨
arkk
¨
ainnen, 2016). The agreement is made between
each student in the group and the university. The uni-
versity signature shows students that the university
does not use the students’ work outside the agreement
and, importantly, makes the IPR questions formal and
noticeable to the students.
The agreement is applied in two phases. In the
first phase, at the beginning of the project, students
sign an agreement text by which they make a com-
mitment to agree on the IPR in their group by the end
of the project. Each student in a particular project is
then able to trust that IPR are addressed within the
group. In the second phase, during the last third of
the project, students sign another document, an at-
tachment to the former, where they announce the IPR
related to their project outcomes. Usually this means
announcing an open license that they have attached
to their product. We have noticed that it is natural to
make final decisions on the IPR during the last third
of the project, as by then the students are able to form
a realistic picture of the project outcomes.
4 THE STUDY
We present a thematic analysis of students’ responses
to IPR questions after our attempts to raise students’
awareness of IPR by the agreement practice. The
study reflects a step in an action research project
where actions taken are put under validation and re-
flected on. It must be emphasized that validation here
signified an aim to describe the phenomenon instead
of controlled experimentation. The resultant cate-
gories on the students’ reactions to IPR can inform
a follow-up quantitative study on the relative impor-
tance of the categories.
The data used were the students’ reviews of IP in
their personal learning reports prepared in the end of
the autumn 2015 course. These reports were received
from the whole course population (N=21). The anal-
ysis followed data-driven (inductive) content analy-
sis. We began by extracting IP-related extracts from
the learning reports. Thereafter, the first author per-
formed a thematic analysis, the outcomes of which
were reviewed by the second author for reaching an
agreement. Similarities and differences in the data
indicated a set of categories. Finally, the resultant
categories were arranged into a holistic “display,” as
shown in Figure 1; A similar analytic approach is
described by many, for instance, by Attride-Stirling
(2001), who suggests that themes discovered in the
data are developed into “thematic networks.”
Our data concerns only single course instance and
yielded a single patterned display. In this connection,
it must be stressed that the current study is under-
pinned by our previous improvement efforts on the
same matter (IPR) and context; In improving educa-
tion as an action research project, continuity in the re-
search process, such that one and the same researchers
stay together, is an important validity aspect (Melrose,
2001).
Habituating Students to IPR Questions During Creative Project Work
97

5 STUDENTS’ RESPONSES TO
IPR
This section reviews the students’ responses to IPR
questions. The main themes of the thematic analysis
are presented in Sections 5.1–5.7 and summarized in
Section 5.8.
5.1 Temporariness
Looking at the students’ responses to IPR, we noticed
that an educational project is readily perceived to be
a temporary organization, with this temporariness re-
ducing students’ genuine interest in the project out-
comes and related IPR issues:
I was not interested in IPR questions during
the course, as I had no plans to further develop
our product, and the rights to it were then not
interesting.
However, the same student continues:
As for the future, it was useful to explore the
different licenses and figure out their purpose.
The same contradiction, albeit in a milder form, is il-
lustrated by the below quotation from another student:
Although it may seem a bit useless to consider
IPR on the project outcome in the context of
a short-term student project such as this, IPR
questions play such a big role in the software
business that it is good to start pondering them
at this point.
These contradictions reveal that the attribute of tem-
porariness “pushes” students’ interest away from a
matter that they consider will be important in the fu-
ture.
5.2 Incompleteness
The intensive 12-week course yields useful and illus-
trative prototypes, although of course many parts of
such prototyped products should be refactored in or-
der to become technically sound products. Accord-
ingly, students refer to the incompleteness of their
product as a factor affecting the selection of a licence,
which, in this case, can simply be very open in nature:
We had no problems in selecting the license
within our group, as we knew that the quality
of the code was not that good. So we selected
a very open license, as the whole thing would
have to be implemented afresh if one wanted
to make it a really usable [deployable] prod-
uct. [...] Well it [the code] was not that bad
nor unreadable, but reworking it would help
in figuring out what we were actually doing.
