
Clustering Goal-Driven Security Factors for Protecting Data in
Cloud Storage using Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA):
An Empirical Study
Fara Yahya, Robert J Walters and Gary B Wills
Electronics and Computer Science, University of Southampton, U.K.
Keywords: Cloud Storage, Exploratory Factor Analysis, Loadings, Factor Extraction, Factor Rotation, Security Factor.
Abstract: The purpose of this paper is to explore the important security factors for protecting data in cloud storage
from the perspective of security practitioners. The study consist of 43 security variables (or indicator items)
from a survey participated by security practitioners in Malaysia. Exploratory factor analysis (EFA) is
conducted to understand the clusters of variables (or indicator items) and the inter-relationships constructing
the security factors (or components). Most of the respondents are from public sector organisations
(government and higher education organisations) in Malaysia. The clusters of variables resulting from this
analysis can be used as a reference for security practitioners planning to produce security policies to protect
data stored in a cloud storage. The top security factors identified from this study are shown in terms of
policy implementation and controls in confidentiality, integrity, availability, non-repudiation, authenticity,
reliability, accountability and auditability of data services in cloud storage.
1 INTRODUCTION
The main idea of factor analysis is that numerous
observed variables have correlated patterns of
responses since they are all related with a latent (i.e.
not specifically measured) variable. The relationship
with an underlying latent variable, the factor, which
cannot be directly measured is assumed to be
identified with various quantifiable variables. The
security variables (or indicator items) are analysed to
construct the security factors using factor analysis.
In this study factor analysis is applied to summarise
data so that relationships and patterns can be easily
interpreted and understood (Gie Yong and Pearce,
2013).
Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) is utilised to
reduce the data to a smaller set of summary variables
and to explore the underlining hypothetical structure
(Tabachnick and Fidell, 2007). It is applied to
distinguish the structure of relationship between the
variables and respondent. EFA was also conducted
to understand the measurements and significance of
the variables from our survey (or questionnaire). In
addition, EFA can help to provide a summary for
data inter-relationship and place those variables into
their groups accordingly (Hair, Black, Babin and
Anderson, 2014). In this paper, EFA will be carried
out to data obtained from our Security Rating Score
(SecRaS) instrument. The SecRaS instrument is
developed using a goal-driven approach, Goal-
Question-Metrics (GQM) using the Cloud Storage
Security Framework (CSSF) as a reference. CSSF
was an initial conceptual work undergone in the first
phase of this study (Yahya, Walters and Wills,
2016). The next section will elaborate on data
collection, initial considerations for performing
EFA, factor extraction, factor rotations and
interpretations, correlations between factors and
analysis of the factors clustered by EFA and finally
conclusion and future work.
2 RELATED WORK
There are a large number of information systems
research that applies factor analysis to provide data
summarisation or data reduction (Hair et al., 2014)
i.e. in software metrics, adoption dimensions,
software vulnerabilities and identifying software
factors qualities (Lake and Cook, 1994; Asnawi,
Gravell and Wills, 2012; Curcio, Malucelli, Reinehr
Yahya, F., Walters, R. and Wills, G.
Clustering Goal-Driven Security Factors for Protecting Data in Cloud Storage using Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA): An Empirical Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0006302304750482
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science (CLOSER 2017), pages 447-454
ISBN: 978-989-758-243-1
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
447

and Paludo, 2016; Stuckman, Walden and
Scandariato, 2016).
3 DATA COLLECTION
The security variables in the exploratory study are
inter-related, 43 questions regarding security
policies and controls were given to security
practitioners in Malaysia. Each security questions
are developed using GQM approach. The survey (or
questionnaire) was posted online using iSurvey.
iSurvey is survey generation and research tool for
distributing online questionnaires provided by the
University of Southampton. The survey was
distributed in cloud security groups in Malaysia
(Linkedin and Facebook). The groups also includes,
Persatuan Juruanalisa Sistem Sektor Awam
(PERJASA), which is the Information Technology
(IT) officers group for Government of Malaysia.
Their experience and expertise in security will help
the study to identify the significant aspect to protect
data in cloud storage. Moreover, the 43 variables
were only answered by security practitioners that
have at least two years’ experience in cloud security.
