
Optimal Combination Rebate Warranty Policy with Second-hand
Products
Sriram Bhakthavachalam
1
, Claver Diallo
1
, Uday Venkatadri
1
and Abdelhakim Khatab
2
1
Department of Industrial Engineering, Dalhousie University, 5269 Morris Street, Halifax, Canada
2
Laboratory of Industrial Engineering, Production and Maintenance (LGIPM), Lorraine University,
National School of Engineering, Metz, France
Keywords:
Second-hand Products, Warranty Policy, Consumer Perspective, Remaining Useful Life.
Abstract:
With the increased awareness for sustainability, many engineered products are being recovered and recondi-
tioned for secondary useful lives. These second-hand products can serve as replacement products to honour
warranty pledges. This paper presents two mathematical models to determine the optimal combination rebate
warranty policy when refurbished products are used for replacements from both the manufacturer and consu-
mer point of views. Several numerical experiments are conducted to derive useful managerial knowledge.
1 INTRODUCTION
A warranty is a contractual agreement offered by the
manufacturer at the point of sale of a product (Blis-
chke, 1995), (Blischke, 1993). The use of warran-
ties is universal and serves numerous purposes. It
helps the buyers to rectify all the failures occurring
within the warranty period at lower or no cost. Whe-
reas, for manufacturers, it acts as a promotional tool
to increase sales and revenue (Blischke, 1995). Ame-
rican manufacturers spend over 25 billion dollars to
service warranty claims which is about 2% of their an-
nual revenue from sales (Chukova and Shafiee, 2013;
Shafiee and Chukova, 2013). In the 2009 General
Motors annual report, the company had a total re-
venue of $104.2 billion and the future warranty cost
on sold cars estimated to be $2.7 billion, about 2.6%
of the revenue (Shafiee and Chukova, 2013). When
buying a product, the consumer usually faces the dif-
ficult task of deciding between buying the warranty
or not. And when the decision is made to get the war-
ranty, choosing between different characteristics and
warranty policies is another daunting task. When the
warranty period is optional, the consumer has to de-
cide if the warranty is worth the additional cost based
a very limited knowledge of the product. This is beco-
ming more and more important, since there is a gro-
wing trend among the manufacturers to offer exten-
ded term warranties. These involve additional costs,
and the terms can vary considerably (Blischke, 1995;
Blischke, 1993; Yun et al., 2008). Blischke & Murthy
gave the example of a warranty or extended warranty
that might cover both labor and parts initially and only
cover parts later in the warranty period. The con-
sumer has to decide, often at the time of purchase
and based on very limited information, whether to opt
for an extended warranty or not and to determine the
best extended terms for his situation when there are
multiple options (Blischke, 1995), (Blischke, 1993).
The everyday consumer is not capable of conducting
a mathematical analysis before making a choice be-
cause the consumer neither has the expertise for such
an analysis nor the bargaining power to obtain rele-
vant data from the manufacturer. However, consumer
bureaus and regulatory agencies can carry out such
analyses and inform the consuming public. Any mo-
del developed from the consumer’s point of view in
this chapter is then assumed to have been done for a
consumer agency on behalf of all consumers and with
data obtained by the agency from the manufacturers
or from established and recognized independent re-
viewing bodies such as the Consumer Reports maga-
zine.
There are many different types of warranty poli-
cies designed to cover the needs of manufacturers,
dealers and consumers. A policy which is based
on one factor (usually age) alone is said to be one-
dimensional, on the other hand a two dimensional
warranty is limited by two factors, usually age and
a measure of usage of the product. One-dimensional
policies are selected for products which are known to
last for a fixed time period. This is common in the
Bhakthavatchalam S., Diallo C., Venkatadri U. and Khatab A.
Optimal Combination RebateWarranty Policy with Second-hand Products.
DOI: 10.5220/0006293504910498
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES 2017), pages 491-498
ISBN: 978-989-758-218-9
Copyright
c
2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
491

marketplace for products such as cell-phones, com-
puters, and projectors. Two-dimensional warranties
apply to products that display wear and tear, degra-
dation with usage. Automobiles, aircraft and heavy-
duty machinery are examples of products with 2-D
warranty policies. It is common to see car advertise-
ments stating coverage of 60 months, 120 000 kilo-
metres which ever occurs first.
Some basic warranty types are the Free replace-
ment (FRW), Pro-rata (PRW), and Rebate warranty.
1. Free replacement warranty (FRW): The manu-
facturer agrees to repair/replace a failed item du-
ring the warranty period at no charge to the custo-
mer. Example: small household appliances, elec-
tronics.
2. Pro-rata warranty (PRW): The customer covers
a proportion of the repair cost prorated to the age
of the item at failure. Example: Tires.
3. Rebate warranty: The seller agrees to refund
some proportion of the sale price to the buyer,
if the product fails during the warranty period.
The refund amount may be a linear or non-linear
function of the failure time. Example: Money
back Guarantee for electronic components such as
hard drives, computer screens, and storage devi-
ces.