We should note here that creative product develop-
ment has been associated with continuous prototyp-
ing. Silva et al. (2009), who also implement a course
drawing on student creativity, aptly state that “the
more you build prototypes, the more you understand
the product.” Our experiences align with the need for
continuous prototyping, and we must place more em-
phasize on this feature of software process to the stu-
dents.
5.3 Humor in Project Topic
Creative topics may turn out to be humorous in nature,
which may, however engaging they may be, lead stu-
dents to develop only a minor interest in IPR. Educa-
tionally, as we emphasize conceptual learning about
group processes and software processes as the key
learning goals, such topics have worked out well, and
we have not blocked student creativity in this regard.
The quotation below nonetheless illustrates a con-
strained reaction to IPR with respect to such a project
topic:
On my part, licensing questions were hardly
at all relevant, as I thought from the beginning
that our project was, as you may find in its
topic, made up so much with tongue in cheek
and a twinkle in the eye that I didn’t even want
to think about immaterial rights. [...] For me
the project was about implementing a jolly
idea, for which reason I felt up to doing the
project and avoided boredom.
Although we guide students to consider a target group
for their projects, the quotation suggests that this must
be particularly emphasized for humorous project top-
ics. Students should perceive their project, however
humorous, to be relevant outside their own project
scope.
5.4 Perceived Relevance
A project topic perceived to be relevant (serviceable,
of real value) increases student interest in IPR, a fac-
tor counteracting the above constraining factors:
IPR questions did not really emerge in the dis-
cussions of the group. In the beginning, we
simply thought that if someone earned large
amounts of money with the product, the topic
would begin to make sense. At the end, the
group members, including me, pondered the
licensing much more. Especially because we
received a pat on the back for our project idea
and implementation. We finally selected the
AGP license instead of the MIT license.
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
98

The quotation illustrates how students’ thinking con-
cerning IPR develops during projects, as they begin to
gradually picture the characteristics of the end prod-
uct. This observation matches our use of the two-
phased agreement practice. Moreover, the quotation
also illustrates how the student group considered sev-
eral licensing options when the project was perceived
to be relevant (not only the very concise and open
MIT license). As an interesting aside, the theme of
perceived relevance has emerged in the context of ed-
ucational projects with external customers as a fac-
tor affecting students’ opinions concerning potential
financial compensation for their coursework (Heikki-
nen and Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen, 2015).
5.5 Uncertainty with a New and
Difficult Topic
When students use a wide range of available resources
in their projects, uncertainty emerges:
The licensing thing was totally new to me. [...]
We had to be very careful with how to use In-
stagram and Twitter. The terms and conditions
were difficult texts to read. We had to, for
instance, change our site appearance because
Twitter and Instagram required particular ap-
pearances and functionalities.
The uncertainty also relates to agreements within
teams:
Frankly, I am not sure if the licensing of our
work followed all the regulations. We spent
time on exploring the matter but we certainly
are not lawyers.
In a similar tone, another student states:
I have not needed to think over programming-
related immaterial rights before, in particu-
lar when work is done in a group and exist-
ing code is utilized. [...] The large number
of available licenses complicates the selection,
as many include only small adjustments com-
pared to the others. For this reason, we have
not reached a consensus in our group yet, at
the time I am writing this report.
5.6 Eye-opening toward Professionalism
A positive learning outcome is reflected in the transi-
tions from initially considering IPR as a useless topic
to seeing it as a necessary topic in professional prac-
tice:
Although the IPR questions were really alien
to me at first and I regarded the whole topic as
useless, it was, after all, good that they were
raised. When programming code is created, it
is good to talk through who have the rights to
that code. [...] Now, being a bit more aware of
these things, I’ve been pondering questions re-
lated to immaterial and other rights as regards
programming and other functions of compa-
nies.
