
Interaction in Situated Learning Does Not Imply Immersion
Virtual Worlds Help to Engage Learners without Immersing Them
Athanasios Christopoulos, Marc Conrad and Aslan Kanamgotov
Department of Computer Science & Technology, University of Bedfordshire, Luton, U.K.
Keywords: Immersion, Situated Learning, Virtual Worlds, OpenSim, Learner Engagement, Interaction, Teaching.
Abstract: Immersion is a central theme when using virtual worlds; the feeling of ‘being there’ is generally considered
a positive attribute of virtual worlds, in particular when these are used for recreation. However, within
educational context it may be debatable how far immersion can be expected or is even desirable: if we want
students to be reflective and critical on their assignment task, wouldn’t it be more important for them to
have a critical distance, rather than being immersed? In this paper, we approach this question by examining
and discussing how interactions, learner engagement and immersion are linked together when a virtual
world is being used in a Hybrid Virtual Learning scenario. Findings from our experiment seem to suggest
that even though this learning approach aids positively the educational process, high levels of immersion do
not occur. Nevertheless, more research in that direction is highly recommended to be undertaken.
1 INTRODUCTION
Immersion is often considered to be central to
Virtual Worlds (VWs) (Bredl et al, 2012; Childs,
2010; Christopoulos, 2013). However, it might be
debated how far immersion might help or hinder an
education experience within a university assignment.
While situated learning (Herrington and Oliver,
2000) is generally considered a futile approach to
facilitate practical student experience it may be
questioned if ‘too much’ immersion might hinder
students to critically reflect on their learning
experience. This is in particular relevant on
postgraduate level where this critical reflection is
typically a key learning outcome of the course.
In order to shed some light on this issue we draw
data from observations from an experiment
conducted in the wider context of student interaction
and engagement and re-interpret the findings in view
of the level of student immersion.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 Interacting with Virtual Worlds
VWs provide the necessary context for different
types of interactions either between the users and the
content of the VW or the users themselves. Typical
examples of these types of interactions are the object
creation and manipulation (Bredl et al, 2012), terrain
editing (Allison et al., 2012), and navigating around
the world (Hockey et al., 2010). Communication is,
indeed, another important factor which increases the
opportunities for interaction between the users; be it
synchronous or asynchronous, verbal or written or
through the use of avatar gestures (Hockey et al.,
2010). VWs have been used in various paradigms as
they provide fertile ground for the implementation of
different learning styles (e.g. Problem Based
Learning, Exploratory Learning, and Distance
Learning) (Christopoulos, 2013). Vygotsky’s (1978)
Social Constructivist Learning Theory has great
practical application in VWs since it covers issues
such as the fact that students become active learners
while building, at the same time, their cognitive
structures and knowledge through the complex
network of interactions that motivate them to engage
with the VW and the learning material, by extension.
Indeed, as Jones (2013) suggests, learners have the
ability to actively affect, alter, and enhance the
content of the VW in a manner that will enable them
to construct their cognitive schemes and engage with
the subject they study. Zhao et al. (2010) further
extend the aforementioned claim and also suggest
that learning becomes more self-directed and
student-centered, whereas educators get the role of
Christopoulos, A., Conrad, M. and Kanamgotov, A.
Interaction in Situated Learning Does Not Imply Immersion - Virtual Worlds Help to Engage Learners without Immersing Them .
DOI: 10.5220/0006316203230330
In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2017) - Volume 1, pages 323-330
ISBN: 978-989-758-239-4
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
323

instructional designers or supporters of activities that
aim to engage students in learning (Anasol et al.,
2012).
Educators’ new role has triggered the conduct of
several studies focusing on the interactivity of the
VWs and the in-world interactions that can – or need
to – be developed in order to cover students’
learning needs. Some studies investigate the use of
VWs in distance learning scenarios (de Freitas et al.,
2009) aiming to identify an evaluation method to
measure students’ learning experiences, while others
cover the skills students acquire when they start
using VWs (Childs, 2010). Another group of studies
focuses on the elements that affect a VW’s
interactivity (Steuer, 1992), whereas others
attempted to address the aforementioned topic from
a different perspective (Chafer and Childs, 2008) as
they identified additional parameters. However,
most of these studies disregard the perspective of
learning in the physical classroom in conjunction
with the VW (Camilleri et al., 2013).