A basic taxonomy of warranty policies is presen-
ted by (Blischke, 1993; Blischke, 1995). An in-
tegrated warranty-maintenance taxonomy based on
three categories ,i.e. product type, warranty policy,
and maintenance strategy, is proposed in (Shafiee and
Chukova, 2013).
Hybrid (combination) warranties are designed
to utilize the desirable characteristics of the pure
warranties and downplay some of their drawbacks
(Blischke, 1993; Blischke, 1995). The combination
warranty gives the buyer full protection against
full liability for later failures, where the buyer has
received nearly the full amount of service that was
guaranteed under the warranty. It has a significant
promotional value to the seller while at the same time
providing adequate control over costs for both buyer
and seller. An example for hybrid warranty is seen
in the FRW/PRW policy offered on Firestone tires.
During the first 2 years of service, the tire is replaced
free of charge. Beyond year 2, the replacement
price is pro-rated based on years of service from
the original purchase date. Some advantages of
combination warranties are improved protection
towards the product, customer satisfaction, higher
ownership lifetime for the buyers and higher sales
volume to increase profit to manufacturers.
Combination warranty is a good type of war-
ranty for second-hand products (SHPs) as its offers a
good protection to both manufacturers and consumers
(Chari, 2015). Two main problems faced by the con-
sumers acquiring SHPs are their uncertainty and du-
rability (Shafiee and Chukova, 2013) due to the lack
of past usage and maintenance history. In order to re-
duce the risk and impact of product malfunctioning,
dealers offer generous warranty policies. A review of
warranty models currently available in the literature
for SHPs show that there are very few of them and all
deal with the manufacturers perspective (Shafiee and
Chukova, 2013; Chari et al., 2016b; Su and Wang,
2016; Diallo et al., 2016). The goal of this article is to
address this shortcoming by proposing a warranty po-
licy and develop mathematical models from both the
manufacturer and consumer perspectives.
2 OPTIMAL COMBINATION
WARRANTY MODELS USING
SHPS
For most warranty policies, failed products are re-
paired or replaced with new components or products.
In the context of remanufacturing, second-hand pro-
ducts may be available and can therefore be re-used as
replacements when consumers return failed products
(Yeh et al., 2005; Yeh et al., 2011; Chari et al., 2016a).
In doing so, the manufacturers can lower their costs
and consumers can extend their ownership of the pro-
ducts. However, due to the lower reliability of SHP,
it is crucial to determine the optimal parameters of
the warranty policy to be offered to avoid higher costs
to the manufacturer and less than anticipated perfor-
mance/ownership time for the consumer. In this ar-
ticle, we will develop two mathematical models for
a combination rebate warranty policy using SHPs as
replacement products.
2.1 Proposed Warranty Policy
Under the proposed warranty policy, a brand new pro-
duct is sold with a total warranty coverage period of
length w. Under this policy, the seller will replace a
defective product with:
• A new product if the failure occurs before w
1
(Phase 0);
• A refurbished product of high quality if the failure
occurs between w
1