The survey received a total of 218 responses, which
were therefore included in the factor analysis. The
data were analysed using IBM SPSS Statistics
version 22. Each variable for this analysis has a five
point Likert-type scale; from strongly disagree
(which is equal to one) to strongly agree (which is
equal to five).
4 INITIAL CONSIDERATION
The suitability and appropriateness to conduct factor
analysis is undertaken before performing EFA
(Tabachnick and Fidell, 2007; Pallant, 2013; Hair et
al., 2014). Two main issues to be considered when
deciding the suitability of factor analysis be
performed to the data are sample size, and the
strength of inter-relationship among the variables.
4.1 Sample Size
The common rule for sample size is generally: the
larger the better. Tabachnick & Fidell (2007)
suggest that a study has at least 300 cases for factor
analysis. However, Tabachnick and Fidell concede
(in smaller sample) that it is suitable as long as there
are several high loadings variables (above 0.80)
(Tabachnick and Fidell, 2007).
4.2 Strength of Inter-Correlations
among Variables
Another test to ensure the data is suitable for factor
analysis is by observing the strength of inter-
correlations among the variables. Kaiser-Meyer-
Olkin (KMO) is one of the statistical test carried out
to identify the strength of inter-correlations. The test
will measure the sampling adequacy which ranges
from 0 to 1. If the value yields more than 0.7, then
the correlation on the whole are sufficient to perform
factor analysis.
Values between 0.5 and 0.7 are mediocre, values
between 0.7 and 0.8 are good, values between 0.8
and 0.9 are great and lastly values above 0.9 are
superb (Kaiser, 1974). A KMO with 0.6 is suggested
as the lowermost value for a good factor analysis
(Tabachnick and Fidell, 2007). As measured from
the sample, a KMO value of 0.856 was acquired
from the data (Table I). Hence, it is reasonable that
factor analysis is appropriate for these data sets.
Table 1: KMO and Bartlett’s Test.
KAISER-MEYER-OLKIN MEASURE OF
SAMPLING ADEQUACY.
0.856
Bartlett's Test of
Sphericity
Approx. Chi-
Square
7818.674
df
903
Sig.
<0.001
4.3 Data Screening
Before running the analysis, data was screened to
remove any variables that should be excluded before
the analysis is run. Some of the test includes
detecting for outliers. Factor analysis can be
sensitive to outliers, so as part of the preliminary
data screening process, outliers are detected by
through extreme values (Pallant, 2013). Another
data screening involves observing the correlation
matrix with all variables. The matrix will indicate
which variables that do not correlate with any other
variables or correlate very highly with other
variables (r < 0.9) (Field, 2013). None of the
variable in this study fits the description therefore all
the variables are included in the analysis.
5 FACTOR EXTRACTION
Factor extraction is performed as one of the steps in
factor analysis. It involves finding the minimum
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
448
number of factors (or components) that can be
identified to best represent the interrelations among
the set of variables. There are a range of methods
that can be used to specify and extract the number of
underlying factors or dimensions. The most
commonly used approach is principal components
analysis. In this analysis, principal component
analysis is used as the extraction method.
The adoption of an exploratory approach is
recommended; whereby different numbers of factors
are tested until a reasonable solution is found
(Pallant, 2013). In order to determine how many
numbers of factors (or components) are extracted,
eigenvalues (or Kaiser criterion) and scree plot are
two sets of information that can be referred (Field,
2013; Pallant, 2013).
5.1 Kaiser Criterion
The first method, the Kaiser’s criterion or
eigenvalues will extract and maintain the factors that
obtain the value of eigenvalues more than 1 to be
included in next investigations. The eigenvalue of a
factor denotes the whole of the total variance
explained by that factor. Table 2 summarises the
factors that have eigenvalues greater than one (factor
1 to 9).
Table 2: Total Variance Explained.
Factors (or
Components)
Eigenvalues
(Total)
Eigenvalues
(% of
Variance)
Eigenvalues
(Cumulative
%)
1
12.485
29.034
29.034
2
3.690
8.582
37.616
3
2.917
6.783
44.399
4
2.603
6.052
50.451
5
2.289
5.324
55.775
6
2.125
4.942
60.717
7
1.940
4.512
65.230
8
1.768
4.113
69.342
9
1.626
3.782
73.124
10
0.961
2.234
75.358
.