Based on the review of the literature that we
have conducted, only a few studies attempted to
examine interactions both from the inside and from
the outside (Levesque and Lelievre, 2011) whereas
the authors suggest that great emphasis should be
given on the enhancement of interactions both in the
VW but also in the physical classroom. De Freitas et
al. (2010) also underline the importance and need for
further investigation of the potential and the
affordances of hybrid spaces with simultaneous
student physical and virtual presence. Other
researchers (Elliott et al., 2012) highlight the lack of
detailed taxonomy of all the interactions related to
the educational use of VWs, which would aid in a
better understanding of their affordances, in a more
expedient design of educational activities, and in a
more thorough exploitation of their potential.
2.2 Immersion in Virtual Worlds
Immersion, according to Brown and Cairns (2004),
denotes a “sense of being there” or a “Zen-like state
where your hands just seem to know what to do, and
your mind just seems to carry on with the story”. As
a phenomenon to describe the immersion experience
this is not something new and applicable only to the
VW. We can feel immersed while reading books
(Nell, 1988), watching films (Bazin, 1967) or doing
something else, no matter what but it needs to
involve us fully in order we, as “users”, could
achieve that state of the mind. With the relatively
recent advent of VWs, however, the phenomenon
described received a new momentum, involving the
user through not only observation of the material,
but while actively interacting with environment,
establishing the cybernetic circuit between the user
and the VW. This phenomenon is described as
“presence” and “immersion”. Though both
definitions are widely used and have been discussed
for decades, there seems to be a lack of consensus
achieved so far (Brown and Cairns, 2004).
Nevertheless, the phenomenon these two terms have
been enlisted to describe is crucial to our
understanding of the relationship between user and
VW, as it represents one end of a continuum of
intensity of involvement with VWs and addresses
the very notion of being in the context of such
simulated environments. As Calleja (2014) argues,
the main challenge and confusion between two terms
is “based on a number of challenges they pose to a
clear understanding of the phenomenon they have
been employed to describe”, since neither of the
terms fully and adequately describes the relationship
between the user and VW, assuming that the human
being interacts with the VW in a unidirectional
manner, that there is a certain split between the user
in his real world (“here”) and the virtual counterpart
he interacts with (“there”). Both definitions,
“presence” and “immersion”, are used frequently
and interchangeably, though there is a certain level
of contradiction between them. Slater and Wilbur
define immersion as a technological feature, an
option which belongs to the side of “technicalities”,
rather than the state of the mind: “A description of a
technology […] that describes the extent to which
the computer displays are capable of delivering an
inclusive, extensive, surrounding and vivid illusion
of reality to the sense of a human participant” (Slater
and Wilbur, 1997). In contrast, Witmer and Singer
(1998) describe the immersion as “a psychological
state characterized by perceiving oneself to be
enveloped by, included in, and interacting with an
environment that provides a continuous stream of
stimuli and experiences”, which aligns quite closely
to Slater and Wilbur’s definition of “presence”.
Moreover, Calleja (2014) introduces a “more
productive and precise” definition, where “the VW
assimilated into the user’s consciousness as a space
that affords the exertion of agency and expression of
sociality in a manner coextensive with our everyday
reality” which he calls “Incorporation”.
While the exact definition of ‘immersion’ is still
open to debate we note that it is (in any definition) a
central theme and expected outcome when
interacting with virtual worlds. The evaluation of
which of the definitions describes the phenomenon
more precisely lies beyond the scope of this research
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
324

and in order to avoid further confusion in the
terminology, the term “immersion” is used
throughout, denoting the user’s involvement into his
activities within a virtual environment.
3 MATERIALS & METHODS
To investigate the relationship between interaction
and immersion we draw data from an experiment
which lasted one month involving postgraduate
Computer Science & Technology students
participating in the study. Indeed this experiment is
part of a wider study on how different types of VWs
help or hinder student engagement.
Figure 1: Snapshot of the content of the virtual world
which has been developed for the needs of the experiment.
An institutionally hosted OpenSimulator VW was
used for students to work with the built-in
programming language and design 3D objects. At
the end of this assignment, all student groups were
expected to present their work, prepare a video about
their virtual showcase and submit a report. This class
was being held, besides the traditional lecture form,
in two-hour practical sessions which ran once a
week. Finally, the focus of this experiment was to
examine the impact that the educational and leisure
games have on interactions, learner’s engagement
and consequently immersion (see Figure 1).
