
An Analysis of Strategic Goals and Non-Functional Requirements in
Business Process Management
Adson Carmo
1
, Marcelo Fantinato
1
, Lucin
´
eia Thom
2
, Edmir Prado
1
, Mauro Spinola
1
and Patrick Hung
3
1
University of Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, SP, Brazil
2
Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil
3
University of Ontario Institute of Technology, Oshawa, ON, Canada
Keywords:
Strategic Alignment, Strategic Goals, Business Processes, Non-Functional Requirements, Systematic Review.
Abstract:
Business processes’ Non-Functional Requirements (NFR) can foster the strategic alignment in organizations.
Our goal was to evaluate to what extent there are approaches that seek to support the modeling of business
processes’ NFR based on strategic goal-related information. To achieve this goal, we conducted a literature
study based on systematic review concepts. As a result, we identified 19 works addressing strategic goals and
business processes with NFRs. The most commonly used techniques are: i* and Key Performance Indicators
(KPI) for modeling strategic goals and Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) for modeling business
processes. According to our analysis, no approach fully addresses business processes’ NFR based on strategic
goals which was our primary question in conducting this study.
1 INTRODUCTION
Organizations need the support of Information Tech-
nology (IT) to quickly evolve their business processes
and gain competitive edge (Lee et al., 2011). How-
ever, the strategic alignment between business and IT
is required to achieve this dynamism (Tallon, 2008).
Strategic alignment enables efficient communication
among the strategic, tactical and operational levels of
an organization (Sousa and Leite, 2014).
Business Process Management (BPM) can sup-
port strategic alignment (de Bruin and Rosemann,
2006). However, only addressing both func-
tional requirements and Non-Functional Require-
ments (NFR), a complete strategic alignment between
business and IT can be achieved. Nevertheless, while
functional requirements have been well explored in
BPM, NFRs have been neglected (Salles et al., 2013).
A good practice is to use strategic goals to iden-
tify business processes’ NFRs since strategic goals
represent the major organizational interests, which in
turn need to be mapped to business processes. Strate-
gic goals are fundamental to strategic alignment since
they are the basis for organizing and planning activi-
ties at the tactical and operational levels.
This paper presents the results of a literature study
conducted to identify and evaluate approaches that
propose using strategic goals as support for modeling
business processes’ NFRs. Although we could find
some published literature studies exploring strategic
goals and business processes, none of them was par-
ticularly concerned with business processes’ NFRs.
This study is mainly an empirical and qualitative
research with some quantitative aspects. We focused
on the search for relevant and convenient data re-
ported through scientific papers that represent prior
experiences. Our goal was to reach new outcomes
from the experimental maturity of the works evalu-
ated. The selected works were evaluated in a pre-
dominantly qualitative way, based on the main infor-
mation presented in each one. From the quantitative
outlook, we do not produce strong statistical evidence
since the number of selected works represents a small
sample to allow in-depth quantitative analyzes. Some
results could be measured in numbers and then classi-
fied and analyzed through basic descriptive statistics.
As main results, we identified 19 works address-
ing strategic goals, business processes and NFRs. The
most commonly used techniques are: i* and Key
Perfomance Indicators (KPI), for modeling strate-
gic goals; and Business Process Model and Notation
(BPMN), for modeling business processes. Accord-
262
Carmo, A., Fantinato, M., Thom, L., Prado, E., Spinola, M. and Hung, P.
An Analysis of Strategic Goals and Non-Functional Requirements in Business Process Management.
DOI: 10.5220/0006314702620273
In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2017) - Volume 3, pages 262-273
ISBN: 978-989-758-249-3
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

ing to our analysis, although partial solutions have
been found, no approach fully addresses business pro-
cesses’ NFR based on strategic goals which was our
primary research question in conducting this study.
This paper presents: necessary background and
rationale; summary of related work; description of
the applied research method; analysis of the selected
works; and discussion of the obtained results.
2 STUDY BACKGROUND
We present here the main concepts related to this
study, i.e., strategic goals, BPM and NFRs.
2.1 Strategic Alignment and Goals
Strategic alignment between business and IT refers to
the synchronization between these two organization’s
sides to ensure that the services provided by IT are
adherent to the strategic needs of the business areas
(Henderson and Venkatraman, 1993). Business areas
are those that represent the functions of an organi-
zation, such as: finance, human resources, manufac-
turing, marketing, logistics, accounting etc. Strategic
alignment represents the dynamic adequacy of the IT
structure and tasks so that it is always in tune with
the organization’s business areas, which represent the
IT’s customers (Henderson and Venkatraman, 1993).
Strategic goals are used to foster strategic align-
ment. Strategic goals are qualitative or quantita-
tive values to be achieved at a predetermined future
time. They represent business or organizational re-
quirements (Janes and Faganel, 2013). Examples of
strategic goals are: “increasing customer satisfaction
to 99% by 2020” and “reducing project execution
time by 25% over the next two years”. Once modeled,
strategic goals are used as the basis for setting expec-
tations and aligning communication among different
organization areas, including the business areas and
IT. Each business area can model specific subgoals,
which rely on IT services to be met.
IT solutions applied in line with strategic goals
lead to business success (De Bruin and Rosemann,
2006). A strategic goal consists of: description, ex-
pected benefits, ways to achieve it, and ways to mea-
sure its achievement (Pl
¨
osch et al., 2011). Most orga-
nizations represent strategic goals via KPI. KPIs can
model quantitative indicators, which are measurable
and useful for monitoring the progress and success of
strategic goals (Parmenter, 2015).
Organizations can manage their business goals via
KPIs (Parmenter, 2015). Business analysts interpret
the combination of KPIs and their target values as
goals (e.g., “order approval time up to three days”)
(Wetzstein et al., 2009). Metrics varying during pro-
cess execution can influence KPIs, and IT services
can influence these metrics (e.g., “processing time”,
“results accuracy”, “services availability” etc.). Thus,
KPIs are specified based on business goals matched
with expected values, which are transformed into tar-
gets, including delimitations of deviations below and
above the expected value (Friedenstab et al., 2012).
Also related to this context, the i* framework is
a goal-based technique, used to model organizational
contexts based on dependencies among actors (Yu
et al., 1996). The i* framework uses: actor, role, de-
pendency, goal, softgoal, resource and task. It aims
to model the involved actors (whose behavior is ab-
stractly characterized by roles) and the dependencies
among them, so that their goals are reached, resources
are provided, tasks are performed and softgoals are
minimally fulfilled (Yu et al., 1996). This technique is
driven by a set of organizational goals to be achieved.
A goal represents a condition or state that stakehold-
ers want to achieve. Goals (also called rigid goals
or concrete goals) are complemented by softgoals,
which represent conditions or a state that the stake-
holders wish to achieve, but without a clear definition
of the expected values. Softgoals in i* share some
concepts and aims with strategic goals in KPIs.