and w
2
(Phase 1);
• A refurbished product of normal quality if the fai-
lure occurs between w
2
and w
3
(Phase 2).
ICORES 2017 - 6th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
492
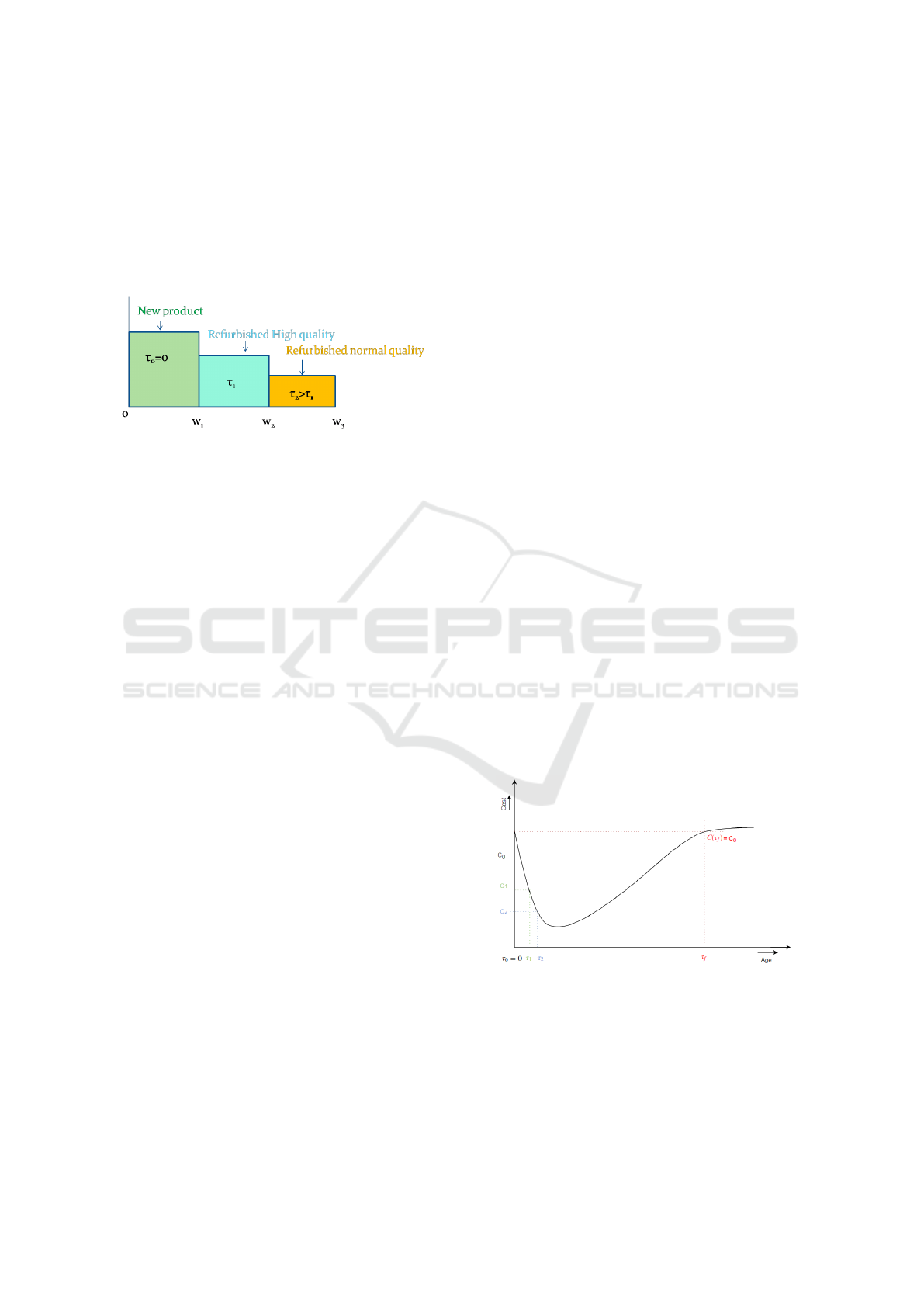
It should be noted that w = w
1
+w
2
+w
3
. The pro-
posed warranty policy is depicted in Figure 1. New
products have age τ
0
= 0. Refurbished or second-
hand products of high quality have age τ
1
that is grea-
ter than 0. Refurbished or second-hand products of
normal quality have age τ
2
that is greater than τ
1
.
Therefore, we have: 0 < τ
1
< τ
2
.
Figure 1: Proposed Warranty Policy.
The policy offered here is Non Renewing Free Re-
placement Warranty policy (NRFRW). The following
notation is used.
2.1.1 Parameters
C
i
: Cost of replacement product in phase i
C
0
: Unit cost for a new product
C
u
: Warranty cost
a: Price coefficient
b
i
: Warranty coefficient
d
0
: Market demand amplitude factor
ε,η: Age coefficients for the acquisition
cost of reconditioned components
β: Slope parameter of the Weibull distribution
θ: Scale parameter of Weibull distribution
λ: Inverse of the Scale parameter (λ = 1/θ)
m: Number of warranty periods
2.1.2 Functions
f (t): lifetime prob. density function (pdf)
F(t): Cumulative distribution (cdf)
π: Expected unit profit
P (p, w
i
,τ
i
): Total expected profit for the Seller
D(p,w
i
): Total demand
EOT : Expected ownership time
MT T F
0
: Expected lifetime of the original new
product
MT T F
1
: Expected lifetime for high quality SHPs
MT T F
2
: Expected lifetime for low quality SHPs
EOCR
1
: EOT per cost ratio of the product when
warranty is purchased
EOCR
2
: EOT per cost ratio of the product
without warranty
2.1.3 Decision Variables
p: Unit sale price of the new product
w
i
: Warranty periods
τ
i
: Age of the SHP products offered as
replacements in phase i
In the following section, two mathematical mo-
dels will be developed for the maximization of the
manufacturer’s expected profit and the maximization
of the consumer’s ownership time.
2.2 Model 1: Maximization of
Manufacturer’s Expected Profit
If the product fails within w
1
, a full refund of C
0
is
given to the customer to buy a new product. When
it fails between w
1
and w
2
a refund of C
1
is returned
to the customer that is sufficient to buy a high reliabi-
lity SHP. When the product fails between w
2
and w
3
,
a lump sum C
2
is given back to the consumer which
is sufficient to buy a normal quality SHP. Warranty is
not extended when the system fails.
C(τ
i
), the unit cost of a replacement product with
age τ
i
, is given by Equation (1) where C
0
is the base
price and ε,η are positive parameters (Chari, 2015).
Parameter ε represents the discount rate offered on
used products, and parameter η models the increase
in cost due to aging.
C(τ
i
) = C
0
× (1 + τ
i
)
(−ε)
+ τ
η
i
(1)
A new product will therefore cost
C(τ
0
= 0) = C(0) = C
0
(2)
Figure 2: Cost as a function of age.
The profile of C(τ
i
) is depicted in Figure 2.
The cost of replacement products initially decrease
with age (refurbished cost less) but reaches a mini-
mum then increases with age to account for techni-
cal and practical difficulties encountered when trying
to disassemble and recondition very old products
Optimal Combination RebateWarranty Policy with Second-hand Products
493

(availability of parts, obsolescence, corrosion, etc.).