3.1 Research Methodology
Research through observation may have several
strengths but three were the main aspects that
indicated observation as the most suitable method
for this study. Firstly, as described in Cohen et al.
(2011), that led to the emergence of unique primary
data, the most essential advantage of observation is
considered to be the principles of ‘immediate
awareness’ and ‘direct cognition’ — i.e. the
opportunity given to a researcher to have a ‘direct
look’ at the actions that take place without having to
rely on second-hand accounts. Secondly, observation
is a very flexible form of data collection that allows
researchers to alter their focus, depending on the
observed actions and behaviours. Finally, the
method of observation allows the researcher to
gather any necessary data, while the participants
unimpededly follow their own agenda and priorities.
Nevertheless, when conducting observation
research, there are unavoidably – as with most
methods – certain disadvantages in the data
collection process. Even though a great effort was
made to eliminate them as much as possible, they
cannot be disregarded. In particular, the main
challenge, when collecting primary data through
observation, is the ‘selective attention of the
observer’. In addition, the ‘reactivity’ of the sample
can also run the risk of bias. Finally, observations
are recording only what happens in a given period of
time or what can be seen in a given interface.
4 LEARNER ENGAGEMENT,
INTERACTIONS &
IMMERSION
In order to identify the impact that different types of
interactions have on users – or in this case students –
while being (physically) present in a university
laboratory and also in the VW, we developed our
own observation checklist (see Tables 1 and 2). The
focus points – though not all of them are presented
in this paper as we are focusing exclusively on those
who have impact on immersion – were developed
after using the findings of a research conducted by
one of the authors (Christopoulos, 2013), under the
principles and guidelines of the Grounded Theory
(Strauss and Corbin, 1998) and the suggestion of
pedagogists on how to make these observation
checklists effective (Cohen et al., 2011).
Consequently, we correlated these focus points
in accordance with the framework related to the
factors affecting immersion as presented by Witmer
and Signer’s (1998), and namely are:
Control Factors: such as ‘degree of control’,
immediacy of control’, ‘anticipation of events’,
‘mode of control’, ‘physical environment
modifiability’
Sensory Factors: such as sensory modality,
environmental richness, multimodal presentation,
consistency of multimodal information, degree of
Interaction in Situated Learning Does Not Imply Immersion - Virtual Worlds Help to Engage Learners without Immersing Them
325
movement perception, active search
Distraction Factors: such as isolation, selective
attention, interface awareness
Realism Factors: scene realism, information
consistent with objective world, meaningfulness
of experience, separation anxiety / disorientation.
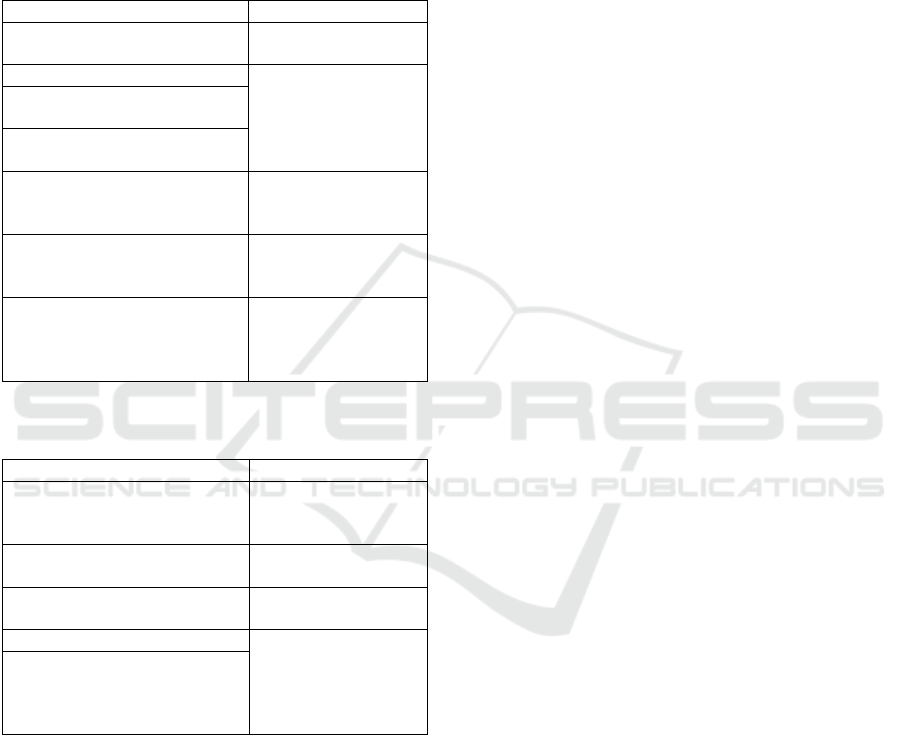
Table 1: Observation checklist (actions & interactions in
the physical classroom) and linkage to level of immersion.