Another quotation reveals that students value being
awoken to the topic in order to avoid being acciden-
tally negligent:
IPR questions were fairly strange to me in
the context of computer science. I heard in-
teresting and important examples of how you
should act depending on the situation [your
aims] during the lecture. You easily ignore
these topics but after hearing of them, I cer-
tainly do not leave anything [IP related] un-
marked in any decent projects.
It should be noted that even in cases where we ob-
served a clear constraining factor, we find students
anticipating that IPR will be generally an important
topic; see the latter two quotations in Section 5.1. The
student we quoted in Section 5.3 also concludes in
this manner:
I suppose I need to start thinking of these
questions [IPR] in the future.
Furthermore, we interpret the instances when stu-
dents kept on posing questions after the briefing lec-
ture as indications of eye-opening:
After the license lecture, I was still unclear
about what open source code you can use and
how it should be marked in your own code if
you use it. It would be nice to receive further
clarification on how you can use open code
and what conventions are involved.
Students’ comments also reveal that they have
considered different options within their groups—a
desired learning outcome:
Our group selected GNU GPL 2.0 as the li-
cense, as we thought that it would be easier
to move from a stricter license to a more open
one, if we [later] wanted to do so. It is more
difficult to tighten up an open one.
5.7 Within-team Fairness
Students value that IPR is raised as their group situa-
tion becomes clarified from the perspective of owner-
ship:
Habituating Students to IPR Questions During Creative Project Work
99

I experienced the considerations on the rights
as useful because each group member pro-
duced a considerable amount of code into the
final version and the work took a lot of time
from each of us. Each of us could further de-
velop the software, for what reason it is good
that things [IPR] have been agreed on.
This quote highlights the experience of fairness
within a group, which is reinforced through making
an agreement on immaterial rights.
5.8 Summary Pattern
The course seems to “expose” students to the topic of
IPR instead of “integrating” previously learned items,
as is the case with many other skills involved in the
course. Students’ comments reveal that the topic of
IPR was previously strange to them and that this ex-
posure to the topic initiated their knowledge and in-
terest. Our interpretation is that this eye-opening ex-
perience counteracted the frustrations caused by their