Beyond this point C(τ
f
) = C
0
, customers should buy
a new product rather than a second-hand product be-
cause the cost of a new product is less than SHP.
C(τ
1
) = C
1
= C
0
× (1 + τ
1
)
(−ε)
+ τ
η
1
(3)
C(τ
2
) = C
2
= C
0
× (1 + τ
2
)
(−ε)
+ τ
η
2
(4)
The probability that a product will fail between
w
i−1
and w
i
for i = 1, ...,m is given by:
[F(w
i
) − F(w
i−1
)] (5)
where w
0
= 0.
The total expected warranty cost (C
u
) is given by
the weighted average of the replacement costs in each
phase i given in Equation (7) shown below.
C
u
=
m
∑
i=1
C(τ
i
) × [Prob. failure in phase i] (6)
C
u
= C
0
"
m
∑
i=1
(1 + τ
i−1
)
−ε
+
τ
η
i−1
C
0
[F(w
i
) − F(w
i−1
)]
#
(7)
Failure Distribution:
The Weibull distribution is used as the product fai-
lure distribution. The lifetime cumulative distribution
function of the product is then given by
F(x) = 1 − exp
−(
x
θ
)
β
, 0 ≤ x (8)
Demand Function:
The market demand function D(p,w
i
) for the pro-
duct is modelled to take into account consumers’ pre-
ferences for lower prices and longer warranty co-
verage. D(p,w
i
) is modelled as a displaced log-linear
function of w
i
and p as in (Glickman and Berger,
1976; Chari et al., 2016b).
D(p,w
i
) = d
0
p
−a
Π
m
i−1
(d
1
+ w
i
)
b
i
(9)
Parameter a is the rate of decrease of the sales vo-
lume with the increasing price of the product. Para-
meters b
i
are the rate of increase of the sales volume
with the increasing of the warranty lengths w
i
. The
factor d
0
is the demand amplitude and d
1
is the war-
ranty displacement constant.
Total Expected Profit:
The total expected profit (TEP) P is the product of the
expected unit profit with the demand as in Equation
(10). The expected unit profit is obtained in Equation
(11) by subtracting the cost of the original product C
0
and the expected warranty cost C
u
from the sale price
p of each unit sold.
P = π · D(p, w
i
) (10)
P = (p −C
0
−C
u
) · D(p,w
i
) (11)
2.2.1 Numerical Results
For illustration purposes and without loss of genera-
lity, an example with only two decision variables is
considered by setting τ
2
as a proportion of τ
1
using:
τ
2
= k · τ
1
. For the arbitrarily chosen parameter va-
lues given below, we solve for the solution (p,τ
1
)
which maximizes the manufacturers’ total expected
profit: w
1
= 0.5;w
2
= 1;w
3
= 2 : m = 3, θ = 1.5,β =
1.5;C
0
= 15; d
0
= 100,000; a = 2.6;b
1
= 1.9,b
2
=
1.5,b
3
= 1.1; ε = 3.3; η = 0.7; λ = 1/θ; k = 1.5. Fi-
gure 3 shows a 3D-plot of the total expected profit P
as a function of purchase price p and age τ
1
. There
is a clear optimal solution at p
∗
= $30.68, τ
∗
1
= 1.43
and P
∗
= $3,287.
Several numerical experiments have been con-
ducted to analyze the behavior of the model when key
parameters change. The first experiment consisted in
varying the values of k, a parameter that dictates how
old the replacement products are in phase 2 in com-
parison with the replacement products used in phase
1 according to the formula: τ
2
= k · τ
1
. The results
obtained are plotted in Figures 4 to 6.
In Figure 4, P increases until the value of k rea-
ches 1 and after that point, P decreases. For k = 1,
the replacement products in phase 1 and 2 are the
same. This represents the best case scenario as pro-
fit is maximum and price is the lowest. For k < 1,
phase 2 replacement products are younger than phase
1 products, which is bad because components failing
in phase 1 are replaced with older parts and the larger
proportion of failures occurring in phase 2 are covered
with newer products which are more expensive. This
explains why the slope when k < 1 is steeper than the
slope when k > 1. Figure 5 shows that price p beha-
ves in an exact opposition to the behavior of P . For
values near and around k = 1, it is the cheapest to ho-
nour the warranty, so the manufacturer can afford to
reduce the price of the product and therefore increase
demand, which in return boosts profit.
Figure 6 depicts the relationship between the op-
timal value τ
∗
1
and τ
∗
2
. For smaller values of τ
∗
1
the
model uses larger values of τ
∗
2
to keep warranty costs
under control. When the values of τ
∗
1
start to incre-
ase (1 < τ
∗
1
< 3), the model restricts the values of τ
∗
2
between values of 3 and 1.5 to keep warranty costs
low by decreasing the probability of failure in phase
2. For values of τ
∗
1
> 3 the values of τ
∗
2
tend to stabi-
lize around 1 and 1.5 for the same reasons as before.