.
.
.
..
..
..
..
43
0.048
0.111
100.000
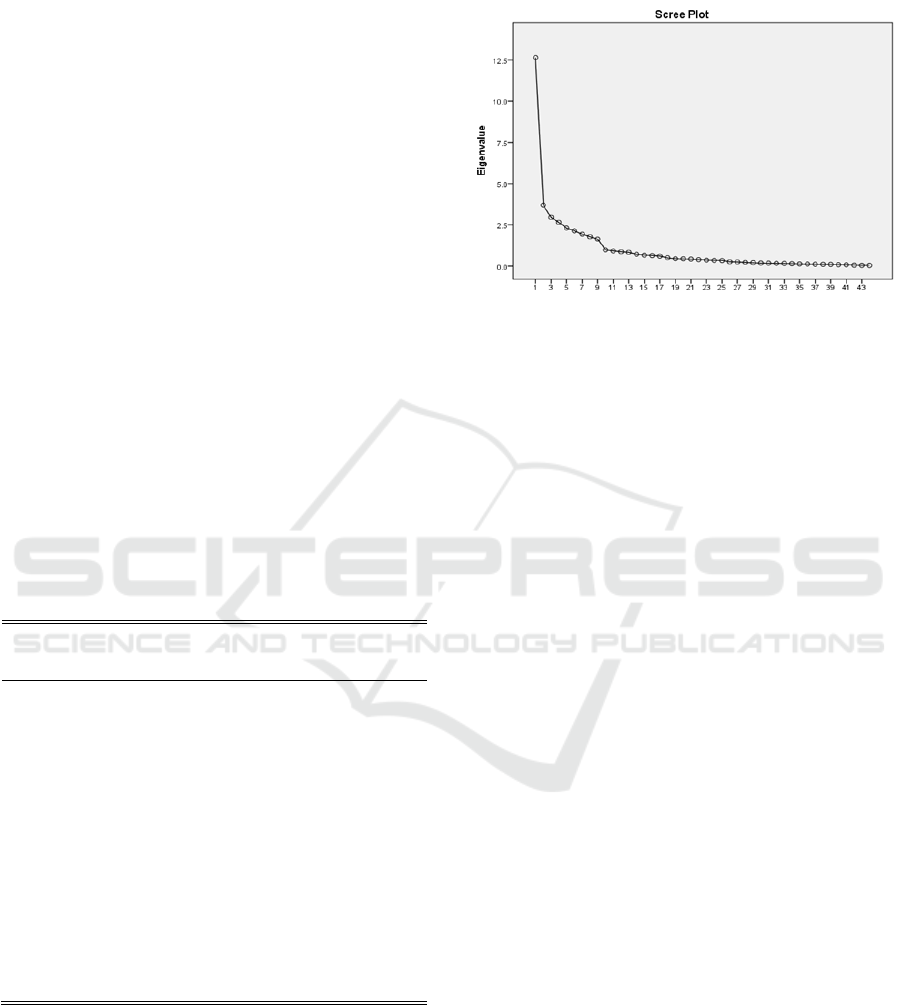
5.2 Scree Plot
On the other hand, using the scree plot, the point at
which there is a drastic change of direction and
becomes horizontal recommends the number of
factors. Each point is plotted based on each of the
eigenvalues of the factors. The plots are inspected to
find a point at which the changes of curve directions
in the scree plot.
Factor (or Component) Number
Figure 1: Factor Analysis Scree Plot.
It is recommended to retain all factors above the
drastic change of the curve direction (elbow, or
break in the plot), as these factors explains the
variance in the data set the most (Pallant, 2013; Hair
et al., 2014). Based on the scree plot above (as
shown in Figure 1), it suggests retaining only factors
above eigenvalue 1.
6 FACTOR ROTATION AND
INTERPRETATION
After the number of factors have been identified, the
next step is to interpret the set of grouped variables.
Factor rotation is useful to assist in this process. The
factors are presented in the pattern of loadings in a
manner that is easier to interpret.
The two well-known rotation techniques in factor
analysis are; orthogonal (varimax) and oblique
(oblimin). In this study, we tried both rotation to
look into which is more suitable for our data set
(Pallant, 2013). In the first rotation (varimax), the
pattern matrix explains the factor loadings after the
rotation.