Other techniques to model strategic goals are:
Tropos, Security i* (Si*), Balanced Scorecard (BSC),
Keep All Objectives Satisfied (KAOS), User Re-
quirements Notation (URN) / Goal-oriented Require-
ments (GRL), Unified Modeling Language (UML) di-
agrams, Business Activity Monitoring (BAM), Busi-
ness Motivation Model (BMM), among others. Al-
though all these techniques are applicable to strategic
goal modeling, they can target different purposes and
work in different degrees of abstraction.
2.2 Business Process Management
BPM is an interdisciplinary area that involves aspects
of business administration and information systems to
manage business processes supported by automated
systems. A business process consists of tasks per-
formed by an organization, in a specific sequence, to
achieve a specific goal (Weske, 2012). Examples of
business processes are: “granting real estate credit by
a financial organization” and “enrollment of new stu-
dents by an educational organization”.
BPM organizes work to ensure consistent results
and take advantage of opportunities for improvement
(Dumas et al., 2013). BPM includes concepts, tech-
niques and tools to support technical and managerial
aspects of business processes (van der Aalst et al.,
An Analysis of Strategic Goals and Non-Functional Requirements in Business Process Management
263

2003). The BPM lifecycle includes: modeling, im-
plementation, execution, administration, monitoring,
auditing, evaluation and improvement (Weske, 2012).
BPM contributes to achieve the strategic align-
ment between business and IT via management and
improvement of technological solutions related to or-
ganizational value-added business processes (Fanti-
nato et al., 2010). BPM enables one to transform the
dialog between business and IT in an interactive and
iterative approach. BPM combines top-down strate-
gic vision with bottom-up continuous improvement.
Modeling business process means represent
generically all actions and decisions that can be per-
formed during process execution, considering that
different actions can be performed for specific cases.
The main notation currently used by organizations for
this goal is BPMN (Kocbek et al., 2015). BPMN al-
lows to model business processes assuming their ex-
ecution through the integration of services offered by
various information systems. Before the emergence
of BPMN, many organizations adapted the UML ac-
tivity diagrams for this goal (Mili et al., 2010), which
are focused on software internal processes.
Other techniques to model business processes
are: Event-driven Process Chains (EPC), Role Ac-
tivity Diagrams (RAD), User Requirements Notation
(URN) / Use Case Maps (UCM), Integrated DEFini-
tion’s Process Description Capture (IDEF3), Yet An-
other Workflow Language (YAWL), Petri nets, Finite
State Machines (FSM), among others.
2.3 Non-Functional Requirements
NFRs are used mainly in software engineering, al-
though this concept is adaptable to other types of
products (Chung et al., 2000; Pressman, 2009; Som-
merville, 2010). A requirement is a condition, prop-
erty or capability that a product must meet. A func-
tional requirement defines a behavior (including in-
puts and outputs) that a product must perform. NFRs
define constraints on how a function can or should be
used, associated with minimum levels of quality.
NFRs typically relate to performance, usabil-
ity, availability, security, technologies that should be
used, and constraints on the development process
(Pressman, 2009). NFRs should consider customer
needs. Failure to meet certain NFRs may render the
entire product ineffective (Sommerville, 2010).
The concept of requirements, both functional and
non-functional, can be mapped from software engi-
neering to BPM by considering business processes as
the product being developed (Charfi and Zhi, 2015).
In BPM, functional requirements represent what the
business process must perform while NFRs represent
quality constraints which need to be met during the
process execution. Typical examples of NFRs of soft-
ware engineering may also be used in BPM such as
those related to performance and usability. For ex-
ample, “a sequence of activities in a business process
must run within a maximum of 24 hours”.
NFRs are commonly declared late and informally
during product development, making it difficult their
enforcement (Pressman, 2009; Sommerville, 2010).
This weakness is evident in BPM by BPMN not sup-
porting NFRs (Bocciarelli and D’Ambrogio, 2014).
Moreover, some techniques that have been proposed
to represent business processes’ NFRs have not fully
addressed the problem. Such techniques usually ad-
dress only how to represent NFRs without address-
ing the source of information needed to model them
(Salles and Fantinato, 2012).
Considering the need for strategic alignment, a
business process should be implemented and executed
in line with the strategic goals linked to the scope that
encompasses this process. This alignment could be
supported by NFRs specified in the business process
model, which is used to guide the process implemen-
tation. Thus, a strategic goal would be represented in
a process model via NFRs, which would in turn be
used to support the process implementation.
3 RELATED STUDIES
We present here an analysis of other reviews – sys-
tematic or not – with a purpose similar to ours. We
identified six BPM-related reviews that address some
aspect of strategic goals. None of the identified re-
views fully meets the purpose of our literature study
that is “identifying and assessing approaches that use
strategic goals as support for modeling business pro-
cesses’ NFRs”. In addition, several of the identified
reviews have been driven to specific contexts such as
aspect-orientation (Pourshahid et al., 2012) and ser-
vice choreography (Leite et al., 2013) while our study
is intended to be context free.
Evidence that these previously published reviews
have purposes other than our literature study is the
low overlap of selected papers among them. One
of the related reviews evaluated 19 papers, of which
four are also the target of our study, which represents
about only 20% of overlap. However, this existing re-
view presents a broader purpose – “investigating goal-
oriented requirements engineering for business pro-
cesses” (Poels et al., 2013) in a generic way rather
than focused on NFRs. The only other existing over-
lap refers to a single work also evaluated in another re-
view whose main purpose is to evaluate “compliance
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
264

measurement based on goals and indicators” (Sham-
saei et al., 2011). Its authors do not specifically ad-
dress the representation of business processes’ NFRs;
instead, they are concerned with a following step, i.e.,
measuring how much business processes comply to
strategic goals. We do not identified any other over-
lap of our study with some other identified review.
Two additional related reviews were found, but
also without addressing the same target of our study,
and only tangentiating it. The first one presents a very
wide proposal, which is “business process modeling
challenges and solutions” (Alotaibi, 2014). Like other
existing reviews, this one is not concerned with the
representation of business processes’ NFRs. Finally,
the latest identified review is concerned with “busi-
ness process modeling quality” (de Oca et al., 2015),
assuming that the quality of process modeling is key
to achieving strategic goals. Its authors are focused
on identifying approaches that analyze whether pro-
cess models have quality and whether such quality in-
fluences strategic alignment.
4 RESEARCH METHOD
This literature study was based on systematic review
concepts. A systematic review refers to the identifica-
tion, evolution and interpretation of all available rele-
vant research papers that address the issues defined in
a research protocol (Kitchenham and Charters, 2007).
Individual studies evaluated in a review are called pri-
mary studies, and a systematic review is a secondary
study. A systematic review differs from traditional
reviews and surveys because it is a transparent, scien-
tific and replicable approach used to avoid bias (Biol-
chini et al., 2005). To conduct this literature study, the
guidelines proposed by Kitchenham and Chartes were
used (Kitchenham and Charters, 2007). The follow-
ing subsections present the study planning and con-
duction.