uncertainties about a novel and difficult topic. The
constraining factors related to the temporariness and
incompleteness of educational projects. These factors
were nevertheless counteracted when the students no-
ticed that they had ideated and implemented a use-
ful, serviceable project. Finally, as course providers,
we regard the “within-team fairness” outcome as a
professional condition that we sought to introduce
through the agreement practice described in Section
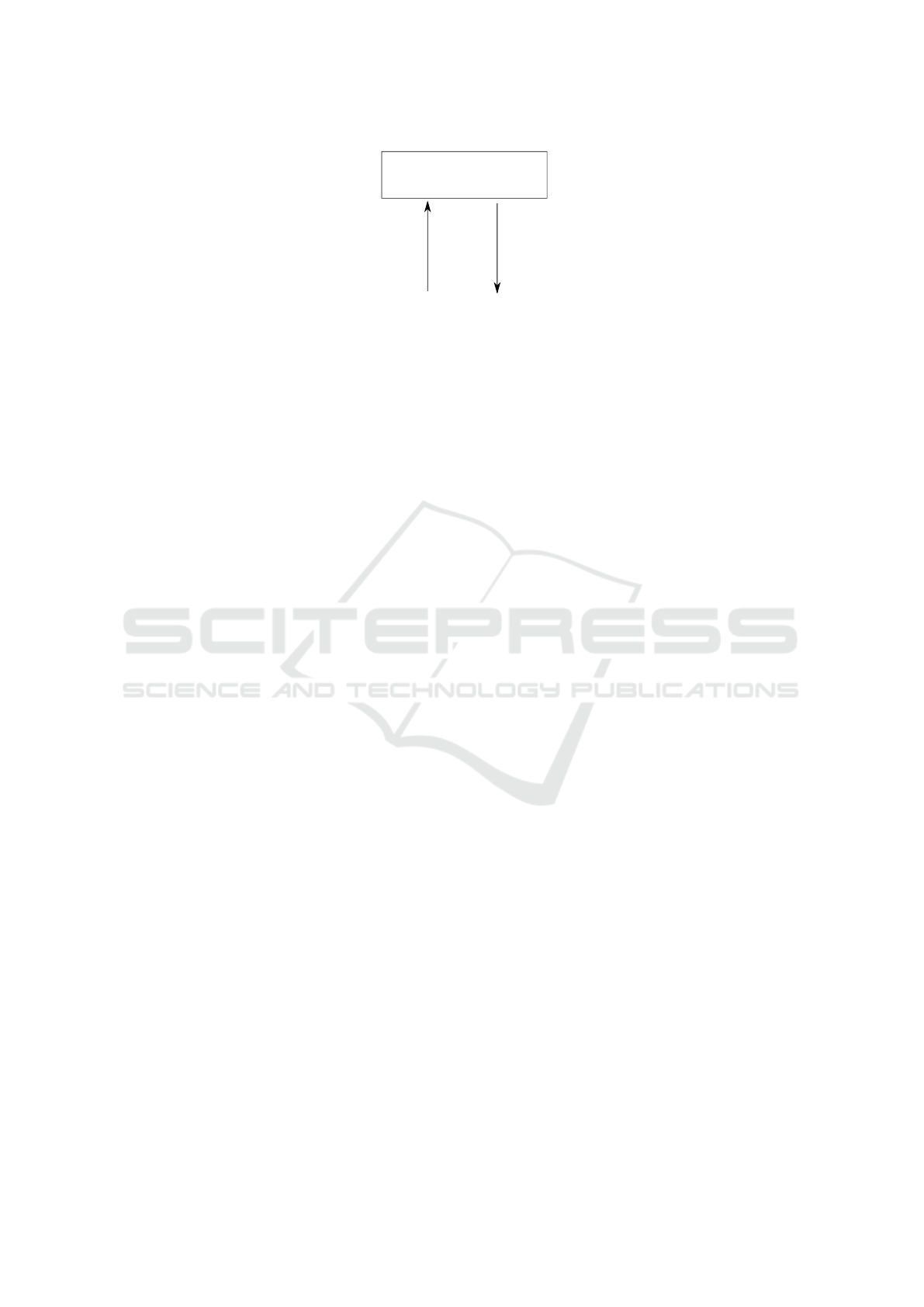
3. Figure 1 conceptualizes results into pull and push
factors. For instance, issues such as temporariness
“push” students’ interest away from the matter, while
a project topic perceived to be relevant “pulls” their
interest back. Students’ responses may also vary
within teams: one team member may consider fair-
ness in terms of rights to reuse the code (“pull”),
whereas another one straightforwardly shows lowered
interest in IP due to the temporary and humorous na-
ture of the project (“push”).
6 DISCUSSION
This paper has reported on students’ responses to IPR
during creative collaborative work. Based on our ob-
servations concerning the initial orientations in the
course, the push factors (e.g., temporariness) that con-
strain students’ interest in IPR may be rooted in a
broad educational challenge: how students perceive
being in formal education. The third-year project
students have principally attended big introductory
classes after their schooling background. Their per-
ceptions of themselves as potentially self-directed ac-
tive agents may be constrained, and their orientations
reflect a mode of being where they expect course
providers to instruct them in what to do and where
they principally work for credits. We have accord-
ingly overheard and witnessed in the end-of-course
learning reports students being overwhelmed by the
very open course assignment and the active role re-
quired, which we illustrate with a quotation below:
The only thing addressed during the course,
in which I did not really develop myself, was
ideating. Our group had severe difficulties
with ideating, which can be seen in the out-
come. We could not come up with a good idea
and a topic everyone was interested in. Many
courses do not at all require student ideation,
which is a bit negative [unfortunate] thing. We
have learned to work on predefined topics or
problems, which is likely to cause passivity
and makes ideating painful. You do not learn
to ideate just like that but, encouraged by this
course, I started to think over this matter more
closely and will work on the matter somehow
in the future.