The interpretation is mainly completed from the
pattern matrix; however the structure matrix is
useful for the purpose of double checking (Field,
2013). The second rotation (oblique) was performed
to obtain the component correlation matrix that
shows the relationship between factors extracted in
general.
Clustering Goal-Driven Security Factors for Protecting Data in Cloud Storage using Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA): An Empirical Study
449

7 CORRELATION
The correlation matrix shows the strength of
relationship between the components. The
correlation gives us information to decide whether it
was reasonable to assume that the components were
not related (the assumption underlying the use of
varimax rotation) or whether it is necessary to use,
and report the oblimin rotation in the previous
section. When applying correlation between the
extracted factors, the correlation matrix retrieved is
shown in Table 3. The results shows the significant
correlations for the factors related to this research. In
this case, most of the correlations value is between
0.2 to 0.3.
Conceptually, the factors has a moderate relationship
among most of the factors. The relationship are low
between factors that measures on data accessed and
stored in cloud storage (such as confidentiality,
integrity, availability non-repudiation, auditability
and authenticity) and factors that measures on
services provided by the cloud storage (such as
accountability and reliability). This result is
expected as it measures different concepts therefore
it is expected to have a fairly low relationship
between the components.
Some correlations value have values of negative.
A negative sign does not indicate any meaning
regarding the strength among the factors. However,
it gives meaning that the variable is related in the
opposite direction with the factor that may need to
be reverse when interpreted (Gie Yong and Pearce,
2013).
8 ANALYSIS OF THE FACTORS
This section presents analysis of factors obtained
from the Security Rating Score (SecRaS) instrument.
Table 4 provides summary for the nine factors and
their related indicators.
8.1 The Security Implementation for
Protecting Data in Cloud Storage
This factor can be interpreted as the cloud security
implementation in general. The indicator item with
the highest loadings are security procedures
implementations in an organisation.
This factor looks into the policy implementation,
procedure/process and security controls/practices in
an organisation. With these loadings, this factor can
be interpreted as the ‘Security Implementation for
Cloud Storage Aspects’.
8.2 The Confidentiality of Data
Accessed in Cloud Storage
This factor shows the importance of security
controls implementation for data accessed in cloud
storage. The indicator items with highest loading are
access management, authorisation and
authentication. In general, the controls associated in
this cluster describes securing data access to the data
stored in cloud storage. Having these loadings,
factor 1 is interpreted as ‘Confidentiality Aspects’.
8.3 The Integrity of Data Stored in
Cloud Storage
The third factor is loaded by six indicators. The
highest loadings explain the important of data
stewardship in a cloud storage service. Data
stewardship involves the management of data. This
is followed by the encryption mechanisms items that
indicates the importance of having data encrypted at
rest.
From the loadings, it can be seen that
practitioners are concern with the key management.
It is considered reasonable to name these six
loadings as ‘Integrity Aspects’.
8.4 The Availability of Data Stored in
Cloud Storage
The fourth factor resulting from factor analysis
explained on the accessibility to the data aspect. A
variable, ‘In my organisation, data recovery
mechanisms are in place in case of a security event’
shows that the practitioners strongly agree that
recovery of data ensures the availability of data
stored in cloud storage.
The rest of the loadings in this factor are clearly
showing the importance of the availability of access
to the data stored in cloud storage. This factor is
interpreted as ‘Availability Aspects’.
8.5 The Non-repudiation of Data
Stored in Cloud Storage
The factor contains loadings that provide meanings
about non-repudiation of data stored in cloud
storage. The top items are time stamp, bind and
validations between identities and geographical
location as authenticating factor. Time stamp
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
450

Table 3: Component Correlation Matrix.
Factor
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
1.000
-0.226**
0.261**
-0.317**
-0.337**
0.308**
0.314**
-0.251**
-0.225**
2
1.000
-0.083
0.256**
0.207**
-0.119*
-0.319**
0.318**
0.346**
3
1.000
-0.286**
-0.113*
0.174*
0.188*
-0.253**
-0.191*
4
1.000
0.211**
-0.128*
-0.270**
0.200**
0.238**
5
1.000
-0.163*
-0.212**
0.254**
0.268**
6
1.000
0.186*
-0.146*
-0.193*
7
1.000
-0.252**
-0.257**
8
1.000
0.357**
9
1.000
*correlation is significant at 0.05 level (2-tailed)
**correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed)
involves using a synchronised time-service/protocol
(e.g., Network Time Protocol (NTP) etc.).