Type of interaction Immersion
Student seems focused on his/her
project
High (meaningfulness
of experience)
Student seems “absent-minded”
Inconclusive
Student seems to enjoy the
project
Student seems unpleased using
the VW
Student makes positive/negative
comments about the technology
or emotional experience.
Low (detached from the
VW to interact in the
real)
Student refers to avatar in the
first person/ identifies with avatar
(avatar as ‘I’)
High (embodiment)
Student refers to avatar in the
second person/ addresses avatar
directly (‘you’), third person
(‘him’, ‘her’ or as an object (‘it’)
Low (demonstrates
distance)
Table 2: Observation checklist (actions & interactions in
the VW) and linkage to immersion.
Type of interaction Immersion
Student works on project
(building/scripting)
High (physical
environment
modifiability)
Student refers to avatar within
VW.
High (indicates
interaction)
Student modifies his/her
avatar’s appearance
Inconclusive (might
indicate distance)
Student uses avatar gestures
High (as it happens
in-world, rather than
direct interaction
with classmates)
Student uses existing content,
in-world tools, his/her own
virtual creations, explores
classmates’ virtual artifacts
5 REFLECTION ON THE
OBSERVED DATA
In this Section we will discuss the actions that
students performed during their practical sessions as
they have been observed by the researcher, both in
the physical classroom and the VW, during the
course of this experiment. In order to observe all the
participants for an equal amount of time, students’
actions were logged in rotation for approximately 30
seconds (per student or pair of students) until the
completion of the practical session. In total, 18
students participated in our study among which
fifteen (15) were males and 3 (females).
5.1 Actions & Interactions in the
Physical Classroom
5.1.1 Student Attitude towards the Use of
the VW
Week 1. Most of the students dedicated their time to
explore the content of the VW, play with the games
(amusement park, lake, café, maze), discover and
familiarise themselves with the tools of the VW, and
only a few of them – almost at the end of the
practical session – were observed being at their
team’s workspace in order to discuss, plan and make
some initial design of their project’s infrastructure.
Indeed, as it was as introductory session and most of
the students were not familiar with the building and
scripting tools of the environment, they were not
expected to be either working right away or to be
focused on their project. A couple of students were
quite often observed being absent-minded or
completely detached from the VW, as they were on
their phones or staring at their friends without
actively engaging or participating in the
conversations. The main source of disappointment or
displeasure was the difficulty some students had in
understanding the tools of the VW (even the
navigational ones). As a general note, it is worth
mentioning that all of them acknowledged the
importance of having pre-existing content in place,
as it provided them with the opportunity to get a
taste of what their simulation or showcase should
contain or look like.
Week 2. Almost all the students (including some
of them who were responsible for the development
of the virtual showcase) spent a considerable amount
of time (in total duration) working or helping their
teammates with the documentation needs of their
project. However, most of the developers were
usually interacting more with the VW and less with
their team members who were working on other
aspects of the project. Nevertheless, as most of them
(the developers) were still not comfortable with the
building and scripting tools of the technology, very
few of them, and only for a few times, were
observed working ‘focused’ on their project. Indeed,
the difficulty most of the students had manipulating
the tools of the VW was undoubtedly a good reason
to be displeased or even frustrated (in some cases).
Likewise, very few times were students observed
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
326

being happy or enjoying the process, as they were
not directly engaged with the actual development
process, but, instead, they were trying to deal and
familiarise with the tools of the VW.
Week 3. All the teams but one (infancy stage)
had shown some actual effort to work and develop
parts of their virtual showcase as they had now
reached the middle-end stage of their projects.