4.1 Need for Literature Study
No previous literature study has been conducted with
the specific goal presented here (cf. Section 3), with
which our research group is interested. In addi-
tion, given the importance of research relating strate-
gic goals, strategic alignment and BPM, this liter-
ature study may be of interest and utility to other
researchers and the industry. We have empirically
identified that strategic goals can be an important
source of information for modeling business pro-
cesses’ NFRs. We intend to work along this train of
thought, and hence decided to carry out this study.
We aimed to investigate previous approaches in
this context to be used as the basis by us and other
researchers interested in such subject. The interested
researchers should be able to know which techniques
have been more widely applied in this context as well
as know its features, benefits and drawbacks. With the
outcomes obtained, next research works with the aim
of improving the strategic alignment with the support
of BPM can be developed more consciously.
4.2 Research Questions
The main research question guiding this study is:
“Are there approaches proposed to modeling busi-
ness processes’ NFRs based on strategic goals?”
In addition, in order to better characterize the
found approaches, two subquestions were defined:
• What Strategic Goal Modeling Techniques are
used in the Found Approaches? Per the ratio-
nale presented in Section 2, our empirically raised
hypothesis was that KPIs should be the technique
most often used to model strategic goals in BPM.
Nevertheless, we also expected to find other tech-
niques, including, for example, i*.
• What Business Process Modeling Techniques
are Used in the Found Approaches? Per the
rationale presented in Section 2, our empirically
raised hypothesis was that BPMN should be the
technique most often used to model business pro-
cesses in strategic goal-driven BPM. Neverthe-
less, we also expected to find other techniques,
including, for example, UML activity diagrams.
4.3 Data Sources and Search Strategy
The selected data sources are Scopus (www.scopus.
com) and Web of Science (pcs.webofknowledge.
com). Both databases together provide access to pa-
pers published and indexed by leading international
publishers in the area of interest, including IEEE,
ACM, Springer, among several others.
As for the search strategy, we created a search
string that expresses the goals of this literature
study and should filter papers that could answer
our research questions. The following basic search
string was created, without the syntax influences of
each data source’s search engine: (“business pro-
cess model” OR BPMN OR “activity diagram” OR
“use case maps” OR UCM OR “event-driven pro-
cess chain” OR EPC OR “integrated definition” OR
“process description capture” OR IDEF3 OR “role
activity diagram” OR RAD OR “yet another work-
flow language” OR YAWL OR “petri nets” OR “state
machine” OR statecharts) AND (“strategic goal” OR
An Analysis of Strategic Goals and Non-Functional Requirements in Business Process Management
265

“business goal” OR “business requirement” OR “or-
ganizational requirement” OR “key performance in-
dicator” OR KPI OR i* OR Si* OR “balanced score-
card” OR BSC OR “keep all objectives satisfied” OR
KAOS OR “user requirements notation” OR URN OR
“goal-oriented requirements” OR GRL OR “business
activity monitoring” OR BAM).
Overall, we searched for papers addressing con-
cepts related to both “business process modeling” and
“strategic goals”. To increase the chance of find-
ing all related papers, we also used different expres-
sions identified as synonyms or related to business
process modeling and to strategic goals, which are
resulting of an exploratory study of the area. For
“business process modeling”, we also used the names
and acronyms for the most important process model-
ing notations and languages as introduced in Section
2.2. Moreover, for “strategic goals”, we used similar
or related expressions as presented in Section 2.1 and
2.3. In order to create the string used, a series of it-
erative exploratory searches were conducted, testing
different keyword combinations, in order to minimize
the number of returned records while maximizing the
likelihood of finding the most important works.
4.4 Selection Strategy
We specified Inclusion Criteria (IC) and Exclusion
Criteria (EC) aiming to ensure that only papers actu-
ally related to the investigated context were selected
as primary studies for this literature study. Each result
returned by the search engines, in order to be selected
for this literature study, should satisfy both inclusion
criteria and not be eliminated by any of the exclu-
sion criteria. The defined criteria are presented below.
Inclusion Criteria:
• IC-1: the paper addresses strategic goals.
• IC-2: the paper addresses process modeling.
• IC-3: the paper addresses NFRs at some level.
Exclusion Criteria:
• EC-1: the paper is not available on the web.
• EC-2: the publication is not a peer-reviewed sci-
entific paper such as: technical reports, books,
book chapters, proceedings preface, journal edi-
torials, master’s dissertations, doctoral theses.
• EC-3: the paper is not written in English.
• EC-4: the paper is not primarily related to infor-
mation systems or business administration.
• EC-5: business processes are addressed in the
scope of software engineering instead of BPM.
4.5 Paper Selection
Paper selection was performed in three steps (cf. Fig-
ure 1) described as follows (Kitchenham and Char-
ters, 2007). Table 1 presents the list of the works se-
lected as primary studies for this literature study.
Figure 1: Identification and selection of primary studies.
Step 1. Applying Search String to Databases:
the search string was submitted to the chosen data
sources. As a result, 465 records were obtained in
Scopus and 215 in Web of Science. Disregarding
those repeated, 488 initial records were obtained.
Step 2. Applying Inclusion and Exclusion Crite-
ria: each record resulting from the search described
in the previous step was subjected to the inclusion and
exclusion criteria. For this, we analyzed the following
parts of each paper: title, abstract and keywords. For
some cases, a more thorough reading of the content of
the paper was required. Based on this analysis, papers
that did not meet the criteria were removed. When
two similar papers of the same authors were found,
only the most up-to-date and complete one was cho-
sen. As a result, 19 primary studies were selected.
Step 3. Assessing the Quality of Selected Papers:
the exclusion criteria EC-1, EC-2 and EC-3 were used
as quality criteria. For the first case (EC-1), we as-
sumed that the unavailability of a paper on the web is
an indication of lack of quality of the publication ve-
hicle, considering the current web readiness. For the
second case (EC-2), we considered that papers peer-
reviewed have a higher quality assurance than those
papers that have not undergone this type of review
process before publication such as invited book chap-
ters. Finally, for the third case (EC-3), we assumed
that papers not published in English also present an
indication of lack of quality considering that the great
majority of high-quality conferences use the English
language as universal standard. No extra paper was
removed since no new criterion was used for this step.
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
266

Table 1: Final list of the 19 works selected as primary studies.