The factor also explains that the practitioners
agreed that binding keys to identifiable owners and
support integration of location as an authentication
factor (e.g. generation location-based cryptographic
keys etc.). However, capability to restrict the storage
of user data to specific countries or geographic
locations has a loading of less than 0.5. Therefore,
these loadings are interpreted as ‘Non-repudiation
Aspects’.
8.6 The Authenticity of Data Stored
and Accessed by Authorised User
in Cloud Storage
This factor has five loadings representing the
importance of authenticity of data stored and
accessed in cloud storage. The highest indicator is
cryptographic protection, ‘My organisation has
cryptographic protection mechanisms (e.g. digital
signatures, signed hashes using asymmetric
cryptography, key to generate the hash, public key to
verify the hash information etc.)’.
The loadings for the factor can be described as
‘Authenticity Aspects’.
8.7 The Reliability of Service Provided
by Cloud Storage
Factor seven is showing loadings about the
reliability and consistency of cloud storage services.
The loadings describe the importance of service
continuity in cloud storage. This involves the
disaster recovery, system maintenance and patch
management, system monitoring and malicious
protection.
In this analysis, there is one loading in this factor
(‘My organisation has Patch Management or System
Maintenance policy’) which is the highest indicator
loading in the survey. The loadings demonstrate on
consistency of services in cloud storage and can be
described as the ‘Reliability Aspects’.
8.8 The Accountability of Service
Provided by Cloud Storage
This factor has five loadings in total. Three of the
loadings which are describing the conformance with
external and internal and the transparency of the
responsibilities etc. The key loading- ‘My
organisation allows for transparency and external
participation’ indicates the importance of clarity, or
in other words – ‘In my organisation, the clarity of
Service Level Agreement/Guarantee (SLAs/SLGs) is
emphasised’. This reflects the importance of
conformance with external, internal etc.
responsibilities are vital.
Besides that, the loading also indicates the
importance of security functionality and security
assurance. All of these have supported the
interpretation of factor 8 ‘Accountability Aspects’.
8.9 The Auditability of Data Stored
and Accessed in Cloud Storage
In the last component (factor 9), all the five loadings
are describing mainly on the needs of having a well
in cases of security events. The indicator, ‘My
organisation has on demand and automated audit
Clustering Goal-Driven Security Factors for Protecting Data in Cloud Storage using Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA): An Empirical Study
451

Table 4: Factor Loadings.
Factor
Variables
Loadings
1
Cloud Security Policy
0.861
Cloud Security Procedures
0.930
Cloud Security Practices
0.902
2
Identity Management
0.685
Authentication
0.798
Access Management
0.794
Authorisation
0.793
Secure API
0.684
Standards authenticating user accounts
0.617
Secure Access Communication Channel
0.789
3
Encryption
0.784
Key management
0.786
Data ownership
0.763
Data stewardship
0.772
Data deletion
0.818
Data protection for sensitive data
0.802
4
Accessibility to data stored
0.800
Backup of data stored
0.830
Recovery of data
0.823
Verify data authenticity
0.866
5
Bind and Validation Between the
Identities
0.886
Time Stamp
0.860
Geographical Location as an
Authentication
*0.465
Restrict the storage of user data to
specific countries or geographic
locations
0.841
6
Cryptographic Protection
0.821
Origin authentication
0.765
Verification assurances
0.636
Anti-counterfeit/Anti-tampering
0.587
Authenticity of session
0.714
7
Multi-Failure Disaster Recovery
Capability
0.741
Monitoring service continuity
0.830
System Maintenance
0.799
System Monitoring
0.728
Malicious Code Protection Mechanism
0.822
8
Conformance to External Responsibility
Roles
0.842
Mechanisms to put internal security
policies in effect
0.846
Transparency and participation
0.840
Security Functionality
0.840
Security Assurance
0.601
9
Audit Policy
0.729
Audit Record logs
0.816
Automated audit logs
0.865
Report Generation
0.853
Original content or time of audit records
0.685
* Loading below 0.5
audit policy, audit log review and report generation
review’ has the highest agreement with 0.865
showing emphasis of the agreement that audit logs
can be generated automatically and on demand.