During the course of the practical session, all of the
developers were most of the time located at their
teams’ workspaces, working on their projects.
However, very few times were students observed
working focused on their task, as they were often
distracted by other matters (talking, helping,
searching on the web). Likewise, no great levels of
enjoyment were observed, as the students were
trying to do some serious work without losing time
in playing or entertaining themselves along the way.
A couple of students were observed a few times
being absent-minded or actually completely
detached from the VW (use of mobile phone), while
some more students were quite displeased, as they
were still struggling a lot to understand the tools of
the VW. As these students were part of the
aforementioned team that was still in an infancy
stage, their disappointment turned into frustration
and anger towards the use of the VW, leaving no
space for other students or the teaching team to help
them out.
Week 4. Even though all the students were
working on the finalisation of their virtual showcase,
very few times were they observed working focused
on their projects. In fact, quite often their attention
was being distracted by other matters such as the
documentation process. Apart from not being
focused on their task, a group of three students were
observed being several times completely detached
from the VW, as they were browsing the news on
the web, staring at other students or using their
phones. Not very obvious levels of enjoyment were
observed either. Most of the students were rushing to
finish off the development of their showcase or to
make some ‘last-minute’ modifications on their
objects, while also offering some help to other team
members that were working on other matters.
5.1.2 Student Identity and Avatar Identity
Week 1. Students that managed to familiarise
themselves with the VW faster than others were
quite keen to help their fellow students to perform
some, at least, basic changes in their avatars’
appearance editing, and, thus, a large portion of the
session’s time was centred around this process.
Indeed, several comments were made by most of the
students, such as ‘why am I a lady?’, ‘I want to be a
man, how do I change my gender?!’, ‘he is very
ugly, how we can fix it?’, ‘can I make it black like
me?’, ‘get a brush and start painting it bro! haha!’. A
fairly common and often repeated action was the
observation of students pushing their avatars to go
far beyond the VW’s ‘invisible’ borders, something
which caused their avatars to seem stuck or gave the
illusion of flying to ‘nowhere’. As expected, help
requests to ‘unstuck’ the avatars were made to the
teaching team ‘he lost his way [referring to his own
avatar]! Can you help me get back to ground?’.
Interestingly, one of the students lost his way out
while visiting one of the workspaces and asked the
lab demonstrator to help him find his way out ‘sir, I
got myself in this room, how can I go out?’.
Week 2. Very few students were observed
modifying their avatars’ appearance for a fairly short
period of time, whereas equally rare were the
references made in relation to them. A quote worth
mentioning was the one made by one of the students
asking his life-partner, and eventually fellow
student, to modify his own avatar as he was
struggling to do so ‘[partner’s name] can you make
it look like me?’. Another interesting comment was
made by the only student who slightly ‘drifted’ from
the mainstream attitude that most students had
towards their avatars, i.e. mirroring their physical
identity in the VW, and differentiated himself by
modifying his avatar’s body shape in a completely
different way, completely opposed to his physical
identity (overweight-underweight) ‘guess I need to
start training! Lol’.
Week 3. Only two students were observed
modifying their avatars’ appearance. However, both
of them performed minor changes for an overall
short period of time. In particular, one of them was
observed making modifications mainly for his own
favour and desire, whereas the second one was
performing changes that were required for the needs
of his team’s showcase (demonstration of smart
devices attached to human body or, in this case, the
avatar’s body). In any case, very few references
related to avatars were observed mainly during the
natural talk-flow, and, interestingly, all of them in
the second person ‘poseballs can help you do it’,
‘You need to attach it in your left shoulder otherwise
it is not going to work’, ‘Where are you going?’.
Week 4. None of the students was observed
making direct reference or mention to avatars at any
point during the practical session. However, one
student was observed editing his avatar’s appearance
for a couple of minutes, for the needs of the
Interaction in Situated Learning Does Not Imply Immersion - Virtual Worlds Help to Engage Learners without Immersing Them
327

showcase demonstration.
5.2 Actions & Interactions in the VW
5.2.1 Student Identity and Avatar Identity
Observation week 1. Almost all the students were
observed modifying their avatars’ appearance for a
considerable amount of time. Some of them
performed basic changes, such as hair and body
style, whereas others made some more detailed and
intensive one, such as clothing and accessories.