ICORES 2017 - 6th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
494
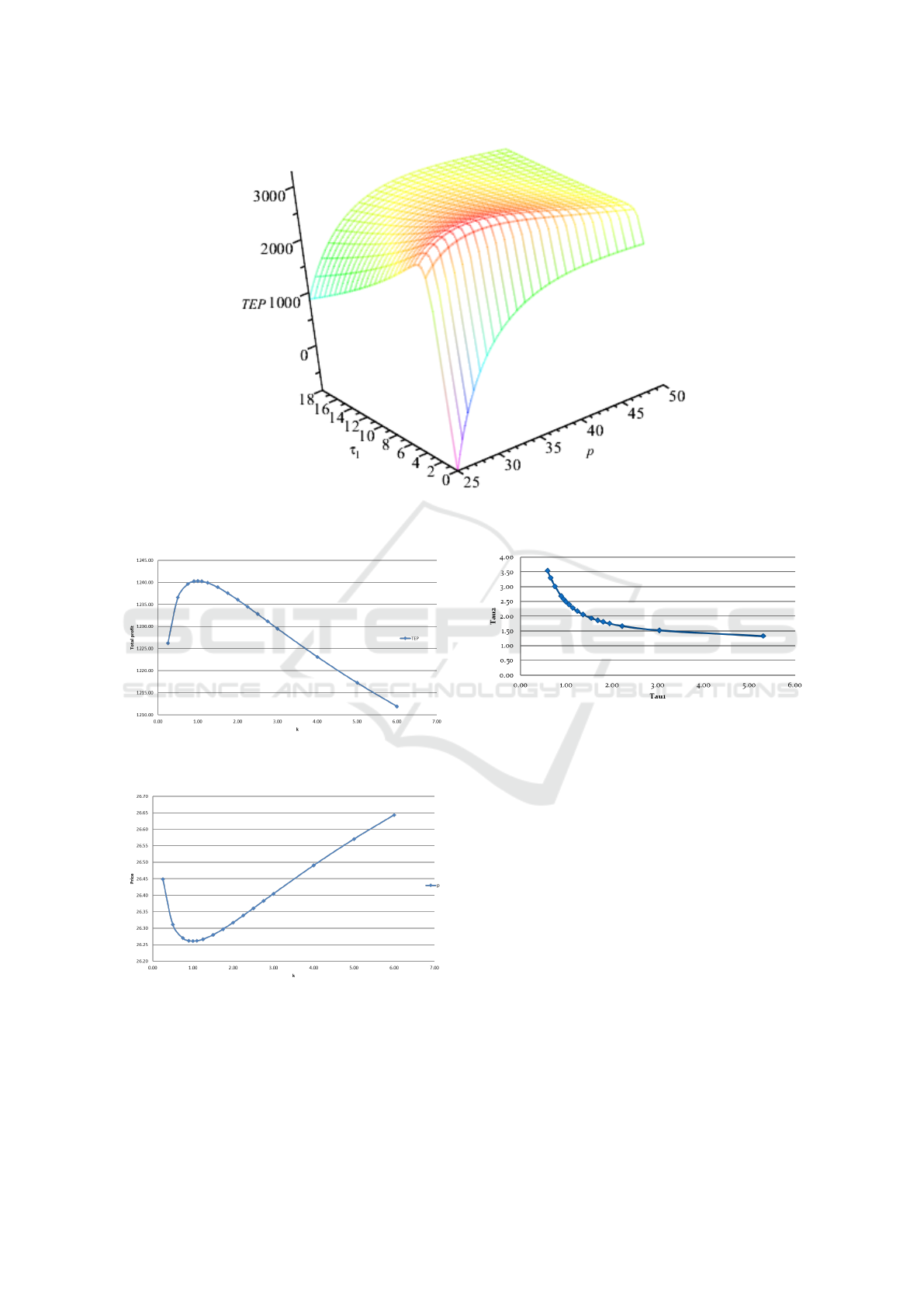
Figure 3: Total expected profit as a function of purchase price p and age τ
1
.
Figure 4: Seller expected profit as a function of k.
Figure 5: Optimal price as a function of k.
Another set of numerical experiments was con-
ducted by varying β, the shape parameter of the Wei-
bull distribution. The results are plotted on Figure 7.
In general, the figure shows an increasing trend and a
plateau after β = 4. Increasing the shape parameter β
Figure 6: τ
1
vs τ
2
for varying values of k.
newpage
increases reliability of the product so that the warranty
cost reduces. There is very little return on investment
to improve reliability of the products beyond β = 4.
Figure 8 shows that with improving reliability (incre-
asing β), the warranty costs reduce and therefore the
model can afford to reduce the unit price which in-
creases profits. For the same reliability reasons, when
β increases, the model can afford to use newer parts
which causes τ
∗
1
to decrease as depicted in Figure 9.