Other loading are also high (greater than 0.8);
audit record logs and audit report generation.
Therefore, these loadings are best to be described as
‘Auditability Aspects’.
In summary, exploratory factor analysis was
suitable to test the data set in an unconstrained
manner. The result have shown that a cluster of data
are grouped into factors; 43 items indicators are
clustered into nine factors. Based on the
interpretation of the factors identified, EFA has
defined the structure of the data as nine security
factors to protect data in cloud storage: cloud storage
security implementation, confidentiality, integrity,
availability, non-repudiation, authenticity, reliability,
accountability, and auditability as presented in
Figure 2.
9 CONCLUSIONS
In this exploratory study, factor analysis was
conducted for 43 security items that indicates the
security factors of data stored in cloud storage from
the perspective of security practitioners in Malaysia.
The security practitioners in this study were found to
be mainly from public sector (government
organisation and public universities) and works as IT
officers. Other security practitioners are security
managers and security consultants with experience
more than six years in cloud security.
Following the eigenvalue rules, nine factors were
extracted and retained for further investigation. Each
clusters of factors were found to have high loadings
(greater than 0.8). A Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO)
statistical measure was also carried out and resulted
a value of more than 0.8 indicating a good value for
factor analysis. Therefore, the sample of data has
undergone initial considerations of suitability for
performing factor analysis.
After the rotation is performed, the indicators
that were loaded into those nine factors are
interpreted and they are defined as: (I) Factor 1: the
security implementation to protect data in cloud
storage, (II) Factor 2: the Confidentiality of Data
accessed in Cloud Storage, (III) Factor 3: the
Integrity of Data stored in Cloud Storage, (IV)
Factor 4: the Availability of Data stored in Cloud
Storage, (V) Factor 5: the Non-repudiation of Data
stored in Cloud Storage, (VI) Factor 6: the
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
452
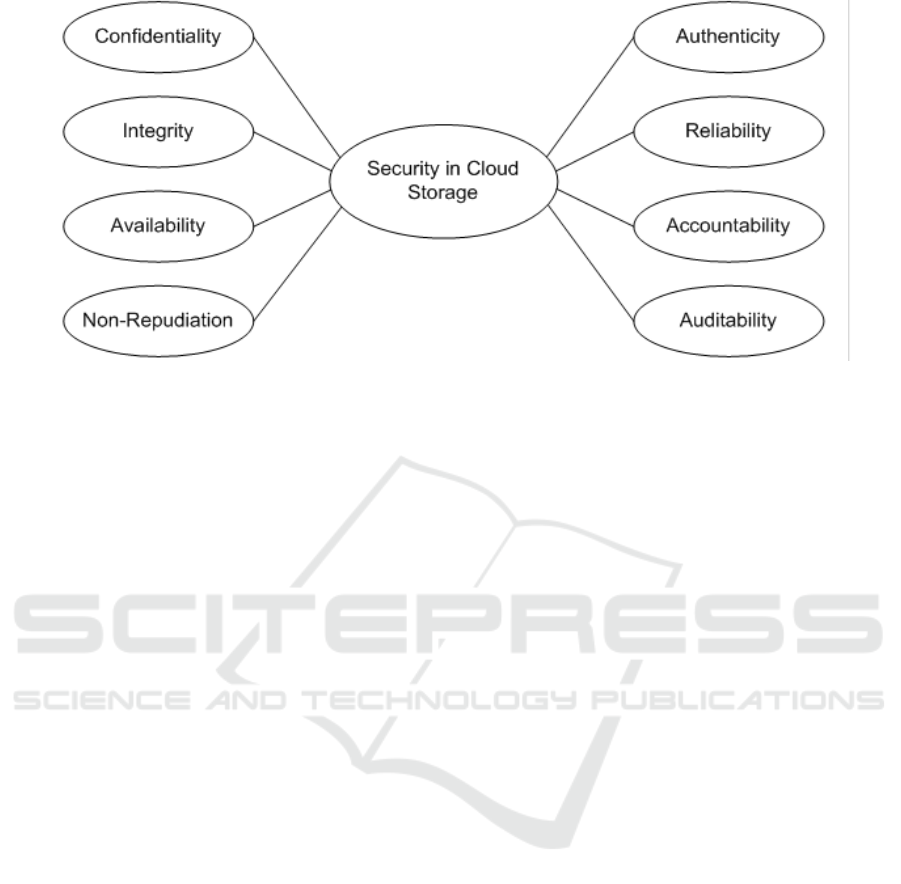
Figure 2: Nine Construct in Security Rating Score (SecRaS) Instrument.