Interestingly, none of the students were observed
role-playing (opposite gender than their real one or
converting their avatar into something unrealistic
e.g. robot, animal). However, several students
modified their avatars’ appearance according to their
desire, without mirroring their real identity (physical
condition). As the use of the chat tool was quite
intense, several times students were observed
referring to avatars through it.
Week 2. As the use of the chat tool was almost
non-existent, no comments about avatars were
observed. Likewise, only a few students were
observed modifying their avatars’ appearance, with
the most striking examples being the appearance
editing made by one of the students on behalf of her
friend, and the student that slightly role-played by
modifying his avatar’s body shape to look
differently than his physical one.
Week 3. Only two students were observed
modifying their avatars’ appearance. However, none
of them performed extreme or unrealistic
modifications. In particular, one of them made some
basic changes whereas, the other one, who was
performing modifications on the avatar’s appearance
in order to be used as part of the showcase
demonstration, spent a considerable amount of time
carefully editing body parts as the project of his
team was dealing with the development of a
smart/security vest for cyclists. In any case, none of
the students was observed using the chat tool to
make references or mentions to avatars at any given
time.
Week 4. Only one student was observed working
on the modification of his avatar’s appearance in
order to attach and correctly position the finalised
scripted objects that were meant to be used for the
demonstration of this team’s showcase. As regards
the chat tool, some very inappropriate comments
(considering the university context) were observed
being made by two students while commenting on
the avatars of other students. It is, however, quite
interesting to know and ponder on the fact that even
though students were aware of being observed in
real-time as well as of the existence of chat-logs,
they still decided to use the in-world chat tool to
make a rather inappropriate conversation.
5.2.2 Interactions with the World
Week 1. Only a few students were observed working
or, more precisely, making some preliminary work
related to their project for a couple of minutes just
before the end of the practical session. Instead,
students’ attention almost monopolised by the
content exploration and use (developed by other
students/the researcher), the modification of their
avatars’ appearance, and the exploration of the in-
world building tools. Indeed, most of the students
spent a considerable amount of time exploring the
content that had been developed by other students,
visited and played with the games located at the
amusement park, the mini lake and the café, though
only one student was observed going through the
maze. In any case, none of the students/teams was
observed using or even being at the racing game. As
to the exploration of the in-world tools, almost all
the students exchanged friend requests both with
their team members and their fellow students, and
used the chat tool including the Instant Messages
option. After being suggested by the lecturer, all the
teams were observed setting up their own group
(using the in-world function) and some students
further explored the tools of the VW (e.g. weather
settings, gestures). As far as the building tools are
concerned, nearly all the students were observed
using and editing some of the default library prims
in order to better understand their capabilities,
without, however, spending a considerable amount
of time modifying them in a meaningful way. On the
other hand, none of the students was observed
exploring the programming language even though a
mention was made by the lecturer.
Week 2. At the starting point of the practical
session, most of the students were observed
wandering around the showcases developed by
others, in order to observe and discuss their
functionality and get some ideas for their own work.
However, all of them were quite sceptical and
uncertain regarding the development process of their
own showcases, due to the fact that they were still
very unfamiliar with the development tools of the
VW. Thus, a considerable amount of time, during
the practical session, was dedicated for
experimentation with the primitives that could be
found in the in-world library, the importing process
of textures and objects and, in some cases, even of
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
328

scripts (mostly premade ones that can be found on
the web). After reaching half-way of the practical
session, some students became keener to use objects
developed by their class or team mates, to request
some feedback or help from others and to teach
others what they had discovered (peer-tutoring/peer-
learning). It is worth mentioning that none of the
students was observed approaching, visiting or using
the content developed by the instructional designer
at all, or performing in-world actions irrelevant to
their project, other than some avatar appearance
modification. Finally, a couple of students that were
observed roaming quite often to other workspaces
discovered and used the landmark tool, which
allowed them to ‘mark’ several locations on the
virtual map and, so, they could instantly teleport
back and forth.
Week 3. Overall, it was a fairly ‘silent’ in-world
observation as students were working focused on
their task without being disrupted too often. This can
be justified by the fact that only one week had been
left prior to the submission of their assignment and,
by extension, the completion of their virtual
showcase and, thus, all of them had to hurry towards
the final implementation and development of their
showcases. The relatively few times during which
students were observed performing actions irrelevant
to their project, included visits to other workspaces
and use of the scripted objects developed by others.