2.3 Model 2: Maximization of
Customers’ Expected Ownership
Time
In the previous model, the focus was on the manufac-
turers’ interests. In this subsection, a model develo-
ped from the consumer’s perspective will be presen-
ted. The warranty policy introduced in sub-section
Optimal Combination RebateWarranty Policy with Second-hand Products
495
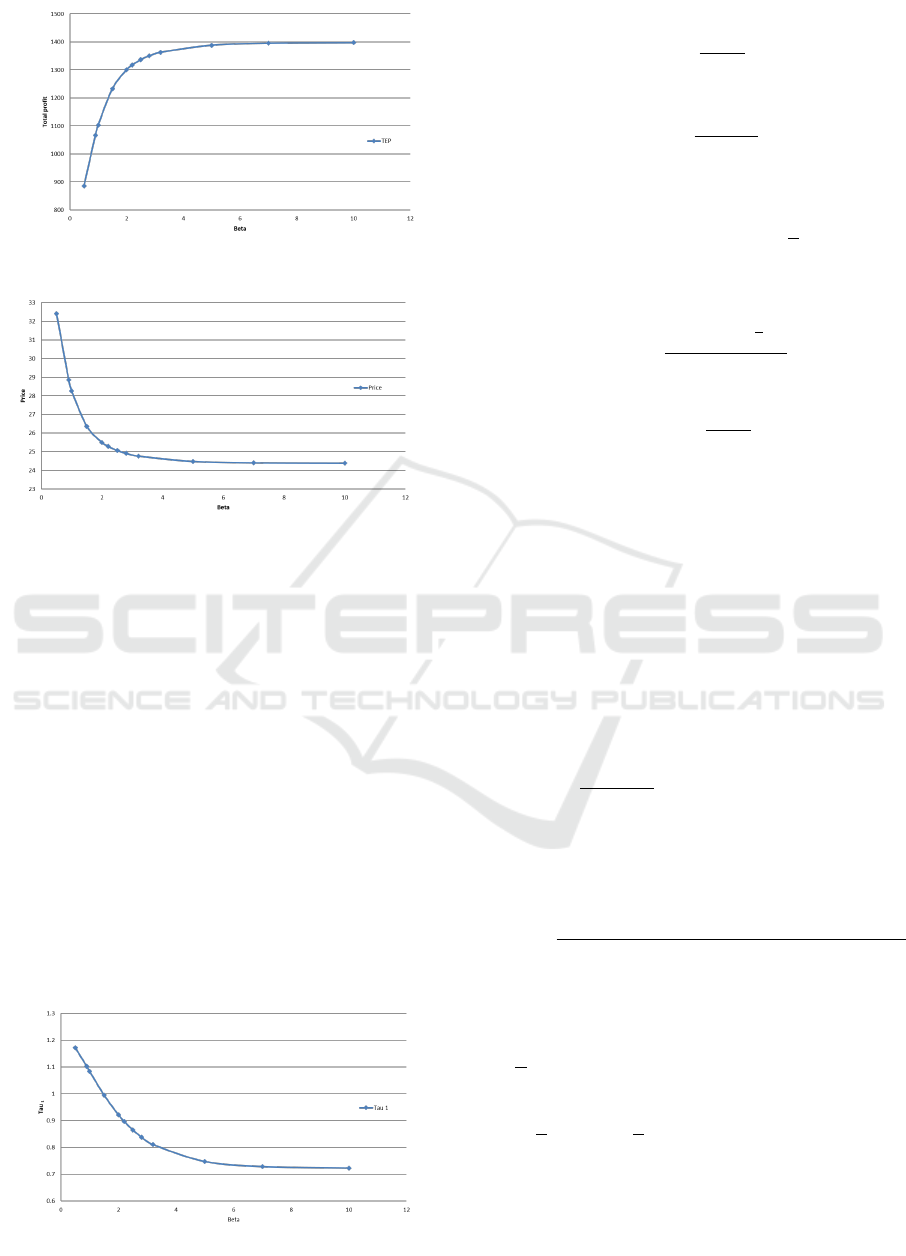
Figure 7: Seller’s expected profit as β varies.
Figure 8: Selling price for varying β.
2.2 is still under consideration here.
At time of purchase, the consumer has two choices:
• Option 1: Buy the original product without war-
ranty at a fraction ρ (0 ≤ ρ ≤ 1) of the price p set
by the manufacturer and determined using model
1 presented above; or
• Option 2: Buy the original product with warranty
at price p.
The goal of model 2 is to formulate the Expected
Ownership Time per Cost Ratio (EOCR
i
) for both op-
tions (i = 1,2) and compare their behaviour through
the analysis of their difference ∆:
∆ = EOCR
2
− EOCR
1
. (12)
Figure 9: Profile of the optimal τ
1
as β varies.
Option 1: without warranty
EOCR
1
=
EOT
1
ρ · p
EOCR
1
=
MT T F
0
ρ · p
where MT T F
0
is the expected lifetime of the ori-
ginal product
EOT
1
= MT T F
0
= θ · Γ
1 +
1
β
.
Γ(.) is the gamma function. Therefore,
EOCR
1
=
θ · Γ
h
1 +
1
β
i
ρ · p
. (13)
Option 2: with warranty
EOCR
2
=
EOT
2
p
(14)
A consumer enjoys his original new product from
purchase time up to the instant of the first failure
which has expected duration MT T F
0
. At failure, the
consumer gets a replacement product that will have an
expected remaining lifetime of length RMT T F
i
if the
failure occurred in phase i. The original product fails
in phase i with probability [F(w
i
) − F(w
i−1
)]. There-
fore, the expected ownership time for option 2 is given
by
EOT
2
= MT T F
0
+
m
∑
i=1
RMT T F
i−1
[F(w
1
) − F(w
i−1
)]
(15)
where
RMT T F
i
=
1
1 − F(τ
i
)
Z
∞
τ
i
[1 − F(x)].dx ∀i ∈ 1, 2.