Id Paper title Paper reference PT
a
P01 A Framework for Integrating Business Processes and Business Requirements (Kazhamiakin et al., 2004) C
P02 B-SCP: A requirements analysis framework for validating strategic alignment of
organizational IT based on strategy, context, and process
(Bleistein et al., 2006) J
P03 A combined approach for supporting the business process model lifecycle (Koliadis et al., 2006) C
P04 Requirements-driven design and configuration management of business pro-
cesses
(Lapouchnian et al., 2007) C
P05 Business process management with the user requirements notation (Pourshahid et al., 2009) J
P06 Scenario-driven approach for business process modeling (Ruokonen et al., 2009) C
P07 Wiki-based requirements management for business process reengineering (Abeti et al., 2009) C
P08 Rule based business process optimization (Aghdasi and Malihi, 2010) C
P09 Towards a pattern-based framework for goal-driven business process modeling (Behnam et al., 2010) C
P10 Synthesizing enterprise strategic model and business processes in active-i* (Xu et al., 2010) C
P11 A method for eliciting goals for business process models based on non-
functional requirements catalogues
(Cardoso et al., 2011) J
P12 Extending BPMN for business activity monitoring (Friedenstab et al., 2011) C
P13 An integration framework for multi-perspective business process modeling (Letsholo et al., 2012) C
P14 Event-driven manufacturing process management approach (Estruch and
´
Alvaro, 2012) J
P15 A bi-directional mapping between i and BPMN models in the context of business
process management
(Alves et al., 2013) C
P16 Making a link between strategy and process model collections: A multi-layered
approach
(Dallilo et al., 2014) C
P17 Modeling organizational alignment (Sousa and Leite, 2014) C
P18 Combining modelling and simulation approaches: How to measure performance
of business processes
(Bisogno et al., 2016) J
P19 A framework for systematic analysis and modeling of trustworthiness require-
ments using i* and BPMN
(Mohammadi and Heisel,
2016)
C
a
Publication Type (PT): C – Conference / J – Journal
5 SELECTED WORKS ANALYSIS
We present here a discussion of the selected works,
per Table 1, following their publication order. We fo-
cused on highlighting how the approaches deal with
modeling of strategic goals and their mapping to busi-
ness processes’ NFRs. All acronyms and initialisms
used in this section are defined in Section 2, except
for those not yet presented in the text.
[P01] “A Framework for Integrating Business Pro-
cesses and Business Requirements” (Kazhamiakin
et al., 2004): this paper proposes a framework for
representing strategic goals using Tropos and imple-
menting related processes through web services or-
chestrated by Web Services Business Process Exe-
cution Language (WS-BPEL). This framework does
not provide an intermediate step of process modeling
prior to its implementation in WS-BPEL. Formal an-
notations are used at all levels to model constraints
to business requirements and to processes. Tropos’
softgoals are used to describe NFRs at the business
requirements level, but no clear direction of how map
them to the web services orchestrations is presented.
[P02] “B-SCP: A requirements Analysis Frame-
work for Validating Strategic Alignment of Orga-
nizational IT based on Strategy, Context, and Pro-
cess” (Bleistein et al., 2006): this paper proposes
cross-referencing processes with organizational goal
models and context diagrams. Tasks, goals and soft-
goals are modeled in i* models, which are integrated
with context diagrams, and in turn are integrated with
RADs to model the processes. In the end, activities
and state descriptions in RADs are cross-referenced
with i*, i.e., processes in RADs are linked to goals in
i*. Softgoals representing NFRs in i* are mapped to
RAD in terms of specific types of actions, i.e., they
are addressed as functional elements.
[P03] “A Combined Approach for Supporting the
Business Process Model Lifecycle” (Koliadis et al.,
2006): this approach addresses the management of
process change throughout the BPM lifecycle sup-
ported by combined notations. i* models are used
for the organizational context, representing strategic
goals, and BPMN for the operational context, rep-
resenting the process model. The authors’ intent is
to provide a way of expressing changes, which arise
in one model, effectively in the other model. With
this purpose, they present constrained development
methodologies capable of guiding an analyst when re-
flecting changes from an i* model to a BPMN model
and vice-versa. As BPMN does not support the mod-
eling of NFRs, the softgoals specified using i* for the
An Analysis of Strategic Goals and Non-Functional Requirements in Business Process Management
267

organizational context cannot be mapped to the pro-
cess model. No clear direction is presented on the
treatment of NFRs through this approach.
[P04] “Requirements-driven Design and Con-
figuration Management of Business Processes”
(Lapouchnian et al., 2007): this paper proposes to
use goal models to address process configurations and
tailor deployed process aiming to meet non-functional
requirements, which represent business priorities or
customer preferences. A technique similar to i* is
used to model strategic goals. NFRs are hence mod-
eled as softgoals in the goal models. Processes are
implemented through WS-BPEL and they are con-
figured considering the goal models, including their
softgoals. Like paper [P01], this approach does not
provide for an intermediate step of process modeling
prior to its implementation in WS-BPEL. The empha-
sis of this approach is on goal-driven process variabil-
ity. NFRs are not directly addressed at the process
level; instead, processes’ functional requirements are
configured (i.e., chosen) based on the goal models’
NFRs represented as softgoals.
[P05] “Business Process Management with the
User Requirements Notation” (Pourshahid et al.,
2009): this approach is based on URN extended with
KPI, including GRL for modeling goals and UCM for
modeling processes. A URN-based framework pro-
vides process monitoring and performance manage-
ment capabilities integrated across the BPM lifecy-
cle. KPIs are used to model NFRs linked to processes
models since they are not supported by UCM. In sum-
mary, GRL supports goals and softgoals, which are
used for the functional modeling of processes, and in
turn must be tied to KPIs representing its NFRs.
[P06] “Scenario-driven Approach for Business
Process Modeling” (Ruokonen et al., 2009): this
approach is formed by four steps: first, the essential
business requirements, representing strategic goals,
are modeled as scenarios using UML sequence dia-
grams; then, the modeled scenarios are synthesized by
a UML state machine, which represents the process
model; next, the process model is translated into a
process skeleton using a UML activity diagram; and,
finally, the process skeleton is implemented in WS-
BPEL. Although NFRs is a concern which can be ad-
dressed by this approach, no clear direction is pre-
sented on their treatment through the approach steps.
NFRs can be modeled as exception behavior in sce-
narios but cannot be directly mapped to process mod-
els and hence need to be recovered and addressed only
during translation to process skeletons.
[P07] “Wiki-based Requirements Management for
Business Process Reengineering” (Abeti et al.,
2009): this paper presents an approach to manag-
ing both organizational and system requirements for
process reengineering. The proposed method uses re-
quirements acquired by a semantic wiki to partially
automate the translation from business requirements
description to processes and system artifacts. The se-
mantic wiki is built by means of Si* concepts which
include the modeling of NFRs as softgoals. Processes
are specified in terms of UML use case diagram (for
the static aspects) and BPMN (for the dynamic inter-
actions). In both UML use case diagram and BPMN,
it is not possible to model the NFRs. Therefore, the
Si* softgoals should be mapped to functional require-
ments at the process level.
[P08] “Rule based Business Process Optimization”
(Aghdasi and Malihi, 2010): these authors propose
process optimization through changing process model
with respect to business goals. KPI-based business
rules represent strategic goals, which are mapped to
rule-based processes. The authors are concerned with
achieving and maintaining strategic alignment by a
changing control. It breaks down business goals into
subgoals so that the desired performance measures
specified in KPIs are met in business rules. NFRs are
inherently addressed by the approach since it is pro-
posed as a single framework in which all the concepts
involved are systematized in a metamodel.