We have fortunately observed transformations (as in
the quotation above), which the first author has re-
ported earlier (Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen, 2014) and which also
emerged in relation to IPR questions (see Section 5.6).
Re-observing such transformations suggests a useful
hidden curriculum for early curriculum project-based
courses, one which reinforces a perception of formal
education as a meaningful activity. Generally, project
work emphasizing complicated problems of open na-
ture has been argued to be suitable for late curricula,
as by then students have developed needed levels of
self direction (Perrenet et al., 2000).
While the challenges observed may be rooted in
the features of the education system, we believe that
remedial actions can be taken. Our results suggest
that these actions should focus on increasing the per-
ceived relevance of projects. One action is to further
support the students’ creative processes at the begin-
ning of the course in order to avoid unrefined and
rashly decided project topics. We could announce
the first two weeks of the course as a specific phase
dedicated only to ideation. Another action relates
to the previously discussed concern that educational
projects without an explicit customer may turn out
“flat” in the end (Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen and K
¨
arkk
¨
ainen, 2015),
as students notice that their efforts are not deployed
in real use. We could introduce more publicity into
students’ coursework by building a portal where stu-
dents can deploy their prototypes together with links
to source code in public repositories (e.g., GitHub).
This would make the possibility of reuse not only the-
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
100
eye-opening exposure
IPRs as an important
professional topic
fairness
temporariness
incompleteness
humor in project topic
difficulty/uncertainty
relevant project
PULL
PUSH
Figure 1: Results summarized as pull and push factors.
oretical but unlikely and likely. This action could be
accompanied with an expert lecture on entrepreneur-
ship provided by a carefully selected, inspiring en-
trepreneur alumnus.
An important educational question is also how
strictly students can and should be guided regarding
IPR. We have learned that interpreting data licenses
and terms and conditions is challenging for teachers
as well. From this perspective, we argue that students
must be “habituated” to the matter and advised that
addressing it is likely to “remain a challenge that must
be tackled as part of professional practice.” We thus
consider students’ increasing questioning induced by
the course to be a desired learning outcome (Section
5.6). That is, students become gradually more pre-
pared to encounter IPR questions.
In ACM/IEEE CS curriculum (2013), it is recom-
mended that professional practice should be taught
through a standalone course, while with a note that
a mere standalone course does not introduce the top-
ics in a context. Our observations indicate that even
when issues are raised within a context, students
must see the relevance to be interested. We conclude
that encountering IPR questions within contexts and
throughout the curriculum, as part of courses where
they are needed and relevant, is educationally benefi-
cial.
Finally, we notice that the students’ responses to
IPR in terms of fairness in group situations (Section
5.7) align with our goal of teaching group work by
conceptualizing and communicating “justice in group
work” to the students (Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen, 2014). Thus, by
increasing attention to IPR we feel that we have better
incorporated a key educational attribute (justice) into
the course.
7 CONCLUSION
We conclude with two main points. First, to attract
students’ interest in IPR during creative project work,
they should perceive their projects as relevant. This
requirement relates to the problem of a “lack of con-
tinuation” in student-ideated projects, an issue sup-
ported by the literature (Pilskalns, 2009) and that we
can confirm. We wish to note that affording stu-
dents with opportunities to continue their self-ideated
projects may be difficult in computing curricula that
do not otherwise emphasize entrepreneurship. The re-
quirement of relevance also signifies support for stu-
dents’ creative processes at the beginning of the in-
novation projects in order to guide students to select
topics they both perceive and can argue to be ser-
viceable. Second, due to student inexperience, we
stress that educators must take responsibility for rais-
ing IPR questions through sound procedures in order
to make learning environments professional spaces
that are able to support fairness in collaborative work.