(16)
By definition, RMT T F
0
= MT T F
0
. Combining Equa-
tions (14) and (15), gives the expression for EOCR
2
:
EOCR
2
=
MT T F
0
+
m
∑
i=1
RMT T F
i−1
[F(w
1
) − F(w
i−1
)]
p
(17)
Finally, Equations (12) becomes:
∆ =
1
p
"
MT T F
0
+
m
∑
i=1
RMT T F
i−1
[F(w
1
) − F(w
i−1
)]
−
θ
ρ
· Γ
1 +
1
β
#
(18)
The obtained mathematical model is solved for va-
rious scenarios in order to derive decision making po-
licies for the consumer organizations.
ICORES 2017 - 6th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
496

2.3.1 Numerical Results
Experiment #1: Change in w
1
and varying β
The first set of experiments is designed to analyze the
recommendations made by the model for 4 warranty
policies when β changes. The 4 warranty policies dif-
fer in their value of w
1
. The values of w
2
and w
3
are
the same for all policies. Table 1 presents the results
obtained.
Table 1: Values of ∆ for various w
1
and varying β.
w
1
= .5 w
1
= .75 w
1
= 1 w
1
= 2
β w
2
= 2 w
2
= 2 w
2
= 2 w
2
= 2
w
3
= 3 w
3
= 3 w
3
= 3 w
3
= 3
0.5 0.06 0.05 0.04 0.03
0.9 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
1.0 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02
1.5 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02
2.0 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01
3.0 0.00 0.01 0.01 0.02
4.0 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.02
5.0 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.02
6.0 -0.01 0.00 0.01 0.02
The results are also plotted on Figure 10 from
where two clear zones can be defined. The zone deli-
mited by the red dotted outline depicts the area where
products can be bought without warranty. Products
falling in the zone above the red zone need to be pur-
chased along with one of the 4 warranty policies offe-
red. The following other observations can be made:
• The general profile of each plot of ∆ as a function
of β shows a fast decrease for low values of β and
a stabilization for higher values. ∆ is higher for
β << 1 because early failures make the purchase
of warranty more valuable. ∆ stabilizes when in-
creasing β because of the resulting increase in re-
liability which decreases the likelihood of failure
and therefore the purchase of warranty does not
add significant value to the consumer.
• Different warranty policies have different slopes
of the same profile.
• A clear crossover point can be noticed on Figure
10. Policies with shorter Phase 0 (shorter w
1
) that
are preferred before the crossover point perform
poorly after the crossover point when the products
have higher reliability. Conversely, policies with
longer Phase 0 (longer w
1
) perform better after the
crossover point. In other words, a policy that is
good for newly designed products do worse with
seasoned or proven products with good reliability.
• Warranty policies with longer w
1
coverage are
less sensitive to increase in β values. It can be seen
on Figure 10 that the 4th policy has the smallest
amplitude over the complete range of β.
Experiment #2: Change in ρ and varying β
Here, numerical results are generated for two values
of ρ (0.95 and 0.85) to analyze the impact of the sel-
ling price over the decision to purchase the warranty
or not. The results obtained are in Table 2.
Table 2: Values of ∆ for varying β.
w
1
= .75 w
2
= 2 w
3
= 3
β ρ=0.95 ρ=0.85
0.5 0.06 0.05
0.9 0.03 0.02
1.0 0.02 0.02
1.5 0.02 0.01
3.0 0.01 0.01
4.0 0.01 0.00
6.0 0.00 0.00
As in the previous experiment, ∆ shows a decre-
asing trend with increasing β. The higher the price
without warranty (or the lower the warranty cost over
premium ratio) the higher the return or incentive to
buy the warranty.
3 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presented two mathematical models to de-
termine the optimal combination rebate warranty po-
licy when refurbished products are used for repla-
cements from both the manufacturer and consumer
point of views. One model was developed from the
manufacturers’ point of view to maximize the total
expected profit and the second model dealt with the
maximization of the consumer’s expected ownership
time. Numerical experiments showed that appropri-
ate optimal decisions can be reached in the reuse of
second-hand products in honouring warranty. Both
the manufacturer and consumer groups can use these
models to improve profitability levels and increase
ownership durations.