[P09] “Towards a Pattern-based Framework for
Goal-driven Business Process Modeling” (Behnam
et al., 2010): related to paper [P05], this paper pro-
poses a goal-driven, pattern-based framework to build
processes from organization goals while maintain-
ing traceability between them. Patterns are made
up of goal templates and process templates as well
as their relationships. As notations, URN/GRL and
URN/UCM are respectively used for modeling goals
and processes. Unlike paper [P05], KPIs are not used
here to model NFRs tied to processes models since
they are not supported by UCM. Thus, NFRs are ex-
plicitly addressed only as softgoals in GRL and not
explicitly addressed at the process level.
[P10] “Synthesizing Enterprise Strategic Model
and Business Processes in Active-i*” (Xu et al.,
2010): this paper proposes to combine goals and pro-
cess modeling through i* models and UML activity
diagrams. Potential synergy points between the i*
framework and UML activity diagrams are found by
matching and mapping the major concepts of their
metamodels. This approach aims at: identifying pro-
cesses out of business objectives, extracting business
goals through process abstraction, and identifying
mismatches between business goals and processes. A
combined metamodel is proposed in which both goals
elements (including softgoals) and process elements
are addressed together. This metamodel is presented
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
268

at a higher level of abstraction without presenting a
clear mapping between softgoals and processes.
[P11] “A Method for Eliciting Goals for Business
Process Models based on Non-functional Require-
ments Catalogues” (Cardoso et al., 2011): these au-
thors propose a systematic way of identifying organi-
zational goals for “as-is” process models. They pro-
pose using NFR catalogs, defined by other authors,
to tackle the difficulty in identifying business goals
and softgoals to be later used in process modeling.
The approach is based on i* and Tropos. No spe-
cific notation is used to model processes. Per these
authors, their approach allows modeling processes
aligned with the business goals identified with the
support of the mentioned catalogs.
[P12] “Extending BPMN for Business Activity
Monitoring” (Friedenstab et al., 2011): this pa-
per proposes a BPMN extension that incorporates
BAM concepts which aims to represent KPIs’ real-
time scores for process activities. A metamodel was
built to systematically describe the aspects of the ex-
tension as well as the symbols added to BPMN to
represent KPIs. The authors recommend that KPIs
should be identified during the modeling phase in par-
allel with the functional requirements elicitation.
[P13] “An Integration Framework for Multi-
perspective Business Process Modeling” (Letsholo
et al., 2012): a multi-perspective integration frame-
work for process modeling is proposed to better align
organizational goals and processes. The proposed
framework is guided by the six models, proposed by
other authors, which covers the following concerns:
“what”, “how”, “where”, “who”, “when” and “why”).
The authors suggest the following techniques for pro-
cess modeling: (i) goal-oriented – i*, KAOS and
Tropos; (ii) data-oriented – entity-relationship model,
data flow diagrams and UML class diagram; and (iii)
process-oriented – BPMN, IDEF3, UML activity di-
agrams, RAD and EPC. Each suggested technique
can be appropriate at different levels for each con-
cern presented. By this approach, NFRs are inher-
ently addressed when combining the techniques use-
ful for that although this is not explicitly addressed.
[P14] “Event-driven Manufacturing Process Man-
agement Approach” (Estruch and
´
Alvaro, 2012):
an approach is proposed to manage process through
an event-driven architecture based on BAM concepts.
The proposed approach is based on concepts such
as BAM, KPI and CEP. The notation used to model
processes is BPMN, which is extended to express
logic for both: processing complex events and evalu-
ating related KPIs. NFRs are addressed through CEP
and KPIs which are embedded in BPMN representing
both strategic goals and processes’ NFRs.
[P15] “A Bi-directional Mapping between i* and
BPMN Models in the Context of Business Process
Management” (Alves et al., 2013): this paper ex-
tends the paper [P03] by refining the proposed heuris-
tics to obtain i* models from BPMN models beyond
BPMN from i*. Similar to the paper [P03], the map-
ping from BPMN to i* also addresses NFRs only in-
directly. As NFRs are not modeled in BPMN, they
should be inferred by searching quality attributes re-
lated to the activities performed by the participants.
[P16] “Making a Link between Strategy and Pro-
cess Model Collections: A Multi-layered Ap-
proach” (Dallilo et al., 2014): this paper proposes a
multi-level approach, including a multi-layered meta-
model, which extends BPMN and links strategic goals
with an organization’s collection processes, based on
the Business Motivation Model (BMM) and BPMN.
KPIs link the BMM and BPMN levels. While BPM
represents the strategic goals, BPMN represents the
process modeled to address such goals. KPIs system-
atically models the indicators responsible for assess-
ing if the process execution is meeting the strategic
goals.
[P17] “Modeling Organizational Alignment”
(Sousa and Leite, 2014): this paper proposes a
conceptual model that merges i*, BPMN and KPI.
The i* models are used to interconnect the other
two. KPIs are linked only to the goals (including
the softgoals that represent NFRs), detailing them
by expressing what is necessary to satisfy them.
Accordingly, NFRs are not directly addressed at the
process level through BPMN. KPIs only insert an
implicit link of traceability that helps identify crucial
elements in the process.
[P18] “Combining Modelling and Simulation Ap-
proaches: How to Measure Performance of Busi-
ness Processes” (Bisogno et al., 2016): a method
is proposed to analyze and improve operational per-
formance of processes. The proposed method em-
ploys BPMN and Business Processes Simulation (BP-
Sim) to measure KPIs. Like paper [P09], this work
uses an inverse approach comparing to other ap-
proaches, i.e., strategic goals (specified as KPIs) are
obtained from process models (modeled in BPMN)
rather than the other way around. Based on process
models, operational performance can then be mea-
sured using BPSim. The method allows testing of
process designs and quantified measurement of vari-
ations in operational performance through four pre-
defined KPIs. The only mapping between NFR and
BPMN is through the four KPIs which should be
modeled based on the process model evaluation.
[P19] “A Framework for Systematic Analysis and
Modeling of Trustworthiness Requirements using
An Analysis of Strategic Goals and Non-Functional Requirements in Business Process Management
269

i* and BPMN” (Mohammadi and Heisel, 2016):
this paper proposes a framework for analyzing and
modeling user-centered trustworthiness requirements.
These authors use goal models to capture users’ trust
strategic goals, which should motivate design deci-
sions with respect to trustworthiness. These authors
use i* for goal modeling and BPMN for process mod-
eling. The framework supports the refinement of
softgoals right up to the elicitation of correspond-
ing trustworthiness requirements. Trustworthiness-
related NFRs are firstly specified as softgoals in i* and
mapped to BPMN, which has been extended to allow
annotations capable of representing such NFRs.