Authenticity of Data stored and accessed by
authorised user in Cloud Storage, (VII) Factor 7: the
Reliability of Service provided by Cloud Storage,
(VIII) Factor 8: the Accountability of Service
provided by Cloud Storage and lastly for (IX)
Factor 9: the Auditability of Data stored and
accessed in Cloud Storage.
10 FUTURE WORK
In this study, EFA was performed whereby the data
was analysed in an unconstrained manner. The aim
was to summarise data and define the structure. By
implying EFA the identified structure has shown a
structure of a model. The future work will test the
structure identified in a constrained manner using
confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). CFA will
validate how much the 43 item indicators explains
the nine constructs (security factors) through a CFA
measurement model. Measurement analysis allows
the author to evaluate how well observed variables
logically and systematically represent hypothesised
constructs.
The measurement model is also the primary step
in Structural Equation Modelling (SEM). Through
measurement analysis, the author will be able to
verify the factor structure of a set of indicators and
this allows the author to define the relationship
between a set of measured variables and a set of
latent variables. Moreover, verification of construct
validation and construct reliability is completed
through the measurement model. Results obtained
from measurement model will further be used to test
the structural model and perform path analysis.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We acknowledge the award of Malaysian Public
Service Department Training (HLP) scholarship to
Fara Yahya allowing the research to be undertaken.
REFERENCES
Asnawi, A.L.,, Gravell, A.M., and Wills, G.B., 2012.
Factor analysis: Investigating important aspects for
agile adoption in Malaysia. Proceedings - Agile India
2012, AgileIndia 2012, pp.60–63.
Curcio, K.,, Malucelli, A.,, Reinehr, S., and Paludo, M.A.,
2016. An analysis of the factors determining software
product quality: A comparative study. Computer
Standards & Interfaces, 48, pp.10–18.
Field, A., 2013. Discovering Statistics using IBM SPSS
Statistics. 4th ed. SAGE Publications.
Gie Yong, A., and Pearce, S., 2013. A Beginner’s Guide
to Factor Analysis: Focusing on Exploratory Factor
Analysis. Tutorials in Quantitative Methods for
Psychology, 9(2), pp.79–94.
Hair, J.F.,, Black, W.C.,, Babin, B.J., and Anderson, R.E.,
2014. Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global
Perspective. Seventh ed. Pearson New International
Edition. Pearson New International Edition.
Kaiser, H.F., 1974. An Index of Factorial Simplicity.
Psychometrika, [online] 39(1), pp.31–36. Available at:
<http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02291575>.
Lake, A., and Cook, C., 1994. Use of factor analysis to
develop OOP software complexity metrics. In: 6th
Annual Oregon Workshop on Software Metrics. pp.1–
15.
Pallant, J., 2013. SPSS Survival Manual: A step by step
guide to data analysis using IBM SPSS. Third Edit ed.
Allen & Unwin.
Clustering Goal-Driven Security Factors for Protecting Data in Cloud Storage using Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA): An Empirical Study
453

Stuckman, J.,, Walden, J., and Scandariato, R., 2016. The
Effect of Dimensionality Reduction on Software
Vulnerability Prediction Models. 66(1), pp.1–21.
Tabachnick, B.G., and Fidell, L.S., 2007. Multivariate
analysis of variance and covariance. Using
multivariate statistics, 3, pp.402–407.
Yahya, F.,, Walters, R.J., and Wills, G.B., 2016. Goal-
based security components for cloud storage security
framework: A preliminary study. 2016 International
Conference on Cyber Security and Protection of
Digital Services, Cyber Security 2016.
CLOSER 2017 - 7th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Services Science
454