A follow-up study should also continue to address
variation in students’ responses to IPR within teams
and how group phenomena such as the effects of ma-
jority affect IP decisions.
REFERENCES
Abdelkafi, N. (2011). Towards open school: How to orga-
nize innovation contests with students. In Heiß, H.-
U., Pepper, P., Schlingloff, B.-H., and Schneider, J.,
editors, Proceedings of Informatik. Lecture Notes in
Informatics, volume P-192, pages 4–10, Bonn. GI.
Alexander, D., Beyerlein, S., and Metlen, S. (2014). Pro-
cesses to formalize sponsored educational activity
agreements between industry and universities related
to capstone design projects. In Capstone Design Con-
ference, Columbus, Ohio.
Attride-Stirling, J. (2001). Thematic networks: An analytic
tool for qualitative research. Qualitative Research,
1(3):385–405.
Bach, L., Cohendet, P., P
´
enin, J., and Simon, L. (2010).
Creative industries and the IPR dilemma between
appropriation and creation: some insights from the
videogame and music industries. Management in-
ternational/Gesti
`
on Internacional/International Man-
agement, 14(3):59–72.
Chesbrough, H. W., editor (2003). Open Innovation: The
New Imperative for Creating and Profiting from Tech-
nology. Harvard Business School Press, Boston, MA.
Fincher, S., Petre, M., and Clark, M., editors (2001). Com-
Habituating Students to IPR Questions During Creative Project Work
101

puter Science Project Work: Principles and Pragmat-
ics. Springer-Verlag, London.
Fuller, U., Little, J. C., Keim, B., Riedesel, C., Fitch, D.,
and White, S. (2010). Perspectives on developing
and assessing professional values in computing. ACM
SIGCSE Bulletin, 41(4):174–194.
Goldberg, J. (2004). Intellectual property and confidential-
ity issues in senior design courses. Engineering in
Medicine and Biology Magazine, IEEE, 23(6):16–18.
Gorka, S., Miller, J. R., and Howe, B. J. (2007). Devel-
oping realistic capstone projects in conjunction with
industry. In Proceedings of the 8th ACM SIGITE con-
ference on Information technology education, pages
27–32. ACM.
Heikkinen, J. and Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen, V. (2015). Students’ opin-
ions on financial compensation from project work. In
Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on
Computer Supported Education, pages 397–406. IN-
STICC.
Henson, K. L. (2010). Student projects as a funding
source. Journal of Information Systems Education,
21(3):291–298.
Hoffman, H. F. (2014). The Engineering Capstone Course -
Fundamentals for Students and Instructors. Springer
International Publishing.
Hossain, M., Islam, K. Z., Sayeed, M. A., and Kauranen,
I. (2016). A comprehensive review of open innova-
tion literature. Journal of Science & Technology Pol-
icy Management, 7(1):2–25.
Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen, V. and K
¨
arkk
¨
ainen, T. (2008). The value of a
real customer in a capstone project. In Software En-
gineering Education and Training. Proceedings. 21st
Conference on, pages 85–92, Los Alamitos, CA. IEEE
Computer Society.
Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen, V. (2014). Making group processes explicit to
student: A case of justice. In Proceedings of the 2014
Conference on Innovation and Technology in Com-
puter Science Education, ITiCSE ’14, pages 195–200,
New York, NY. ACM.
Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen, V. and K
¨
arkk
¨
ainen, T. (2015). Open resources
as the educational basis for a bachelor-level project-
based course. In Proceedings of the 7th International
Conference on Computer Supported Education, pages
46–56.