6 DISCUSSION OF THE RESULTS
This section presents a discussion of our study’s over-
all outcomes. First, Figure 2 shows the distribution
of the 19 selected papers in relation to the publica-
tion year. One can see a low number of found papers,
but steadily since 2009. Considering the importance
of strategic alignment for organizations as well as the
importance of the support provided by BPM in this
context, one could expect a larger number of works
related to this research topic. This low number is
probably reflex of the negligence commonly associ-
ated to NFRs in this and similar contexts.
Figure 2: Distribution of papers by publication year.
Our main result is the absence of approaches that
fully meet the research problem that motivated this lit-
erature review. Our primary goal was to find research
papers proposing some approach to model business
processes’ NFR based on organizational strategic
goals. Per our analysis, no approach has been pro-
posed specifically for this purpose. Aiming to support
our findings, Table 2 presents the main characteristics
of the works found and analyzed in Section 5.
As for “strategic goal modeling”, we found eight
techniques used for this purpose in the 19 evaluated
papers. Figure 3 summarizes the techniques used to
model strategic goals. Two techniques stand out: i*
and KPI, respectively present in 47% and 37% of the
papers. Tropos and URN/GRL (the third and forth
most used technique) as well as Si* are associated
with the i* framework, which highlights the impor-
tance of i* for this context. All three other techniques
are used in no more than one paper each. Per Table 2,
one can verify that, for most of the approaches found,
NFRs are modeled at the goal level through the soft-
goal concept (cf. column “NFRs at goal level”). Soft-
goals are used in 13 papers (of the total of 19 papers),
for which goal modeling is always performed with
i* or some i*-related technique. We were expecting
to find KPI as the most used technique instead of i*,
since KPI is highly known and used in both industry
and academia. Either way, both technique are widely
used and well distributed in time terms for the period
considered. On the other hand, BSC did not occur in
any of the 19 papers found, although it is also widely
used in industry and in scientific research.
Figure 3: Techniques used to model strategic goals.
As for “business process modeling”, we found
nine techniques used for this purpose in the 19 evalu-
ated papers. Figure 4 summarizes the techniques used
to model business processes. Corroborating to our ini-
tial expectation, BPMN is notably the most widely
used technique used to model business processes in
this context, present in 53% of the papers. The sec-
ond most widely used technique is UML Activity Di-
agrams, present in 16% of the papers. BPMN is the
most popular notation used to model business pro-
cesses while UML Activity Diagrams is the most pop-
ular technique used to model internal software pro-
cesses. All seven other techniques are used in no more
than two papers each. There are also three papers that
do not mention any particular modeling technique.
Per Table 2, NFRs are not modeled at the process
level for most of works (cf. column “NFRs at process
level”). In five works, KPI are used to model NFRs
at both goal and process levels. In fact, KPIs are used
to model NFRs in an integrated way for both perspec-
tives. Therefore, there is no direct way of modeling
business processes’ NFRs even for these works.
Figure 4: Techniques used to model business processes.
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
270

Table 2: Summary of the main characteristics of the 19 selected works.
Id Strategic goal modeling Business process modeling Goals’ NFRs Processes’ NFRs
P01 Tropos [None] Softgoals [None]
P02 i* RAD Softgoals [None]
P03 i* BPMN Softgoals [None]
P04 i* [None] Softgoals [None]
P05 KPI, URN/GRL URN/UCM Softgoals + KPI [None]
P06 Sequence diagram Activity diagram, FSM Exception behavior [None]
P07 Si* BPMN, Use cases diagram Softgoals [None]
P08 KPI Rule-based KPI KPI
P09 URN/GRL URN/UCM Softgoals [None]
P10 i* Activity diagram Softgoals [None]
P11 i*, Tropos [None] Softgoals [None]
P12 KPI BPMN KPI KPI
P13 i*, Tropos, KAOS BPMN, Activity diag., RAD, EPC, IDEEF3 [Several] [Several]
P14 KPI, BAM BPMN KPI KPI
P15 i* BPMN Softgoals [None]
P16 KPI BPMN KPI KPI
P17 i*, KPI BPMN Softgoals + KPI [None]
P18 KPI BPMN KPI KPI
P19 i* BPMN Softgoals Annotation
Figure 5 presents a cross-analysis between goal
modeling and process modeling through overlapping
Figures 3 and 4. We found 39 combinations between
a technique to model strategic goals and a technique
to model business processes for Figure 5. The number
of occurrences for each combination is shown within
each circle; larger circles represent a larger number
of occurrences for the respective combination. For
example, two occurrences were found for the com-
bination of i* and RAD. Aligned to Figures 3 and
4, the most widely combinations in this context are
“i* with BPMN” and “KPI with BPMN”, represent-
ing together 26% of found combinations. As for the
other combinations, four are related to some other
goal modeling technique used with BPMN whereas
ten are related to i* or KPI used with some other pro-
cess modeling technique, which represents more 36%
of found combinations. The other 38% refers to com-
binations not involving KPI, i* or BPMN.
Although different techniques were found for both
goal modeling and process modeling, Table 2 indi-
cates the evolution of each one. In terms of goal mod-
eling, i* and KPI are undoubtedly the most used tech-
niques since 2010. On the other hand, in terms of
process modeling, BPMN is practilly the only tech-
nique used in this context since 2011. Therefore, al-
though we did not identify any approach that com-
pletely addresses the modeling of business processes’
NFR based on strategic goals, one can infer that the
way to reach this end, as indicated in the literature,
would be to define an approach based on i* or KPI
for goal modeling and BPMN for process modeling.
7 CONCLUSION
This paper presented the results of a literature study
conducted to identify and evaluate approaches that
propose the use of strategic goals as support for mod-
eling business processes’ NFRs. To the best of our
knowledge, no previous study has been carried out
with this specific goal as presented here.
We identified 19 works addressing strategic goals,
business processes, and NFRs at some level. The
most commonly used techniques are: i* and KPI for
goal modeling and BPMN for process modeling. Al-
though we found partial solutions, no approach fully
addresses business processes’ NFR based on strategic
goals which was our primary research question. Nev-
ertheless, considering the evolution of the techniques
found, we concluded that the indicated way to reach
this end is by defining an approach based on i* or KPI
for goal modeling and BPMN for process modeling.
Our conclusions were obtained from the experi-
mental maturity of the 19 evaluated works. The eval-
uation was primarily qualitative, based on the main
information presented in each paper. In quantitative
terms, we did not produce any strong statistical evi-
dence considering the small sample of found works
which could not allow in-depth quantitative analyses.
In terms of future work, we plan to use the in-
formation obtained from this review to assist in the
proposal of a new approach to address the strategic
alignment between business and IT with BPM as sup-
port. Our proposal should fully address business pro-
cesses’ NFR based on strategic goals through a com-
bination between KPI and BPMN, considering they
are the techniques most widely used in this context.