The authors are currently investigating a joint analysis
that considers both the seller and buyers’ perspectives
by formulating a multi-objective model to integrate
key factors such as brand loyalty and incentives. Case
studies from an appliance remanufacturer will be con-
ducted to validate the theoretical results obtained. A
Optimal Combination RebateWarranty Policy with Second-hand Products
497
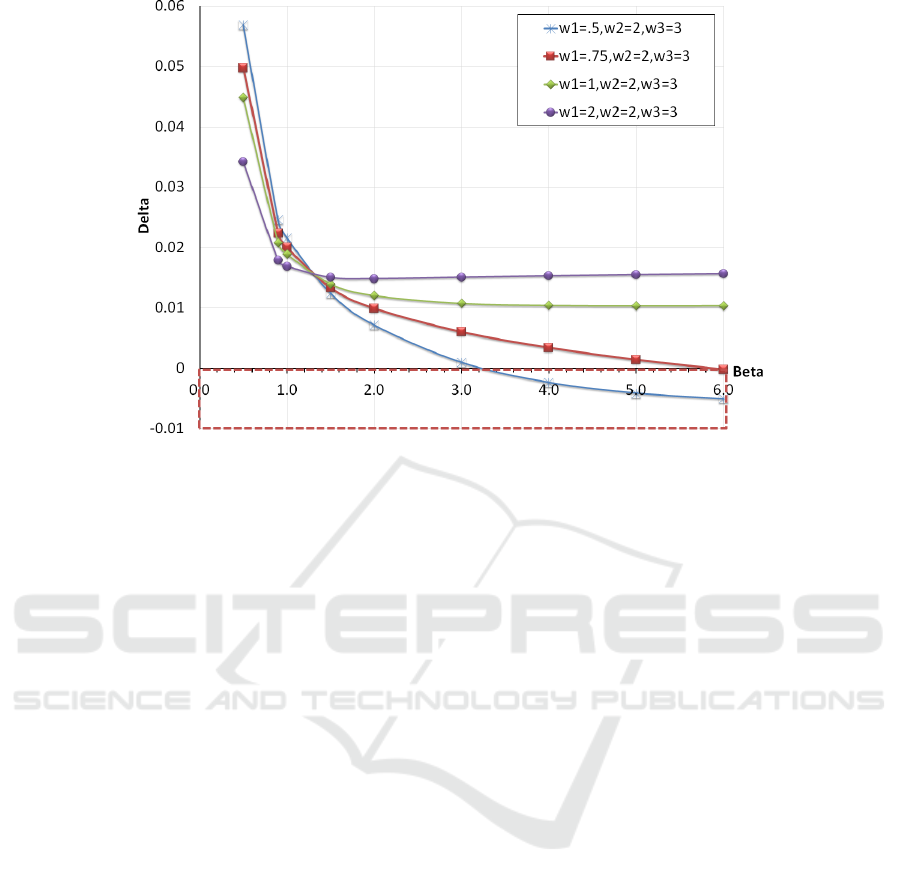
Figure 10: Profile of ∆ for varying β.
variability analysis on a reduced set of selected so-
lutions (with high expected values) will also be per-
formed to test the robustness of the solutions. Future
extensions of this study can also cover new warranty
models suited for remanufactured products such as
pro-rata and hybrid pro-rata policies, and integration
of reconditioned products of different quality levels.
REFERENCES
Blischke, W. (1993). Warranty cost analysis. CRC Press.
Blischke, W. (1995). Product warranty handbook. CRC
Press.
Chari, N. (2015). Thematic Development of Recovery, Re-
manufacturing, and Support Models for Sustainable
Supply Chains. PhD thesis, Dalhousie University, Ha-
lifax.
Chari, N., Diallo, C., Venkatadri, U., and A
¨
ıt-Kadi, D.
(2016a). Production planning in the presence of re-
manufactured spare components: an application in the
airline industry. The International Journal of Advan-
ced Manufacturing Technology, pages 1–12.
Chari, N., Diallo, C., Venkatadri, U., and Khatab, A.
(2016b). Modeling and analysis of a warranty policy
using new and reconditioned parts. Applied Stochastic
Models in Business and Industry, 32:539–553.
Chukova, S. and Shafiee, M. (2013). One-dimensional war-
ranty cost analysis for second-hand items: an over-
view. International Journal of Quality & Reliability
Management, 30(3):239–255.
Diallo, C., Venkatadri, U., Khatab, A., and Bhakthavatcha-
lam, S. (2016). State of the art review of quality, re-
liability and maintenance issues in closed-loop supply
chains with remanufacturing. In Press, International
Journal of Production Research, 0(0):1–20.
Glickman, T. S. and Berger, P. D. (1976). Optimal price
and protection period decisions for a product under
warranty. Management Science, 22(12):1381–1390.
Shafiee, M. and Chukova, S. (2013). Maintenance models
in warranty: A literature review. European Journal of
Operations Research, 229(3):561–572.
Su, C. and Wang, X. (2016). Optimal upgrade policy for
used products sold with two-dimensional warranty.
Quality and Reliability Engineering International.
Yeh, R. H., Chen, G.-C., and Chen, M.-Y. (2005). Optimal
age-replacement policy for nonrepairable products un-
der renewing free-replacement warranty. IEEE Tran-
sactions on Reliability, 54(1):92–97.
Yeh, R. H., Lo, H.-C., and Yu, R.-Y. (2011). A study of
maintenance policies for second-hand products. Com-
puters & Industrial Engineering, 60(3):438–444.
Yun, W. Y., Murthy, D. N. P., and Jack, N. (2008). Warranty
servicing with imperfect repair. International Journal
of Production Economics, 111(1):159–169.
ICORES 2017 - 6th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
498