It is worth mentioning that none of the students was
observed visiting the content developed by the
researcher at any time.
As far as the tools of the VW are concerned, the
group function was proved to be quite helpful and
handy for most of the developers, as they could edit
and/or remove objects that other team members had
created during the past days. In addition, even
though a notable mention regarding poseballs was
made in the physical classroom, only one team
showed intense interest to use them in order to
animate their avatars.
Week 4. Very few times were students observed
performing in-world actions irrelevant to their
project, such as visiting the workspaces of other
students, or using the content developed by the
researcher (actually, the latter was never observed).
Indeed, very few students and for a small period of
time were observed wandering around the
workspaces of their virtual neighbours, though
without using anything located there but only
observing. Instead, most of them were usually
located at their own workspaces, finalising their
showcases by adding cosmetic primitives or scripts.
Only one group was observed missing important
elements from their showcase, as they were fairly
behind the schedule and a considerable amount of
work had to done for its completion.
6 DISCUSSION & CONCLUSIONS
The main advantage of the Hybrid Virtual Learning
approach is that it eliminates the drawbacks and the
disadvantages that each one of the two educational
methods, i.e. the virtual and the traditional
classroom learning, have. However, this has a
critical effect on the levels of immersion that
students can reach due to the different types of
stimuli they get from the physical classroom, the
online (outside of the VW) available resources (as
part of their research for their assignment) or even
aspects related to their personal life and are
completely unrelated to university (social media,
phone-calls and texts).
Even though students had quite intense
interaction with the content of the VW and its tools,
especially during their first contact with the world,
the levels of immersion were almost non-existent
due to the often breaks they have had to discuss their
in-world actions with their fellow-students in the
physical classroom. Likewise, the parallel actions
that most of the students were usually performing be
it to help their fellow-students with other tasks or to
provide some help (demonstrate) to those who were
struggling to cope with the VW and its tools were
also decreased the levels of immersion.
Finally, the fact that students were working over-
focused on their task during the final stages of their
assignment, can also not be considered as an
indication of high levels of immersion given that
most – if not all – of them were stressed and anxious
to complete their in-world task so that they could get
all the bits and pieces of their assignment together
and submit their work.
We may therefore conclude that immersion does
not seem to have much – if any – relevance when it
comes to educational practices as opposed to virtual
games. Even though in both cases in-world goals
and targets are to be achieved (students want to
complete their assignment in order to get ‘real’
marks and gamers want to complete a set of tasks in
order to get the feeling of completion or joy), using a
VW – even with game-like content – as an extension
of the physical university does not lead students to
encounter high levels of immersion.
Counterintuitively, this lack of immersion might
well be a plus. It may lead to a useful distance
between the student and their in-world task and
Interaction in Situated Learning Does Not Imply Immersion - Virtual Worlds Help to Engage Learners without Immersing Them
329

might even foster critical thinking and reflection on
their actions. Educators and instructional/content
designers should be aware of this when designing
educational games: factors that help to support an
immersive experience not necessarily correlate with
factors that foster a situated learning experience. In
any case we highly recommend that further research
is needed to shed more light on this occurrence.
REFERENCES
Allison, C., Campbell, A., Davies, C. J., et al., “Growing
the use of VWs in education: an OpenSim
perspective”. Proc 2
nd
European Immersive Education
Summit, Gardner, M., Garnier, F., and Kloos, C. D.
Eds., pp. 1– 13, Paris, France.
Anasol, P. R., Callaghan, V., Gardner, M., and Alhaddad,
M. J. (2012). “End-user programming and
deconstrutionalism for cocreative laboratory activities
in a collaborative mixed-reality environment,” Proc
2
nd
European Immersive Education Summit, Gardner,
M., Garnier, F., and Kloos, C. D. Eds., pp. 171–182,
Paris, France.
Bazin, A. (1967) What Is Cinema? Essays. Berkeley:
University of California Press.
Bredl, K., Groß, A., Hünniger, J., and Fleischer, J. (2012).
“The avatar as a knowledge worker? how immersive
3d virtual environments may foster knowledge
acquisition,” The Electronic Journal of Knowledge
Management, (10)1, 15–25.