An Analysis of Strategic Goals and Non-Functional Requirements in Business Process Management
271
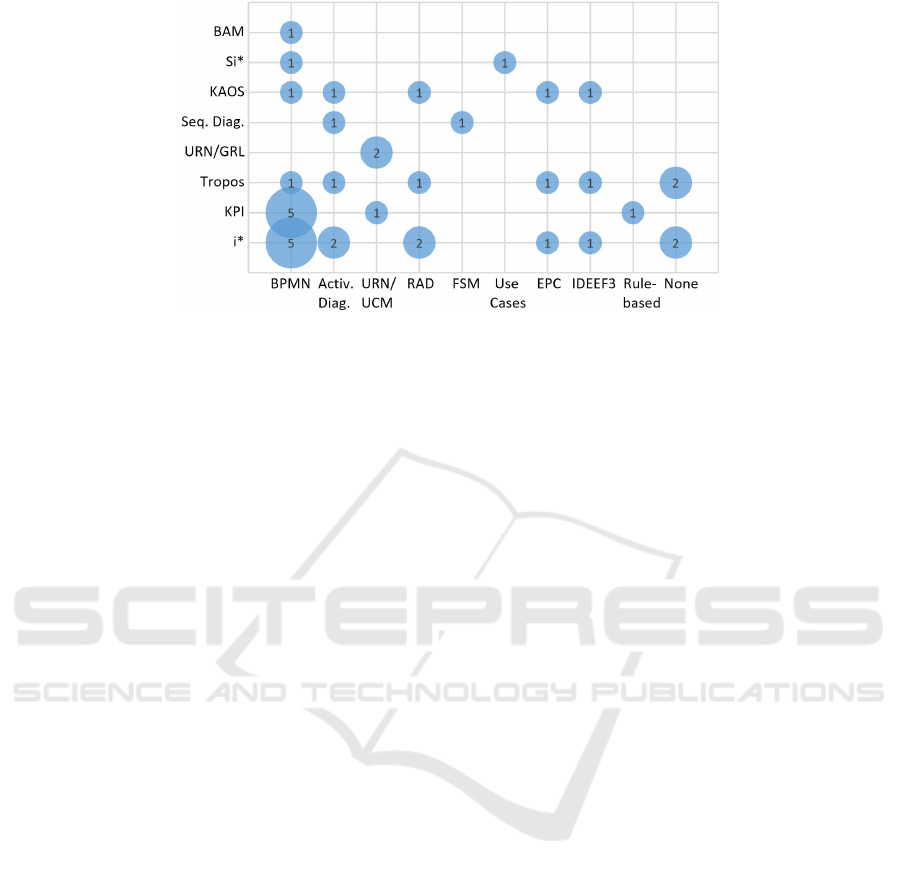
Figure 5: Cross-analysis between techniques to model strategic goals and techniques to model business processes.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the S
˜
ao Paulo Research
Foundation, Brazil, under grant 2015/16615-0.
REFERENCES
Abeti, L., Ciancarini, P., and Moretti, R. (2009). Wiki-
based requirements management for business process
reengineering. In ICSE Works. on Wikis for Soft. En-
gin., pages 14–24. IEEE.
Aghdasi, M. and Malihi, S. (2010). Rule based business
process optimization. In IEEE Int. Conf. on Indust.
Engin. and Engin. Manag., pages 305–309. IEEE.
Alotaibi, Y. (2014). Business process modelling challenges
and solutions: A literature review. J. of Intel. Manu-
fac., 27(4):1–23.
Alves, R., Silva, C., and Castro, J. (2013). A bi-directional
mapping between i and BPMN models in the con-
text of business process management. In Requir. En-
gin.@Brazil, pages 27.1–27.6. CEUR.
Behnam, S. A., Amyot, D., and Mussbacher, G. (2010). To-
wards a pattern-based framework for goal-driven busi-
ness process modeling. In 8th ACIS Int. Conf. on
Soft. Engin. Res., Manag. and Applic., pages 137–145.
IEEE.
Biolchini, J., Mian, P. G., Natali, A. C. C., and Travassos,
G. H. (2005). Systematic review in software engineer-
ing. Technical Report RT-ES 679/05, PESC - COPPE,
UFRJ, Brazil.
Bisogno, S., Calabrese, A., Gastaldi, M., and Levialdi Ghi-
ron, N. (2016). Combining modelling and simulation
approaches: How to measure performance of business
processes. Bus. Proc. Manag. J., 22(1):56–74.
Bleistein, S., Cox, K., Verner, J., and Phalp, K. (2006). B-
SCP: A requirements analysis framework for validat-
ing strategic alignment of organizational IT based on
strategy, context, and process. Inform. and Soft. Tech.,
48(9):846–868.
Bocciarelli, P. and D’Ambrogio, A. (2014). A model-driven
method for enacting the design-time QoS analysis of
business processes. Soft. and Syst. Model., 13(2):573–
598.
Cardoso, E. C. S., Almeida, J. P. A., Guizzardi, R. S. S., and
Guizzardi, G. (2011). A method for eliciting goals for
business process models based on non-functional re-
quirements catalogues. Int. J. of Inform. Syst. Model.
and Design, 2(2):1–18.
Charfi, A. and Zhi, H. (2015). Aspect-based realization of
non-functional concerns in business processes. In 3rd
Int. Conf. on Netw. Syst., pages 140–154. Springer.
Chung, L., Nixon, B. A., Yu, E., and Mylopoulos, J. (2000).
Non-Functional Requirements in Software Engineer-
ing. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 1 edition.
Dallilo, F., De Albuquerque, J., and Fantinato, M. (2014).
Making a link between strategy and process model
collections: A multi-layered approach. In Int. Conf.
on Soft. Engin. and Knowl. Engin., pages 387–392.
de Bruin, T. and Rosemann, M. (2006). Towards under-
standing strategic alignment of business process man-
agement. In 17th Austral. Conf. on Inform. Syst.,
pages 82.01–82.11. AIS.
De Bruin, T. and Rosemann, M. (2006). Towards under-
standing strategic alignment of business process man-
agement. In 17th Austral. Conf. on Inf. Syst., pages
6–8. AAIS.
de Oca, I. M.-M., Snoeck, M., Reijers, H. A., and
Rodr
´
ıguez-Morffi, A. (2015). A systematic literature
review of studies on business process modeling qual-
ity. Inform. and Soft. Tech., 58:187–205.
Dumas, M., La Rosa, M., Mendling, J., and Reijers, H. A.
(2013). Fundamentals of business process manage-
ment. Springer.
Estruch, A. and
´
Alvaro, J. A. H. (2012). Event-driven man-
ufacturing process management approach. In 10th Int.
Conf. on Bus. Proc. Manag., pages 120–133. Springer.
Fantinato, M., de Souza, I. M. G., and Toledo, M. B. F.
(2010). Product line in the business process manage-
ment domain. In Kang, K. C., Sugumaran, V., and
Park, S., editors, Applied Software Product Line Engi-
neering, chapter 20, pages 497–530. Auerbach Public.