Isom
¨
ott
¨
onen, V. and K
¨
arkk
¨
ainnen, T. (2016). Project-
based learning emphasizing open resources and stu-
dent ideation: How to raise student awareness of
IPR? In Zvacek, S., Restivo, T. M., Uhomoibhi, J.,
and Helfert, M., editors, Computer Supported Edu-
cation: 7th International Conference, CSEDU 2015,
Lisbon, Portugal, May 23-25, 2015, Revised Selected
Papers, pages 293–312. Springer International Pub-
lishing, Cham.
Kiili, K., Kiili, C., Ott, M., and J
¨
onkk
¨
ari, T. (2012). To-
wards creative pedagogy: Empowering students to de-
velop games. In Felicia, P., editor, 6th European Con-
ference on Games Based Learning, pages 250–257,
Reading, UK. Academic Conferences Limited.
Kilamo, T., Hammouda, I., Kairamo, V., R
¨
as
¨
anen, P., and
Saarinen, J. P. (2012). Open source, open innovation
and intellectual property rights—a lightning talk. In
IFIP International Conference on Open Source Sys-
tems, pages 298–303. Springer.
Kilpatrick, W. (1918). The project method. The Teachers
College Record, 19(4):319–335.
Melrose, M. J. (2001). Maximazing the rigor of ac-
tion research: Why would you want to? how
could you? Field Methods, 13(2):160–180. doi:
10.1177/1525822X0101300203.
Perrenet, J. C., Bouhuijs, P. A. J., and Smits, J. G. M. M.
(2000). The suitability of problem-based learning for
engineering education: Theory and practice. Teaching
in Higher Education, 5(3):345–358.
Pilskalns, O. (2009). An entrepreneurial approach to
project-based courses. Computer Science Education,
19(3):193–204.
Sahami, M., Danyluk, A., Fincher, S., Fisher, K., Gross-
man, D., Hawthrone, E., Katz, R., LeBlanc, R., Reed,
D., Roach, S., Cuadros-Vargas, E., Dodge, R., Ku-
mar, A., Robinson, B., Seker, R., and Thompson, A.
(2013). Computer science curricula 2013.
Shartrand, A. and Weilerstein, P. (2011). Strategies to pro-
mote entrepreneurial learning in engineering capstone
courses. International Journal of Engineering Educa-
tion, 27(6):1186.
Shaw, M. and Tomayko, J. E. (1991). Models for undergrad-
uate project courses in software engineering. In Pro-
ceedings of the SEI Conference on Software Engineer-
ing Education, pages 33–71, London, UK. Springer-
Verlag.
Silva, A., Henriques, E., and Carvalho, A. (2009). Cre-
ativity enhancement in a product development course
through entrepreneurship learning and intellectual
property awareness. European Journal of Engineer-
ing Education, 34(1):63–75.
Silvernagel, C., Schultz, R. R., Moser, S. B., and Aune, M.
(2009). Student-generated intellectual property: Per-
ceptions of ownership by faculty and students. Jour-
nal of Entrepreneurship Education, 12:13–33.
Stearns, D., Dalbey, J., Turner, C., and Kearns, T. (2003).
Report: A capstone project involving a hundred stu-
dents, for an industrial partner. In Proceedings of the
International Conference on Engineering Education,
July 21–25, Valencia, Spain. INEER.
Todd, R. H. and Magleby, S. P. (2005). Elements of a
successful capstone course considering the needs of
stakeholders. European Journal of Engineering Edu-
cation, 30(2):203–214.
Vallino, J. (2014). Ownership of artifacts and intellec-
tual property for software-intensive capstone design
projects. In Capstone Design Conference, Columbus,
Ohio.
Vanhanen, J., Lehtinen, T. O., and Lassenius, C. (2012).
Teaching real-world software engineering through a
capstone project course with industrial customers.
In Proceedings of the First International Workshop
on Software Engineering Education Based on Real-
World Experiences, pages 29–32. IEEE.
Warnick, G. M. and Todd, R. H. (2011). Importance of
providing intellectual property to sponsoring compa-
nies when recruiting capstone projects. International
Journal of Engineering Education, 27(6):1238.
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
102