Brown, E. and Cairns, P. (2004) ‘A Grounded
Investigation of Game Immersion’. CHI‘04 Extended
Abstracts on Human Factors and Computing Systems
(Vienna, April 2004), ACM Press, pp. 1297–1300.
Calleja, G. (2014) ‘Immersion in VWs’, in Grimshaw, M.
(eds.). The Oxford handbook of Virtuality, Oxford
University Press, New York.
Camilleri, V., de Freitas, S., Montebello, M., and
McDonagh-Smith, P. (2013). “A case study inside
VWs: use of analytics for immersive spaces” Proc 3
rd
International Conference on Learning Analytics and
Knowledge, pp. 230–234, Leuven: Belgium.
Chafer, J. and Childs, M. (2008). “The impact of the
characteristics of a virtual environment on
performance: concepts, constraints and complications”
Proc Researching Learning in Virtual Environments,
94–105, Open University, Milton Keynes:UK.
Childs, M. (2010). Learners’ experience of presence in
VWs [Ph.D. thesis], University of Warwick,
Coventry,UK.
Christopoulos, A. (2013). Higher education in VWs: the
use of Second Life and OpenSim for educational
practices (Master thesis, University of Bedfordshire,
Luton, UK). Retrieved from: http://uobrep.
openrepository.com/uobrep/handle/10547/291117.
Cohen, L., Manion, L., and Morrison, K. (2011). Research
Methods in Education, Routledge Taylor & Francis,
7
th
edition, London: UK.
de Freitas, S., Rebolledo-Mendez, G., Liarokapis, F.,
Magoulas, G, and Poulovassilis, A. (2010). “Learning
as immersive experiences: Using the four-dimensional
framework for designing and evaluating immersive
learning experiences in a VW,” The British Journal of
Educational Technology, 41(1), 69–85.
de Freitas, S., Rebolledo-Mendez, G., Liarokapis, F.,
Magoulas, G., and Poulovassilis, A. (2009).
“Developing an evaluation methodology for
immersive learning experiences in a VW,” Proc
Conference in Games and VWs for Serious
Applications, pp. 43–50, Coventry: UK.
Elliott, J. B., Gardner, M., and Alrashidi, M. (2012).
“Towards a framework for the design of mixed reality
immersive education spaces,” Proc 2
nd
European
Immersive Education Summit, Gardner, M., Garnier,
F., and Kloos, C. D. Eds., Paris, France.
Herrington, J., & Oliver, R. (2000). An instructional
design framework for authentic learning environments.
Educational Technology Research and Development,
48, 23-48.
Hockey, A., Esmail, F., Jimenez-Bescos, C., and Freer, P.
(2010). “Built Environment Education in the Era of
Virtual Learning,” Proc. W089 - Special Track 18
th
CIB World Building Congress, 200–217.
Jones, D. (2013) “An alternative (to) reality,”
Understanding Learning in VWs”, M. Childs and A.
Peachey, Eds., Human–Computer Interaction Series,
1–20, Springer, London: UK.
Levesque, J., and Lelievre, E. (2011). “Creation and
communication in virtual worlds: experimentations
with OpenSim,” Proc Virtual Reality International
Conference, Richir, S., and Shirai, A., Eds., 22–24,
Laval: France.
Nell, V (1988) Lost in A Book: The Psychology of
Reading for Pleasure. New Haven: Yale, University
Press.
Slater, M., and Wilbur, S. (1997). ‘A framework for
immersive virtual environments (FIVE): Speculations
on the role of presence in virtual environments’.
Steuer, J. (1992). “Defining virtual reality: dimensions
determining telepresence” Journal of Communication,
42(2), 73–93.
Strauss, A. and Corbin, J. (1998). Basics of Qualitative
Research – Techniques and Procedures for
Developing Grounded Theory, second edition,
London, Sage Publications.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind Society: The Development
of Higher Mental Processes, Harvard University
Press, Cambridge, Mass:USA.
Witmer BG, Singer MJ (1998) Measuring presence in
virtual environments: A presence questionnaire.
Presence Teleoperators and Virtual Environments,
7:225-240.
Zhao, H., Sun, B., Wu, H. and Hu, X. (2010) “Study on
building a 3D interactive virtual learning environment
based on OpenSim platform” Proc International
Conference on Audio, Language and Image
Processing, pp. 1407–1411, Shanghai: China.
CSEDU 2017 - 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
330