ICEIS 2017 - 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
272

Friedenstab, J.-P., Janiesch, C., Matzner, M., and Mller, O.
(2011). Extending bpmn for business activity monitor-
ing. In Annual Hawaii Int. Conf. on Syst. Sci., pages
4158–4167. IEEE.
Friedenstab, J.-P., Janiesch, C., Matzner, M., and M
¨
uller, O.
(2012). Extending BPMN for business activity moni-
toring. In 45th Hawaii Int. Conf. on Syst. Sci., pages
4158–4167. IEEE.
Henderson, J. C. and Venkatraman, N. (1993). Strate-
gic alignment: Leveraging information technology for
transforming organizations. IBM Syst. J., 32(1):4–16.
Janes, A. and Faganel, A. (2013). Instruments and methods
for the integration of company’s strategic goals and
key performance indicators. Kybernetes, 42(6):928–
942.
Kazhamiakin, R., Pistore, M., and Roveri, M. (2004).
A framework for integrating business processes and
business requirements. In Int. Enterp. Dist. Object
Comp. Works., pages 9–20. IEEE.
Kitchenham, B. and Charters, S. (2007). Guidelines for per-
forming systematic literature reviews in software en-
gineering. Technical Report EBSE 2007-001, Keele
University and University of Durham, UK.
Kocbek, M., Jost, G., Hericko, M., and Polancic, G.
(2015). Business process model and notation: The
current state of affairs. Comp. Sci. and Inform. Syst.,
12(2):509–539.
Koliadis, G., Vranesevic, A., Bhuiyan, M., Krishna, A., and
Ghose, A. (2006). A combined approach for support-
ing the business process model lifecycle. In 10th Pa-
cific Asia Conf. on Inform. Syst., page 76. AIS.
Lapouchnian, A., Yu, Y., and Mylopoulos, J. (2007).
Requirements-driven design and configuration man-
agement of business processes. In 5th Int. Conf. on
Bus. Proc. Manag., pages 246–261. Springer.
Lee, Y.-C., Chu, P.-Y., and Tseng, H.-L. (2011). Cor-
porate performance of ICT-enabled business pro-
cess re-engineering. Indust. Manag. & Data Syst.,
111(5):735–754.
Leite, L. A., Oliva, G. A., Nogueira, G. M., Gerosa, M. A.,
Kon, F., and Milojicic, D. S. (2013). A systematic
literature review of service choreography adaptation.
Serv. Orient. Comp. and Applic., 7(3):199–216.
Letsholo, K., Chioasca, E.-V., and Zhao, L. (2012). An
integration framework for multi-perspective business
process modeling. In 9th Int. Conf. on Serv. Comp.,
pages 33–40. IEEE.
Mili, H., Tremblay, G., Jaoude, G. B., Lefebvre,
´
E., Elabed,
L., and Boussaidi, G. E. (2010). Business process
modeling languages: Sorting through the alphabet
soup. ACM Comp. Surv., 43(1):4.
Mohammadi, N. G. and Heisel, M. (2016). A framework
for systematic analysis and modeling of trustworthi-
ness requirements using i* and BPMN. In 13th Int.
Conf. on Trust, Priv. and Sec. in Dig. Bus., pages 3–
18. Springer.
Parmenter, D. (2015). Key performance indicators: Devel-
oping, implementing, and using winning KPIs. John
Wiley & Sons.
Pl
¨
osch, R., Pomberger, G., and Stallinger, F. (2011). Soft-
ware engineering strategies: Aligning software pro-
cess improvement with strategic goals. In 11th Int.
Conf. on Soft. Proc. Improv. and Capab. Determ.,
pages 221–226. Springer.
Poels, G., Decreus, K., Roelens, B., and Snoeck, M. (2013).
Investigating goal-oriented requirements engineering
for business processes. J. of Datab. Manag., 24(2):35–
71.
Pourshahid, A., Amyot, D., Peyton, L., Ghanavati, S., Chen,
P., Weiss, M., and Forster, A. J. (2009). Business pro-
cess management with the user requirements notation.
Elec. Comm. Research, 9(4):269–316.
Pourshahid, A., Amyot, D., Shamsaei, A., Mussbacher, G.,
and Weiss, M. (2012). A systematic review and as-
sessment of aspect-oriented methods applied to busi-
ness process adaptation. J. of Soft., 7(8):1816–1826.
Pressman, R. S. (2009). Software engineering: a practi-
tioner’s approach.
Ruokonen, A., Pajunen, L., and Syst
¨
a, T. (2009). Scenario-
driven approach for business process modeling. In
IEEE Int. Conf. on Web Serv., pages 123–130. IEEE.
Salles, G. B. and Fantinato, M. (2012). An
´
alise da
incorporac¸
˜
ao de requisitos n
˜
ao funcionais na mode-
lagem de processos de neg
´
ocio. In VIII Simp. Bras. de
Sist. de Inf., pages 79–90.
Salles, G. B. M., Fantinato, M., Nishijima, M., and Al-
buquerque, J. P. (2013). A contribution to organiza-
tional and operational strategic alignment: Incorpo-
rating business level agreements into business process
modeling. In 10th Int. Conf. on Serv. Comp., pages
17–24. IEEE.
Shamsaei, A., Amyot, D., and Pourshahid, A. (2011). A
systematic review of compliance measurement based
on goals and indicators. In 4th Int. Works. on Govern.,
Risk and Compl.: Applic. in Inform. Syst., pages 228–
237. Springer.
Sommerville, I. (2010). Software Engineering. Addison-
Wesley, 9th edition.
Sousa, H. and Leite, J. (2014). Modeling organizational
alignment. In 33rd Int. Conf. on Concep. Model.,
pages 407–414. Springer.
Tallon, P. P. (2008). Inside the adaptive enterprise: An in-
formation technology capabilities perspective on busi-
ness process agility. Inform. Tech. and Manag.,
9(1):21–36.
van der Aalst, W. M. P., Hofstede, A. T., and Weske, M.
(2003). Business process management: A survey.
pages 1–12. Springer.
Weske, M. (2012). Business Process Management.
Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2 edition.
Wetzstein, B., Leitner, P., Rosenberg, F., Brandic, I., Dust-
dar, S., and Leymann, F. (2009). Monitoring and an-
alyzing influential factors of business process perfor-
mance. In IEEE Int. Enterp. Dist. Object Comp. Conf.,
pages 141–150. IEEE.
Xu, T., Ma, W., Liu, L., and Karagiannis, D. (2010). Syn-
thesizing enterprise strategic model and business pro-
cesses in active-i*. In IEEE Int. Enterp. Dist. Object
Comp. Works., pages 345–354. IEEE.
Yu, E. S. K., Mylopoulos, J., and Lesp
´
erance, Y. (1996).
AI models for business process reengineering. IEEE
Expert, 11(4):16–23.
An Analysis of Strategic Goals and Non-Functional Requirements in Business Process Management
273
